-
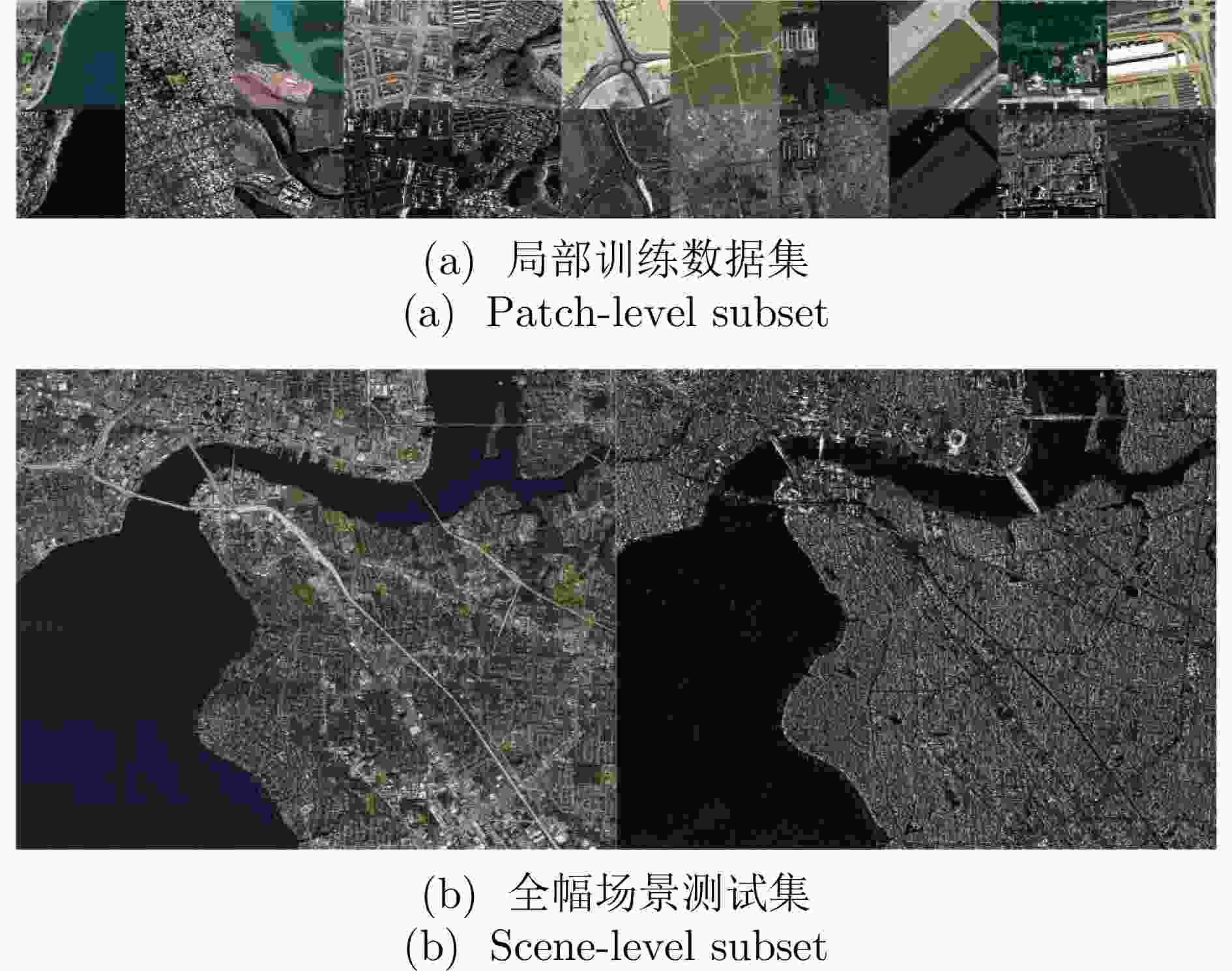
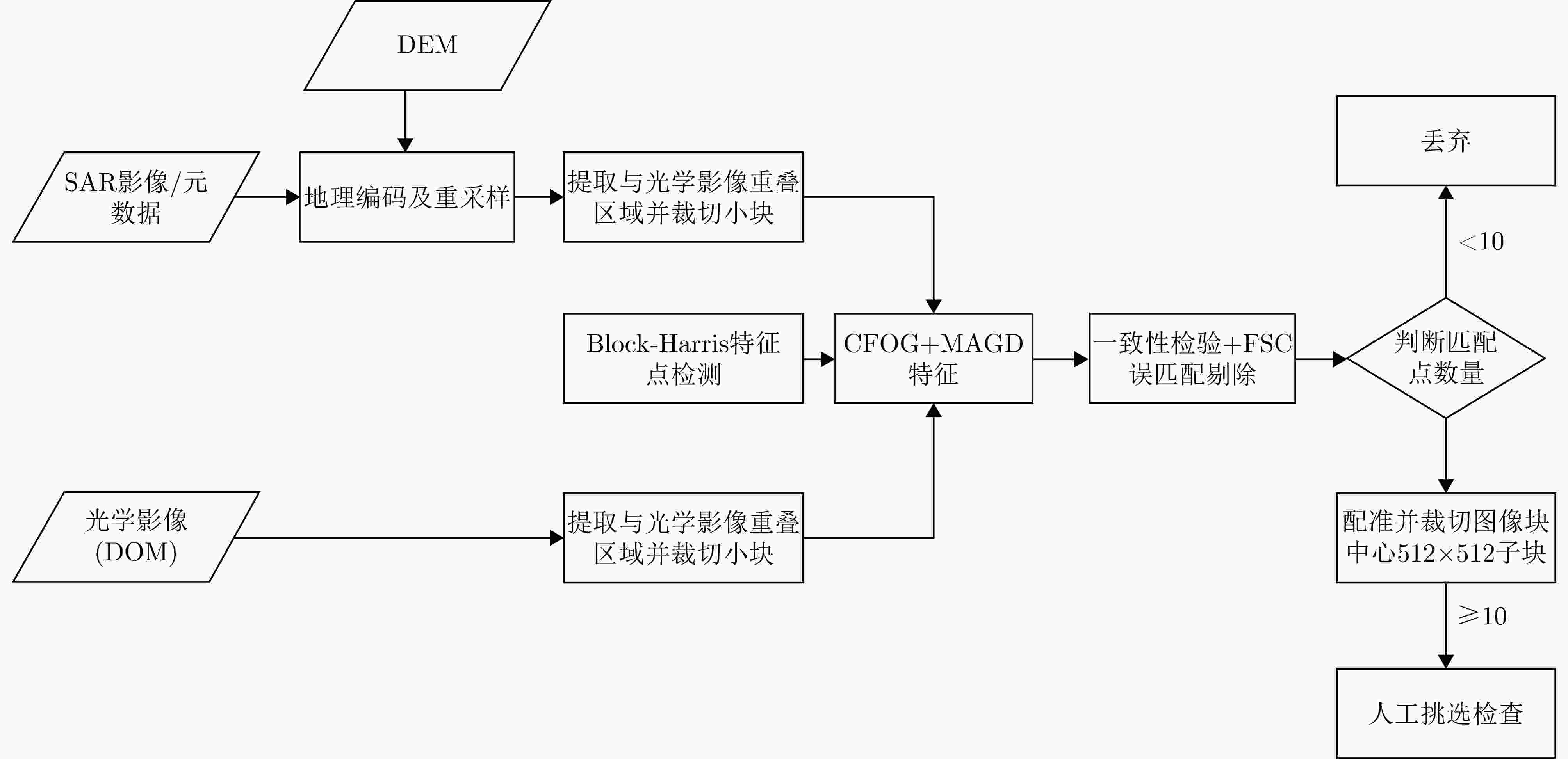
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)和可见光是地球观测领域中两类关键的遥感传感器,其影像匹配在图像融合、协同解译与高精度定位等任务中具有广泛应用。随着对地观测数据的迅猛增长,SAR-光学跨模态影像匹配的重要性日益凸显,相关研究也取得了显著进展。特别是基于深度学习的方法,凭借其在跨模态特征表达与高层语义提取方面的优势,展现出卓越的匹配精度与环境适应能力。然而,现有公开数据集多局限于小尺寸图像块,缺乏涵盖真实大尺度场景的完整影像对,难以全面评估匹配算法在实际遥感场景中的性能,同时也制约了深度学习模型的训练与泛化能力提升。针对上述问题,该文构建并公开发布了OSDataset2.0,一个面向SAR-光学影像匹配任务的大规模基准数据集。该数据集包含两部分:局部训练数据集与全幅场景测试集,局部训练数据集提供覆盖阿根廷、澳大利亚、波兰、德国、俄罗斯、法国、卡塔尔、马来西亚、美国、日本、土耳其、新加坡、印度、中国14个国家的6476块512×512像素的配准图像块,全幅场景测试集则提供一对光学与SAR整景影像。团队为整景影像提供了利用成像机理一致性原则提取出的高精度均匀分布的真值数据,并配套通用评估代码,支持对任意匹配算法进行配准精度的量化分析。为进一步验证数据集的有效性与挑战性,该文在OSDataset2.0上系统评估了11种具有代表性的SAR-光学影像匹配方法,涵盖了传统特征匹配与主流深度学习模型。实验结果表明,该数据集不仅能够有效支撑算法性能对比,还可为后续研究提供可靠的训练资源与统一的评估基准。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery are two key remote-sensing modalities in Earth observation, and cross-modal image matching between them is widely applied in tasks such as image fusion, joint interpretation, and high-precision geolocation. In recent years, with the rapid growth of Earth-observation data, the importance of cross-modal image matching between SAR and optical data has become increasingly prominent, and related studies have achieved notable progress. In particular, Deep Learning (DL)-based methods, owing to their strengths in cross-modal feature representation and high-level semantic extraction, have demonstrated excellent matching accuracy and adaptability across varying imaging conditions. However, most publicly available datasets are limited to small image patches and lack complete full-scene image pairs that cover realistic large-scale scenarios, making it difficult to comprehensively evaluate the performance of matching algorithms in practical remote-sensing settings and constraining advances in the training and generalization of DL models. To address these issues, this study develops and releases OSDataset2.0, a large-scale benchmark dataset for SAR-optical image matching. The dataset comprises two parts: A patch-level subset and a scene-level subset. The patch-level subset is composed of 6,476 registered 512 × 512 image pairs covering 14 countries (Argentina, Australia, Poland, Germany, Russia, France, Qatar, Malaysia, the United States, Japan, Türkiye, Singapore, India, and China); the scene-level subset consists of one pair of full-scene optical and SAR images. For full-scene images, high-precision, uniformly distributed ground-truth correspondences are provided, extracted under the principle of imaging-mechanism consistency, together with a general evaluation codebase that supports quantitative analysis of registration accuracy for arbitrary matching algorithms. To further assess the dataset’s effectiveness and challenge level, a systematic evaluation of 11 representative optical-SAR matching methods on OSDataset2.0 is conducted, covering traditional feature-based approaches and mainstream DL models. Experimental results show that the dataset not only supports effective algorithmic comparisons but also provides reliable training resources and a unified evaluation benchmark for subsequent research.
-
表 1 现有SAR-光学遥感影像数据集
Table 1. Existing SAR-optical Remote Sensing Image Datasets
数据集 空间分辨率 规模 配准方式/真值 OSDataset 1 m 10692对256×256像素影像切片 RPC粗配准后用分块仿射/三角网精配准,人工复核 BRIGHT 0.3~1.0 m 4246对1024×1024像素影像切片 专家人工挑选控制点配准(1.0~1.4像素) Multi-Resolution-SAR 0.16~10.00 m 10850对512×512像素影像切片 互信息+RANSAC粗配准,人工选择8~12个控制点精修,
并对0.16 m子集二次复核确保精度QXS-SAROPT 1 m 20000对256×256像素影像切片 专家人工选取8~12个同名控制点配准,人工复查 OsEval 0.33~0.56 m 1232对3500×3500~5500×5200像素
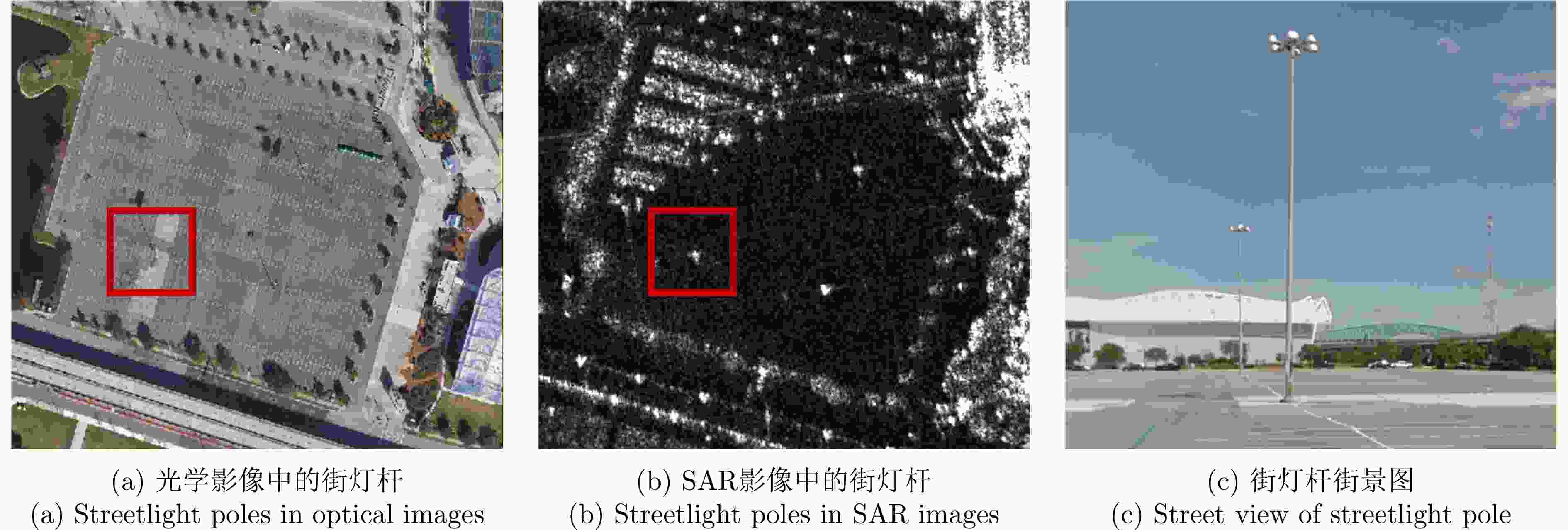
影像块以路灯杆基座为控制点实现亚像素定位 表 2 不同方法在局部训练数据集上的评估结果
Table 2. Evaluation results of different methods on Patch-level subset
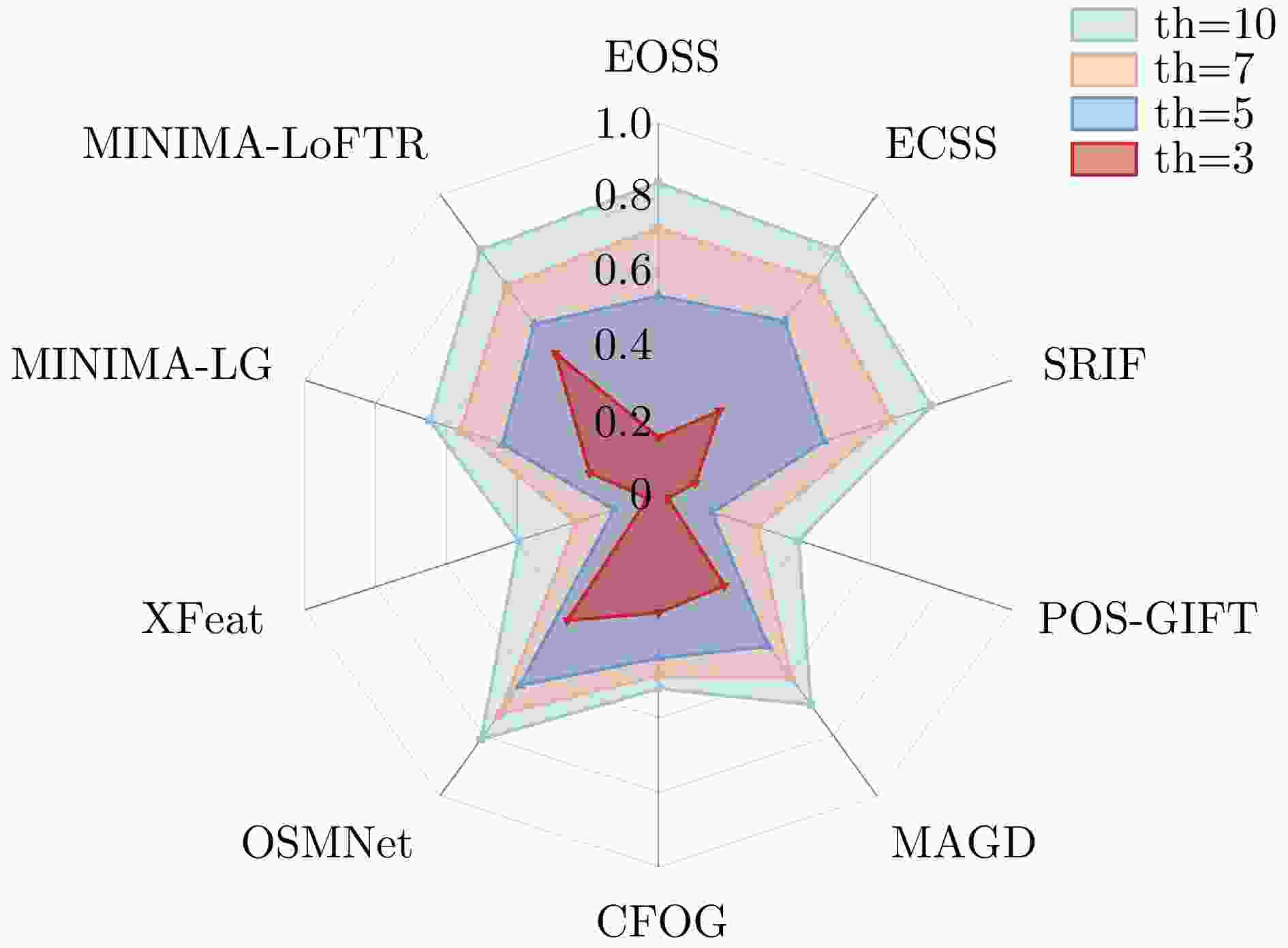
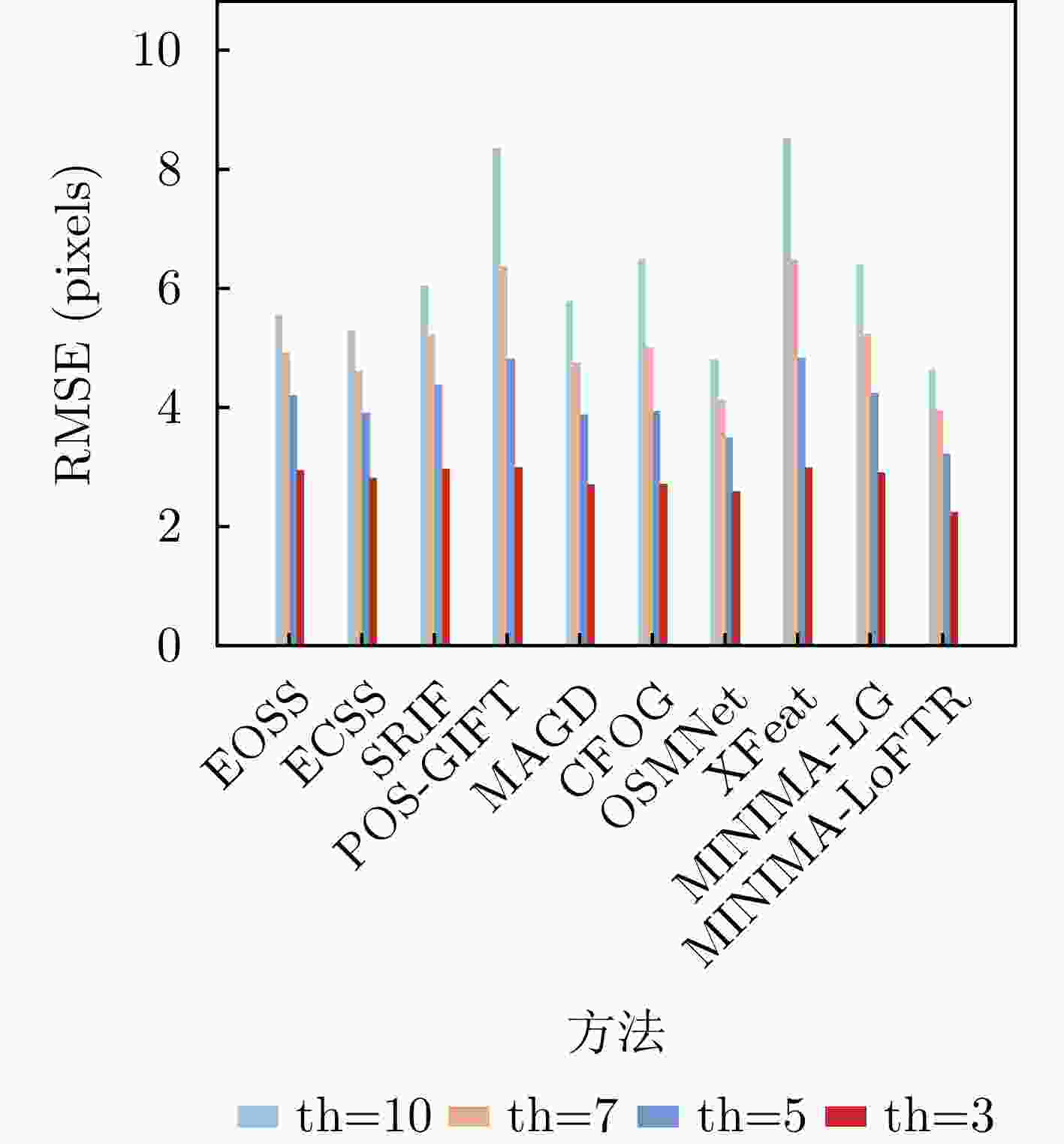
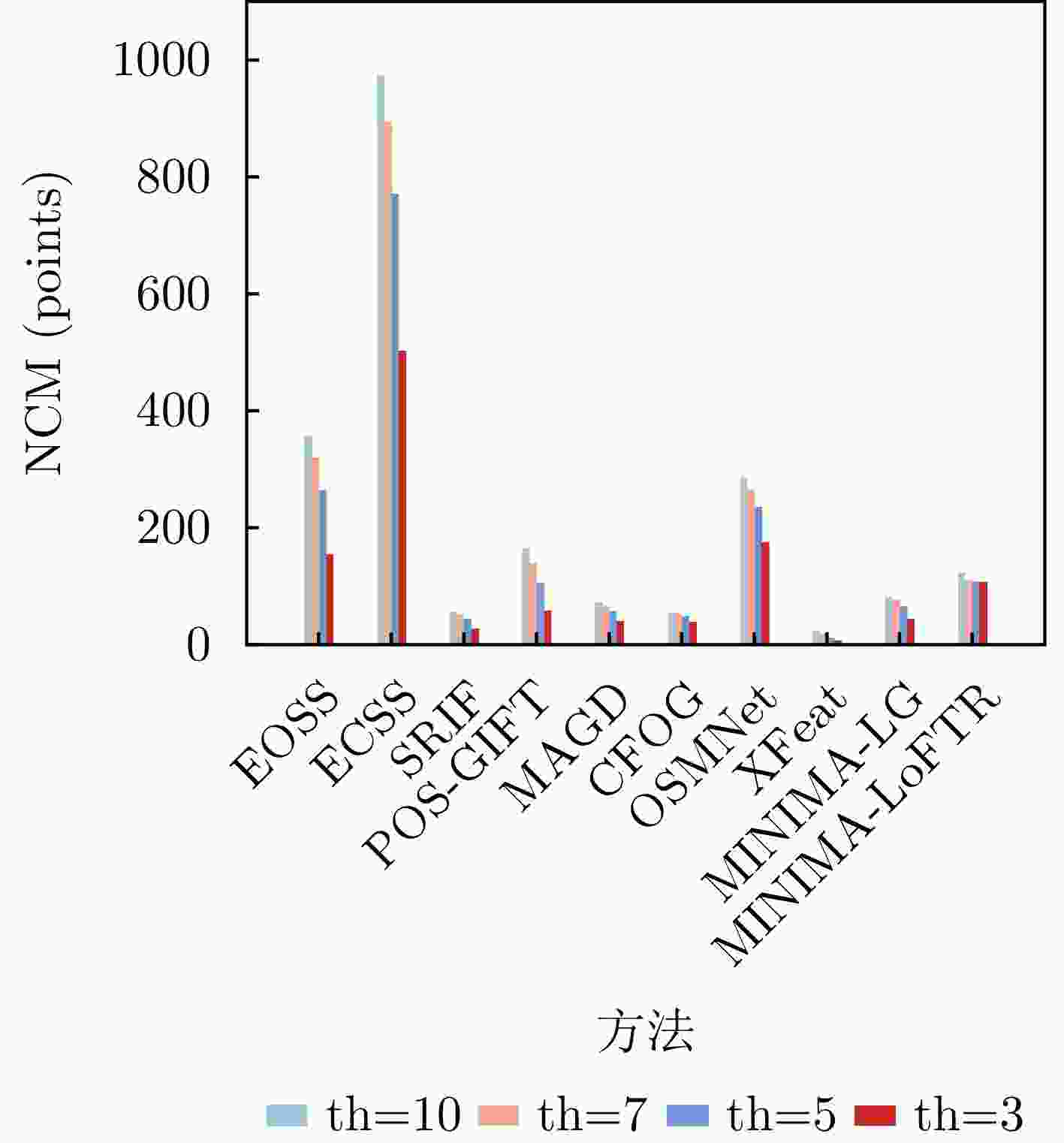
类别 方法 th=3 th=5 th=7 th=10 NCM
(个)↑RMSE
(像素)↓SR
(%)↑NCM
(个)↑RMSE
(像素)↓SR
(%)↑NCM
(个)↑RMSE
(像素)↓SR
(%)↑NCM
(个)↑RMSE
(像素)↓SR
(%)↑特征 EOSS 155 2.94 16 264 4.20 54 320 4.92 72 358 5.55 84 ECSS 503 2.81 28 771 3.92 58 895 4.61 72 974 5.29 82 SRIF 27 2.96 10 44 4.38 47 52 5.22 66 56 6.04 77 POS-GIFT 58 2.99 3 105 4.82 15 139 6.37 28 165 8.34 40 区域 MAGD 41 2.70 30 56 3.88 50 66 4.76 61 72 5.78 70 CFOG 39 2.71 32 48 3.94 44 52 5.00 49 54 6.48 52 深度
学习OSMNet 175 2.58 42 235 3.50 63 264 4.13 73 286 4.80 81 XFeat 6 2.99 3 12 4.83 13 17 6.47 23 23 8.52 40 MINIMA-LG 43 2.90 20 66 4.24 44 76 5.23 56 82 6.40 65 MINIMA-LoFTR 107 2.24 47 108 3.21 57 111 3.94 70 124 4.64 81 注:加粗数值表示最优。 表 3 不同方法在全幅场景测试集上的评估结果
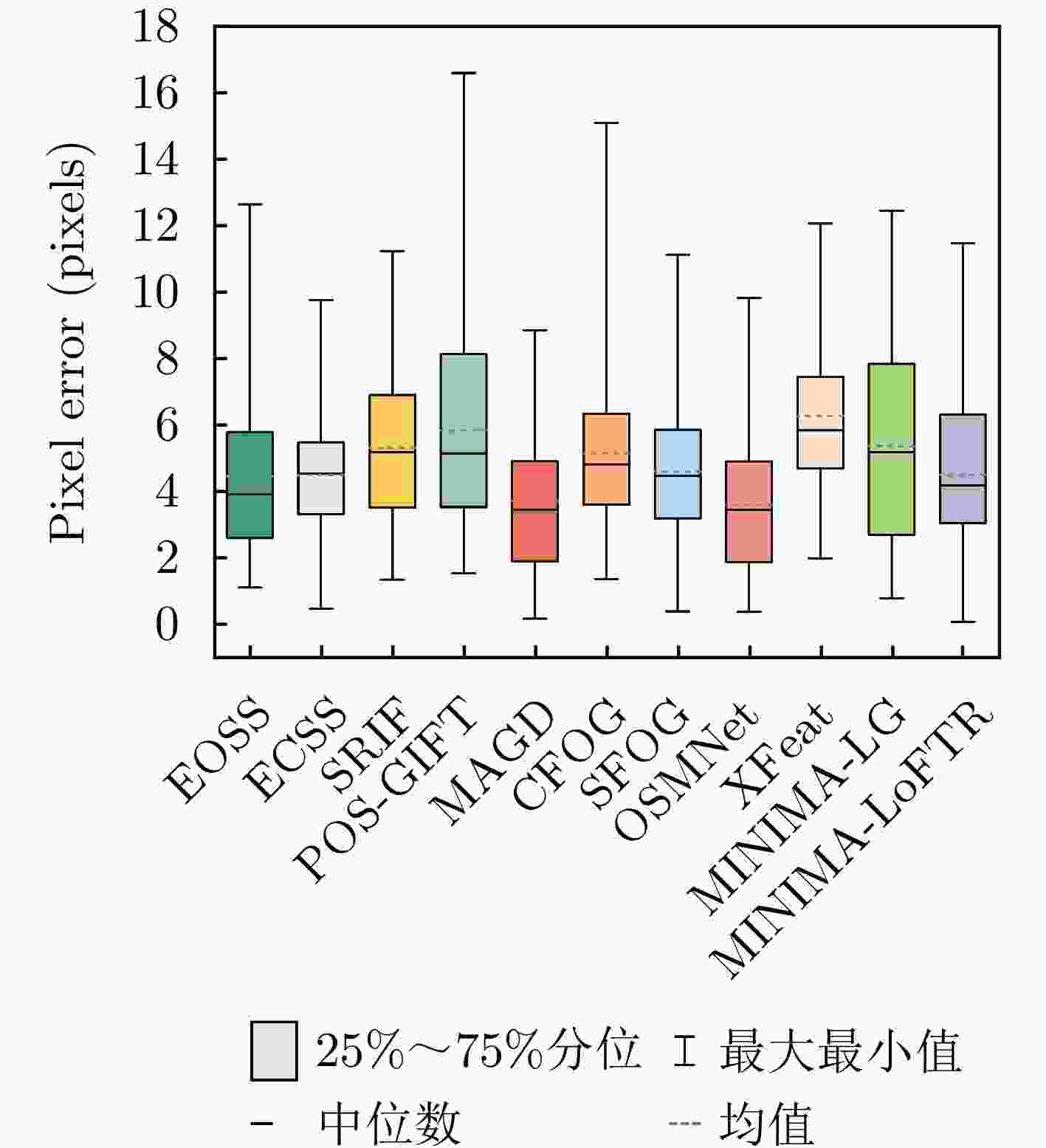
Table 3. Evaluation results of different methods on scene-level subset
类别 方法 RMSE(像素)↓ MEAN↓ MEDIAN↓ MAX↓ 特征 EOSS 5.05 4.46 3.91 12.63 ECSS 4.92 4.50 4.53 9.76 SRIF 5.72 5.04 5.21 11.23 POS-GIFT 6.58 5.84 5.16 16.58 MAGD 4.29 3.71 3.46 8.86 区域 CFOG 5.68 5.15 4.81 15.08 SFOC 5.01 4.61 4.48 11.12 深度
学习OSMNet 4.13 3.59 3.45 9.81 XFeat 6.66 6.28 5.85 12.06 MINIMA-LG 6.16 5.37 5.19 12.45 MINIMA-LoFTR 4.96 4.51 4.19 11.47 注:加粗数值表示最优。 -
[1] 向俞明, 滕飞, 王林徽, 等. 基于快速异源配准的高分辨率SAR影像海岛区域正射校正[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 866–884. doi: 10.12000/JR24022.XIANG Yuming, TENG Fei, WANG Linhui, et al. Orthorectification of high-resolution SAR images in island regions based on fast multimodal registration[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 866–884. doi: 10.12000/JR24022. [2] YE Yuanxin, ZHANG Jiacheng, ZHOU Liang, et al. Optical and SAR image fusion based on complementary feature decomposition and visual saliency features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3366519. [3] HONG Zhonghua, ZHANG Zihao, HU Shangcheng, et al. A robust seamline extraction method for large-scale orthoimages using an adaptive cost A* algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 13322–13347. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3570614. [4] HONG Zhonghua, ZHANG Hongyang, TONG Xiaohua, et al. Rapid fine-grained damage assessment of buildings on a large scale: A case study of the February 2023 earthquake in turkey[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 5204–5220. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3362809. [5] WAN Ling, XIANG Yuming, KANG Wenchao, et al. A self-supervised learning pretraining framework for remote sensing image change detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5630116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3579416. [6] YOO J C and HAN T H. Fast normalized cross-correlation[J]. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 28(6): 819–843. doi: 10.1007/s00034-009-9130-7. [7] YE Yuanxin, SHAN Jie, BRUZZONE L, et al. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(5): 2941–2958. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2656380. [8] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.177. [9] FAN Jianwei, WU Yan, LI Ming, et al. SAR and optical image registration using nonlinear diffusion and phase congruency structural descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5368–5379. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2815523. [10] XIANG Yuming, TAO Rongshu, WANG Feng, et al. Automatic registration of optical and SAR images via improved phase congruency model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 5847–5861. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3026162. [11] YE Yuanxin, BRUZZONE L, SHAN Jie, et al. Fast and robust matching for multimodal remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9059–9070. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2924684. [12] YE Yuanxin, ZHU Bai, TANG Tengfeng, et al. A robust multimodal remote sensing image registration method and system using steerable filters with first-and second-order gradients[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 188: 331–350. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.04.011. [13] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94. [14] XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, and YOU Hongjian. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078–3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483. [15] HOU Zhuolu, LIU Yuxuan, and ZHANG Li. POS-GIFT: A geometric and intensity-invariant feature transformation for multimodal images[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 102: 102027. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102027. [16] TOLA E, LEPETIT V, and FUA P. A fast local descriptor for dense matching[C]. 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587673. [17] LI Jiayuan, HU Qingwu, and ZHANG Yongjun. Multimodal image matching: A scale-invariant algorithm and an open dataset[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 204: 77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.08.010. [18] XIONG Xin, JIN Guowang, WANG Jiajun, et al. Robust multimodal remote sensing image matching based on enhanced oriented self-similarity descriptor[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4010705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3398725. [19] HONG Zhonghua, CHEN Jinyang, TONG Xiaohua, et al. Robust multimodal remote sensing image matching using edge consistency scale-space and significant relative response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5627022. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3577755. [20] ZHANG Han, LEI Lin, NI Weiping, et al. Explore better network framework for high-resolution optical and SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4704418. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3126939. [21] DENG Yuxin and MA Jiayi. ReDFeat: Recoupling detection and description for multimodal feature learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 591–602. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3231135. [22] REN Jiangwei, JIANG Xingyu, LI Zizhuo, et al. MINIMA: Modality invariant image matching[C]. 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2025: 23059–23068. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52734.2025.02147. [23] XIANG Yuming, WANG Xuanqi, WANG Feng, et al. A global-to-local algorithm for high-resolution optical and SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5215320. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3309855. [24] HUANG Meiyu, XU Yao, QIAN Lixin, et al. The QXS-SAROPT dataset for deep learning in SAR-optical data fusion[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08259, 2021. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2103.08259. [25] CHEN Hongruixuan, SONG Jian, DIETRICH O, et al. BRIGHT: A globally distributed multimodal building damage assessment dataset with very-high-resolution for all-weather disaster response[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06019, 2025. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2501.06019. [26] ZHANG Wenfei, ZHAO Ruipeng, YAO Yongxiang, et al. Multi-resolution SAR and optical remote sensing image registration methods: A review, datasets, and future perspectives[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.01002, 2025. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2502.01002. [27] WU Yue, MA Wenping, GONG Maoguo, et al. A novel point-matching algorithm based on fast sample consensus for image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 43–47. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2325970. [28] POTJE G, CADAR F, ARAUJO A, et al. XFeat: Accelerated features for lightweight image matching[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 2682–2691. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00259. [29] FISCHLER M A and BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(6): 381–395. doi: 10.1145/358669.358692. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: