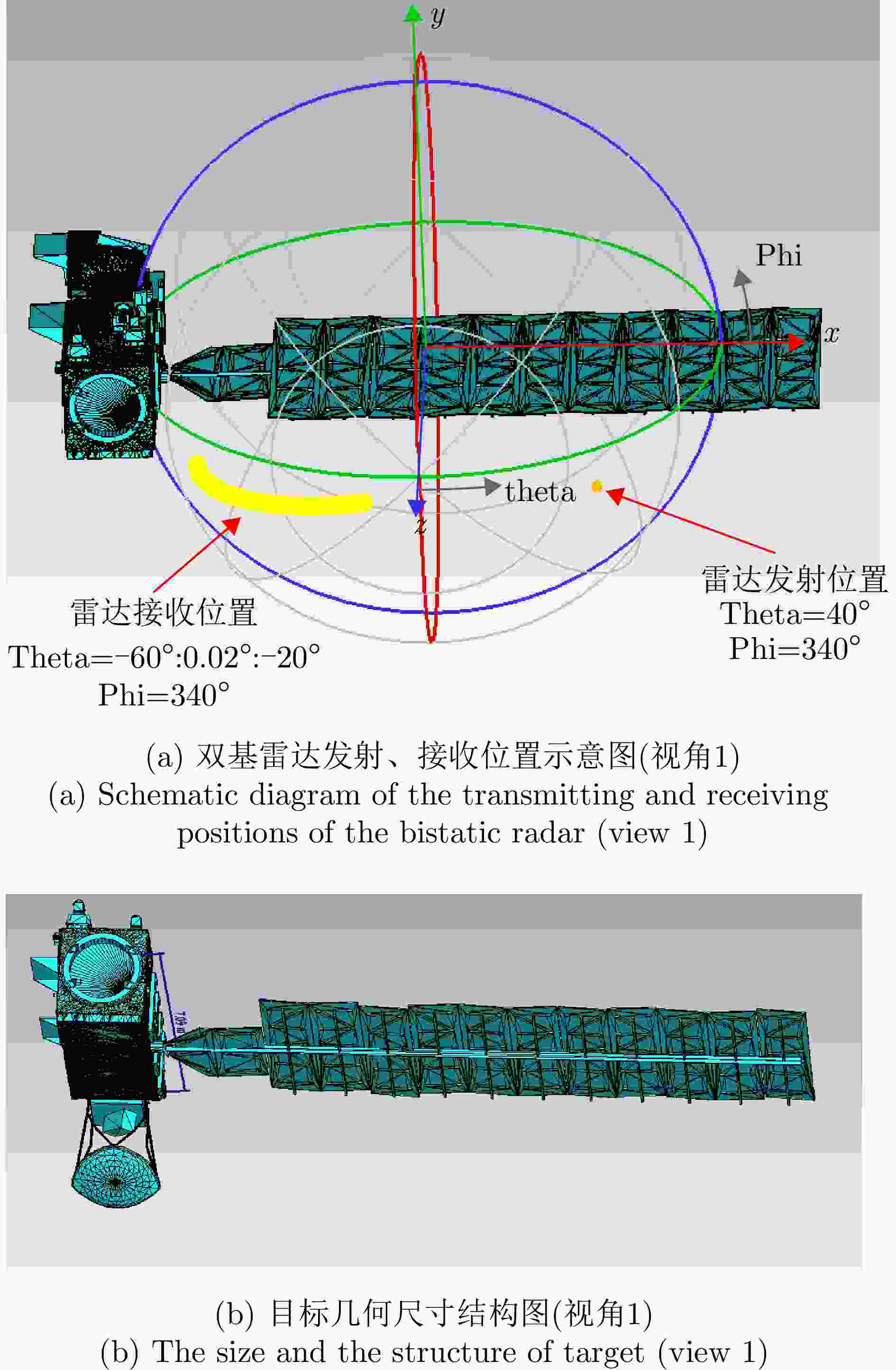
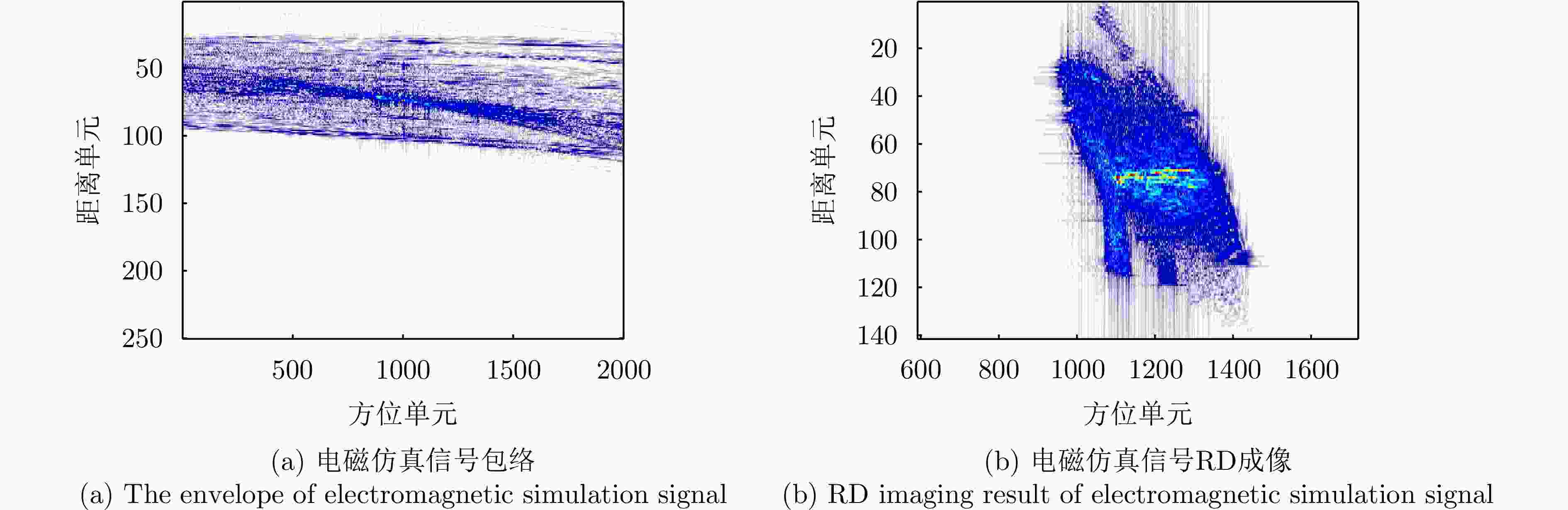
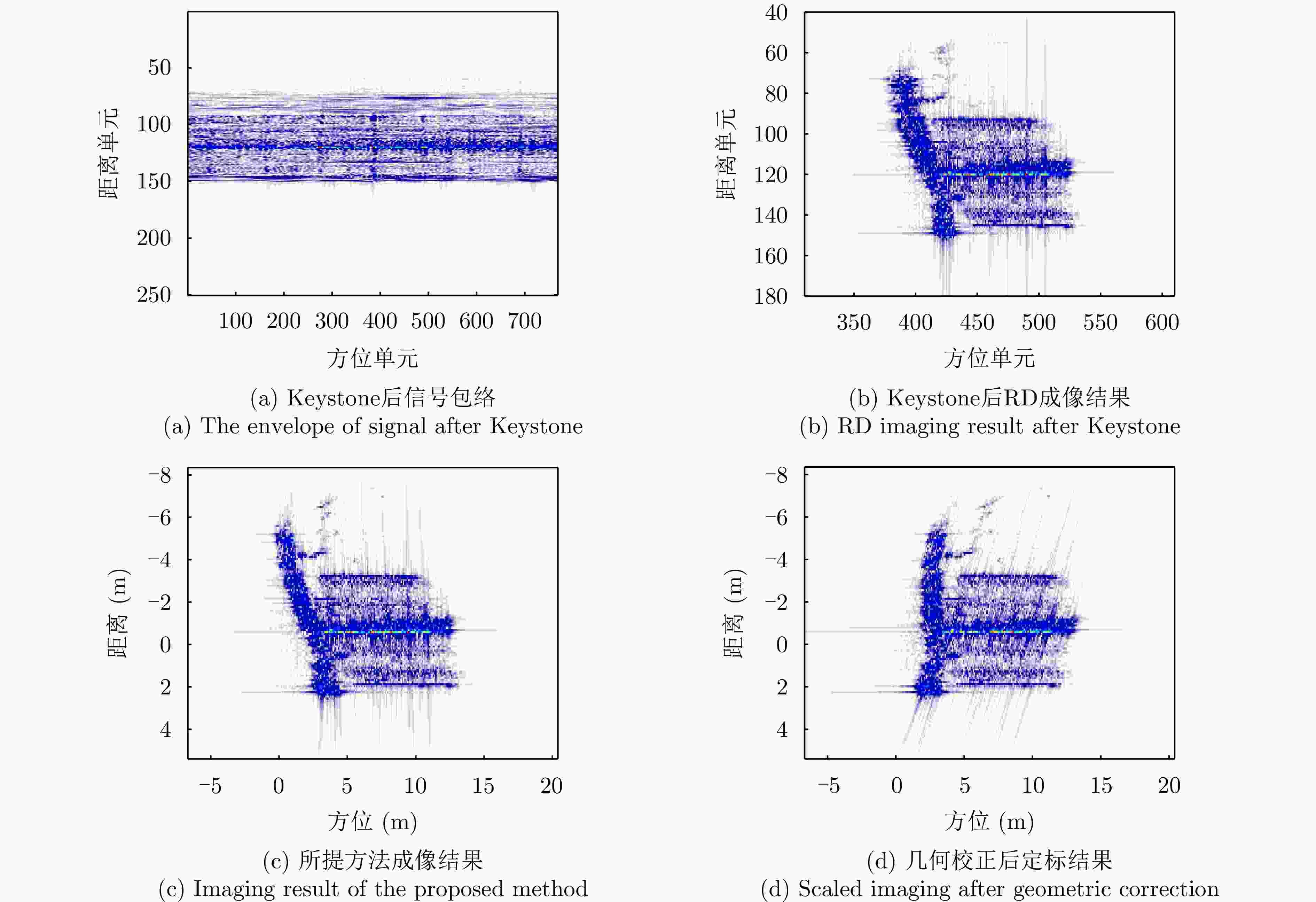
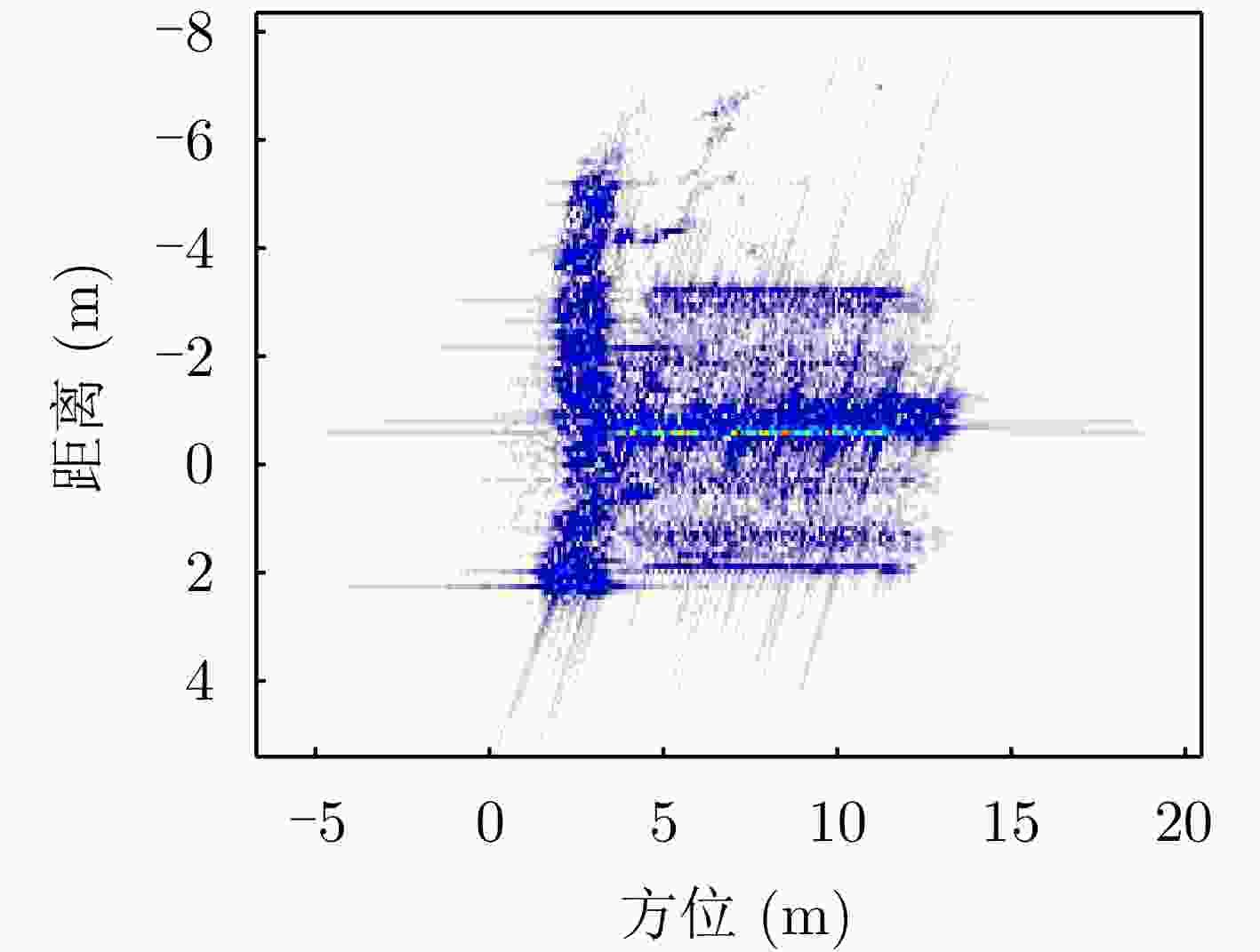
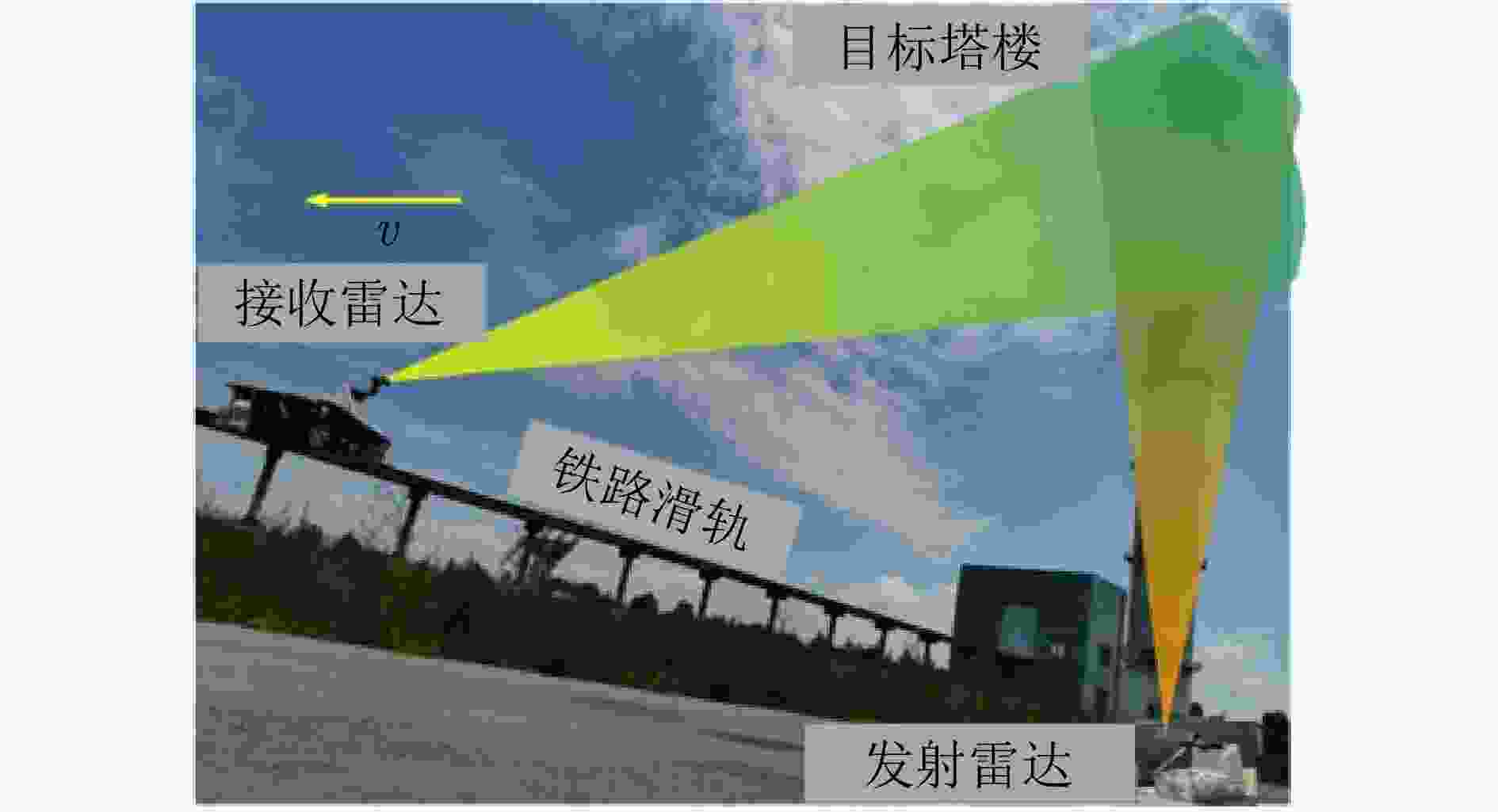
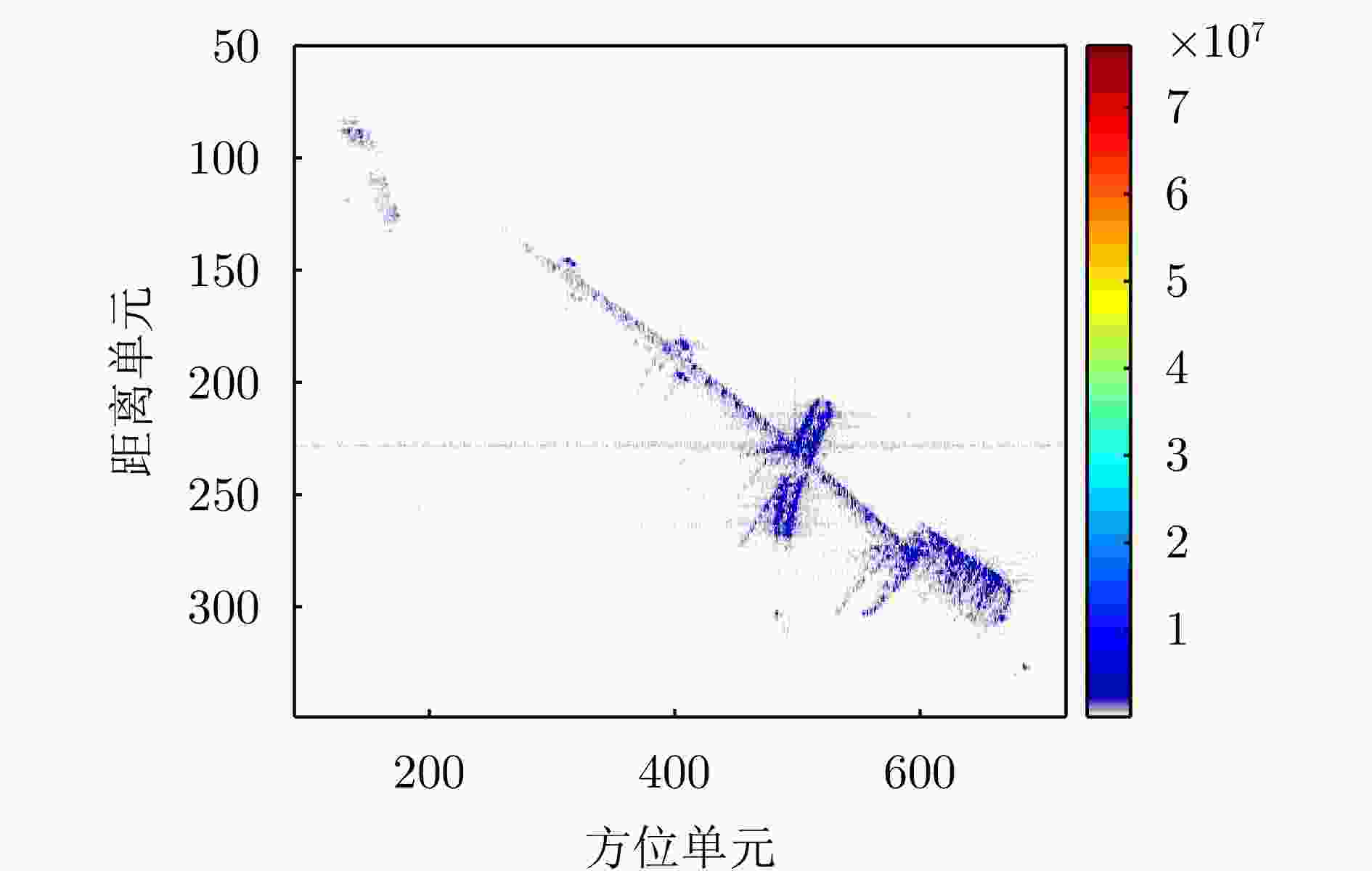
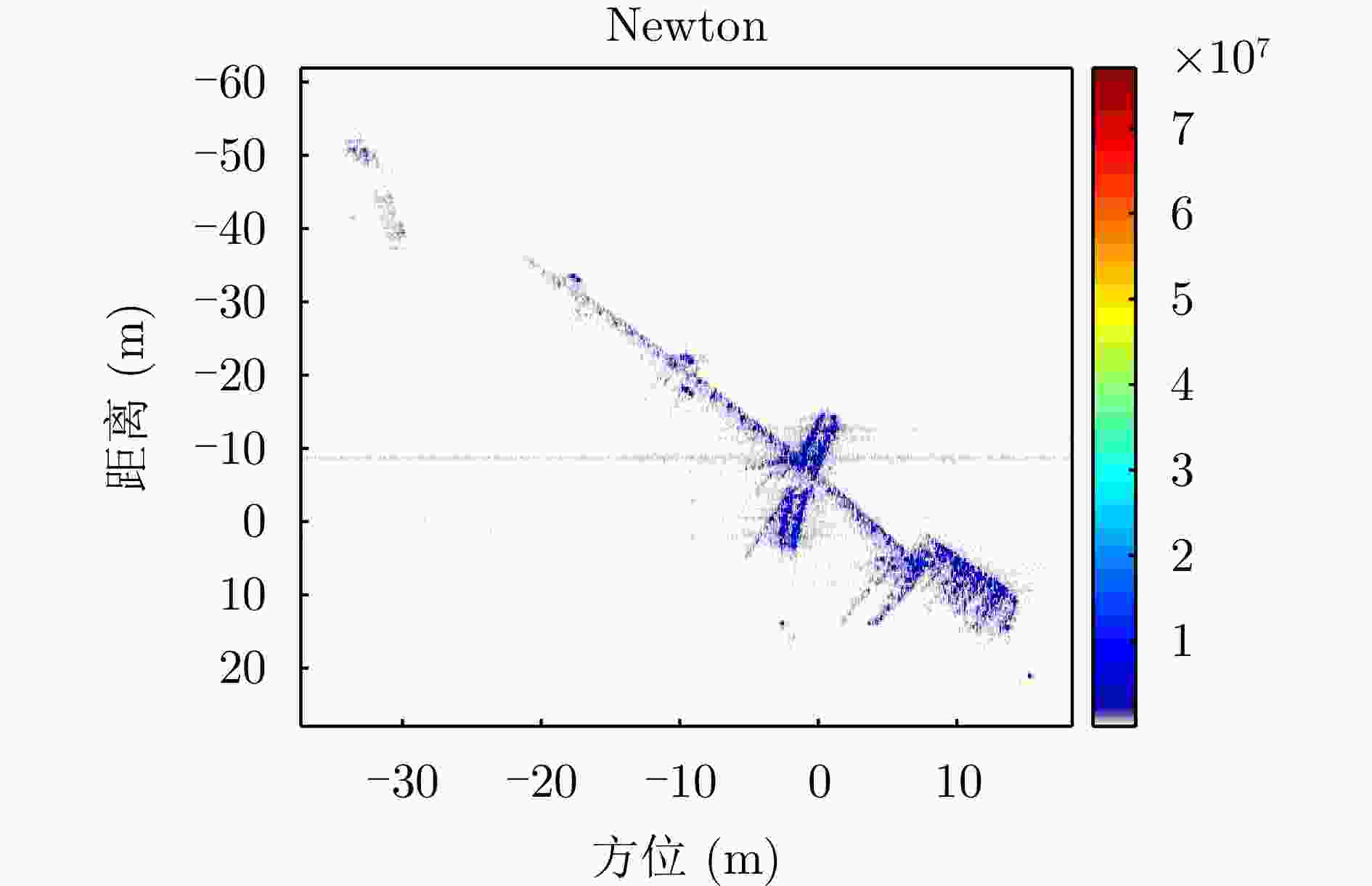
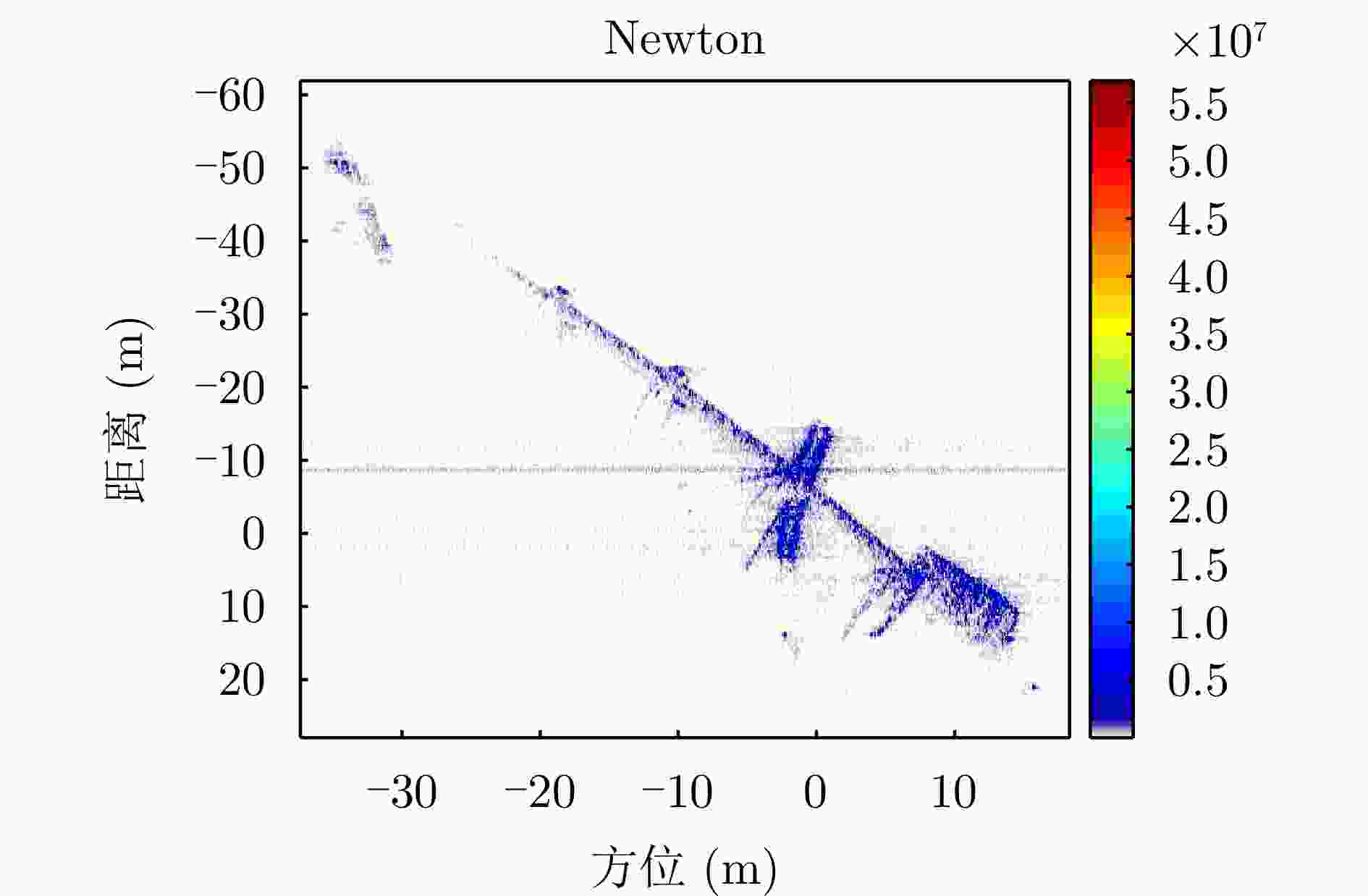
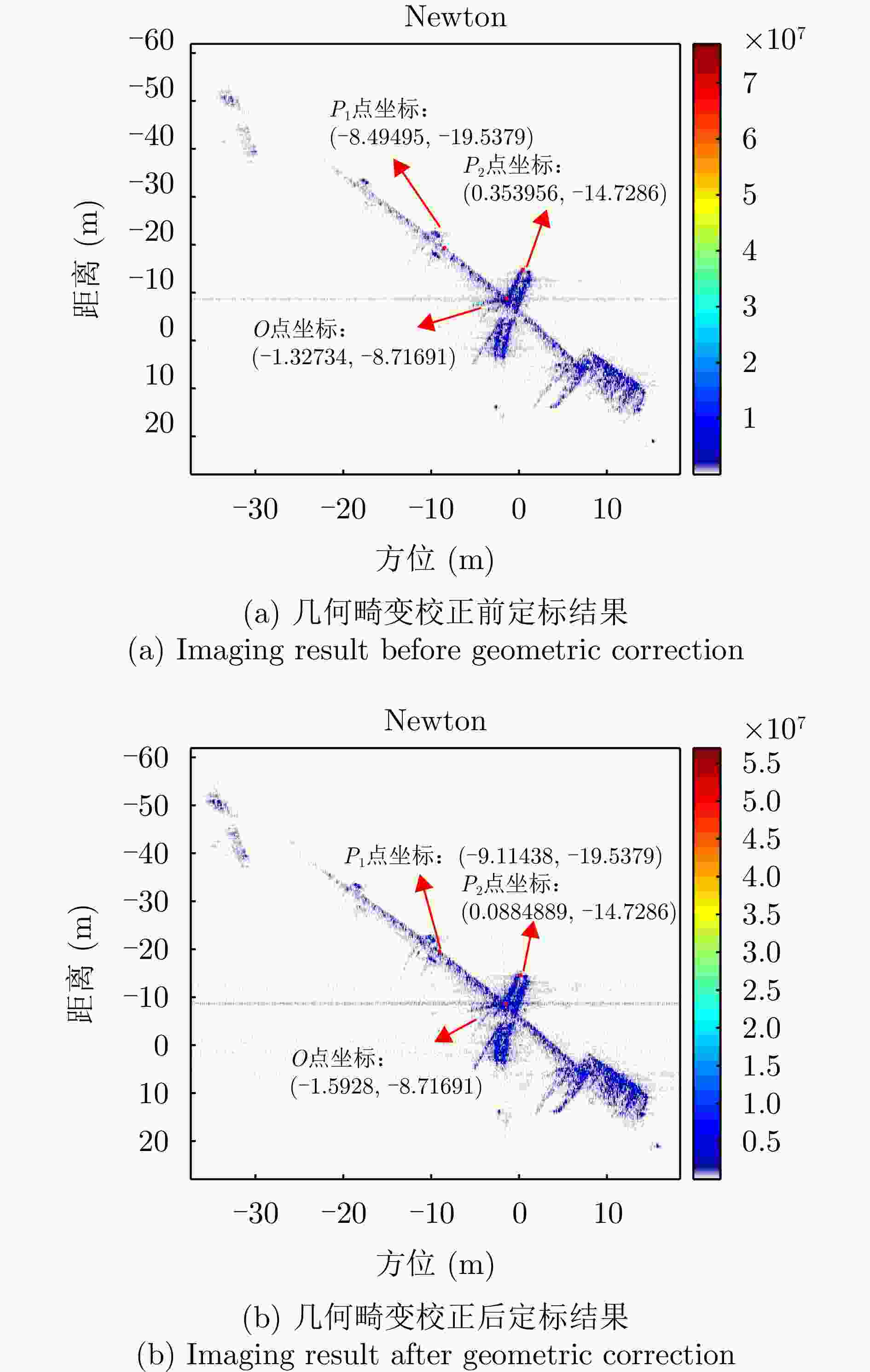
Fast Space-variant Phase Error Compensation and Geometric Correction for Bistatic ISAR Imaging Using a Modified Newton’s Method
-
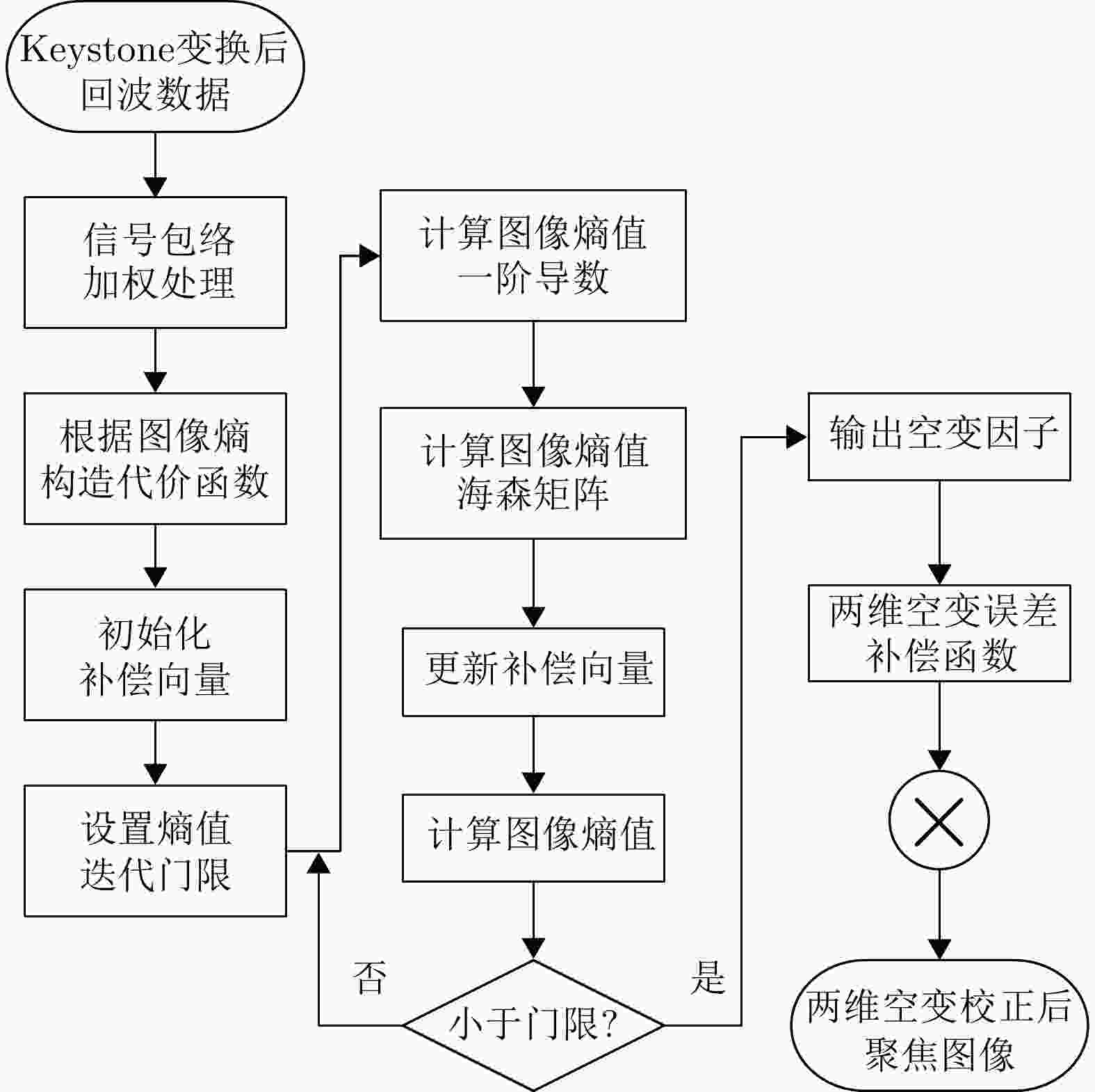
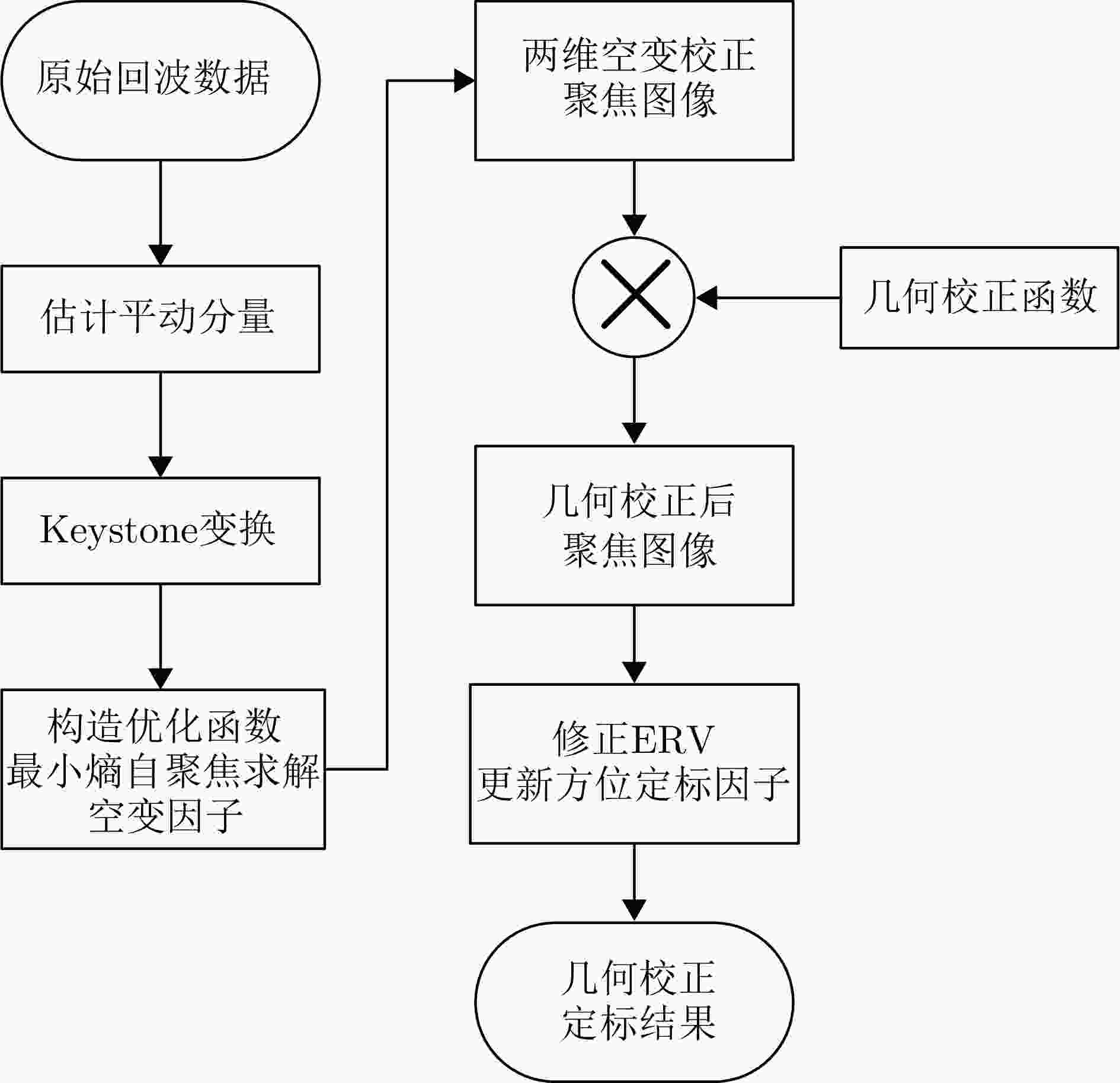
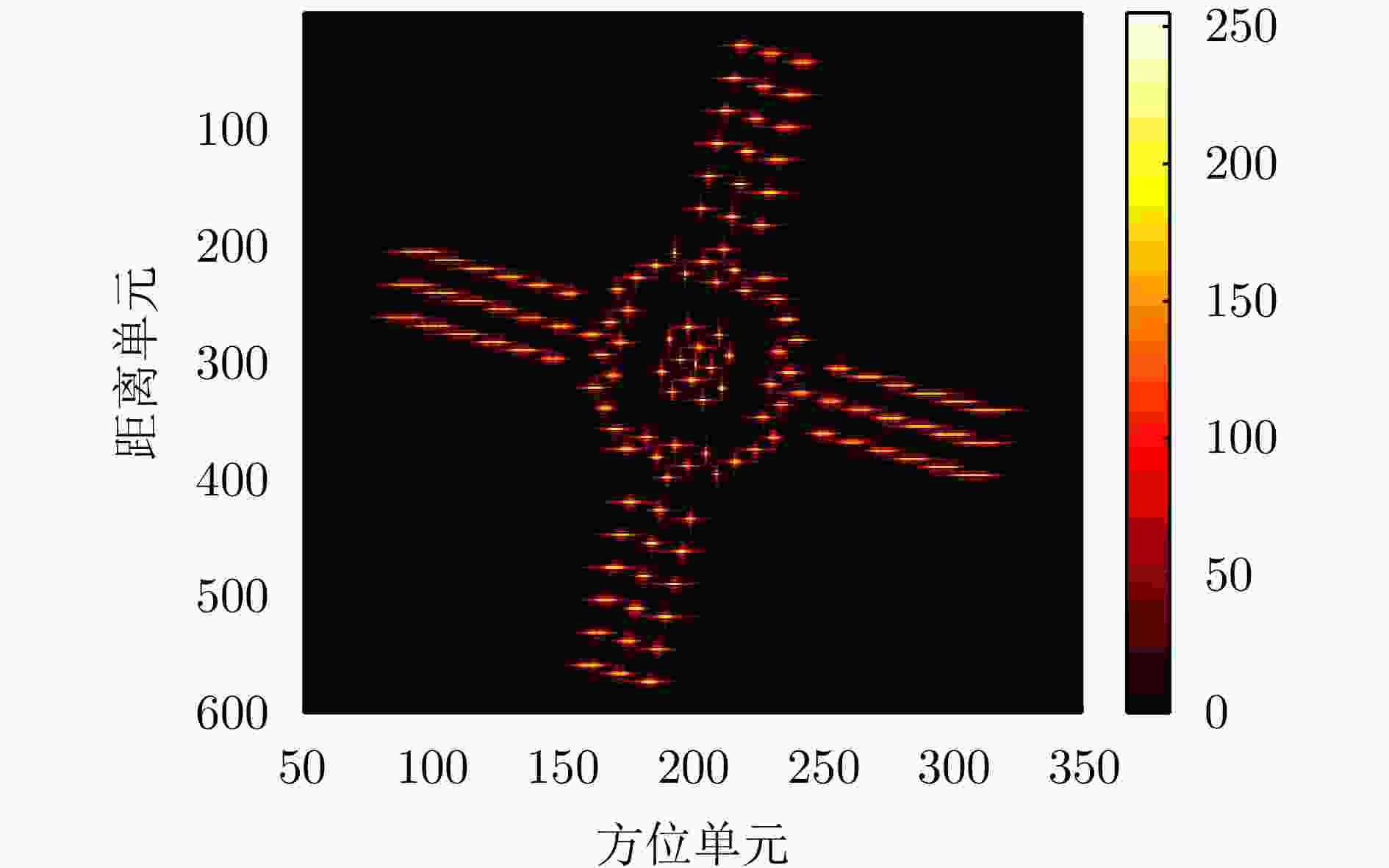
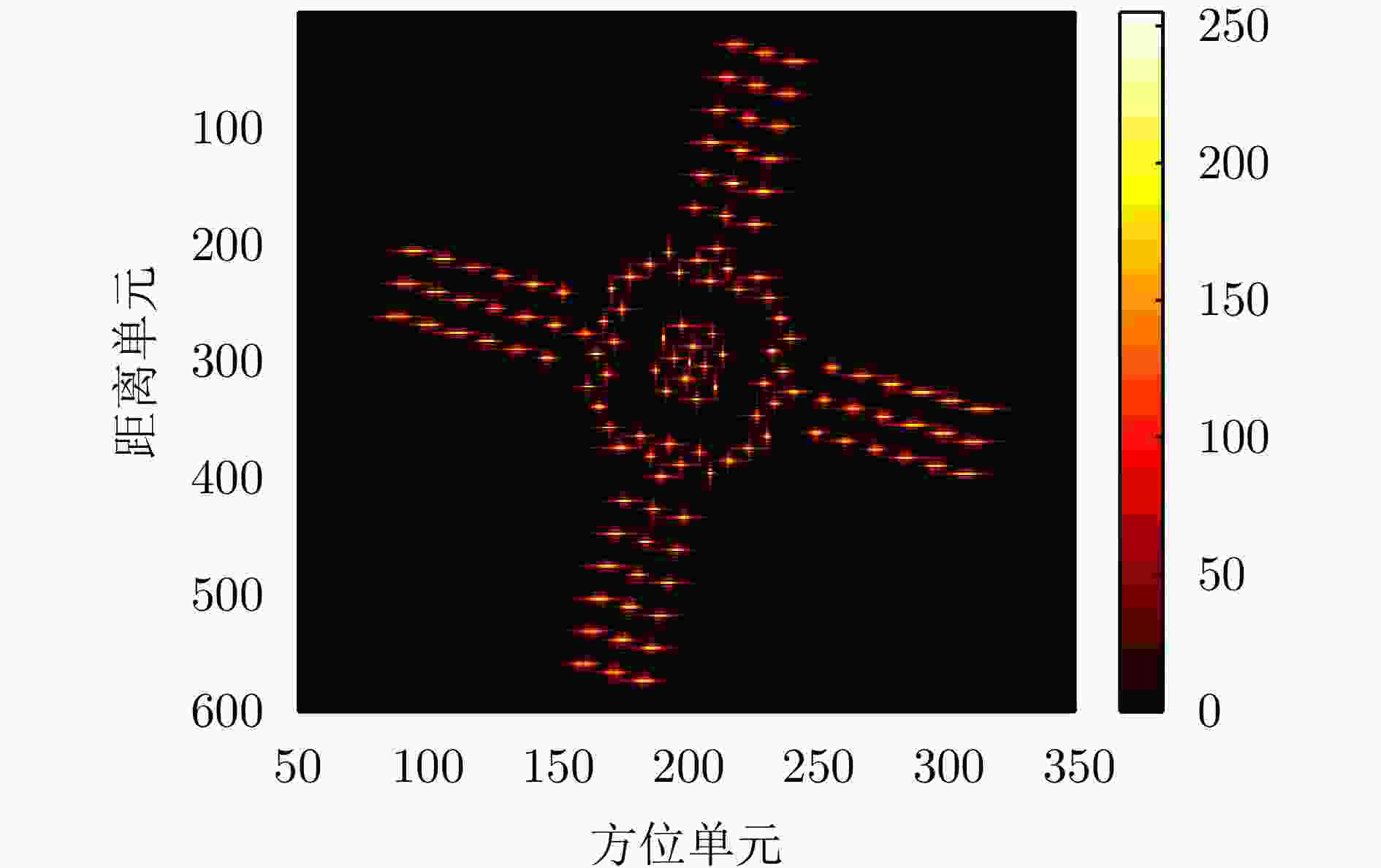
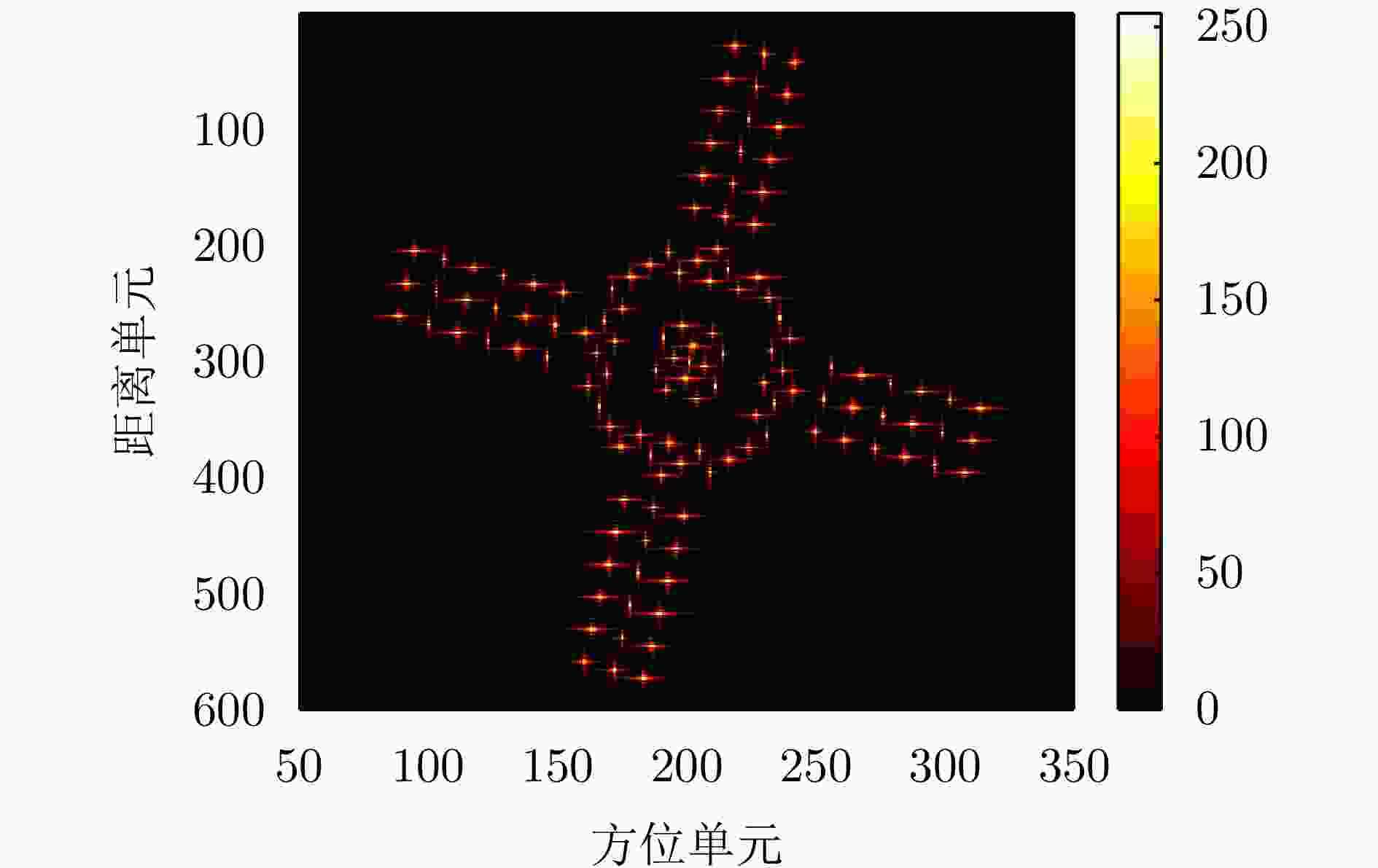
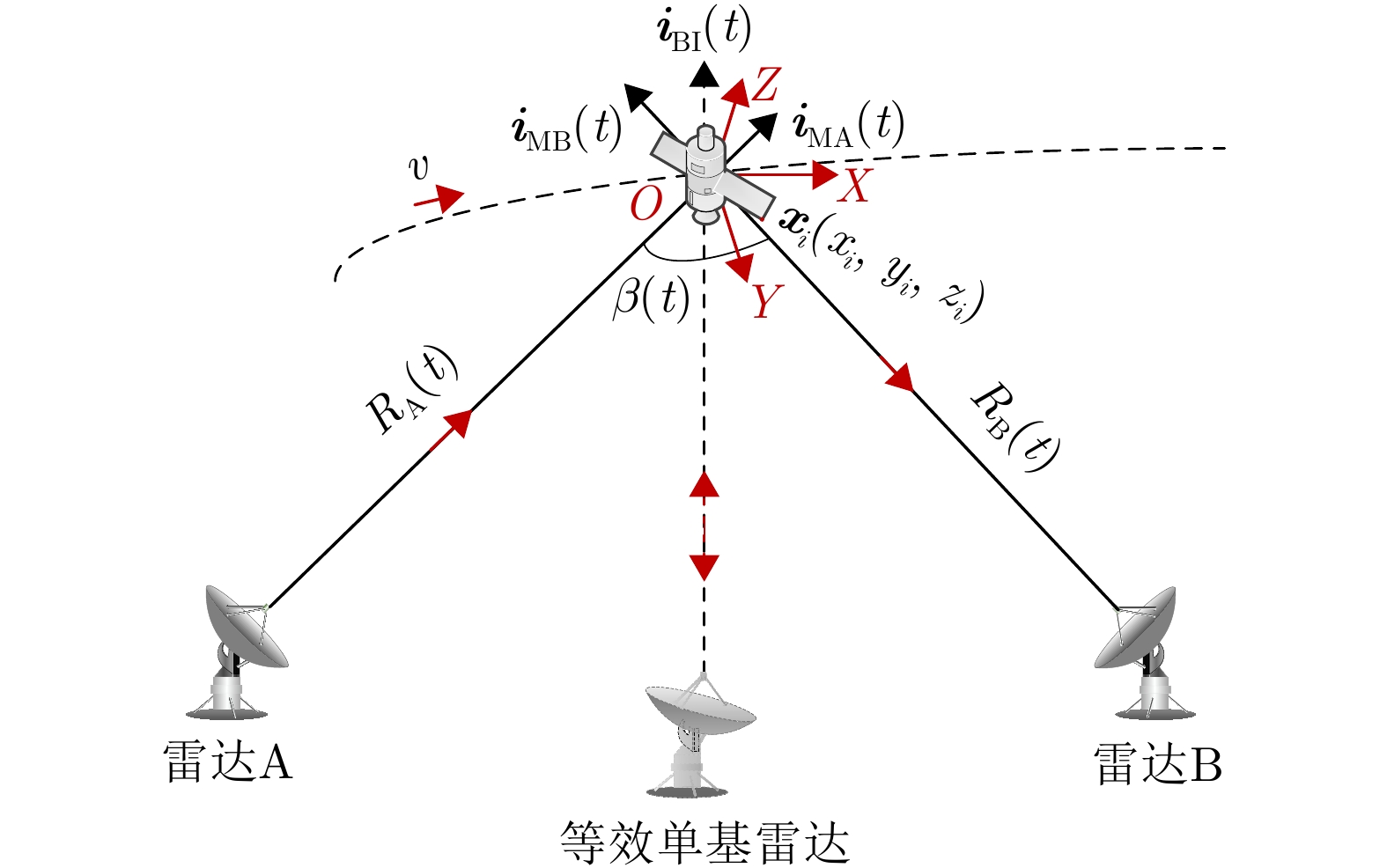
摘要: 双基逆合成孔径雷达(Bi-ISAR)因其卓越的反隐身与抗干扰性能,受到广泛关注。然而,Bi-ISAR成像过程中双基角的变化会导致图像出现空变散焦和几何畸变,严重影响后续信息提取与目标识别的精度。为解决上述问题,该文提出了一种基于修正牛顿法的Bi-ISAR空变补偿快速成像与几何校正图像定标方法。该方法以Bi-ISAR成像结果的图像熵为代价函数,以空变系数和转动参数为优化变量,构建优化方程。通过对传统牛顿法进行修正,确保海森矩阵的正定性,从而保证代价函数在每次迭代中沿下降方向优化。通过求解该优化方程最小化图像熵,同时估计得到转动参数,进而构建几何校正函数并计算分辨率因子,实现对最终成像结果的几何校正与定标。所提方法可同步校正空变散焦误差与几何畸变,且为数据驱动模式(无需先验参数),对初始图像质量要求较低。此外,受益于牛顿法的二次收敛特性,相较于其他方法,该方法具有更高的计算效率。最后,通过对点目标仿真、电磁计算以及地面等效实验数据的处理与对比分析,验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Bistatic Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (Bi-ISAR) has garnered significant attention in the military and civilian domains due to its superior stealth and antijamming capabilities. However, the changing bistatic angle during Bi-ISAR imaging causes space-variant defocusing and geometric distortion in the resulting images, thereby severely compromising the accuracy of subsequent information extraction and target recognition. To address these issues, this study proposes a fast space-variant phase error compensation and geometric correction method for Bi-ISAR imaging based on a modified Newton’s method. This method uses the image entropy of the Bi-ISAR imaging result as the cost function and introduces space-variant coefficients and rotation parameters as optimization variables to formulate an optimization equation. By modifying the traditional Newton’s method to ensure the positive definiteness of the Hessian matrix, the cost function is guaranteed to be optimized along the descent direction in each iteration. Solving this optimization equation to minimize image entropy simultaneously estimates the rotation parameters, which are then used to construct a geometric correction function and calculate the scaling factor, that is, the actual size of each grid in the image, enabling geometric correction and scaling of the final imaging result. The proposed method simultaneously corrects space-variant phase errors and geometric distortion and operates in a data-driven manner, requiring only low initial image quality. Furthermore, due to the quadratic convergence property of Newton’s method, the proposed method offers higher computational efficiency compared with other methods. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through the processing and comparative analysis of the point target simulation, electromagnetic calculation, and ground real target experimental data.
-
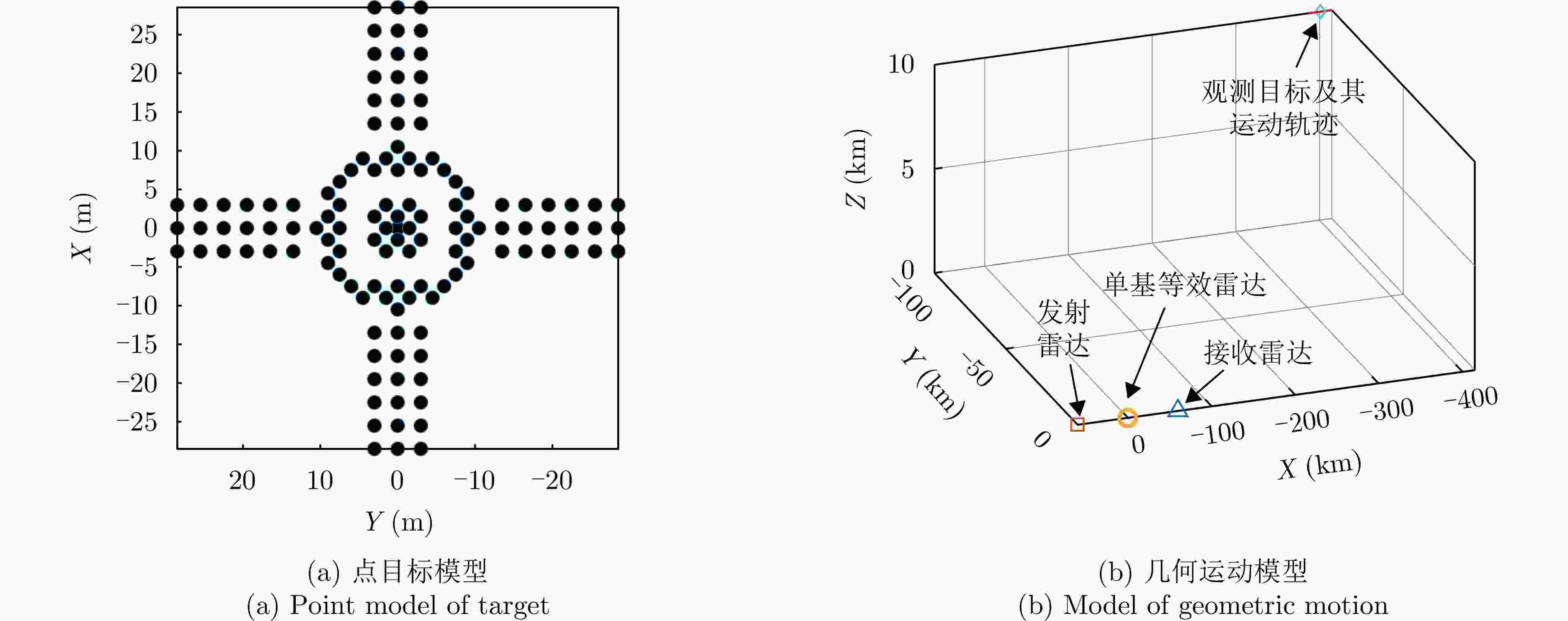
表 1 仿真雷达参数表
Table 1. Parameters of simulated radar
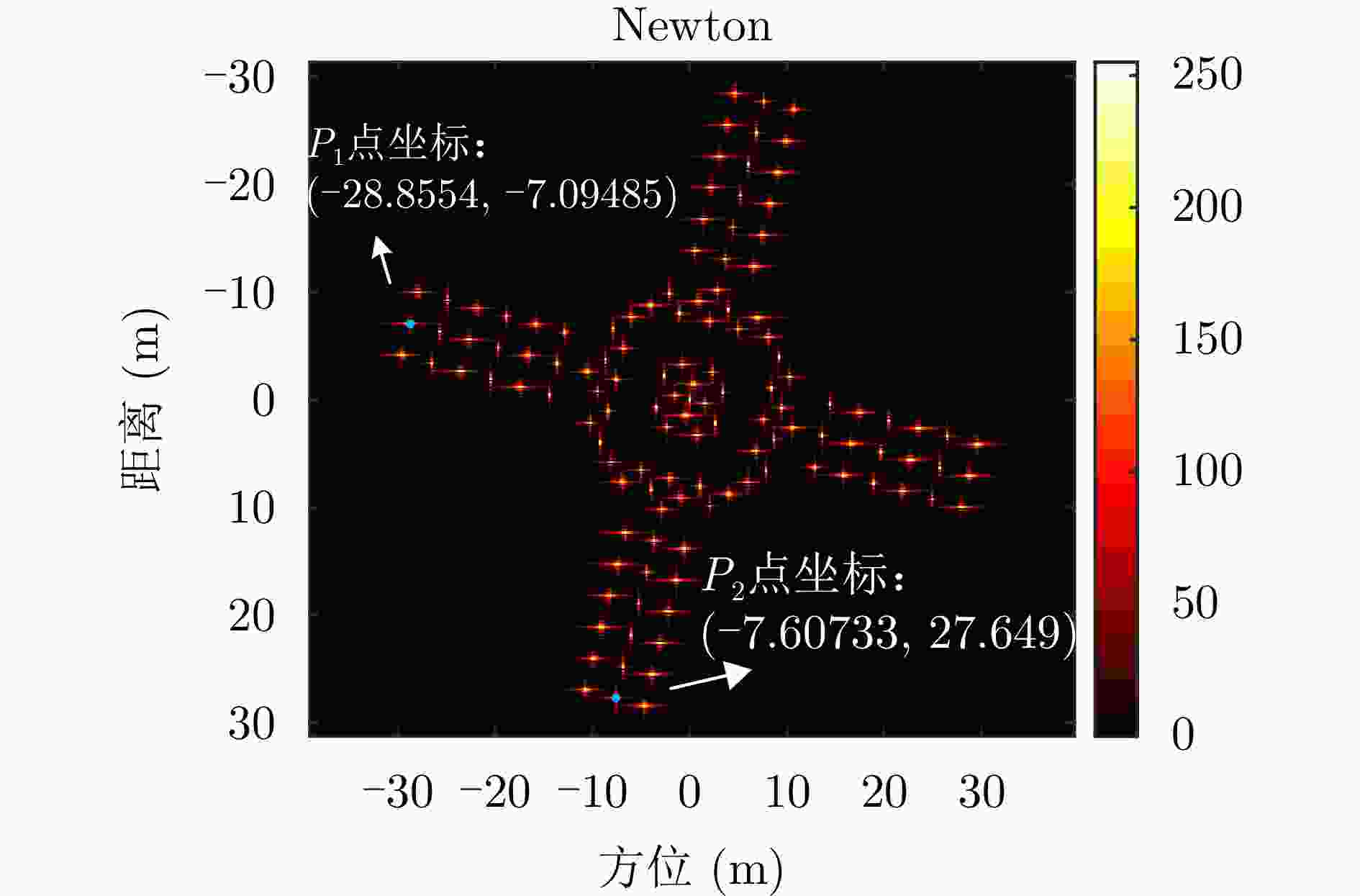
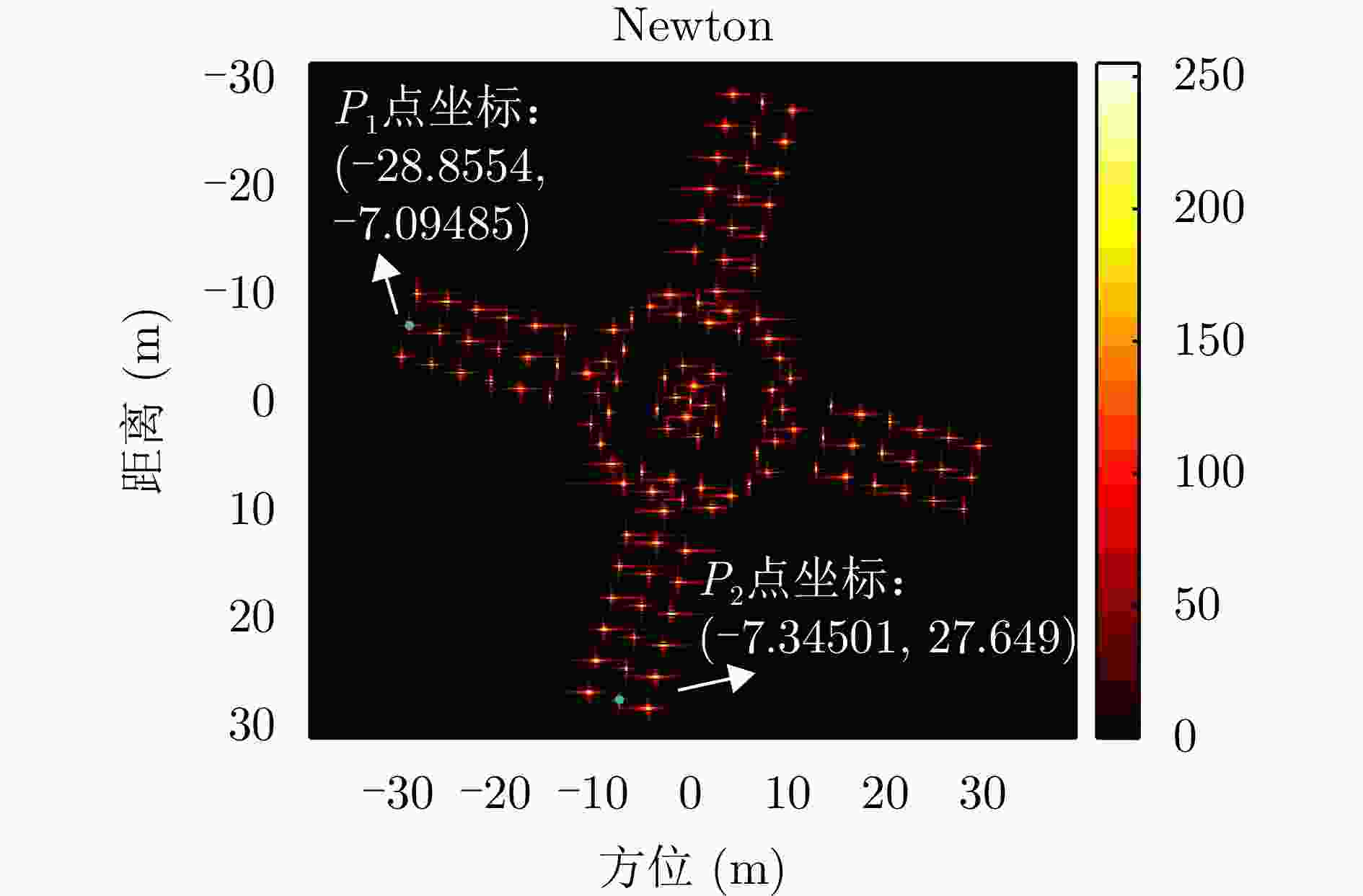
参数 数值 载频 35 GHz 带宽 1 GHz 脉冲重复频率 300 Hz 脉宽 1 μs 脉冲数 2048 表 2 各点补偿前后方位向峰值旁瓣比和积分旁瓣比
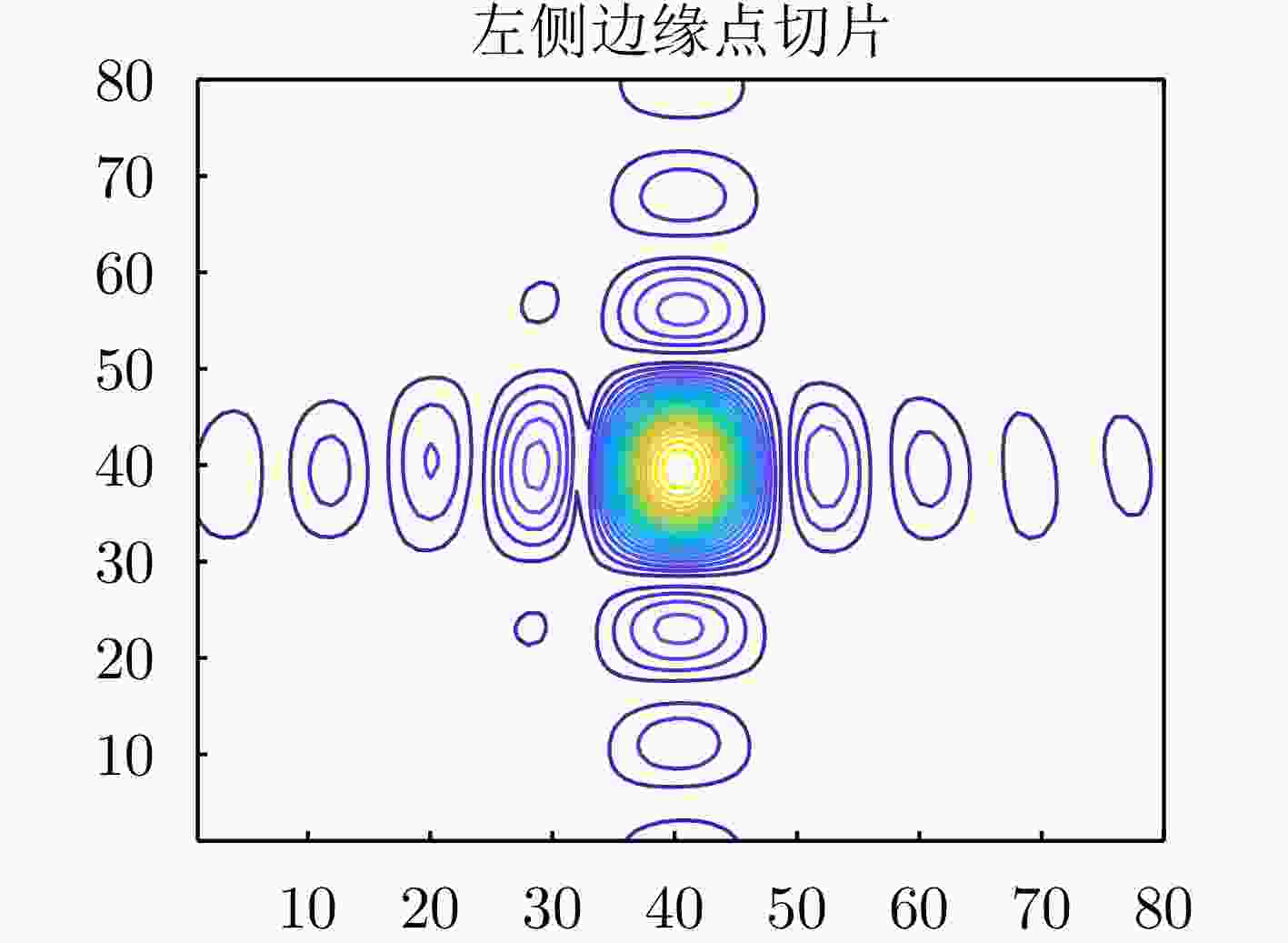
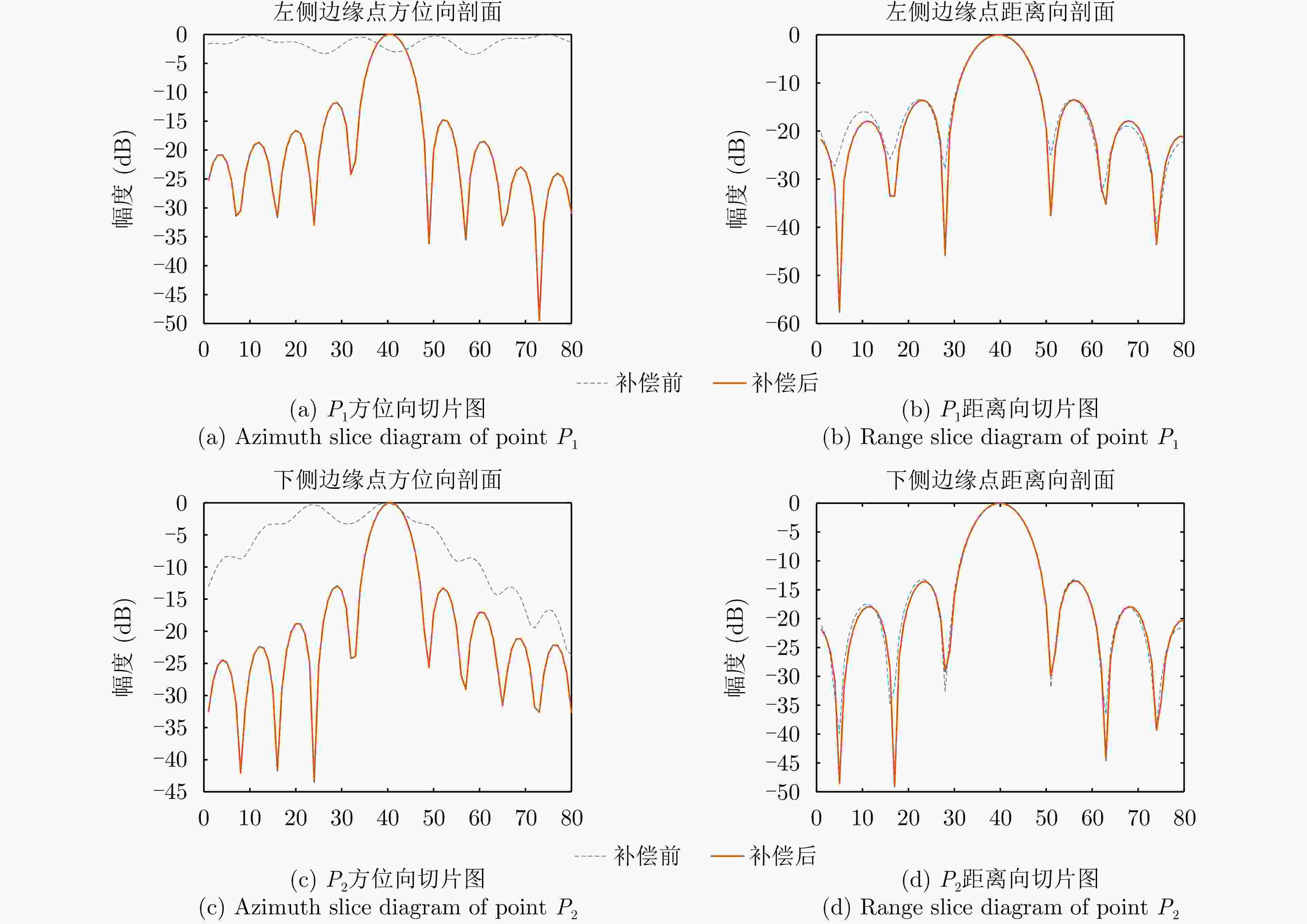
Table 2. Azimuth’s PSLR and ISLR before and after compensation for each point
点 峰值旁瓣比(dB) 积分旁瓣比(dB) 补偿前 补偿后 补偿前 补偿后 P1 – 0.0981 – 11.7714 4.0537 – 10.2959 P2 – 0.2306 – 12.9285 0.3414 – 10.6454 表 3 各点补偿前后距离向峰值旁瓣比和积分旁瓣比
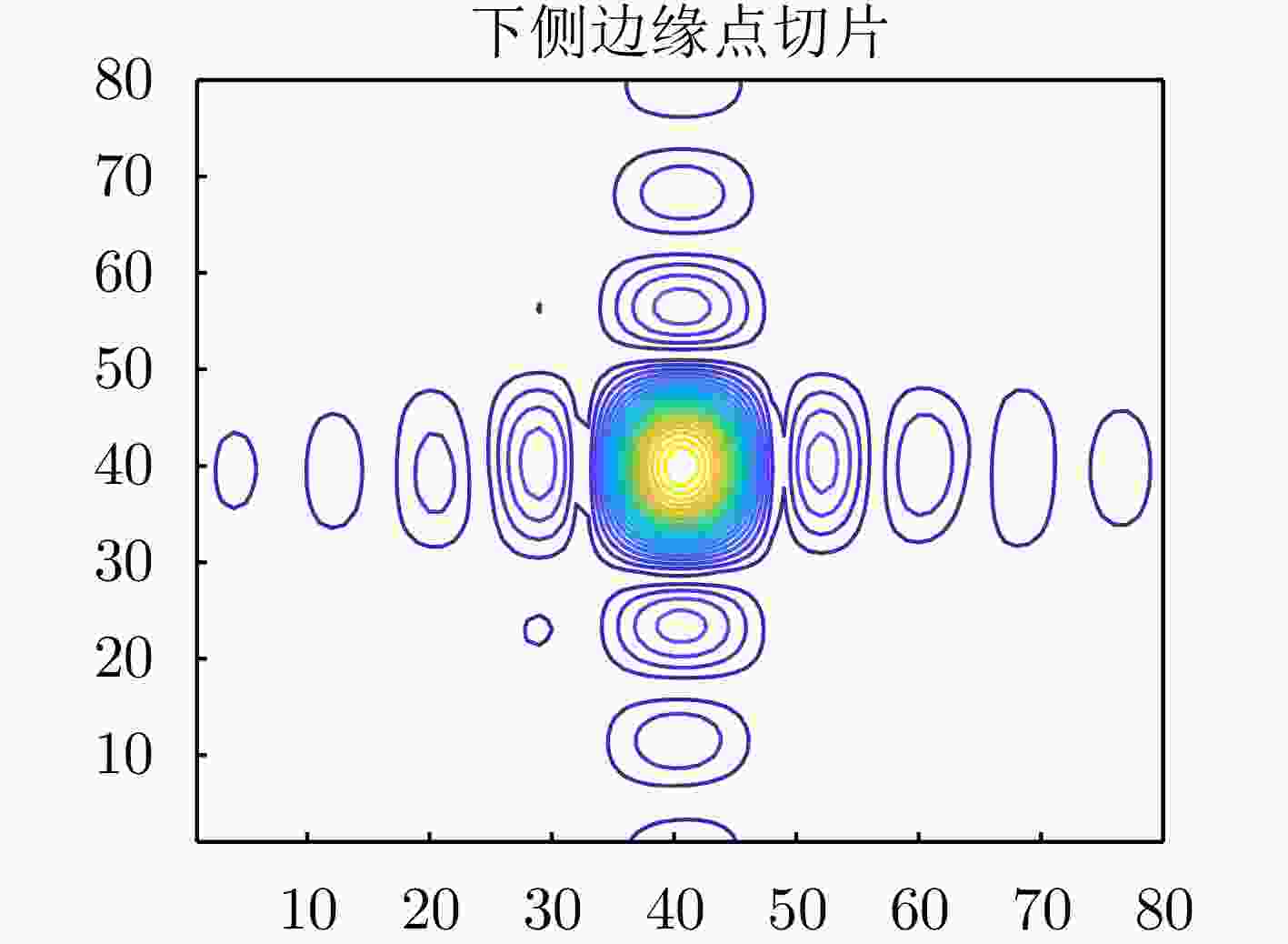
Table 3. Range’s PSLR and ISLR before and after compensation for each point
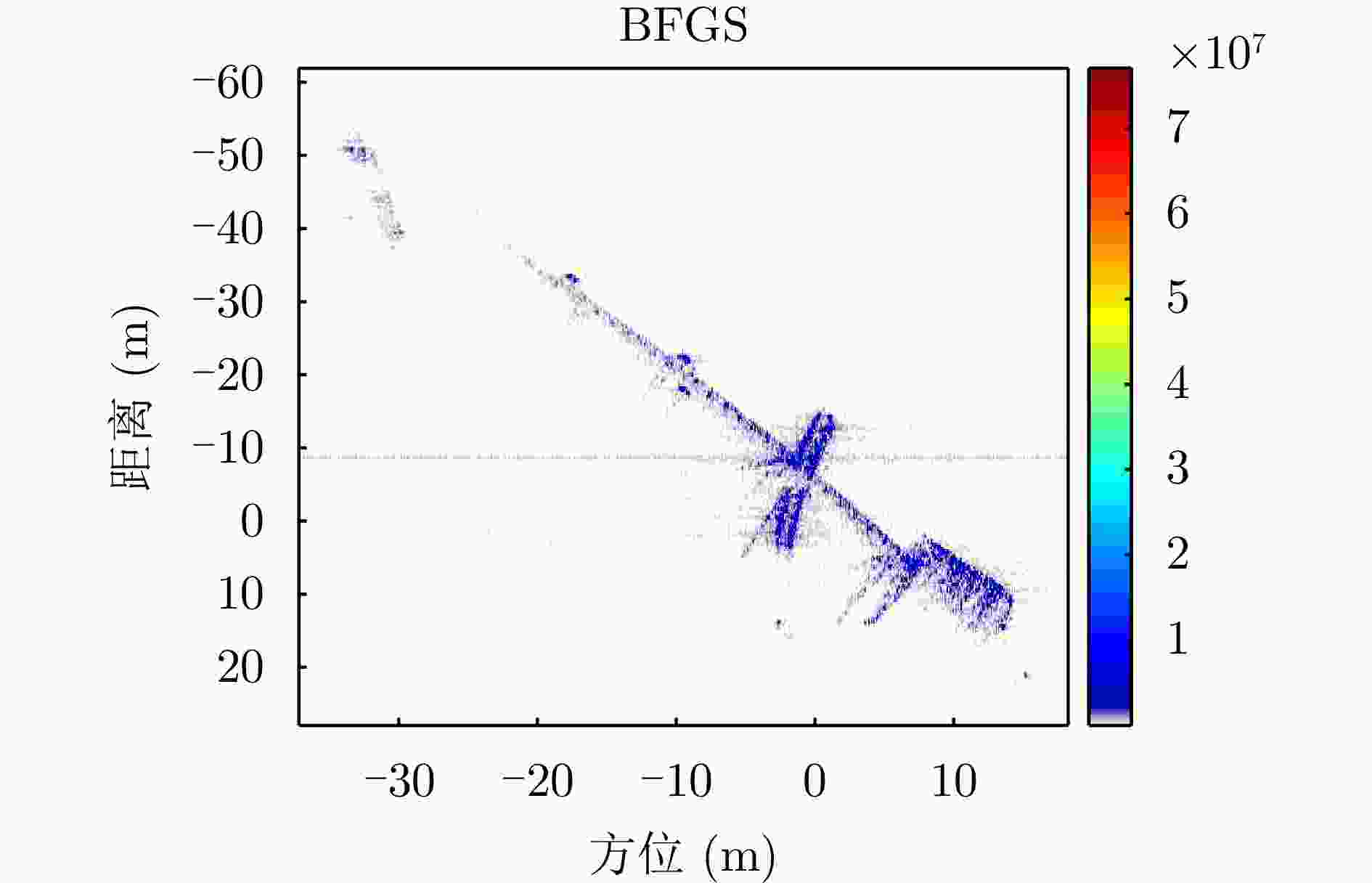
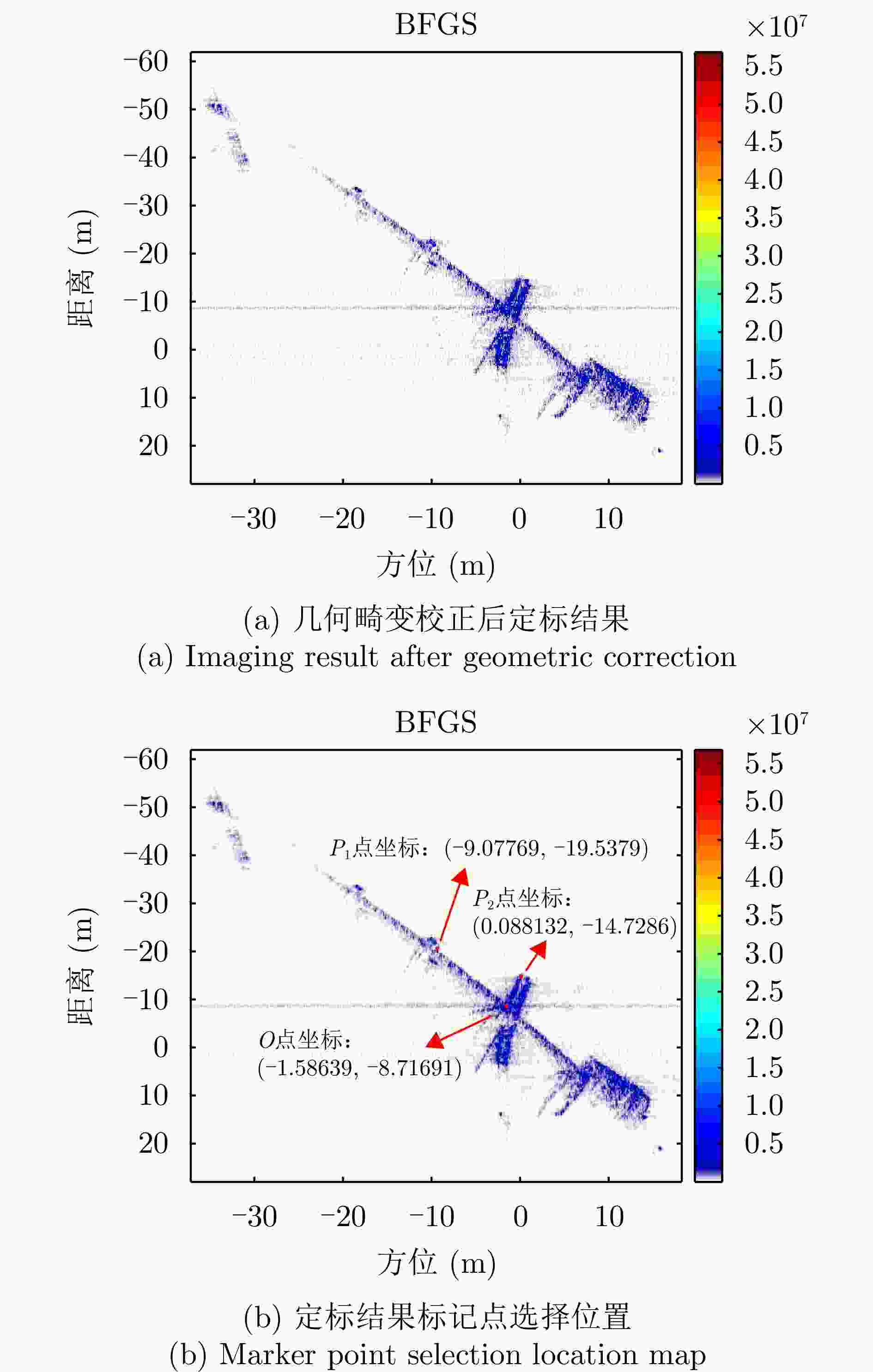
点 峰值旁瓣比(dB) 积分旁瓣比(dB) 补偿前 补偿后 补偿前 补偿后 P1 – 13.1455 – 13.4884 – 11.2785 – 11.2984 P2 – 12.7365 – 13.2731 – 11.2785 – 11.4938 表 4 本文方法与对比方法(BFGS方法)指标对比
Table 4. The method of this paper is compared with the method of comparison (BFGS)
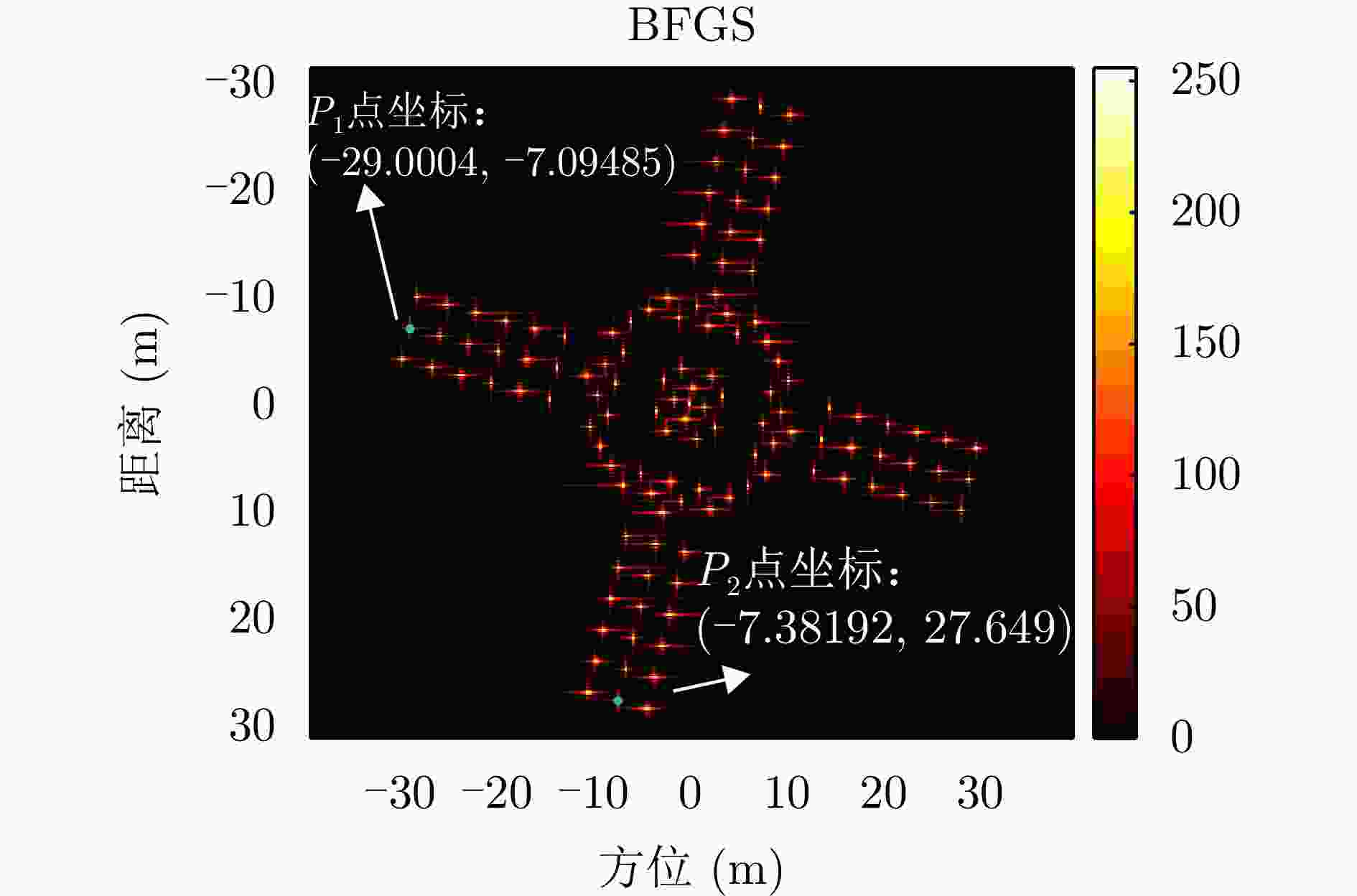
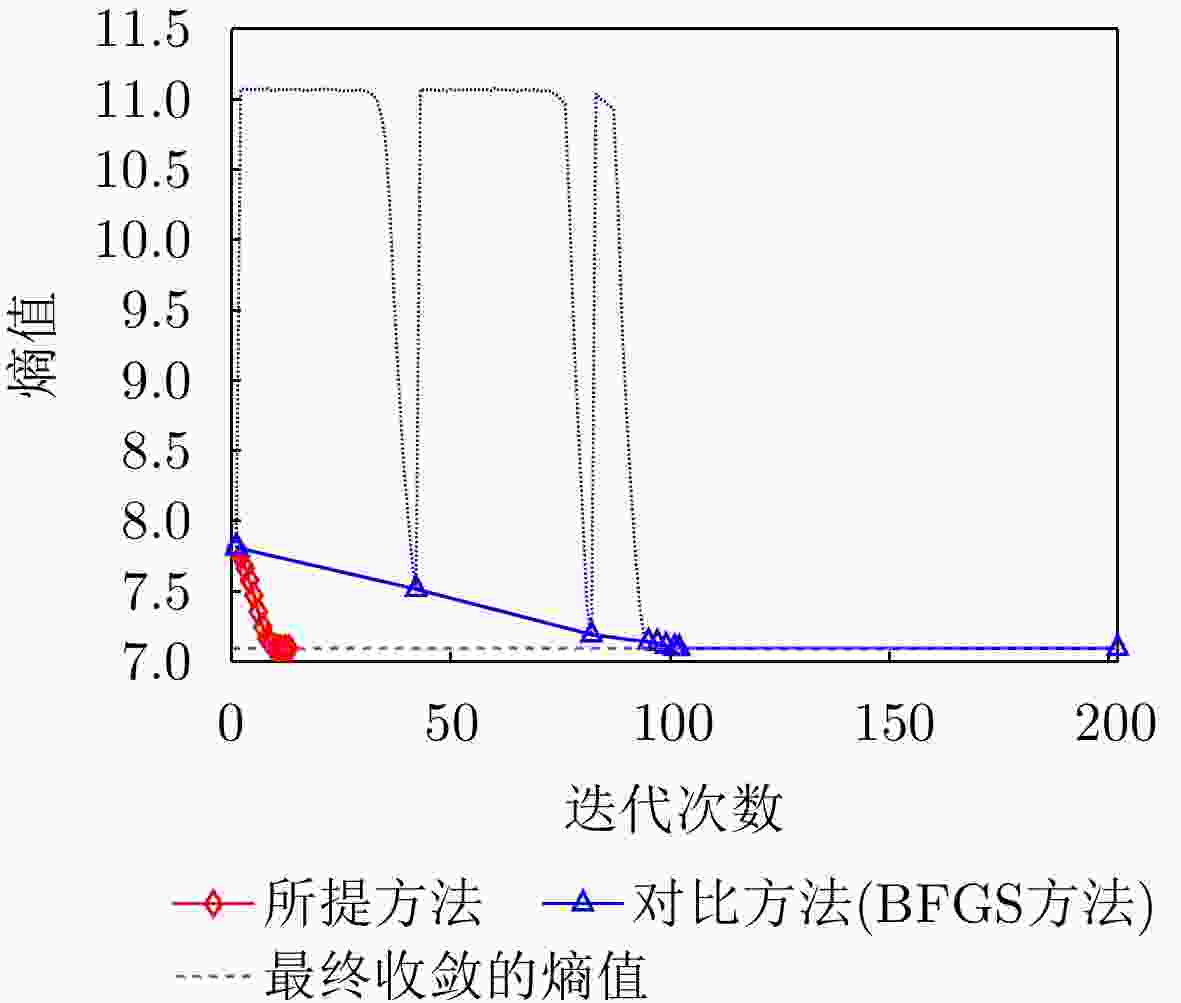
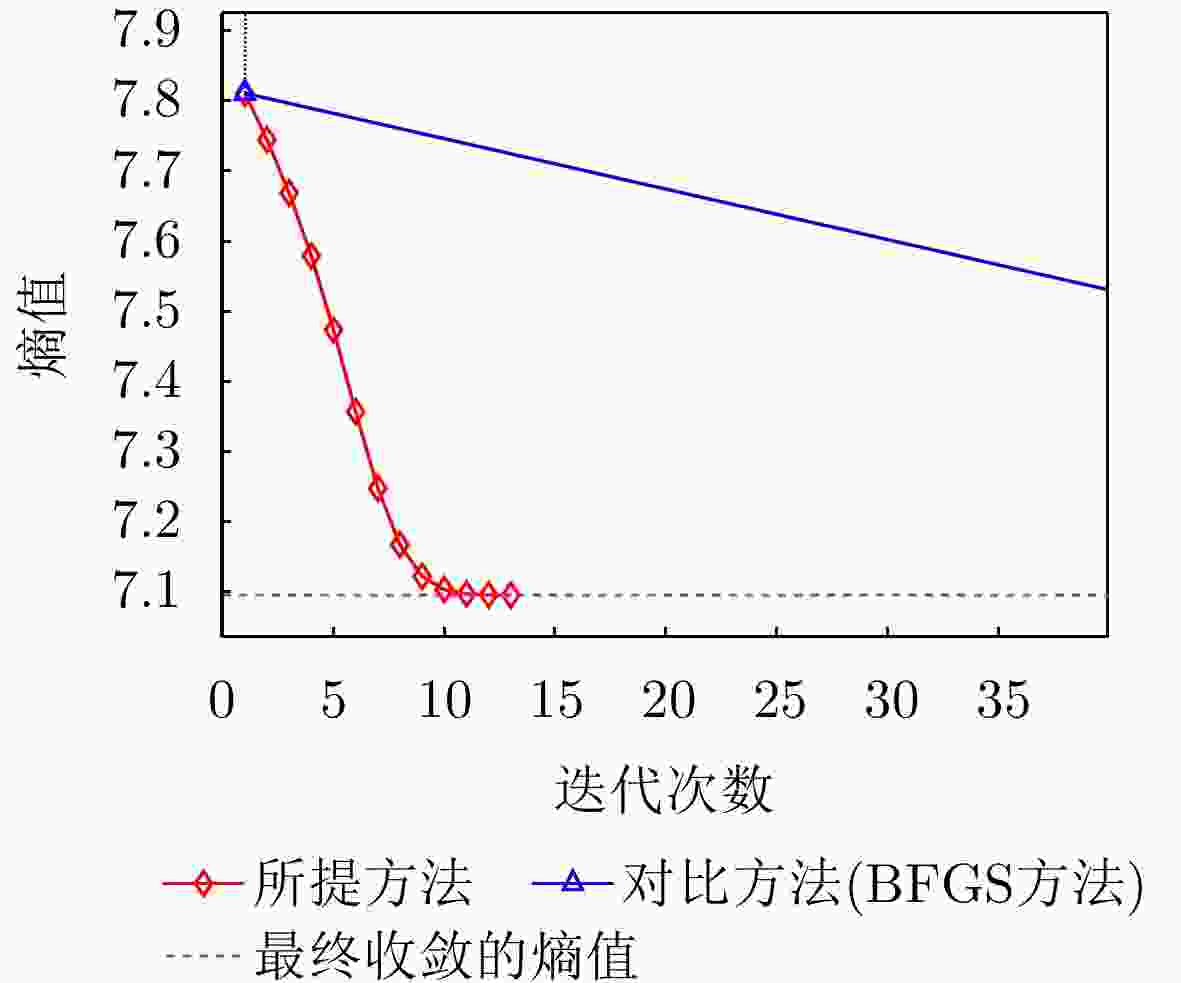
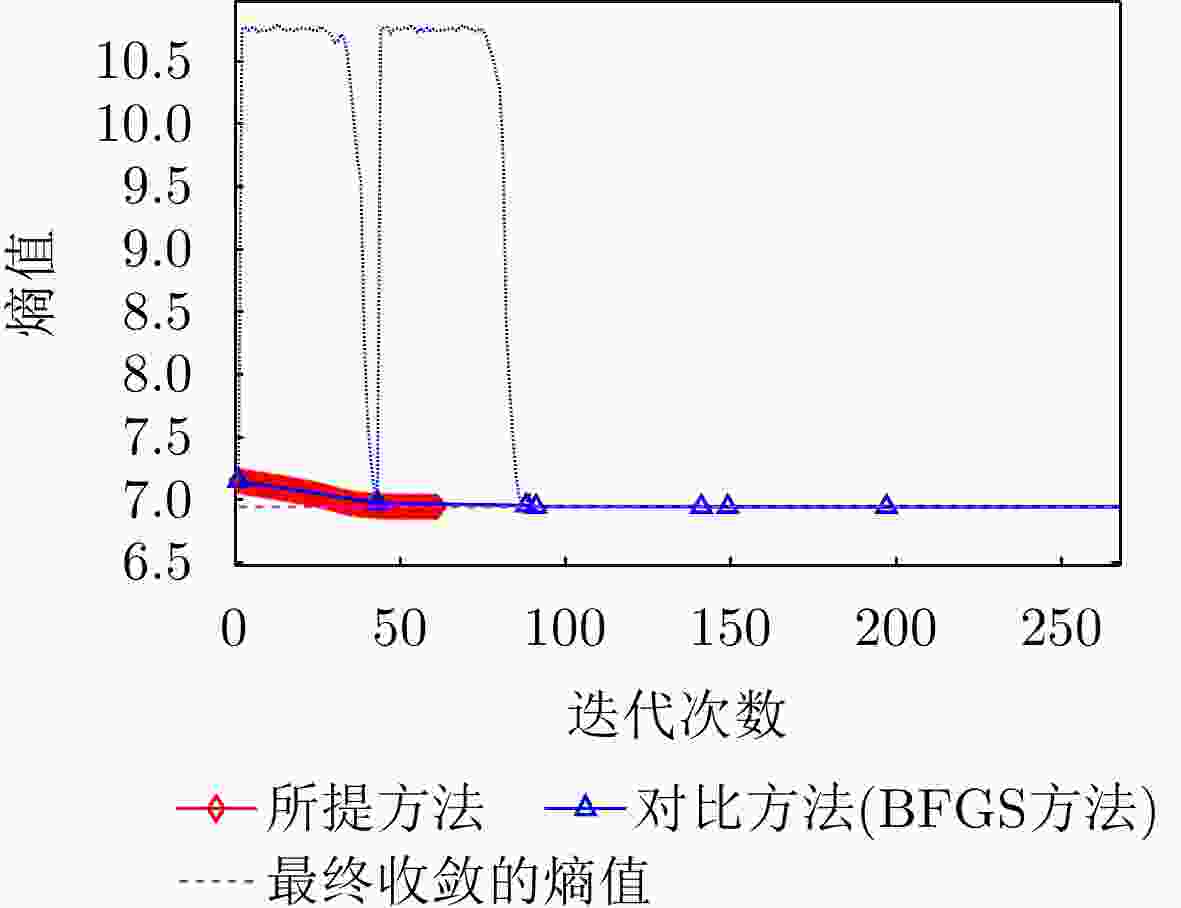
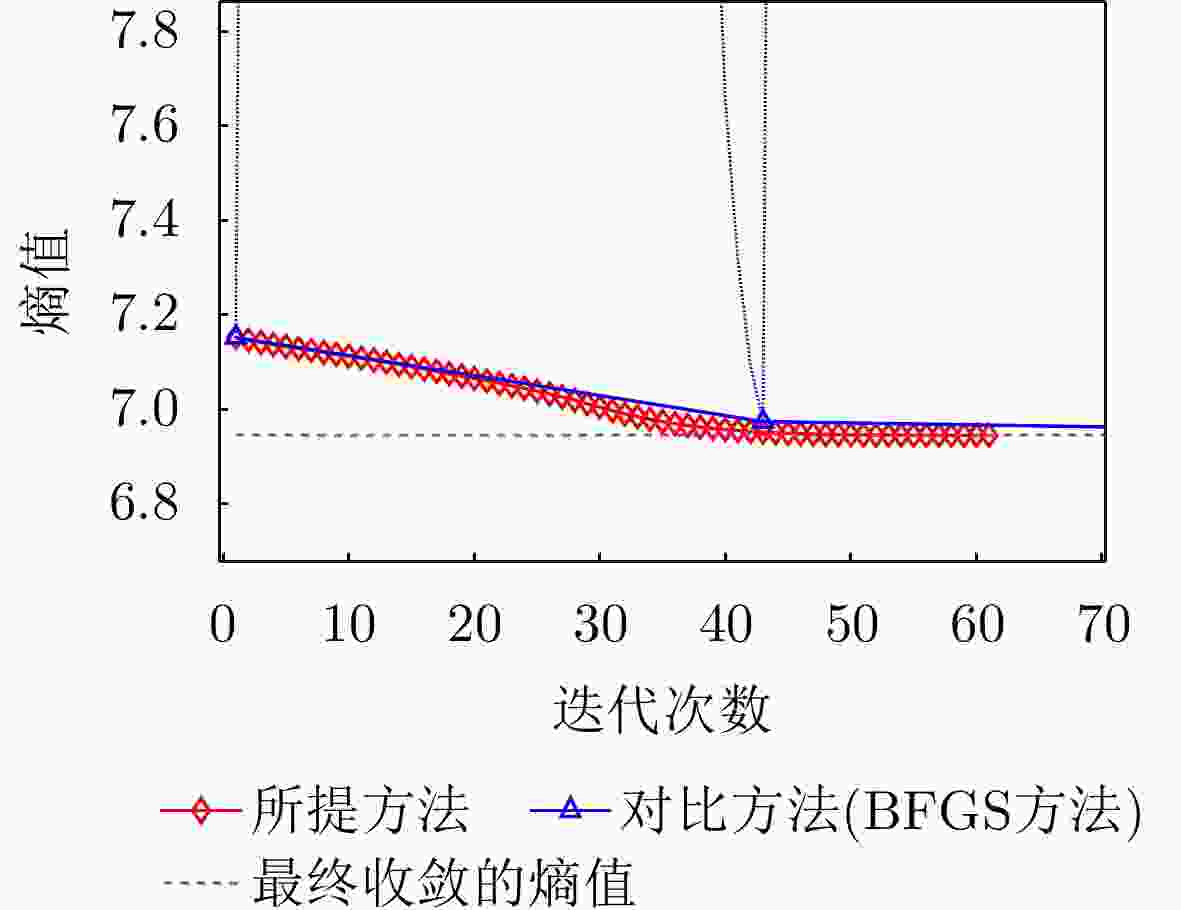
指标 本文所提方法 对比方法 图像熵值 7.0949 7.0952 对比度 23.5014 23.4998 $ O{P_1} $和$O{P_2}$夹角 88.9365 °88.7987 °迭代次数 13 202 运行时间 0.737570 s5.835382 s表 5 不同SNR下两种方法成像指标对比
Table 5. Comparison of imaging indicators of the two methods under different SNRs
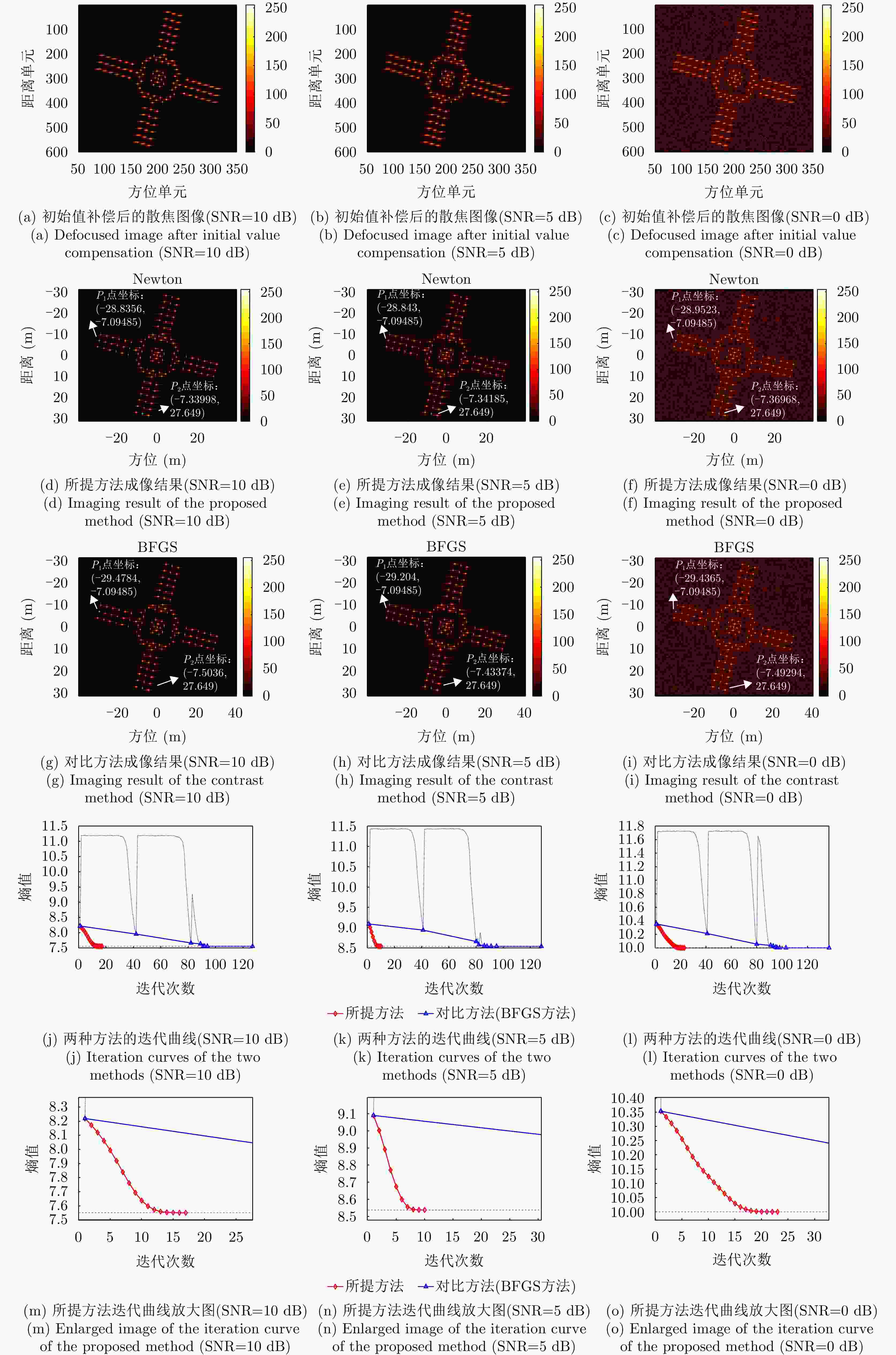
SNR值 图像熵值 对比度 $O{P_1}$和$O{P_2}$夹角 迭代次数 运行时间 本文所提方法 对比方法 本文所提方法 对比方法 本文所提方法 对比方法 本文所提方法 对比方法 本文所提方法 对比方法 10 dB 7.5515 7.5518 22.0521 22.0509 88.9554 °88.3489 °17 127 0.969786 s4.162207 s5 dB 8.5377 8.5378 18.4484 18.4475 88.9483 °88.6062 °10 128 0.568464 s4.012253 s0 dB 10.0005 10.0006 12.1812 12.1809 88.8443 °88.3880 °23 137 1.310209 s4.404005 s表 6 交叉极化下本文方法与对比方法指标对比
Table 6. The index of this method is compared with the comparison method under cross polarization
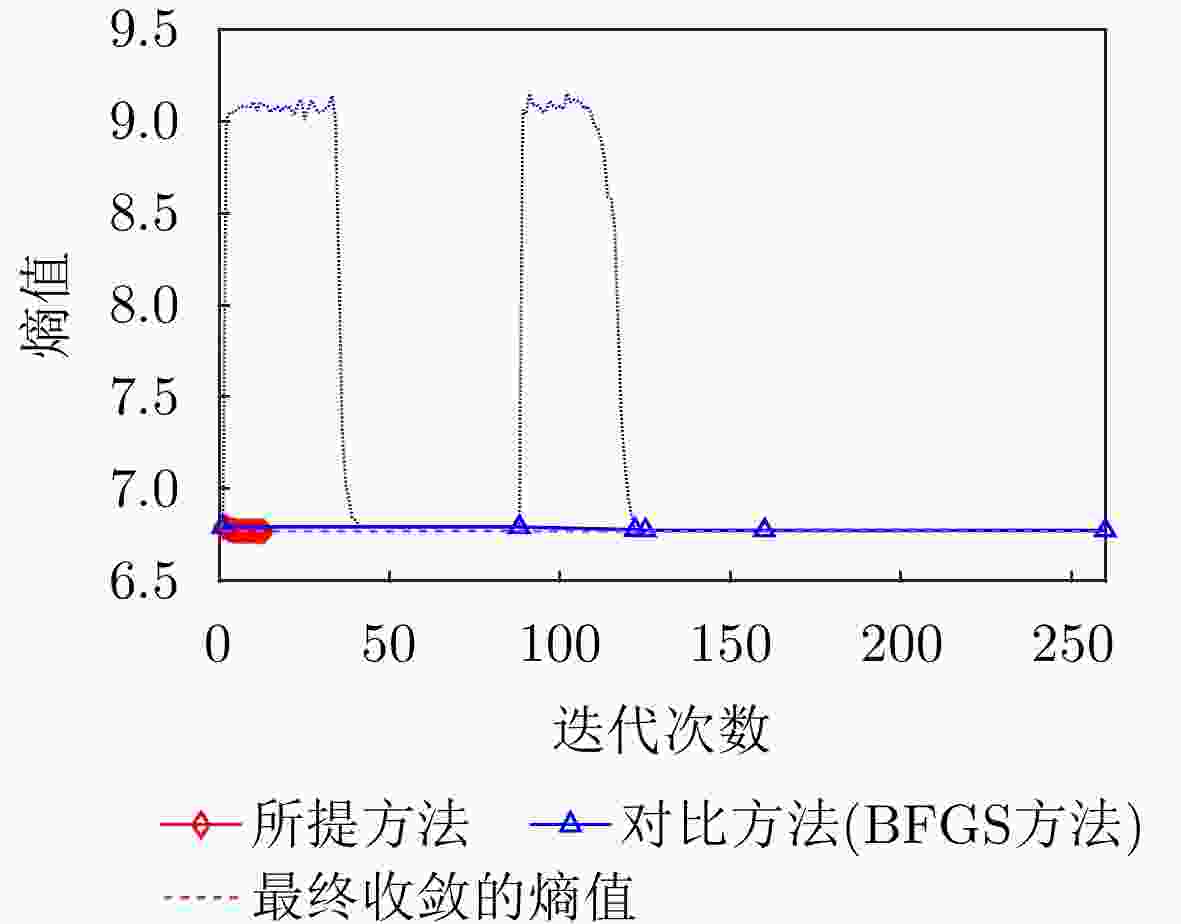
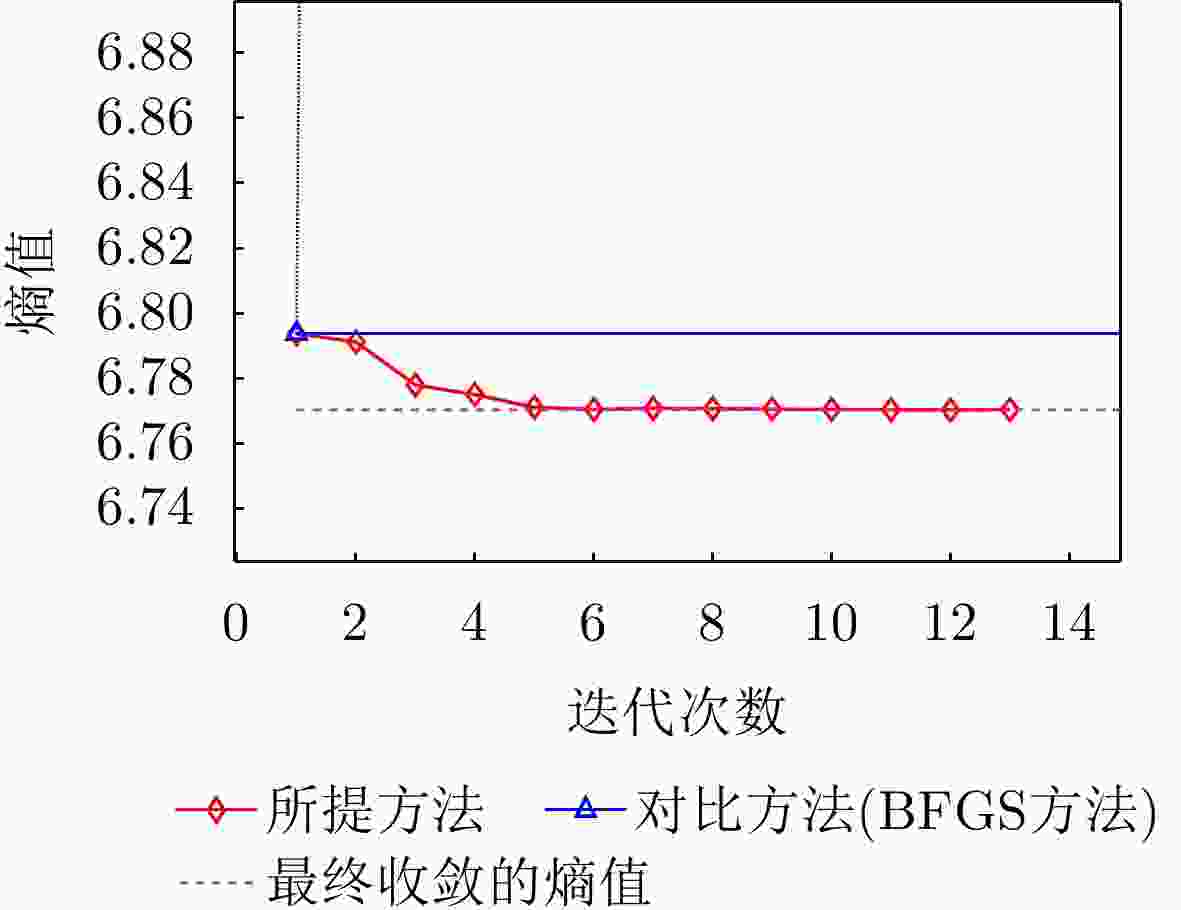
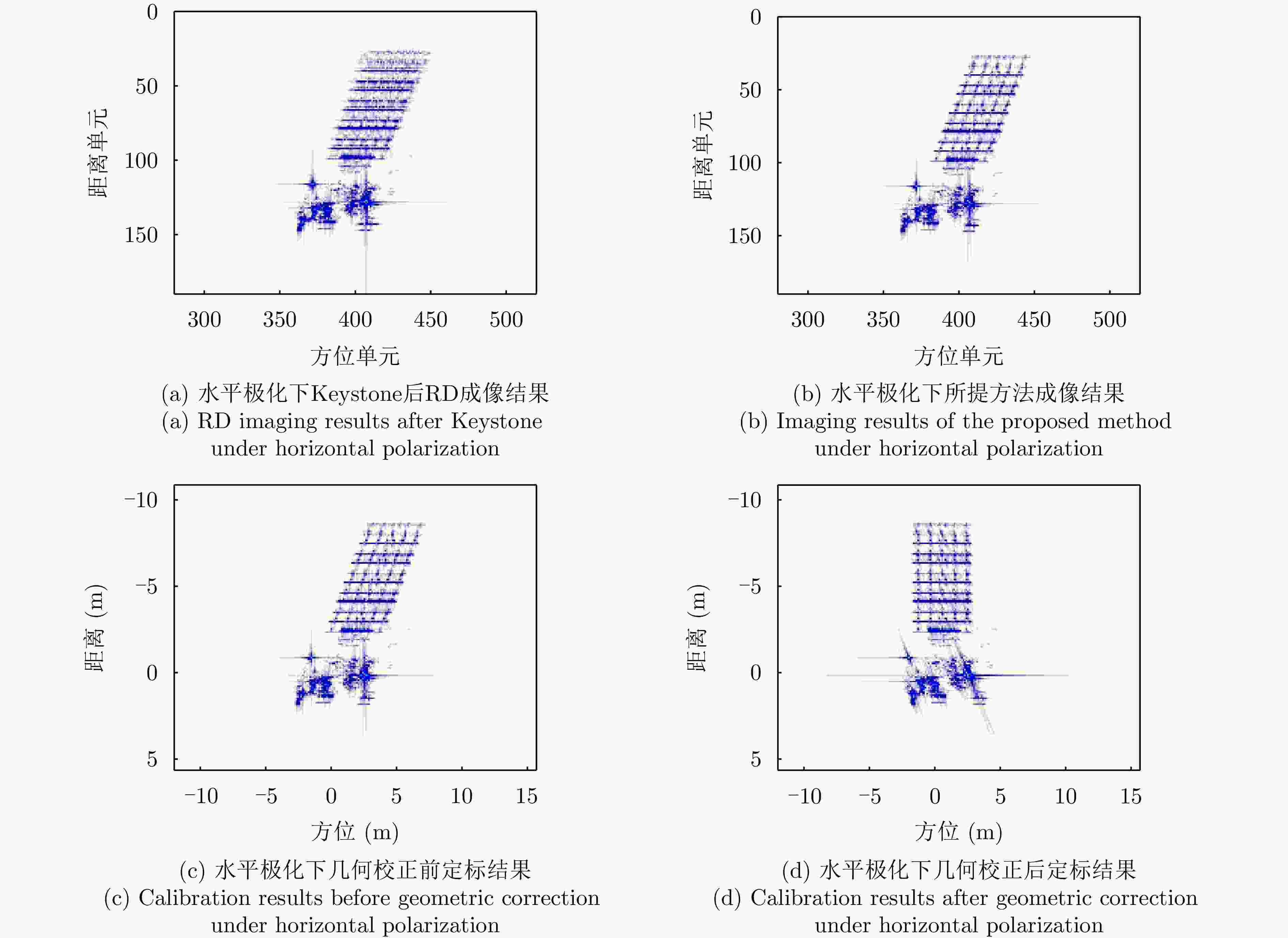
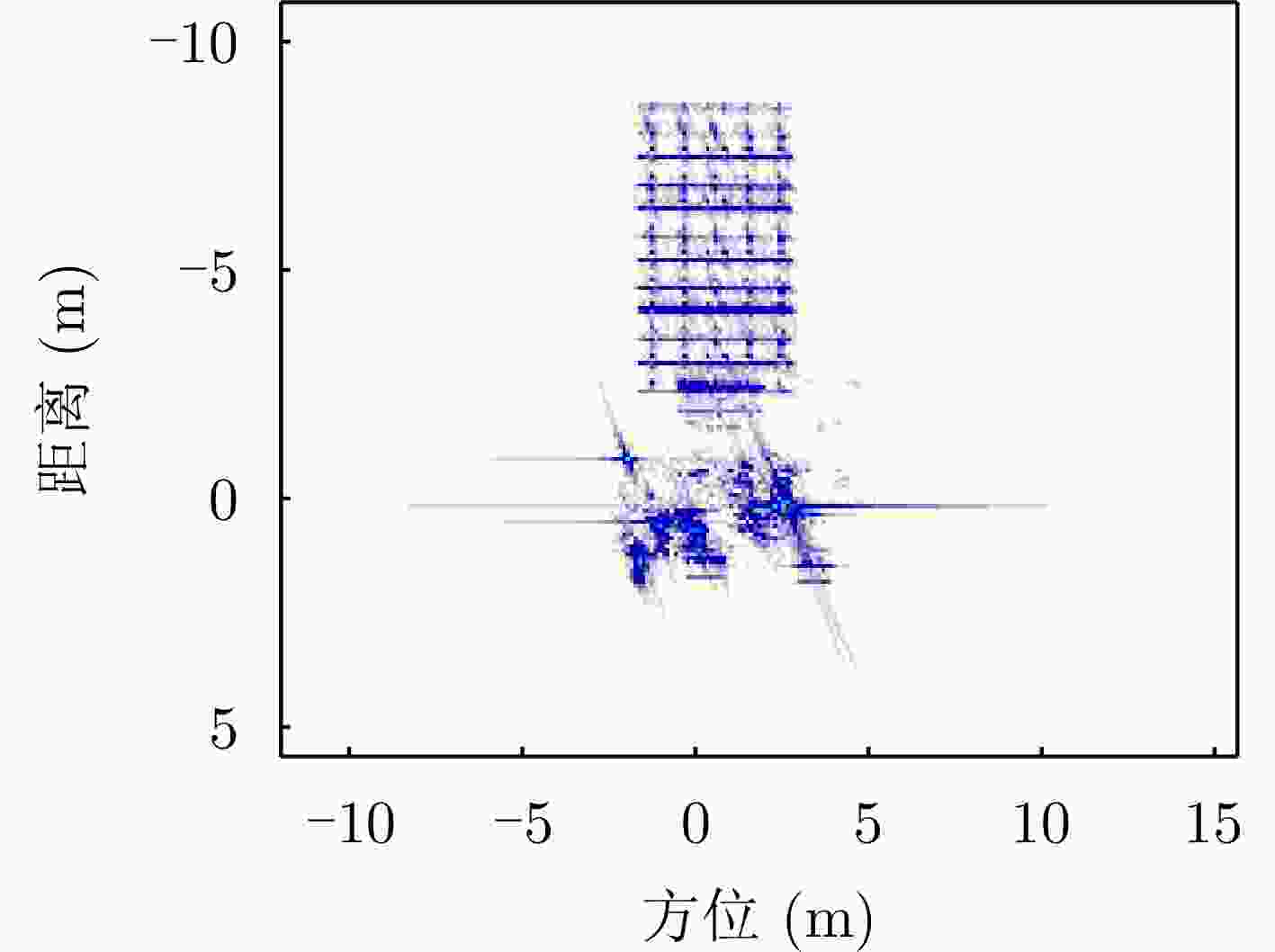
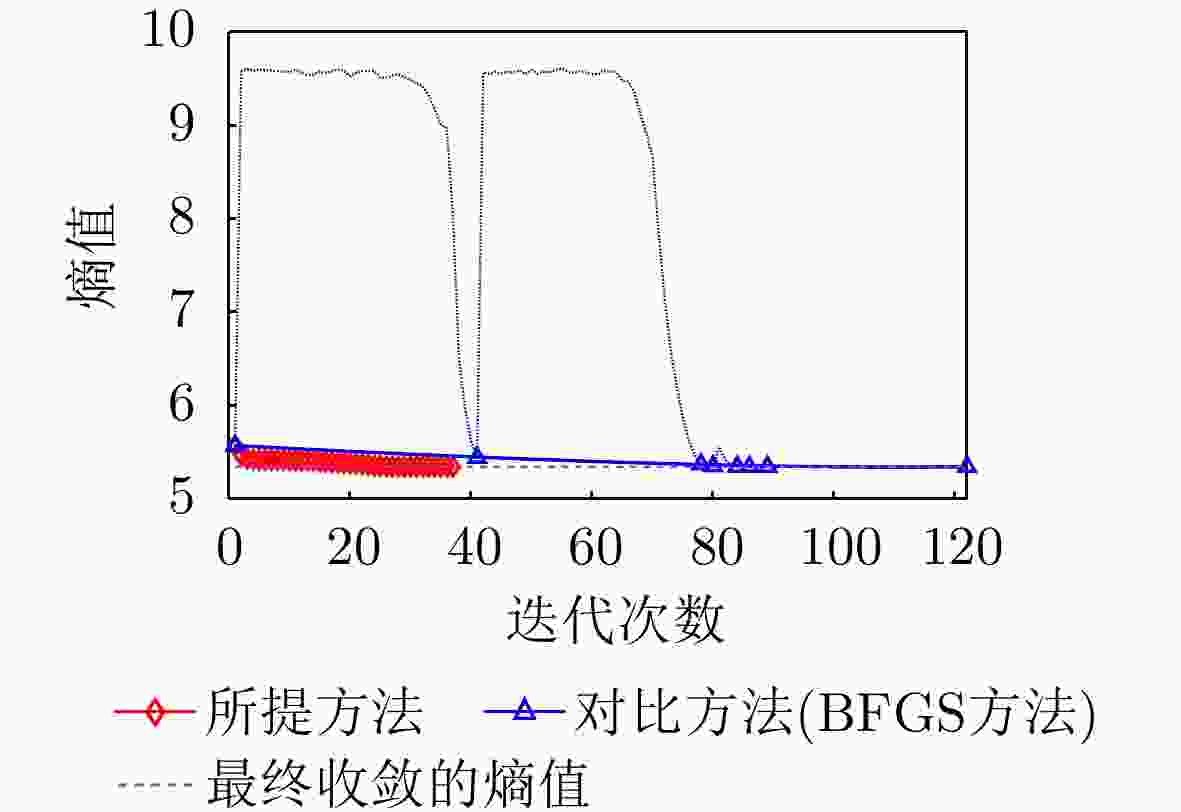
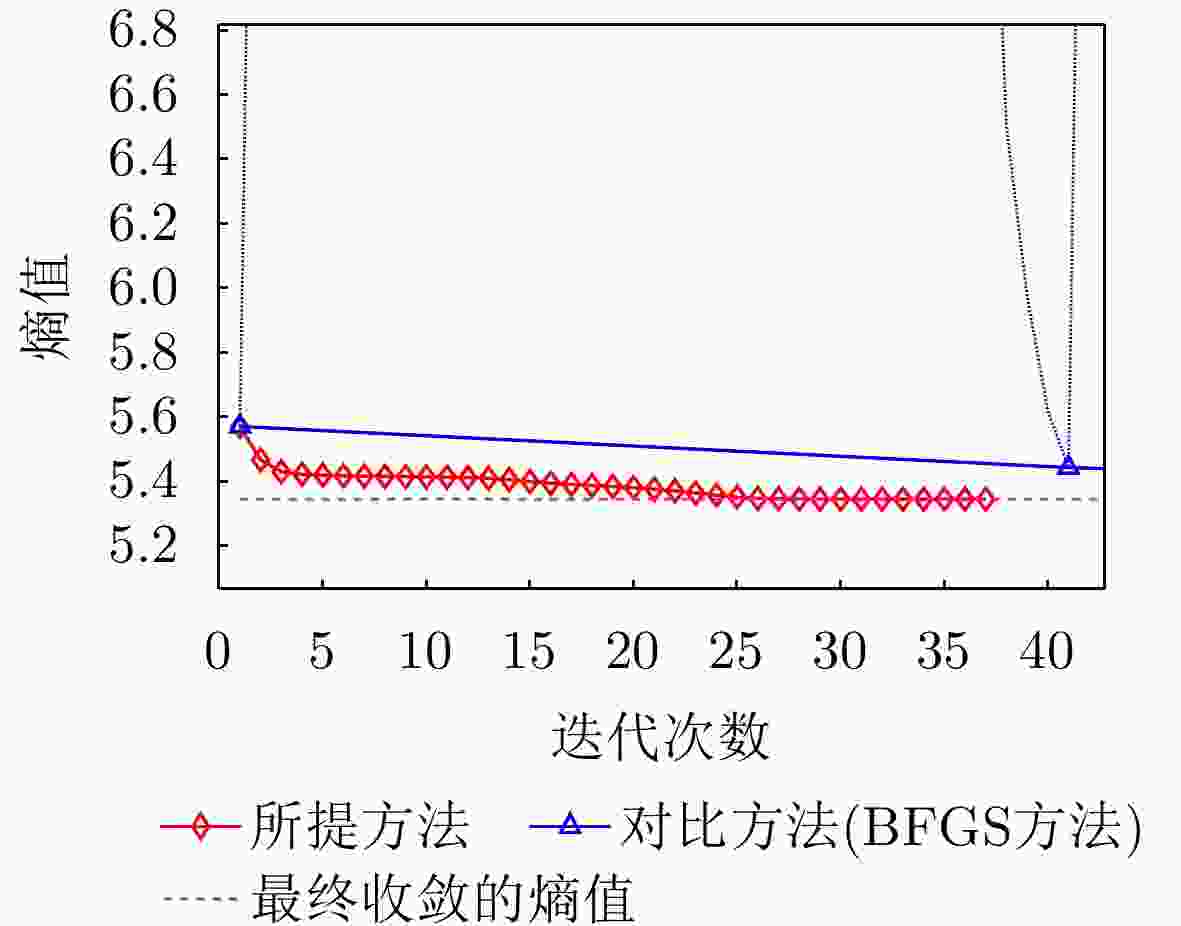
方法 图像熵值 对比度 迭代次数 运行时间 本文所提方法 6.7704 27.9896 13 0.805566 s对比方法(BFGS) 6.7754 28.0345 260 9.678188 s表 7 水平极化下本文方法与对比方法指标对比
Table 7. The index of this method is compared with the comparison method under horizontal polarization
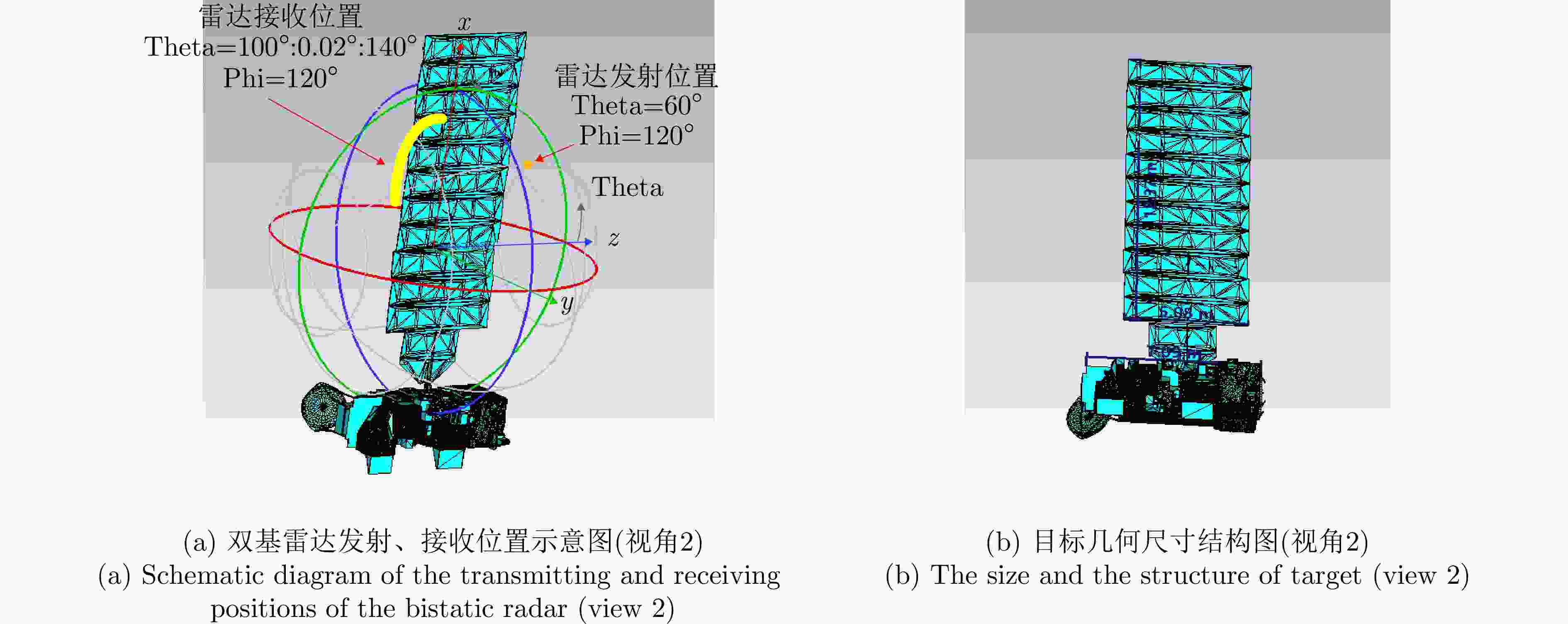
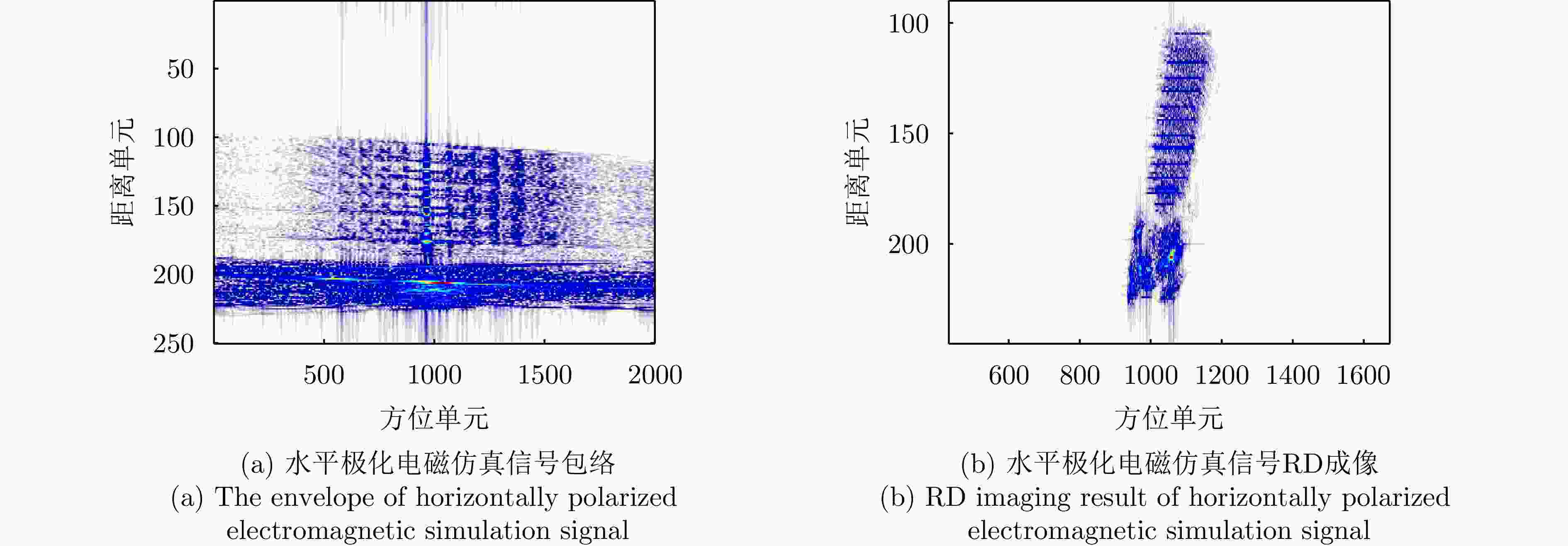
方法 图像熵值 对比度 迭代次数 运行时间 本文所提方法 5.3443 96.2904 37 2.258587 s对比方法(BFGS) 5.3443 96.3270 122 5.285292 s表 8 实测数据雷达参数表
Table 8. Radar parameter table of measured data
参数 数值 载频 33 GHz 带宽 300 MHz 脉冲重复频率 150 Hz 采样率 500 MHz 脉冲数 1024 表 9 本文方法与对比方法(BFGS)指标对比
Table 9. The method of this paper is compared with the method of comparison (BFGS)
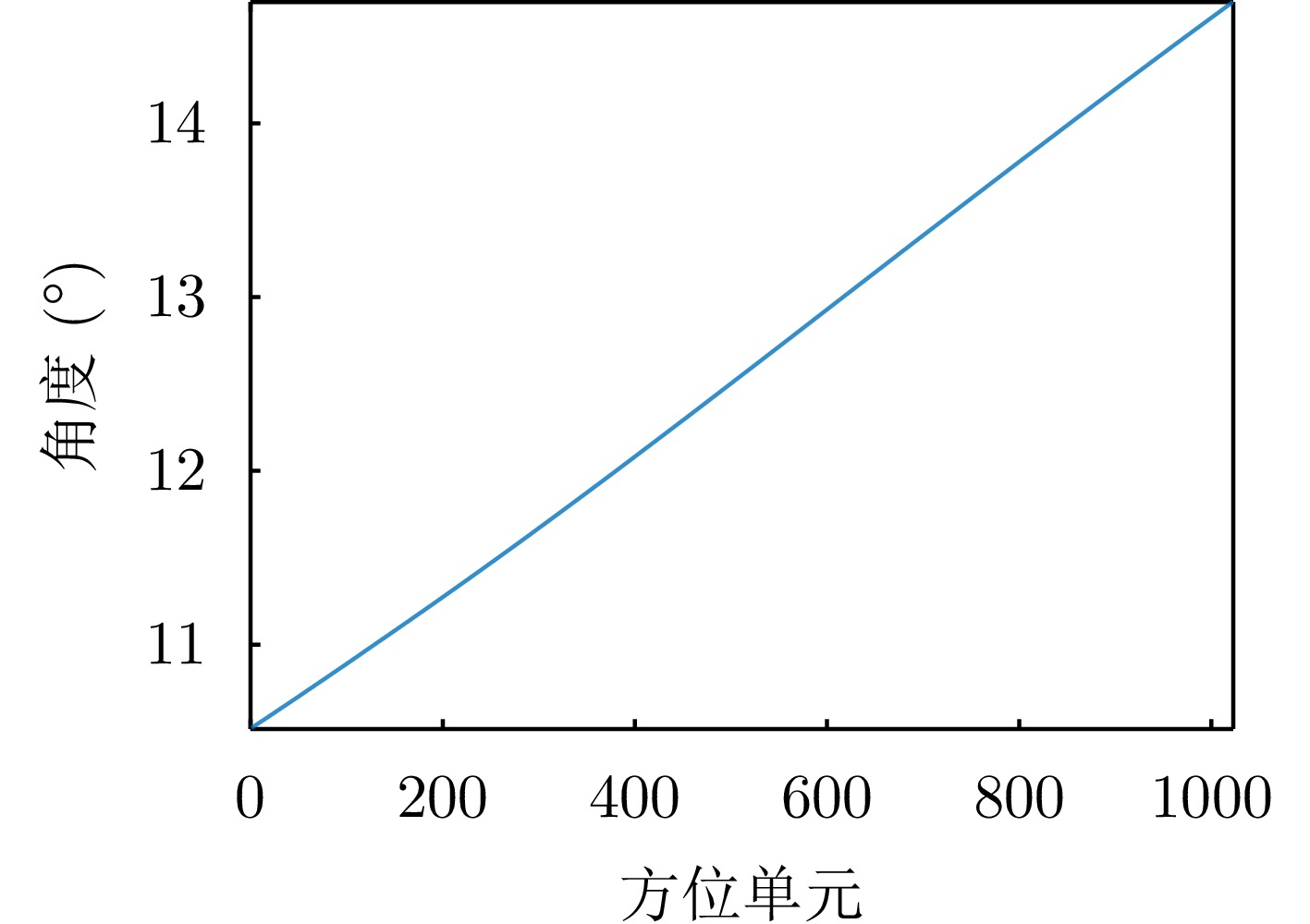
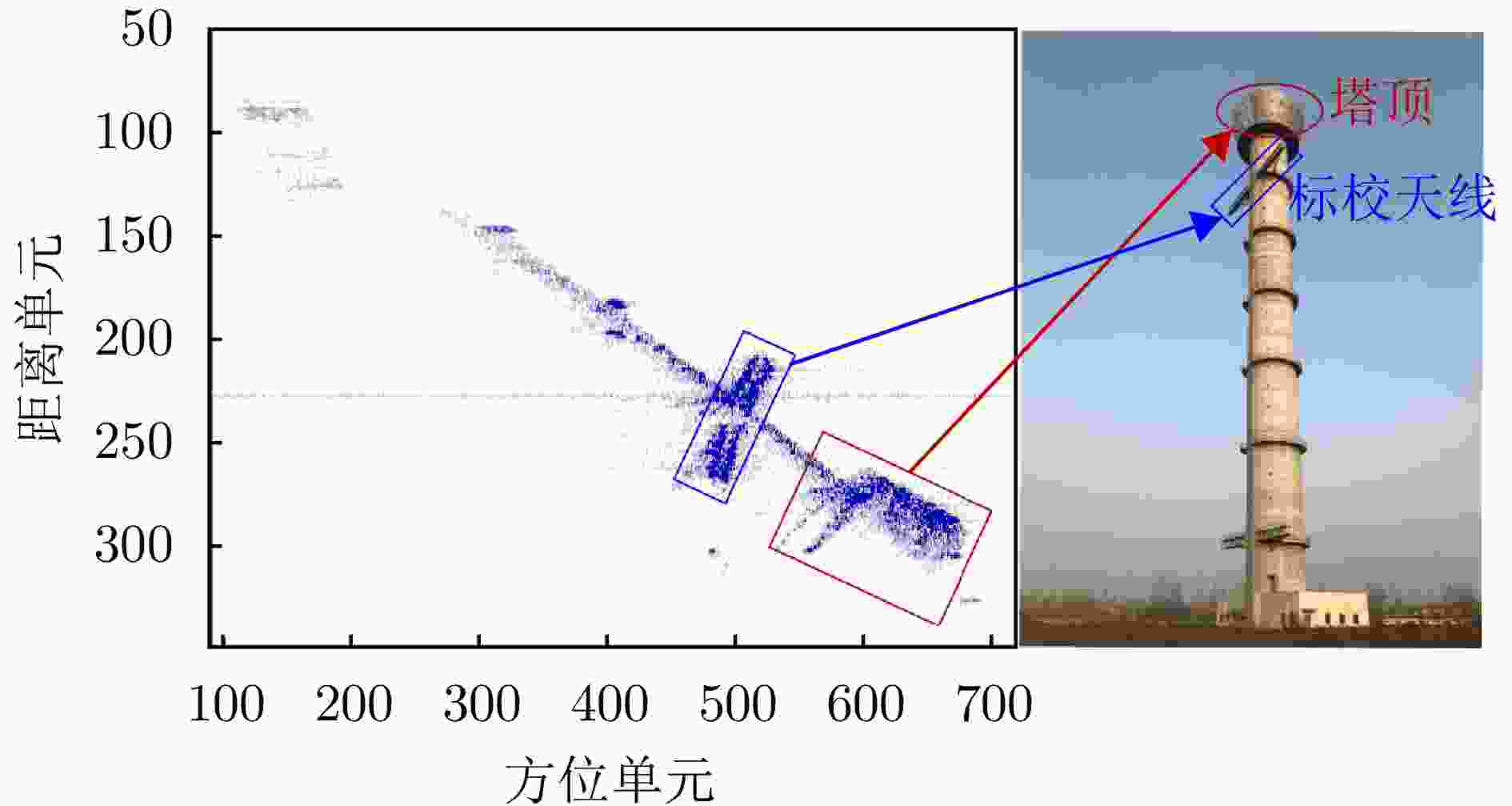
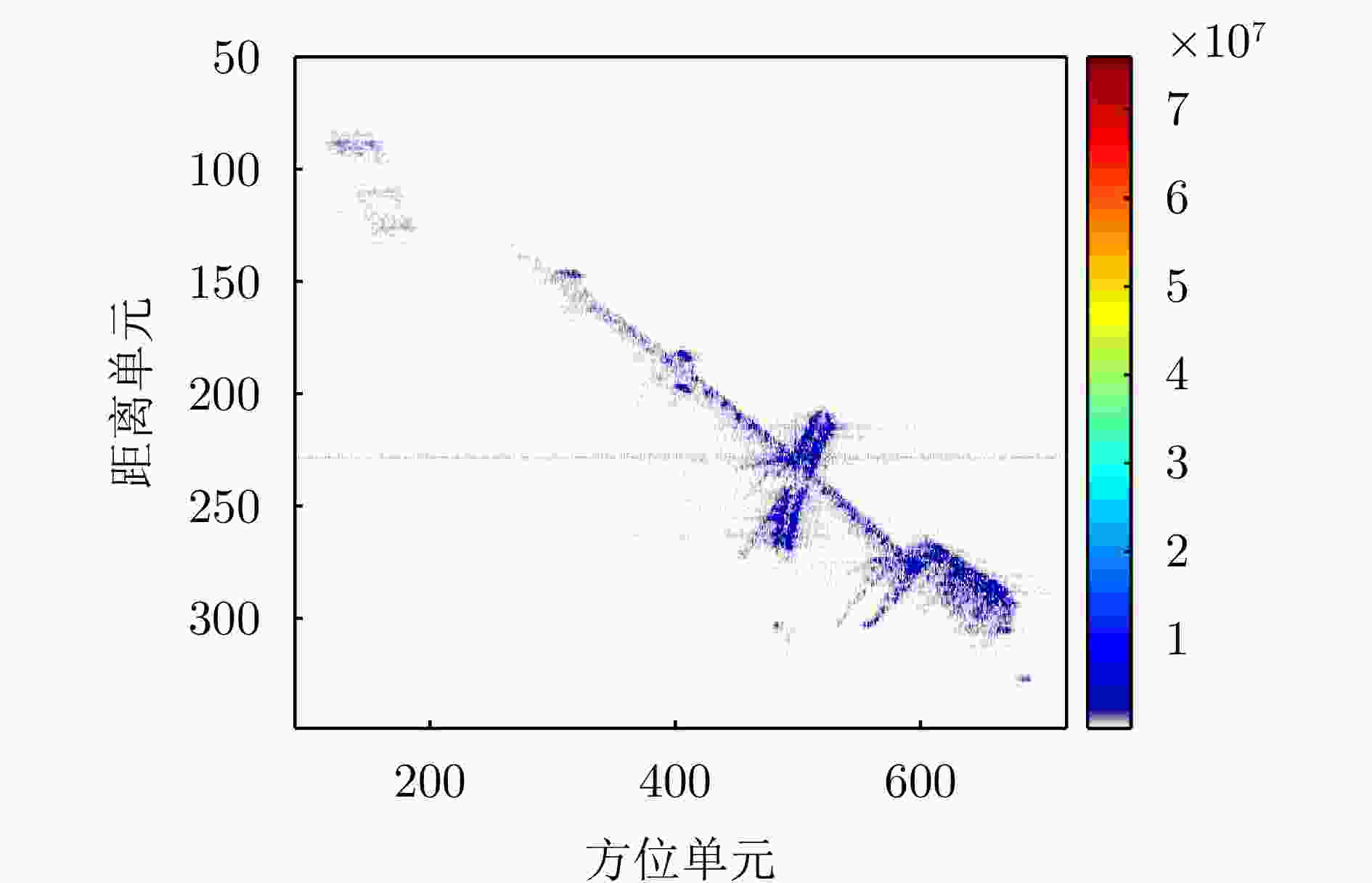
方法 图像熵值 对比度 OP1和
OP2夹角(°)迭代
次数运行时间(s) 本文所提方法 6.9455 111.7340 50.4275 61 11.896714 对比方法 6.9457 111.8247 50.2595 269 29.319547 -
[1] 李俊颜, 杨青, 李中余, 等. 基于空变多普勒参数聚类的微波光子ISAR高精度成像方法[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(12): 3941–3956. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240442.LI Junyan, YANG Qing, LI Zhongyu, et al. High-precision microwave photonic ISAR imaging method based on spatially variant Doppler parameter clustering[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(12): 3941–3956. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240442. [2] 邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. [3] 符吉祥, 邢孟道, 徐丹, 等. 一种基于微波光子超高分辨雷达机翼振动参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001.FU Jixiang, XING Mengdao, XU Dan, et al. Vibration-parameters estimation method for airplane wings based on microwave-photonics ultrahigh-resolution radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001. [4] 田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060.TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. Review of high-resolution imaging techniques of wideband inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. [5] CHEN Hongmeng, LI Jun, ZHOU Rui, et al. Optimal Bi-ISAR imaging arc selection method with bistatic angle derivative constraint[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Zhuhai, China, 2024: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICSIDP62679.2024.10869106. [6] JIANG Yicheng, WEI Jin, and LIU Zitao. Bistatic ISAR imaging and scaling algorithm based on the estimation of bistatic factor and effective rotation velocity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(6): 8522–8538. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3432109. [7] CHEN Hongmeng, LI Jun, ZHOU Rui, et al. Focused bistatic ISAR imaging demonstration with nonparametric autofocusing[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Chongqing, China, 2023: 3370–3374. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1643. [8] DING Jiabao, LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, et al. Integration of high-order motion compensation and 2-D scaling for maneuvering target bistatic ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5205120. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3533881. [9] FU Jixiang, YANG Weichao, XUE Min, et al. A novel bistatic ISAR space-variant phase error compensation and geometric correction method based on entropy minimization[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 3536–3539. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10641057. [10] DING Jiabao, WANG Jiadong, LI Yachao, et al. A spatial variant phase compensation algorithm for bistatic ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets based on optimal parameter estimation[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar, Haikou, China, 2021: 2087–2090. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10027972. [11] QIAN Guangzhao and WANG Yong. Satellite-missile bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging of ship target via hybrid SAR-ISAR algorithm[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Chongqing, China, 2023: 2669–2674. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1510. [12] QIAN Guangzhao and WANG Yong. Monostatic-equivalent algorithm via Taylor expansion for BiSAR ship target imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5200919. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3233384. [13] 朱瀚神, 胡文华, 郭宝锋, 等. 双基地ISAR稀疏孔径机动目标MTRC补偿成像算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(7): 2022–2030. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.07.12.ZHU Hanshen, HU Wenhua, GUO Baofeng, et al. Bistatic ISAR sparse aperture maneuvering target MTRC compensation imaging algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 2022–2030. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.07.12. [14] LI Rui, LUO Ying, ZHANG Qun, et al. Time-varying bistatic radar coincidence imaging for rotating targets[C]. IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology, Harbin, China, 2019: 495–498. doi: 10.1109/ICEICT.2019.8846253. [15] 李中余, 桂亮, 海宇, 等. 基于变分模态分解与优选的超高分辨ISAR成像微多普勒抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043.LI Zhongyu, GUI Liang, HAI Yu, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution ISAR micro-Doppler suppression methodology based on variational mode decomposition and mode optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043. [16] ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Fast ISAR cross-range scaling using modified newton method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1355–1367. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2785560. [17] 柴守刚, 陈卫东, 陈畅. 联合几何畸变校正及定标的B-ISAR稀疏成像算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2015, 37(1): 32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2015.01.008.CHAI Shougang, CHEN Weidong, and CHEN Chang. B-ISAR sparse imaging algorithm with geometric distortion correction and calibration[J]. Modern Radar, 2015, 37(1): 32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2015.01.008. [18] 史林, 郭宝锋, 马俊涛, 等. 基于图像旋转相关的空间目标ISAR等效旋转中心估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1280–1286. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181086.SHI Lin, GUO Baofeng, MA Juntao, et al. Rotation center estimation algorithm for ISAR image of the space target based on image rotation and correlation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1280–1286. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181086. [19] AI Xiaofeng, HUANG Yan, ZHAO Feng, et al. Imaging of spinning targets via narrow-band T/R-R bistatic radars[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 362–366. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2205893. [20] JIANG Yicheng, SUN Sibo, YEO T S, et al. Bistatic ISAR distortion and defocusing analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(3): 1168–1182. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140028. [21] 夏靖远, 杨志雄, 周治兴, 等. 一种基于元学习的稀疏孔径ISAR成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121.XIA Jingyuan, YANG Zhixiong, ZHOU Zhixing, et al. A metalearning-based sparse aperture ISAR imaging method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121. [22] YUAN Zhengkun, WANG Junling, ZHAO Lizhi, et al. An MTRC-AHP compensation algorithm for Bi-ISAR imaging of space targets[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(5): 2356–2367. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2951735. [23] WANG Jiannan, MA Jingtao, HUANG Penghui, et al. Linear-geometry distortion correction for bistatic inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging based on deep learning model[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 11414–11417. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10640941. [24] DING Jiabao, LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, et al. Joint motion compensation and distortion correction for maneuvering target bistatic ISAR imaging based on parametric minimum entropy optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5118919. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213579. [25] FU Jixiang, XING Mengdao, and AMIN M G. ISAR imaging motion compensation in low SNR environments using phase gradient and filtering techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4296–4312. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098129. [26] KRAGH T J. Monotonic iterative algorithm for minimum-entropy autofocus[C]. Adaptive Sensor Array Processing Workshop, Lexington, USA, 2006: 1147–1159. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: