Moving Target Detection Method Based on Intelligent Multiclassification and Transfer Learning for Missile-borne Radars with Sum-difference Beams
-
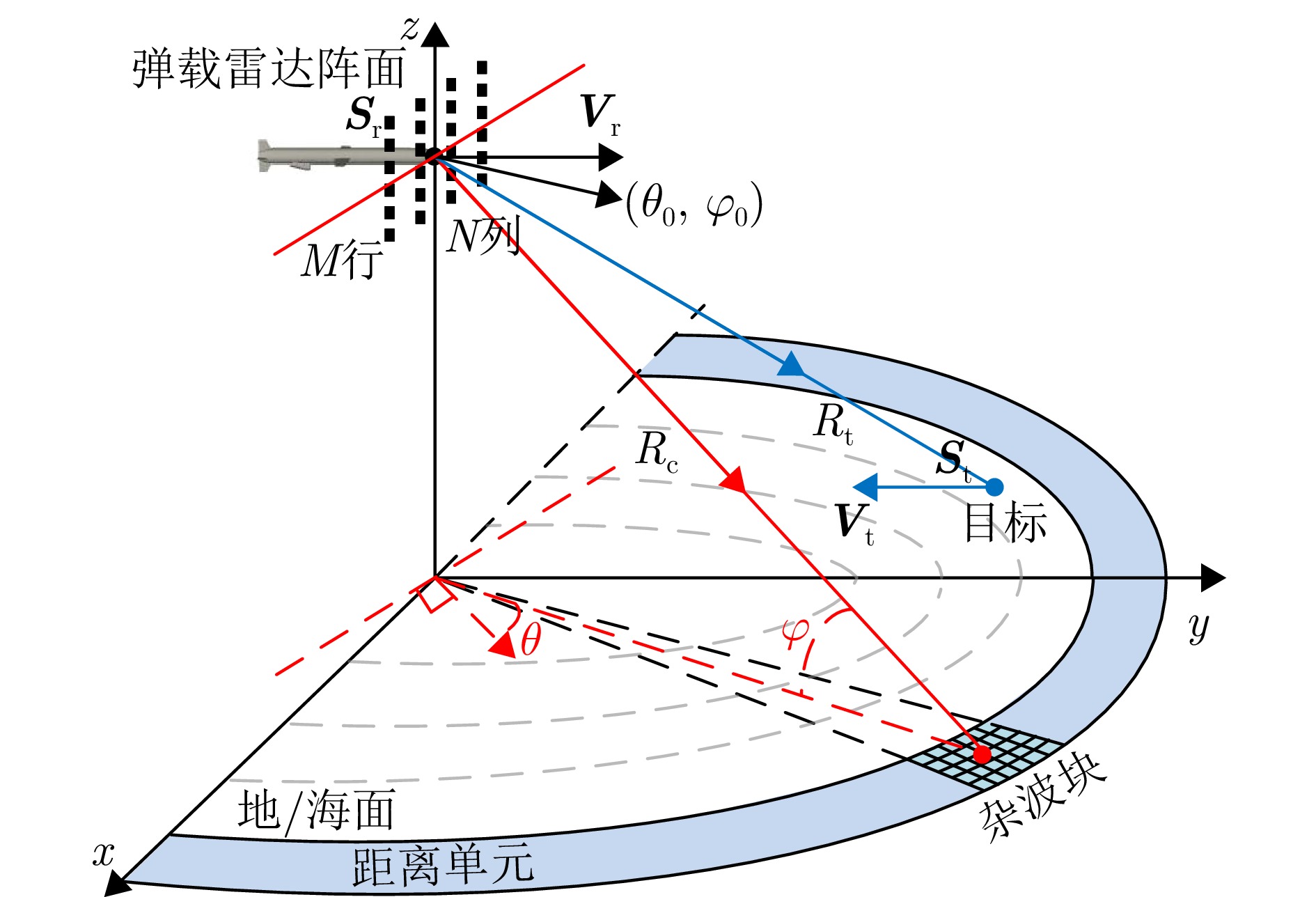
摘要: 针对现有和差波束弹载雷达运动目标检测方法所需训练距离单元数量较大、实际检测性能较低的问题,该文提出了一种基于智能多分类和网络参数迁移学习的运动目标检测新方法,其基本思路为利用少量训练距离单元数据构建数据集对深度卷积神经网络进行训练,将待测距离单元数据分类为杂波类(即无目标类)和对应不同多普勒频率的目标类。考虑到利用实测数据进行在线训练所需的计算资源较多、时间较长,该文首先构建了和差波束弹载雷达运动目标检测的回波信号模型,并基于实测数据进行验证,用于产生仿真数据进行网络离线训练。针对现有典型卷积神经网络参数较多、复杂度较高、训练效率较低等问题,该文基于特征融合模块(FFM)和空间注意力模块(SAM)对DenseNet网络进行改进,构建了FFM-SAM-DenseNet智能多分类器。由于基于智能多分类的检测方法在对不同待测距离单元数据进行处理时需重新训练网络,其整体收敛时间较长、速度较低。为解决该问题,该文引入迁移学习策略,将不同待测距离单元所对应多分类器的网络参数进行共享,以加快所提方法的整体收敛速度。仿真和实测数据处理结果表明,该文所提方法可以基于少量训练距离单元数据,获得相比现有方法更优的运动目标检测性能。Abstract: Existing moving-target detection methods for missile-borne sum-difference beam radars require large amounts of training range cell data, yet still exhibit low detection performance. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a new detection method based on intelligent multiclassification and network parameter transfer learning. The proposed method uses a small set of training range cell data to construct a dataset for training a deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which classifies data from the Range Cell Under Test (RCUT) into clutter (target-free) or target classes with different Doppler frequencies. To avoid the high computational cost and time associated with online training on measured data, an echo signal model is first established for moving target detection in the missile-borne sum-difference beam radar. This model is validated using measured data and subsequently used to generate simulated data for offline network training. In addition, to overcome common limitations of typical CNNs, such as large parameter sets, high computing complexity, and low training efficiency, this paper enhances the DenseNet architecture by incorporating a Feature Fusion Module (FFM) and a Spatial Attention Module (SAM), resulting in an improved FFM-SAM-DenseNet multiclassifier. Furthermore, conventional detection methods based on intelligent multiclassification require retraining the network when processing data from different RCUTs, leading to long convergence time and reduced efficiency. To solve this problem, transfer learning is introduced to share network parameters across multiclassifiers for different RCUTs, accelerating the overall convergence speed. Simulation and measured data show that, even with limited training range cell data, the proposed method achieves better moving target detection performance than existing typical methods.
-
表 1 训练数据集仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters for generating training dataset
参数 数值 P 64 Q 8 $ \hat L $ 8 H 101 $ [\alpha _0^ - ,\alpha _0^ + ] $ [0, 5] dB $ [{\alpha ^ - },{\alpha ^ + }] $ [10, 50] dB 表 2 智能多分类器网络参数
Table 2. Network parameters of intelligent multiclassifier
网络层 所含模块 模块构成 滤波器大小/步长 输出数据大小 参数量 输入层 – – – (64,3,2) – 初始
化层特征融合模块 Conv_x1 1/1 (64,3,32) 96 Conv_x2 3/1 (64,3,32) 608 Cat_1 – (64,3,64) – BN – – 128 ReLU – – – Conv_FFM 1/1 (64,3,64) 4160 特征提取层 密集连接块 Conv_2 3/1 (64,3,8) 4616 Cat_2 – (64,3,72) – Conv_3 3/1 (64,3,8) 5192 Cat_3 – (64,3,80) – Conv_4 3/1 (64,3,8) 5768 Cat_4 – (64,3,88) – 连接层 Conv_5 1/1 (64,3,44) 3916 AvgPool2d_1 (2,1)/(2,1) (32,3,44) – 密集连接块 Conv_6 3/1 (32,3,8) 3176 Cat_5 – (32,3,52) – Conv_7 3/1 (32,3,8) 3752 Cat_6 – (32,3,60) – Conv_8 3/1 (32,3,8) 4328 Cat_7 – (32,3,68) – 连接层 Conv_9 1/1 (32,3,34) 2346 AvgPool2d_1 (2,1)/(2,1) (16,3,34) – 密集连接块 Conv_10 3/1 (16,3,8) 2456 Cat_8 – (16,3,42) – Conv_11 3/1 (16,3,8) 3032 Cat_9 – (16,3,50) – Conv_12 3/1 (16,3,8) 3608 Cat_10 – (16,3,58) – 空间注意力模块 Conv_SAM 3/1 – 18 sigmoid – – – 输出层 全局平均池化层 GlobalAvgPool – 58 – 全连接层 Linear – 128 7552 ReLU – – – Linear – 65 8385 最终分类层 softmax – – – 表 3 实测数据测量场景参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters for real-measured data scenario
参数 数值 参数 数值 载机速度Vr [0, 120, 0] m/s 带宽B 20 MHz 目标速度Vt [0, –120, 0] m/s 脉冲宽度Tp 1 μs 载机高度Hr 1200 m脉冲重复周期Tr 50 μs 目标高度Ht 100 m 相干脉冲数K 64 中心频率fc 15 GHz 阵元间距dr 0.01 m 天线阵元个数 32×32 - - 表 4 不同分类器的测试性能对比(%)
Table 4. Performance comparison of different classifiers (%)
分类器 准确率 精度 召回率 F1分数 AlexNet[16] 79.63 72.78 73.99 73.38 VGGNet16[22] 84.72 81.22 81.83 81.53 ResNet50[23] 88.85 86.41 87.32 86.86 DenseNet[17] 90.80 90.61 89.94 90.28 MDSCAN[18] 91.60 90.56 90.80 90.68 FFM-DenseNet 92.78 90.96 92.12 91.54 SAM-DenseNet 95.94 96.18 95.78 95.98 FFM-SAM-DenseNet 96.78 96.85 96.68 96.77 -
[1] HUANG Penghui, YANG Hao, ZOU Zihao, et al. Multichannel clutter modeling, analysis, and suppression for missile-borne radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3236–3260. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3147136. [2] 许京伟, 廖桂生, 朱圣棋, 等. 前视阵高速雷达空时处理方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(3): 509–515. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00992.XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Research on STAP approach of forward looking array radar with high-velocity[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 509–515. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00992. [3] MELVIN W L. A STAP overview[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 19–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263229. [4] REED I S, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893. [5] SHI Jieming, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. Pulse interval optimization for Doppler ambiguity clutter suppression in missile-borne STAP radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3506205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3371438. [6] 何松华, 胡霞, 张军. 弹载宽带相控阵雷达高度目标检测的通道级STAP方法[J]. 信号处理, 2016, 32(5): 528–535. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2016.05.004.HE Songhua, HU Xia, and ZHANG Jun. Channel-level STAP method for lofty target detection of missile-borne wideband phased-array radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2016, 32(5): 528–535. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2016.05.004. [7] XIONG Yuanyi, XIE Wenchong, WANG Yongliang, et al. Short-range nonstationary clutter suppression for airborne KA-STAP radar in complex terrain environment[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 2766–2776. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3522257. [8] LI Jun’ao, LI Zhongyu, YANG Qing, et al. Efficient matrix sparse recovery STAP method based on Kronecker transform for BiSAR sea clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5103218. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3362844. [9] WANG Xiangrong, ABOUTANIOS E, and AMIN M G. Reduced-rank STAP for slow-moving target detection by antenna-pulse selection[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(8): 1156–1160. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2390148. [10] WANG Haihong, DUAN Keqing, SHEN Wei, et al. Reduced-dimensional STAP method for nonstationary clutter suppression in endfire array airborne radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(17): 27750–27762. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3429173. [11] 许京伟, 廖桂生, 朱圣棋, 等. 弹载俯冲非正侧阵雷达杂波特性与抑制方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(8): 1631–1637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.08.08.XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Clutter characteristic and suppression approach for missile-borne diving non-broadside array radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(8): 1631–1637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.08.08. [12] 李浩冬, 廖桂生, 许京伟. 弹载雷达和差通道稳健自适应杂波抑制方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.02.08.LI Haodong, LIAO Guisheng, and XU Jingwei. Robust adaptive clutter suppression approach for missile-borne radar with $\Sigma\Delta $-beam[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.02.08. [13] EL KHATIB A, ASSALEH K, and MIR H. Learning-based space-time adaptive processing[C]. The 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2013: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICCSPA.2013.6487279. [14] EL KHATIB A, ASSALEH K, and MIR H. Space-time adaptive processing using pattern classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(3): 766–779. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2385653. [15] 刘喆, 许晓晴. 基于支持向量机的动目标显示方法研究[C]. 第十四届全国雷达学术年会, 成都, 2017: 1–6.LIU Zhe and XU Xiaoqing. Research on moving target indication method based on support vector machine[C]. The 14th National Radar Conference, Chengdu, China, 2017: 1–6. [16] LIU Zhe, HO D K C, XU Xiaoqing, et al. Moving target indication using deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 65651–65660. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877018. [17] 李贵锋, 童宁宁, 冯为可, 等. 基于DenseNet的机载雷达动目标检测[J]. 空军工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 22(2): 83–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2021.02.013.LI Guifeng, TONG Ningning, FENG Weike, et al. Airborne radar moving target detection based on DenseNet[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 22(2): 83–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2021.02.013. [18] HOU Yunfei, ZHANG Yingnan, GUI Wenzhu, et al. CNN-based moving target detection for airborne radar with controllable false alarm module[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3508405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3438948. [19] 陶海红, 郭晓双, 孙晨伟, 等. 相控阵雷达降维四通道和差波束测角[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(1): 75–80. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.01.013.TAO Haihong, GUO Xiaoshuang, SUN Chenwei, et al. Dimensionality reduction of phased array and 4-channel monopulse angle measurement of sum and difference beams[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(1): 75–80. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.01.013. [20] 佘胜团. 毫米波单脉冲天线阵和低副瓣天线阵的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2006: 30–34.SHE Shengtuan. Study of millimetre-wave monopulse antenna arrays and low paraflap antenna arrays[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2006: 30–34. [21] BROWN R D, SCHNEIBLE R A, WICKS M C, et al. STAP for clutter suppression with sum and difference beams[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(2): 634–646. doi: 10.1109/7.845254. [22] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. [23] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. [24] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 40–49. [25] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [26] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. [27] ZHU Xizhou, CHENG Dazhi, ZHANG Zheng, et al. An empirical study of spatial attention mechanisms in deep networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6687–6696. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00679. [28] SHAO Ling, ZHU Fan, and LI Xuelong. Transfer learning for visual categorization: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(5): 1019–1034. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2330900. [29] 陈一凡, 刘剑刚, 贾勇, 等. 基于仿真样本迁移学习的穿墙雷达高分辨成像方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049.CHEN Yifan, LIU Jiangang, JIA Yong, et al. High-resolution imaging method for through-the-wall radar based on transfer learning with simulation samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049. [30] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.123. [31] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: