A Low-complexity Beampattern Shaping Method for Large-scale Rectangular Phased Arrays
-
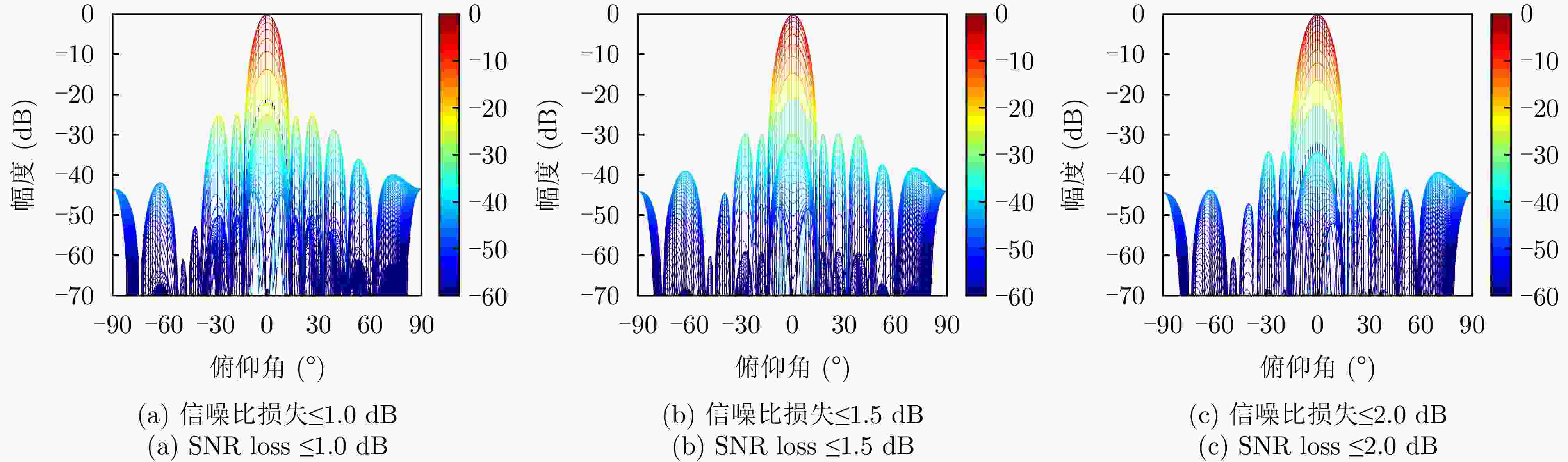
摘要: 针对大规模矩形相控阵波束赋形面临的高计算复杂度瓶颈,该文提出一种基于维度解耦的波束加权向量快速设计方法,显著提升设计效率与波束调控灵活性。首先,充分利用矩形面阵的构型特性,推导方位维与俯仰维导向矢量解耦的波束形成表达式,将传统高维加权向量设计问题高效转化为两个低维加权向量的联合优化问题,从根本上降低计算复杂度。在此基础上,构建以峰值旁瓣电平最小化为代价函数、波束电平与噪声输出功率为约束条件的优化模型,开发基于近端-交替方向乘子法的迭代求解算法,并严格推导算法收敛的充分条件,保障求解稳定性与可靠性。仿真结果验证,所提方法在大幅提升计算效率的同时,不仅能依据先验信息灵活调控主瓣宽度与零陷深度,还可通过调整信噪比损失实现峰值旁瓣抑制性能的精准权衡,展现出优异的工程实用性。Abstract: To address the high computational complexity of beamforming in large-scale rectangular phased arrays, this paper proposes a low-complexity beampattern shaping method based on dimension decoupling, which markedly enhances design efficiency and beampattern adjustment flexibility. By fully exploiting the configuration characteristics of rectangular arrays, an analytical beamforming expression is derived that decouples the azimuth and elevation steering vectors. This transformation converts the traditional high-dimensional weight vector design problem into a joint optimization of two low-dimensional weight vectors, thereby substantially reducing computational complexity. On this basis, an optimization model is formulated that minimizes the peak sidelobe level under constraints on beam levels and noise output power. To solve the resultant optimization problem, an iterative algorithm based on the proximal alternating direction method of multipliers is developed, and sufficient conditions for algorithmic convergence are rigorously derived to ensure solution stability and reliability. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method substantially improves computational efficiency and enables flexible adjustment of mainlobe width and null depth according to prior information. Furthermore, it achieves a precise trade-off between peak sidelobe suppression and signal-to-noise ratio loss, exhibiting excellent potential for engineering applications.
-
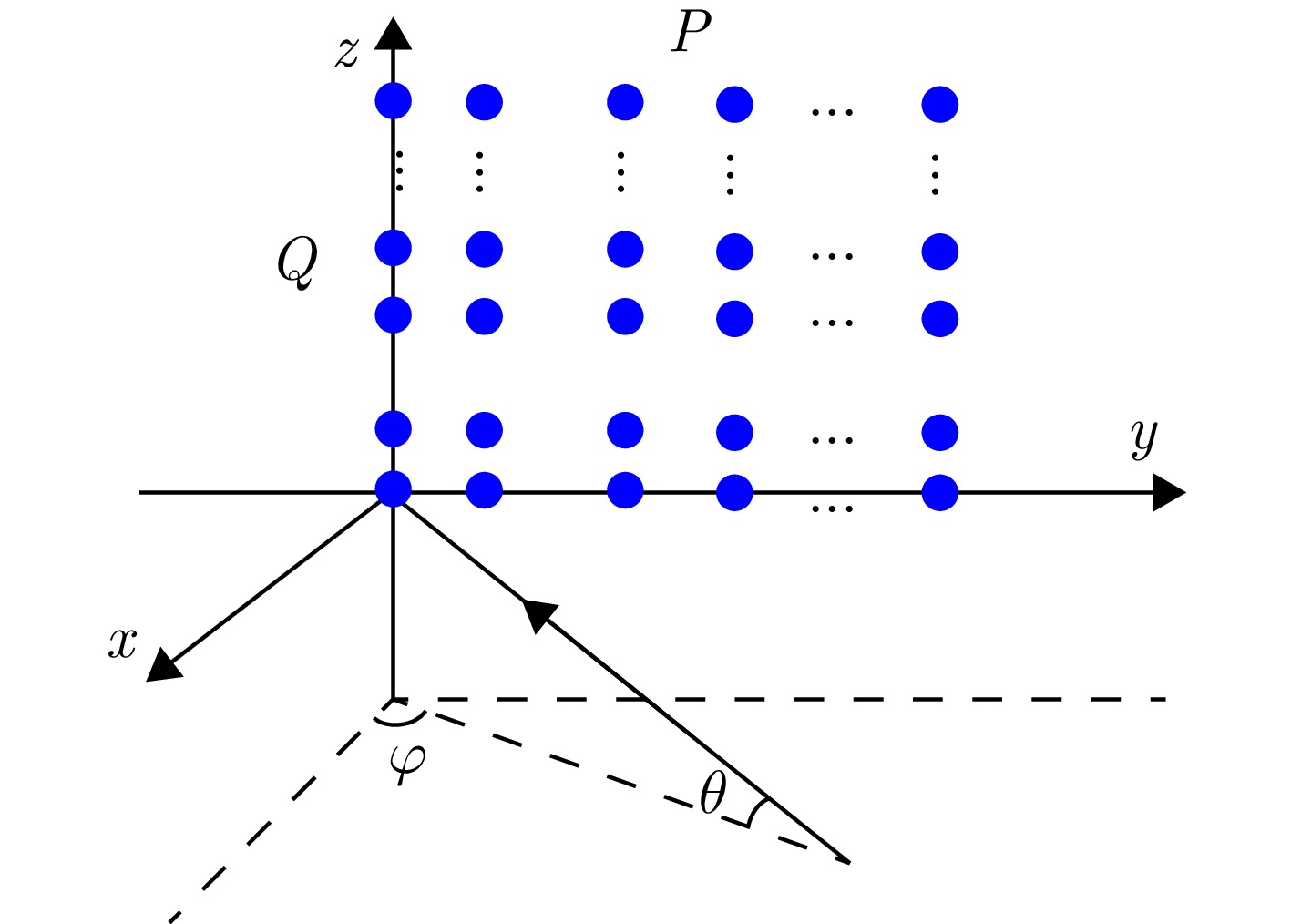
1 矩形相控阵波束加权向量设计
1. The design of weight vector for the rectangular phased array
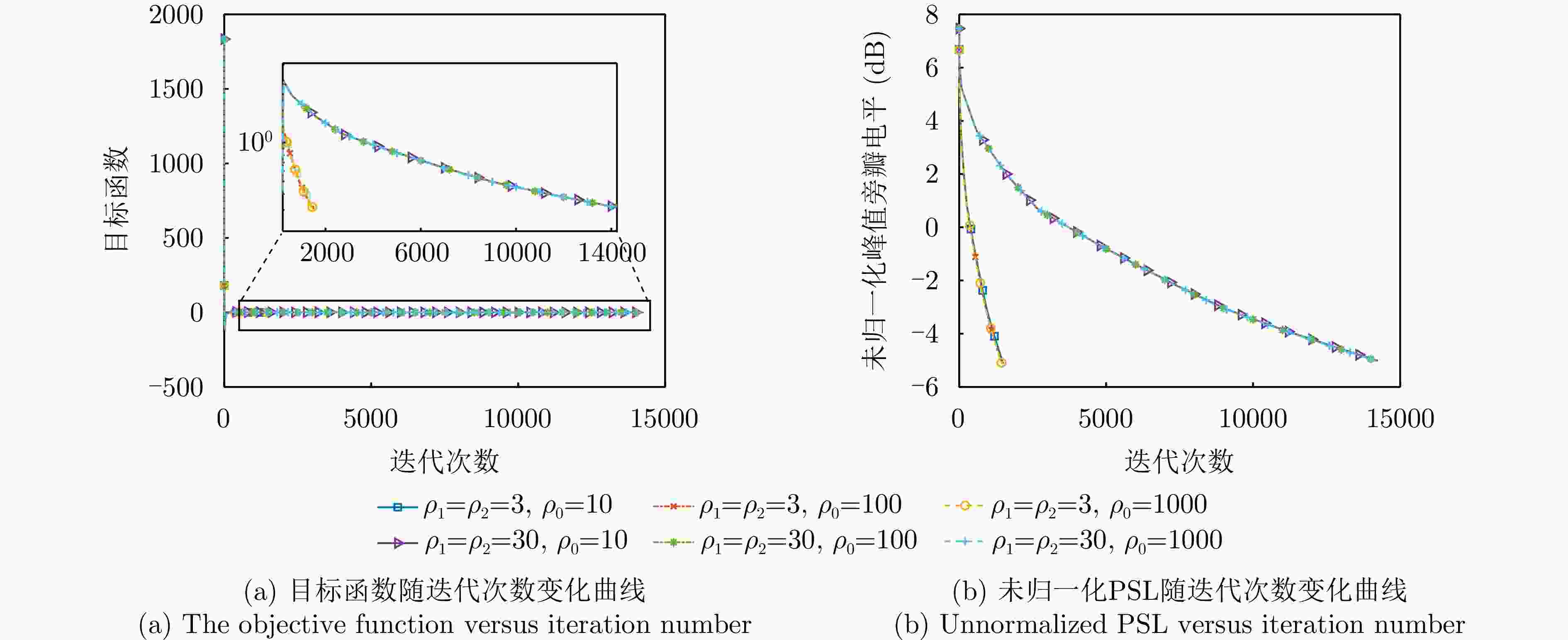
输入:$ P,Q,{\varTheta _{{\text{side}}}},{\varTheta _{{\text{main}}}},{\varTheta _{{\text{null}}}},{\rho _0},{\rho _1},{\rho _2},\alpha ,\beta ,\varepsilon $ 步骤1:初始化${\boldsymbol{w}}_y^{\left( 0 \right)},{\boldsymbol{w}}_z^{\left( 0 \right)},\left\{ {{x_k}} \right\},\left\{ {{v_k}} \right\},\iota = 0$; 步骤2:$\iota = \iota + 1$; 步骤3:利用式(19)更新$\left\{ {\tilde x_k^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\}$; 步骤4:利用二分法求得$ \bar \delta $,根据式(23)更新$ {\eta ^{\left( \iota \right)}} $; 步骤5:利用式(24)更新$ \left\{ {x_k^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\} $,并利用式(25)更新$ \left\{ {\omega _k^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\} $; 步骤6:分别利用式(20)、式(27)与式(28)更新$ \left\{ {\tilde v_{\bar k}^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\} $, $ \left\{ {v_{\bar k}^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\} $与
$ \left\{ {\varpi _{\bar k}^{\left( \iota \right)}} \right\} $;步骤7:利用二分法求得${\bar \lambda _1}$,根据式(34)更新$ {\boldsymbol{w}}_y^{\left( \iota \right)} $; 步骤8:类似步骤7,更新$ {\boldsymbol{w}}_z^{\left( \iota \right)} $; 步骤9:判断是否满足退出条件,若不满足,返回步骤2;否则,
结束迭代;输出:${\boldsymbol{w}} = {\boldsymbol{w}}_y^{\left( \iota \right)} \otimes {\boldsymbol{w}}_z^{\left( \iota \right)}$ 表 1 不同算法综合指标:窄主瓣波束赋形
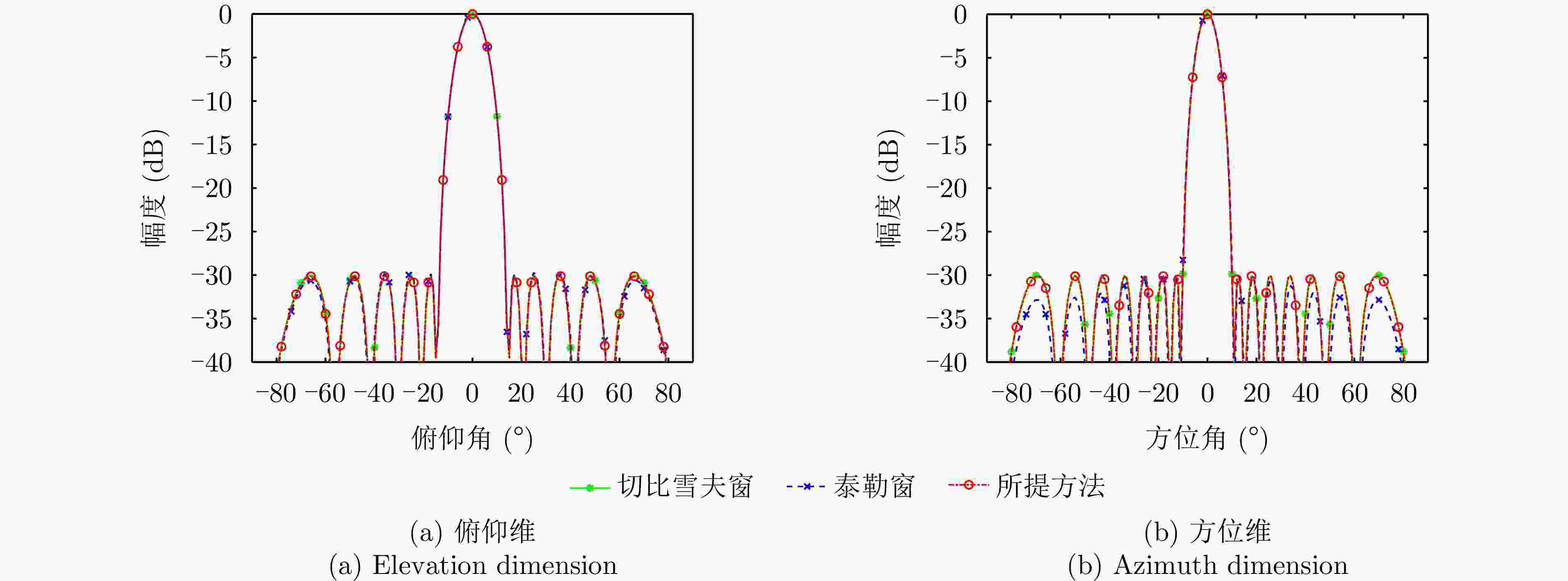
Table 1. Comprehensive indicators of different algorithms: Beampatterns synthesis with narrow mainlobe
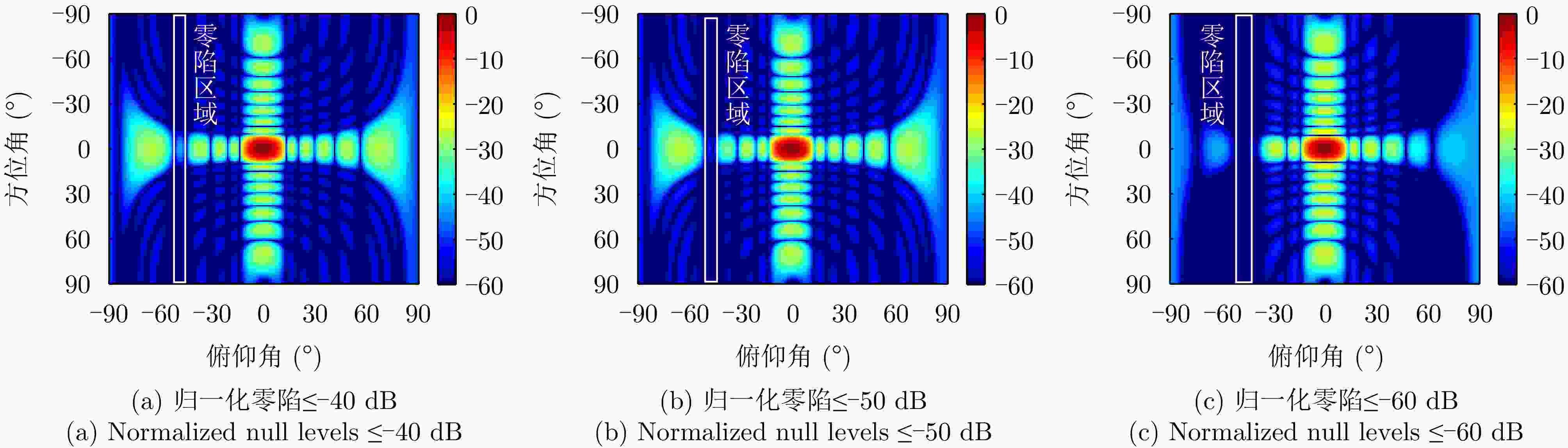
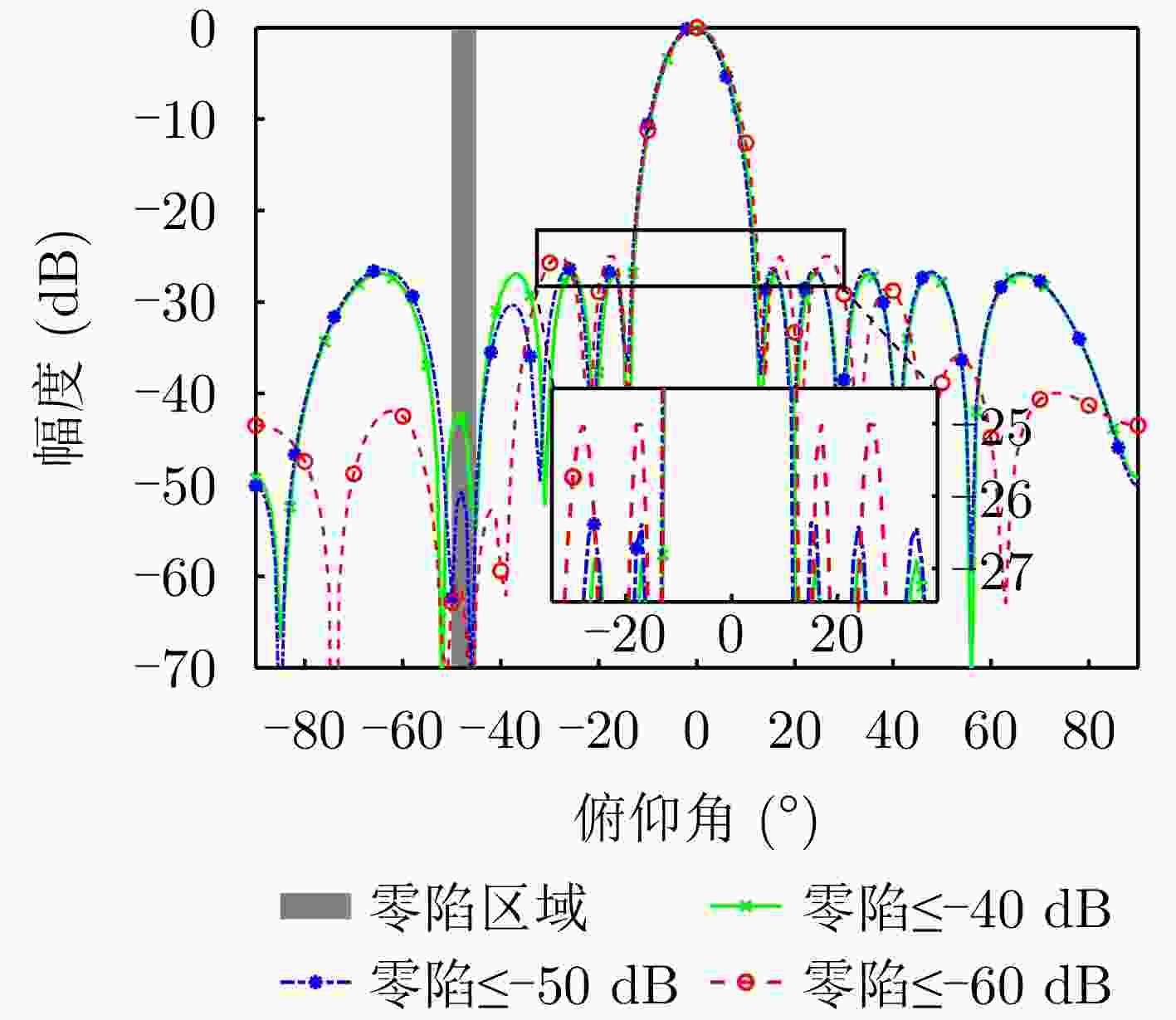
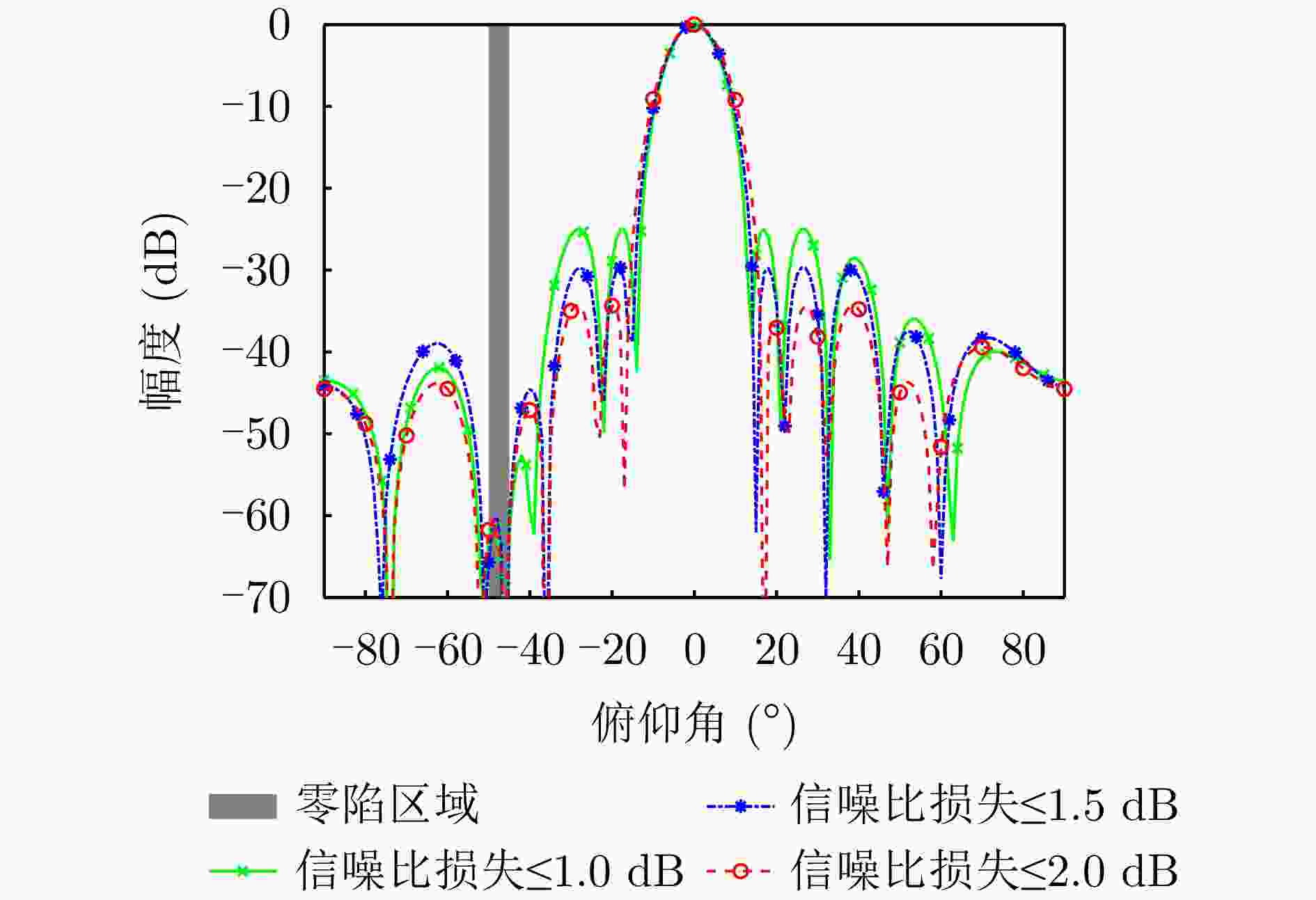
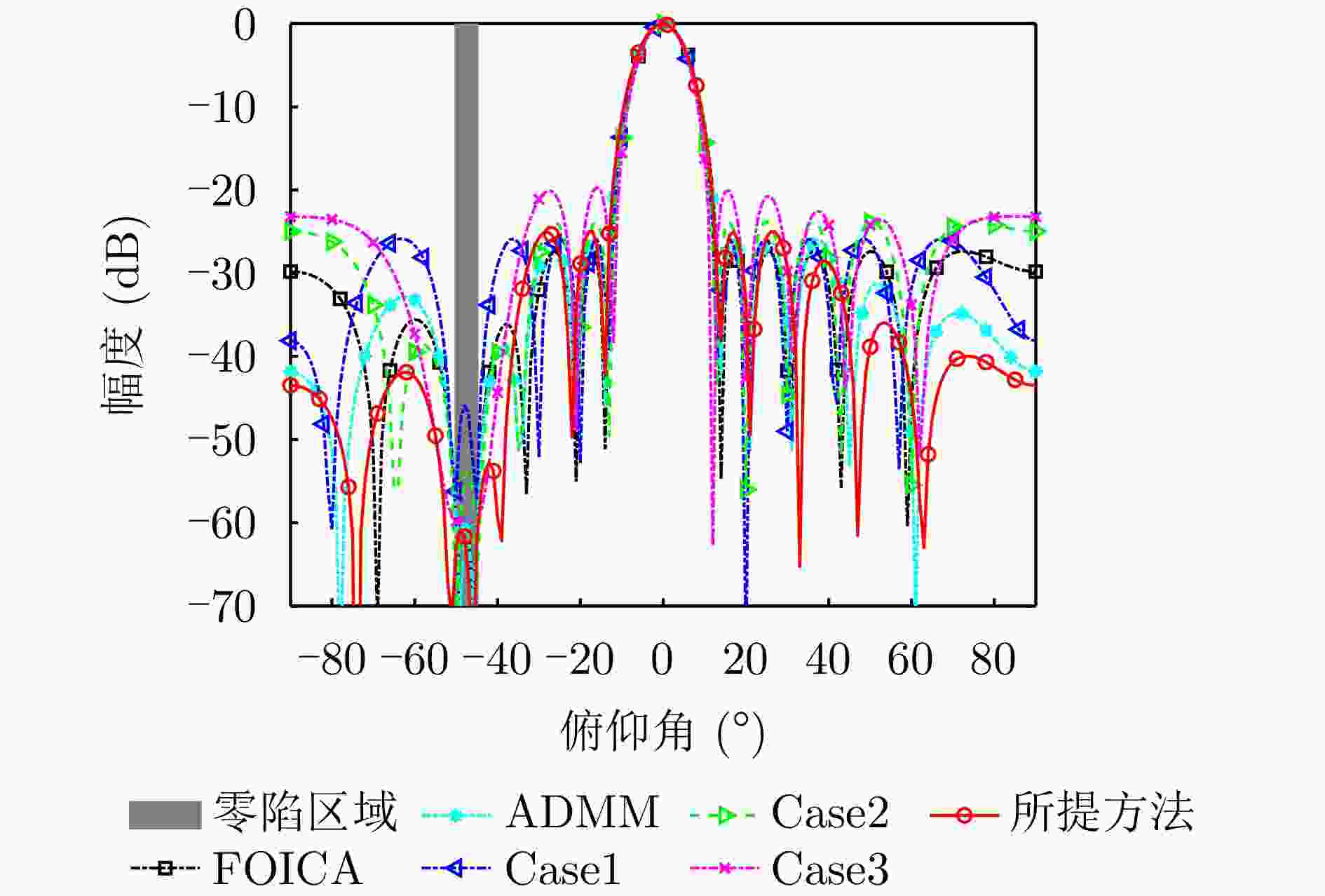
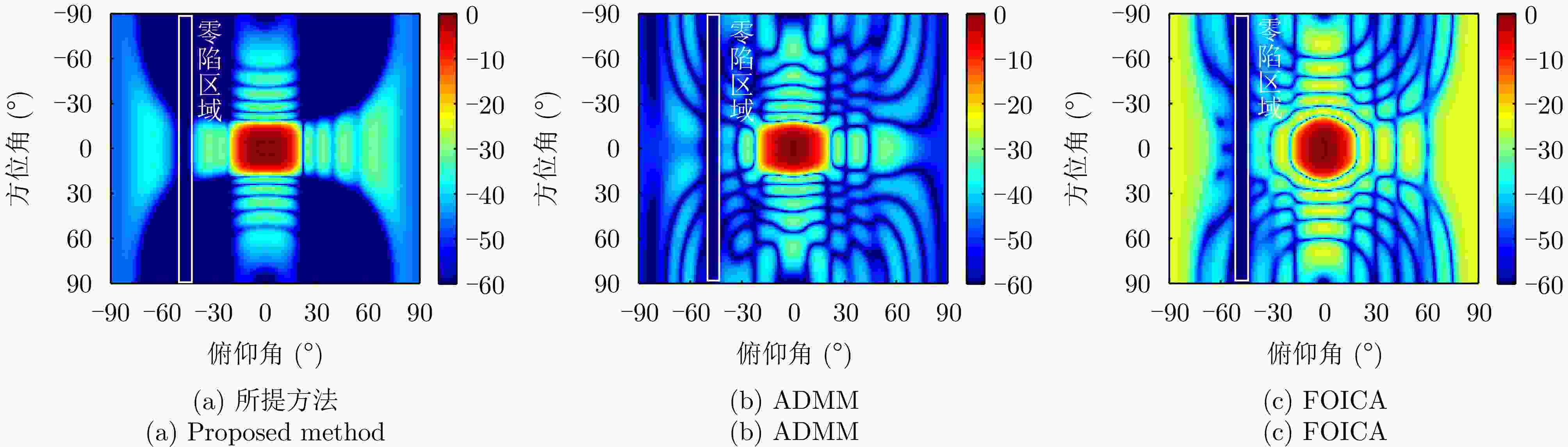
算法 归一化零陷(dB) 归一化PSL (dB) 计算时间(s) 所提方法 ≤–60.7 –25.0 12.80 ADMM ≤–60.2 –26.0 80.40 FOICA ≤–60.0 –27.3 22329.00 Case1 ≤–45.8 –25.7 67.50 Case2 ≤–53.6 –23.8 28.70 Case3 ≤–59.7 –19.6 4.18 表 2 不同算法综合指标:宽主瓣波束赋形
Table 2. Comprehensive indicators of different algorithms: Beampatterns synthesis with wide mainlobe
算法 归一化零陷(dB) 归一化PSL (dB) 计算时间(s) 所提方法 ≤–61.8 –30.9 32.1 ADMM ≤–61.9 –30.3 112.1 FOICA ≤–61.4 –24.2 21698.0 -
[1] VAN TREES H L. Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2002. [2] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [3] WANG Xiangrong, GRECO M S, and GINI F. Adaptive sparse array beamformer design by regularized complementary antenna switching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 2302–2315. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3064183. [4] WEI Wenqiang, YU Xianxiang, LU Qinghui, et al. Window function design for asymmetric beampattern synthesis and applications[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 284–288. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3259163. [5] 梁军利, 涂宇, 马云红, 等. 任务驱动的自组织蜂群柔性阵列波束赋形算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 517–529. doi: 10.12000/JR22130.LIANG Junli, TU Yu, MA Yunhong, et al. Task-driven flexible array beampattern synthesis for self-organized drone swarm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 517–529. doi: 10.12000/JR22130. [6] WANG Xiangrong, AMIN M, WANG Xianghua, et al. Sparse array quiescent beamformer design combining adaptive and deterministic constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(11): 5808–5818. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2751672. [7] 余显祥. 基于约束优化理论的MIMO雷达波形设计算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.003924.YU Xianxiang. Research on MIMO radar waveform design algorithms based on constrained optimization theory[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2020.003924. [8] 王向荣, 黄嘉怡, 谢晋东, 等. 面向艇载气象雷达的稀疏相控阵优化设计[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(9): 1569–1586. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2024.09.001.WANG Xiangrong, HUANG Jiayi, XIE Jindong, et al. Sparse phased array optimization for airship-borne weather radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(9): 1569–1586. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2024.09.001. [9] FUCHS B. Application of convex relaxation to array synthesis problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(2): 634–640. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2290797. [10] LIANG Junli, FAN Xuhui, FAN Wen, et al. Phase-only pattern synthesis for linear antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 3232–3235. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2017.2771380. [11] DOLPH C L. A current distribution for broadside arrays which optimizes the relationship between beam width and side-lobe level[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1946, 34(6): 335–348. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1946.225956. [12] TAYLOR T T. Design of line-source antennas for narrow beamwidth and low side lobes[J]. Transactions of the IRE Professional Group on Antennas and Propagation, 1955, 3(1): 16–28. doi: 10.1109/TPGAP.1955.5720407. [13] ZHOU P Y and INGRAM M A. Pattern synthesis for arbitrary arrays using an adaptive array method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(5): 862–869. doi: 10.1109/8.774142. [14] SHI Zhan and FENG Zhenghe. A new array pattern synthesis algorithm using the two-step least-squares method[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2005, 12(3): 250–253. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.842282. [15] WANG Fan, BALAKRISHNAN V, ZHOU P Y, et al. Optimal array pattern synthesis using semidefinite programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(5): 1172–1183. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2003.810308. [16] CAO Pan, THOMPSON J S, and HAAS H. Constant modulus shaped beam synthesis via convex relaxation[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 617–620. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2594141. [17] LIANG Junli, FAN Xuhui, SO H C, et al. Array beampattern synthesis without specifying lobe level masks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(6): 4526–4539. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2972331. [18] ZHANG Xuejing, HE Zishu, LIAO Bin, et al. A2RC: An accurate array response control algorithm for pattern synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(7): 1810–1824. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2649487. [19] ZHANG Xuejing, HE Zishu, LIAO Bin, et al. Pattern synthesis with multipoint accurate array response control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(8): 4075–4088. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2718582. [20] ZHANG Xuejing, HE Zishu, LIAO Bin, et al. Pattern synthesis for arbitrary arrays via weight vector orthogonal decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1286–1299. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2787143. [21] LU Qinghui, CUI Guolong, LIU Ruitao, et al. Beampattern synthesis via first-order iterative convex approximation[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(8): 1493–1497. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3088472. [22] 王德伍, 虞泓波, 袁耀辉, 等. 大规模阵列Kronecker稳健波束形成器[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(6): 1847–1854. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.03.WANG Dewu, YU Hongbo, YUAN Yaohui, et al. Kronecker robust adaptive beamformer for large array[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 1847–1854. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.03. [23] WEI Wenqiang, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Asymmetric beampattern synthesis for rectangular planar array via window function design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 400–414. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2023.3338417. [24] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, LU Guangshan, et al. Spectrally-agile waveform design for wideband MIMO radar transmit beampattern synthesis via majorization-ADMM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1563–1578. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3052997. [25] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [26] FAN Wen, FAN Xuhui, LIANG Junli, et al. Joint waveform design and antenna selection for MIMO radar beam scanning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 4479–4492. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3468724. [27] GEMECHU A Y, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Beampattern synthesis with sidelobe control and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(1): 297–310. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2938730. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: