Adaptive PHD-BOF: A Slow-moving Targets Tracking Method with Air Surveillance Radar
-
摘要: 以旋翼无人机为代表的低空目标可采用慢速巡航模式,使自身回波落于雷达多普勒盲区内,以躲避雷达检测跟踪。此外,低空环境中存在的复杂地固杂波,更进一步加剧了雷达对慢速目标的检测跟踪任务难度。为解决上述问题,该文基于随机有限集框架,提出一种基于低空监视雷达的慢速目标跟踪方法。首先基于贝叶斯占用滤波思想,将雷达监视区域分割为沿角度-距离向的均匀网格,并依据慢速目标与地固杂波的动力学特性差异设计自适应滤波参数模块;之后,基于概率假设密度滤波器对多普勒盲区内的网格数据进行统一的滤波处理;最后,利用聚类方法从滤波结果中提取感兴趣目标的信息,实现对慢速目标的检测跟踪。在包含多个慢速目标、环境噪声、面杂波及地固点杂波的典型低空监视场景下,结合实测背景杂波数据的实验证明了所提算法对多个低空慢速目标跟踪的有效性、稳健性及性能优势。Abstract: Low-altitude targets, represented by rotor unmanned aerial vehicles, can typically adopt a slow-cruise mode. As a result, their echoes fall within the Doppler Blind Zone (DBZ) and evade radar detection and tracking. The cluttered low-altitude environment adds to further complexity. To address this issue, this study proposes a method grounded in the framework of random finite set and designed for tracking slow-moving targets with a low-altitude surveillance radar. Inspired by the Bayesian occupancy filter, the proposed method initially models the radar Field of View (FoV) as a grid map. It is uniformly partitioned along the angle-range axis, ensuring that each cell captures a specific segment of the FoV. Then, adaptive filtering parameter modules are meticulously designed by leveraging the distinct dynamic characteristics of slow-moving targets and ground clutter. Subsequently, a probability hypothesis density filter is deployed to conduct unified filtering on the grid map situated within the DBZ. The final step involves the use of clustering methods to extract information about the target of interest. Simulation results validate the effectiveness, robustness, and superior performance of the proposed method across typical surveillance scenarios involving multiple slow-moving targets, noise, and clutter.
-
1 算法伪代码
1. Algorithm pseudo-code
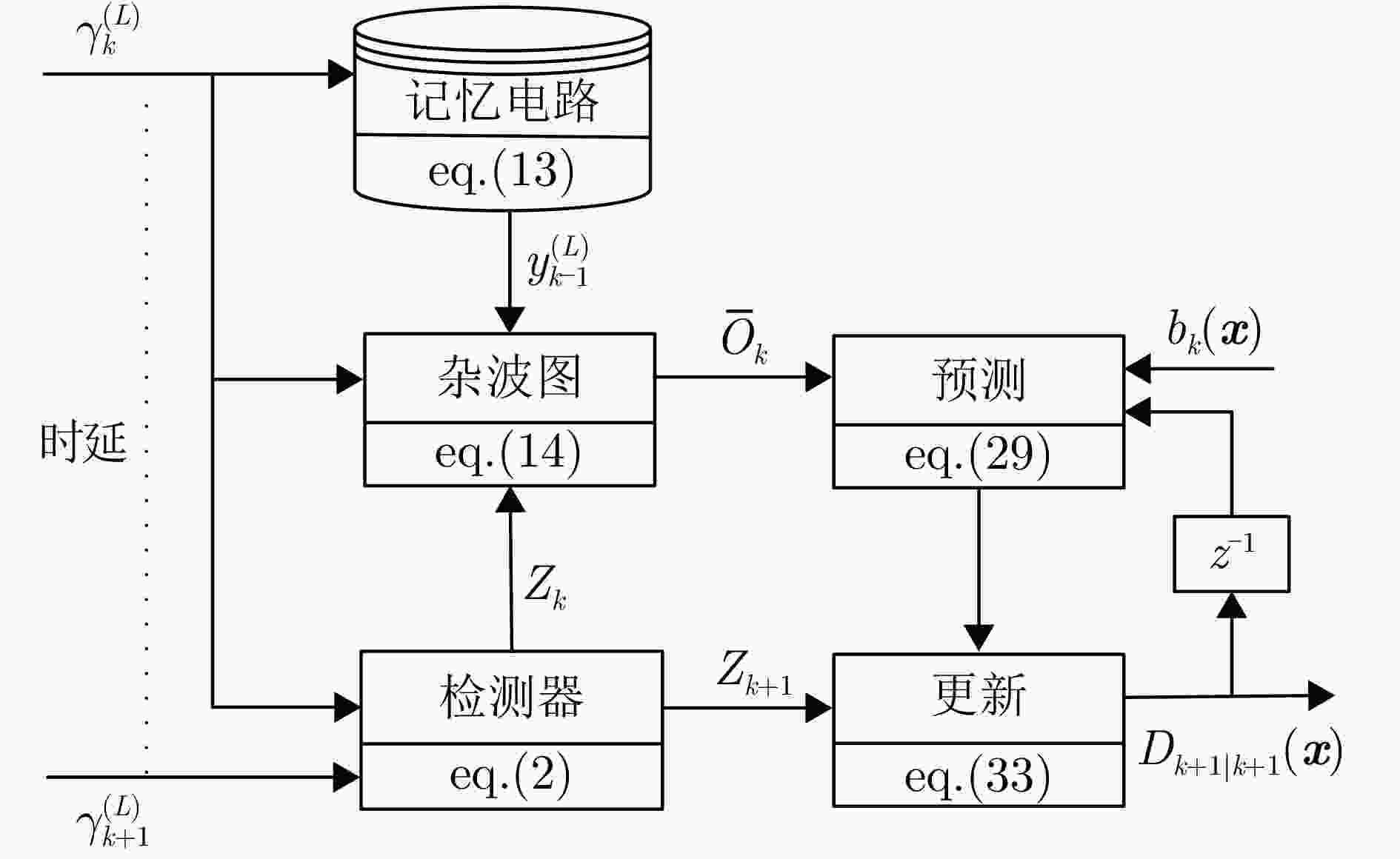
自适应PHD-BOF预测步 输入:$ {\bar O_k},{\hat O_k},\{ \omega _{k|k}^i,{\boldsymbol{x}}_{k|k}^i\} _{i = 1}^{{v_{k|k}}} $ 输出:$ \omega _{k + 1|k}^i,{\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i\} _{i = 1}^{{v_{k + 1|k}}} $ 步骤1. 计算新生粒子 $ {B_k} \leftarrow {Z_k} \cap \hat O_k^\neg $ for $n = 1$ to ${n_k}$ do for $j = 1$ to ${N_b}$ do $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{k|k}^{n,j}{\text{~}}\mathcal{U}( \cdot |{S_{{l_n}}}) \cdot {f_0}({\boldsymbol{v}}) $ end for end for $ {v_{k + 1|k}} \leftarrow {v_{k|k}} + {N_b} \cdot {n_k} $ 步骤2. 计算存活概率 for $l = 1$ to L do if $l \in {\bar O_k}$then $ {p_{\mathrm{S}}}(l) \leftarrow {\dot p_{\mathrm{S}}} $ else $ {p_{\mathrm{S}}}(l) \leftarrow {\tilde p_{\mathrm{S}}} $ end if end for 步骤3. 计算${D_{k + 1|k}}({\boldsymbol{x}})$的权矢量 for $i = 1$ to ${v_{k + 1|k}}$ do if $i \le {v_{k|k}}$ then $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i \sim {f_{k + 1|k}}( \cdot |{\boldsymbol{x}}_{k|k}^i) $ $ \omega _k^i \leftarrow \omega _{k|k}^i $ else $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i \sim {f_{k + 1|k}}( \cdot |{\boldsymbol{x}}_{k|k}^{n,j}) $ $ \omega _k^i \leftarrow u/{N_b} $ end if $ \omega _{k + 1|k}^i \leftarrow {p_{\mathrm{S}}}({l^i}) \cdot \omega _k^i $// $ {l^i} $为$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{k|k}^i $的单元索引 end for 自适应PHD-BOF更新步 输入:$ {Z_{k + 1}},{I_k},\{ \omega _{k + 1|k}^i,{\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i\} _{i = 1}^{{v_{k + 1|k}}} $ 输出:$ \{ \omega _{k + 1|k + 1}^i\} _{i = 1}^{{v_{k + 1|k}}} $ 步骤1. 计算$ {\tau _{k + 1}}({\boldsymbol{z}}) $ for $m = 1$ to ${m_{k + 1}}$ do if $m \in {I_k}$ then $ {p_{\mathrm{D}}}(m) \leftarrow {\stackrel \frown{p} _{\mathrm{D}}} $ else $ {p_{\mathrm{D}}}(m) \leftarrow {\bar p_{\mathrm{D}}} $ end if $\tau _{k + 1}^{{{\boldsymbol{z}}_m}} \leftarrow {p_{\mathrm{D}}}(m) \cdot \omega _{k + 1|k}^{{{\boldsymbol{z}}_m}}$ // $ {{\boldsymbol{z}}_m} $为${Z_{k + 1}}$的第m个单元 end for for $i = 1$ to ${v_{k + 1|k}}$ do if $ h({\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i) \in {S_{{Z_{k + 1}}}} $ then $ {{\boldsymbol{z}}_m} \leftarrow l:h({\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i) \in {S_l} $ $ \tau _{k + 1}^{{{\boldsymbol{z}}_m}} \leftarrow \tau _{k + 1}^{{{\boldsymbol{z}}_m}} + {p_{\mathrm{D}}}({\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i) \cdot \omega _{k + 1|k}^i $ end if end for 步骤2. 计算权矢量${D_{k + 1|k + 1}}({\boldsymbol{x}})$ for $i = 1$ to ${v_{k + 1|k}}$ do 根据式(24)计算$ {L_{{Z_{k + 1}}}}({\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i) $ $ \omega _{k + 1|k + 1}^i \leftarrow \omega _{k + 1|k}^i \cdot {L_{{Z_{k + 1}}}}({\boldsymbol{x}}_{k + 1|k}^i) $ end for 表 1 滤波器参数设置
Table 1. Parameters of the filter
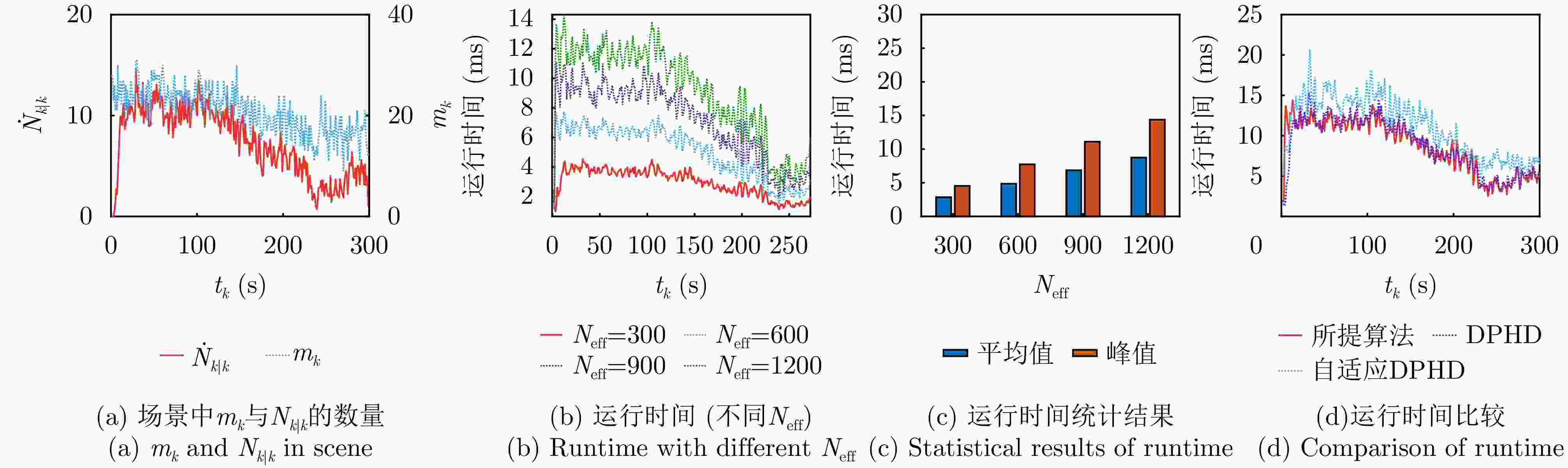
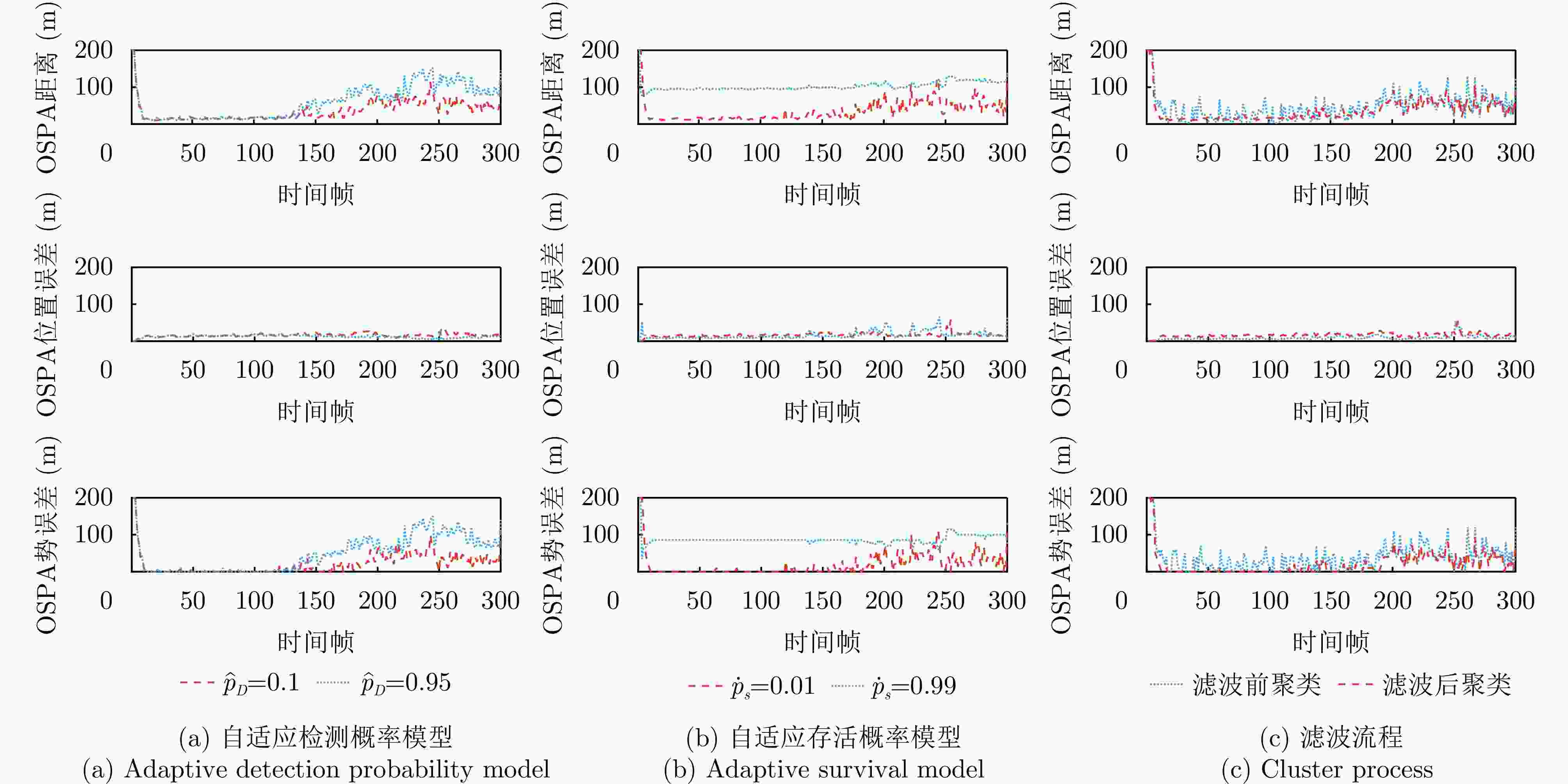
参数 数值 参数 数值 参数 数值 L 10000 ${\dot p_{\mathrm{S}}}$ 0.01 $\alpha $ 2.5 d 2 ${\tilde p_{\mathrm{S}}}$ 0.99 ${k_{\mathrm{T}}}$ 0.05 ${N_b}$ 60 ${\stackrel \frown{p} _{\mathrm{D}}}$ 0.1 $ {\stackrel \frown{\rho } _0} $ 0.01 ${N_{{\text{eff}}}}$ 1200 ${\bar p_{\mathrm{D}}}$ 0.95 $ {\bar \rho _0} $ 0.3 u 0.001 ${\lambda _c}$ 0.1 ${\sigma _{\text{V}}}$ 0.1 表 2 雷达系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of radar system
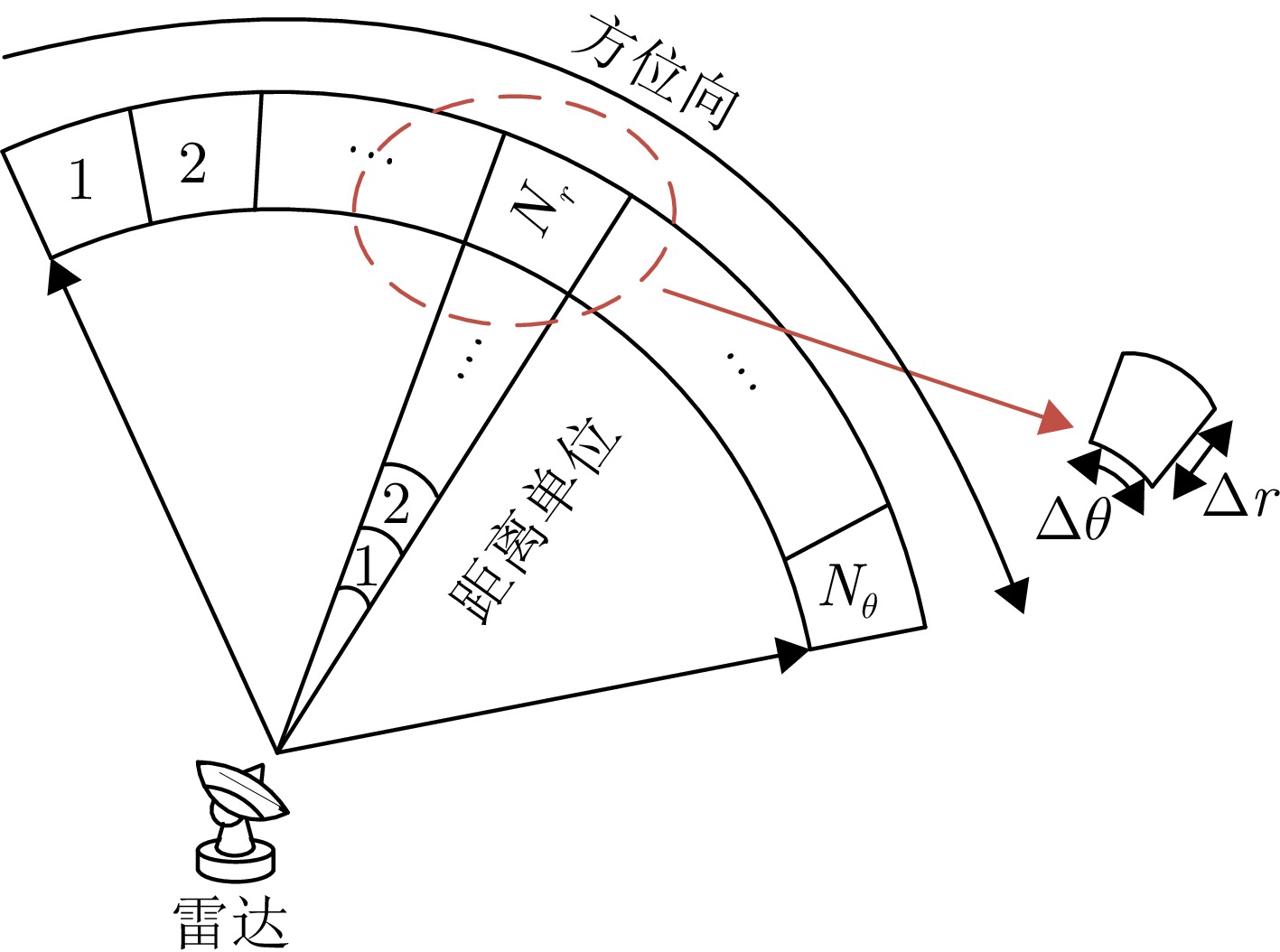
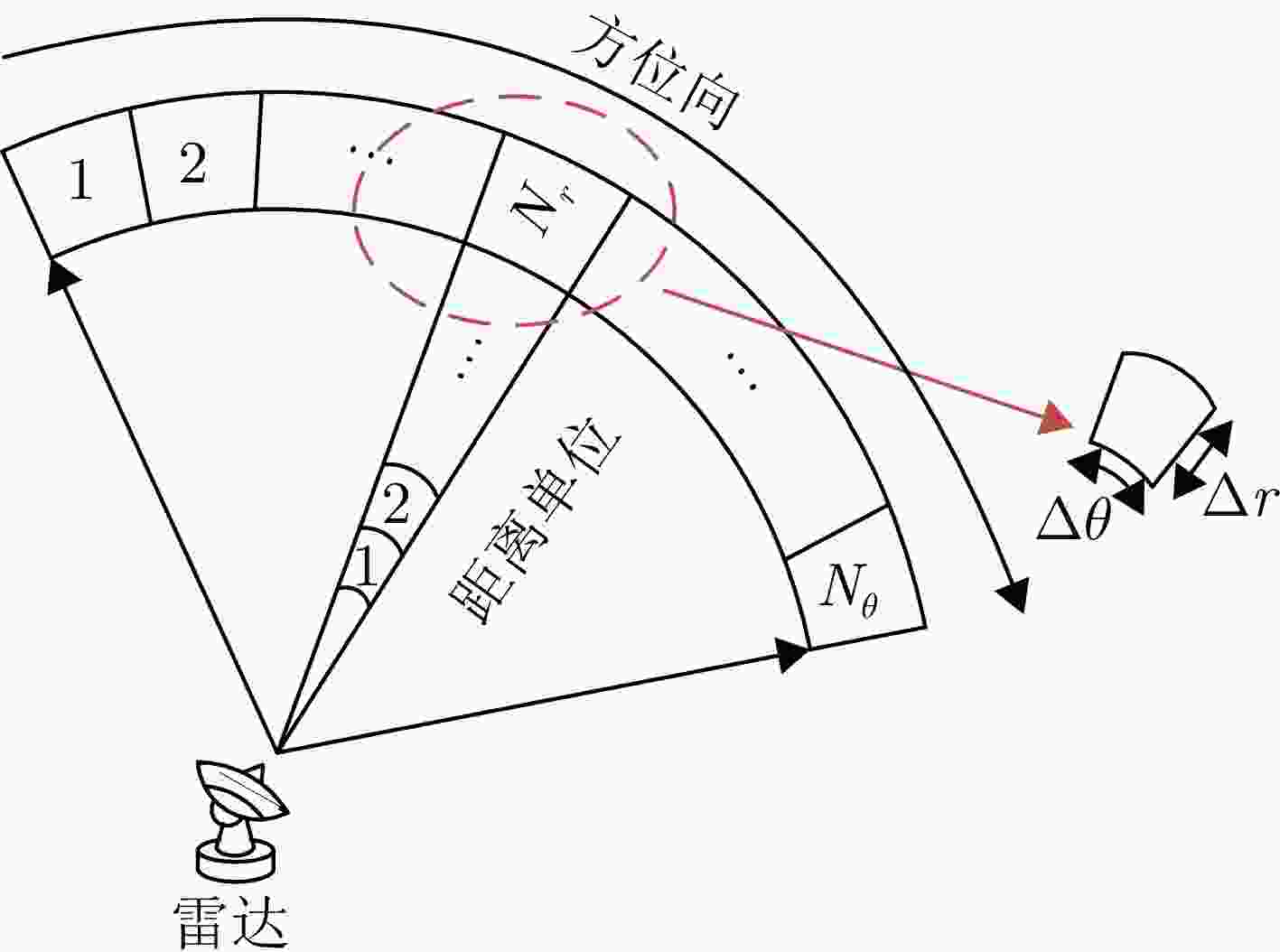
参数 数值 参数 数值 参数 数值 参数 数值 距离范围 $[{R_{\min }},{R_{\max }}]$ $ [300\; {\text{m}},1800 \;{\text{m}}] $ 距离分辨力$\Delta r$ 15 m 脉冲重复周期 20 μs 带宽B 10 MHz 角度范围 $[{\theta _{\min }},{\theta _{\max }}]$ [–60°, 60°] 角度分辨力$ \Delta \theta $ 1.2° 载频${f_0}$ 3 GHz 波长$\lambda $ 0.1 m 速度范围 $ [ - {v_{{m} {\text{dv}}}},{v_{{m} {\text{dv}}}}] $ $ [ - 4.5 \;{\text{m/s}},4.5 \;{\text{m/s}}] $ 信噪比 25 dB 脉冲数 500 CPI 0.01 s 距离单元数${N_r}$ 100 噪声标准差$ \sigma $ 1 采样快拍数 512 扫描时间${T_{\mathrm{s}}}$ 1 s 方位单元数 ${N_\theta }$ 100 脉宽$\tau '$ 2 μs 阵元数${N_{\mathrm{a}}}$ 64 扫描帧数N 300 表 3 对象状态真值
Table 3. Truth of object state
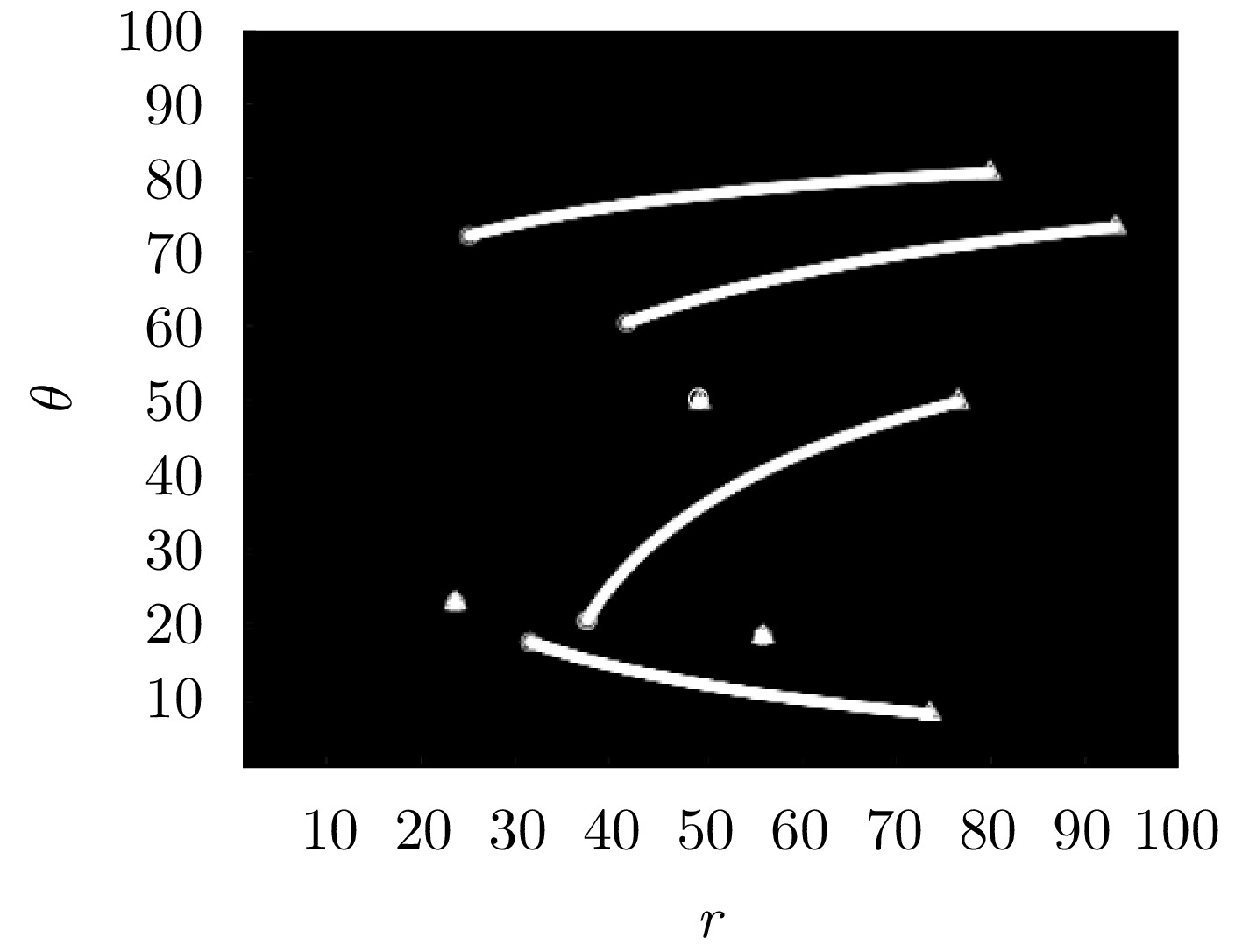
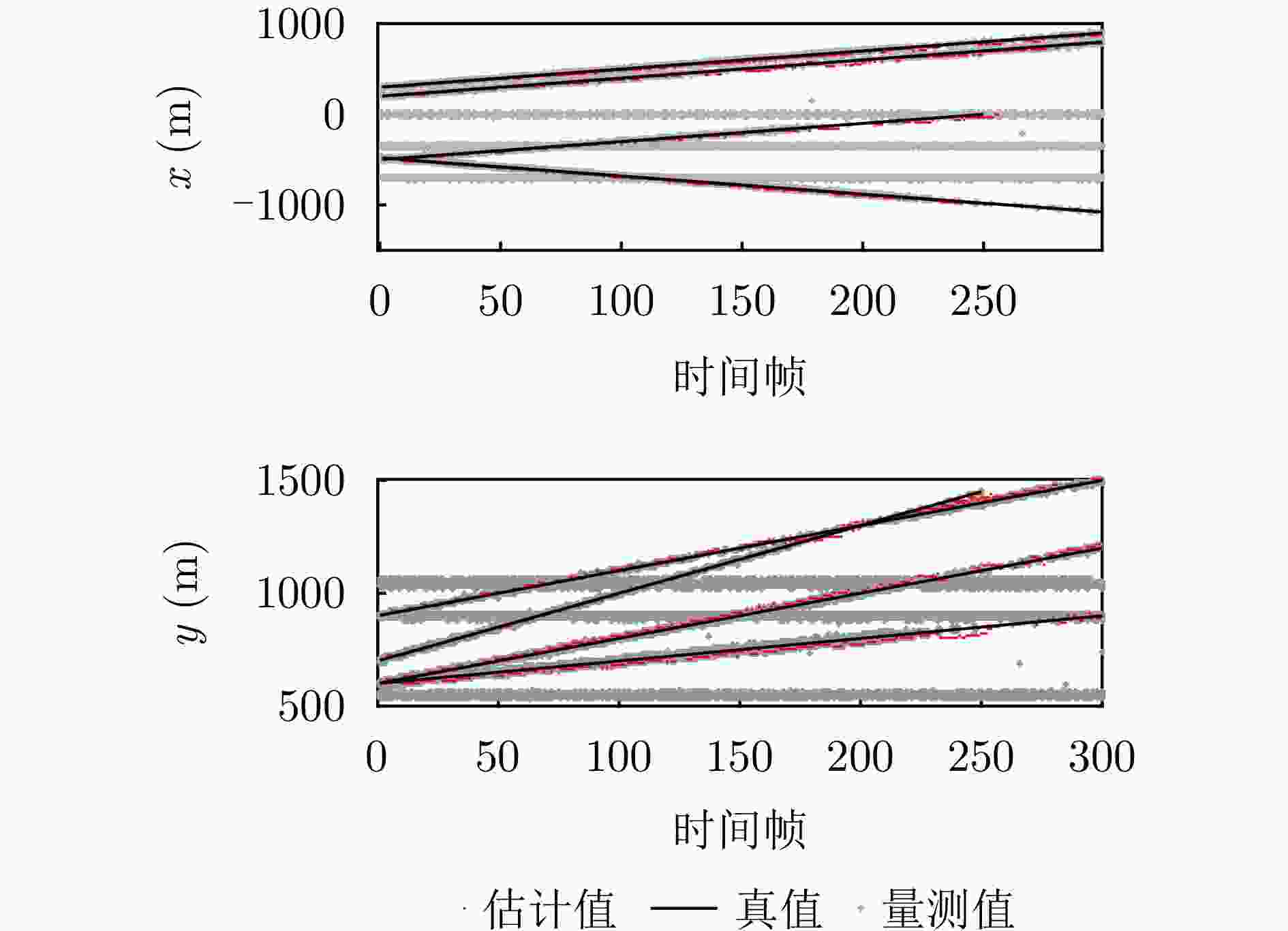
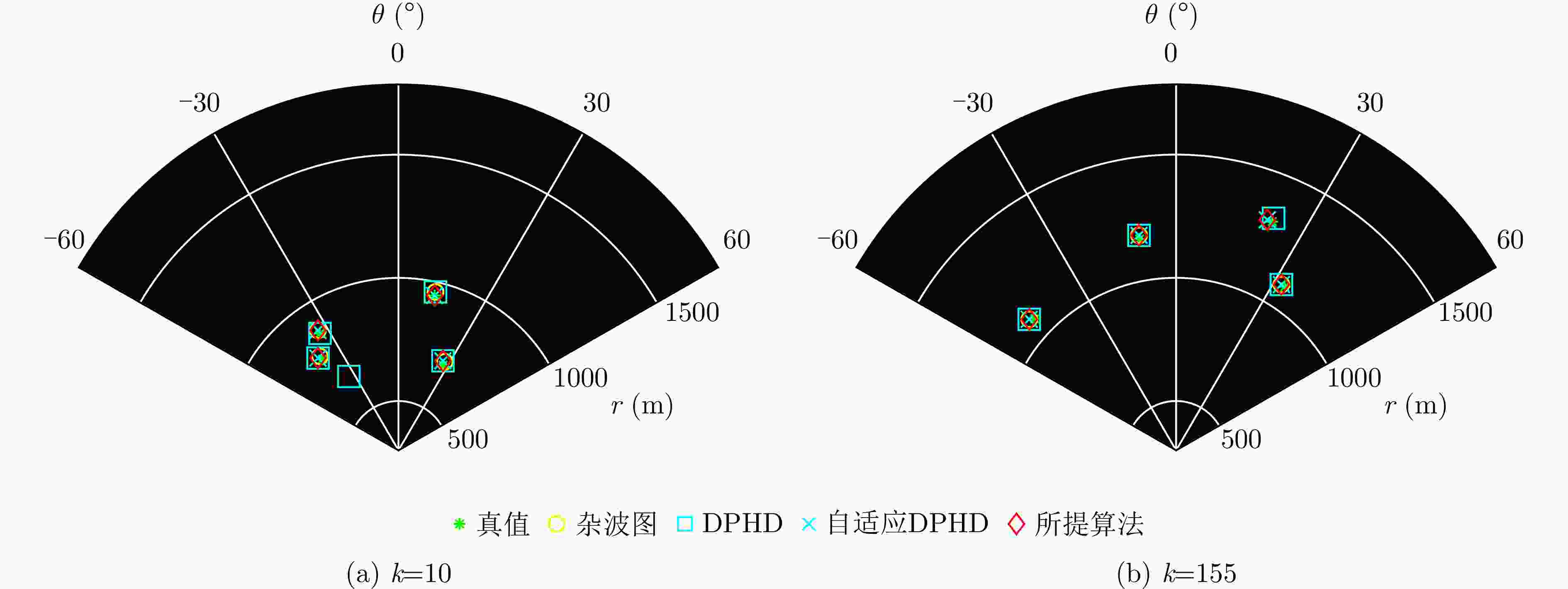
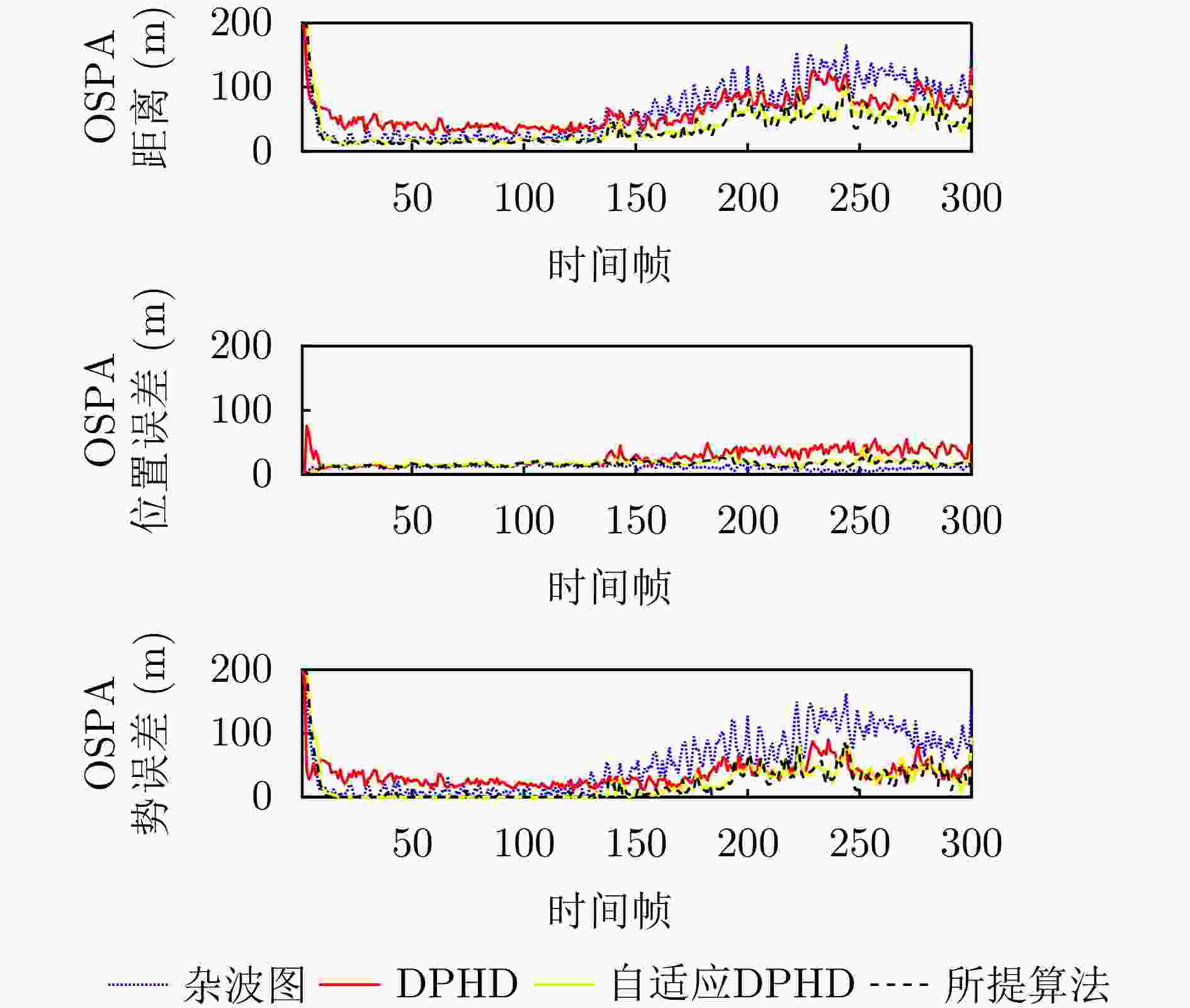
身份 初始状态 新生时刻 死亡时刻 T1 $ [ - 500,700,2,3] $ 1 250 T2 $ [ - 480,600, - 2,1] $ 1 300 T3 $ [300,600,2,2] $ 1 300 T4 $ [200,900,2,2] $ 1 300 C1 $[ - 350,550]$ 1 300 C2 $[ - 700,900]$ 1 300 C3 $ [0,1040] $ 1 300 -
[1] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1. 0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 439–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 439–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. [2] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段多角度FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-2.0)及特征融合分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multi-band multi-angle FMCW radar low-slow-small target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-2.0) and feature fusion classification methods[J]. Journal of Radar, 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004. [3] LUO Jiawei, HUANG Yulin, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Optimal search strategy of low-altitude target for airborne phased array radar using digital elevation model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 8025–8037. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3206793. [4] 鲁其兴, 汤新民, 齐鸣, 等. 一种改进的交互多模型算法在机场运动目标跟踪中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(7): 2225–2236. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241150.LU Qixing, TANG Xinmin, QI Ming, et al. An improved interacting multiple model algorithm and its application in airport moving target tracking[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(7): 2225–2236. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241150. [5] YANG Yong and YANG Boyu. Overview of radar detection methods for low altitude targets in marine environments[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(1): 1–13. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2024.000026. [6] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008: 1-1328. [7] WU Weihua, SUN Hemin, CAI Yichao, et al. MM-GLMB filter-based sensor control for tracking multiple maneuvering targets hidden in the Doppler blind zone[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4555–4567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3009497. [8] HAN Wei, TANG Ziyue, and ZHU Zhenbo. Method of target tracking with Doppler blind zone constraint[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24(6): 889–898. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00103. [9] SONG T L, MUSICKI D, and KIM Y. Tracking through occlusions and track segmentation reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 623–631. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404126. [10] YEOM S W, KIRUBARAJAN T, and BAR-SHALOM Y. Track segment association, fine-step IMM and initialization with Doppler for improved track performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(1): 293–309. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1292161. [11] 徐开明, 王佰录, 李溯琪, 等. 低空监视雷达“走-停-走”目标跟踪技术[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 443–458. doi: 10.12000/JR21211.XU Kaiming, WANG Bailu, LI Suqi, et al. Move-stop-move target tracking with low-altitude surveillance radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 443–458. doi: 10.12000/JR21211. [12] MBOUOMBOUO MBOUNGAM A H, ZHI Yongfeng, and FONZEU MONGUEN C K. Clutter map constant false alarm rate mixed with the Gabor transform for target detection via Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(7): 2967. doi: 10.3390/app14072967. [13] PETROVSKAYA A, PERROLLAZ M, OLIVEIRA L, et al. Awareness of Road Scene Participants for Autonomous Driving[M]. ESKANDARIAN A. Handbook of Intelligent Vehicles. London: Springer, 2012: 1383–1432. doi: 10.1007/978-0-85729-085-4_54. [14] BAIG Q, PERROLLAZ M, and LAUGIER C. A robust motion detection technique for dynamic environment monitoring: A framework for grid-based monitoring of the dynamic environment[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2014, 21(1): 40–48. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2013.2297812. [15] DANESCU R, ONIGA F, and NEDEVSCHI S. Modeling and tracking the driving environment with a particle-based occupancy grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 12(4): 1331–1342. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2011.2158097. [16] NÈGRE A, RUMMELHARD L, and LAUGIER C. Hybrid sampling Bayesian occupancy filter[C]. 2014 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, Dearborn, MI, USA, 2014: 1307–1312. doi: 10.1109/IVS.2014.6856554. [17] MAHLER R. Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2007. [18] MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119. [19] VO B N and MA W K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881190. [20] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3553–3567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894241. [21] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924. [22] VO B T and VO B N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(13): 3460–3475. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2259822. [23] VO B N, VO B T, and PHUNG D. Labeled random finite sets and the Bayes multi-target tracking filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(24): 6554–6567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2364014. [24] NUSS D, REUTER S, THOM M, et al. A random finite set approach for dynamic occupancy grid maps with real-time application[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2018, 37(8): 841–866. doi: 10.1177/0278364918775523. [25] FAN H Q, KUCNER T P, MAGNUSSON M, et al. A dual PHD filter for effective occupancy filtering in a highly dynamic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(9): 2977–2993. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2770152. [26] COUÉ C, PRADALIER C, LAUGIER C, et al. Bayesian occupancy filtering for multitarget tracking: An automotive application[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2006, 25(1): 19–30. doi: 10.1177/0278364906061158. [27] CHEN C, TAY C, LAUGIER C, et al. Dynamic environment modeling with gridmap: A multiple-object tracking application[C]. 2006 9th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, Singapore, 2006: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICARCV.2006.345399. [28] SAVAL-CALVO M, MEDINA-VALDÉS L, CASTILLO-SECILLA J M, et al. A review of the Bayesian occupancy filter[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(2): 344. doi: 10.3390/s17020344. [29] MAHAFZA B R and ELSHERBENI A Z. Matlab Simulations for Radar Systems Design[M]. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2004. [30] MAHLER R. Advances in Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2014. [31] HUANG Zicheng, LIANG Zuoping, ZHOU Shibo, et al. An improved density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise algorithm with an adaptive parameter based on the sparrow search algorithm[J]. Algorithms, 2025, 18(5): 273. doi: 10.3390/a18050273. [32] SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.920469. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: