Adaptive Detection of Range-distributed Targets in Weighted Generalized Inverse Gaussian Clutter
-
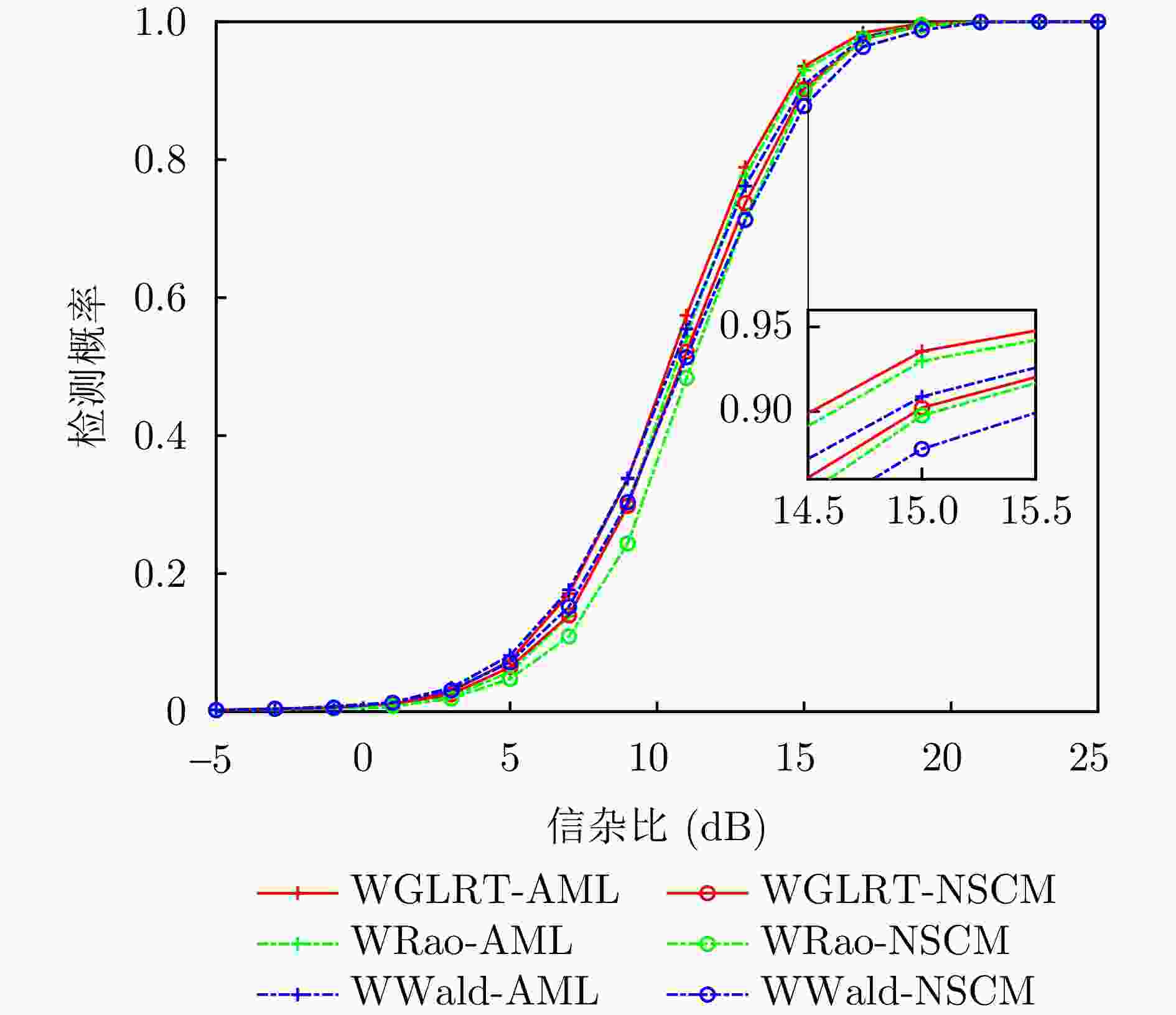
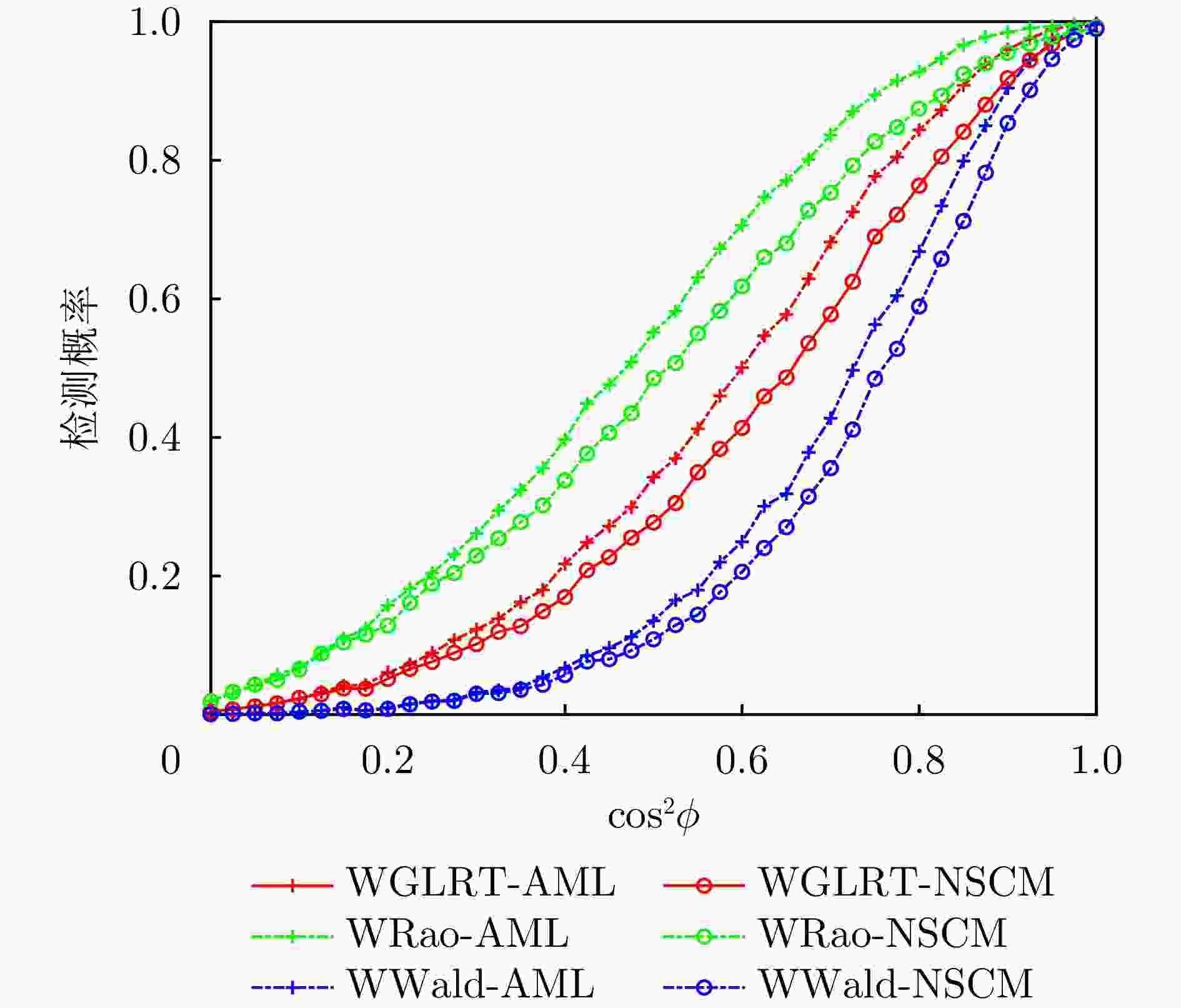
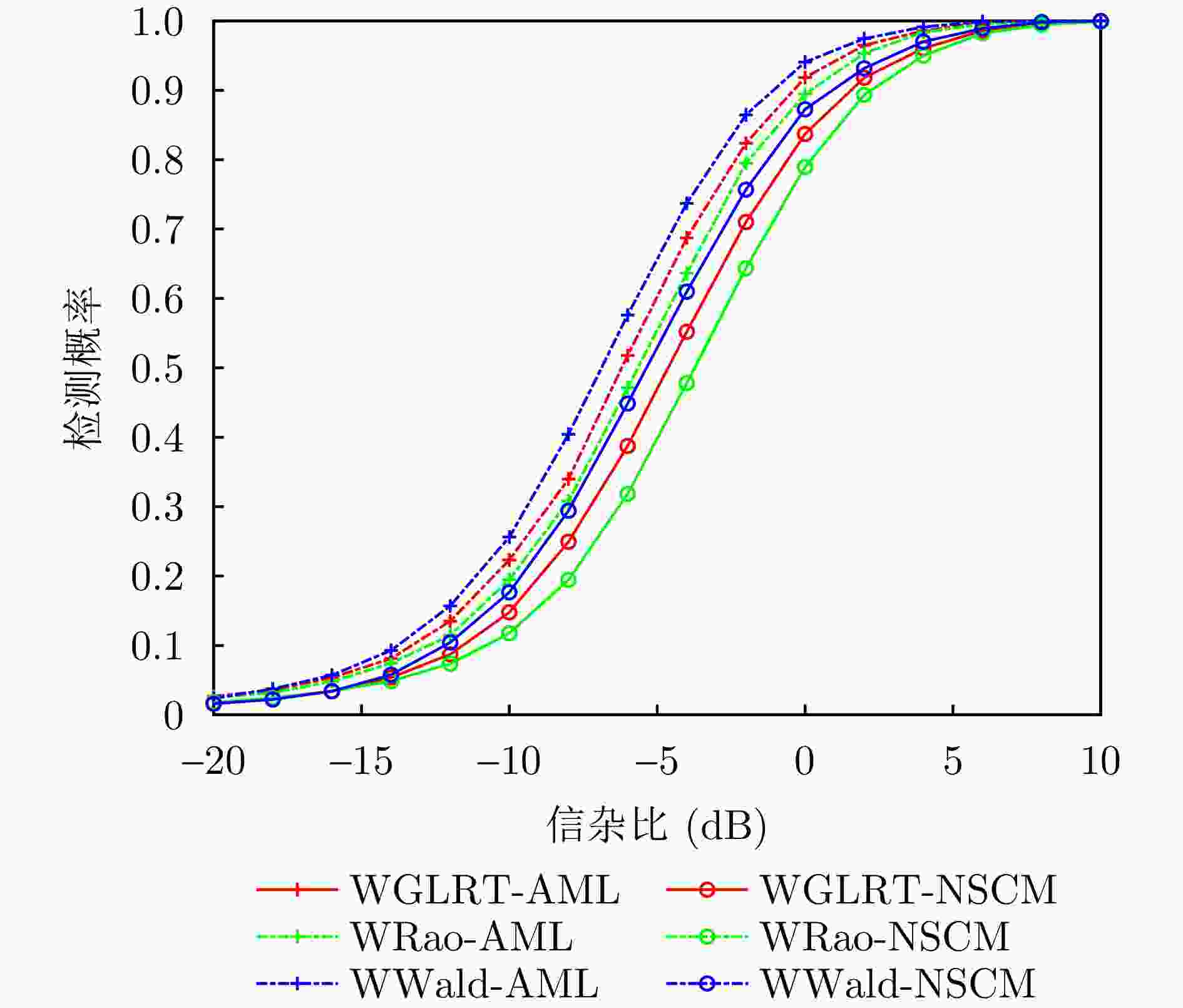
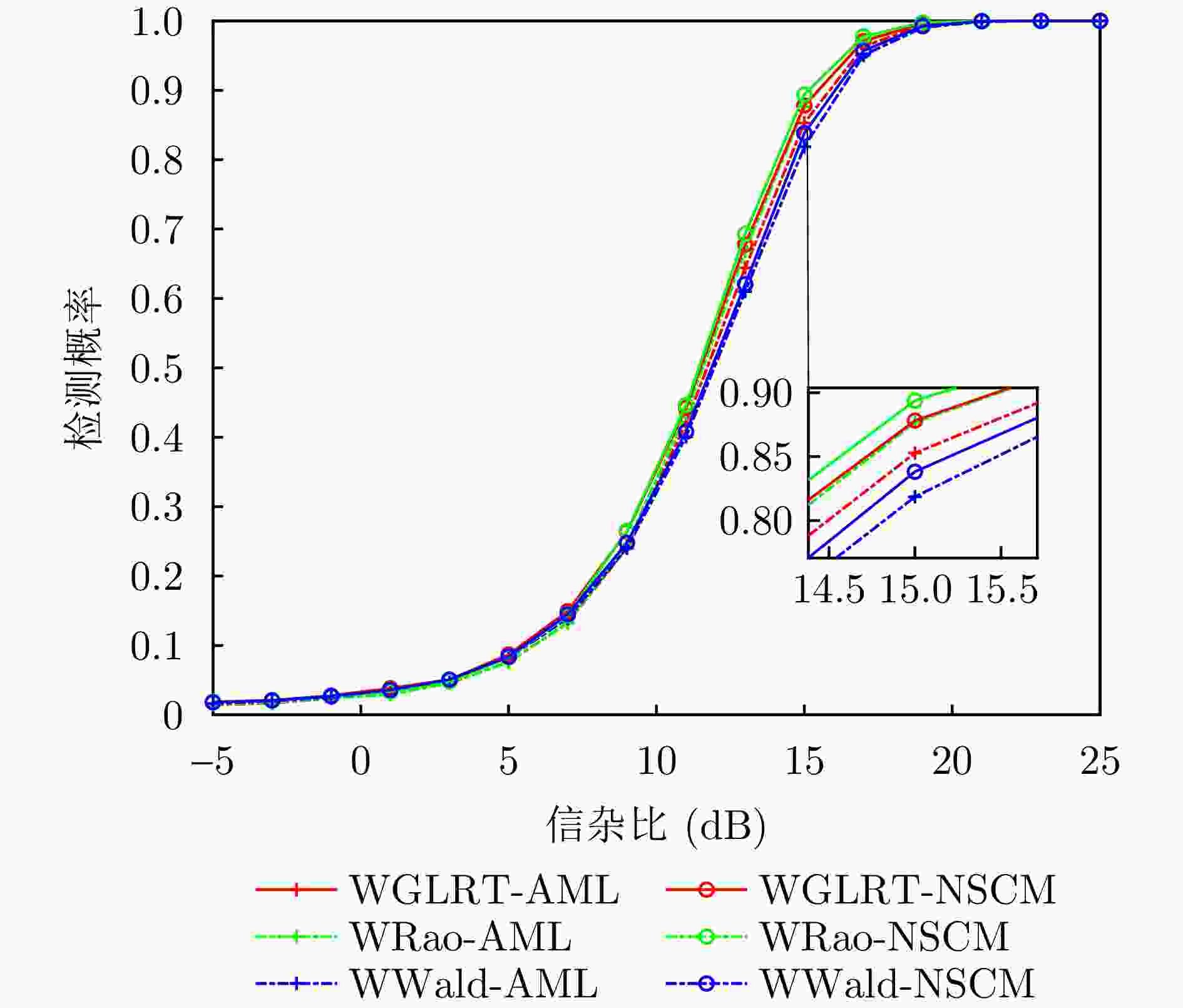
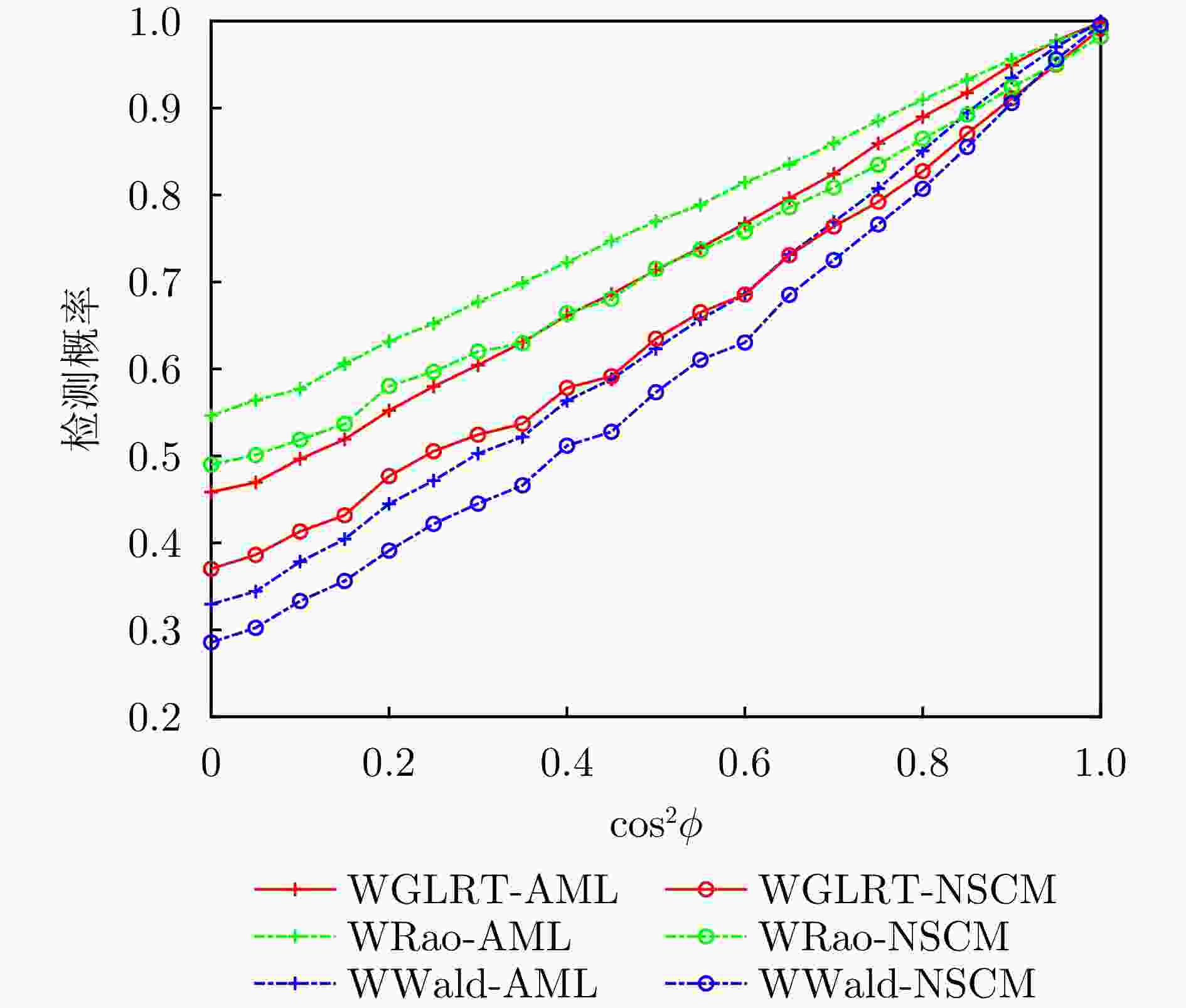
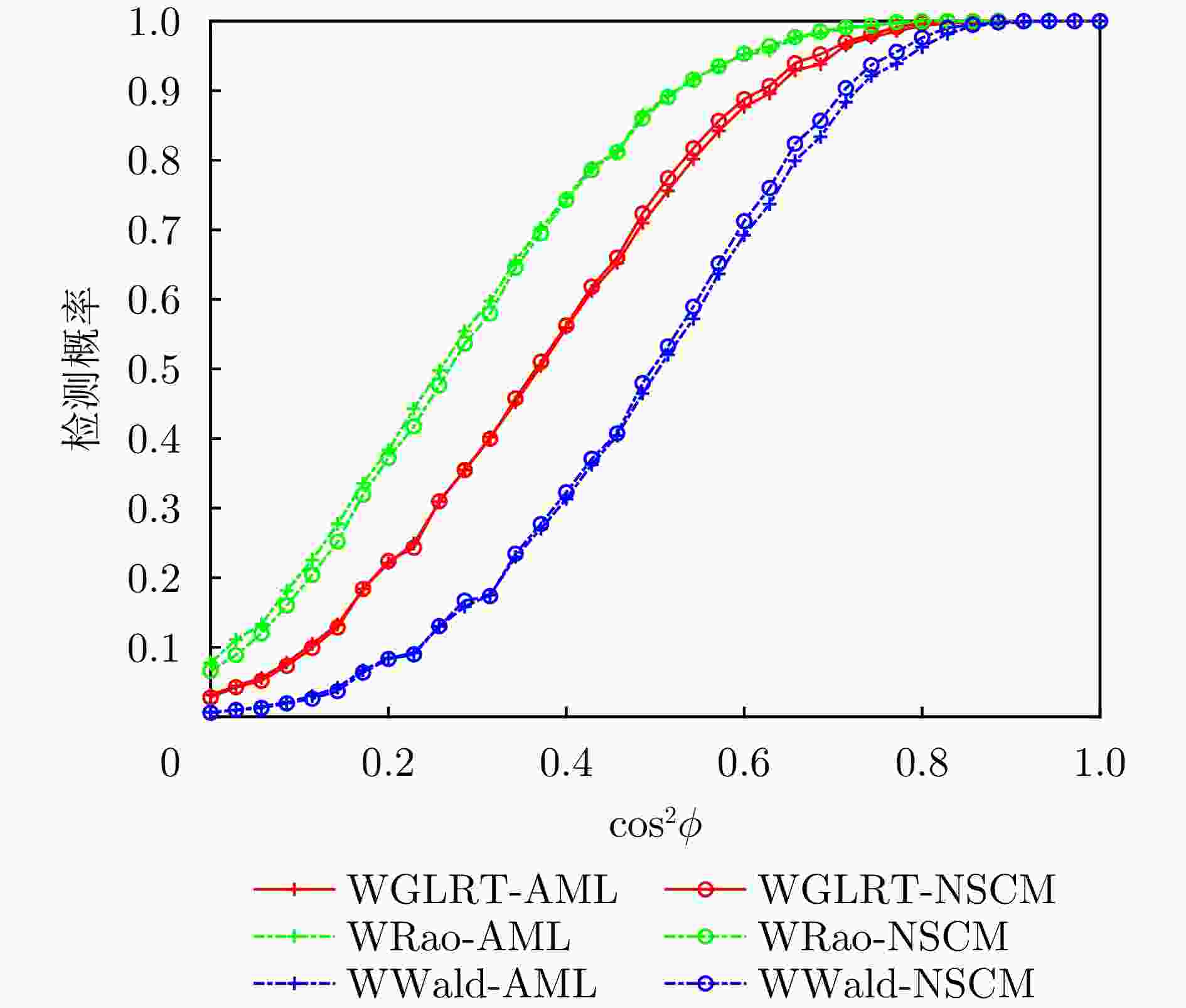
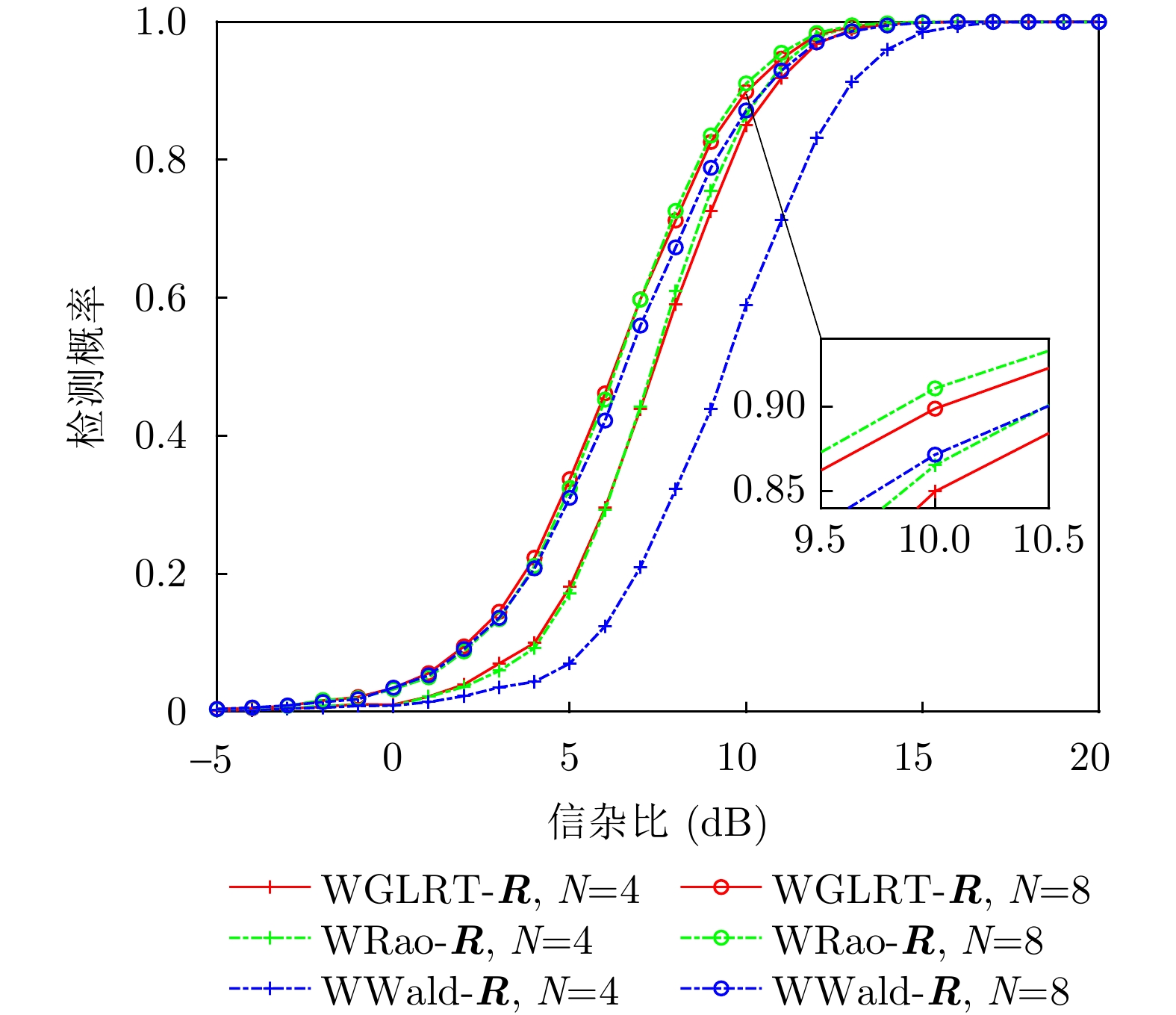
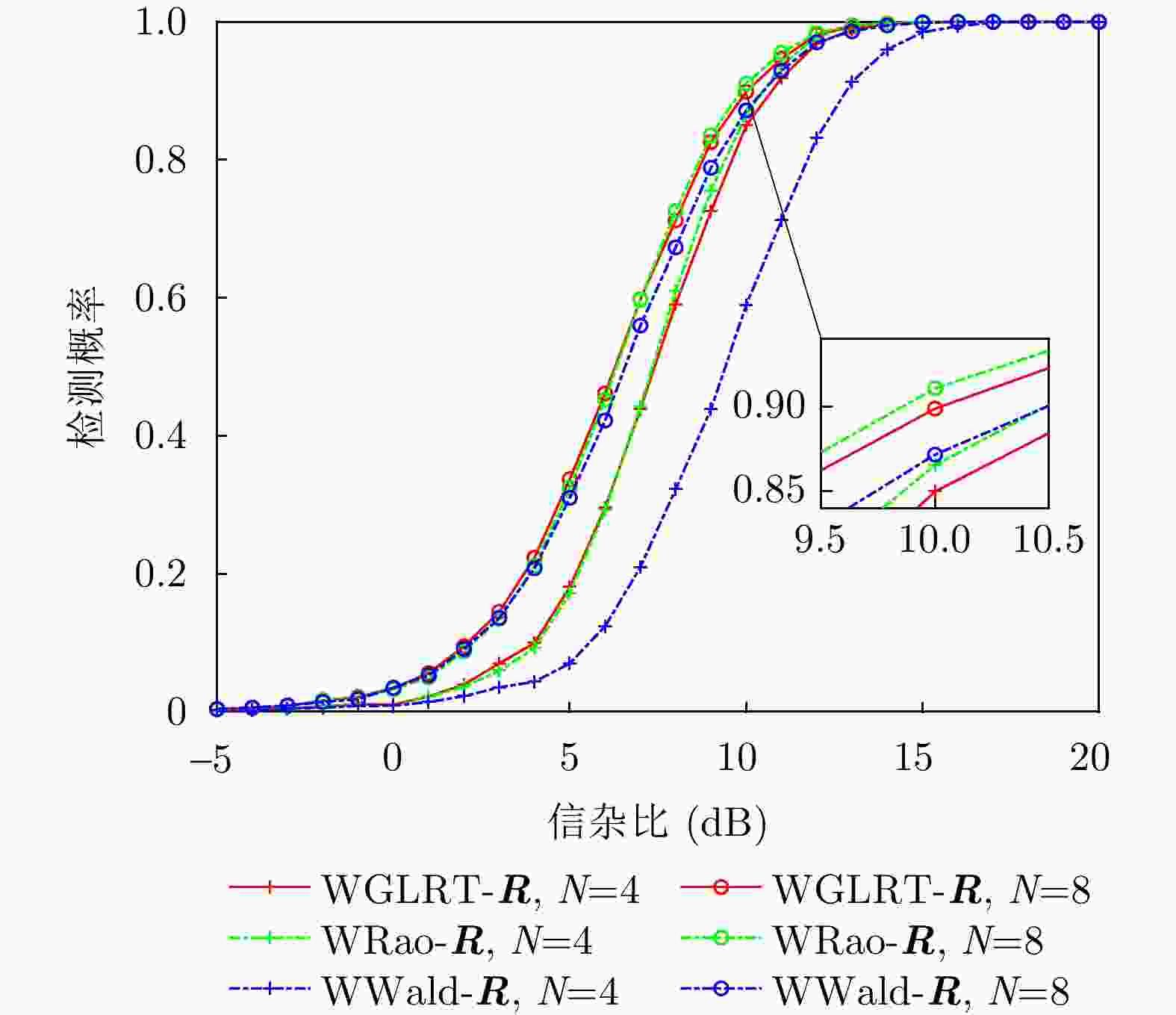
摘要: 该文研究了复合高斯杂波中距离扩展目标的自适应检测问题,其中杂波纹理分量服从加权广义逆高斯(WGIG)分布。该文基于两步Rao, Wald, Durbin和Gradient检验分别设计加权广义逆高斯杂波下的自适应检测器。针对未知协方差矩阵,分别采用近似最大似然(AML)和归一化采样协方差矩阵(NSCM)两种方法进行估计。由于纹理分量的最大后验(MAP)估计难以解析求解,因此在Rao, Wald和Durbin检验的检测器设计中,采用纹理分量的倒数期望的MAP进行替代;而在Gradient检验的检测器设计中,则基于后验概率密度函数推导检验统计量。理论分析表明,基于Rao, Durbin和Gradient检验所得到的检测器具有一致性。在性能评估方面,通过仿真数据和实测数据,分别对无信号失配和存在信号失配两种情况下的检测性能进行了系统评估。实验结果表明:(1)该文提出的基于AML的检测器均具有恒虚警率(CFAR)特性;(2)在无信号失配情况下,基于Rao准则和Wald准则的检测器在两种实测数据集上分别表现出最优的检测性能,并且相较于两步GLRT检测器的检测性能分别提升0.1~0.5 dB和0.7~0.8 dB;(3)在信号失配情况下,基于Rao准则与AML估计的检测器具有最佳的稳健性,而基于Wald准则的检测器对失配信号表现出最强的抑制能力。Abstract: In this paper, we investigate the adaptive detection of range-distributed targets in compound-Gaussian clutter, where the texture component follows a Weighted Generalized Inverse Gaussian (WGIG) distribution. We propose adaptive detectors for WGIG-distributed clutter based on two-step Rao, Wald, Durbin, and Gradient tests. The unknown covariance matrix is estimated using Approximate Maximum Likelihood (AML) and the Normalized Sample Covariance Matrix (NSCM). To address the analytical intractability of Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) estimation for the texture component, we adopt an alternative approach: The MAP estimator of the reciprocal expectation of the texture component, which is used in designing adaptive detectors based on the Rao, Wald, and Durbin tests. For the Gradient test-based detector, the test statistic is derived directly from the posterior probability density function. Our theoretical analysis confirms the consistency of the detectors derived from the Rao, Durbin, and Gradient tests. Extensive evaluations on both simulated and real data yield three key findings: (1) The proposed AML-based detectors maintain the constant false alarm rate property; (2) Under matched signal conditions, the detectors based on the Rao and Wald tests achieve the best performance on both the IPIX radar dataset and the Journal of Radar’s maritime surveillance dataset—specifically, they outperform the two-step generalized likelihood ratio test-based detector, requiring 0.1~0.5 dB and 0.7~0.8 dB lower Signal-to-Clutter Ratio (SCR) to achieve the same detection probability, respectively; and (3) Under mismatched signal conditions, the Rao test-based detector with AML estimation exhibits superior robustness, while the Wald test-based detector demonstrates the strongest suppression capability against mismatched signals.
-
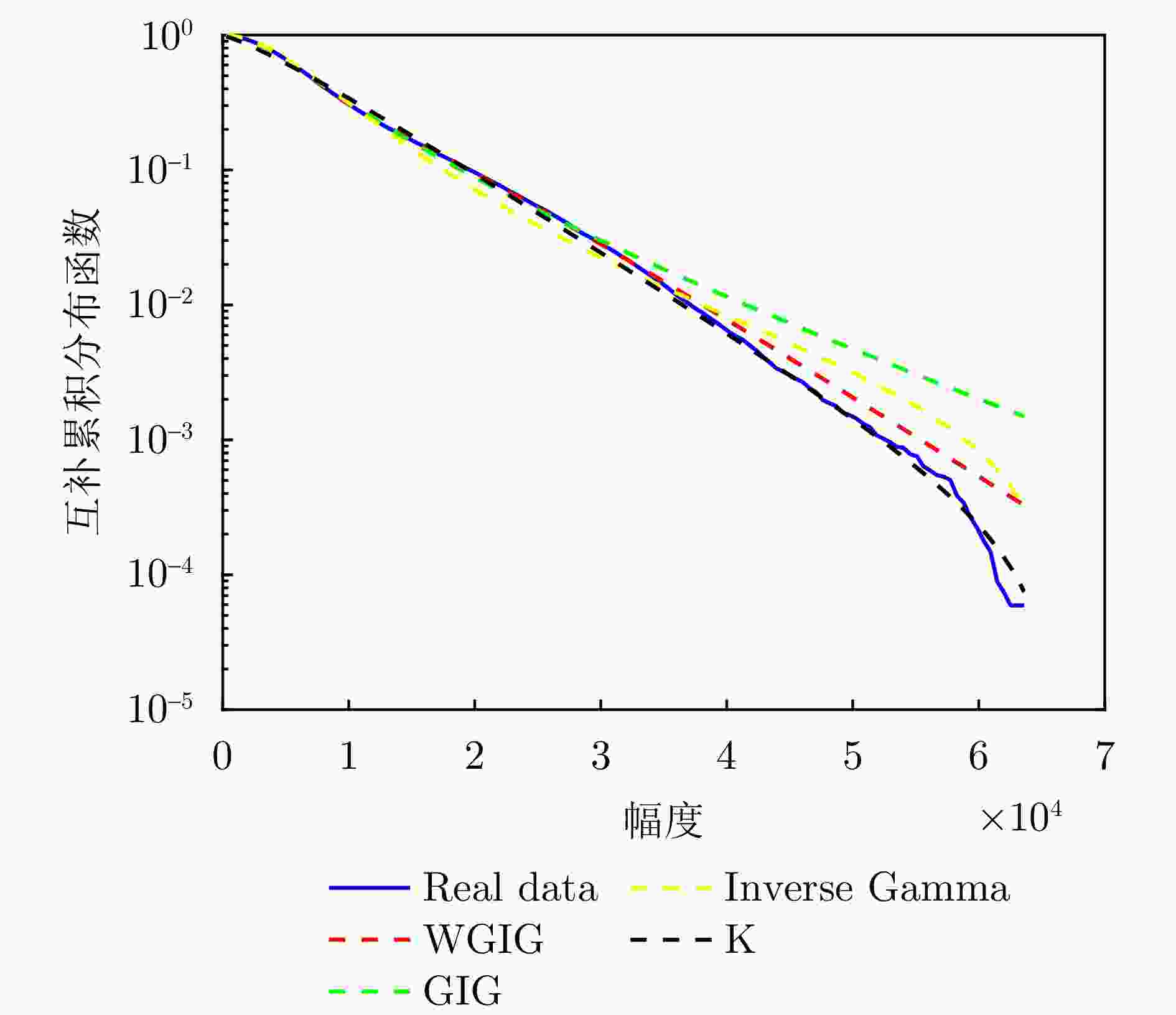
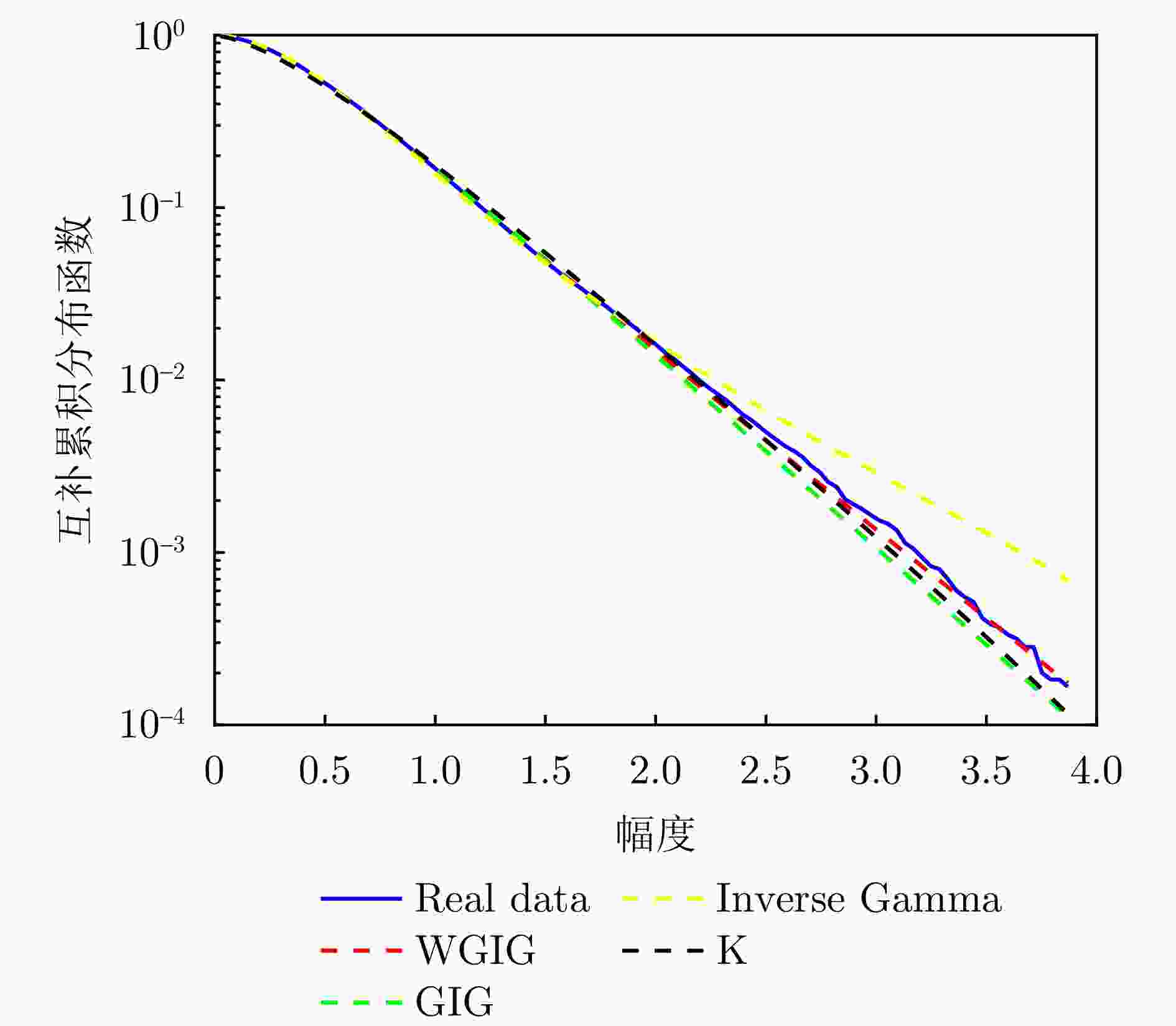
表 1 M = 2时各个分布模型拟合
20221112175025 _stare_VV海杂波数据结果Table 1. When M = 2, the fitting results of various distribution models to
20221112175025 _stre_VV sea clutter模型 参数 MSE WGIG $ {\boldsymbol{w}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 0.5514 \\ 0.4486 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ a = \left[ \begin{gathered} 1.0905{\text{E}}-06 \\ 1.0434{\text{E}}-08 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ {\boldsymbol{b}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} {\text{1}}{\text{.1835E08}} \\ 1.6943{\text{E}}08 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ {\boldsymbol{v}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 18.0474 \\ 0.9568 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $ 3.4592E–06 GIG $a = 2.0837{\text{E}} - 09$,$b = 7.4187{\text{E}}07$, $ v = - 0.6409 $ 2.2676E–05 Inverse Gamma $\lambda = 1.5807$, $\beta = 9.8920{\text{E07}}$ 1.2227E–04 K $\lambda = - 0.2396$, $\beta = 7.0049{\text{E03}}$ 3.9341E–04 表 2 M = 2时各个分布模型拟合IPIX_
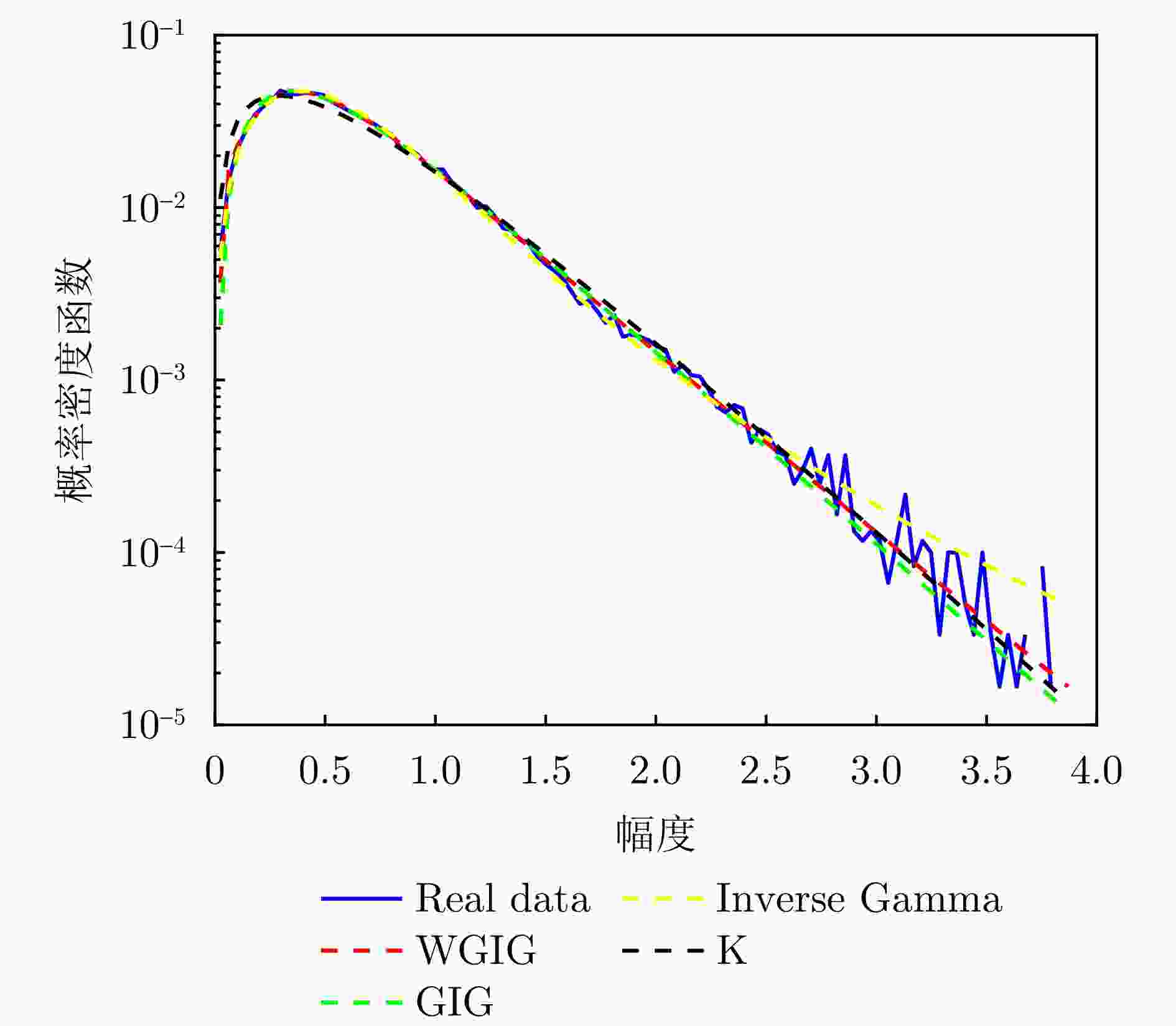
19980223 _170435 海杂波数据结果Table 2. When M = 2, the fitting results of various distribution models to IPIX_
19980223 _170435 sea clutter模型 参数 MSE WGIG $ {\boldsymbol{w}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 0.9631 \\ 0.0369 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ {\boldsymbol{a}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 2.7812 \\ 0.4670 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ {\boldsymbol{b}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 0.5408 \\ 0.0014 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $, $ {\boldsymbol{v}} = \left[ \begin{gathered} 0.0077 \\ 0.0446 \\ \end{gathered} \right] $ 4.0693E–07 GIG $a = 3.4697$, $b = 0.2546$, $ v = 0.5968 $ 2.6538E–06 Inverse Gamma $\lambda = 2.3372$, $\beta = 0.8660$ 1.4781E–05 K $\lambda = 0.2602$, $\beta = 0.3532$ 1.4312E–04 -
[1] BANDIERA F, DE MAIO A, GRECO A S, et al. Adaptive radar detection of distributed targets in homogeneous noise plus subspace interference[C]. Conference Record of the Thirty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2005: 765–769. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2005.1599856. [2] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8. [3] LIU Weijian, XIE Wenchong, LIU Jun, et al. Adaptive double subspace signal detection in Gaussian background—Part I: Homogeneous environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(9): 2345–2357. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2309556. [4] HUGHES P K. A high-resolution radar detection strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(5): 663–667. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309368. [5] GRECO M, GINI F, and RANGASWAMY M. Non-stationarity analysis of real X-band clutter data at different resolutions[C]. 2006 IEEE Radar Conference, Verona, USA, 2006: 44–50. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631774. [6] GINI F and GRECO M. Texture modelling, estimation and validation using measured sea clutter data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2002, 149(3): 115–124. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20020272. [7] RANGASWAMY M. Spherically invariant random processes for modeling non-Gaussian radar clutter[C]. The 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1993: 1106–1110. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.1993.342399. [8] ZOU Pengjia, CHANG Siyuan, and SHUI Penglang. Compound-Gaussian clutter model with Weibull-distributed textures and parameter estimation[J] Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(16): 2912. doi: 10.3390/rs16162912. [9] XU Shuwen, SHUI Penglang, and CAO Yunhe. Adaptive range-spread maneuvering target detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2015, 36: 46–56. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2014.09.010. [10] CONTE E, DI BISCEGLIE M, LONGO M, et al. Canonical detection in spherically invariant noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1995, 43(2/4): 347–353. doi: 10.1109/26.380053. [11] HE You, JIAN Tao, SU Feng, et al. Novel range-spread target detectors in non-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1312–1328. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545191. [12] JIANG Qing, WU Yuntao, LIU Weijian, et al. Subspace-based distributed target detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 140: 104141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2023.104141. [13] 许述文, 石星宇, 水鹏朗. 复合高斯杂波下抑制失配信号的自适应检测器[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030.XU Shuwen, SHI Xingyu, and SHUI Penglang. An adaptive detector with mismatched signals rejection in compound Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030. [14] YANG Yong, XIAO Shunping, WANG Xuesong, et al. Performance analysis of radar detection for correlated Gamma fluctuating targets in K distributed sea clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 79: 136–141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.05.001. [15] SHANG Xiuqin, SONG Hongjun, WANG Yu, et al. Adaptive detection of distributed targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse gamma texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2012, 22(6): 1024–1030. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2012.05.002. [16] WANG Qing, ZHOU Xuan, LIU Weijian, et al. Adaptive detection of point targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse gamma texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 3967–3978. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3374715. [17] 丁昊, 王国庆, 刘宁波, 等. 逆Gamma纹理背景下两类子空间目标的自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088.DING Hao, WANG Guoqing, LIU Ningbo, et al. Adaptive detectors for two types of subspace targets in an inverse Gamma textured background[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088. [18] GAO Yongchan, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. A persymmetric GLRT for adaptive detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with random texture[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(6): 615–618. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2259232. [19] OLLILA E, TYLER D E, KOIVUNEN V, et al. Compound-Gaussian clutter modeling with an inverse Gaussian texture distribution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(12): 876–879. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2221698. [20] GAO Yongchan, LIAO Guisheng, and ZHU Shengqi. Adaptive signal detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[C]. 2013 14th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 935–940. [21] XUE Jian, XU Shuwen, and SHUI Penglang. Knowledge-based target detection in compound Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 95: 102590. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.102590. [22] XUE Jian, XU Shuwen, LIU Jun, et al. Model for non-Gaussian sea clutter amplitudes using generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 892–896. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2886782. [23] GUO Hongzhi, WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, et al. Persymmetric adaptive subspace detection in compound Gaussian sea clutter with generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Signal Processing, 2024, 216: 109300. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109300. [24] XUE Jian, MA Manshan, LIU Jun, et al. Wald- and Rao-based detection for maritime radar targets in sea clutter with lognormal texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5119709. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3217615. [25] XUE Jian, FAN Zhen, XU Shuwen, et al. Persymmetric adaptive radar target detection in CG-LN sea clutter using complex parameter suboptimum tests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5111211. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3330865. [26] XUE Jian, FAN Zhen, and XU Shuwen. Adaptive coherent detection for maritime radar range-spread targets in correlated heavy-tailed sea clutter with lognormal texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3505805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3397850. [27] CHEN Xiaolin, LIU Kai, ZHANG Zhibo, et al. Mixture texture model with weighted generalized inverse Gaussian distribution for target detection[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2024, 154: 104677. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2024.104677. [28] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, LIU Tao, et al. Detector design and performance analysis for target detection in subspace interference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 618–622. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3270080. [29] TANG Peiqin, XU Zhenyu, XU Hong, et al. Distributed target detection based on gradient test in deterministic subspace interference[J]. Signal Processing, 2025, 227: 109673. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2024.109673. [30] TANG Peiqin, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A tunable detector for distributed target detection in the situation of signal mismatch[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2961838. [31] SUN Mengru, LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, et al. Complex parameter Rao, Wald, Gradient, and Durbin tests for multichannel signal detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 117–131. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3132485. [32] XIAO Daipeng, LIU Weijian, CHEN Hui, et al. An adaptive radar target detection method based on alternate estimation in power heterogeneous clutter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(13): 2508. doi: 10.3390/rs16132508. [33] LI Na, YANG Haining, CUI Guolong, et al. Adaptive two-step Bayesian MIMO detectors in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 161: 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.03.008. [34] WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Persymmetric range-spread targets detection in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8018305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3101369. [35] ABRAMOWITZ M and STEGUN I A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions: With Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 1965: 375–376. [36] DEVROYE L. Random variate generation for the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2014, 24(2): 239–246. doi: 10.1007/s11222-012-9367-z. [37] ATKINSON A C. The simulation of generalized inverse Gaussian and hyperbolic random variables[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 1982, 3(4): 502–515. doi: 10.1137/0903033. [38] TANG Peiqin, PENG Xinyu, XU Hong, et al. Durbin tests for distributed target detection in deterministic subspace interference and noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2025, 234: 110009. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2025.110009. [39] LIU Weijian, WANG Yongliang, and XIE Wenchong. Fisher information matrix, Rao test, and Wald test for complex-valued signals and their applications[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 94: 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.06.032. [40] GUO Qiang, LIU Lichao, HUANG Shuai, et al. Adaptive detectors for mismatched subspace target in clutter with lognormal texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2024, 154: 104692. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2024.104692. [41] GINI F and GRECO M. Covariance matrix estimation for CFAR detection in correlated heavy tailed clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2002, 82(12): 1847–1859. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(02)00315-8. [42] CUI Yufeng, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A tunable adaptive detector for distributed targets when signal mismatch occurs[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(4): 873–878. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000029. [43] 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089.LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089. [44] 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011.LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. [45] 关键, 刘宁波, 王国庆, 等. 雷达对海探测试验与目标特性数据获取——海上目标双极化多海况散射特性数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 456–469. doi: 10.12000/JR23029.GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting radar experiment and target feature data acquisition for dual polarization multistate scattering dataset of marine targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 456–469. doi: 10.12000/JR23029. [46] LI Dongfang, ZHAO Zhiqin, and ZHAO Yanwen. Analysis of experimental data of IPIX radar[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics, Chengdu, China, 2018: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/COMPEM.2018.8496687. [47] XU Xiaoke. Low observable targets detection by joint fractal properties of sea clutter: An experimental study of IPIX OHGR datasets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(4): 1425–1429. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2041144. [48] MEZACHE A, SAHED M, and LAROUSSI T. K-distribution parameters estimation based on the Nelder-Mead algorithm in presence of thermal noise[C]. 2009 International Conference on Advances in Computational Tools for Engineering Applications, Beirut, Lebanon, 2009: 553–558. doi: 10.1109/ACTEA.2009.5227861. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: