Deep Learning-based Integrated Search-imaging Waveform Design for Coherent Frequency Diverse Array Radar
-
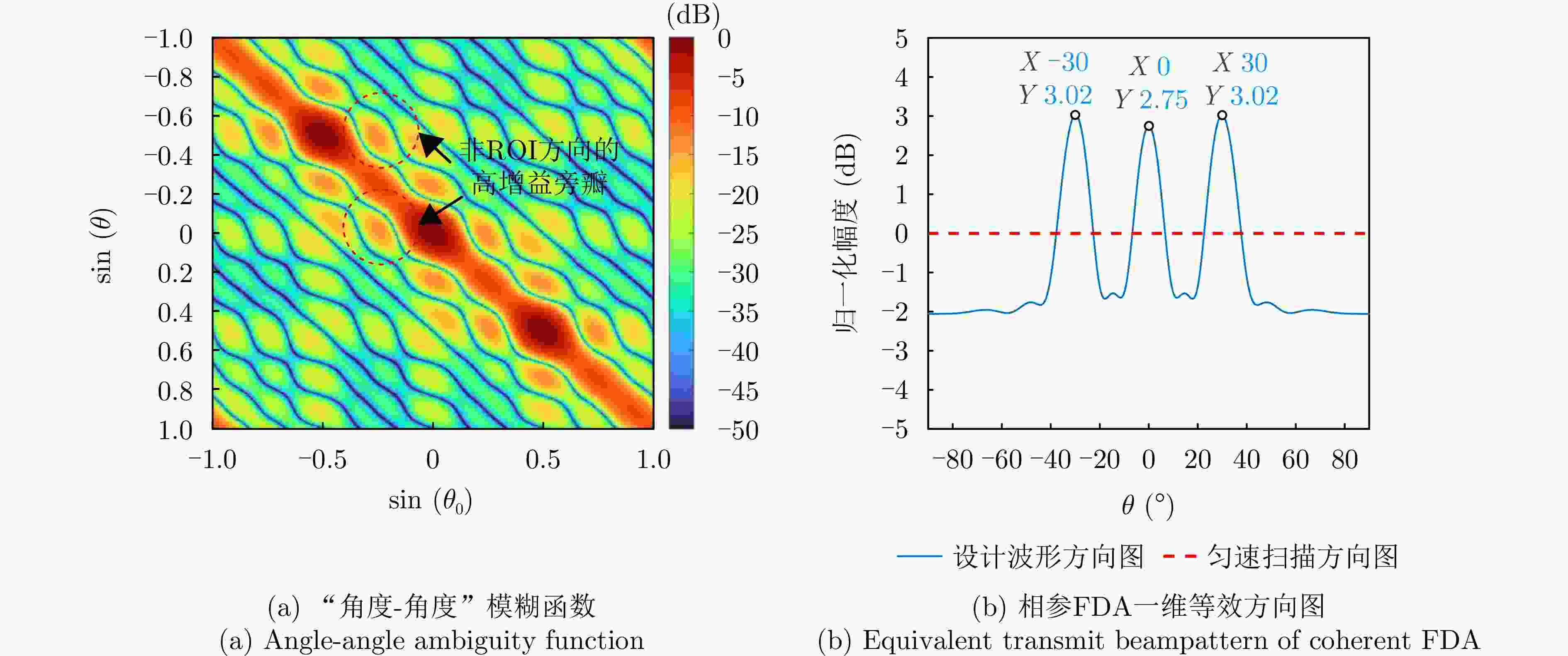
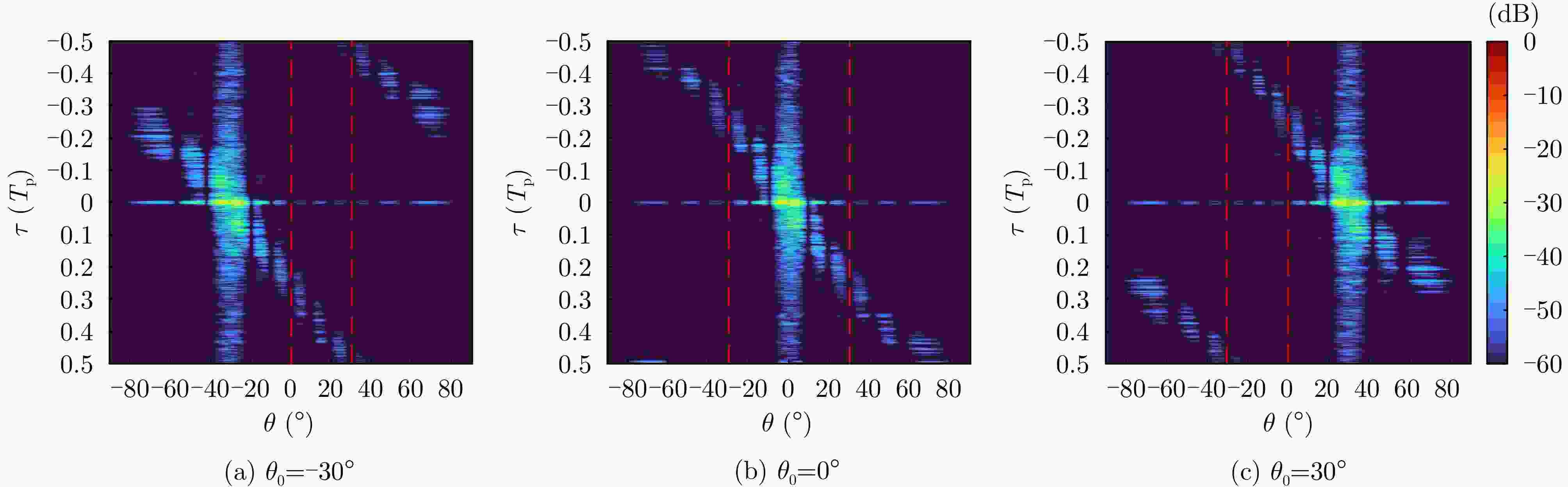
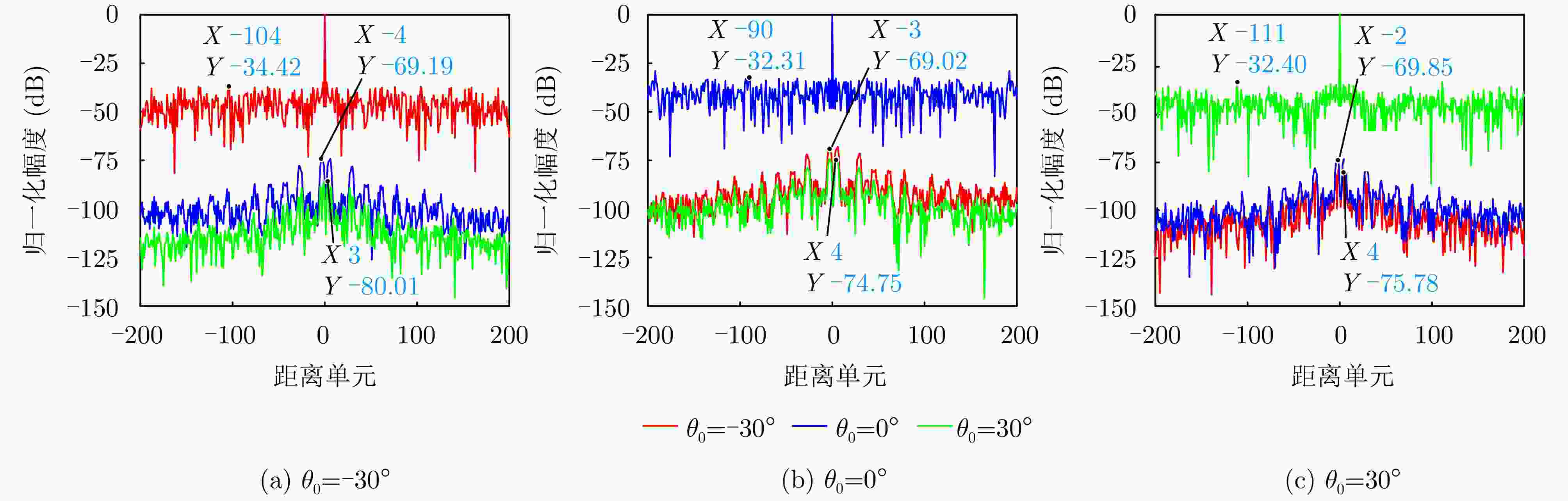
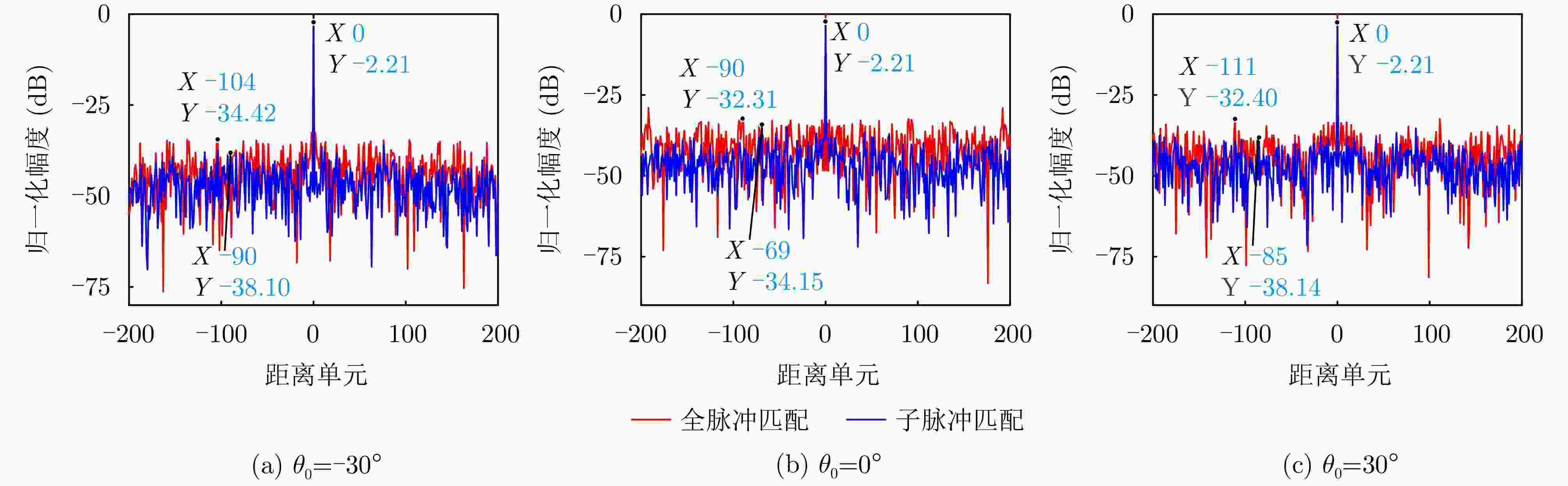
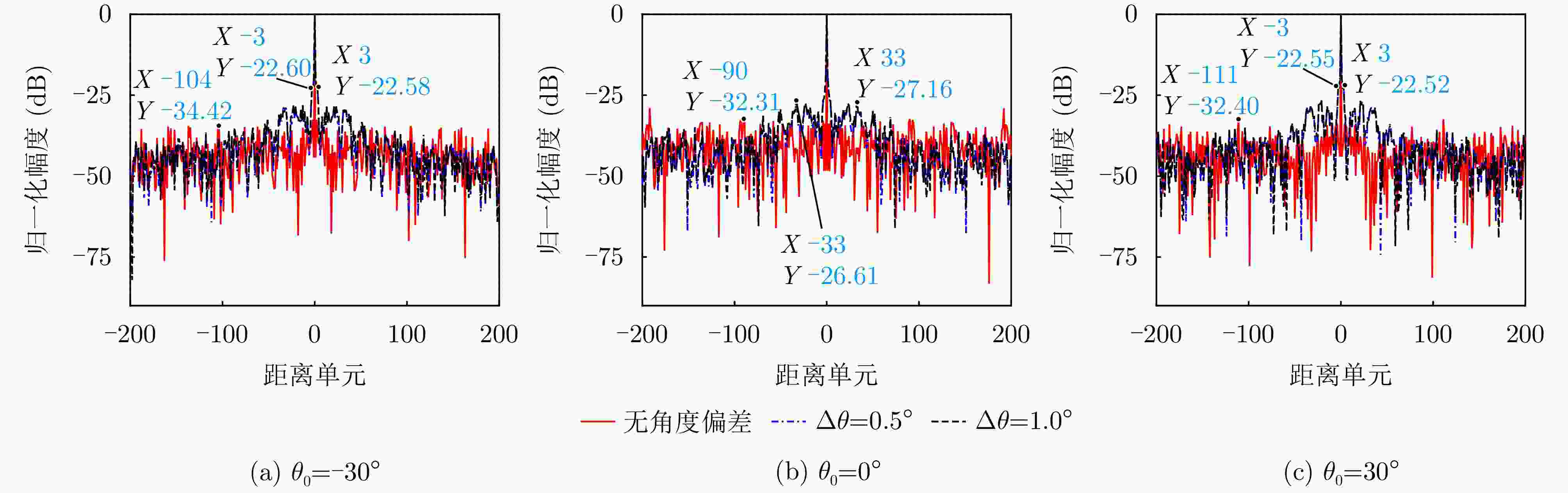
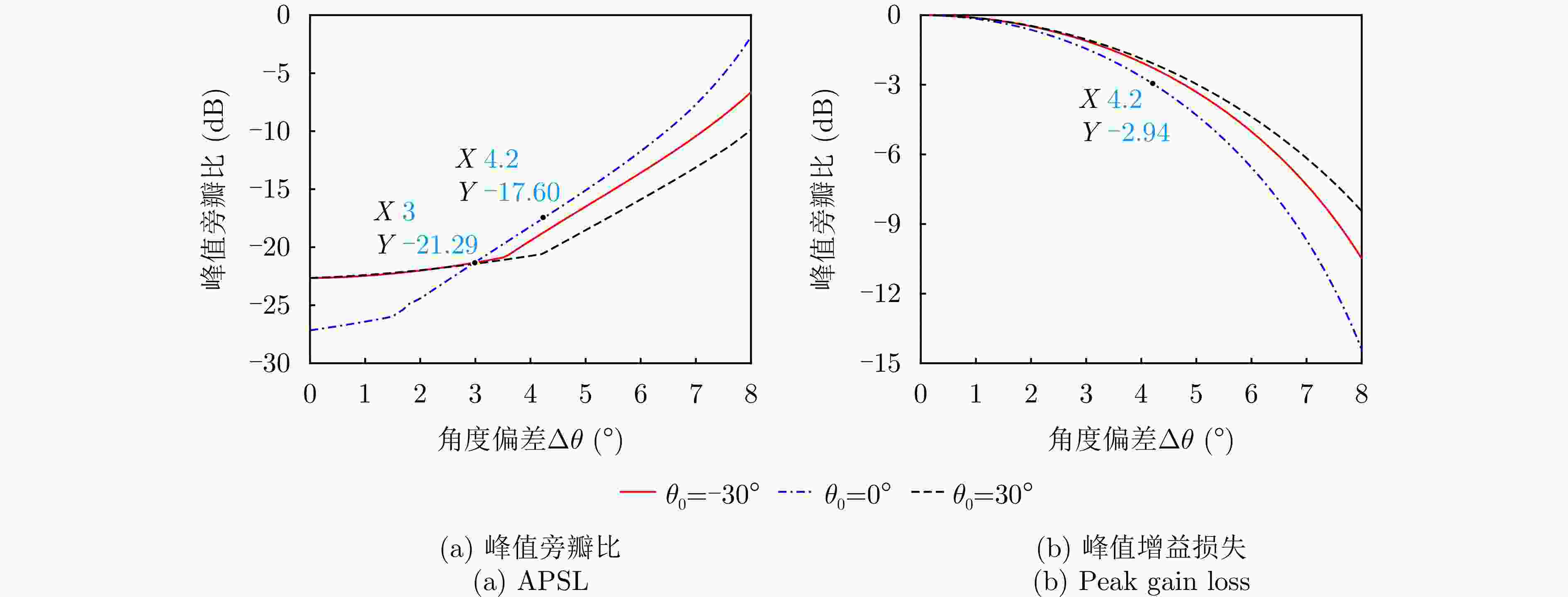
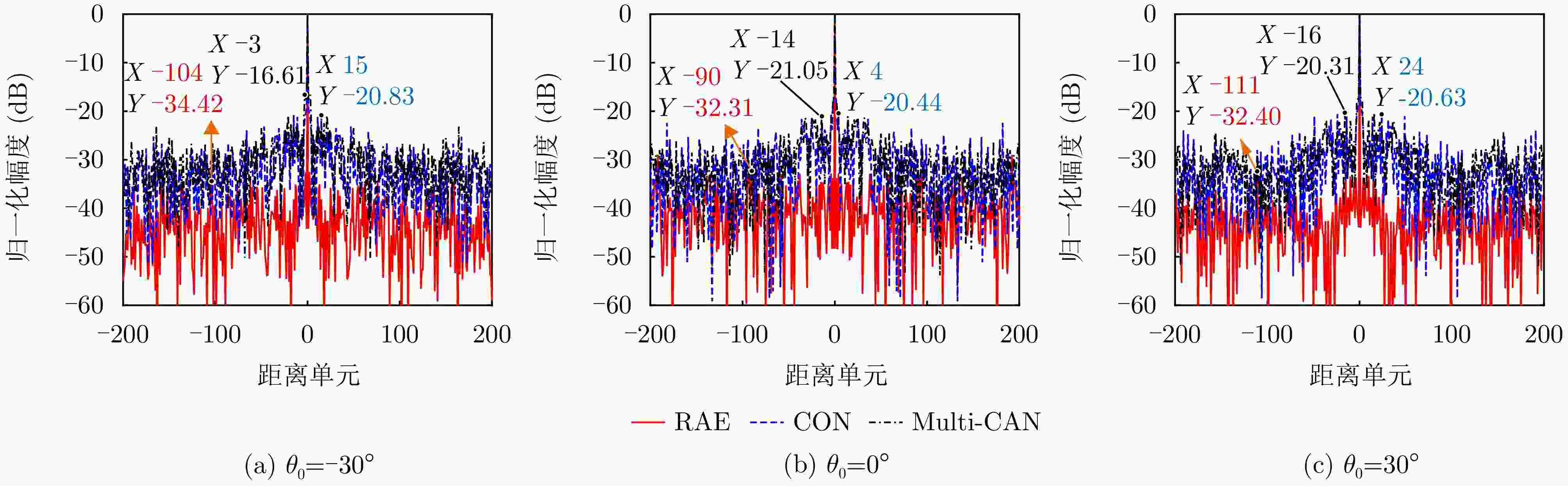
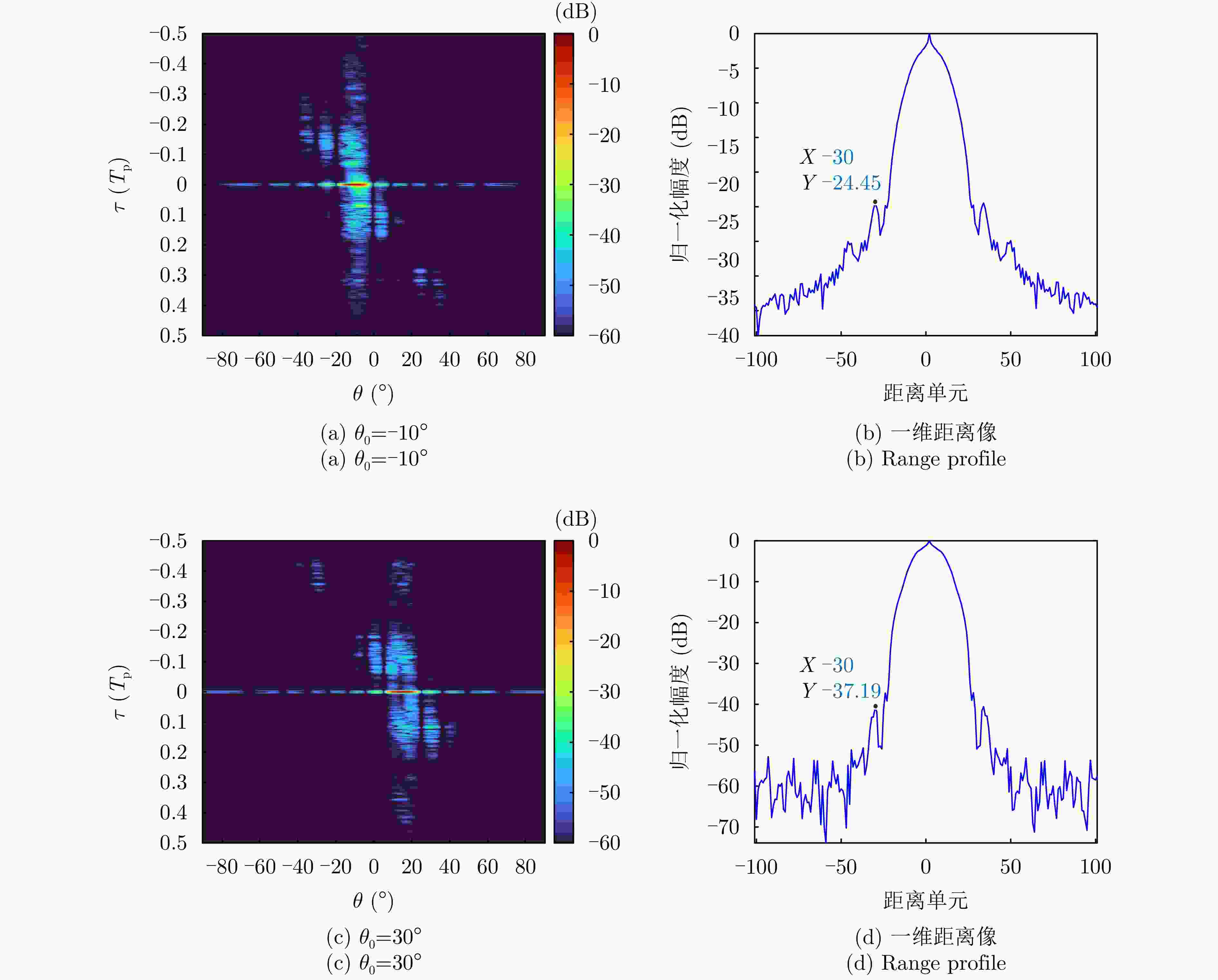
摘要: 相参频率分集阵列(FDA)雷达具有系统结构简单、波束扫描灵活和发射自由度高等优点,在宽覆盖对空探测任务中展现出巨大潜力,但固有的波束扫描机制导致其在特定方向的驻留时间缩短,从而限制了传统宽带波形成像时的距离分辨率。为解决广域搜索与高分辨率成像之间的内在矛盾,该文提出了一种基于深度学习的相参FDA搜索成像一体化波形设计方法。该方法利用相参FDA多自由度灵活发射的优势,在保证宽覆盖搜索能力的同时,为多个感兴趣区域(ROI)定制化地设计波形、带宽、发射增益等多维发射资源。为了解决基带波形设计中恒模与相关性双重约束的非凸优化问题,该文构建了以残差自编码网络为核心优化器,旨在直接学习并建立从初始相位空间到满足预设性能准则的最优相位空间的高维非线性映射关系。该网络能够高效地生成一组在多个ROI方向上同时具备低自相关旁瓣和低互相关电平的相位编码子波形。仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性,表明其设计的波形在同步执行搜索与多目标成像任务时,(相比于窄带搜索模式)能够在指定ROI方向同时获得发射增益和距离分辨率提升,且自相关与互相关性能相较于传统方法具有显著优势,为提高现代雷达系统的同时多任务探测能力提供了一种有效途径。Abstract: Coherent Frequency Diverse Array (FDA) radar demonstrates significant potential for wide-area search tasks due to its simple system architecture, flexible beam scanning, and high transmit Degrees of Freedom (DOF). However, its inherent beam-scanning mechanism reduces dwell time in specific directions, thereby limiting the imaging range resolution when a conventional wideband waveform is used. To resolve the intrinsic contradiction between wide-area search and high-resolution imaging, this paper proposes a deep learning-based integrated search-imaging waveform design method. By leveraging the multi-DoF flexible transmission capability of coherent FDA, the proposed method customizes multidimensional transmit resources, including waveform, bandwidth, and transmit gain, for multiple Regions of Interest (ROIs) while preserving wide-coverage search performance. To address the nonconvex optimization problem with dual constraints of constant modulus and low correlation in baseband waveform design, a residual autoencoder-based optimizer is developed. This network directly learns and establishes a high-dimensional nonlinear mapping from the initial phase space to the optimized phase space that satisfies predefined performance criteria. The network efficiently generates a set of phase-coded subwaveforms exhibiting low autocorrelation sidelobes and low cross-correlation levels for multiple ROIs. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of this method, demonstrating that the designed waveforms achieve higher processing gain (compared with the narrowband searching mode) and improved imaging resolution in the designated ROIs during simultaneous search and multitarget imaging. Moreover, the autocorrelation and cross-correlation performance of the proposed method significantly outperforms that of conventional approaches, indicating that it provides an effective solution for enhancing the multitask capabilities of modern radar systems.
-
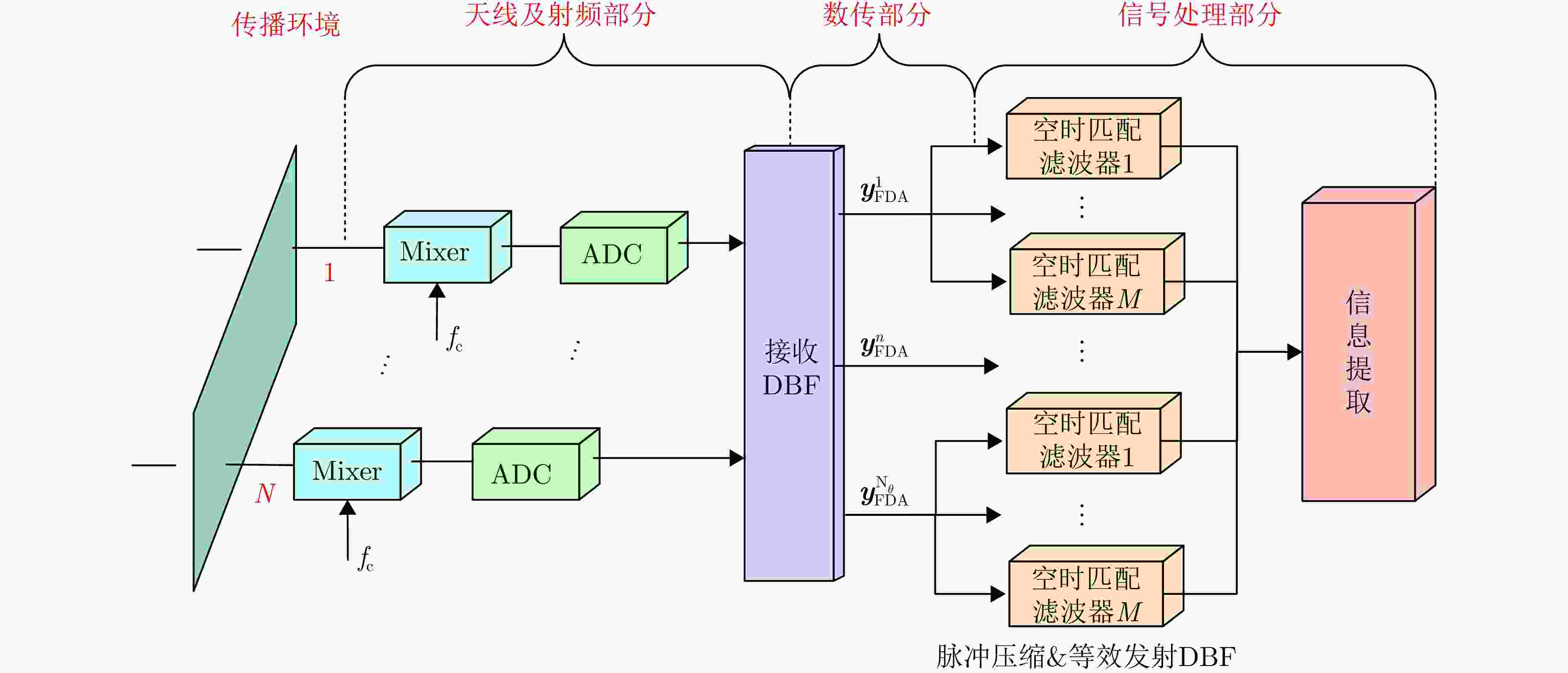
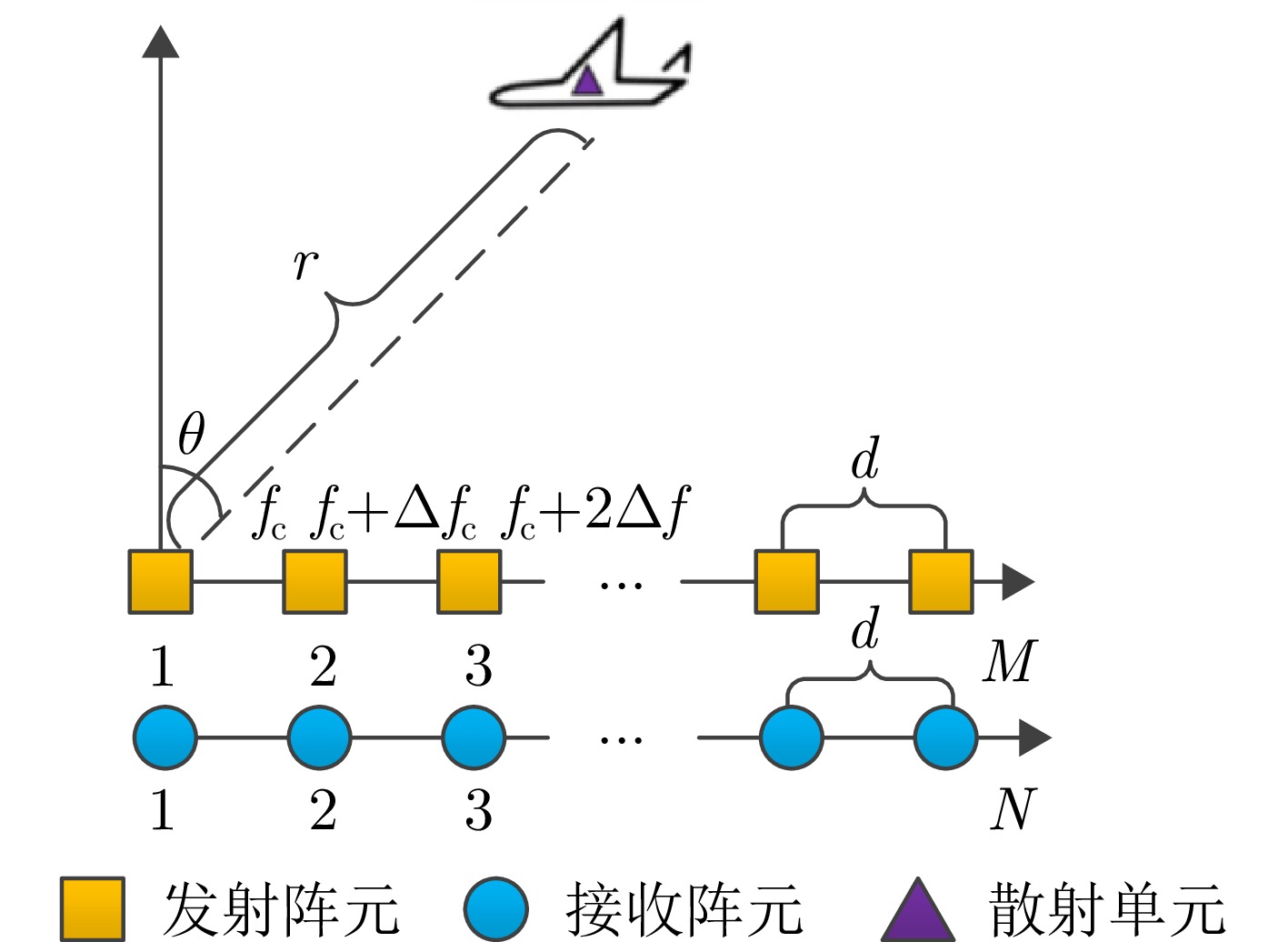
1 多目标成像模式的相参FDA雷达系统参数设计方法
1. System design of multi-targets imaging mode based on coherent FDA radar
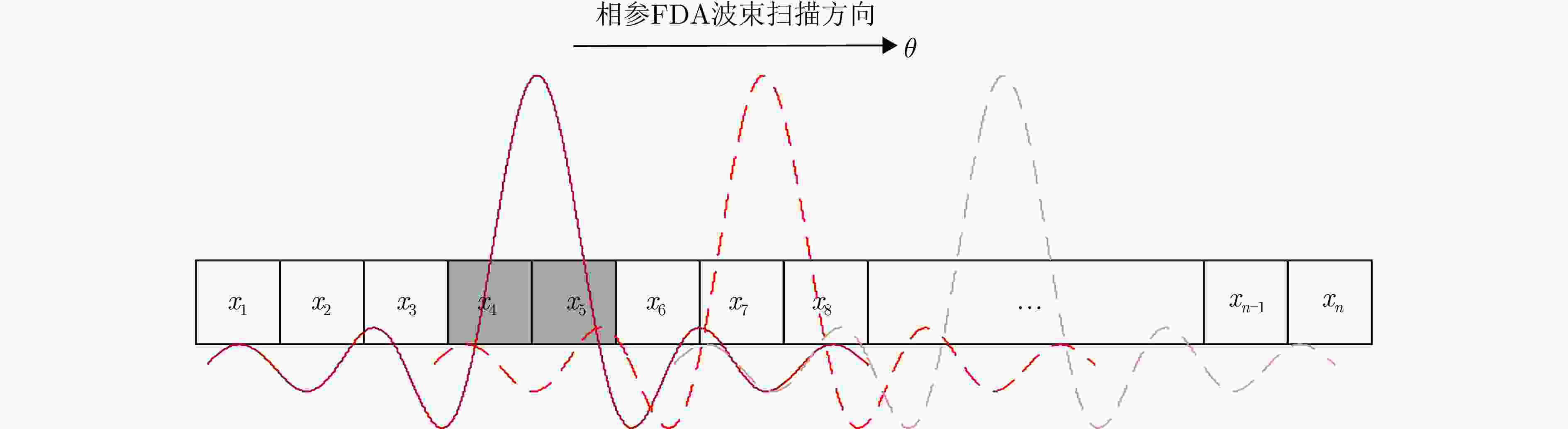
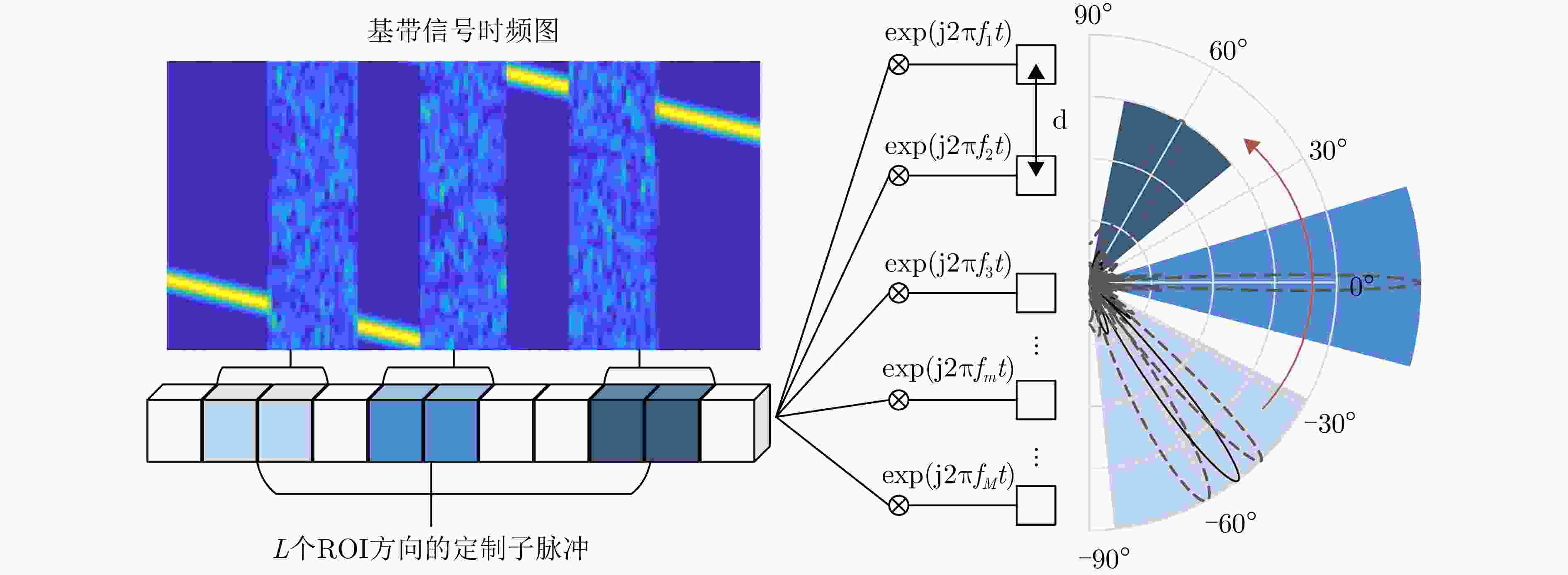
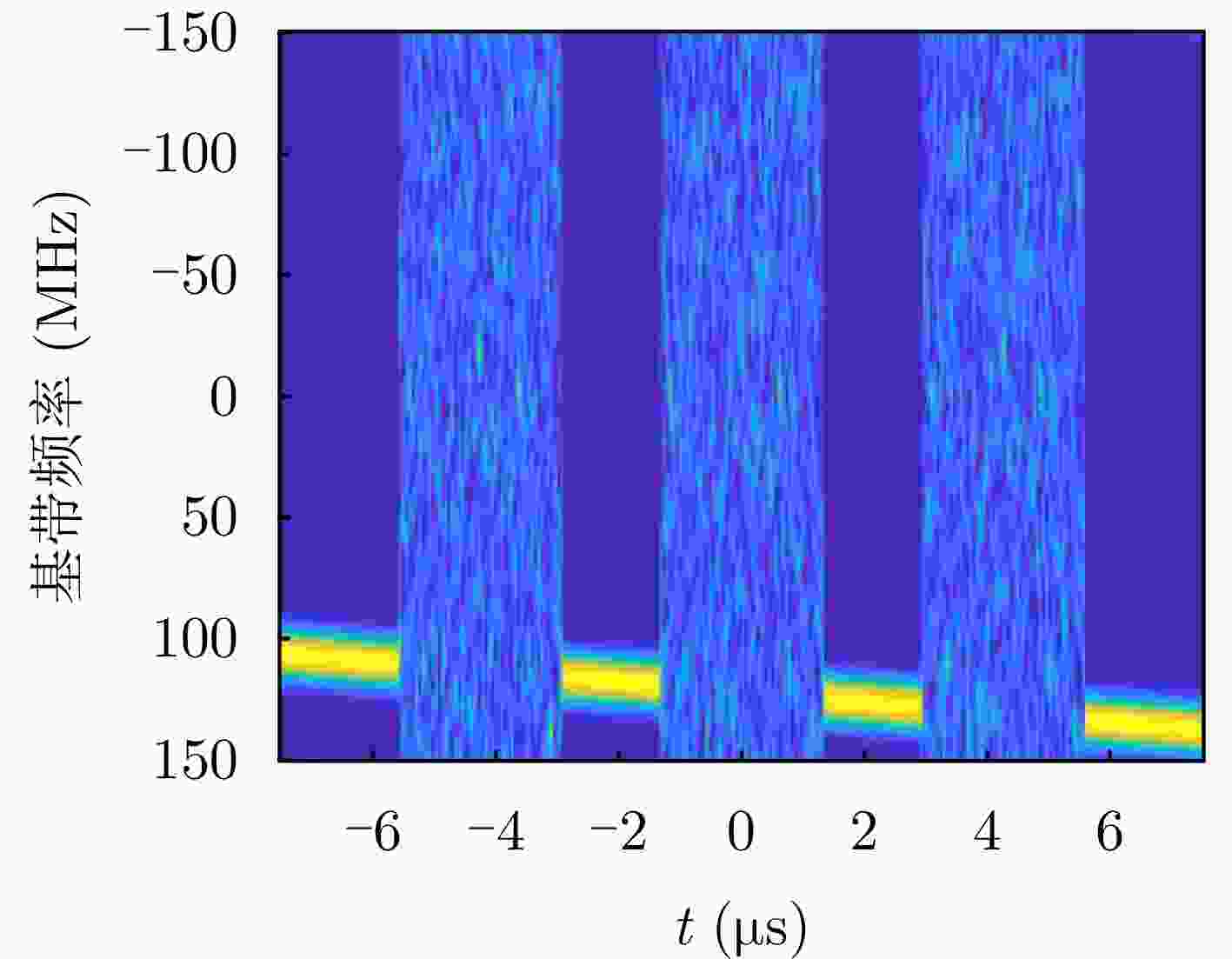
输入:相参FDA发射/接收阵元数$ {M} $, $ {N} $,阵元间距d,参考载频$ {f}_{\rm c} $,脉冲宽度$ {T}_{\rm p} $,搜索阶段确定的L个ROI方向$ \boldsymbol{{\varTheta }}=\left[{{\varTheta }}_{\text{1}},{{\varTheta }}_{2},\cdots,{{\varTheta }}_{L}\right] $。 初始化:阵元间载频差$ \Delta {f}^{0} $,L个方向上的波束驻留时间序列$ \left[T_{{\mathrm{s}},1}^{\text{0}},T_{\mathrm{{s}},\text{2}}^{\text{0}},\cdots,T_{{\mathrm{s}},L}^{\text{0}}\right] $,目标方向上的设计发射增益$ \left[{G}_{1},{G}_{2},\cdots,{G}_{L}\right] $,迭代步
长$ {\varDelta }_{T} $和发射增益设计拟合误差$ {\delta }_{g} $。1 代入当前参数,通过式(5)计算L个方向上的发射增益。 2 for $ l=1,2,\cdots,L $ do 3 while $ \Delta {G}_{l} > {\delta }_{g} $ do 4 针对第l个目标方向,令$ T_{s,l}^{q}\leftarrow \left(1+i{\varDelta }_{T}\right)T_{{\mathrm{s}},l}^{0} $; 5 适当调整并代入$ T_{{\mathrm{s,}}l}^{i} $,通过式(12)计算第l个子脉冲内的载频差$ \Delta {f}_{l}{}^{i} $; 6 代入当前参数,通过式(5)计算第l个方向上的发射增益; 7 计算第l个方向上的实际增益与设计增益$ {G}_{l} $差的绝对值$ \Delta {G}_{l} $; 8 $ i\leftarrow i+1 $; 9 end 10 end 11 更新系统参数,通过式(15)计算K个非ROI子脉冲对应的载频差$ \Delta {f}_{K} $; 12 通过式(12)计算K个非ROI子脉冲的子脉冲宽度; 13 针对L个定制子脉冲设计低APSL, ICSL的相位编码波形; 14 针对K个非ROI子脉冲设计窄带搜索波形; 15 根据设计所得系统参数及基带波形,通过式(13)组合$ {N}_{\mathrm{{p}}} $个子脉冲得到M个通道的发射波形组。 输出: 相参FDA雷达M个通道发射波形组$ \boldsymbol{s}\left(t\right)={\left[{s}_{1}\left(t\right),{s}_{2}\left(t\right),\cdots,{s}_{M}\left(t\right)\right]}^{\rm T} $。 表 1 相参FDA雷达系统参数
Table 1. System parameters of coherent FDA radar
参数 数值 参考载频$ {f}_{\rm c} $ 10 GHz 发射/接收阵元数目N/M 12 阵元间距d 0.015 m 脉冲重复周期$ {T}_{\rm p} $ 10 μs 采样频率$ {F}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 300 MHz 波束扫描覆盖范围$ {{\varOmega }}_{\text{FDA}} $ $ \left[-{90}^{\circ },{90}^{\circ }\right] $ 目标1位置$ {{\varTheta }}_{1} $ –30° 目标2位置$ {{\varTheta }}_{2} $ 0° 目标3位置$ {{\varTheta }}_{3} $ 30° 表 2 RAE网络参数设计
Table 2. Parameters of RAE network
参数 数值 编码器残差块维度 [512, 256, 128] 潜在空间维度$ {d}_{{\mathrm{lat}}} $ 64 解码器残差块维度 [128, 256, 512] 损失函数权重系数 $ {\lambda }_{a}=\text{1} $, ${\lambda }_{c}=\text{0}.1 $ 学习率 0.001 批处理大小(Batch size) 10 训练周期(Epochs) 1000 -
[1] 吴曼青, 赵逸超, 何峰, 等. 计算阵列-计算赋能的数字阵列技术[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2022, 52(12): 2270–2289. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0368.WU Manqing, ZHAO Yichao, HE Feng, et al. Computational array-digital array with computational empowerment[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2022, 52(12): 2270–2289. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0368. [2] 郭瑞, 张月, 田彪, 等. 全息凝视雷达系统技术与发展应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Review of the technology, development and applications of holographic staring radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153. [3] YU Lei, HE Feng, and SU Yi. Multiscale observation in wide-spatial radar surveillance based on coherent FDA design[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2024, 67(2): 122304. doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3816-3. [4] ANTONIK P, WICKS W, GRIFFITHS H, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 470–475. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631800. [5] 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 廖桂生, 等. 频率分集阵雷达技术探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023.XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, LIAO Guisheng, et al. An overview of frequency diverse array radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023. [6] 桂荣华. 频控阵雷达自适应处理关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.000097.GUI Ronghua. Research on adaptive processing technology for frequency diverse array radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.000097. [7] 许京伟, 兰岚, 朱圣棋, 等. 相干频率分集阵雷达匹配滤波器设计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(8): 1720–1728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.08.08.XU Jingwei, LAN Lan, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Design of matched filter for coherent FDA radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(8): 1720–1728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.08.08. [8] 于雷, 何峰, 董臻, 等. 一种基于非线性调频信号和空域编码的FDA雷达波形设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 822–832. doi: 10.12000/JR21008.YU Lei, HE Feng, DONG Zhen, et al. A waveform design method based on nonlinear frequency modulation and space-coding for coherent frequency diverse array radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 822–832. doi: 10.12000/JR21008. [9] WANG Huake, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Transmit beampattern design for coherent FDA by piecewise LFM waveform[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 161: 14–24. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.03.010. [10] YU Lei, HE Feng, SU Yi, et al. Transmitting strategy with high degrees of freedom for pulsed-coherent FDA radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(4): 659–667. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12210. [11] 王华柯. 新型发射分集MIMO雷达方向图设计及信号处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.000001.WANG Huake. Research on beampattern design and signal processing for transmit diversity MIMO radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.000001. [12] WANG Huake, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Space-time matched filter design for interference suppression in coherent frequency diverse array[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2020, 14(3): 175–181. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2019.0227. [13] YU Lei, ZHANG Qilei, HE Feng, et al. A controllable range resolution enhancement method for coherent FDA radar[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 1963–1967. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028540. [14] YU Lei, HE Feng, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Low-PSL mismatched filter design for coherent FDA radar using phase-coded waveform[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3507405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3309827. [15] QIU Xiangfeng, JIANG Weidong, ZHANG Xinyu, et al. Simultaneous design of PCFM waveforms and receive filters toward ISRJ suppression[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3509305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3457536. [16] LI Yongzhe and VOROBYOV S A. Fast algorithms for designing unimodular waveform(s) with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1197–1212. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2787104. [17] KANG B, KWEON J, RANGASWAMY M, et al. Deep learning for radar waveform design: Retrospectives and the road ahead[C]. 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Sydney, Australia, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR54928.2023.10371126. [18] ZHAO Ziwei, HU Jinfeng, ZHONG Kai, et al. MIMO radar waveform design for range-ISL optimization via iterative deep unfolding network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3503405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3368446. [19] SEKIYA R, MORI H, HASHIMOTO H, et al. Design of long-sequence unimodular waveforms using an original autoencoder for MIMO radar systems[C]. 2023 20th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Berlin, Germany, 2023: 339–342. doi: 10.23919/EuRAD58043.2023.10289508. [20] SEKIYA R, MORI H, HASHIMOTO H, et al. Use of ResNet autoencoders for designing phase-quantized sequences with good correlation for MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2025, 3: 681–694. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2025.3562698. [21] HU Jinfeng, WEI Zhiyong, LI Yuzhi, et al. Designing unimodular waveform(s) for MIMO radar by deep learning method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(2): 1184–1196. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3037406. [22] GUI Ronghua, WANG Wenqin, CUI Can, et al. Coherent pulsed-FDA radar receiver design with time-variance consideration: SINR and CRB analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(1): 200–214. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2764860. [23] BARTON D K. Low-angle radar tracking[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(6): 687–704. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9509. [24] HE Hao, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Designing unimodular sequence sets with good correlations-including an application to MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(11): 4391–4405. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2025108. [25] ZHANG Ben, ZHANG Yongsheng, HE Feng, et al. Range resolution control and fractional Fourier domain target localization with nonlinear time-variant phase diverse FDA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(6): 17151–17171. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3601572. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: