Three-dimensional Tomographic Imaging of Urban Buildings and Structures Using Chinese Commercial SAR Satellite Data
-
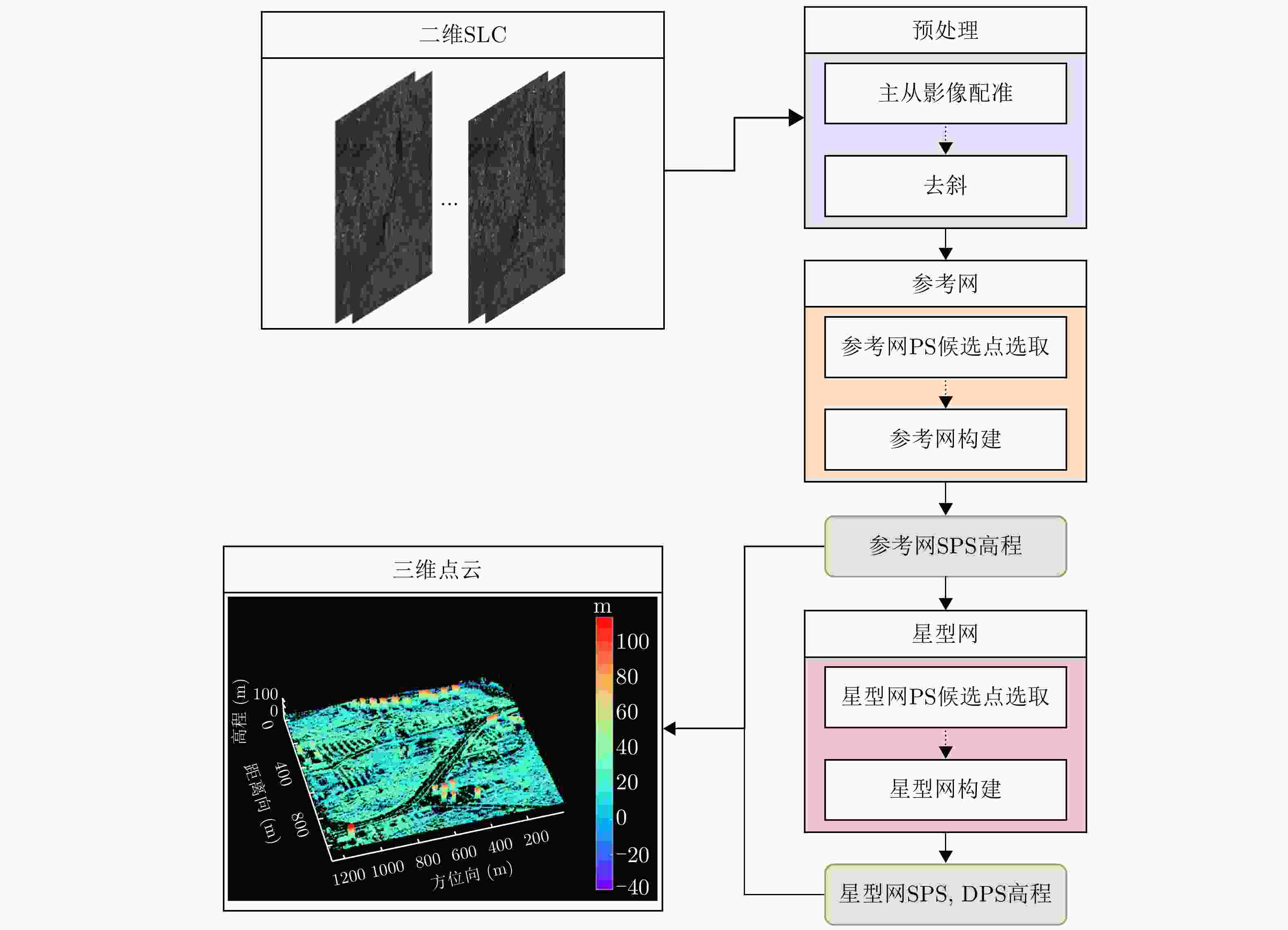
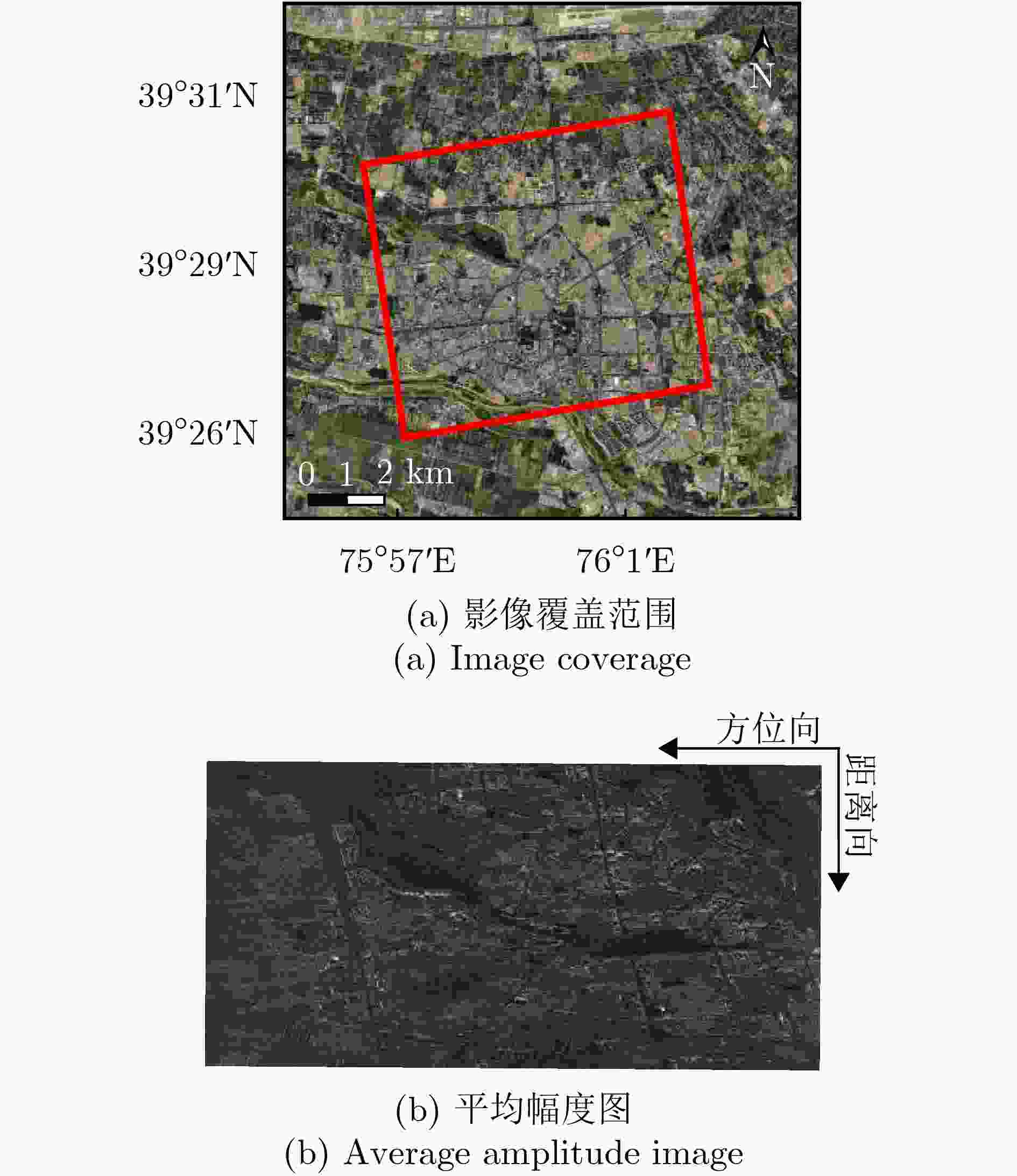
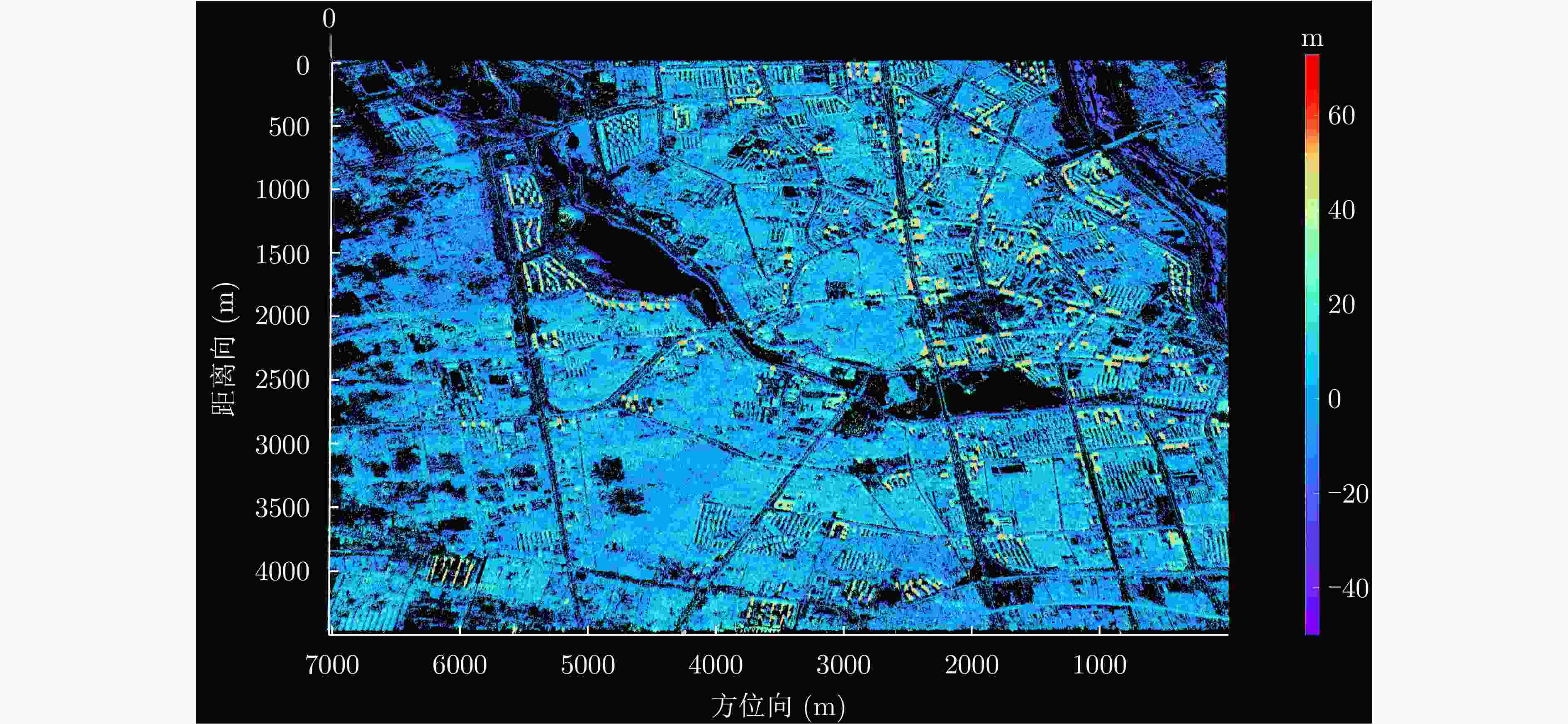
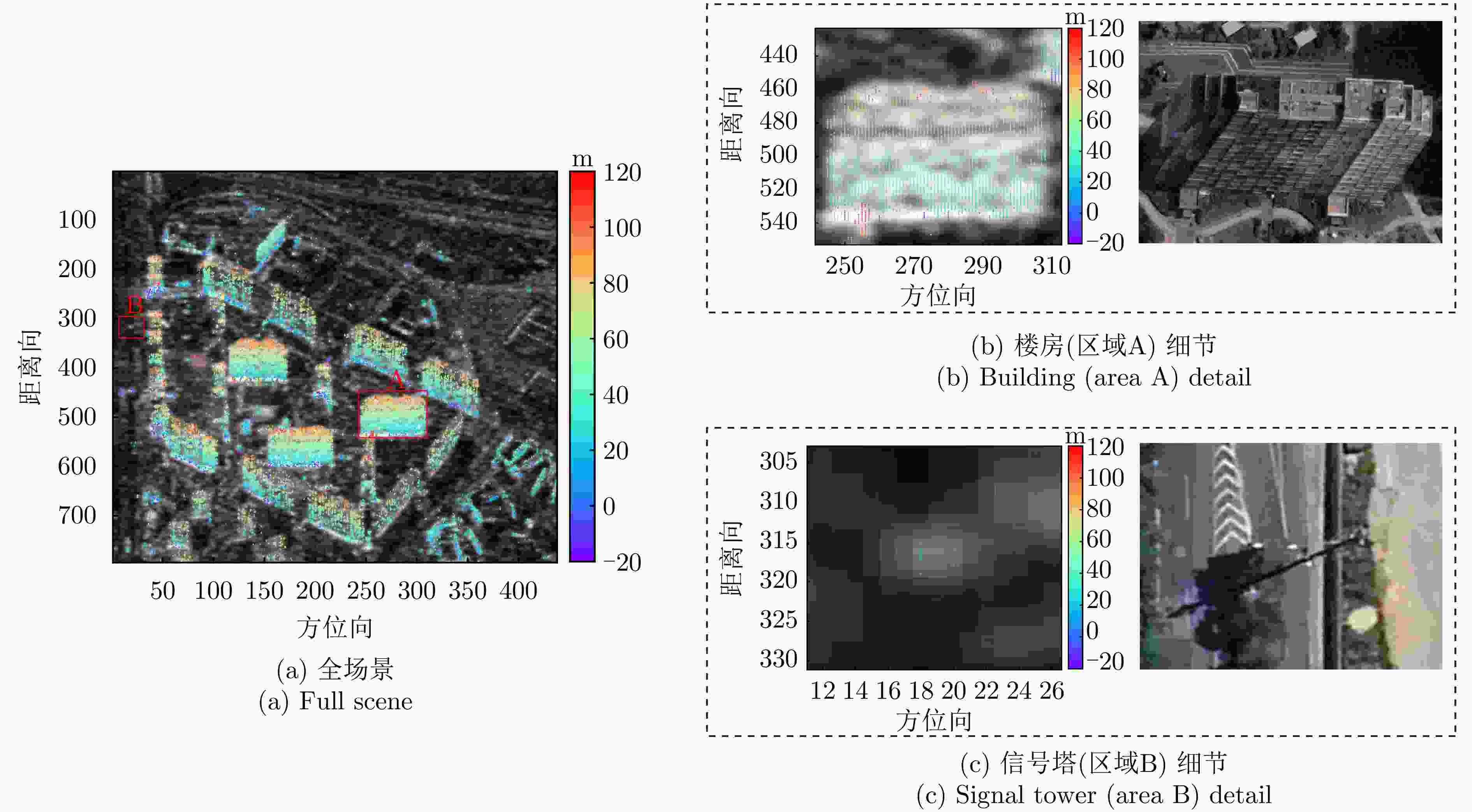
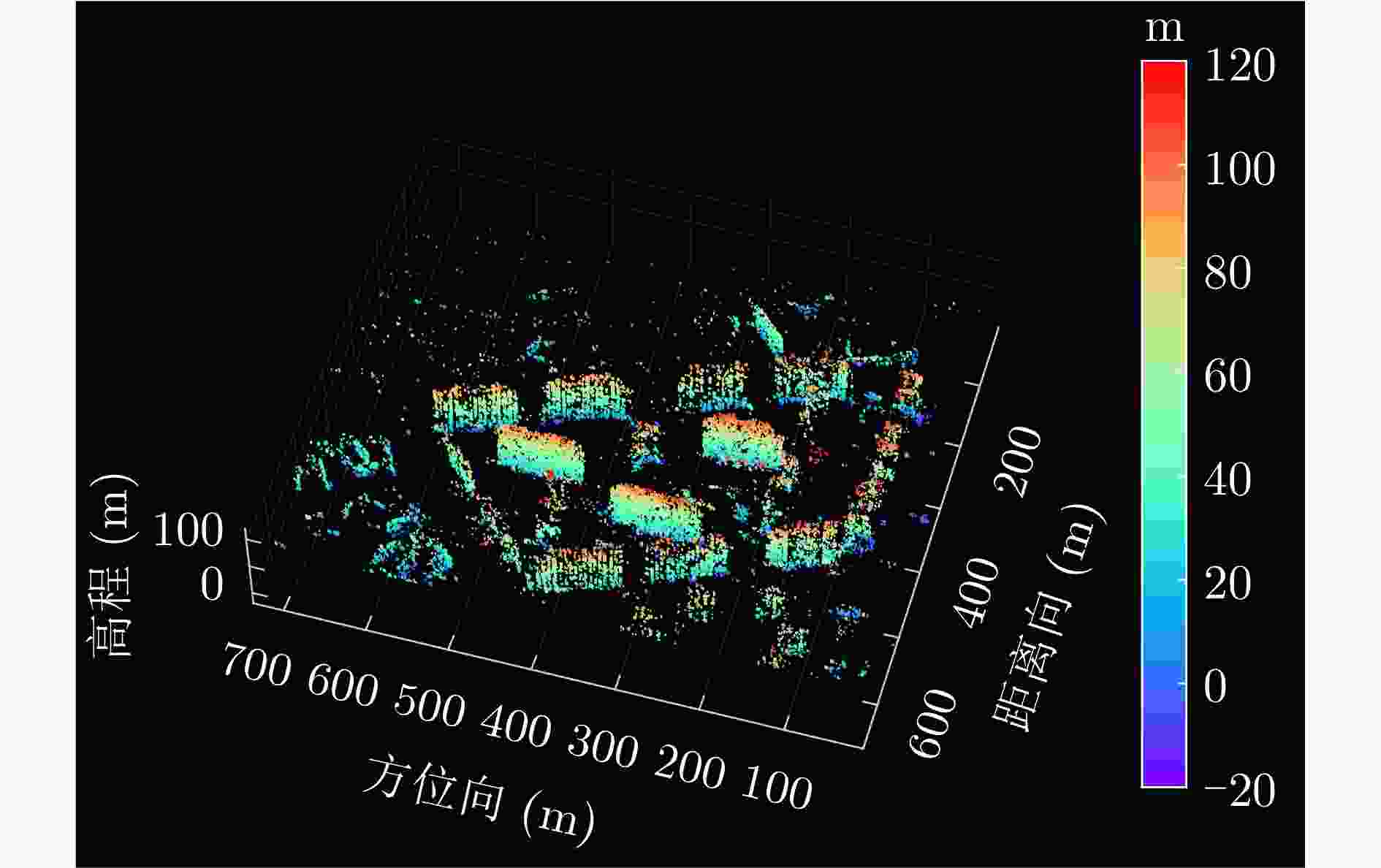
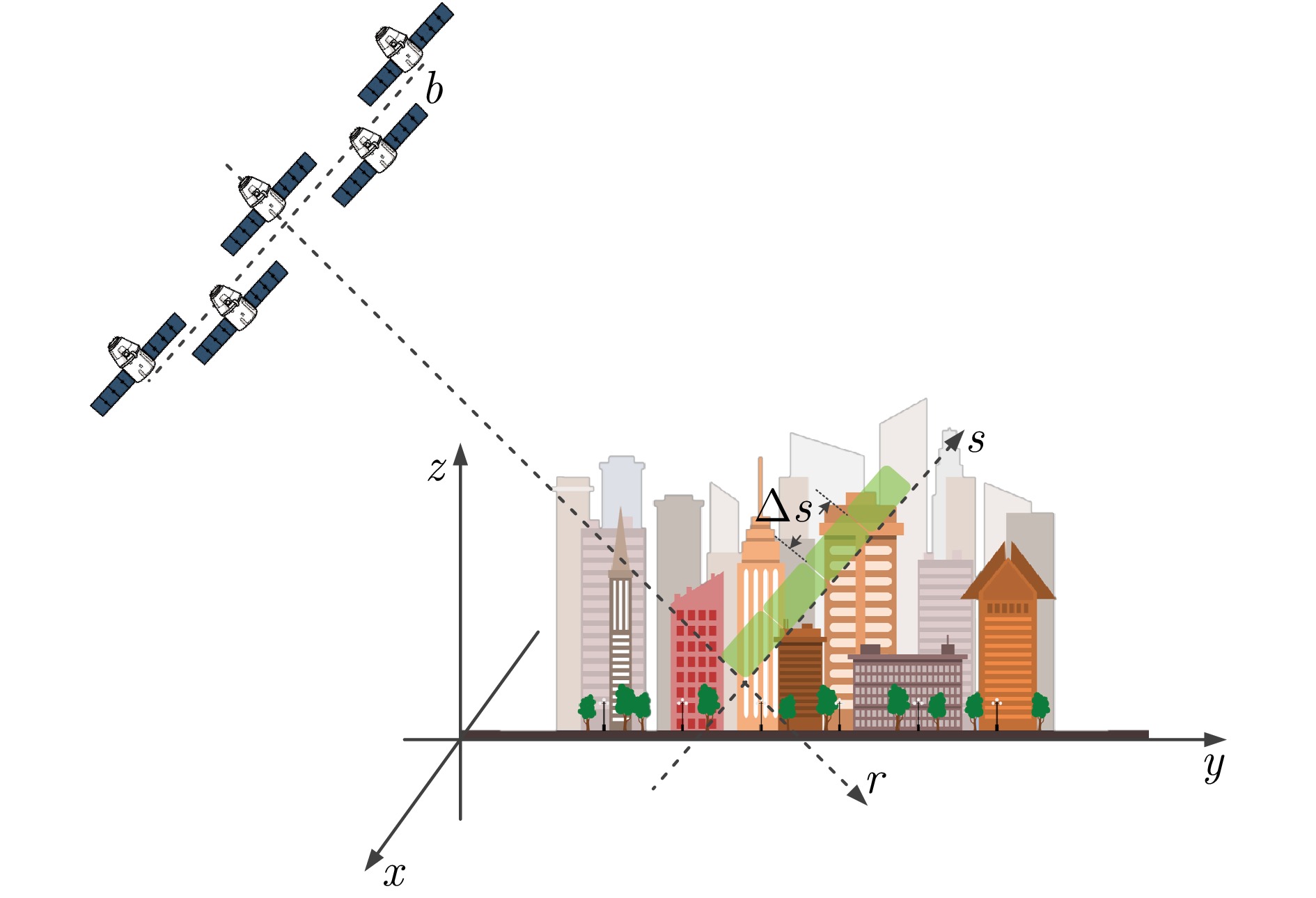
摘要: 单幅合成孔径雷达(SAR)影像仅能获取二维平面信息,传统多时相干涉SAR (InSAR)技术难以解决在城区表现尤为突出的叠掩问题。层析SAR (TomoSAR)技术的出现为获取三维信息提供了契机,同时也为解决叠掩问题给出了可行性方案。该技术依赖于对目标场景的多次重复观测,通过在高度向合成孔径提供第三维分辨能力。星载TomoSAR早期数据来源主要为TerraSAR-X, COSMO-SkyMed等国外卫星,这在一定程度上制约了国内TomoSAR技术的发展。近些年随着国内商业SAR卫星(如涪城一号、宏图一号等)的发射,丰富了数据获取来源,但目前已有的基于国产商业SAR卫星数据的城区建构筑物层析三维反演研究仍然较少。为了验证国产商业SAR卫星数据在城区层析三维参数反演方面的可用性以及在已有层析成像方法上的有效性,该文构建了城区TomoSAR三维反演框架,并利用长沙天仪空间科技研究院有限公司涪城一号和航天宏图信息技术股份有限公司宏图一号SAR卫星数据开展了城市建构筑物三维反演研究。实验结果验证了上述两个卫星系统的层析应用潜力,为后续深入研究和应用提供了先导性技术支撑。Abstract: A single Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image can capture only two-dimensional information, and traditional multitemporal Interferometric SAR (InSAR) techniques struggle with the layover problem, particularly in urban areas. SAR Tomography (TomoSAR) provides the advantage of obtaining three-dimensional (3-D) information while offering a feasible solution to the layover problem. This technique relies on repeated observations of the target scene to achieve 3-D resolution by synthesizing the aperture in the elevation direction. In China, early data sources for spaceborne TomoSAR primarily came from foreign satellites such as TerraSAR-X and COSMO-SkyMed, which constrained the development of the country’s TomoSAR technology. In recent years, the launch of Chinese commercial SAR satellites (e.g., Fucheng-1 and Hongtu-1) has expanded the range of data acquisition sources. However, studies on the tomographic 3-D inversion of urban buildings and structures using data from Chinese commercial SAR satellites remain limited. To validate the usability of Chinese commercial SAR satellite data in urban tomography 3-D parameter inversion and the effectiveness of applying these data to existing tomography imaging methods, this paper develops a 3-D inversion framework for urban TomoSAR and conducts a 3-D inversion study of urban buildings and structures using data from the Fucheng-1 satellite of Spacety Co., Ltd. (Changsha) and the Hongtu-1 SAR satellite of Piesat Information Technology Co., Ltd. The experimental results validate the potential of these two satellite systems for tomographic applications, providing pioneering technical support for future in-depth research and applications.
-
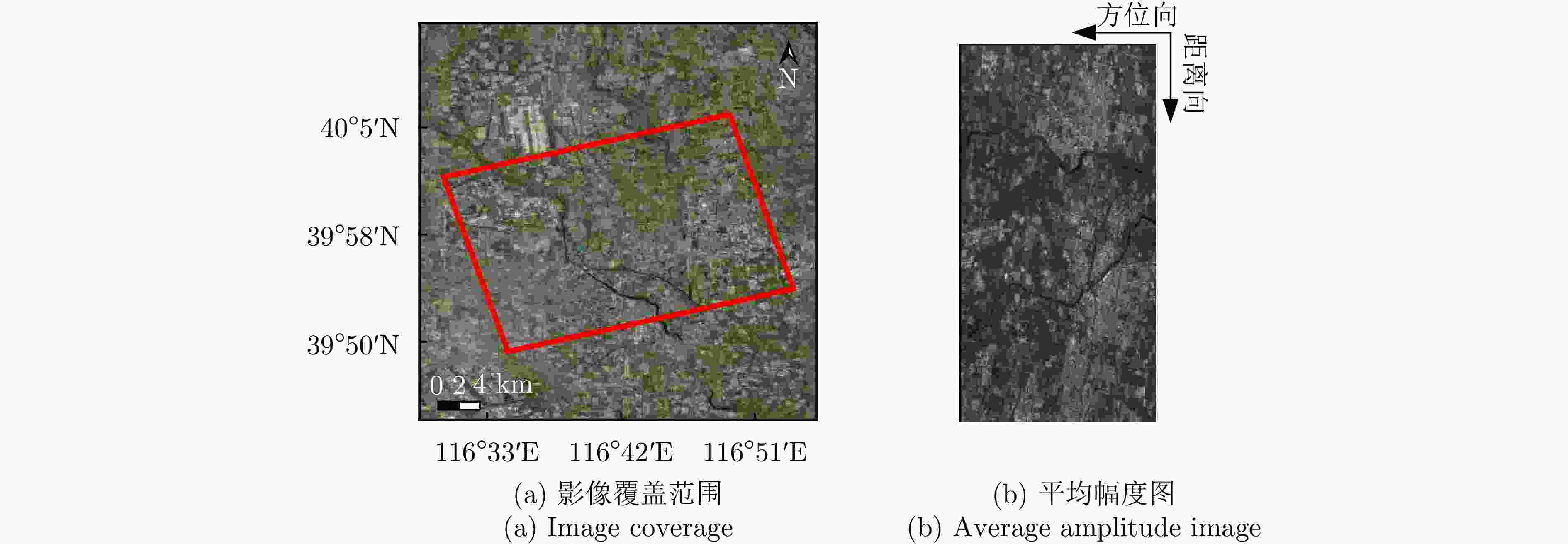
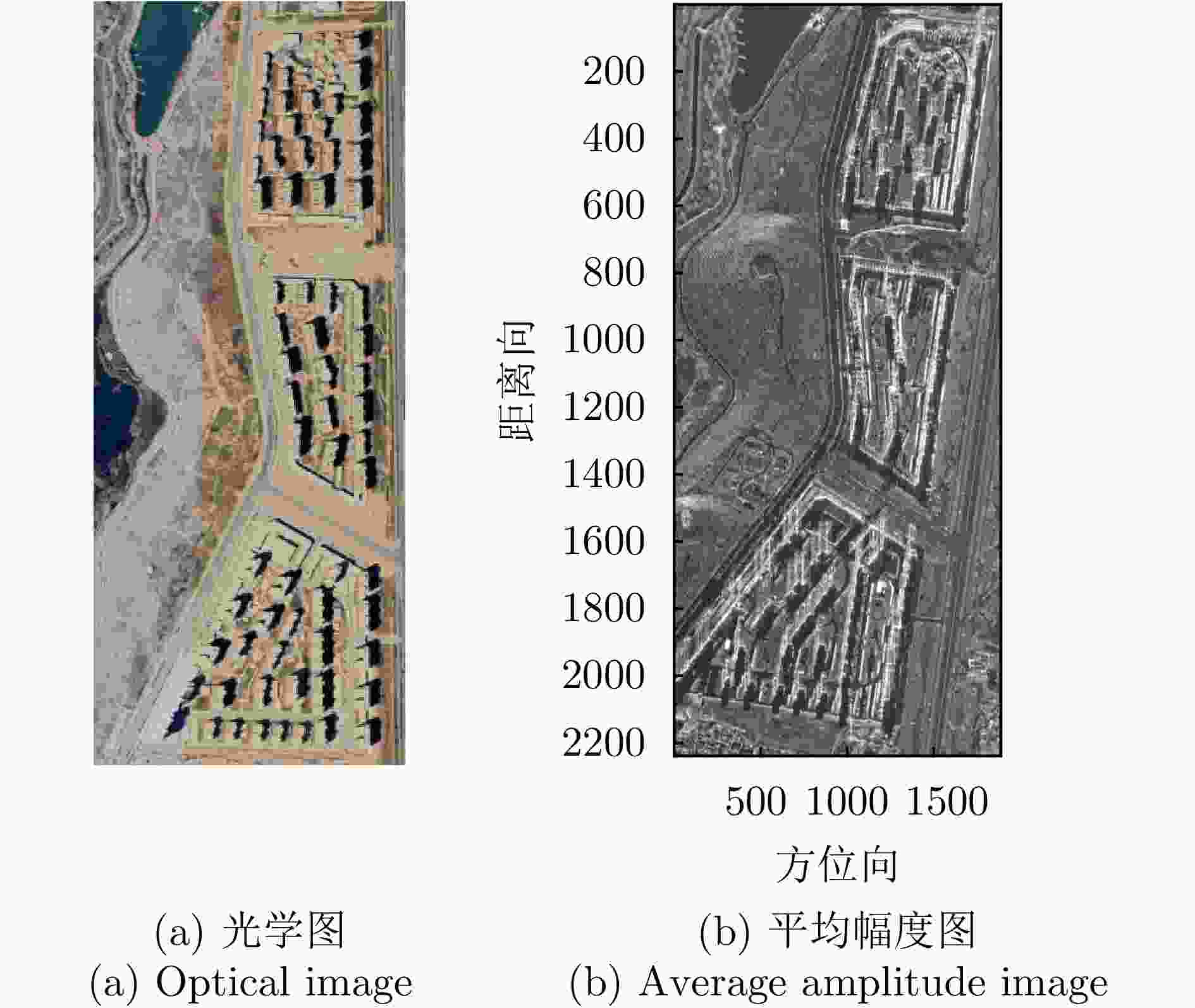
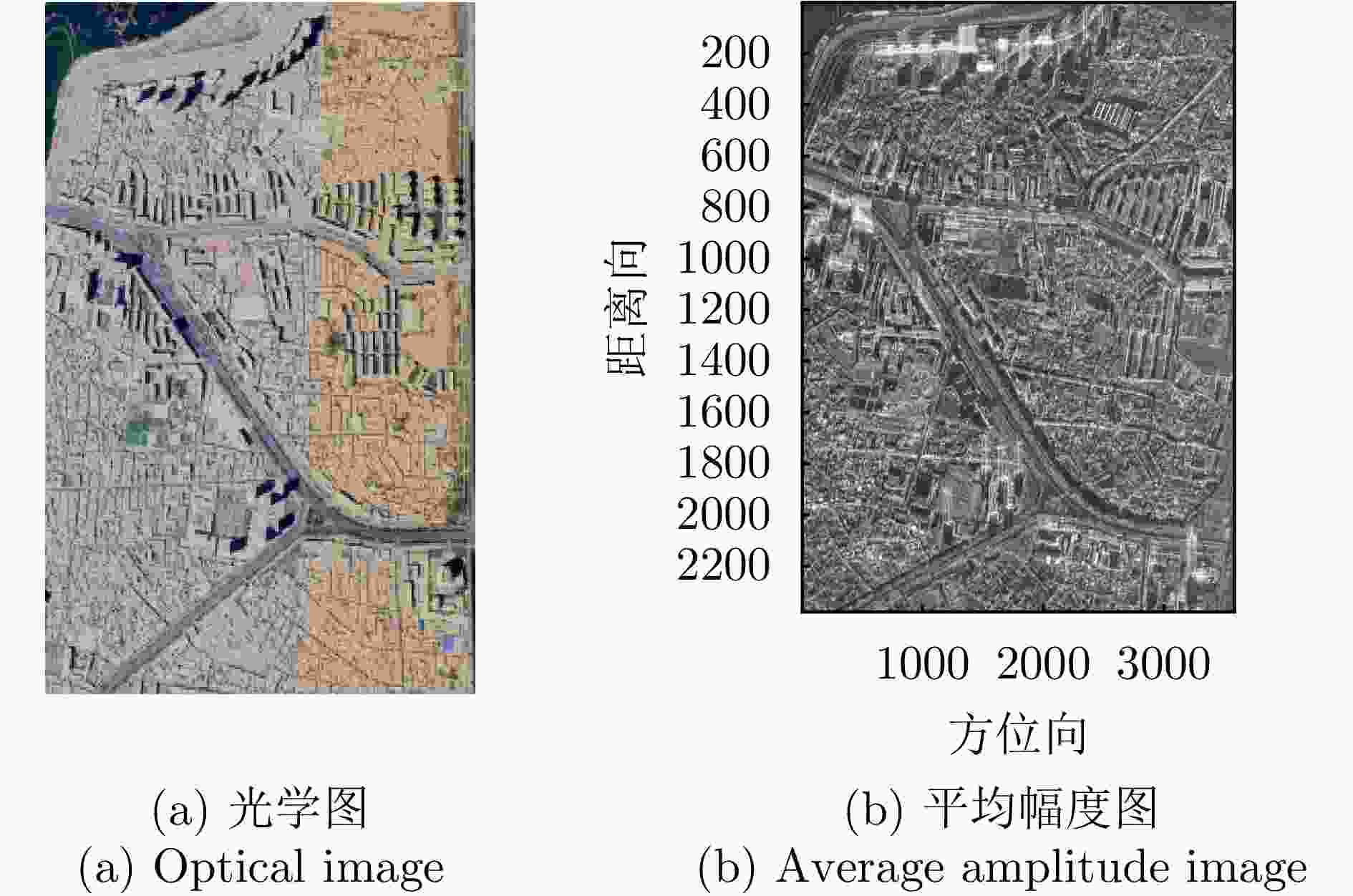
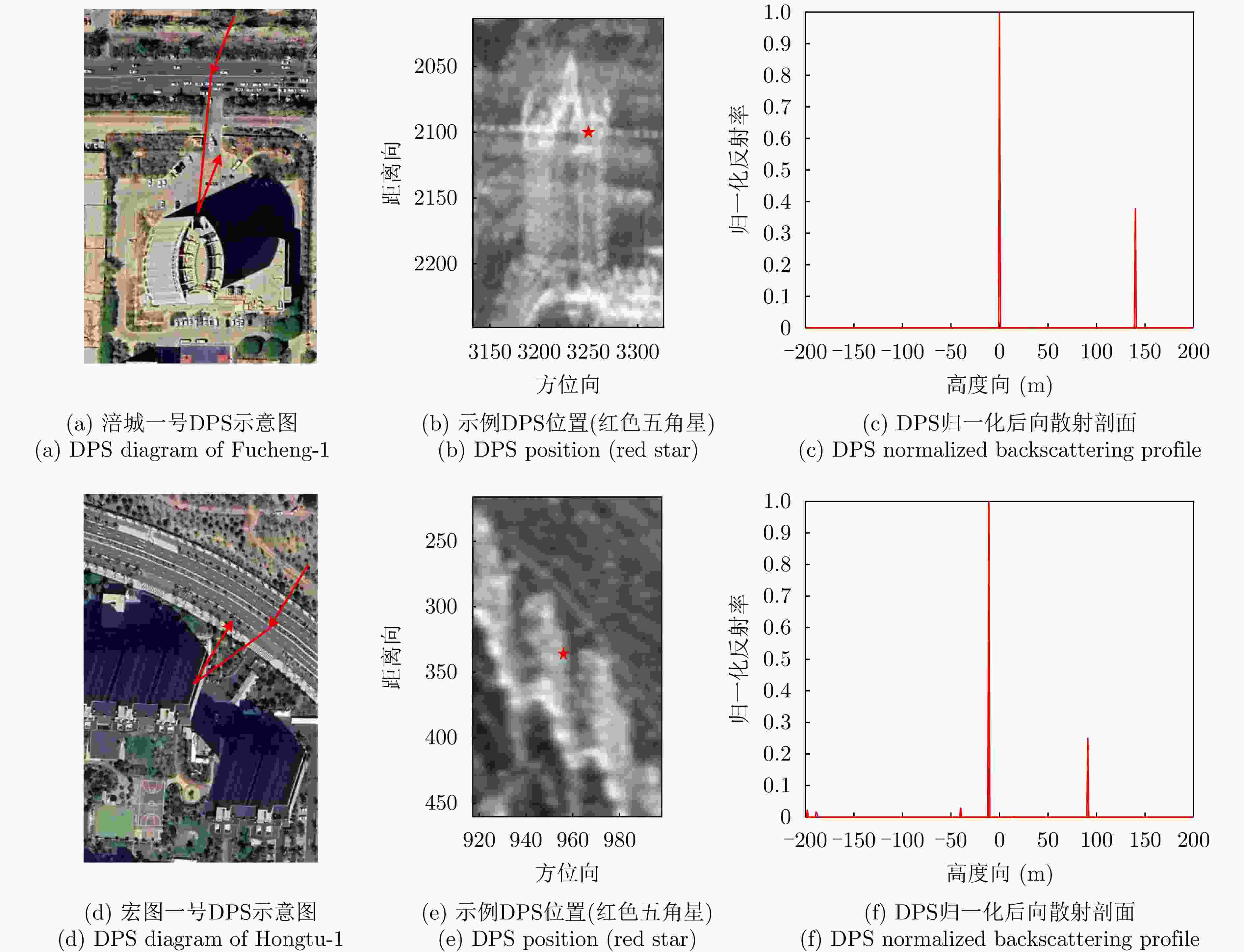
表 1 涪城一号数据集相关参数
Table 1. Parameters of Fucheng-1 dataset
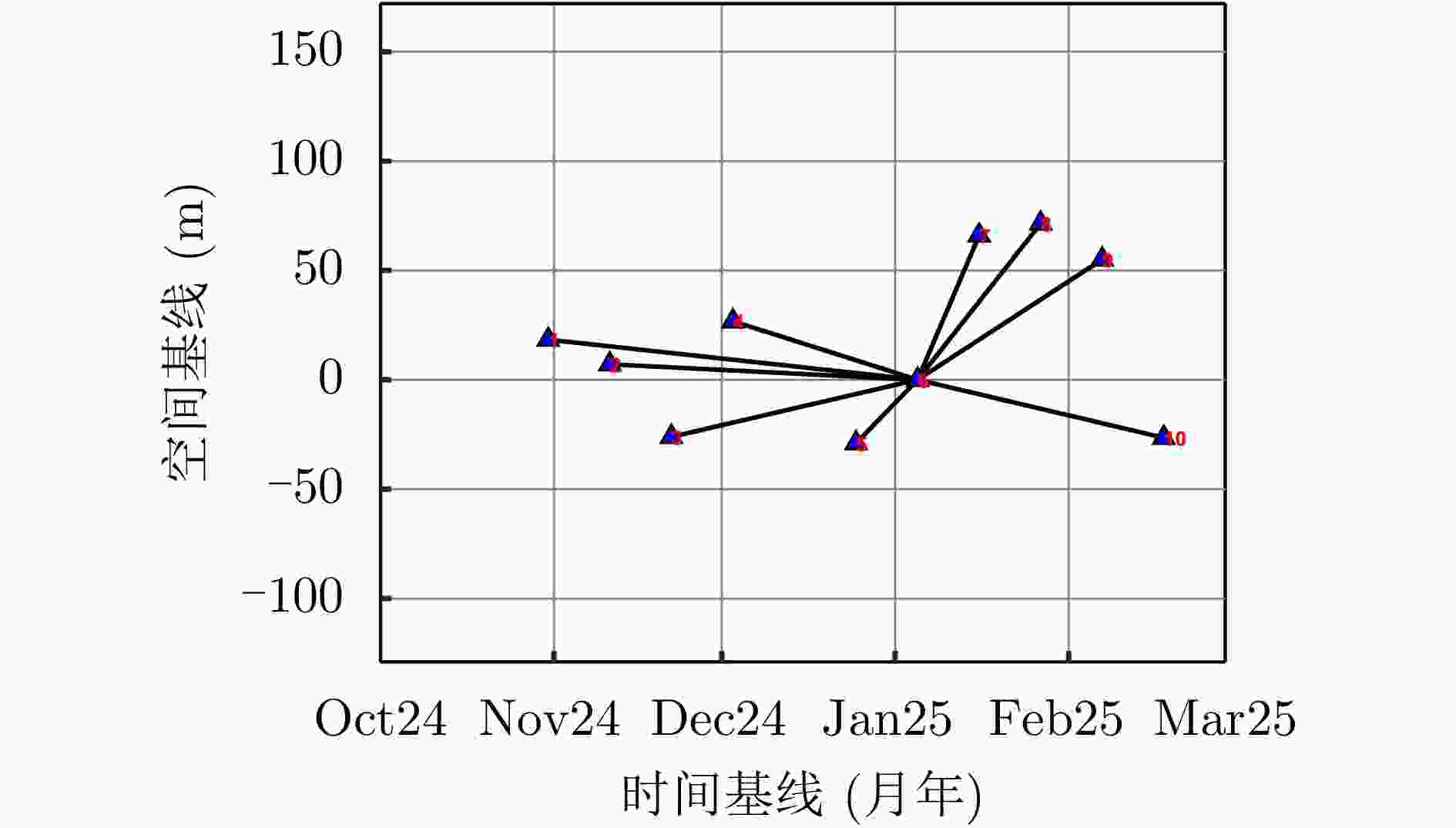
参数 指标 轨道方向 升轨 成像模式 聚束 入射角 37.23° 极化方式 VV 波长 0.056 m 中心斜距 631.01 km 重访周期 11 d 载频 5.4 GHz 带宽 300 MHz 距离向像素间隔 0.45 m 方位向像素间隔 0.35 m 影像数 10 垂直基线跨度 100.44 m 高度向理论分辨率 174.51 m 表 2 宏图一号数据集相关参数
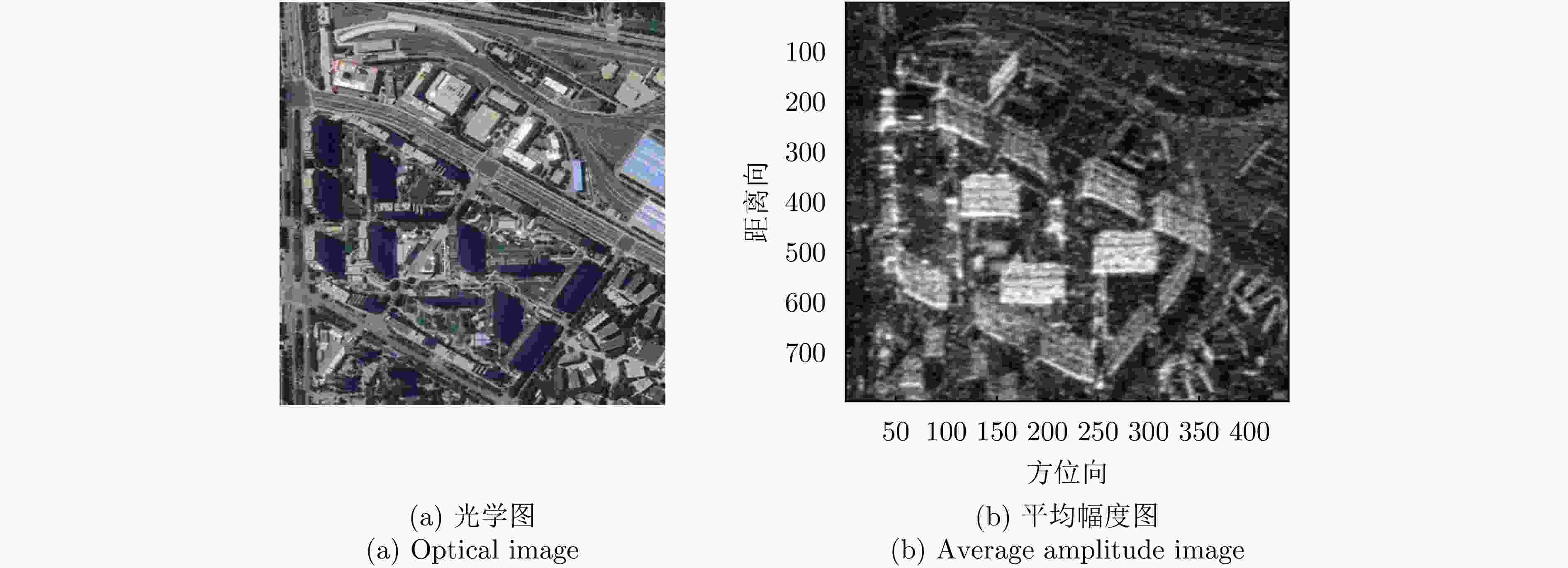
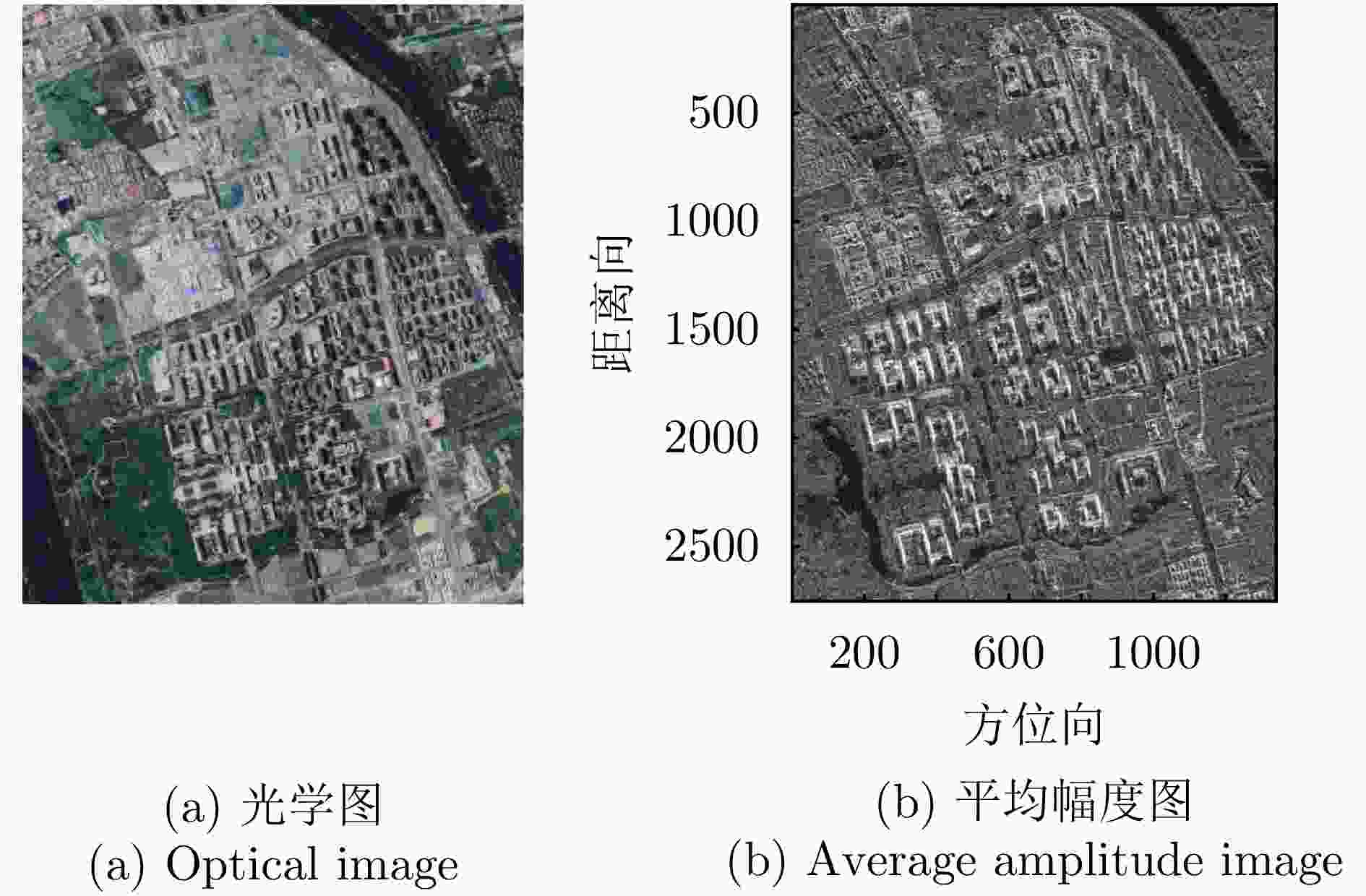
Table 2. Parameters of Hongtu-1 dataset
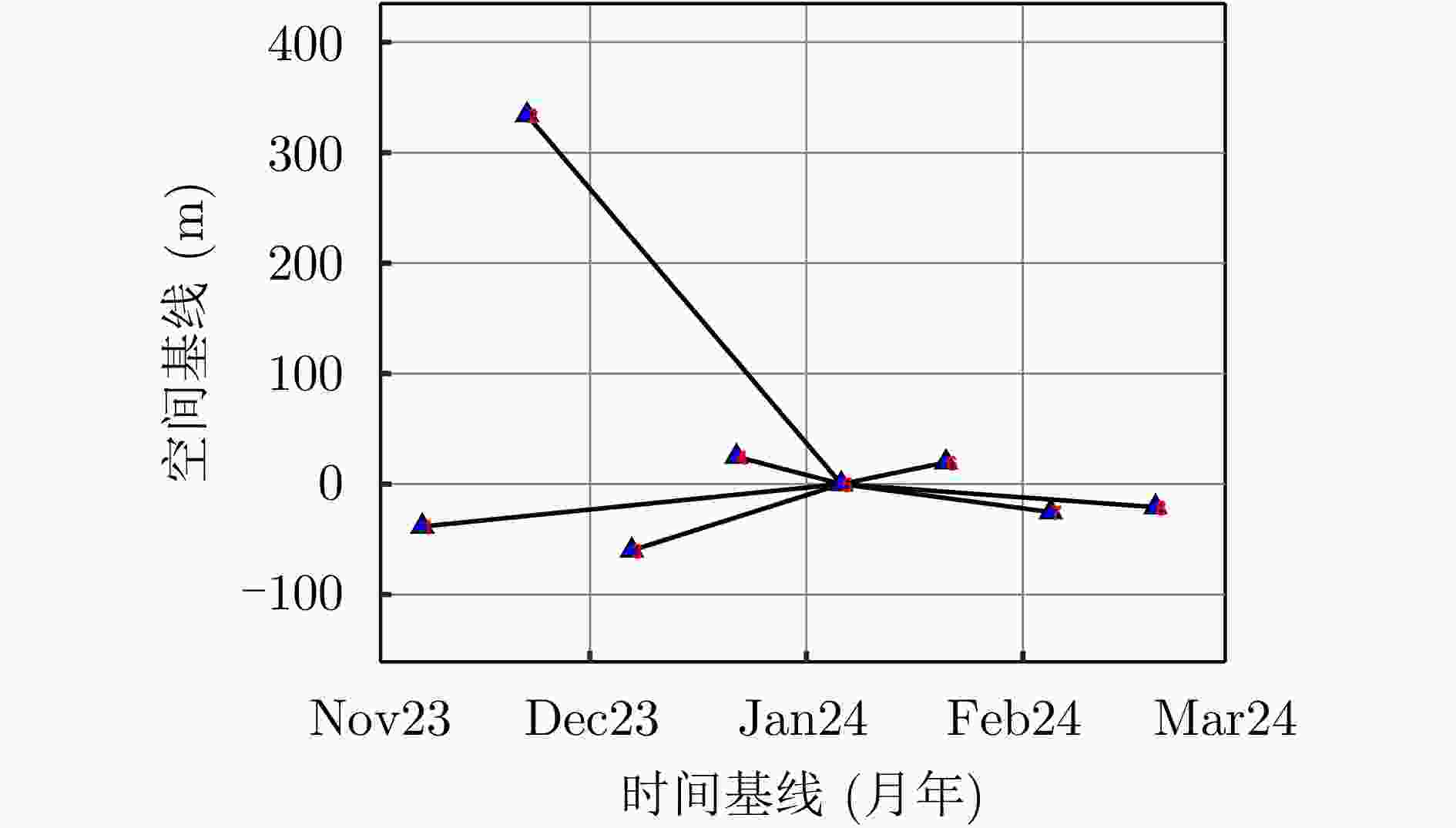
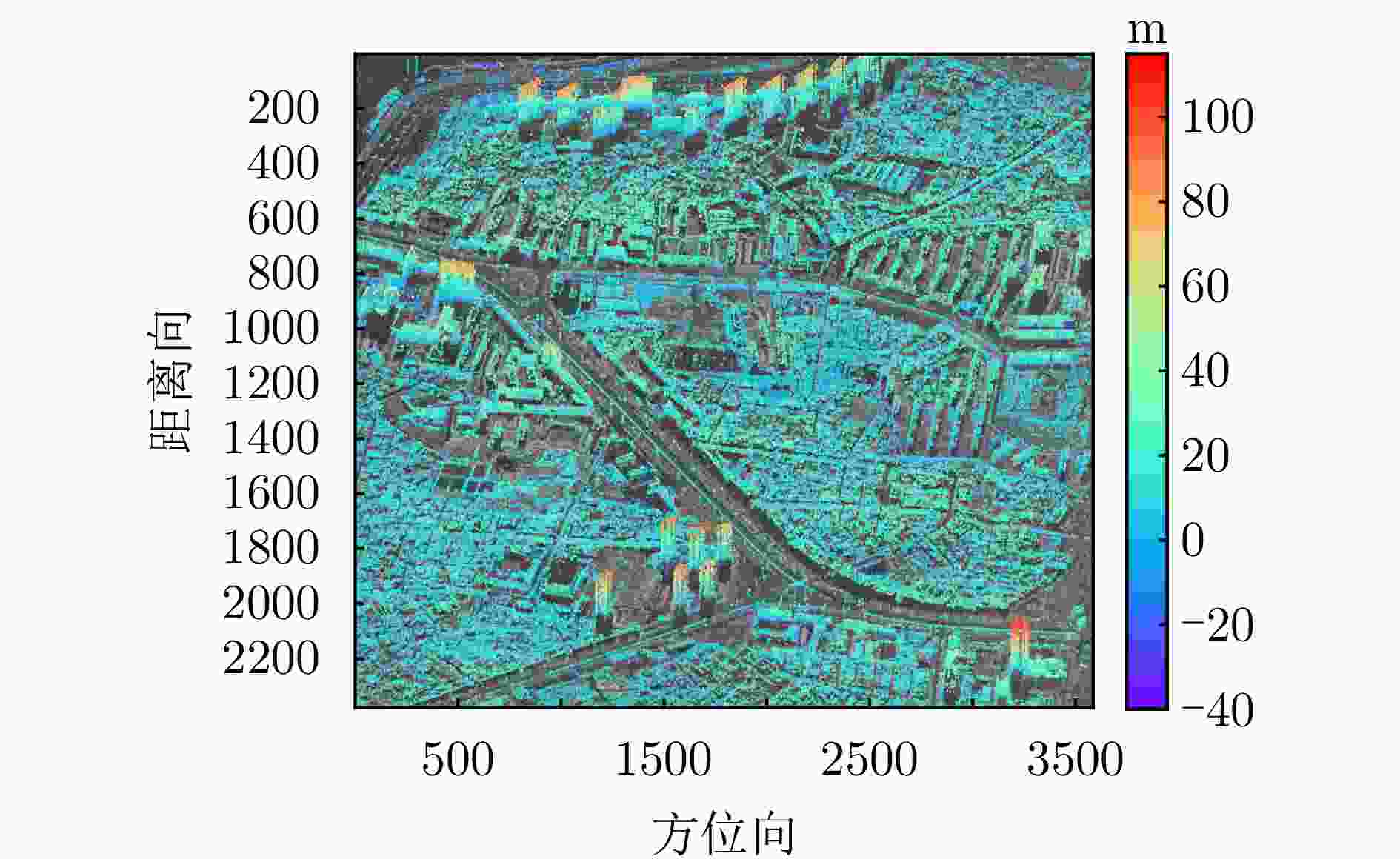
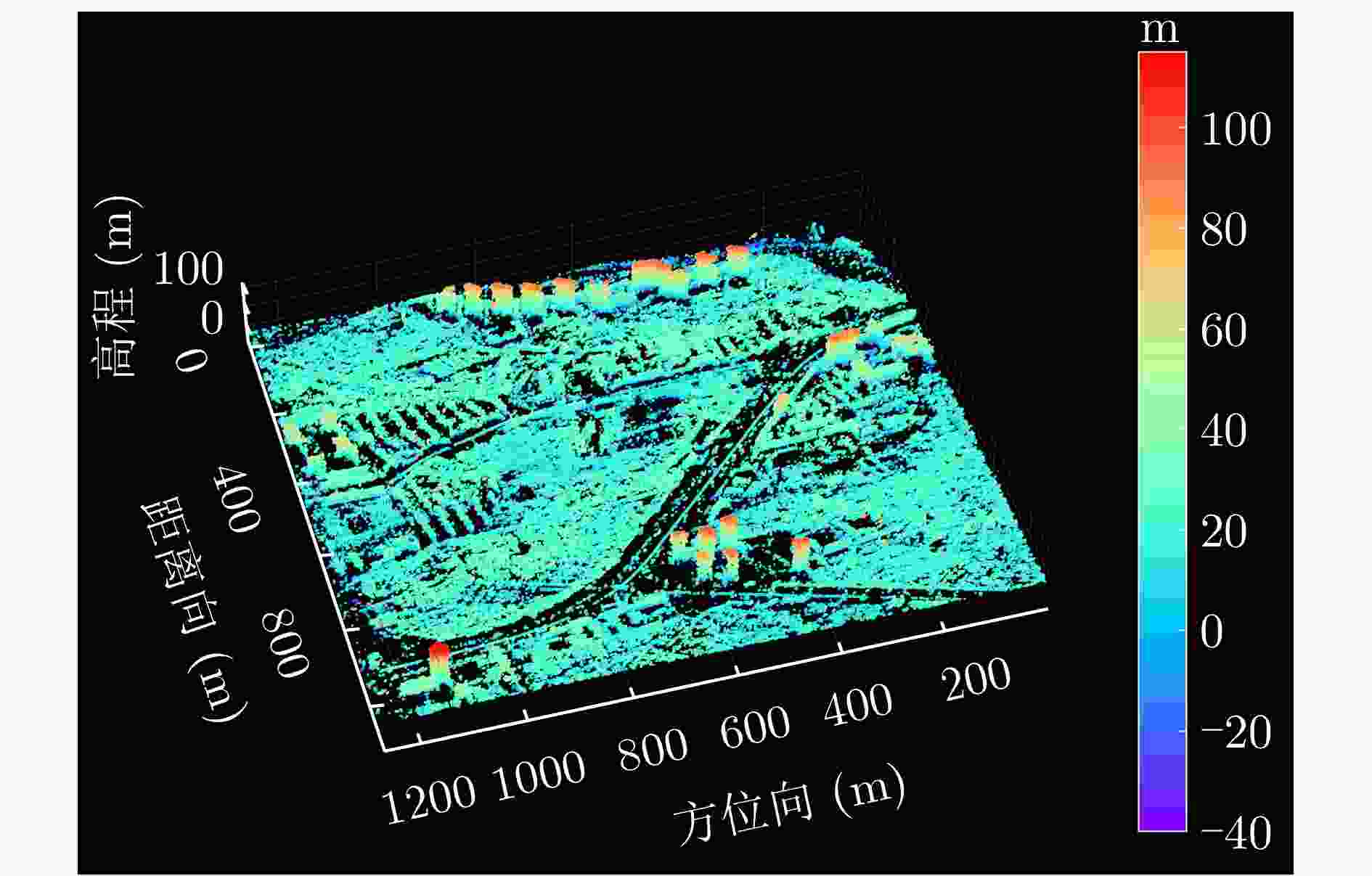
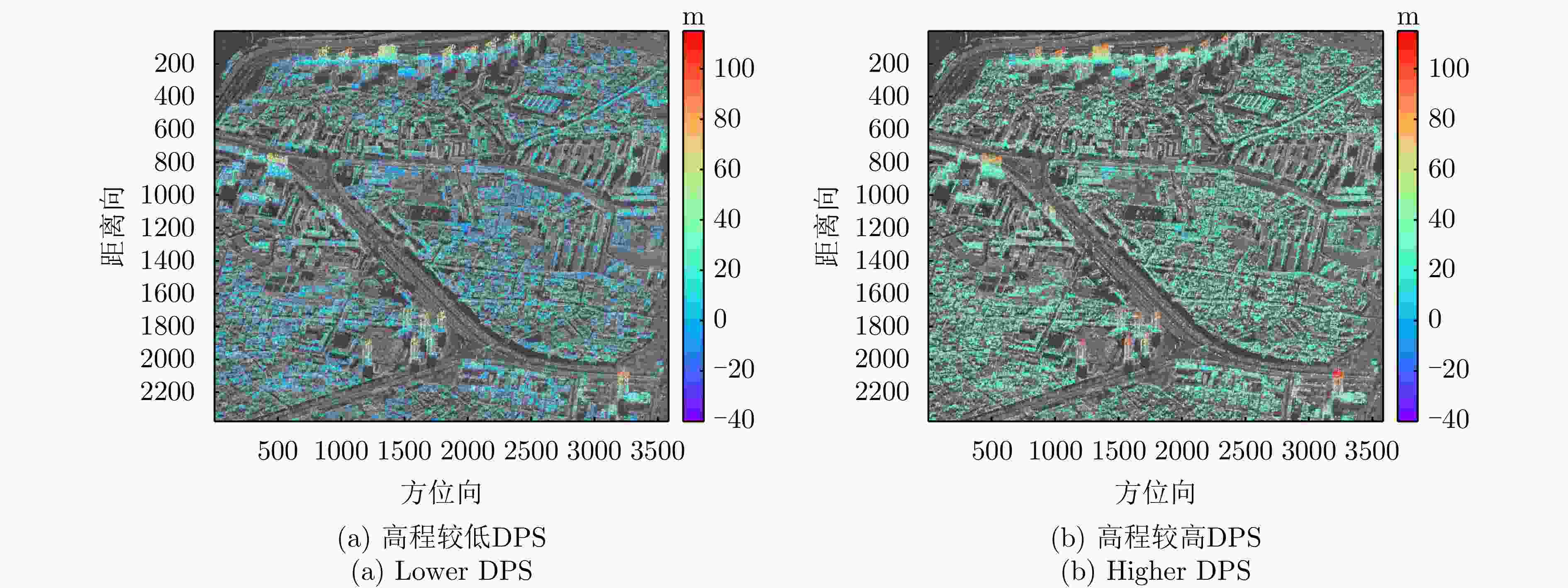
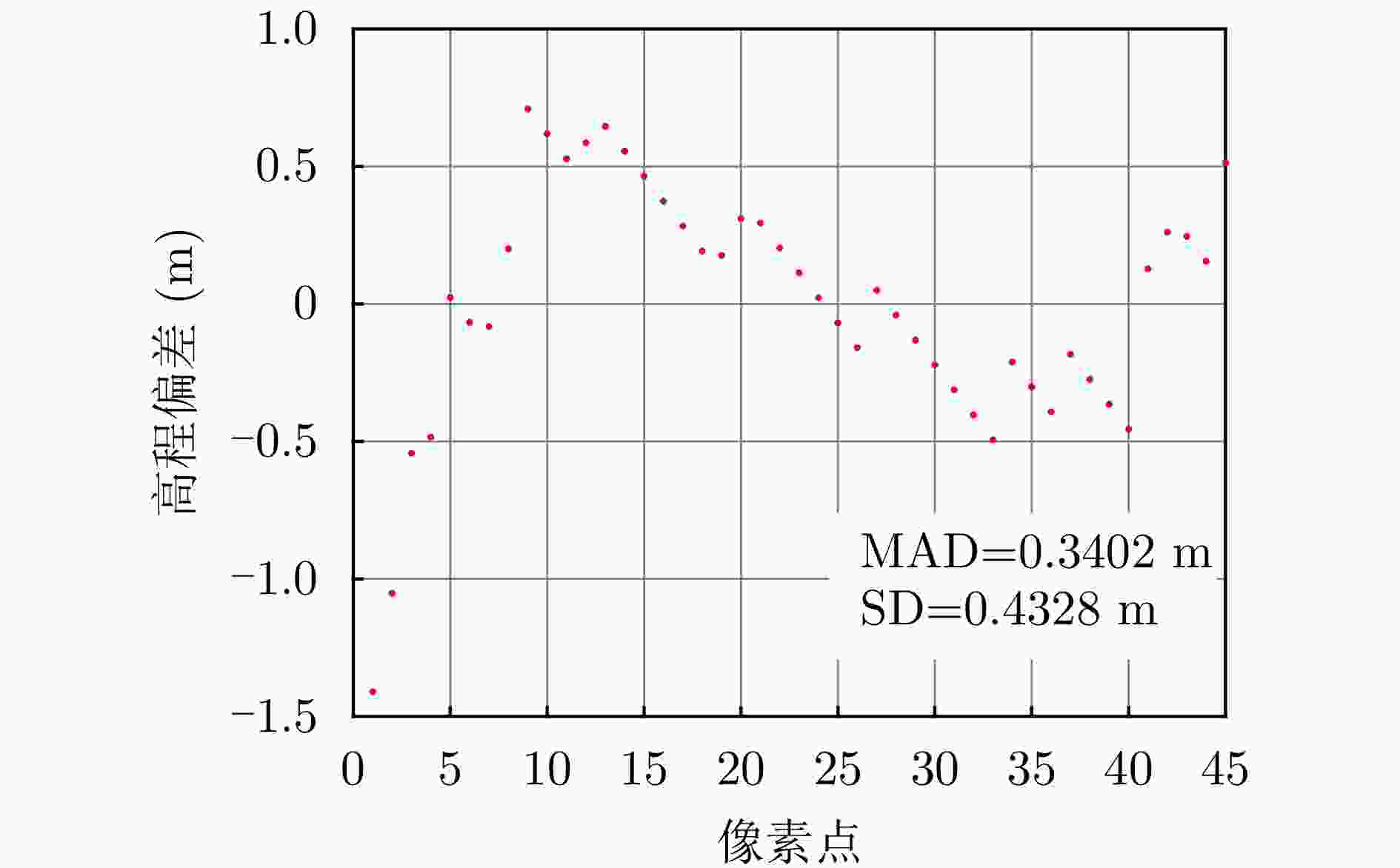
参数 指标 轨道方向 升轨 成像模式 条带 入射角 42.36° 极化方式 HH 波长 0.031 m 中心斜距 695.96 km 重访周期 15 d 载频 9.6 GHz 带宽 100 MHz 距离向像素间隔 0.75 m 方位向像素间隔 1.68 m 影像数 8 垂直基线跨度 394.18 m 高度向理论分辨率 27.57 m 表 3 DPS估计精度统计
Table 3. DPS estimation accuracy statistics
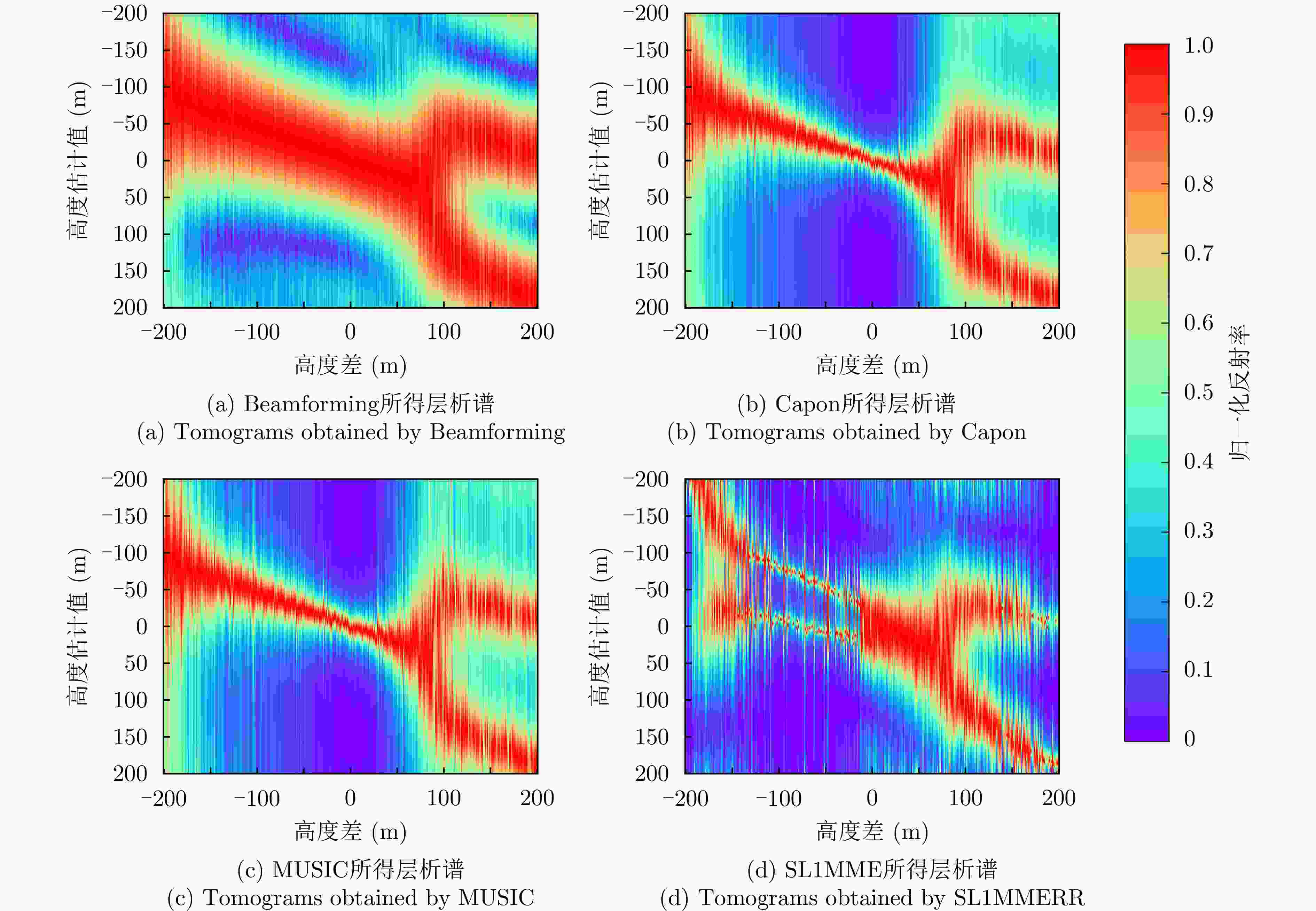
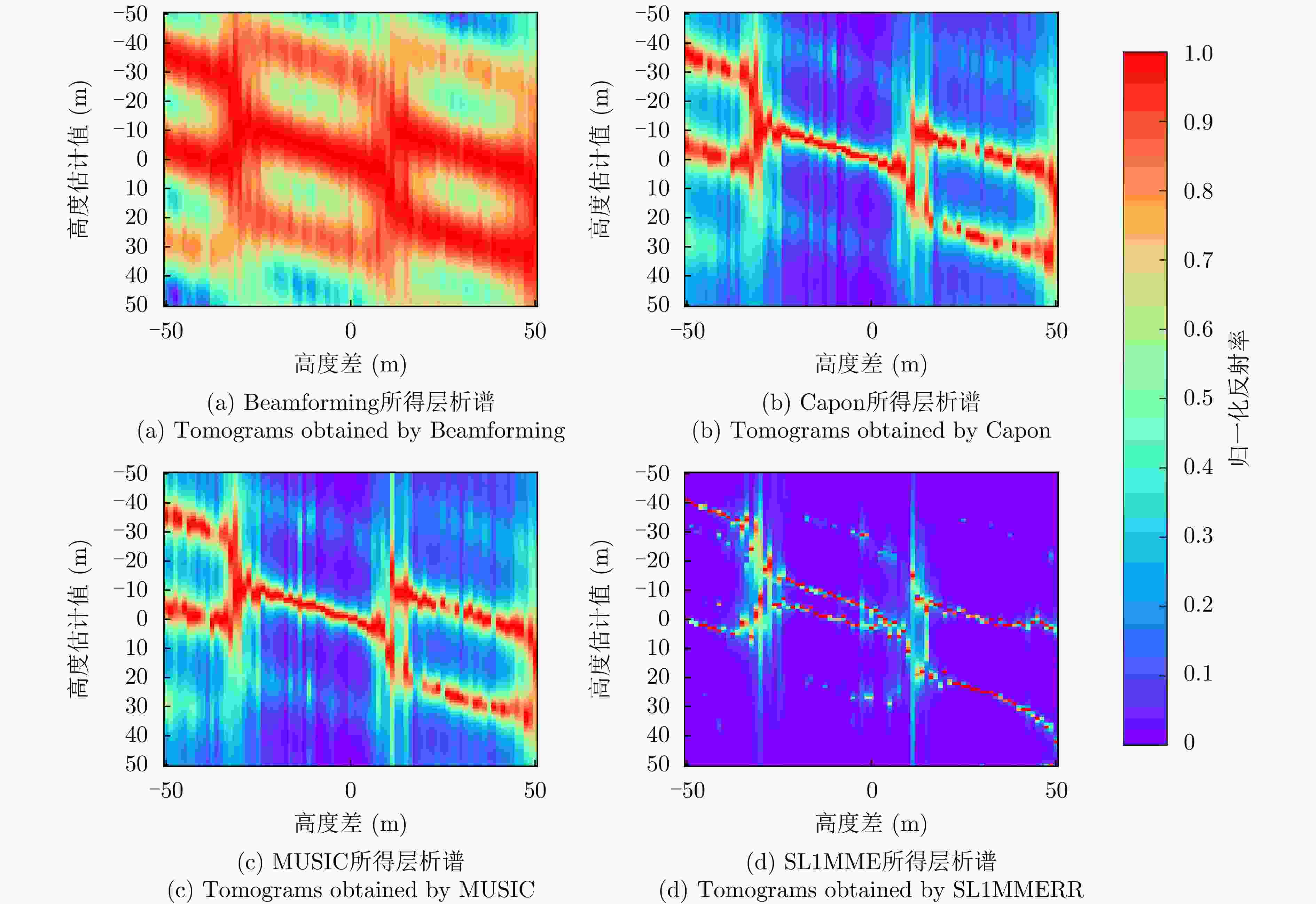
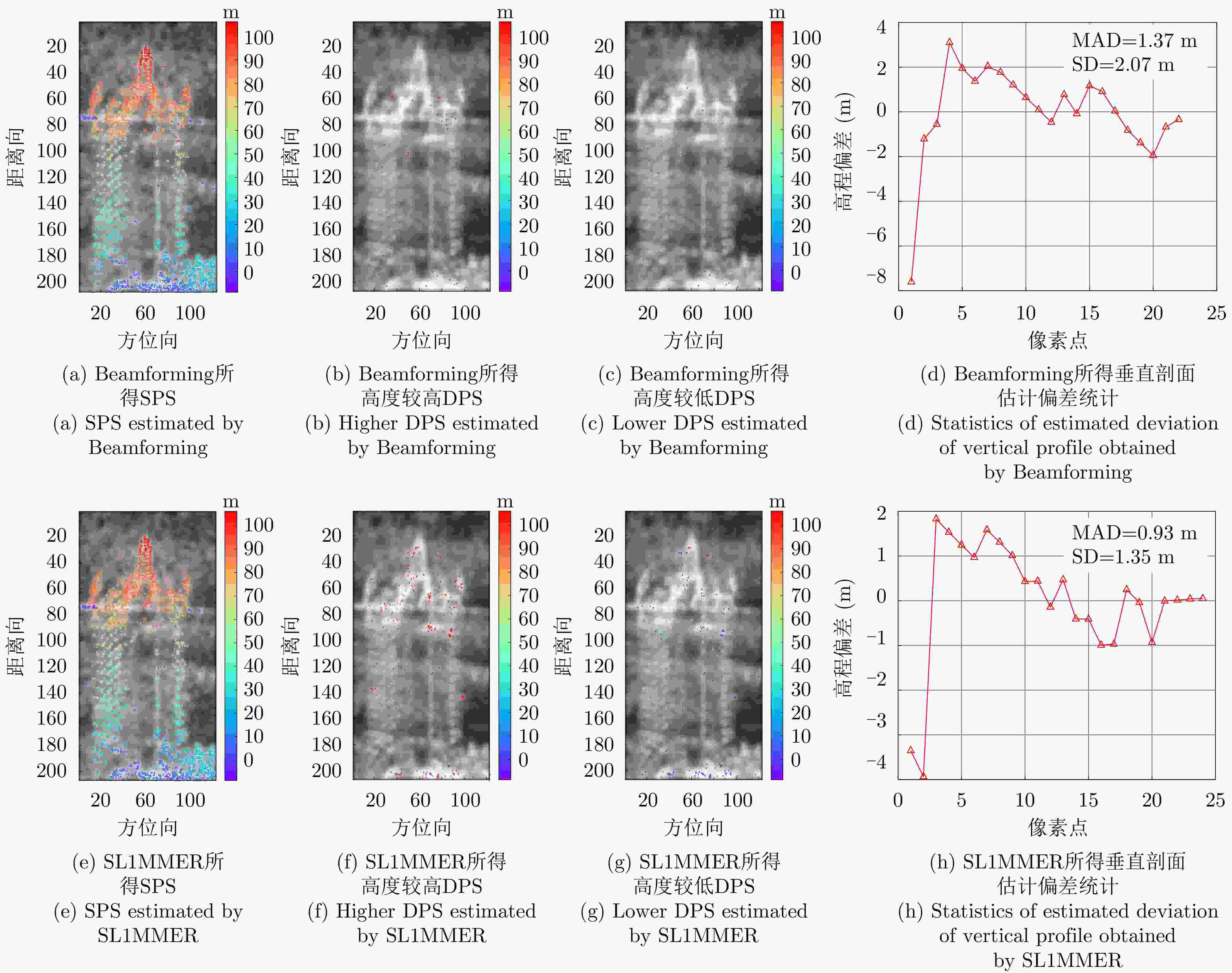
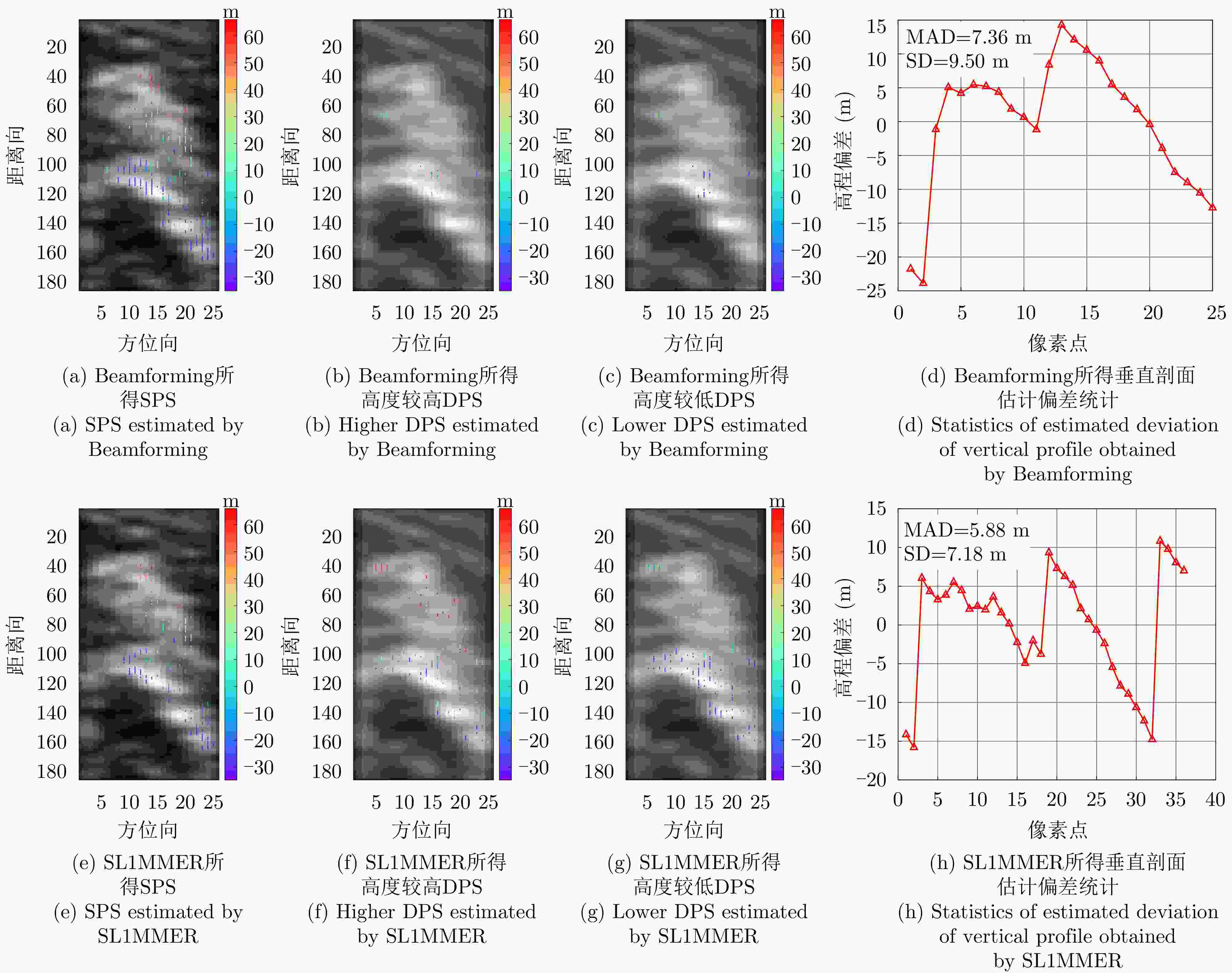
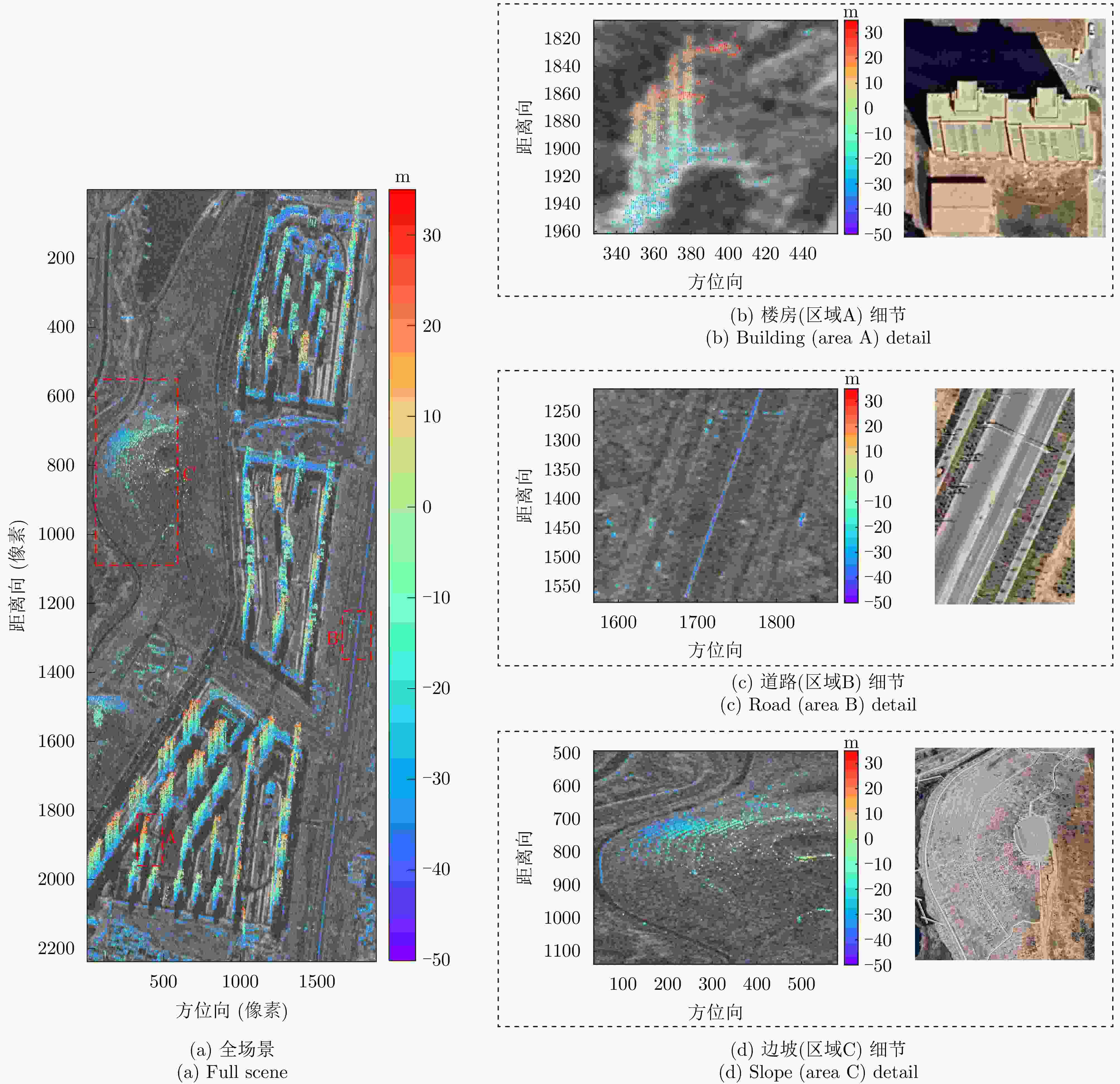
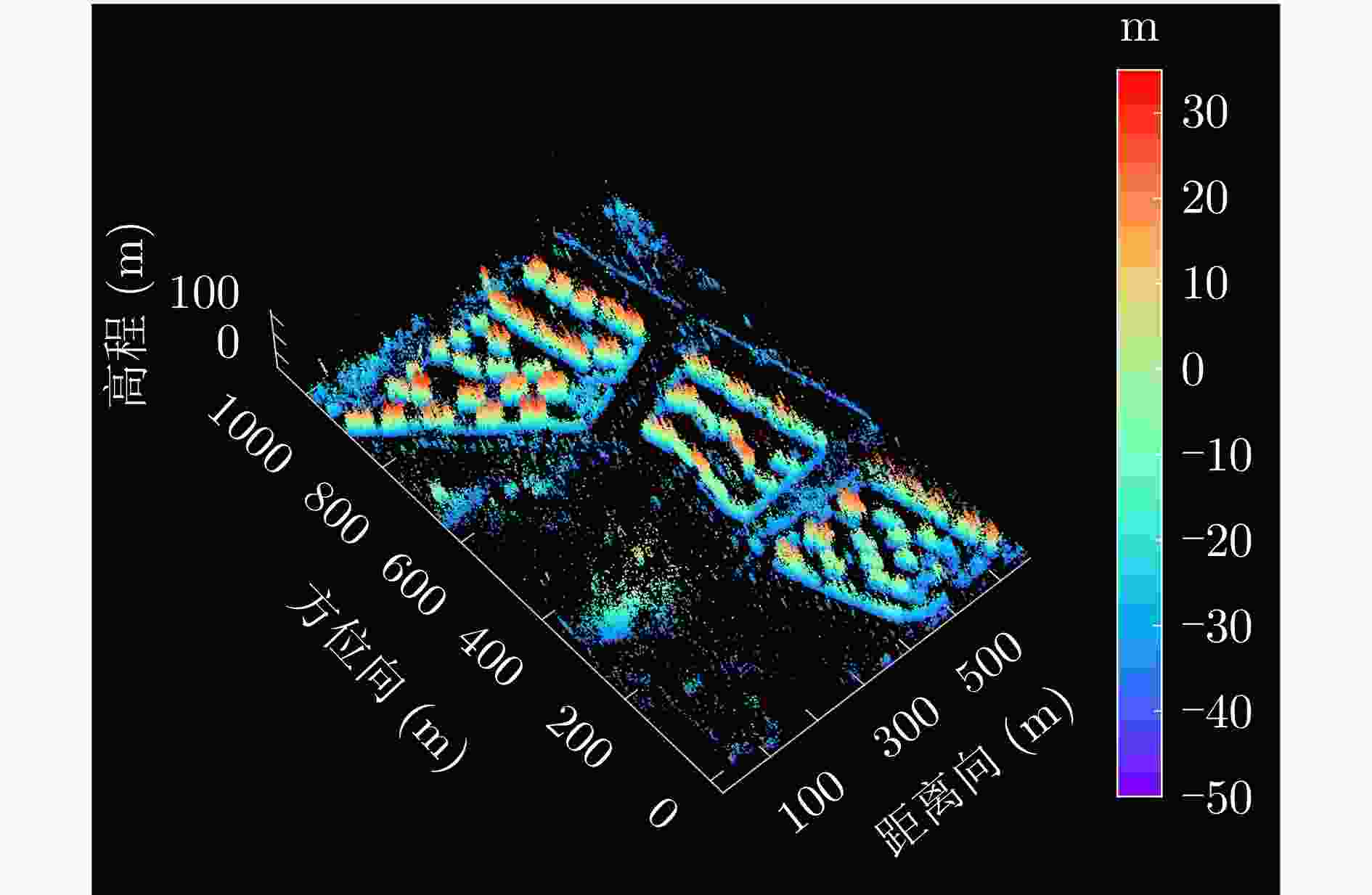
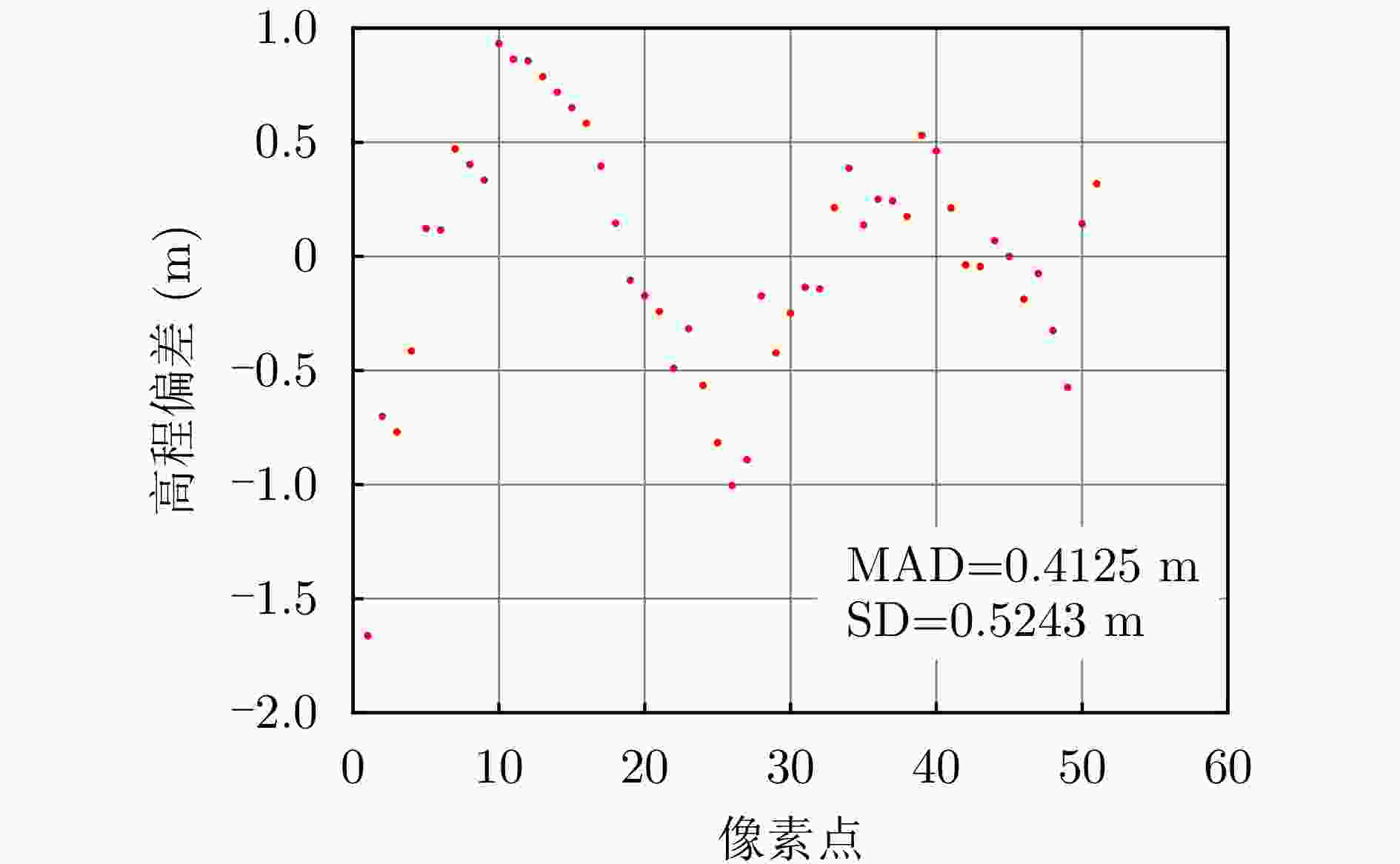
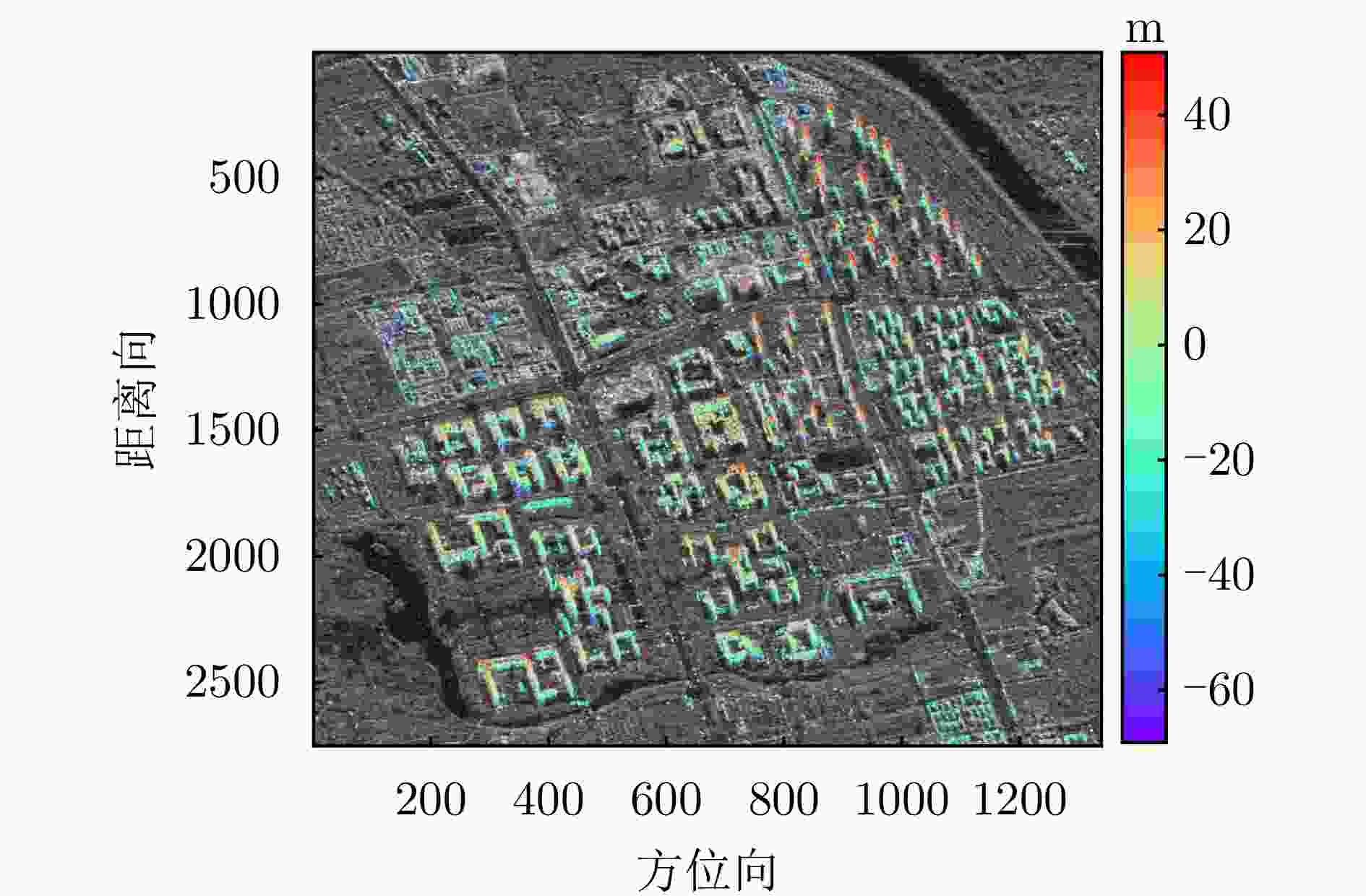
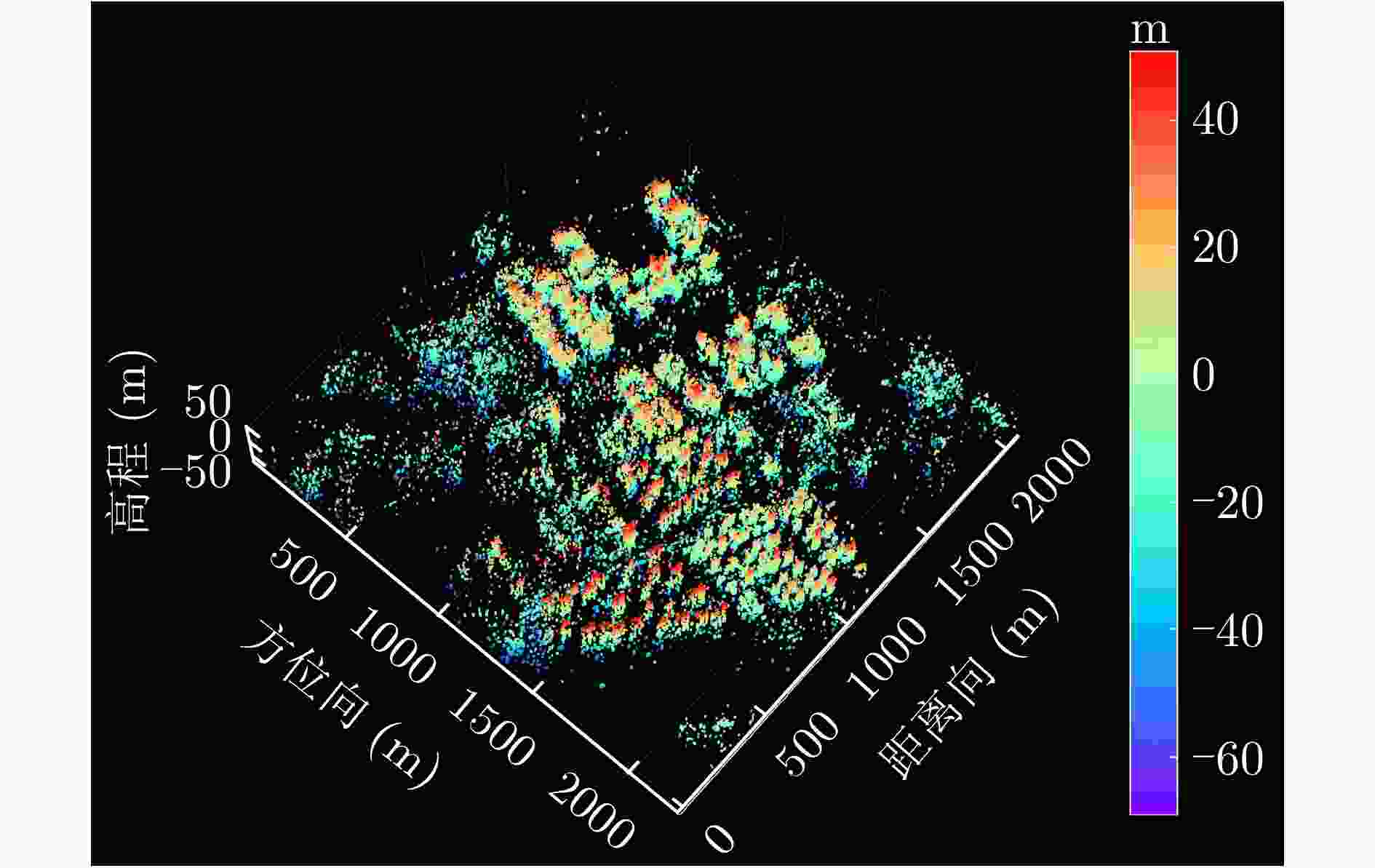
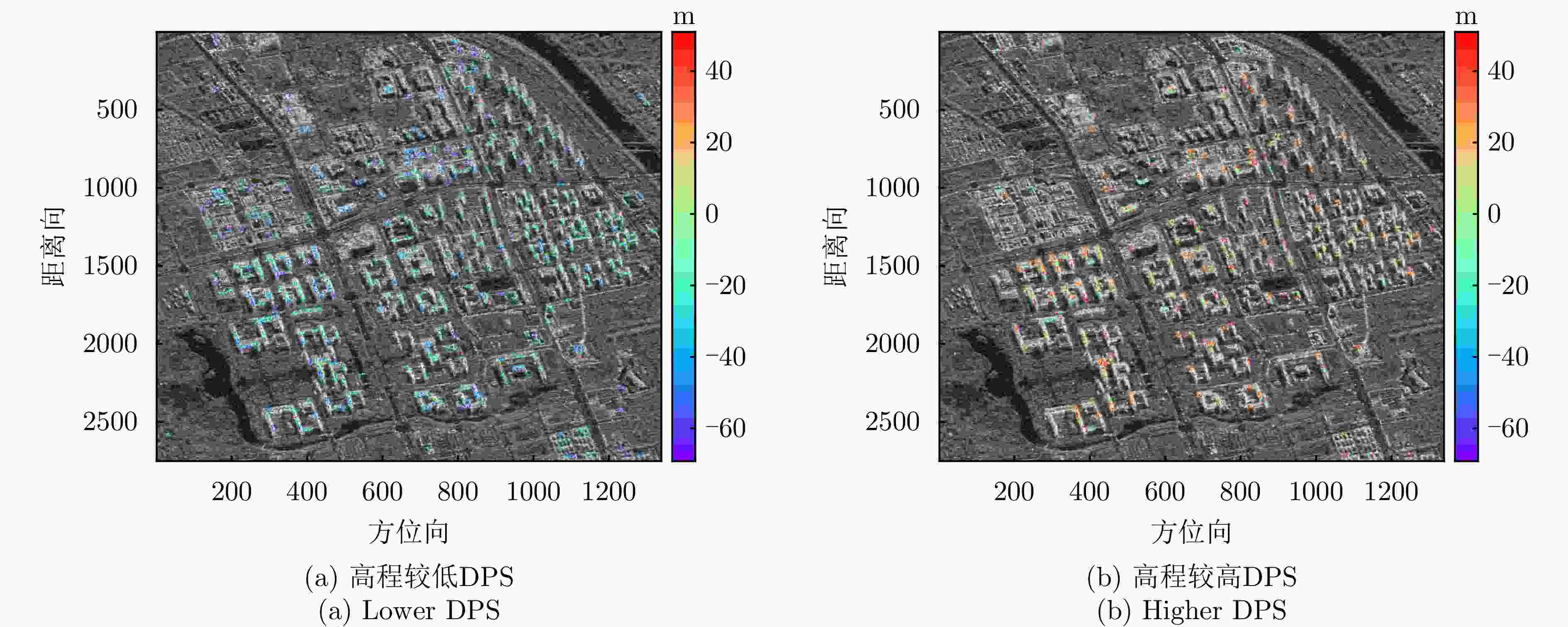
数据集 方法 DPS探测率(%) RMSE (m) 涪城一号 Beamforming 65 31.70 Capon 50 40.71 MUSIC 50 40.71 SL1MMER 76 26.34 宏图一号 Beamforming 79 12.93 Capon 49 23.07 MUSIC 49 23.07 SL1MMER 87 7.98 表 4 层析反演时长统计
Table 4. Time statistics for tomographic inversion
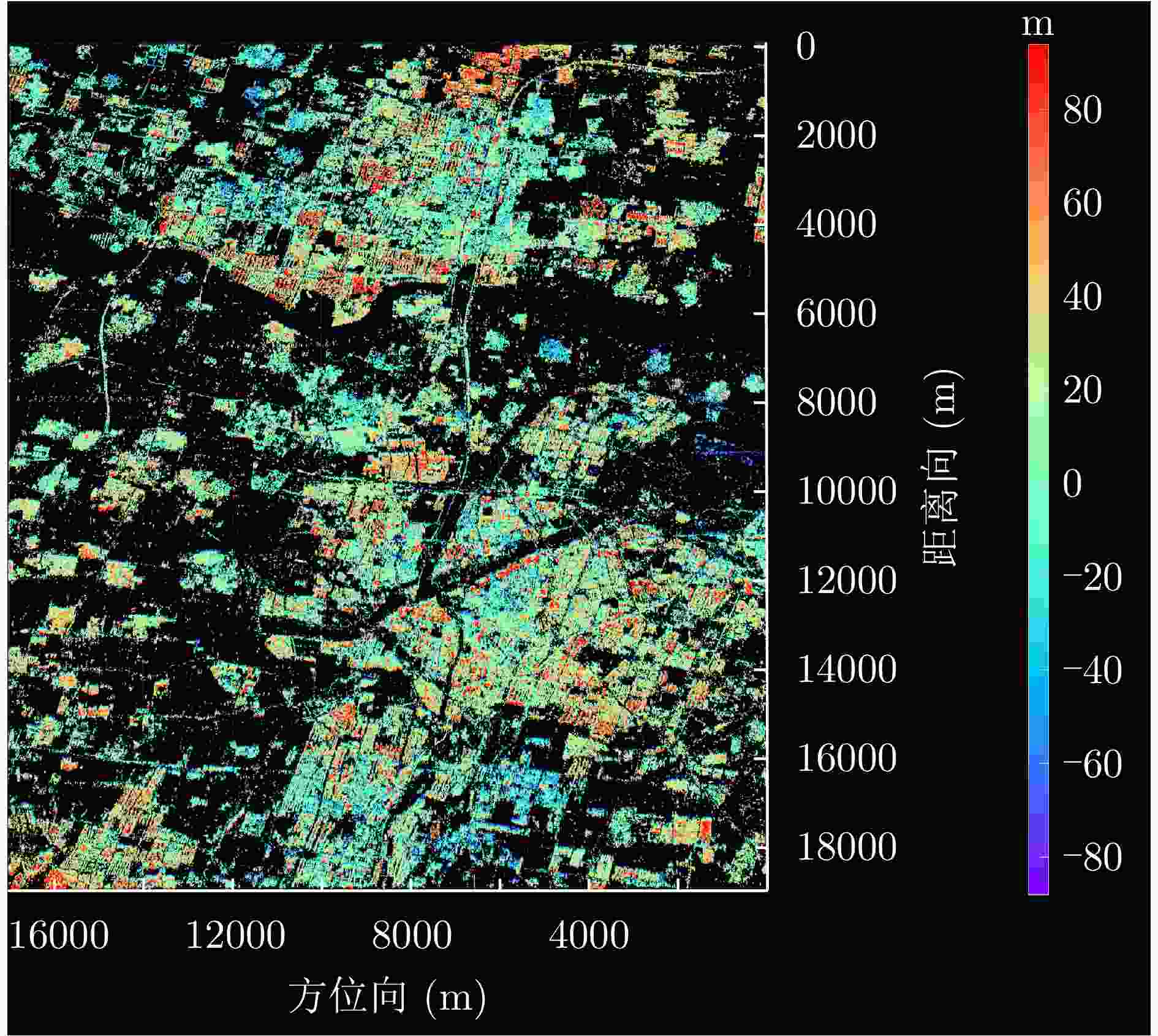
数据集 参考网 星型网 PSC数量 时长 PSC数量 时长 涪城一号 580111 8.56 h 13098408 18.32 h 宏图一号 465144 5.80 h 15429353 21.94 h -
[1] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, PAUCIULLO A, et al. Tomographic processing of interferometric SAR data: Developments, applications, and future research perspectives[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 41–50. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312073. [2] ZHU Xiaoxiang, WANG Yuanyuan, MONTAZERI S, et al. A review of ten-year advances of multi-baseline SAR interferometry using TerraSAR-X data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1374. doi: 10.3390/rs10091374. [3] 郭华东, 吴文瑾, 张珂, 等. 新型SAR对地环境观测[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(6): 862–872. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220098.GUO Huadong, WU Wenjin, ZHANG Ke, et al. New generation SAR for earth environment observation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(6): 862–872. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220098. [4] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661. [5] BUDILLON A, CROSETTO M, JOHNSY A C, et al. Comparison of persistent scatterer interferometry and SAR tomography using sentinel-1 in urban environment[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(12): 1986. doi: 10.3390/rs10121986. [6] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873. [7] CHAN Chi and FARHAT N. Frequency swept tomographic imaging of three-dimensional perfectly conducting objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1981, 29(2): 312–319. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1981.1142571. [8] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098. [9] 李芳芳, 刘宁, 李新武, 等. 层析SAR技术研究进展[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(5): 610–624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.05.019.LI Fangfang, LIU Ning, LI Xinwu, et al. Research progress on tomographic SAR techniques[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(5): 610–624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.05.019. [10] LIANG Lei, GUO Huadong, and LI Xinwu. Three-dimensional structural parameter inversion of buildings by distributed compressive sensing-based polarimetric SAR tomography using a small number of baselines[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(10): 4218–4230. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2351803. [11] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031.LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031. [12] MA Peifeng, LIN Hui, LAN Hengxing, et al. Multi-dimensional SAR tomography for monitoring the deformation of newly built concrete buildings[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 106: 118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.04.012. [13] WANG Xiantao, DONG Zhen, WANG Youjun, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of partially coherent scatterers using iterative sub-network generation method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(19): 3707. doi: 10.3390/rs16193707. [14] 李新武, 郭华东, 彭星, 等. SAR对地观测技术及应用新进展[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 12(2): 170–180. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.004.LI Xinwu, GUO Huadong, PENG Xing, et al. New advances of SAR and its application in earth observation[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 12(2): 170–180. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.004. [15] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567. [16] LOMBARDINI F and REIGBER A. Adaptive spectral estimation for multibaseline SAR tomography with airborne L-band data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 2014–2016. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1294324. [17] GINI F and LOMBARDINI F. Multibaseline cross-track SAR interferometry: A signal processing perspective[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2005, 20(8): 71–93. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2005.1499278. [18] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization—The compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117. [19] DE MAIO A, FORNARO G, and PAUCIULLO A. Detection of single scatterers in multidimensional SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2284–2297. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2011632. [20] PAUCIULLO A, REALE D, DE MAIO A, et al. Detection of double scatterers in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(9): 3567–3586. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2183002. [21] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487. [22] LOMBARDINI F and GINI F. Model order selection in multi-baseline interferometric radar systems[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2005, 2005(20): 108784. doi: 10.1155/ASP.2005.3206. [23] HUANG Yang, ZHU Xiaoxiang, WANG Xiantao, et al. Reference network construction for persistent scatterer detection in SAR tomography: Ant Colony Search Algorithm (ACSA)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 4496–4506. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3176498. [24] ZHU Xiaoxiang, ADAM N, BRCIC R, et al. Space-borne high resolution SAR tomography: Experiments in urban environment using TS-X data[C]. IEEE Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 2009: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/URS.2009.5137534. [25] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183. [26] MA Peifeng and LIN Hui. Robust detection of single and double persistent scatterers in urban built environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 2124–2139. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2496193. [27] WANG Youjun, DONG Zhen, WANG Xiantao, et al. An improved bridge reference network for 3-D SAR tomography based on regional growing strategy[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2024, 17(1): 2398072. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2024.2398072. [28] WANG Xiantao, DONG Zhen, WANG Youjun, et al. Optimizing the reference network by minimum spanning tree approach in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 1–16. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3472670. [29] SHI Yilei, BAMLER R, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. SAR tomography at the limit: Building height reconstruction using only 3-5 TanDEM-X bistatic interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(11): 8026–8037. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2986052. [30] PENG Xing, WANG Changcheng, LI Xinwu, et al. Three-dimensional structure inversion of buildings with nonparametric iterative adaptive approach using SAR tomography[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1004. doi: 10.3390/rs10071004. [31] FENG Lang. Elevation and deformation extraction from TomoSAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University College London, 2020. [32] LU Hongliang, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Heng, et al. SAR tomographic imaging demonstration using GF-3 data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 3645–3648. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8899832. [33] 毕辉, 金双, 王潇, 等. 基于高分三号SAR数据的城市建筑高分辨率高维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113.BI Hui, JIN Shuang, WANG Xiao, et al. High-resolution high-dimensional imaging of urban building based on GaoFen-3 SAR data[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113. [34] 毕辉, 金双, 任维佳, 等. 涪城一号SAR三维成像数据集1.0[J/OL]. 雷达学报, 2024. https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging.BI Hui, JIN Shuang, REN Weijia, et al. Fucheng-1 SAR 3D Imaging Dataset 1.0[J/OL]. Journal of Radars, 2024. https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging_en&pageType=en. [35] 李震, 张平, 乔海伟, 等. 层析SAR地表参数信息提取研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095.LI Zhen, ZHANG Ping, QIAO Haiwei, et al. Advances in information extraction of surface parameters using tomographic SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095. [36] 孙希龙, 余安喜, 杜海东, 等. 基于模拟干涉相位去斜的SAR层析处理方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2011, 33(3): 105–110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2011.03.021.SUN Xilong, YU Anxi, DU Haidong, et al. SAR tomography based on simulated interferometric phase[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2011, 33(3): 105–110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2011.03.021. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: