Antijamming Target Detection Method Based on Expectation-Maximization Classification
-
摘要: 在存在有源人工干扰的复杂环境中,雷达信号参数估计精度往往显著下降,目标检测性能相应发生退化。为有效解决这一问题,该文提出了一种基于期望最大化分类辅助的抗干扰检测框架。具体而言,在雷达被动工作模式下,提出被动探测模式下的抗噪声覆盖脉冲(NCP)检测方法,建立被动干扰预警机制:构建表征NCP类别的潜在变量模型,结合期望最大化算法与特征值分解实现NCP样本分类与角度/能量参数估计,实现稳健NCP自适应检测。在雷达主动工作模式下,提出主动探测模式下的抗相干干扰(CJ)目标检测方法:构建目标回波与CJ存在性假设的分类模型,利用网格搜索与期望最大化算法完成样本分类与角度估计,实现CJ识别与目标自适应检测。仿真结果表明,所提方法能够有效识别目标或干扰存在的样本单元,准确估计目标与干扰的入射角度,提升恒虚警目标检测的抗干扰性能。Abstract: In complex environments with active artificial jammers, the accuracy of signal parameter estimation often deteriorates substantially, thereby degrading target-detection performance. To address this challenge, this paper proposes an anti-jamming detection framework based on Expectation-Maximization (EM) classification. For passive detection, a Noise Covered Pulse (NCP) detection method is developed, together with a passive jamming early-warning mechanism. A latent variable model representing NCP categories is constructed, and by integrating the EM algorithm with matrix decomposition, NCP sample classification and angle/energy parameter estimation are jointly achieved, enabling robust adaptive NCP detection. For active radar operation, a Coherent Jamming (CJ) target-detection method is proposed. A classification model based on the presence hypotheses of target echoes and CJ is formulated, and grid search combined with the EM algorithm is employed to perform sample classification and angle estimation, thereby enabling CJ identification and adaptive target detection. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework effectively identifies range bins containing targets or jammers, accurately estimates their angles of incidence, and significantly enhances the anti-jamming performance of constant false-alarm-rate target detection.
-
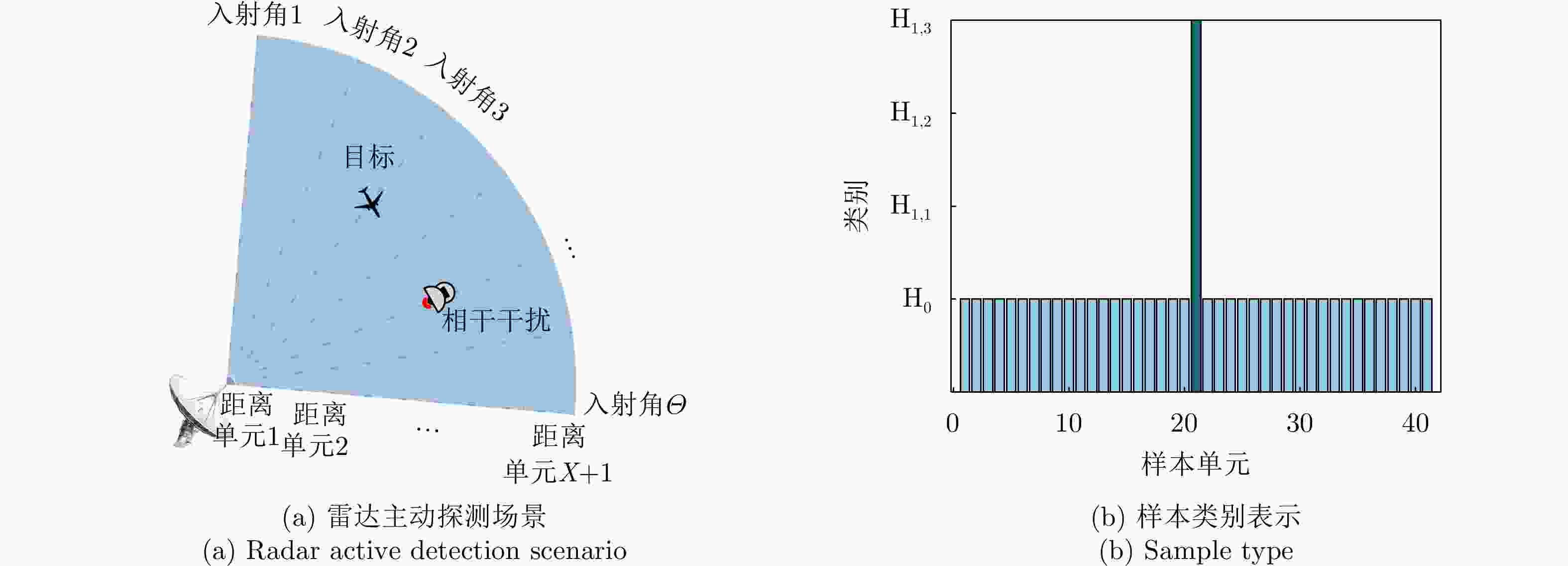
1 NCP样本分类与参数估计流程
1. Estimation procedure of NCP classification and parameters
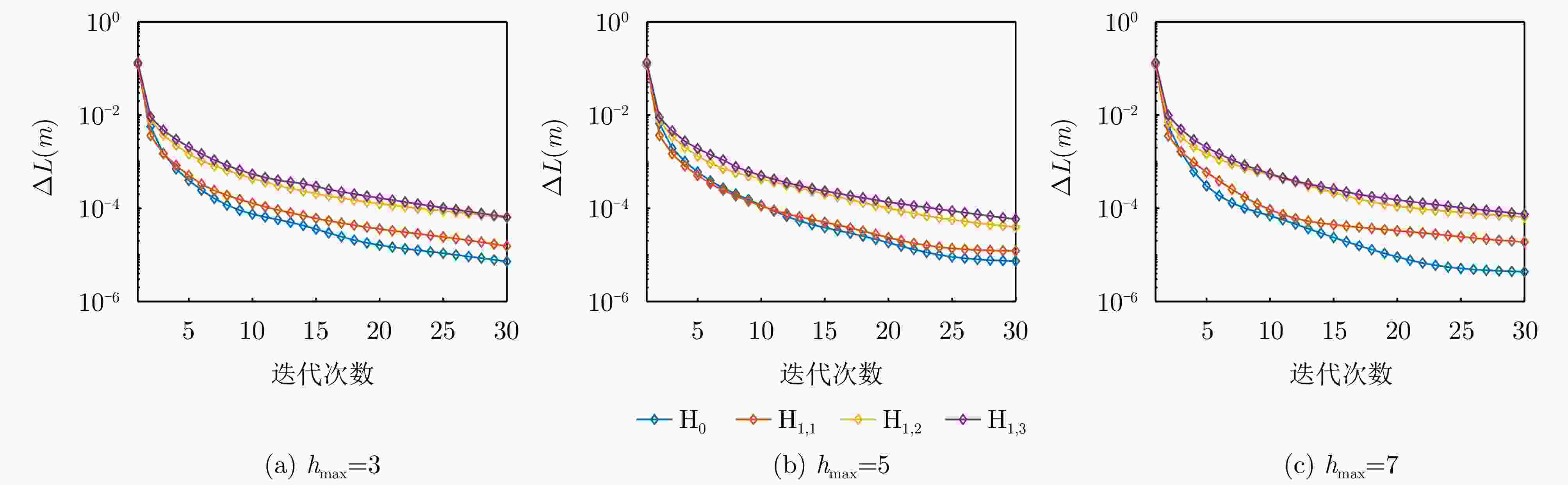
输入:$ {{\boldsymbol p}_l},l = 1,2,\cdots,L $ 初始化:${\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)^{(0)}}$, $ {\boldsymbol{M}}_{{\rm{NCP}},t}^{(0)} $, $ \mu _r^{(0)} $ for:$m = 1:\bar m $ E步优化:计算$ {{\boldsymbol p}_l} $的条件期望,得到
$ {q_l}(r),l = 1,2,\cdots,L,r = 0,1,\cdots,T $的更新规则式(9);M步优化: (1) 通过最大化对数似然函数更新$ {\mu _r} $,如式(11)所示; (2) 利用式(17)更新${\sigma ^2}$; (3) 利用式(18)更新$ {{\boldsymbol{M}}_{{\rm{NCP}},t}} $; end 输出:$ {\hat \sigma ^2} $, $ {\hat {\boldsymbol{M}}_{{\rm{NCP}},t}} $, ${\hat {\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{1,t}}$, ${\hat {\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{1,0}}$ 2 目标干扰场景分类与参数估计流程
2. Estimation procedure of scenario classification and parameters
输入:z, ${{\boldsymbol{z}}_x},x \in 1,2,\cdots,X$, ${\theta _1}$, ${\theta _2}$ 初始化:$ {\alpha ^{(0)}} $, $ {w^{(0)}} $, $ \chi _e^{(0)} $ for:${\theta _1} \in \varTheta ,{\theta _2} \in \varTheta $ for:$m = 1:\bar m $ E步优化:利用式(22)计算$ q(e),e = 0,1,2 $的优化结果; M步优化: (1) 结合辅助样本,利用式(24)计算M的估计值; (2) 利用式(25)对$ {\chi _e} $进行优化; for $h = 1:\bar h $ (3) 利用式(27)更新w; (4) 利用式(28)更新$ \alpha $; end end end 利用式(29)、式(30)估计目标与干扰的入射角度$ {\theta _t} $, $ {\theta _{\rm{cj}}} $; 输出:$ \hat \alpha $, $ \hat w $, $ {\hat \theta _t} $, $ {\hat \theta _{\rm{cj}}} $, $\hat e$ 表 1 NCP参数设置
Table 1. Parameter settings of NCP
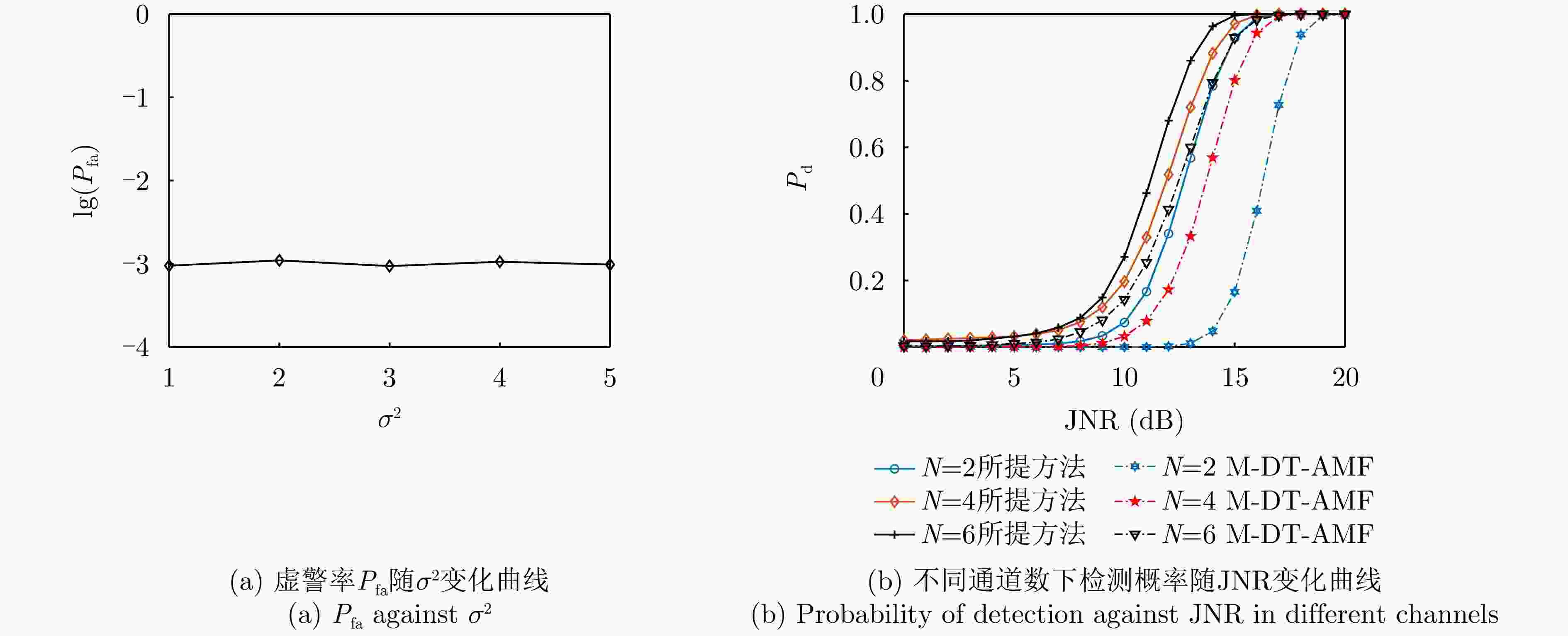
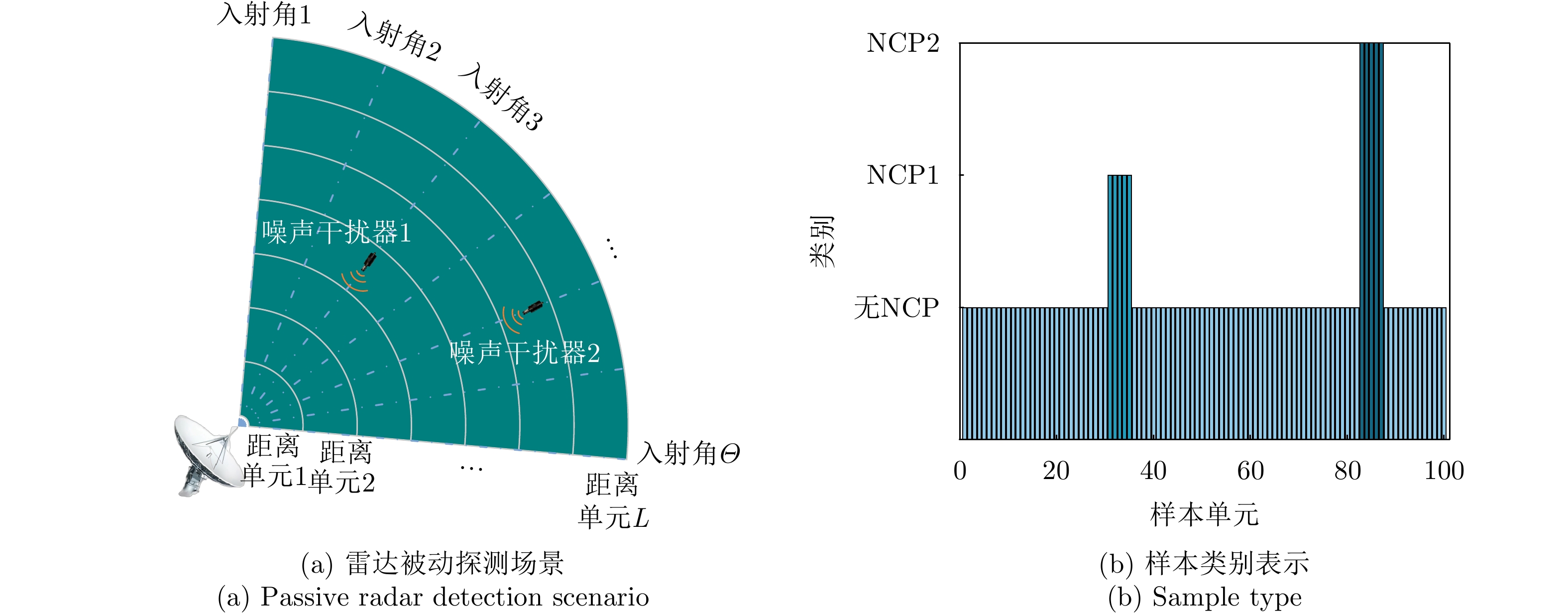
场景 类别 信号成分 JNR 入射角度 所在样本单元 场景1 1 无 \ \ 1~4, 9~19, 25~34, 41~59, 64~74, 80~89, 96~100 2 NCP1 15.0 dB –2° 5~8, 60~63 3 NCP2 15.0 dB 0° 20~24, 75~79 4 NCP3 15.0 dB 2° 35~40, 90~95 场景2 1 无 \ \ 1~4, 9~19, 25~34, 41~59, 64~74, 80~89, 96~100 2 NCP1 15.0 dB 0° 5~8, 60~63 3 NCP2 17.5 dB 0° 20~24, 75~79 4 NCP3 20.0 dB 0° 35~40, 90~95 表 2 CJ与目标参数设置
Table 2. Parameter settings of CJ and targets
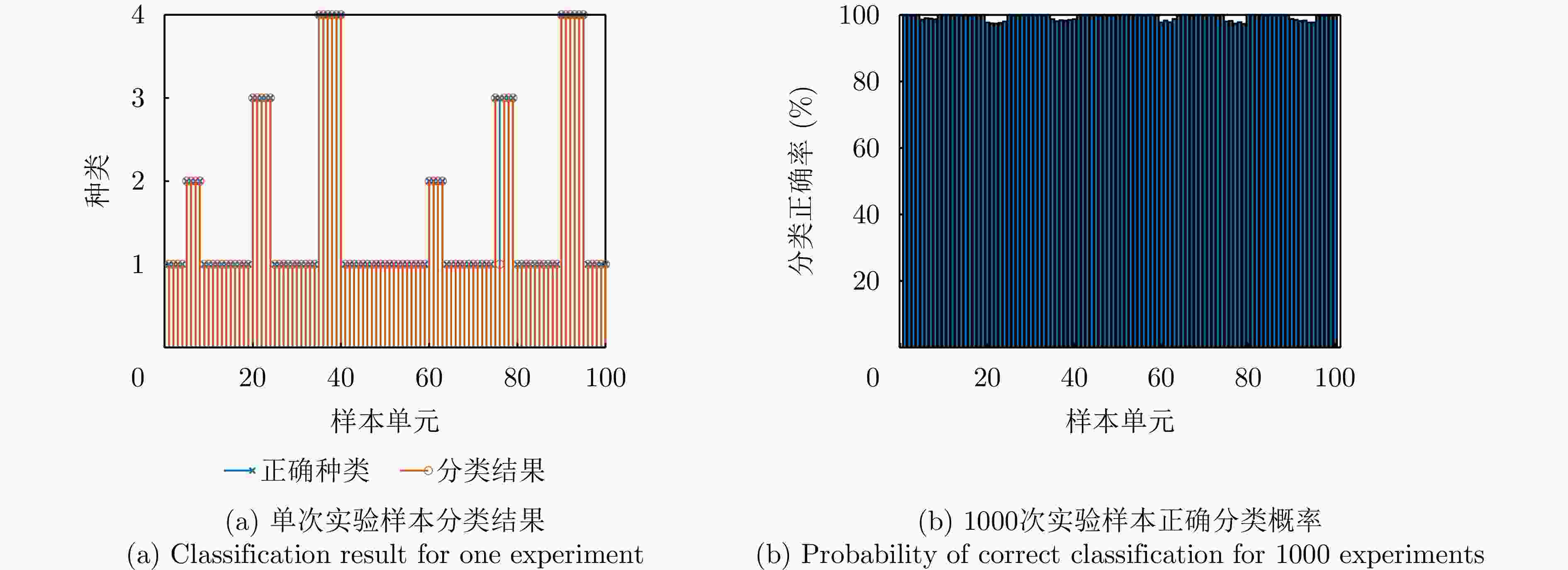
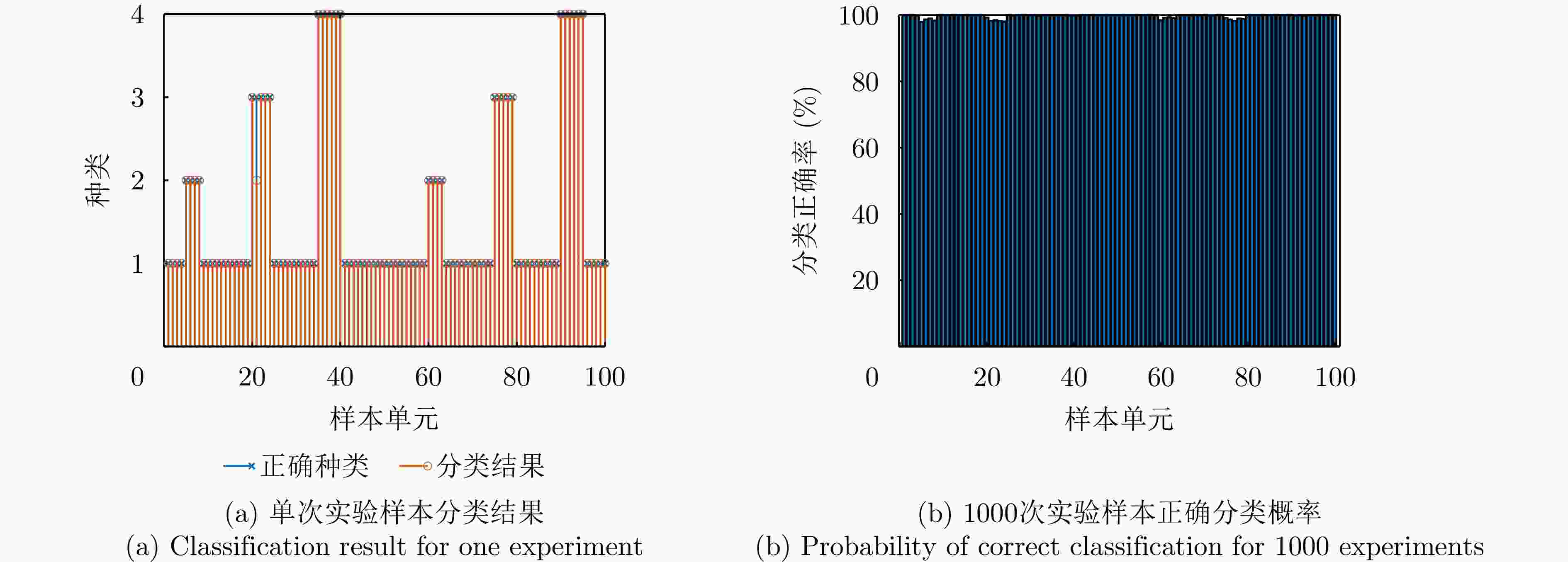
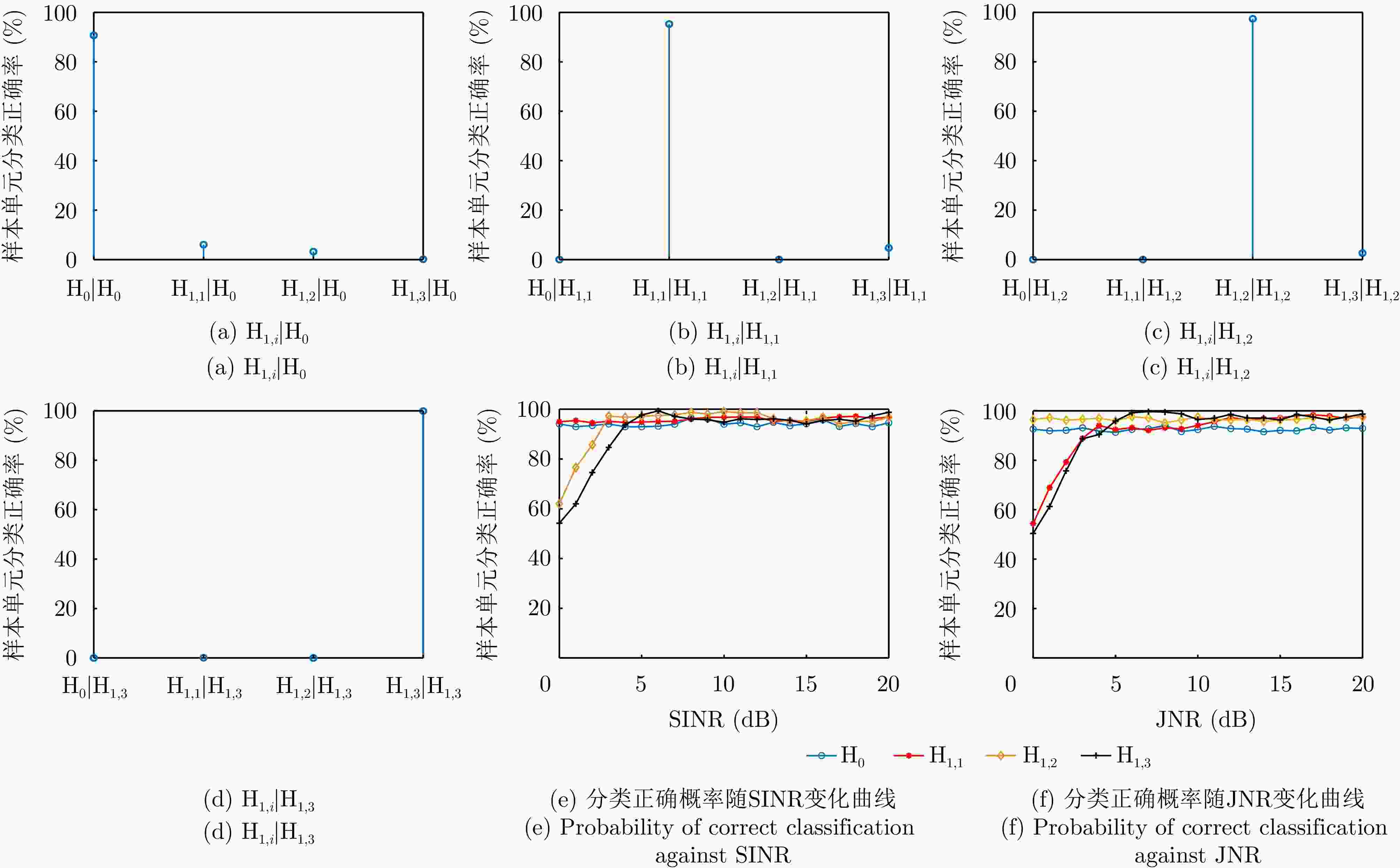
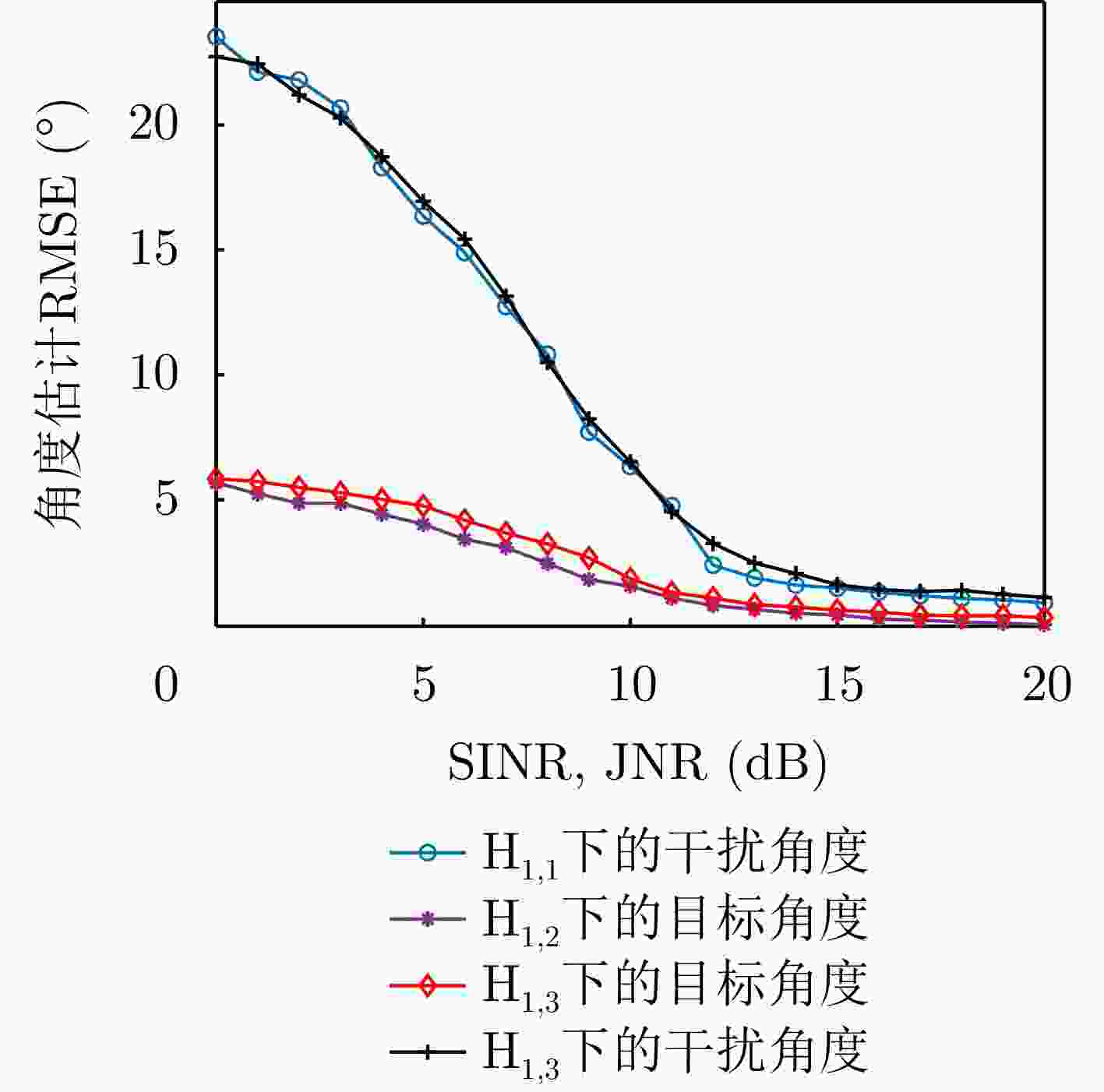
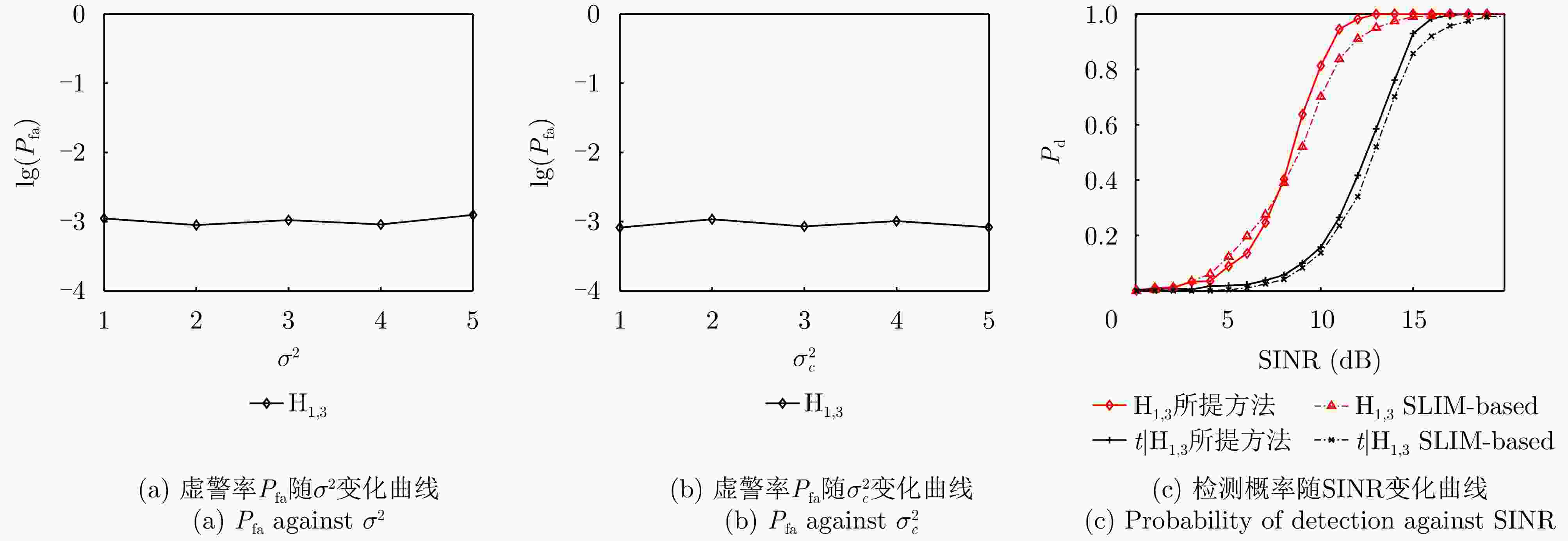
场景 类别 目标数量 SINR 入射角度 CJ数量 JNR 入射角度 $ {{\rm H}_0} $ 1 0 \ \ 0 \ \ $ {{\mathrm{H}}_{1,1}} $ 2 0 \ \ 1 10 dB 20° $ {{\mathrm{H}}_{1,2}} $ 3 1 10 dB 0° 0 \ \ $ {{\mathrm{H}}_{1,3}} $ 4 1 10 dB 0° 1 10 dB 20° -
[1] WANG Tianqi, YIN Chaoran, XU Da, et al. Analysis of MIMO radar detection algorithms with location capabilities: CFAR property and selectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 5426–5435. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3488688. [2] JIN Yuxi, YIN Chaoran, WANG Tianqi, et al. An adaptive target detection architecture for mismatched signals[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2025, 32: 1860–1864. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2025.3560534. [3] YIN Chaoran, WANG Tianqi, YAN Linjie, et al. Joint ML-Bayesian approach to adaptive radar detection in the presence of Gaussian interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 3701–3713. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3493063. [4] SUN Jiarui, HAO Chengpeng, YAN Linjie, et al. Multiple target detection in radar systems: A hybrid approach combining EM clustering and sparsity-based reconstruction[C]. 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Technologies for Defense and Security (TechDefense), Naples, Italy, 2024: 441–445. doi: 10.1109/TechDefense63521.2024.10863468. [5] 金禹希, 吴敏, 郝程鹏, 等. 基于模型阶数选择准则的稳健杂波边缘检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(7): 2703–2711. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230999.JIN Yuxi, WU Min, HAO Chengpeng, et al. A robust clutter edge detection method based on model order selection criterion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(7): 2703–2711. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230999. [6] 张庭赫, 黄学宇, 张启亮. 主瓣掩护式干扰下单脉冲雷达目标检测方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报, 2023, 24(6): 65–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-1915.2023.06.009.ZHANG Tinghe, HUANG Xueyu, and ZHANG Qiliang. A target detection method for monopulse radar under condition of main lobe cover interference[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University, 2023, 24(6): 65–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-1915.2023.06.009. [7] 张顺生, 刘美慧, 王文钦. 基于多普勒扩展补偿的FDA-MIMO雷达运动目标检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 666–675. doi: 10.12000/JR22042.ZHANG Shunsheng, LIU Meihui, and WANG Wenqin. FDA-MIMO radar moving target detection based on Doppler spread compensation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 666–675. doi: 10.12000/JR22042. [8] 王永良, 彭应宁. 空时自适应信号处理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2000.WANG Yongliang and PENG Yingning. Space-Time Adaptive Processing[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2000. [9] SUN Mengru, LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, et al. Multiple subspace-based target detection in deterministic interference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 3134–3138. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3491012. [10] WANG Tianqi, YIN Chaoran, XU Da, et al. Joint detection and delay-Doppler estimation algorithms for MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 809–823. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3355753. [11] 王永良, 刘维建, 谢文冲, 等. 机载雷达空时自适应检测方法研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 201–207. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13081.WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, XIE Wenchong, et al. Research progress of space-time adaptive detection for airborne radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 201–207. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13081. [12] 陈世进, 闫晟, 郝程鹏, 等. 一种适用于多输入多输出声呐的稳健空时自适应检测方法[J]. 声学学报, 2022, 47(6): 777–788. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2022.06.013.CHEN Shijin, YAN Sheng, HAO Chengpeng, et al. A robust space-time adaptive detection method for multiple-input multiple-output sonar[J]. Acta Acustica, 2022, 47(6): 777–788. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2022.06.013. [13] HAN Sudan, ZHANG Yuxuan, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Sparsity-based classification approaches for radar data in the presence of clutter edges and discretes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 2141–2162. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3210072. [14] 闫林杰, 郝程鹏, 殷超然, 等. 部分均匀环境下适用于空间对称线阵的修正广义似然比检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 443–452. doi: 10.12000/JR20140.YAN Linjie, HAO Chengpeng, YIN Chaoran, et al. Modified generalized likelihood ratio test detection based on a symmetrically spaced linear array in partially homogeneous environments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 443–452. doi: 10.12000/JR20140. [15] KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES–22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745. [16] KELLY E J. Performance of an adaptive detection algorithm; rejection of unwanted signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1989, 25(2): 122–133. doi: 10.1109/7.18674. [17] CHEN W S and REED I S. A new CFAR detection test for radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 1991, 1(4): 198–214. doi: 10.1016/1051-2004(91)90113-Y. [18] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446. [19] DE MAIO A. Rao test for adaptive detection in Gaussian interference with unknown covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3577–3584. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894238. [20] DE MAIO A. A new derivation of the adaptive matched filter[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(10): 792–793. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.835464. [21] STINCO P, GRECO M, and GINI F. Adaptive detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse-gamma texture[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 434–437. doi: 10.1109/CIE-Radar.2011.6159570. [22] WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Polarimetric target detection in compound Gaussian Sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4021205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3140057. [23] WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Adaptive CFAR detectors for mismatched signal in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3502705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3047390. [24] WU Haoqi, GUO Hongzhi, WANG Zhihang, et al. Adaptive nonzero-mean detection algorithm in compound gaussian sea clutter with generalized inverse gaussian texture[C]. IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 9853–9857. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10640542. [25] XU Shuwen, WANG Zhexiang, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Optimum and near-optimum coherent CFAR detection of radar targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 1692–1706. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3120045. [26] LEE W K I and ROMERO R A. Detection performance of enhanced electronic protection mitigation in space-time adaptive processing against adaptive shaped interference[C]. 2024 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf24), Denver, USA, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2458775.2024.10548950. [27] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [28] BENVENUTI D, ADDABBO P, GIUNTA G, et al. ECCM strategies for radar systems against smart noise-like jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 3912–3926. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3445530. [29] CAROTENUTO V and DE MAIO A. A clustering approach for jamming environment classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1903–1918. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3050655. [30] GHOJAVAND K, DERAKHTIAN M, and BIGUESH M. Rao-based detectors for adaptive target detection in the presence of signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1662–1672. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2969047. [31] 兰岚, 张翔, 许京伟, 等. 阵列雷达时空多维域编码抗主瓣转发式欺骗干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 439–455. doi: 10.12000/JR24229.LAN Lan, ZHANG Xiang, XU Jingwei, et al. Main-lobe deceptive jammers with array radars using space-time multidimensional coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 439–455. doi: 10.12000/JR24229. [32] ORLANDO D. A novel noise jamming detection algorithm for radar applications[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(2): 206–210. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2645793. [33] JING Xinchen, SU Hongtao, JIA Congyue, et al. Adaptive target detection based on GLRT in the presence of clutter and noise-like jamming[C]. 2022 5th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 224–228. doi: 10.1109/ICICSP55539.2022.10050641. [34] YAN Linjie, ADDABBO P, ZHANG Yuxuan, et al. A sparse learning approach to the detection of multiple noise-like jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4367–4383. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2988960. [35] CAROTENUTO V, HAO Chengpeng, ORLANDO D, et al. Detection of multiple noise-like jammers for radar applications[C]. 2018 5th IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Rome, Italy, 2018: 328–333. doi: 10.1109/MetroAeroSpace.2018.8453566. [36] YAN Linjie, ADDABBO P, HAO Chengpeng, et al. A sparse learning approach to multiple noise-like jammers detection[C]. 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium - Fall (PIERS - Fall), Xiamen, China, 2019: 155–161. doi: 10.1109/PIERS-Fall48861.2019.9021566. [37] BANDIERA F, BESSON O, ORLANDO D, et al. GLRT-based direction detectors in homogeneous noise and subspace interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(6): 2386–2394. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.893927. [38] BANDIERA F, FARINA A, ORLANDO D, et al. Detection algorithms to discriminate between radar targets and ECM signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(12): 5984–5993. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2077283. [39] SUN Mengru, LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, et al. Rao and Wald tests for target detection in coherent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 1906–1921. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3122833. [40] YAN Sheng, LOTFI F, CHEN Shijin, et al. Innovative two-stage radar detection architectures in adverse scenarios using two training data sets[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1165–1169. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3084868. [41] YAN Linjie, ADDABBO P, HAO Chengpeng, et al. New ECCM techniques against noiselike and/or coherent interferers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1172–1188. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2929968. [42] ADDABBO P, HAN Sudan, ORLANDO D, et al. Learning strategies for radar clutter classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1070–1082. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3050985. [43] PRADEEPA R, PETER R J, THEAGARAJAN L N, et al. EM based GLRT detector for MIMO active sonar using bistatic reverberation model[C]. OCEANS 2023 - Limerick, Limerick, Ireland, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/OCEANSLimerick52467.2023.10244593. [44] SCHNITER P and BYRNE E. Adaptive detection of structured signals in low-rank interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3439–3454. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2917810. [45] COLUCCIA A, FASCISTA A, ORLANDO D, et al. Adaptive radar detection in heterogeneous clutter plus thermal noise via the expectation-maximization algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(1): 212–225. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3322389. [46] YAN Linjie, HAN Sudan, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Innovative cognitive approaches for joint radar clutter classification and multiple target detection in heterogeneous environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 1010–1022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2023.3250084. [47] ZHANG Xun, DENG Jiale, and SU Rui. The EM algorithm for a linear regression model with application to a diabetes data[C]. 2016 International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing (PIC), Shanghai, China, 2016: 114–118. doi: 10.1109/PIC.2016.7949477. [48] STOICA P and SELEN Y. Model-order selection: A review of information criterion rules[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2004, 21(4): 36–47. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2004.1311138. [49] 徐震宇, 刘维建, 陈小龙, 等. 加权广义逆高斯杂波下距离扩展目标的自适应检测[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(6): 1393–1410. doi: 10.12000/JR25072XU Zhenyu, LIU Weijian, CHEN Xiaolong, et al. Adaptive detection of range-distributed targets in weighted generalized inverse Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(6): 1393–1410. doi: 10.12000/JR25072. [50] YAN Linjie, HAO Chengpeng, ORLANDO D, et al. Parametric space-time detection and range estimation of point-like targets in partially homogeneous environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1228–1242. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2928672. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: