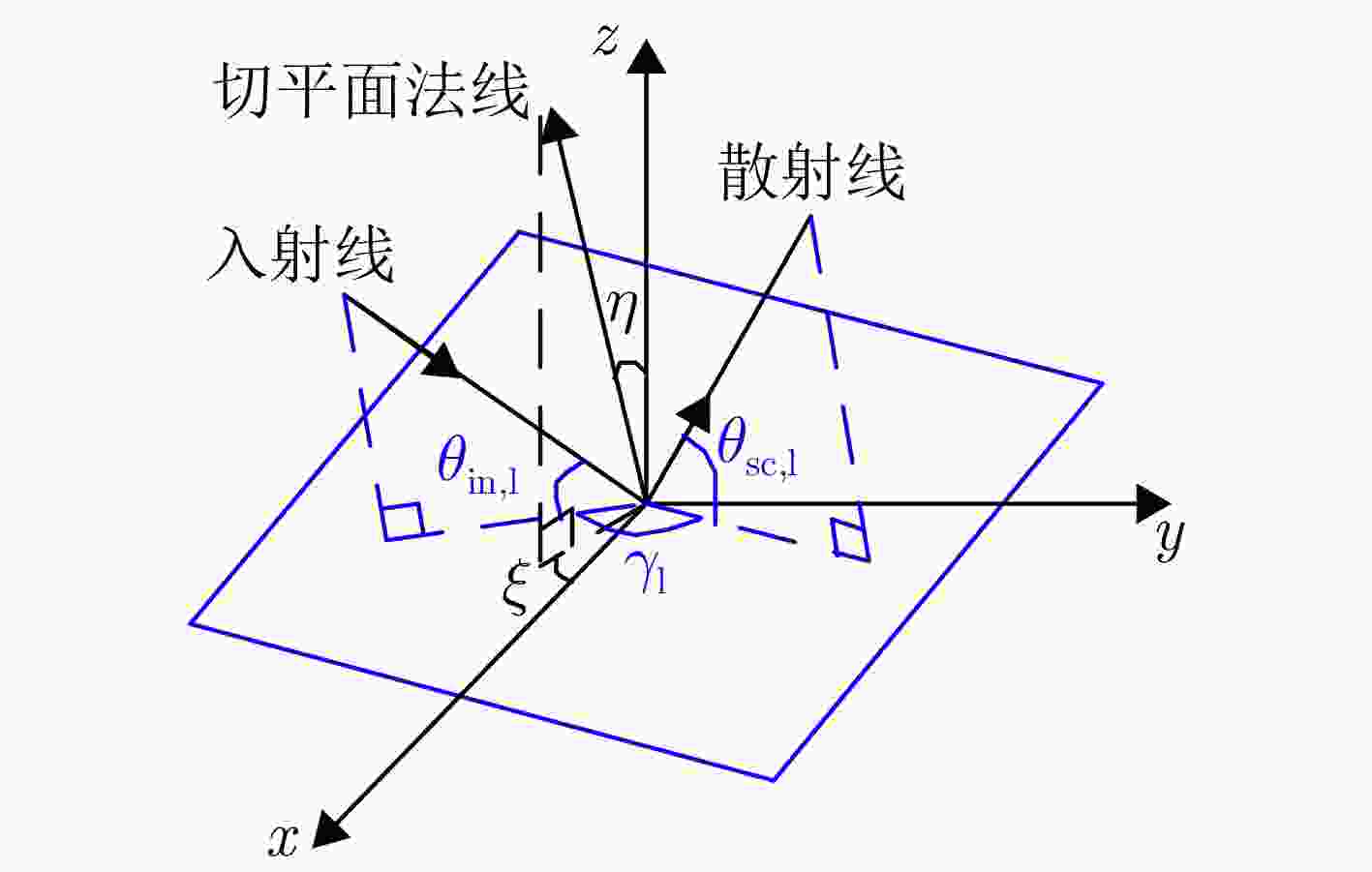
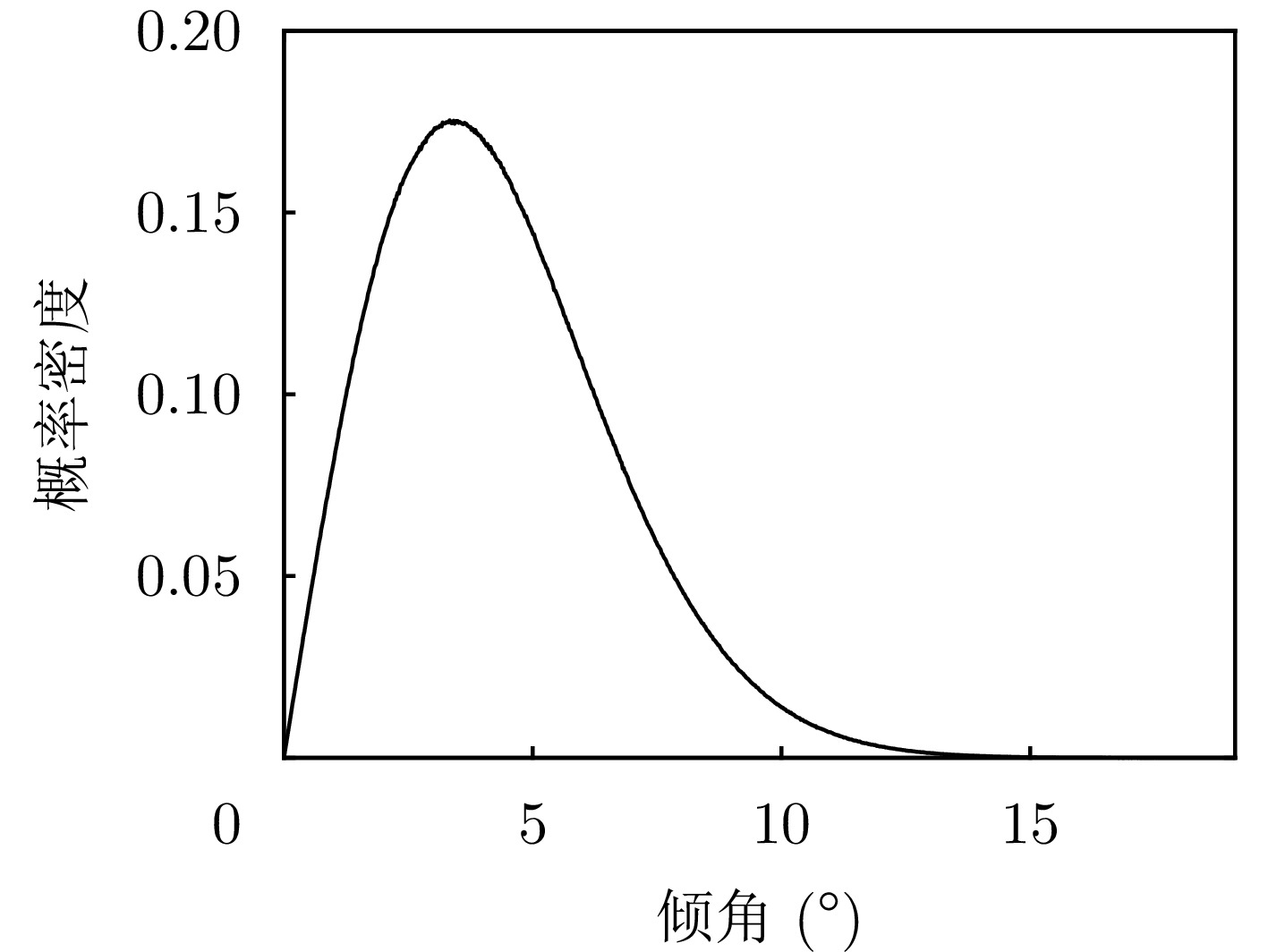
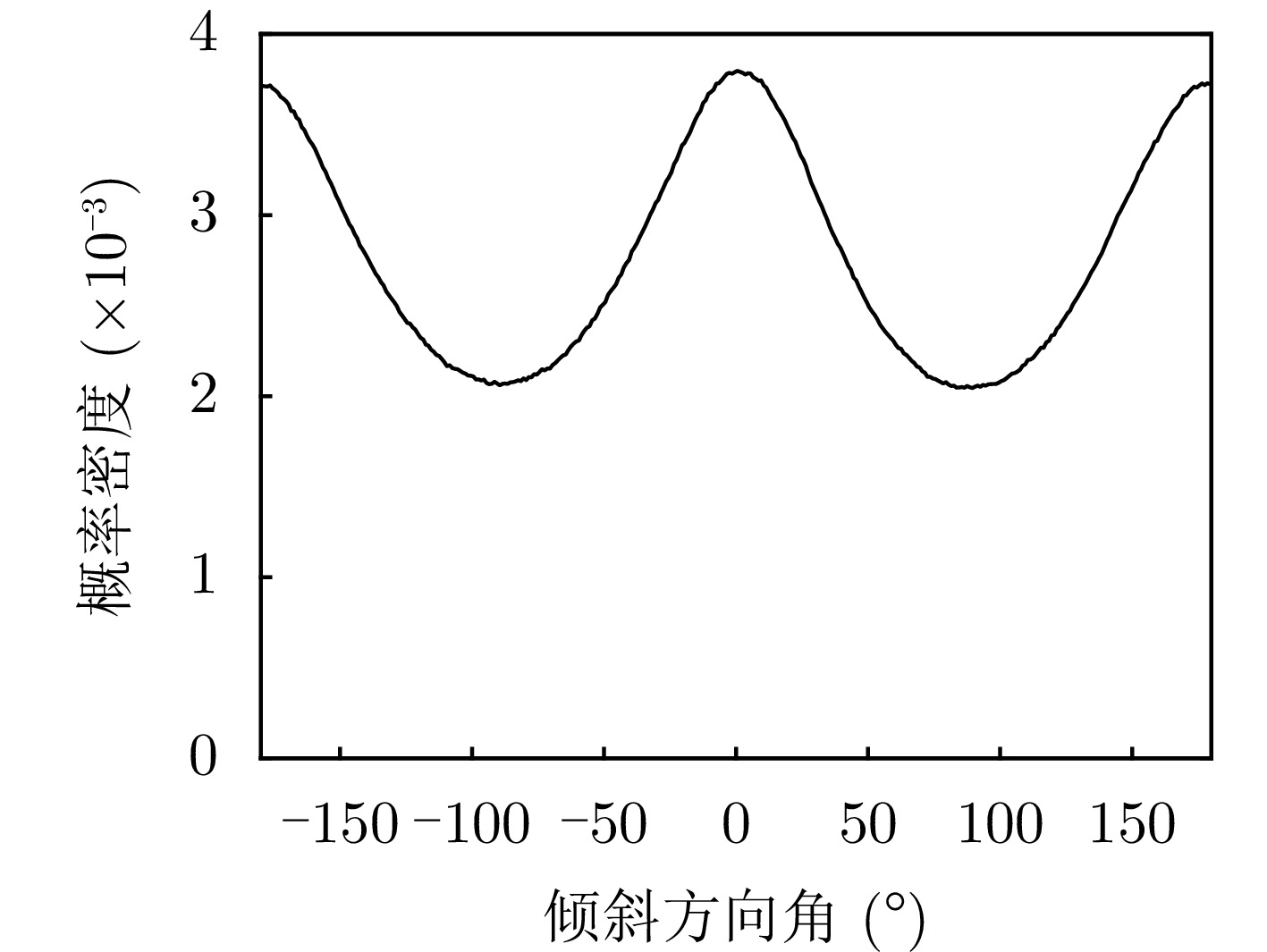
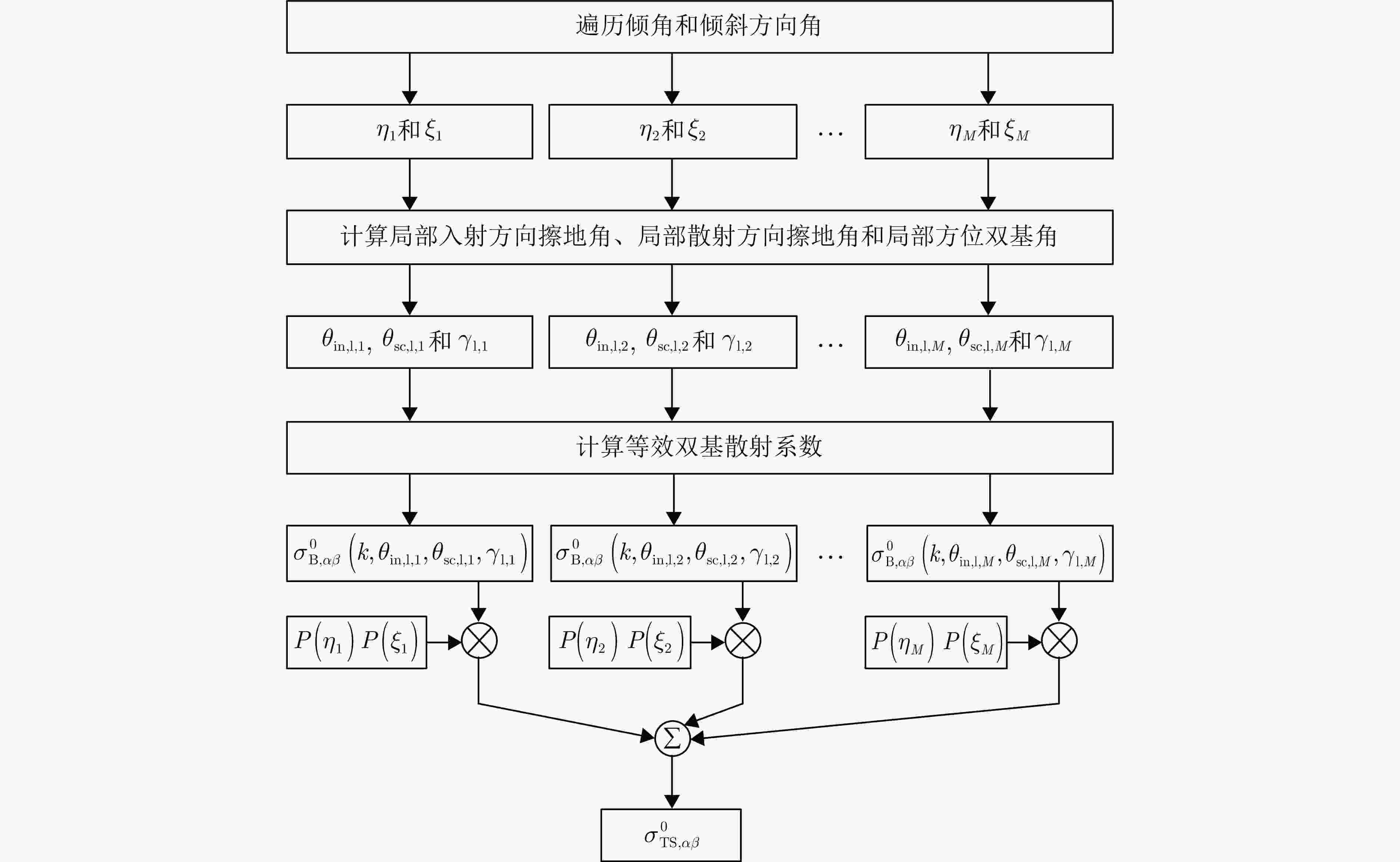
Clutter Suppression Performance Analysis of Spaceborne Bistatic Radar Systems Based on a Semiempirical Bistatic Clutter Scattering Coefficient Model
-
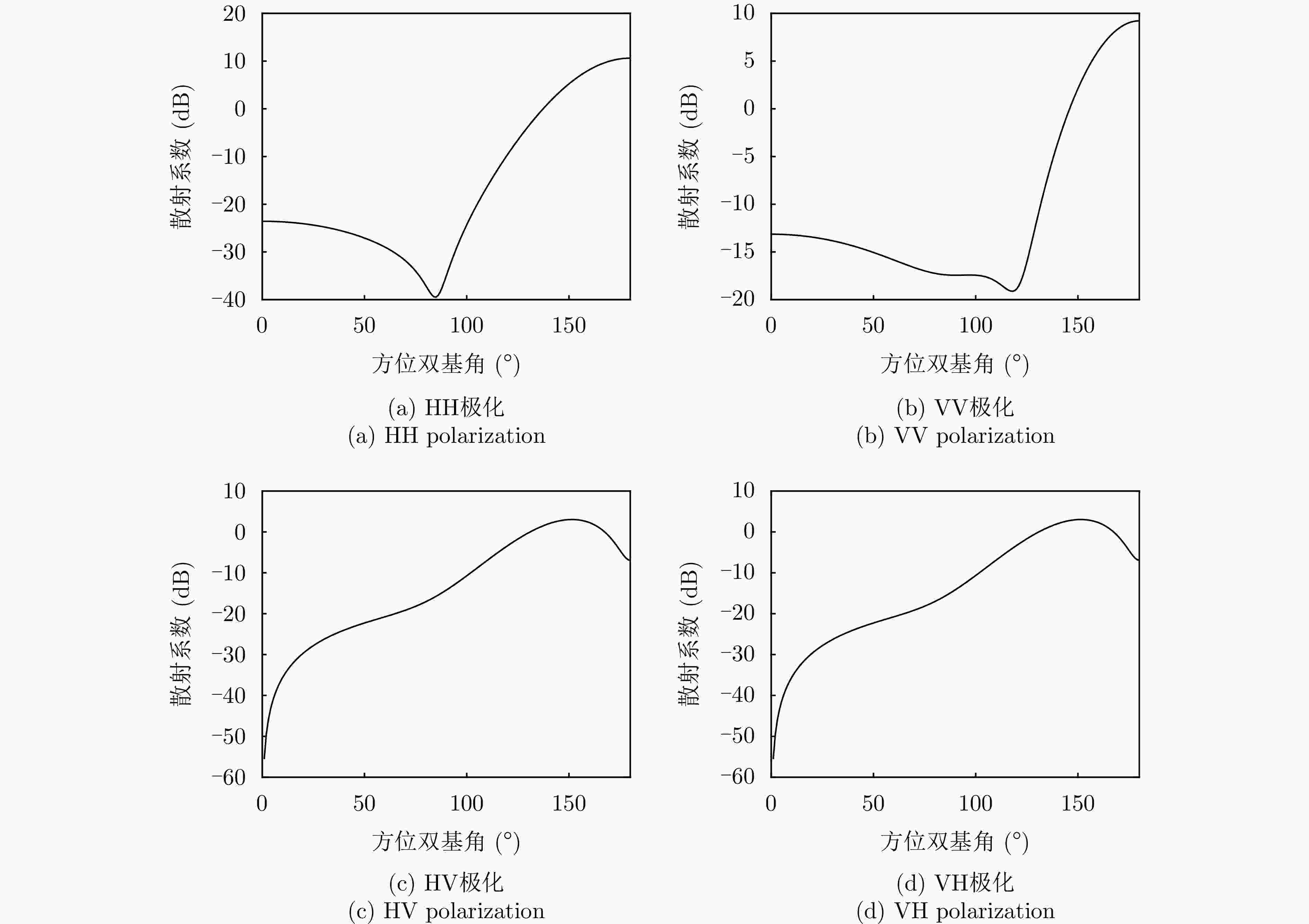
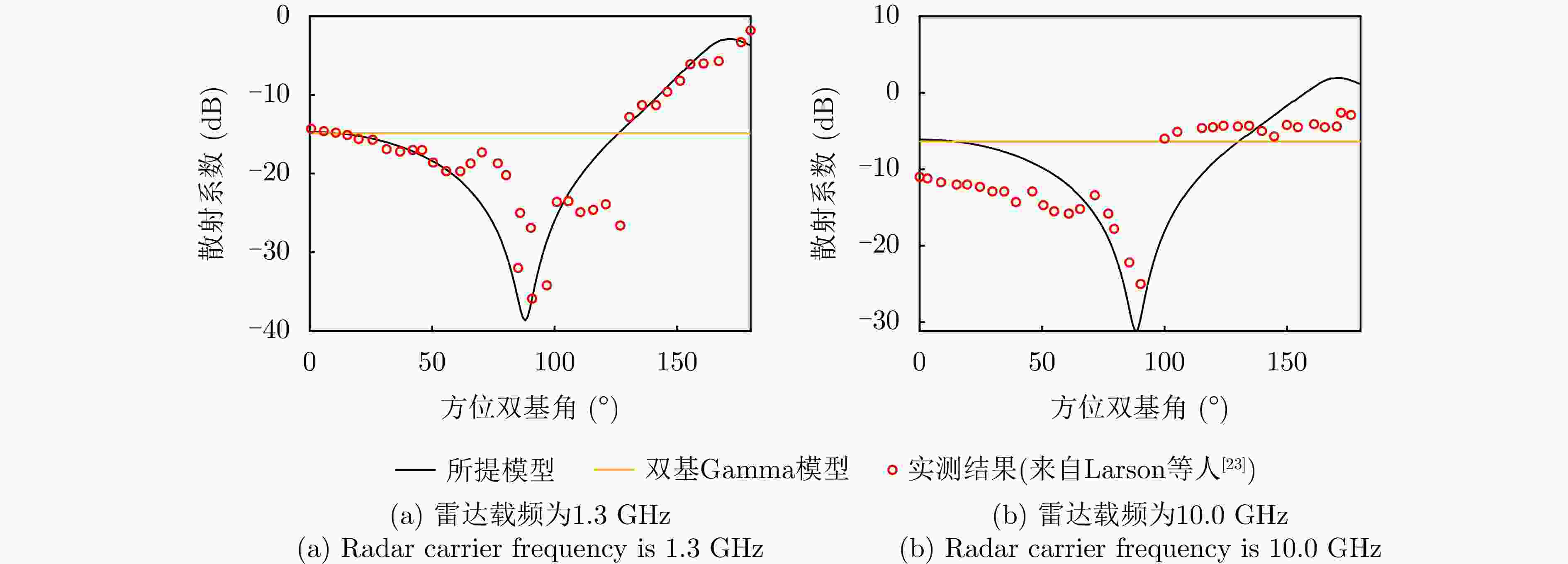
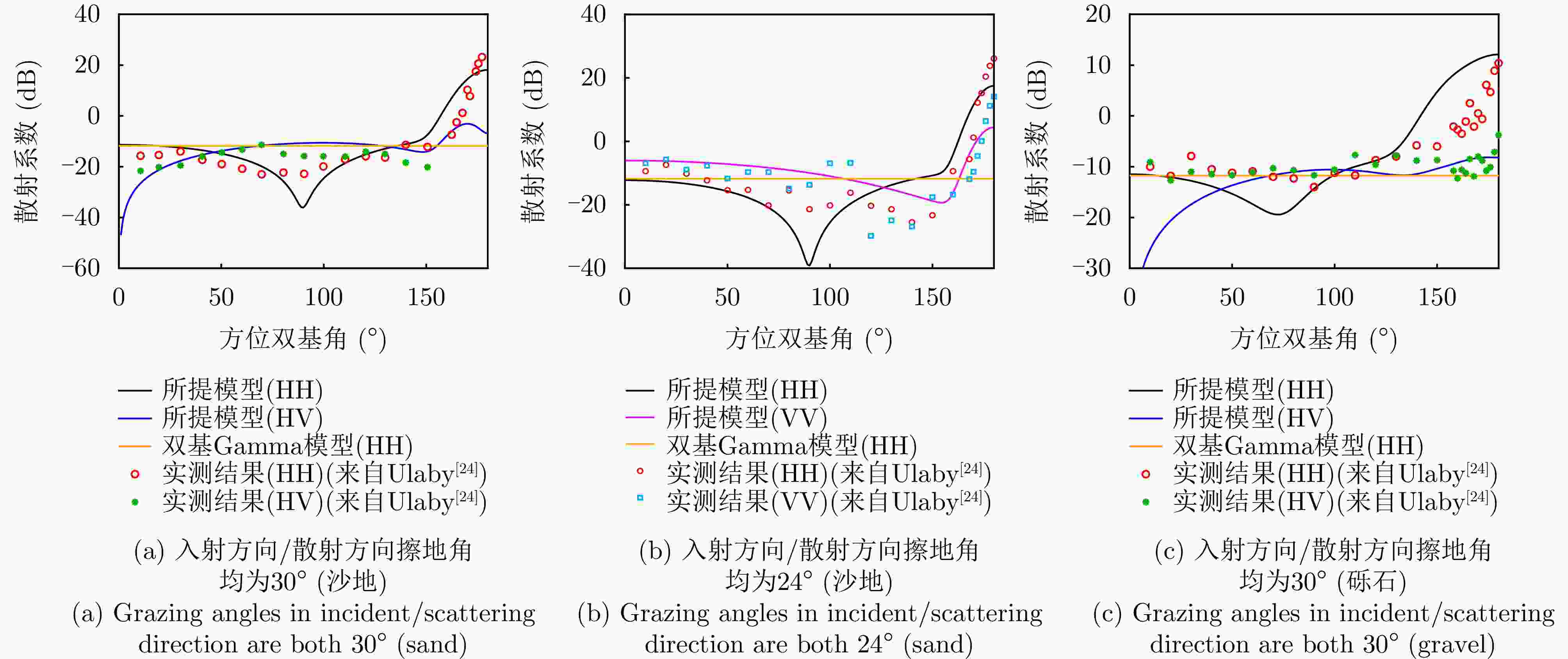
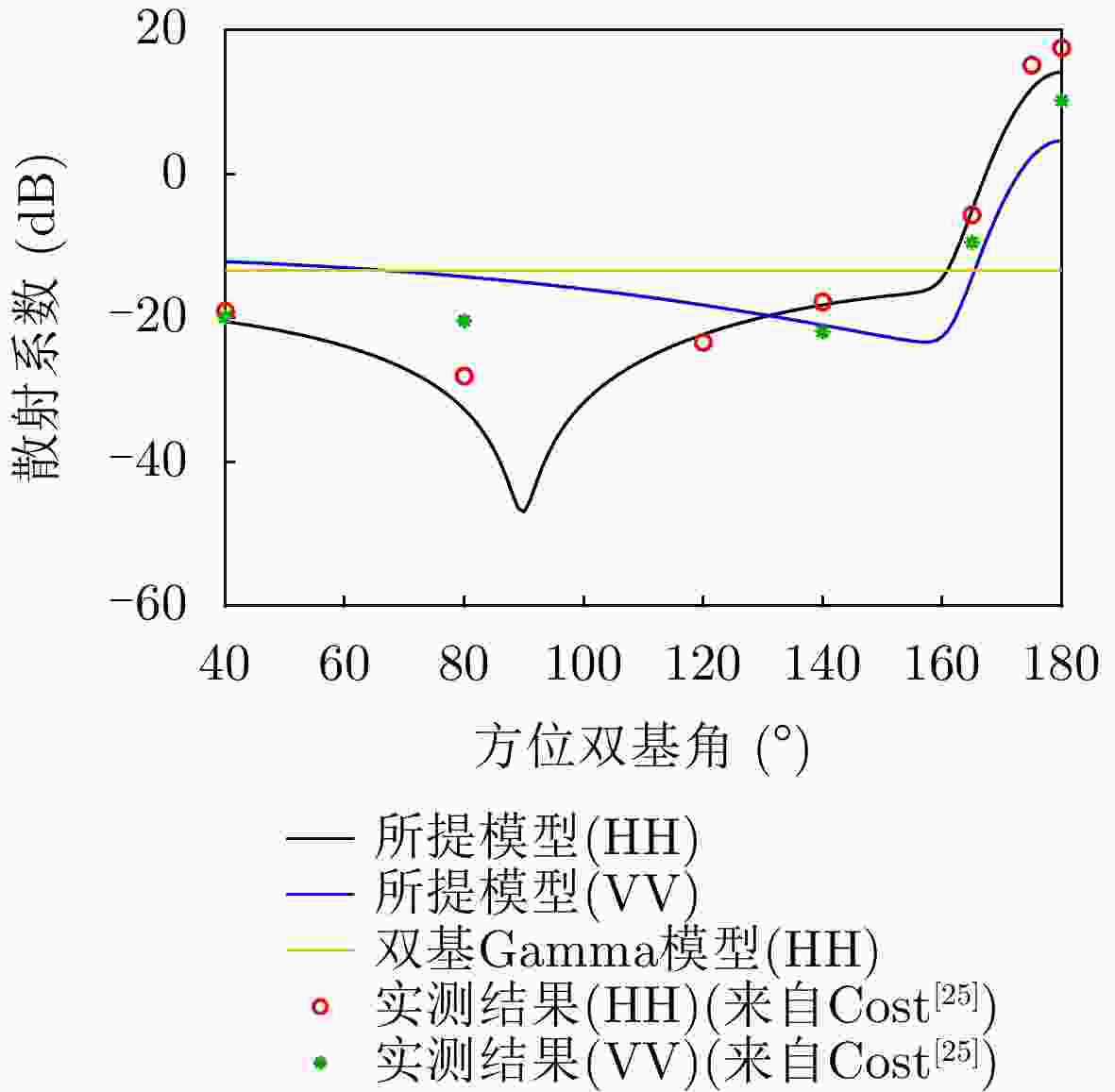
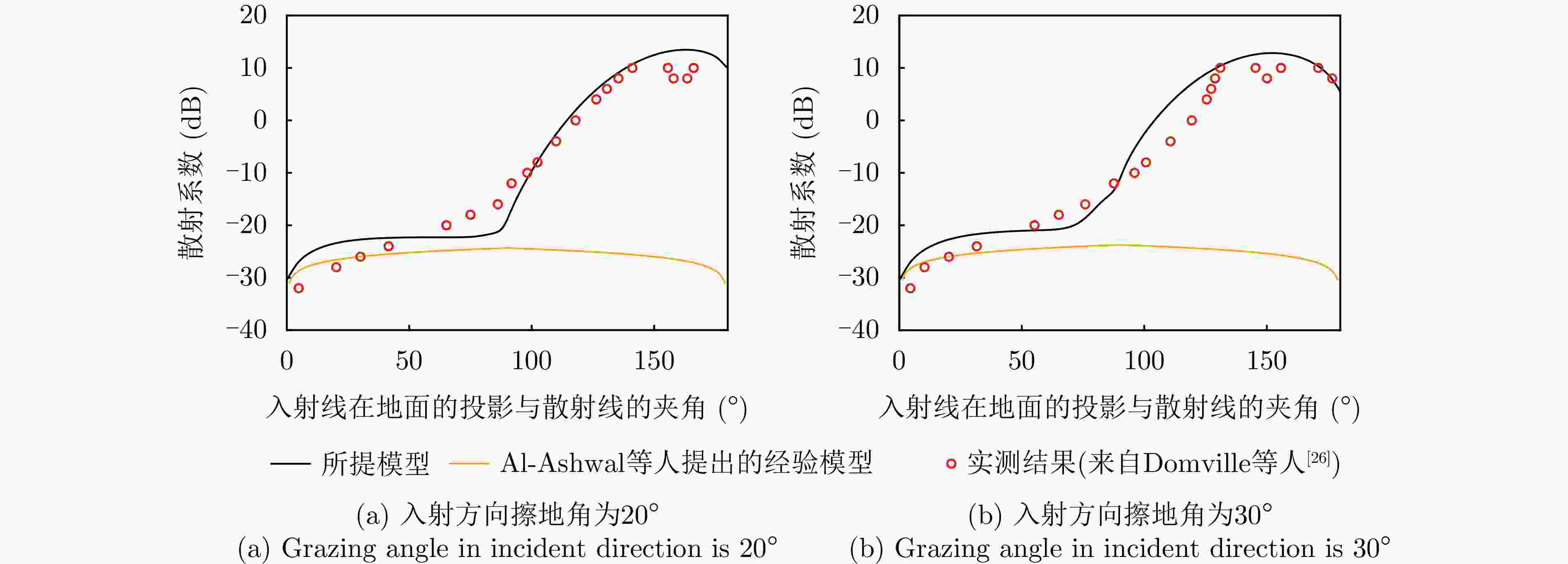
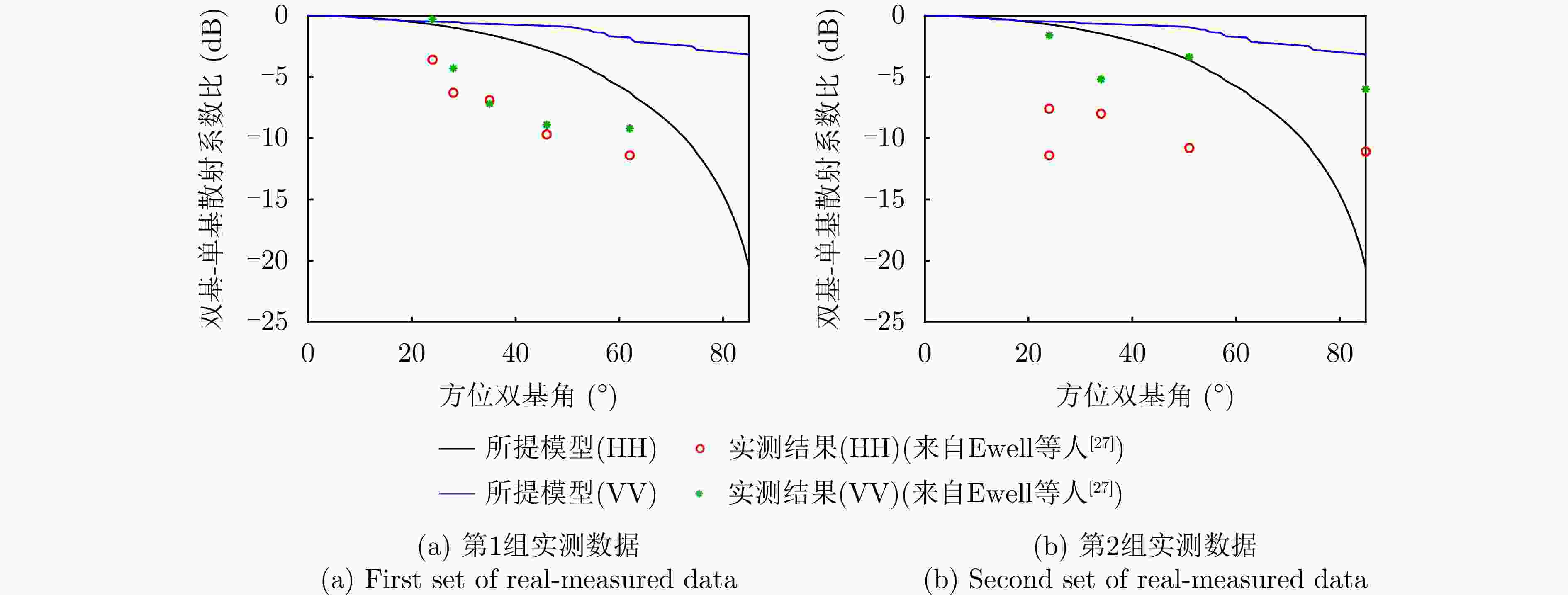
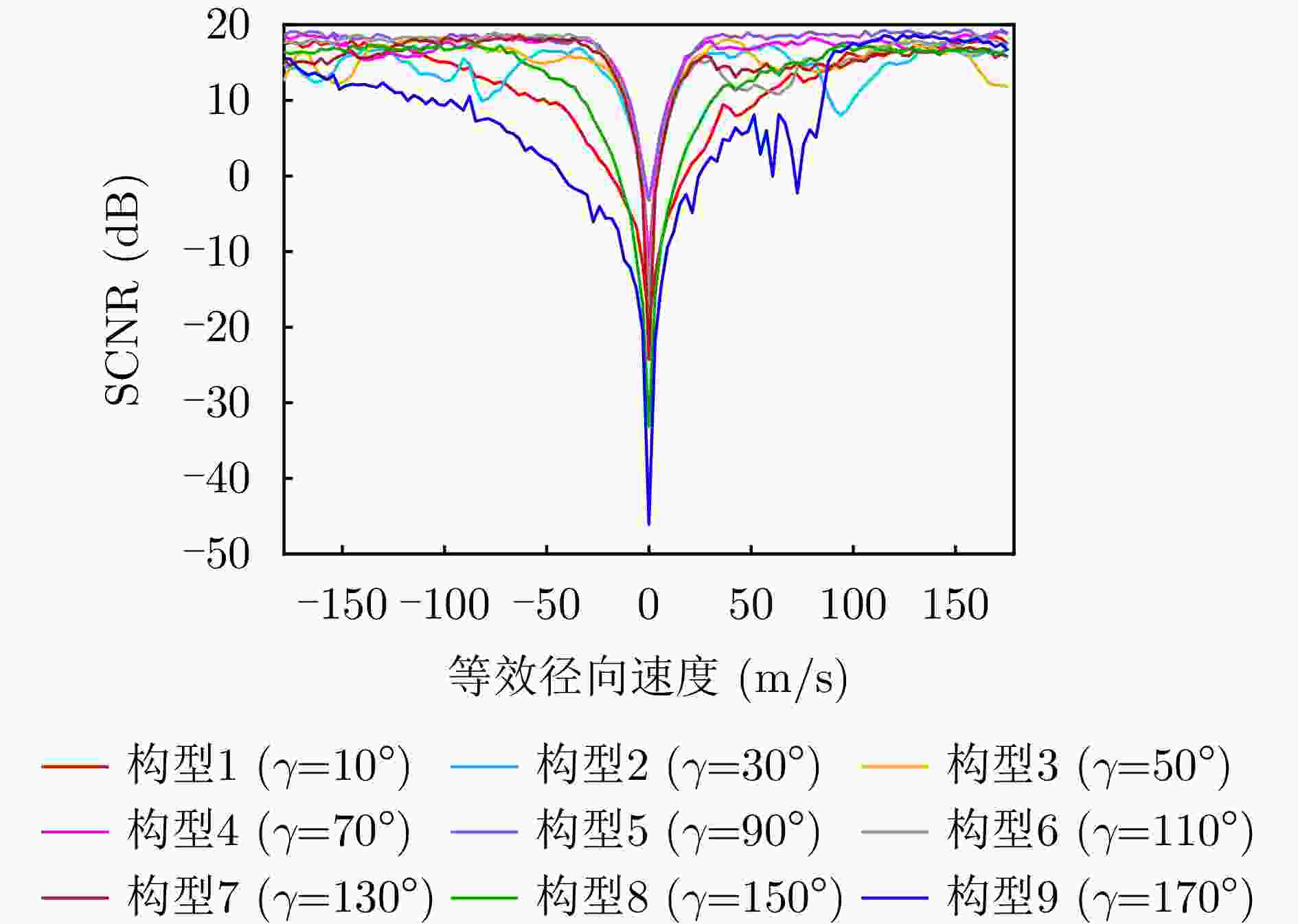
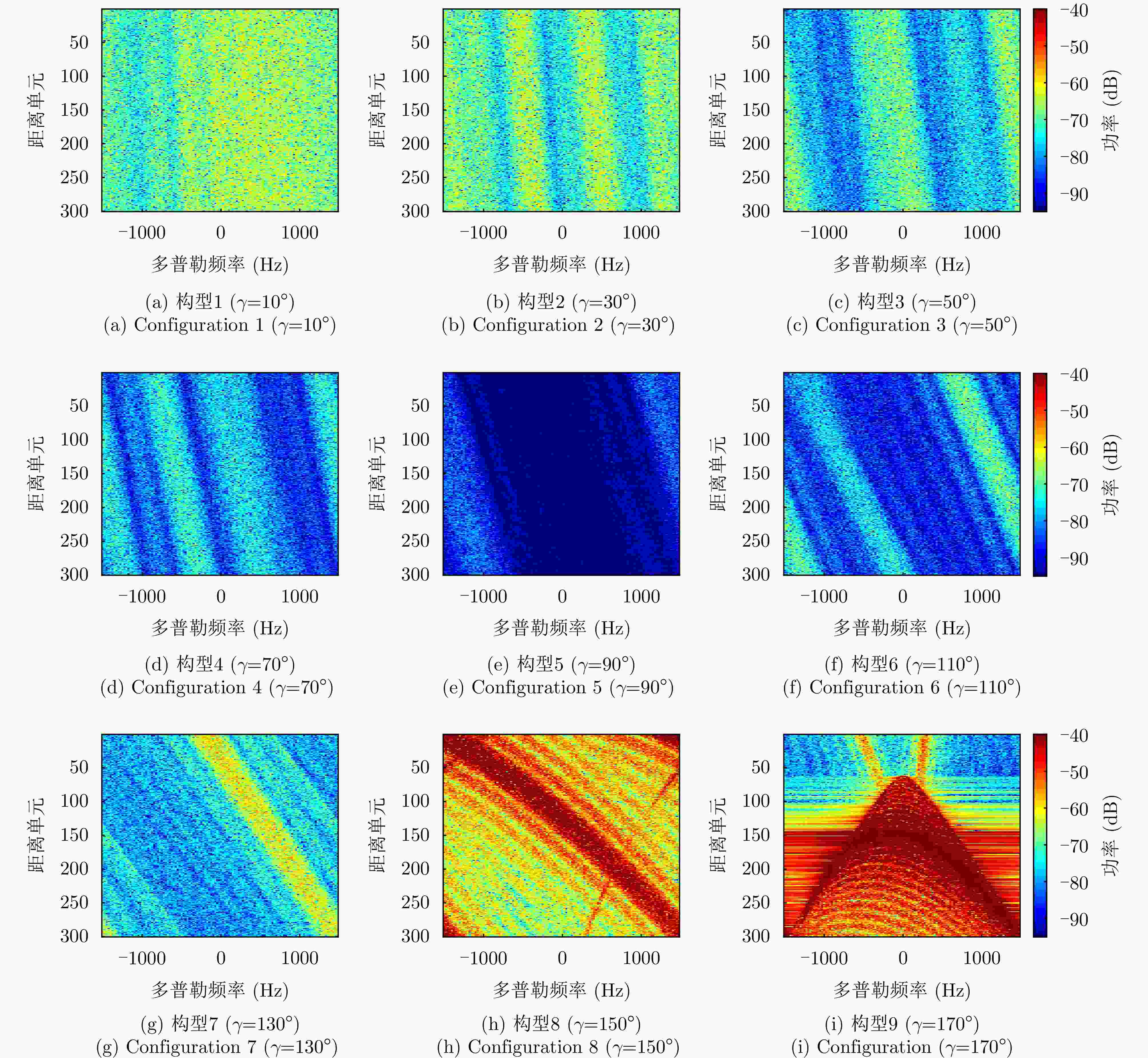
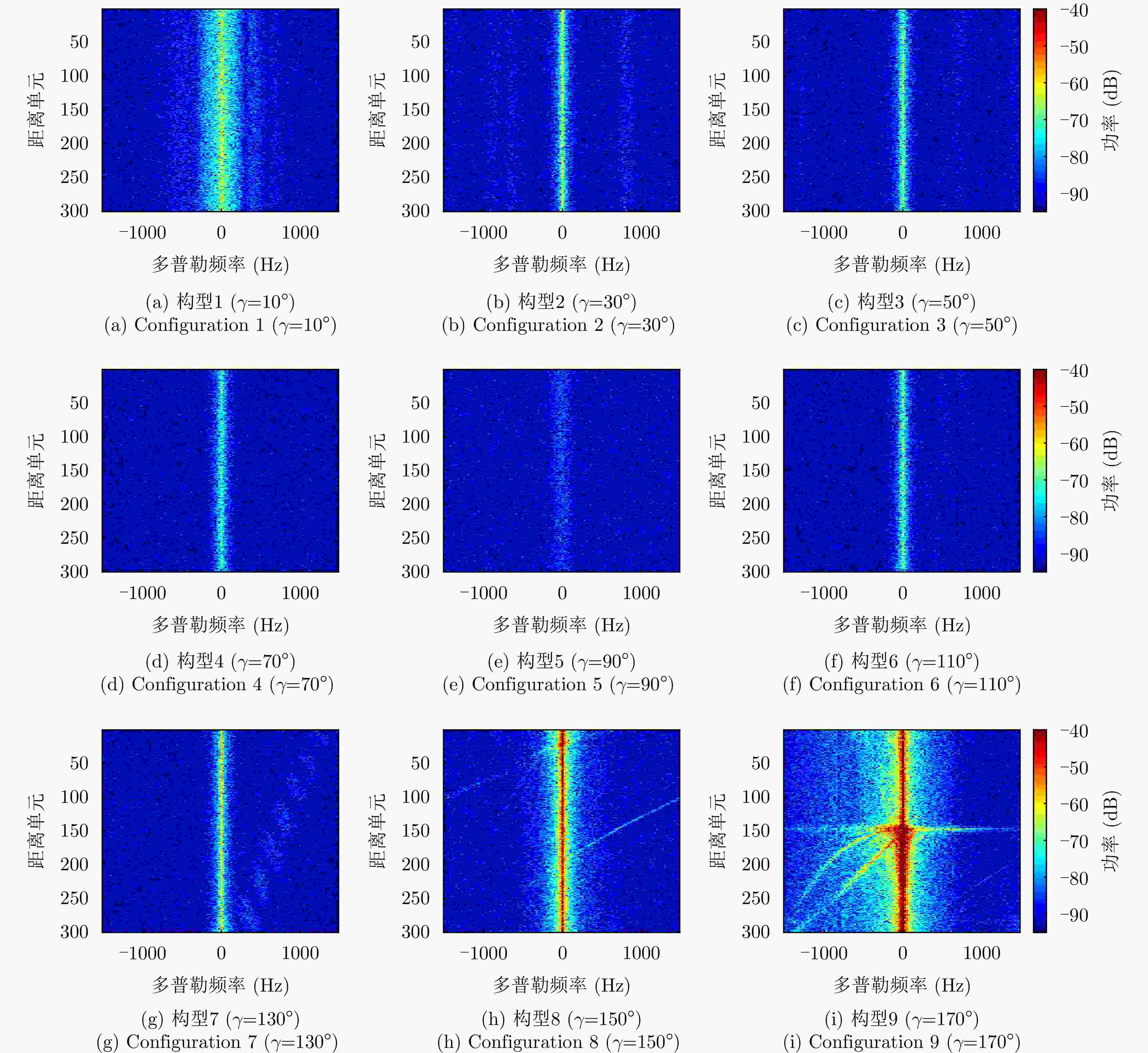
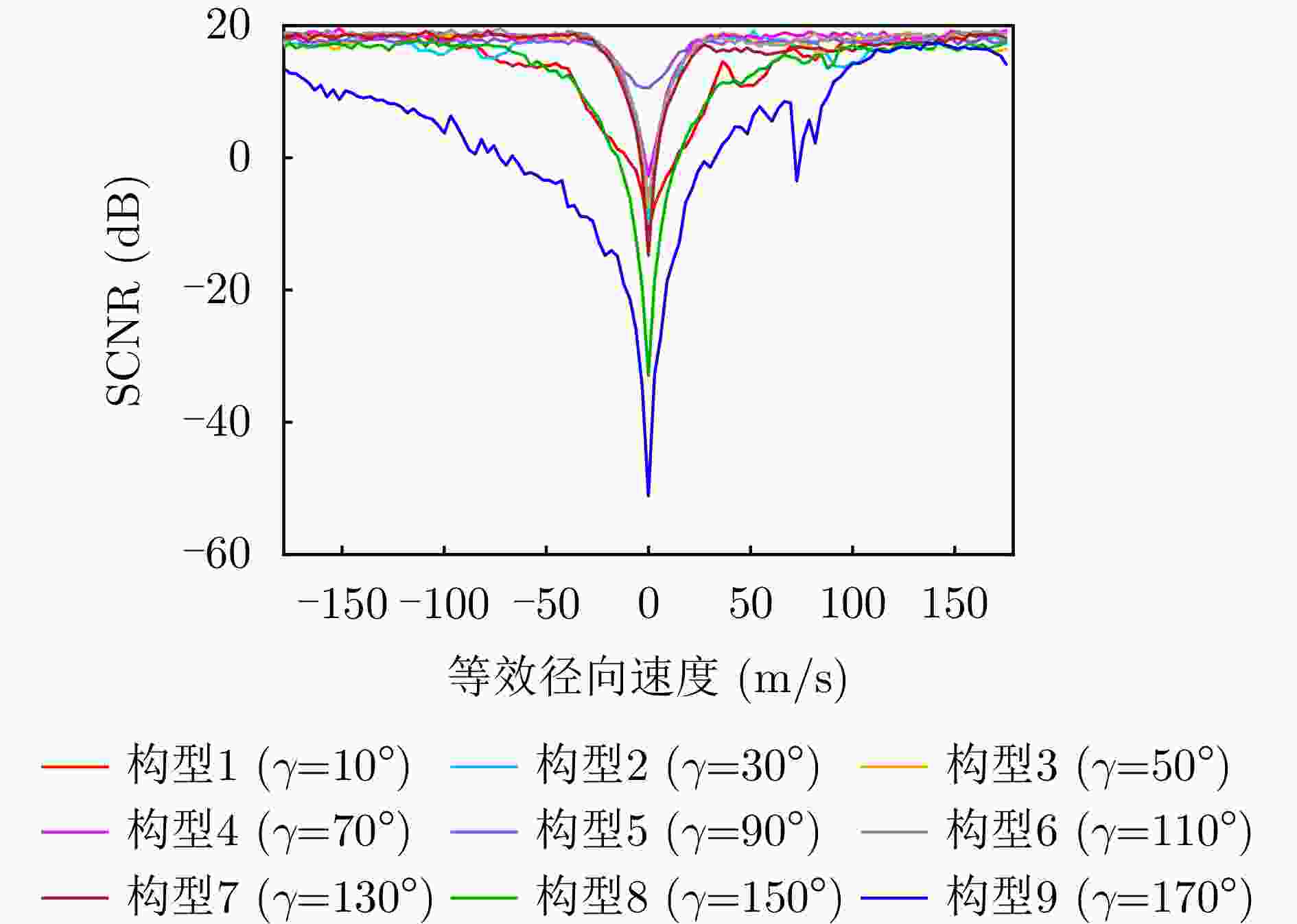
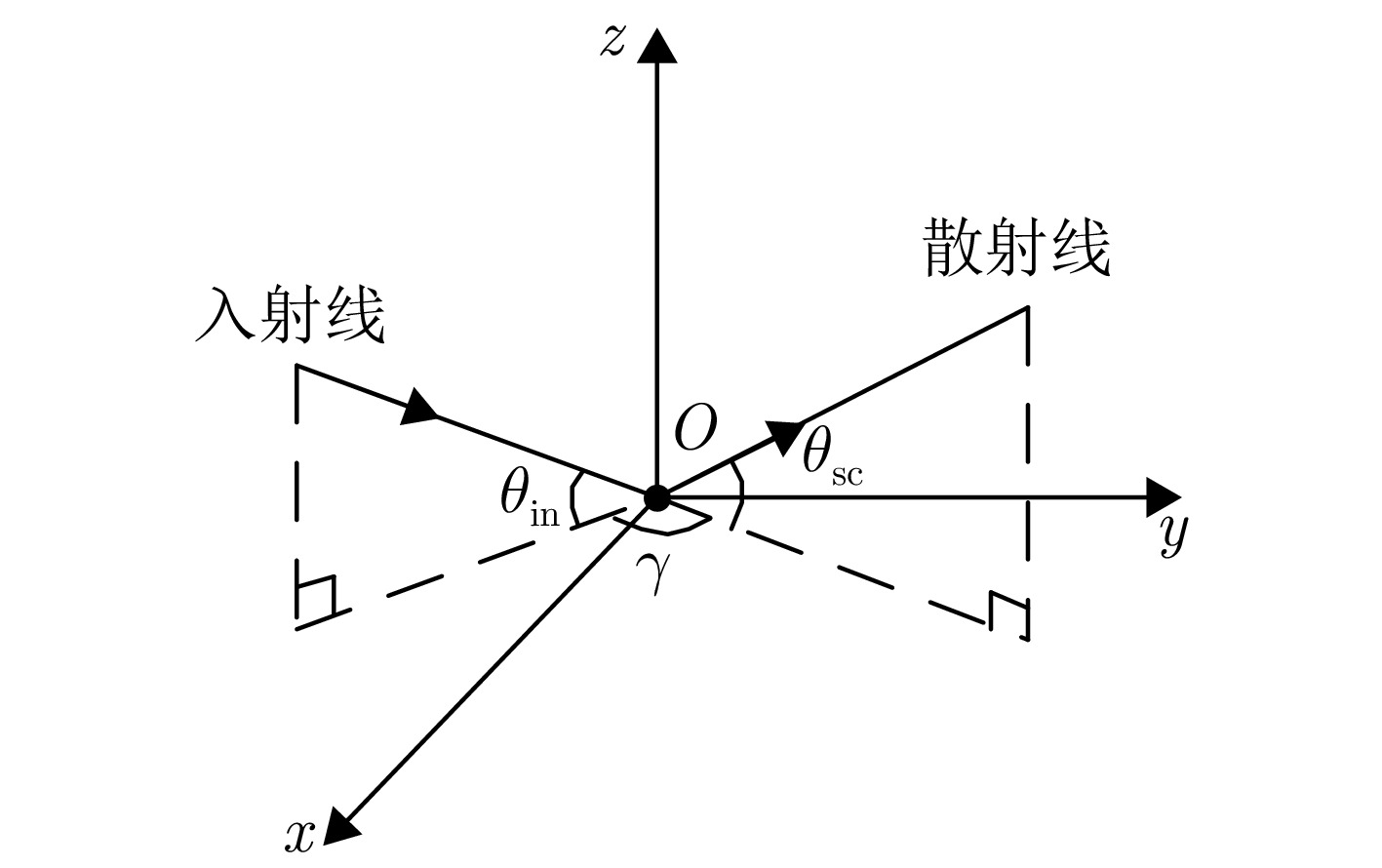
摘要: 针对传统星载单基雷达系统弱小动目标检测工程实现代价大以及抗干扰能力差等问题,星载双基雷达系统利用收发分置特点,通过大方位双基角观测构型有效提高目标的雷达散射截面积,同时有效提升处于“静默”状态的接收机抗干扰能力。然而,相比于星载单基雷达系统,星载双基雷达系统的收发分置构型将导致背景杂波回波特性呈现明显的差异。针对传统经验杂波散射系数模型难以体现散射系数随方位双基角的变化趋势这一问题,该文提出一种基于双尺度模型的半经验双基杂波散射系数模型。所提模型基于电磁散射理论将经验单基后向散射系数模型转换成双基散射系数模型,并基于双尺度模型对散射系数进行修正。该文通过现有文献中的双基杂波散射系数实测结果对所提模型的准确性进行了验证。基于所提双基杂波散射系数模型,该文通过空-时自适应处理杂波抑制方法对不同方位双基角下星载双基雷达的杂波抑制性能进行了仿真分析。根据仿真结果可知,在HH极化下,当方位双基角在30°~130°时,杂波抑制性能相对较好,当方位双基角达到150°以上时,主瓣杂波能量显著增强,使得杂波抑制性能受到明显影响。Abstract: Conventional spaceborne monostatic radar systems incur huge engineering costs to achieve small moving-target detection and low anti-interference ability. By manipulating the transmitter-receiver separation in a spaceborne bistatic radar system, the target radar cross section can be effectively improved by adopting a configuration with a large azimuth bistatic angle, and the anti-interference ability can be improved because the receiver does not transmit signals. However, the characteristics of the background clutter echo in a spaceborne bistatic radar system differ drastically from those in a spaceborne monostatic radar system because of the transmitter-receiver separation in the former. To overcome the limitations of existing empirical clutter scattering coefficient models, which typically do not capture the variation of scattering coefficient with azimuth bistatic angle, this study proposes a semiempirical bistatic clutter scattering coefficient model based on the two-scale model. In the proposed model, an empirical clutter backscattering coefficient model can be converted to a bistatic clutter scattering coefficient model based on electromagnetic scattering theories, and the bistatic scattering coefficient is further modified based on the two-scale model. The proposed model was validated using real measured data of bistatic clutter scattering coefficients obtained from existing literature. Using the proposed model, clutter suppression performance under different azimuth bistatic angles was analyzed by employing space-time adaptive processing in spaceborne bistatic radar systems. Reportedly, under HH polarization, the clutter suppression performance was relatively good when the azimuth bistatic angle was 30°~130°, whereas the clutter suppression performance was considerably affected by large-power main-lobe clutter when the azimuth bistatic angle was >150°.
-
表 1 雷达系统参数
Table 1. Radar system parameters
参数 数值/指标 雷达载频 1.26 GHz 极化方式 HH 信号带宽 3 MHz 采样频率 3.6 MHz 平均发射功率 4 kW 脉冲重复频率 3000 Hz积累时间内脉冲数 120 方位接收通道数 32 俯仰接收通道数 6 发射天线安装倾角 45° 接收天线安装倾角 45° 发射天线方位维/俯仰维尺寸 50 m/2 m 接收天线方位维/俯仰维尺寸 50 m/2 m 发射天线方位维/俯仰维加权 –13 dB/–13 dB(等幅加权) 接收天线方位维/俯仰维加权 –40 dB/–20 dB(切比雪夫加权) 发射天线幅度误差 0.5 dB 发射天线相位误差 5° 接收天线幅度误差 0.5 dB 接收天线相位误差 5° 噪声系数 2 dB 系统损耗 8 dB 表 2 发射卫星轨道参数与波束角度
Table 2. Orbital parameters and beam angles of transmitter
参数 数值 发射卫星轨道高度 508 km 发射卫星轨道倾角 90° 发射卫星轨道升交点赤经 9.24° 发射卫星轨道近地点辐角 0° 发射卫星真近点角 0° 发射波束中心下视角 60° 发射波束中心方位角 90° 表 3 接收卫星轨道参数与波束角度
Table 3. Orbital parameters and beam angles of receiver
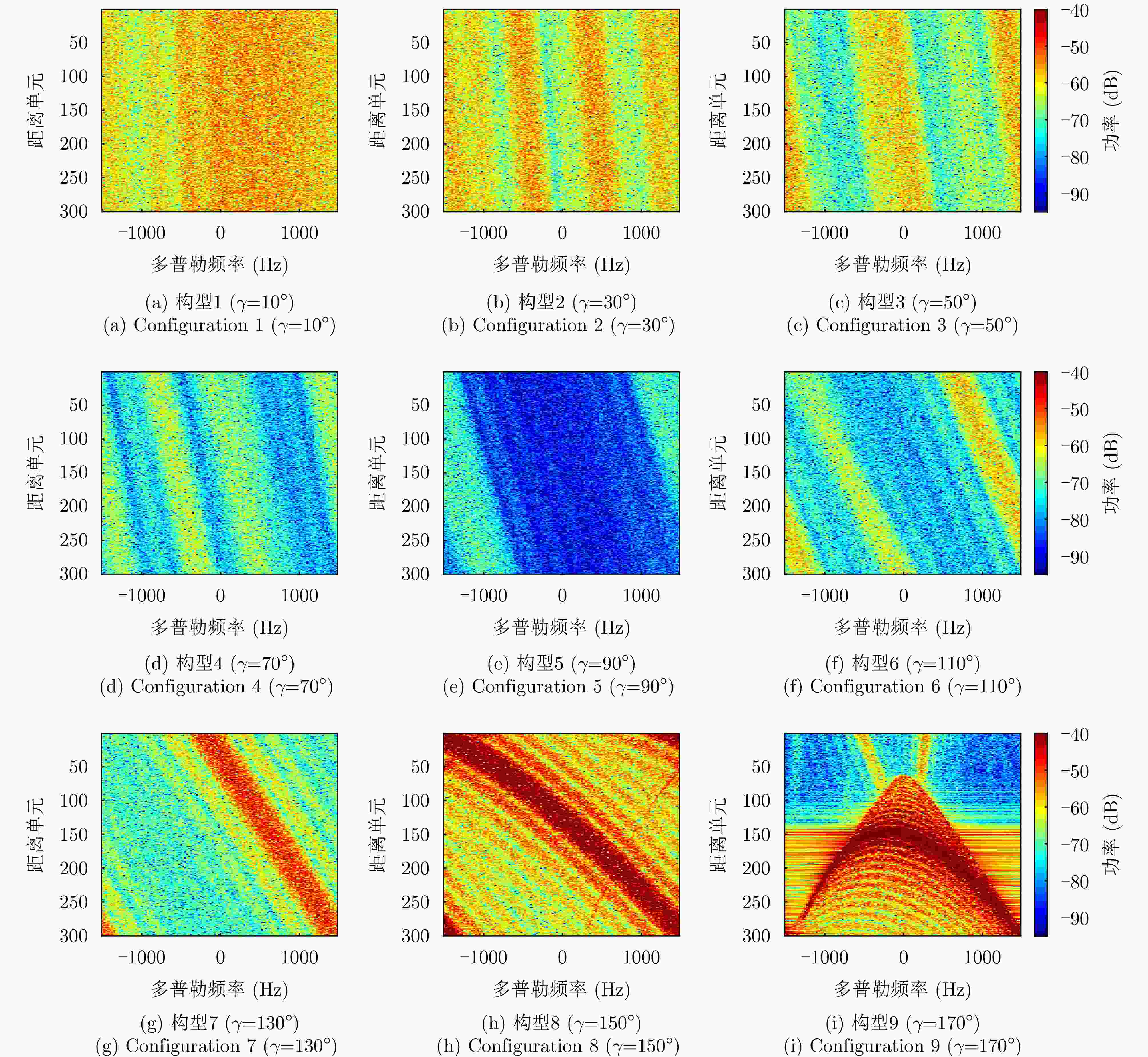
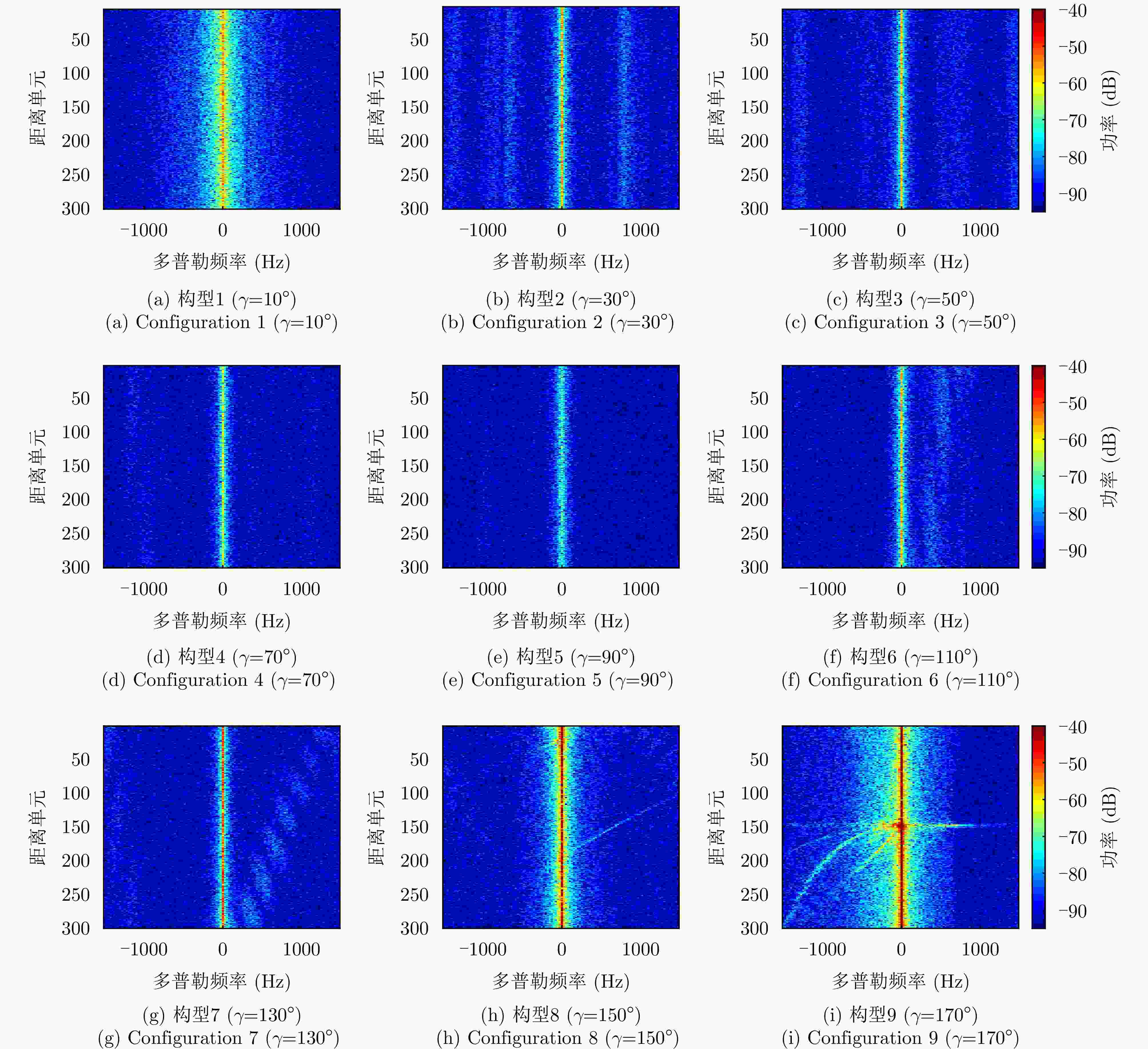
参数 构型1 构型2 构型3 构型4 构型5 构型6 构型7 构型8 构型9 接收卫星轨道高度(km) 508 508 508 508 508 508 508 508 508 接收卫星轨道倾角(°) 99.87 119.57 139.12 158.05 170.76 158.05 139.12 119.57 99.87 接收卫星轨道升交点赤经(°) 9.38 10.64 14.20 25.44 90.00 154.56 165.80 169.36 170.62 接收卫星轨道近地点辐角(°) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 接收卫星真近点角(°) 1.62 5.30 10.83 23.81 90.00 156.19 169.17 174.70 178.38 接收波束中心下视角(°) 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 接收波束中心方位角(°) 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 波束中心方位双基角(°) 10 30 50 70 90 110 130 150 170 表 4 不同星载双基构型下的目标MDV (丘陵杂波)
Table 4. Target MDVs under different bistatic configurations (hill clutter)
构型 目标MDV (m/s) 构型1 (γ=10°) 66.6 构型2 (γ=30°) 18.2 构型3 (γ=50°) 15.1 构型4 (γ=70°) 15.1 构型5 (γ=90°) 15.1 构型6 (γ=110°) 15.1 构型7 (γ=130°) 15.1 构型8 (γ=150°) 39.3 构型9 (γ=170°) 87.8 表 5 不同星载双基构型下的目标MDV (5级海况海杂波)
Table 5. Target MDVs under different bistatic configurations (5-level sea clutter)
构型 目标MDV (m/s) 构型1 (γ=10°) 33.3 构型2 (γ=30°) 15.1 构型3 (γ=50°) 15.1 构型4 (γ=70°) 12.1 构型5 (γ=90°) 6.1 构型6 (γ=110°) 12.1 构型7 (γ=130°) 15.1 构型8 (γ=150°) 39.3 构型9 (γ=170°) 93.8 -
[1] ROSEN P A and DAVIS M E. A joint space-borne radar technology demonstration mission for NASA and the air force[C]. 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.03TH8652), Big Sky, USA, 2003: 437–444. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2003.1235073. [2] FIEDLER S and PREISS B. Geosynchronous space based radar concept development for theater surveillance[C]. 1996 IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference. Proceedings, Aspen, USA, 1996: 77–90. doi: 10.1109/AERO.1996.499404. [3] 王增福, 杨广宇, 金术玲. 考虑综合性能最优的非短视快速天基雷达多目标跟踪资源调度算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 253–269. doi: 10.12000/JR23162.WANG Zengfu, YANG Guangyu, and JIN Shuling. A non-myopic and fast resource scheduling algorithm for multi-target tracking of space-based radar considering optimal integrated performance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 253–269. doi: 10.12000/JR23162. [4] ZOU Zihao, MA Jingtao, HUANG Penghui, et al. Multichannel sea clutter modeling and clutter suppression performance analysis for spaceborne bistatic surveillance radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5108424. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3424562. [5] WANG Jianbo, YE Jianyu, WU Xiaoliang, et al. RCS statistical modeling of stealth targets based on fractional-order Legendre polynomials[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9807–9820. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3309613. [6] ZHU Lei, LIANG Xiaolong, LI Jiong, et al. Simulation analysis on static scattering characteristics of stealth aircraft[C]. 2016 IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Xi’an, China, 2016: 1774–1778. doi: 10.1109/IMCEC.2016.7867524. [7] GUTTRICH G L, SIEVERS W E, and TOMLJANOVICH N M. Wide area surveillance concepts based on geosynchronous illumination and bistatic unmanned airborne vehicles or satellite reception[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 126–131. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1997.588225. [8] BARTON D K. Land clutter models for radar design and analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1985, 73(2): 198–204. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1985.13133. [9] MORCHIN W C. Airborne Early Warning Radar[M]. Norwood, USA: Artech House, 1990: 147–153. [10] HORST M M, DYER F B, and TULEY M T. Radar sea clutter model[C]. International IEEE AP/S URSI Symposium, Washington, USA, 1978: 6–10. [11] ANTIPOV I. Simulation of sea clutter returns[R]. DSTO-TR-0679, 1998. [12] REILLY J P and DOCKERY G D. Influence of evaporation ducts on radar sea return[J]. IEE Proceedings F—Radar and Signal Processing, 1990, 137(2): 80–88. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1990.0012. [13] GREGERS-HANSEN V and MITAL R. An improved empirical model for radar sea clutter reflectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3512–3524. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324732. [14] WILLIS N J. Bistatic Radar[M]. 2nd ed. Raleigh, USA: SciTech, 2005: 157–171. [15] AL-ASHWAL W A, GRIFFITHS H D, and WOODBRIDGE K. An empirical model for bistatic sea clutter normalised radar cross section[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp.2012.1672. [16] GRIFFITHS H D, AL-ASHWAL W A, WARD K D, et al. Measurement and modelling of bistatic radar sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 280–292. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0124. [17] 谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073.XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar: An overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073. [18] JOHNSON J T, BAKER C J, SMITH G E, et al. The monostatic-bistatic equivalence theorem and bistatic radar clutter[C]. 2014 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2014: 105–108. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD.2014.6991218. [19] JOHNSON J T and OUELLETTE J D. Polarization features in bistatic scattering from rough surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1616–1626. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2252909. [20] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill, 2008: 15.30–15.32. [21] PIERSON W J and MOSKOWITZ L. A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(24): 5181–5190. doi: 10.1029/JZ069i024p05181. [22] CHASE J, COTE L J, MARKS W, et al. The directional spectrum of a wind generated sea as determined from data obtained by the Stereo Wave Observation Project[R]. 1957. [23] LARSON R W, MAFFETT A L, HEIMILLER R C, et al. Bistatic clutter measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1978, 26(6): 801–804. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1978.1141947. [24] ULABY F T, VAN DEVENTER T E, EAST J R, et al. Millimeter-wave bistatic scattering from ground and vegetation targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1988, 26(3): 229–243. doi: 10.1109/36.3026. [25] COST S T. Measurements of the bistatic echo area of terrain at X-band[R]. 1965. [26] DOMVILLE A R. The bistatic reflection from land and sea of X-band radio waves[R]. 1967. [27] EWELL G W. Bistatic Radar Cross Section Measurements[M]. CURRIE N C. Techniques of Radar Reflectivity Measurement. Dedham, USA: Artech House, 1984: Chapter 7. [28] HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, RAQUET J F, et al. Localized three-dimensional adaptive spatial-temporal processing for airborne radar[C]. RADAR 2002, Edinburgh, UK, 2002: 191–195. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2002.1174680. [29] 段克清, 李雨凡, 杨兴家, 等. 天基预警雷达低自由度STAP方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 871–883. doi: 10.12000/JR22075.DUAN Keqing, LI Yufan, YANG Xingjia, et al. Reduced degrees of freedom in space-time adaptive processing for space-based early warning radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 871–883. doi: 10.12000/JR22075. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: