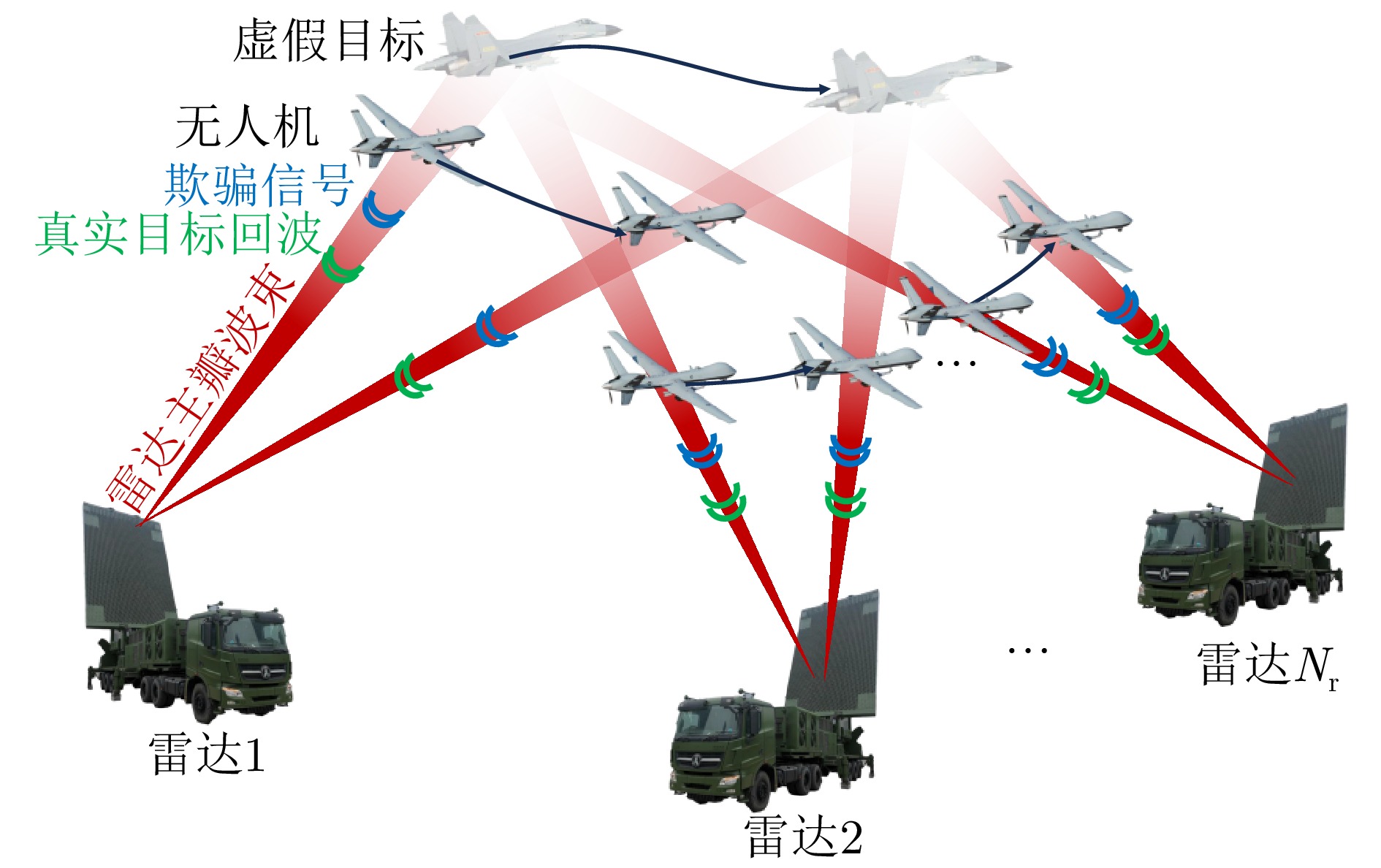
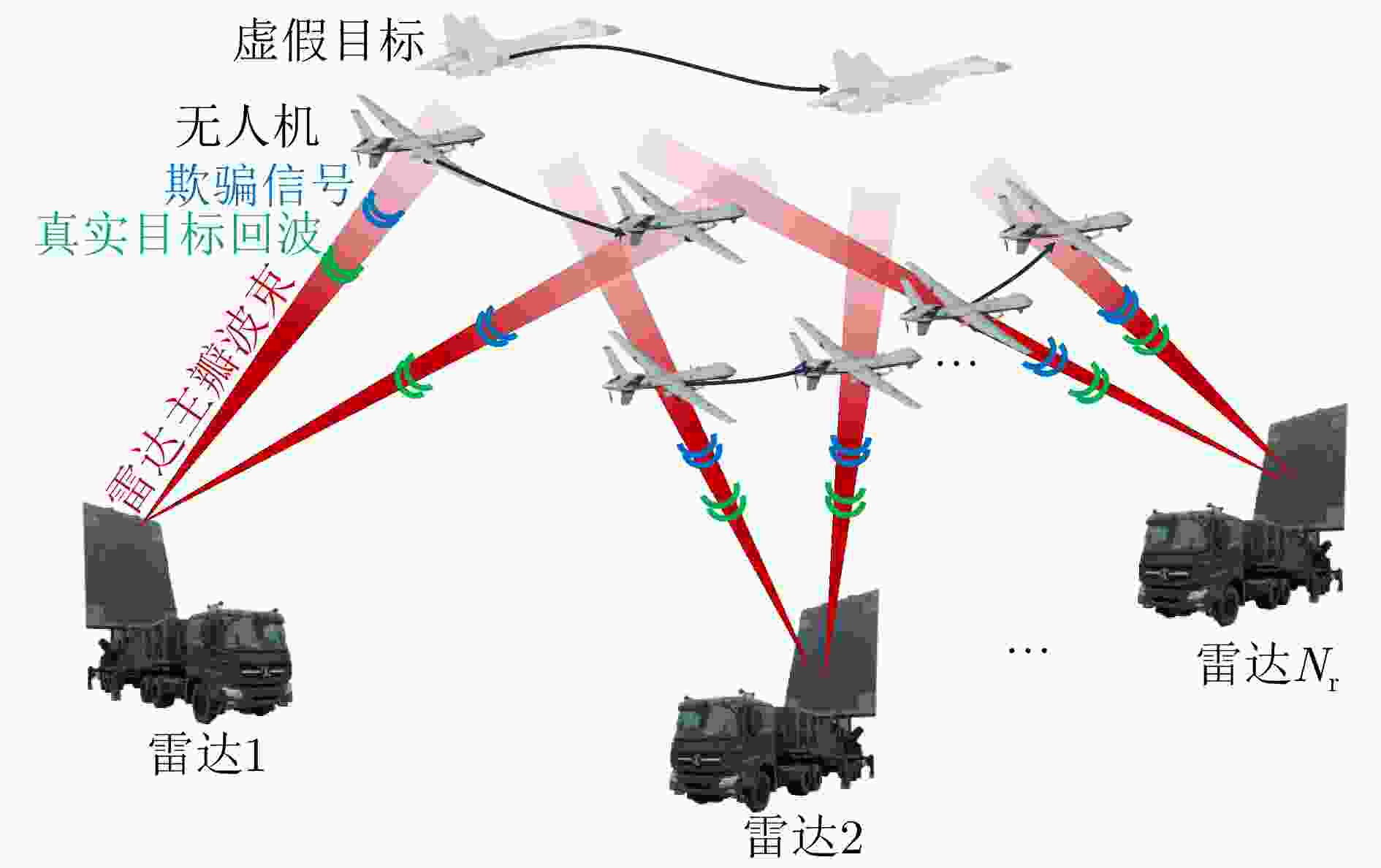
Game Theory-based Joint Optimization Algorithm for UAV Swarm Task Allocation and Trajectory Planning in Phantom Track Deception
-
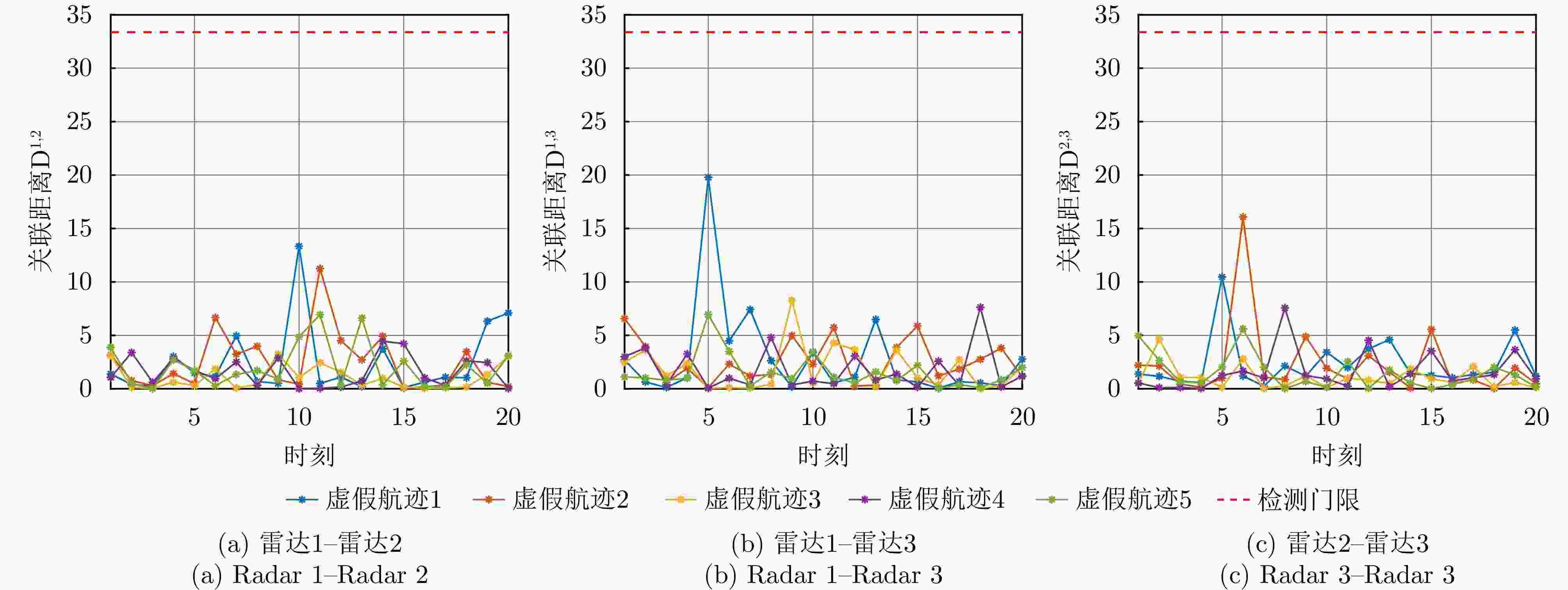
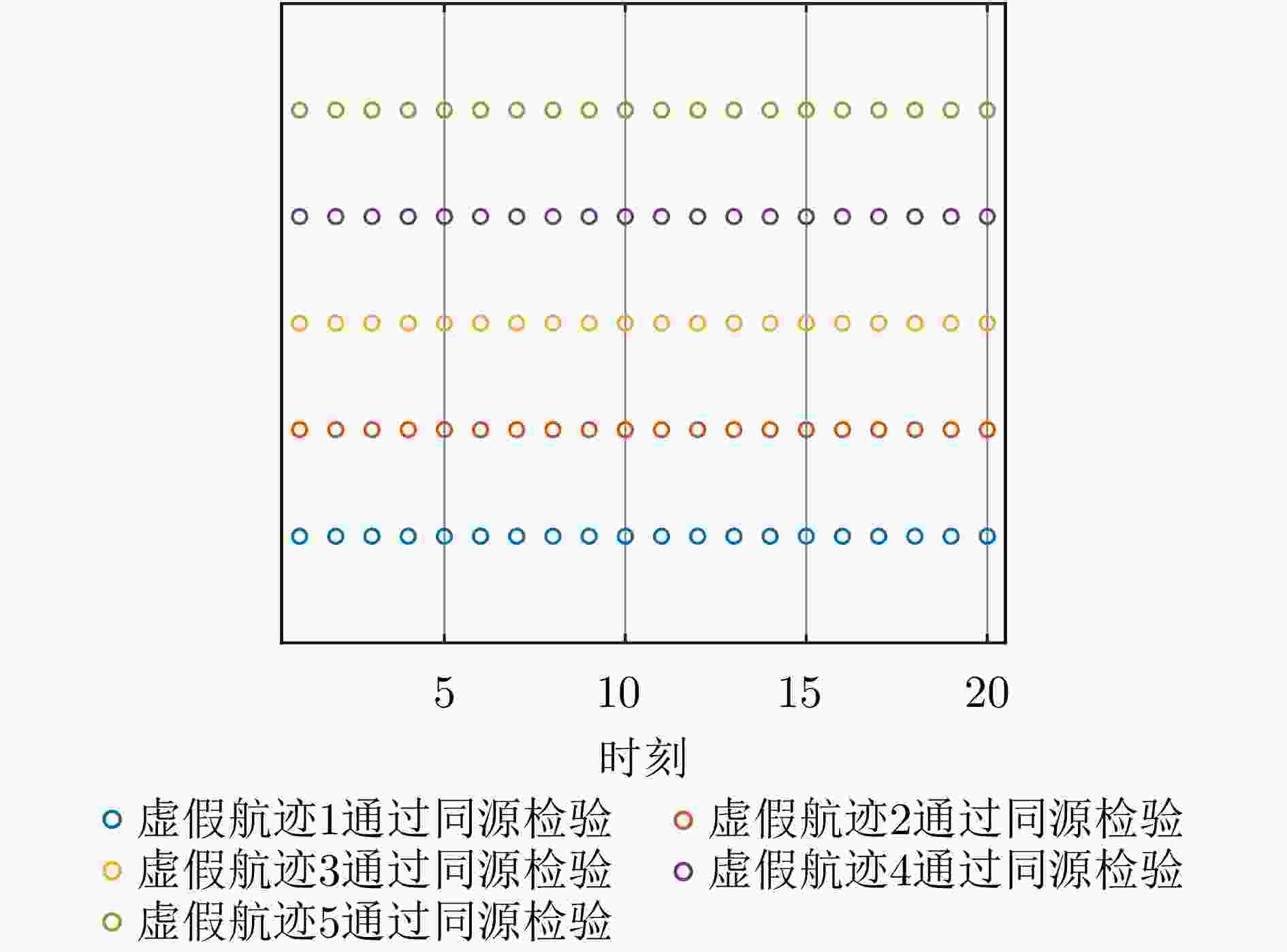
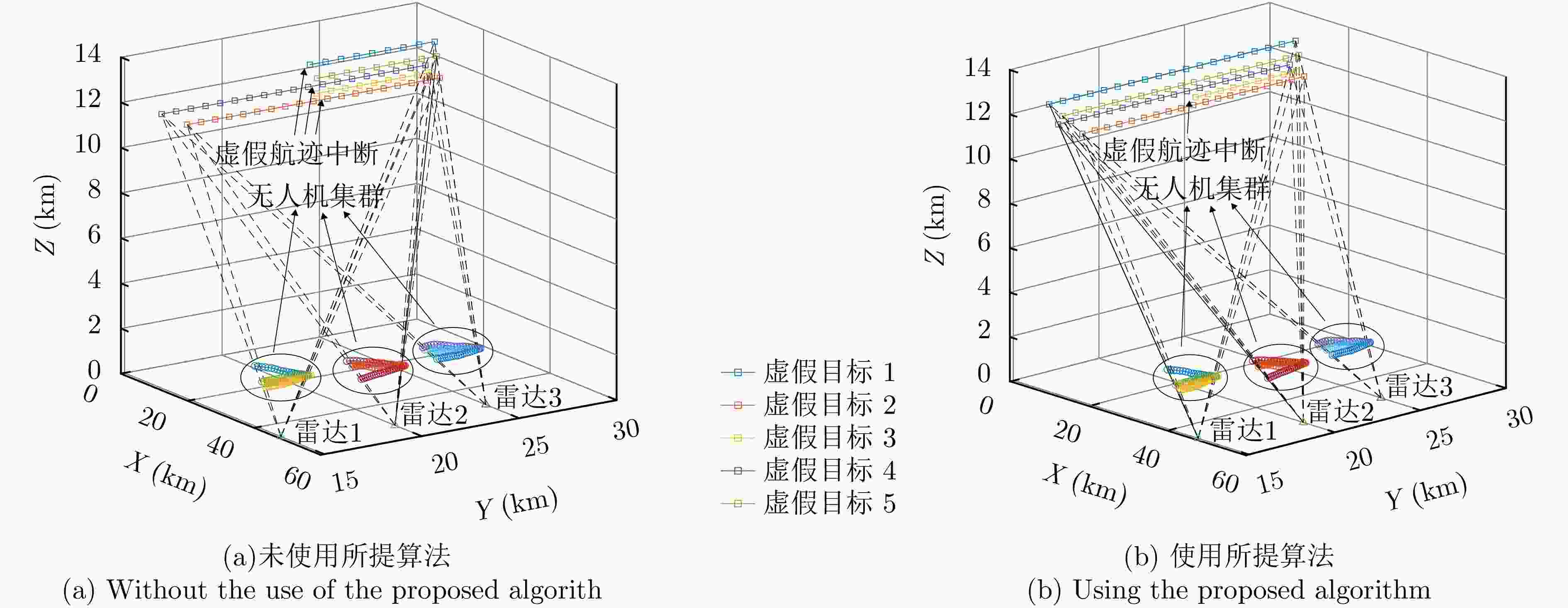
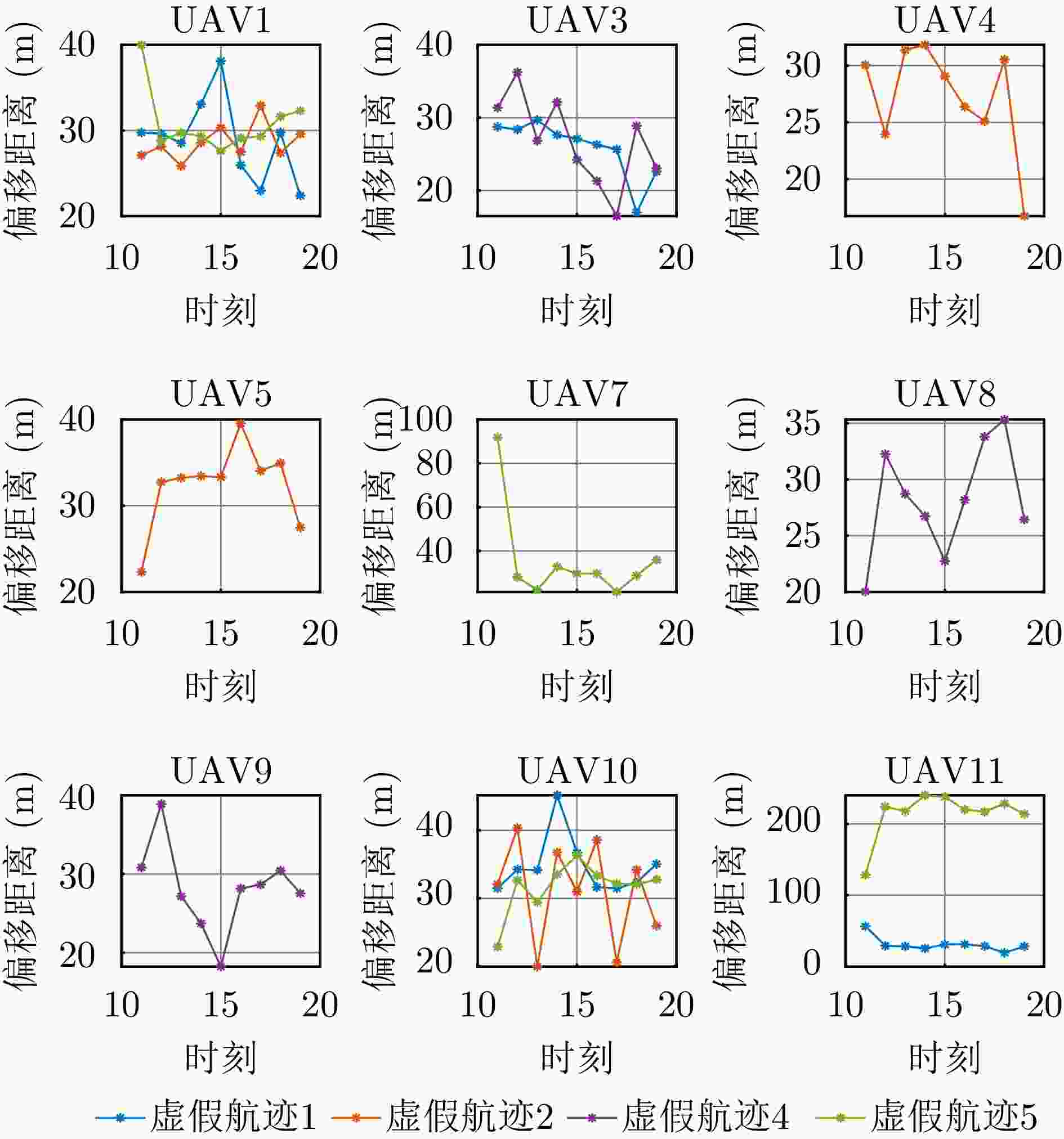
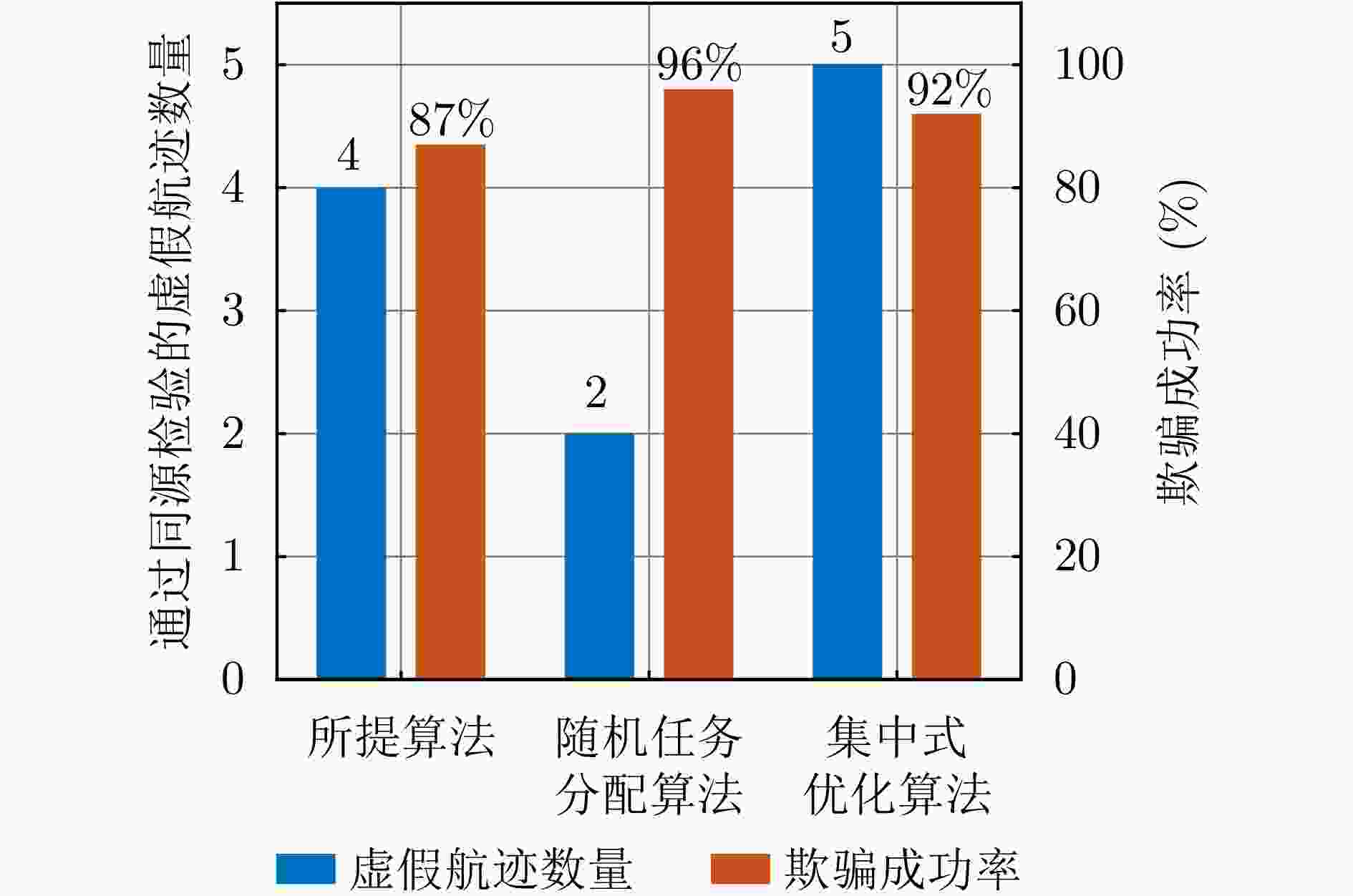
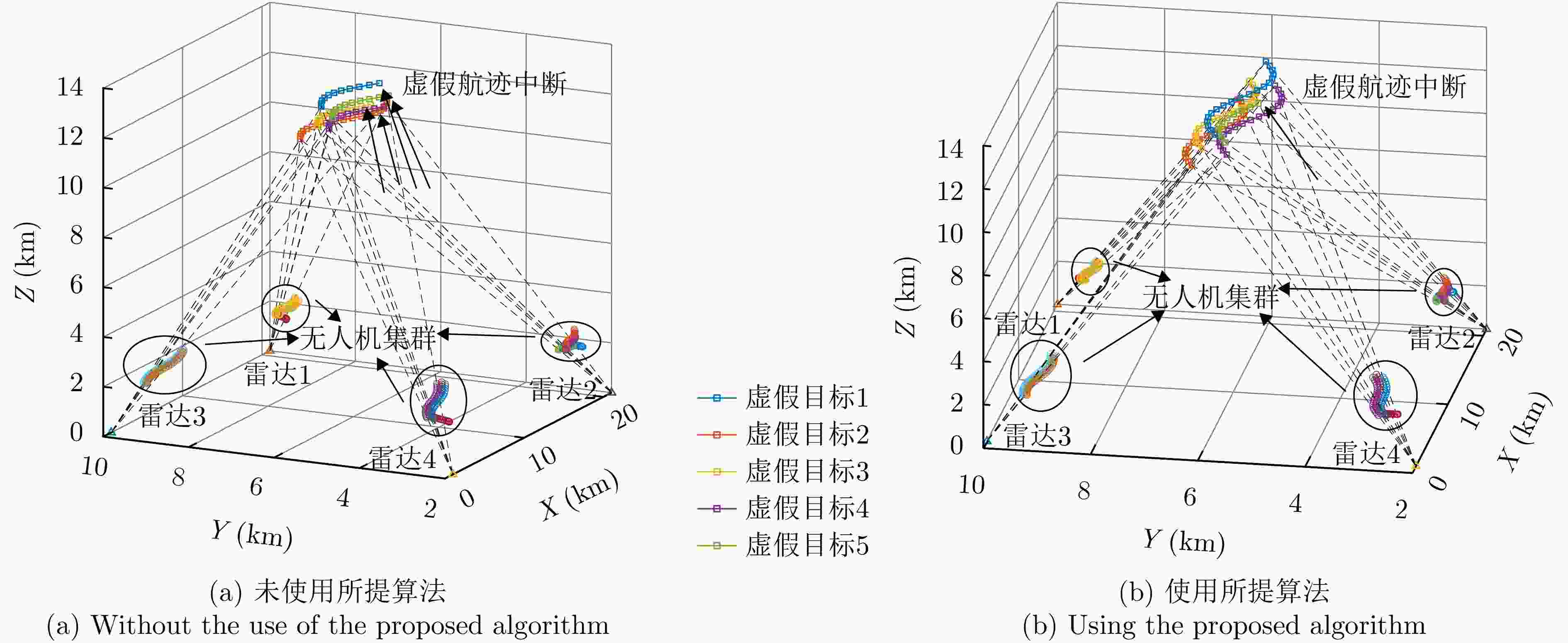
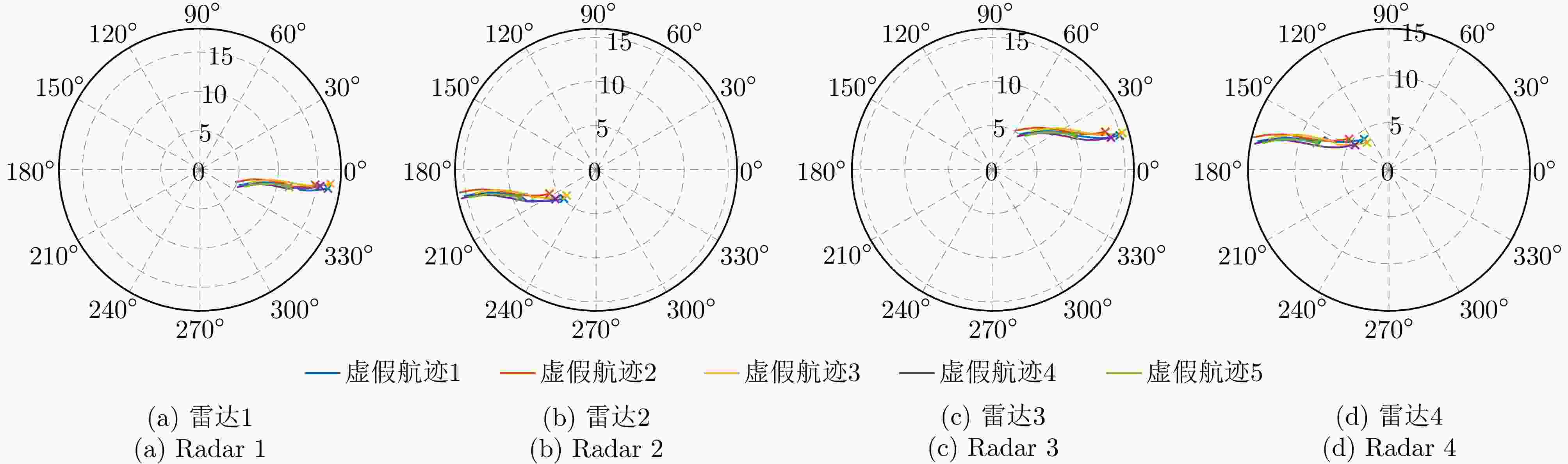
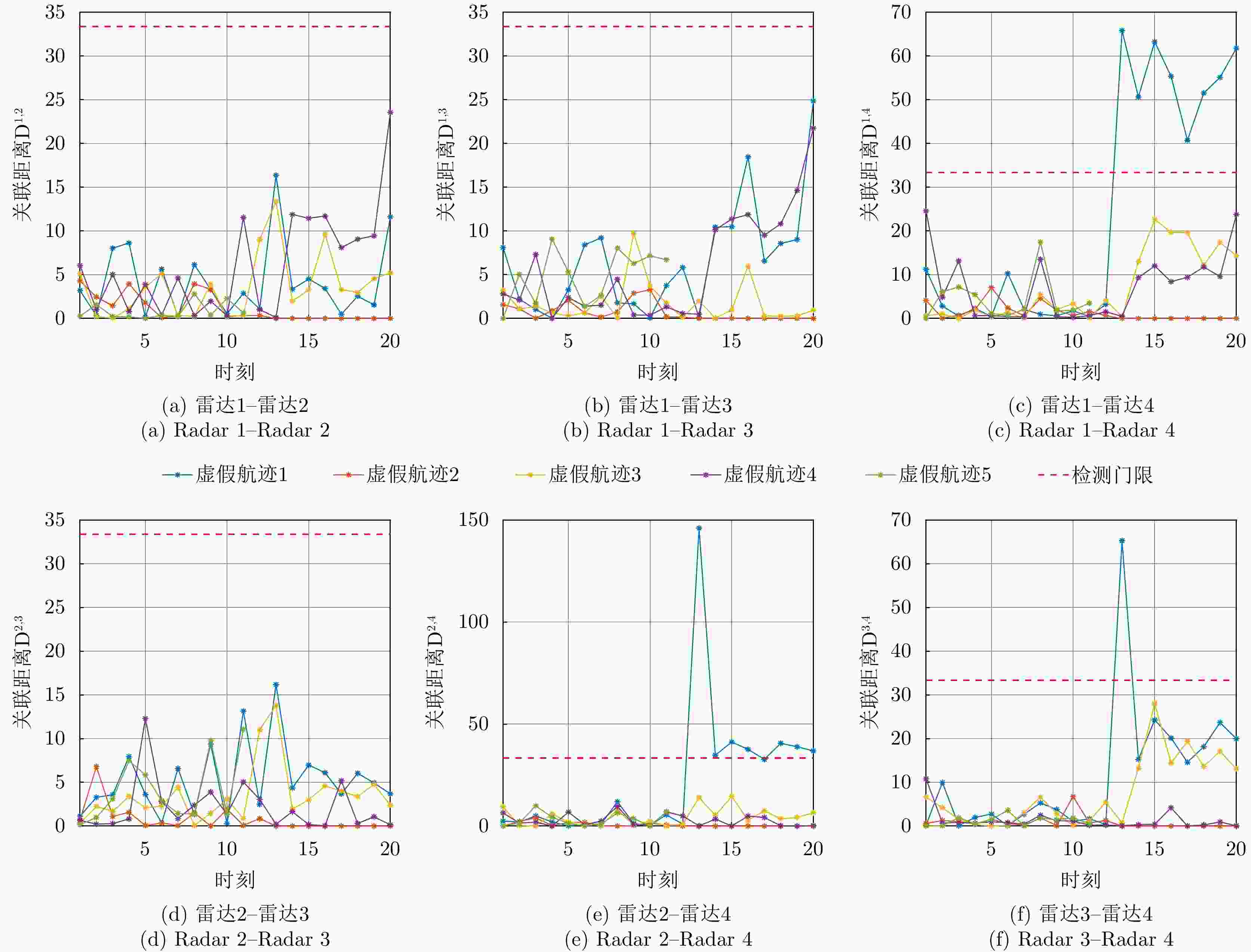
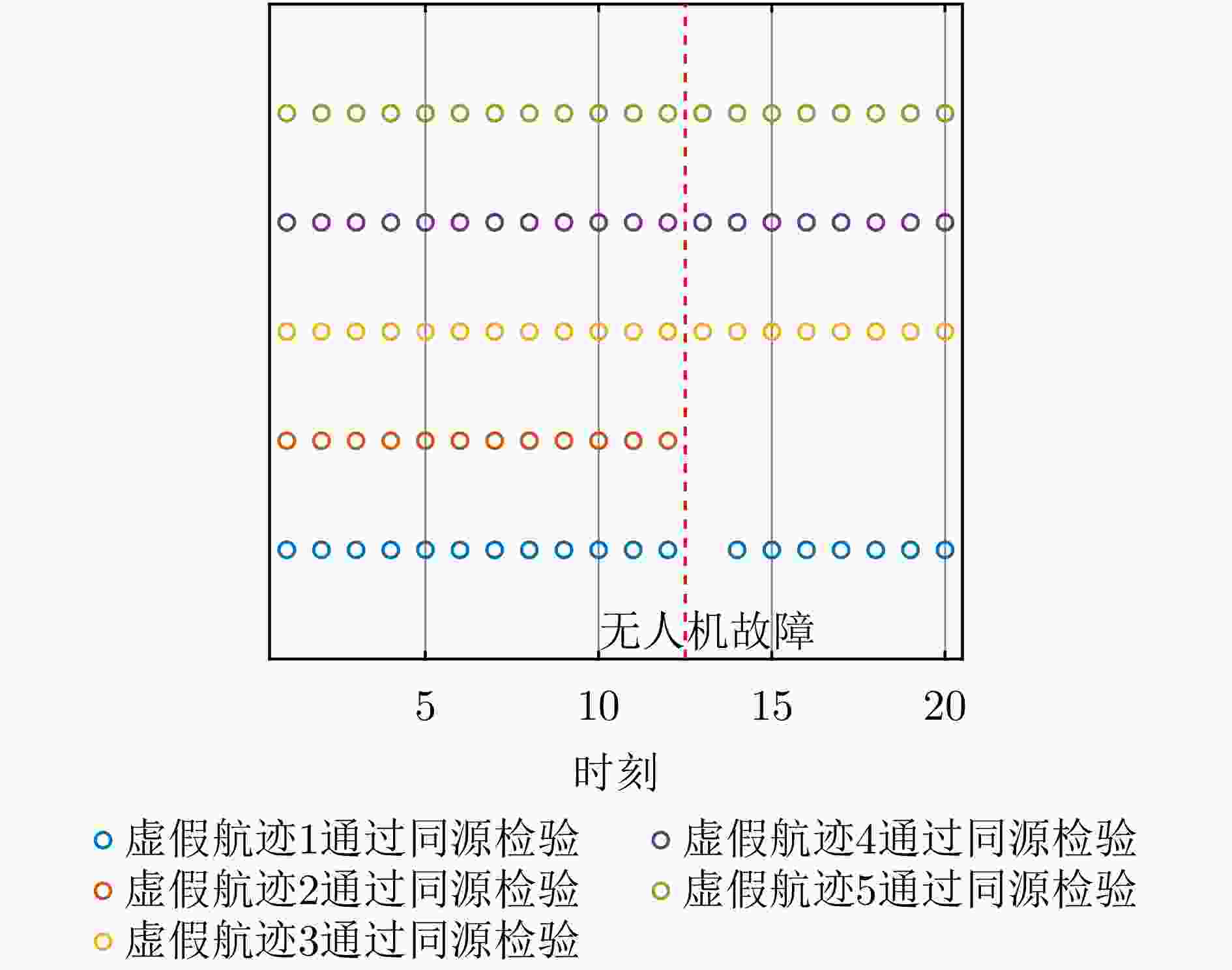
摘要: 针对无人机集群对组网雷达实施航迹欺骗过程中因平台故障、损毁等导致生成虚假航迹中断的问题,提出面向航迹欺骗的无人机集群任务分配与飞行路径联合博弈优化算法。首先,基于去中心化的集群协作机制,构建针对组网雷达的无人机集群航迹欺骗合作博弈模型。在此基础上,根据组网雷达同源检验准则,以最大化无人机集群航迹欺骗博弈效用函数为优化目标,以满足集群动力学性能与任务分配限制为约束条件,建立无人机集群航迹欺骗博弈优化模型,并通过严格势博弈理论证明纳什均衡解的存在性与收敛性。针对上述非凸、非线性混合整数优化问题,采用基于分布式联盟博弈和遗传算法的迭代算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,与现有算法相比,所提算法能够在平台故障、损毁等情况下,对无人机集群欺骗干扰任务和飞行路径进行联合重规划,提升针对组网雷达生成虚假航迹的连续性和航迹欺骗效果。Abstract: To address interruptions in phantom tracks caused by platform failures or damage during Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarm deception operations against radar networks, this study proposes a game theory-based joint optimization algorithm for UAV swarm task allocation and trajectory planning. A decentralized swarm cooperation mechanism is designed to create a cooperative game model for UAV phantom track deception against radar networks. Based on the radar network homology test criterion, an optimization model is developed to maximize the utility function of the phantom track deception game, subject to constraints on UAV swarm kinematic performance and task allocation requirements. The existence and convergence of a Nash equilibrium are rigorously proven using exact potential game theory. To address the resulting non-convex, non-linear, mixed-integer optimization problem, an iterative algorithm is developed that combines distributed coalition game theory with a genetic algorithm. The simulation results demonstrate that, compared with existing approaches, the proposed algorithm effectively replans deception tasks and trajectories in response to platform failures or damage, thereby enhancing the continuity and effectiveness of phantom track generation against radar networks.
-
Key words:
- Phantom track deception /
- UAV swarm /
- Radar network /
- Coalition game /
- Homology test
-
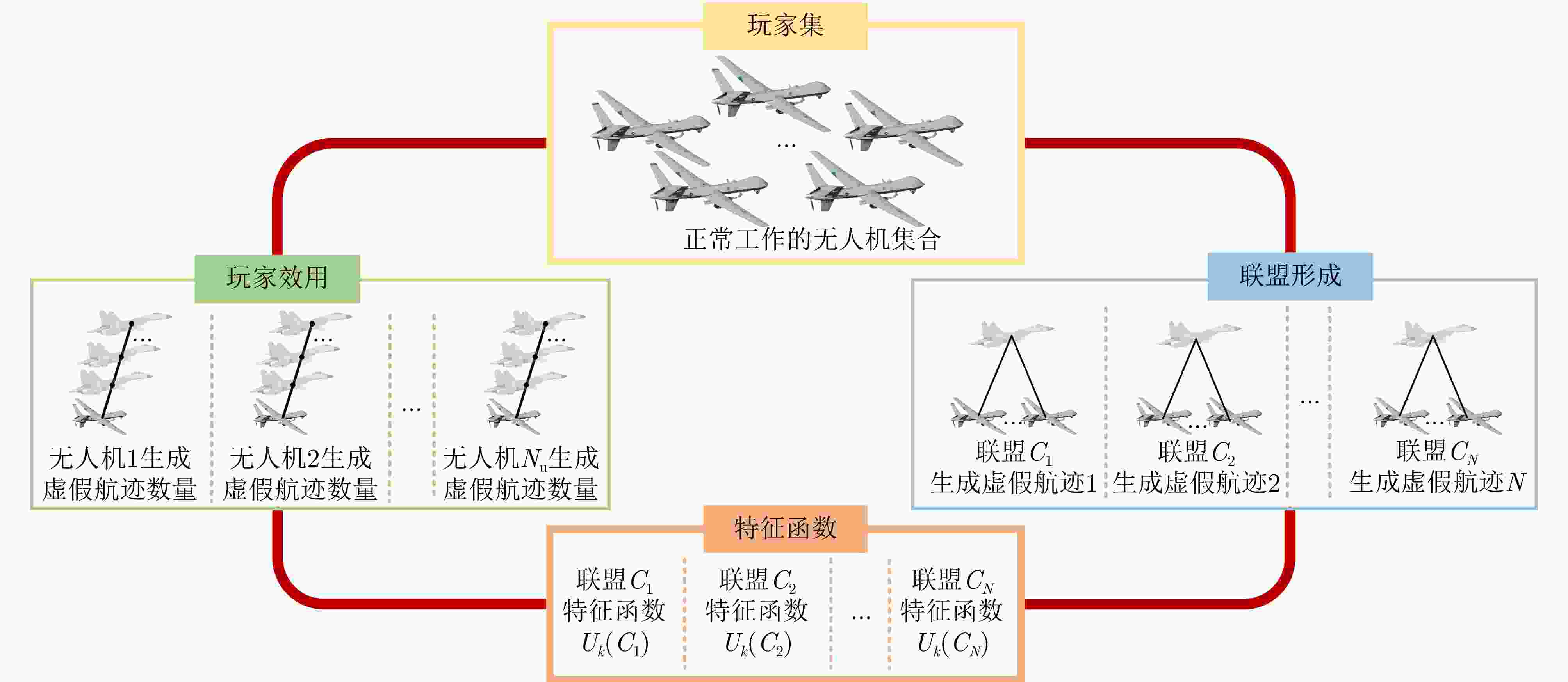
1 基于联盟博弈的无人机集群任务分配与飞行路径联合优化算法
1. Coalitional game-based joint optimization algorithm of task allocation and trajectory planning in UAV swarm
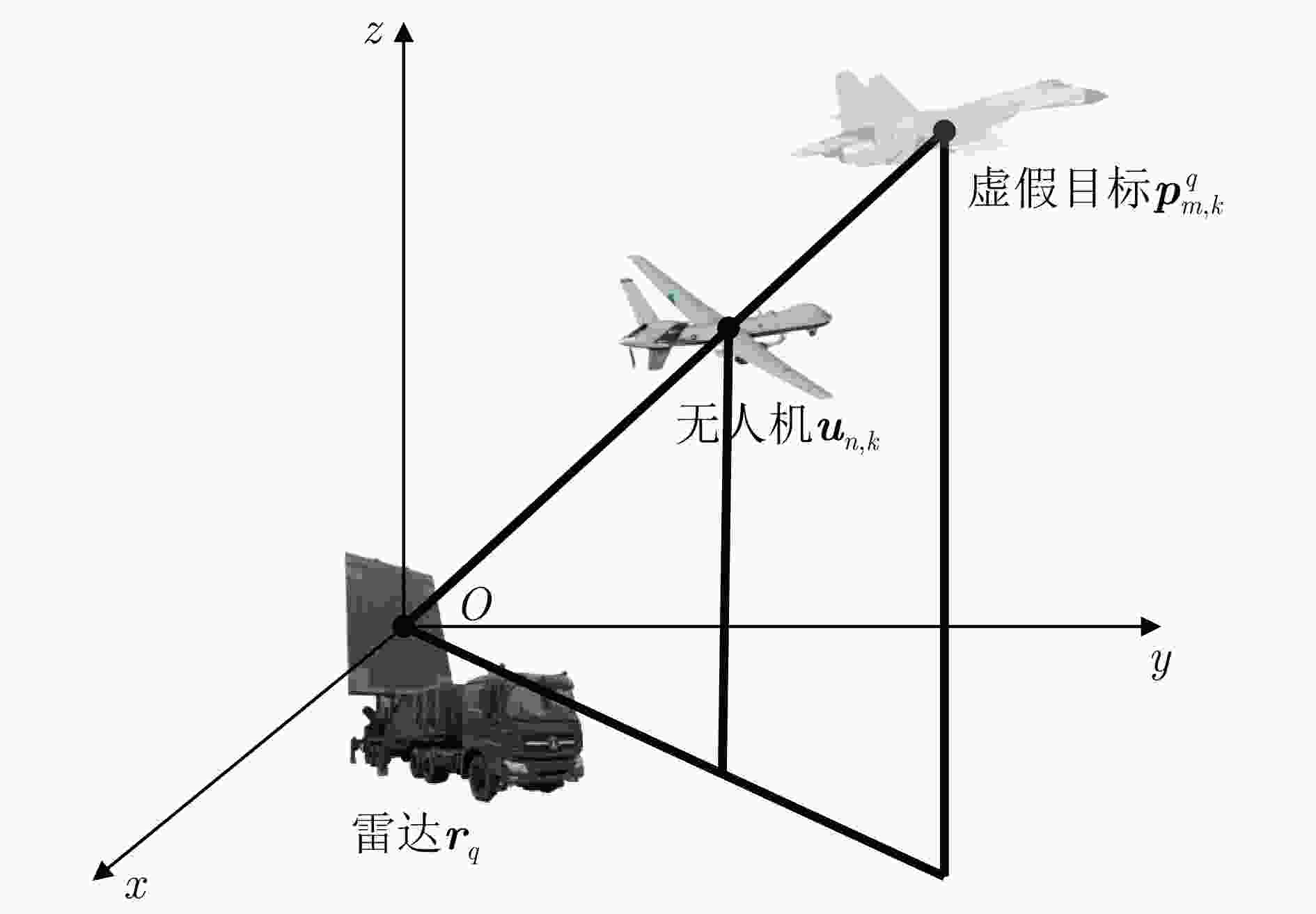
输入:$\left( {k - 1} \right)$时刻无人机集群任务分配方案及空间坐标,k时刻
正常工作的无人机集合$ {\mathcal{W}_k} $,预设虚假航迹空间坐标${\hat p_{m,k}}$,组
网雷达站址坐标、SRC及射频参数,最大迭代次数${I_{\max }}$输出:k时刻的无人机集群任务分配和飞行路径优化结果 1 将$\left( {k - 1} \right)$时刻的无人机集群任务分配方案${{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{k - 1}}$作为k时刻的
无人机集群初始任务分配方案;2 正常工作的各架无人机根据初始任务分配和飞行路径计算自身
效用$ {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{a}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) $;3 for $i = 1:{I_{\max }}$ do: 4 随机选择无人机$ n \in {\mathcal{W}_k} $,利用遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,
GA)求解式(24),在固定其他无人机策略选择情况下得到任务分
配和飞行路径优化结果;5 计算无人机n调整策略后的自身效用 $ {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\tilde {\boldsymbol{a}}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) $; 6 if $ {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\tilde {\boldsymbol{a}}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) \ge $ $ {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{a}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) $ then: 7 无人机n更新其任务分配与飞行路径,无人机集群更新其
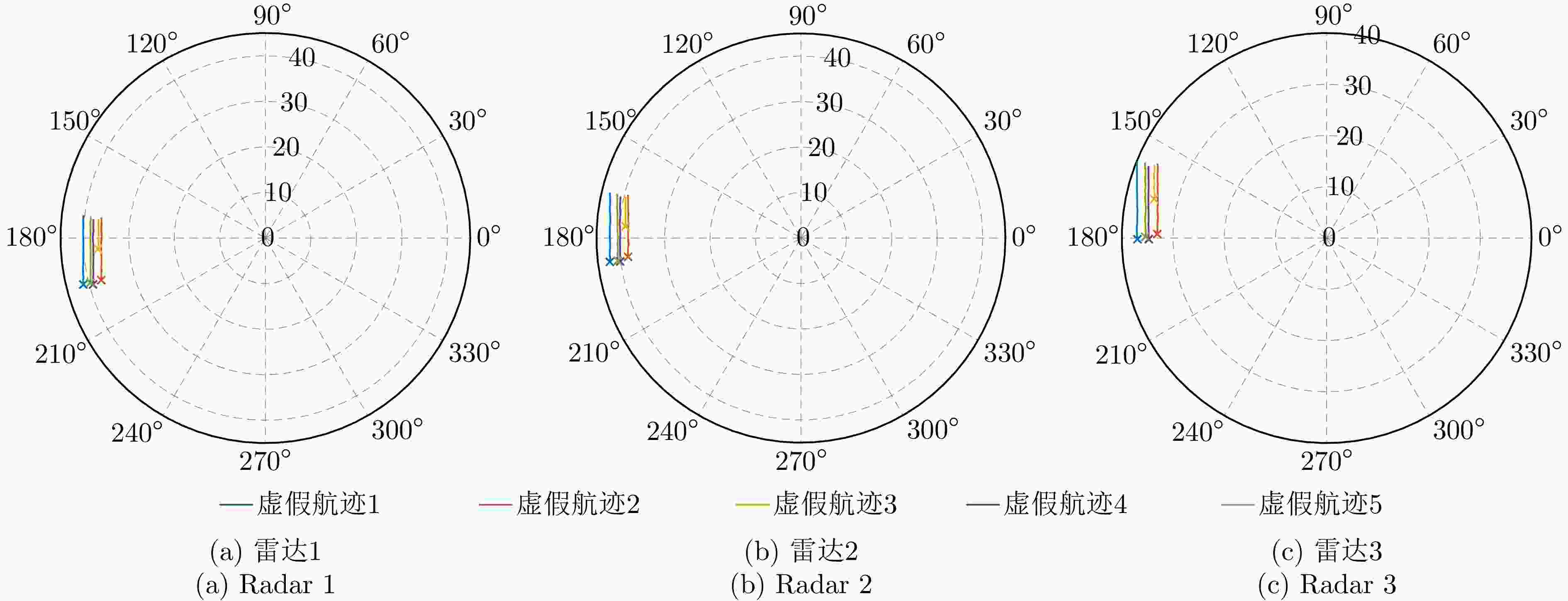
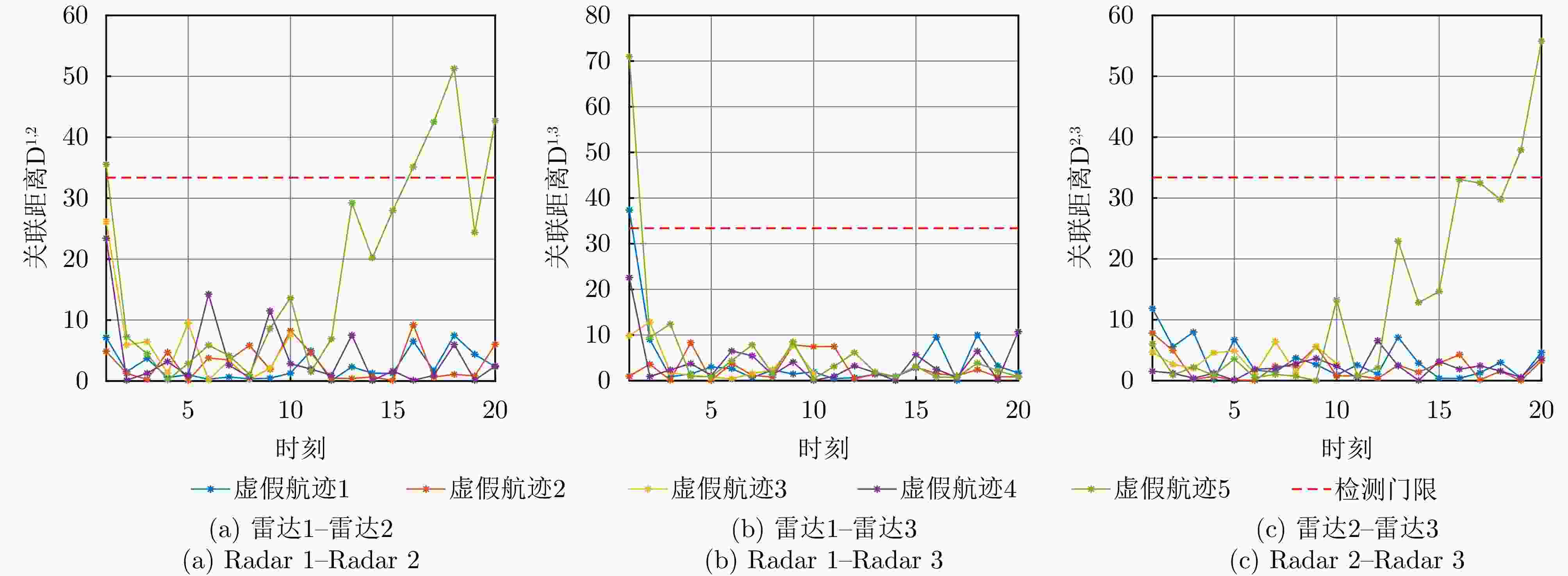
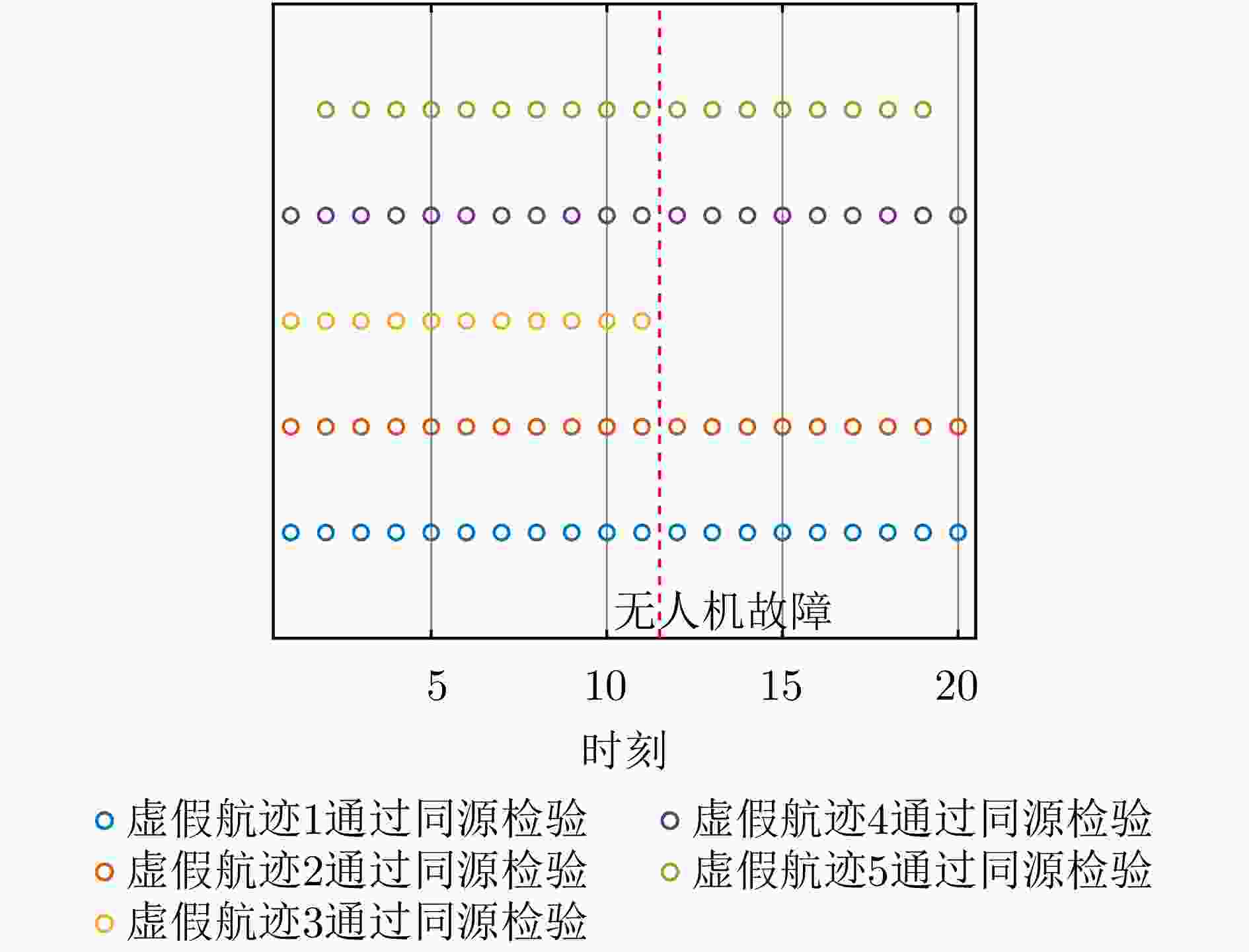
联盟划分;8 更新无人机n的自身效用: $ {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{a}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) = {u_{n,k}}\left( {{{\tilde {\boldsymbol{a}}}_{n,k}},{{\boldsymbol{A}}_{ - n,k}}} \right) $; 9 else: 10 无人机n保持其原有任务分配与飞行路径; 11 end if 12 end for 13 剔除未通过同源检验的虚假航迹任务 表 1 无人机集群初始任务分配
Table 1. The initial task allocation of UAV swarm
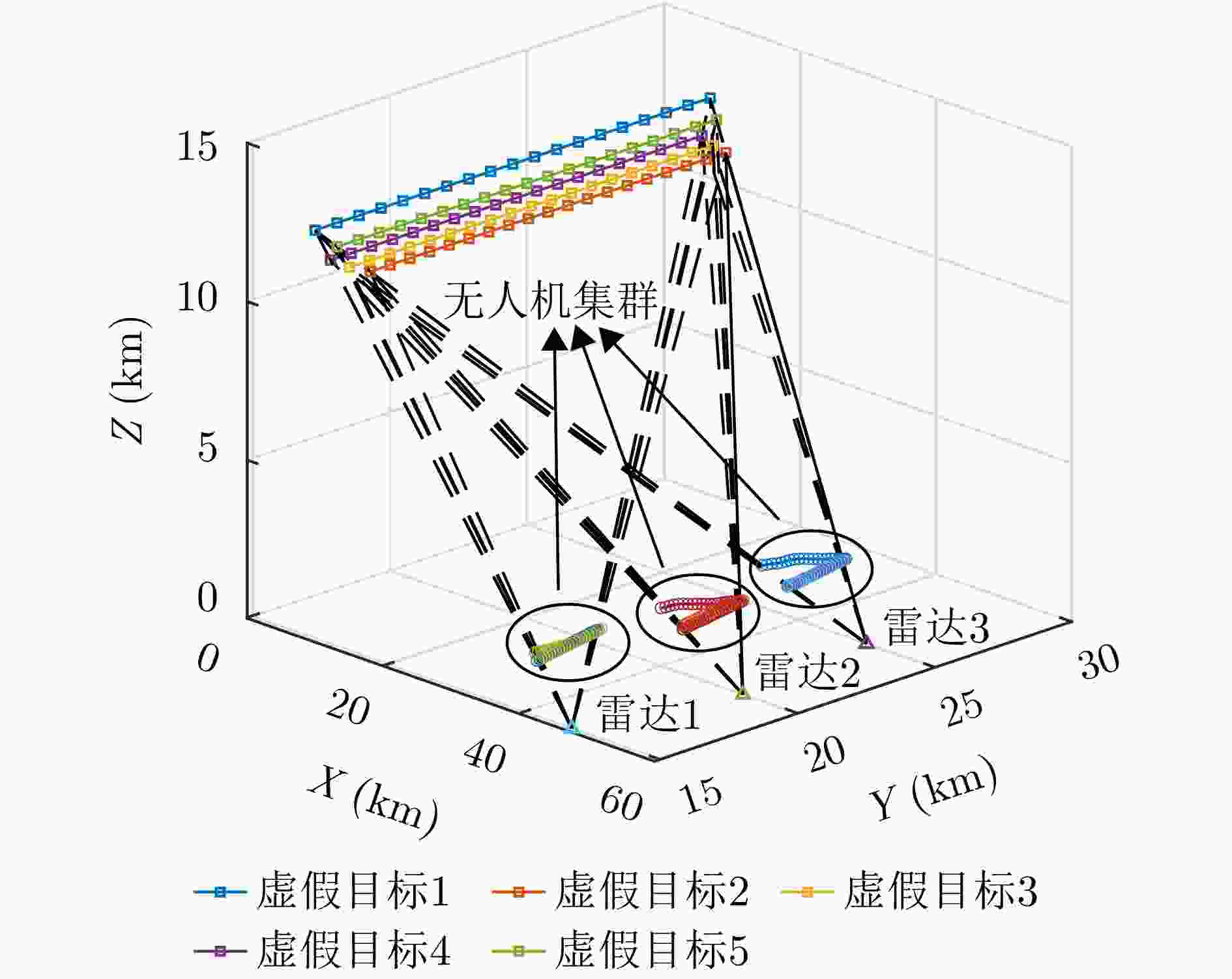
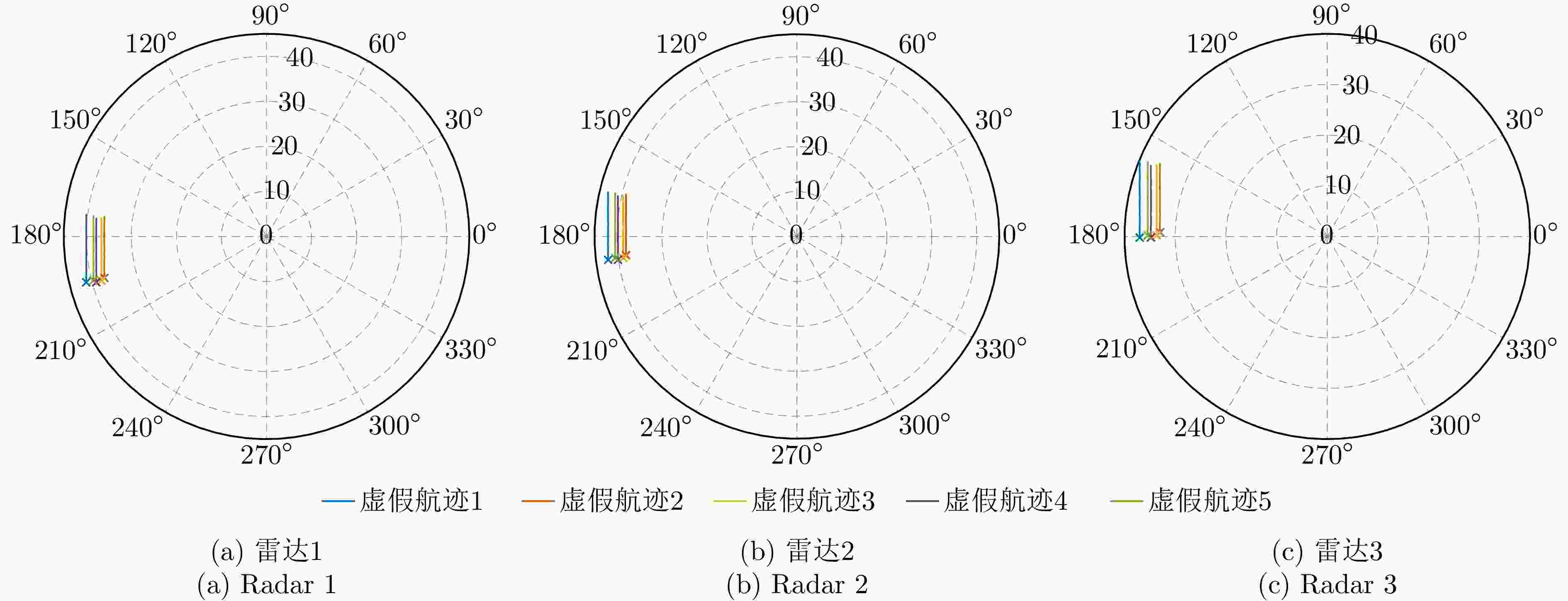
虚假航迹 雷达1 雷达2 雷达3 虚假航迹1 无人机1 无人机2 无人机3 虚假航迹2 无人机1 无人机4 无人机5 虚假航迹3 无人机6 无人机2 无人机7 虚假航迹4 无人机8 无人机9 无人机3 虚假航迹5 无人机10 无人机11 无人机12 -
[1] 黄洁瑜, 谢军伟, 杨子晴, 等. 雷达资源管理技术发展研究综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2025, 47(3): 1–13. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.20230626004.HUANG Jieyu, XIE Junwei, YANG Ziqing, et al. A review of radar resource management technology development research[J]. Modern Radar, 2025, 47(3): 1–13. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.20230626004. [2] 柏鹏, 王玉冰, 梁晓龙, 等. 无人机对雷达组网航迹欺骗综述[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(10): 023912. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23912.BAI Peng, WANG Yubing, LIANG Xiaolong, et al. Phantom track deception against radar networks using UAVs: Review[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 023912. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23912. [3] MAITHRIPALA D H A and JAYASURIYA S. Radar deception through phantom track generation[C]. 2005 American Control Conference, Portland, USA, 2005: 4102–4106. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2005.1470620. [4] MAITHRIPALA D H A, JAYASURIYA S, and MEARS M J. Phantom track generation through cooperative control of multiple ECAVs based on feasibility analysis[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2007, 129(5): 708–715. doi: 10.1115/1.2764512. [5] DHANANJAY N, KUDUVALLI A, and GHOSE D. Realistic coherent phantom track generation by a group of electronic combat aerial vehicles[C]. 2013 American Control Conference, Washington, USA, 2013: 4642–4647. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2013.6580555. [6] MAITHRIPALA D H A and JAYASURIYA S. Phantom track generation in 3D through cooperative control of multiple ECAVs based on geometry[C]. First International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, Tirtayasa, Indonesia, 2006: 255–260. doi: 10.1109/ICIIS.2006.365733. [7] LEE I H and BANG H. Phantom track generation using predictive control concept[C]. 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Gyeonggi-do, Korea (South), 2011: 291–293. [8] PURVIS K B, ASTROM K J, and KHAMMASH M. Online control strategies for highly coupled cooperative UAVs[C]. 2007 American Control Conference, New York, USA, 2007: 3961–3966. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2007.4283125. [9] PURVIS K B and CHANDLER P R. A review of recent algorithms and a new and improved cooperative control design for generating a phantom track[C]. 2007 American Control Conference, New York, USA, 2007: 3252–3258. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2007.4283138. [10] 王强. 针对组网雷达的自卫式航迹欺骗干扰技术[J]. 现代雷达, 2024, 46(12): 40–44. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.12.006.WANG Qiang. Self defense false track simulation technology for netted radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2024, 46(12): 40–44. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.12.006. [11] 王布宏, 黄天奇, 田继伟. 针对自适应滤波的组网雷达欺骗干扰优化策略[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2022, 44(2): 88–95. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202202011.WANG Buhong, HUANG Tianqi, and TIAN Jiwei. Deception jamming optimization strategy against adaptive filtering for netted radar[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2022, 44(2): 88–95. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202202011. [12] 郭中会, 李松松, 张宸宸, 等. 多机协同对组网雷达欺骗干扰的航迹优化[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2020, 35(1): 46–50, 59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2020.01.010.GUO Zhonghui, LI Songsong, ZHANG Chenchen, et al. Track deception model optimization according to the track deception technology[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2020, 35(1): 46–50, 59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2020.01.010. [13] 袁天, 陶建锋, 李兴成. 基于关联准则的主瓣航迹欺骗干扰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.06.YUAN Tian, TAO Jianfeng, and LI Xingcheng. Main lobe track deception jamming method based on association rule[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.06. [14] WANG Yuanhang, ZHANG Tianxian, KONG Lingjiang, et al. Strategy optimization for range gate pull-off track-deception jamming under black-box circumstance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4262–4273. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3241141. [15] MA Zhijie, ZHANG Tianxian, WANG Yuanhang, et al. Strategy optimization for range-velocity gate pull-off jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 5017–5029. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3514593. [16] 蒋雯, 贾琼, 刘真, 等. 面向主被动雷达复合探测的全脉冲多机协同干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 待出版. doi: 10.12000/JR25016.JIANG Wen, JIA Qiong, LIU Zhen, et al. Full-pulse multi-jammer cooperative jamming method for active-passive radar composite detection[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25016. [17] 许恒, 许红, 全英汇, 等. 基于时域编码超表面脉内-脉间编码优化的雷达干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 215–226. doi: 10.12000/JR23186.XU Heng, XU Hong, QUAN Yinghui, et al. A radar jamming method based on time domain coding metasurface intrapulse and interpulse coding optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 215–226. doi: 10.12000/JR23186. [18] WANG Yuanhang, ZHANG Tianxian, KONG Lingjiang, et al. A stochastic simulation optimization-based range gate pull-off jamming method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 27(3): 580–594. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3175517. [19] 时晨光, 闻雯, 宋海伟, 等. 针对组网雷达的无人机集群转发式欺骗干扰时延误差研究[J]. 航空兵器, 2024, 31(2): 131–137. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2023.0143.SHI Chenguang, WEN Wen, SONG Haiwei, et al. Research on delay error of UAV swarm repeater deception jamming against networked radar[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2024, 31(2): 131–137. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2023.0143. [20] 时晨光, 蒋泽宇, 严牧, 等. 针对组网雷达的无人机集群航迹欺骗综合误差分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(12): 4451–4458. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240289.SHI Chenguang, JIANG Zeyu, YAN Mu, et al. Comprehensive error in UAV cluster trajectory deception for networked radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(12): 4451–4458. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240289. [21] 班宏辉, 潘继飞, 王正, 等. 基于多无人机协同的航迹欺骗误差分析[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术, 待出版. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.TN.20250611.1539.048.BAN Honghui, PAN Jifei, WANG Zheng, et al. Trajectory deception error analysis based on multi-UAV collaboration[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, in press. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.TN.20250611.1539.048. [22] BAN Honghui, PAN Jifei, WANG Zheng, et al. Error-constrained entropy-minimizing strategies for multi-UAV deception against networked radars[J]. Entropy, 2025, 27(6): 653. doi: 10.3390/e27060653. [23] 柳向, 李东生. 对分布式组网雷达的航迹欺骗偏差补偿技术[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(6): 1255–1264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.06.10.LIU Xiang and LI Dongsheng. Deviation compensation for phantom tracks jamming against distributed radar network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(6): 1255–1264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.06.10. [24] PURVIS K B, ASTROM K J, and KHAMMASH M. Estimation and optimal configurations for localization using cooperative UAVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2008, 16(5): 947–958. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2007.916348. [25] WANG Yubing, WANG Weijia, ZHANG Xudong, et al. The joint phantom track deception and TDOA/FDOA localization using UAV swarm without prior knowledge of radars’ precise locations[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(10): 1577. doi: 10.3390/electronics11101577. [26] 林文斌, 时晨光, 严牧, 等. 面向欺骗干扰组网雷达的无人机集群稳健航迹规划算法[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术, 待出版. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.tn.20250523.1041.041.LIN Wenbin, SHI Chenguang, YAN Mu, et al. Robust track planning algorithm for UAVs deceiving radar networks[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, in press. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2422.tn.20250523.1041.041. [27] ZHANG Tianxian, WANG Yuanhang, MA Zhijie, et al. Task assignment in UAV-enabled front jammer swarm: A coalition formation game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9562–9575. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3323441. [28] HAI Xingshuo, FENG Qiang, CHEN Weike, et al. Capability-oriented decision-making in multi-UAV deployment and task allocation: A hierarchical game-based framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(7): 4562–4574. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2025.3551500. [29] LI Yibing, ZHANG Zitang, HE Zongyu, et al. A heuristic task allocation method based on overlapping coalition formation game for heterogeneous UAVs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(17): 28945–28959. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3406336. [30] 王跃东, 顾以静, 梁彦, 等. 伴随压制干扰与组网雷达功率分配的深度博弈研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023.WANG Yuedong, GU Yijing, LIANG Yan, et al. Deep game of escorting suppressive jamming and networked radar power allocation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023. [31] TONG Bingda and DUAN Haibin. A game theory-based approach for multiple UAVs cooperative target defense[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(4): 2149–2153. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3333572. [32] QI Nan, HUANG Zanqi, ZHOU Fuhui, et al. A task-driven sequential overlapping coalition formation game for resource allocation in heterogeneous UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(8): 4439–4455. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3165965. [33] CHEN Zhuoyue, YANG Yaozong, XU Jiajie, et al. Task offloading and resource pricing based on game theory in UAV-assisted edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2025, 18(1): 440–452. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2024.3512936. [34] TANG Xin, CHEN Qian, YU Rong, et al. Digital twin-empowered task assignment in aerial MEC network: A resource coalition cooperation approach with generative model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2025, 12(1): 13–27. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2024.3482327. [35] LI Jialiuyuan, SHI You, DAI Chen, et al. A learning-based stochastic game for energy efficient optimization of UAV trajectory and task offloading in space/aerial edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(6): 9717–9733. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3540964. [36] CHEN Jiayi, KUANG Zhufang, ZHANG Yuhao, et al. Blockchain-enabled computing offloading and resource allocation in multi-UAVs MEC network: A Stackelberg Game learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025, 20: 3632–3645. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2025.3550812. [37] MONDERER D and SHAPLEY L S. Potential games[J]. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 14(1): 124–143. doi: 10.1006/game.1996.0044. [38] 赵锋, 艾小锋, 刘进, 等. 组网雷达系统建模与仿真[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2018: 85–86.ZHAO Feng, AI Xiaofeng, LIU Jin, et al. Modeling and Simulation of Networked Radar Systems[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018: 85–86. [39] BAR-SHALOM Y and LI Xiaorong. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Principles and Techniques[M]. Danvers: Clearance Center, 1995: 95. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: