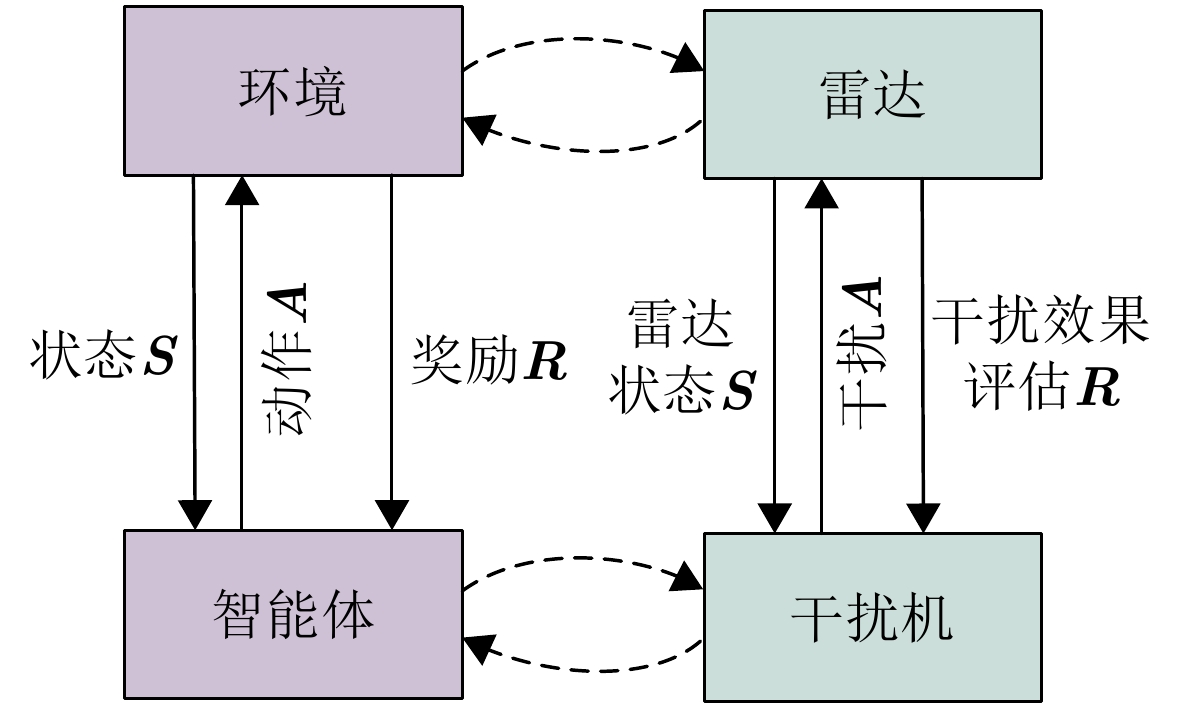
Optimization of Active-passive Interference Strategies for Rainbow Deep Q-network Joint Dichotomy Approach
-
摘要: 智能干扰决策技术的发展,显著提升了敏感目标在战场中的生存对抗能力。然而,现有干扰决策算法仅考虑有源干扰,忽略了无源干扰策略优化问题,严重限制了干扰决策对抗模型的应用场景。针对这一缺陷,该文基于彩虹深度Q网络(Rainbow DQN)与二分法,构建了一种有源-无源干扰策略联合优化方法,利用Rainbow DQN决策有无源干扰样式序列,并以二分法动态搜索无源干扰最优释放位置;考虑干扰对抗环境的非完全观测性,该文进一步设计了基于雷达波束指向点变化的奖励函数,以准确反馈干扰策略的有效性。通过仿真模拟干扰机-雷达对抗实验,与深度Q网络(DQN)、决策优势分离深度Q网络(Dueling DQN)及双重深度Q网络(Double DQN) 3种主流干扰决策模型相比,所提方法的Q值平均提升2.43倍,奖励均值平均提升3.09倍,无源干扰位置决策步数缩短50%以上。实验结果表明,该文所提基于Rainbow DQN与二分法的有源-无源干扰策略联合优化方法,可实现有源干扰与无源干扰联合有效决策,进一步提高了干扰策略决策模型适用性,显著提升了干扰机电子对抗中的价值。Abstract: The development of intelligent jamming decision-making technology has substantially enhanced the survival and confrontation capabilities of sensitive targets on the battlefield. However, existing jamming decision-making algorithms only consider active jamming while neglecting the optimization of passive jamming strategies. This limitation seriously restricts the application of adversarial models in jamming decision-making scenarios. Aiming to address this defect, this paper constructs a joint optimization method for active-passive jamming strategies based on Rainbow Deep Q-Network (DQN) and dichotomy. The method uses Rainbow DQN to determine the sequence of active and passive jamming styles and applies a dichotomy to dynamically search for the optimal release position of passive jamming. Additionally, considering the partially observable nature of the jamming confrontation environment, this paper further designs an optimization method for active-passive jamming strategies based on Rainbow DQN and Baseline DQN. A reward function is also introduced, based on changes in the radar beam pointing point, to accurately feedback the effectiveness of the jamming strategy. Through simulation experiments in jammer-radar confrontations, the proposed method is compared with the following three mainstream jamming decision models: Baseline DQN, Dueling DQN, and Double DQN. Results show that, compared to other interference decision-making models, the proposed method improves the Q value by an average of 2.43 times, the reward mean value by an average of 3.09 times, and reduces the number of decision-making steps for passive interference location by more than 50%. The experimental results show that the proposed joint active-passive jamming strategy optimization method based on Rainbow DQN and dichotomy substantially enhances the effectiveness of decision-making, improving the applicability of jamming strategy models and drastically boosting the value of the jammer in electronic countermeasures.
-
1 Rainbow DQN联合二分法的有源-无源干扰策略优化方法算法伪代码
1. Algorithmic Pseudo-code for active-passive Interference strategy optimisation methods for Rainbow DQN joint dichotomy approach
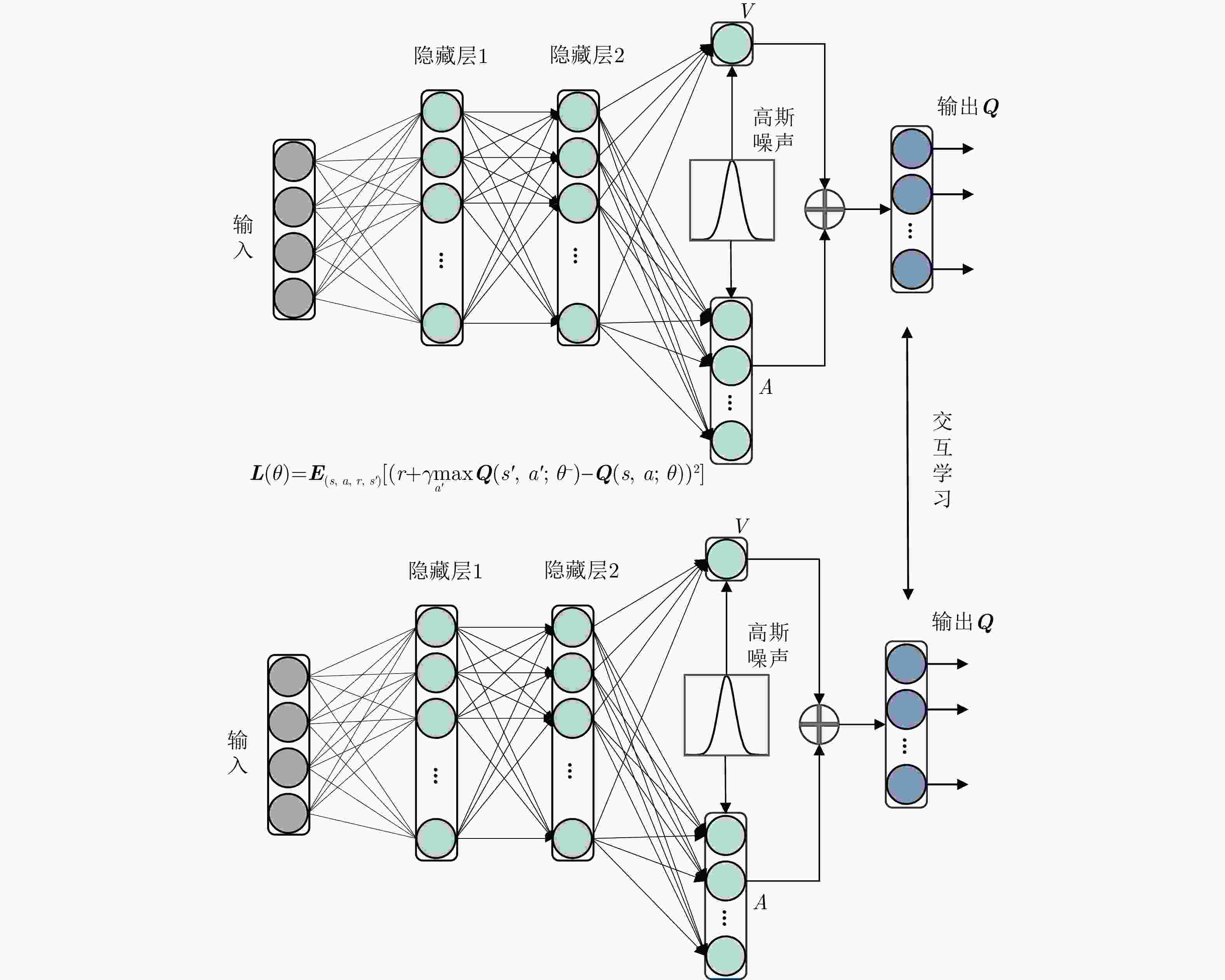
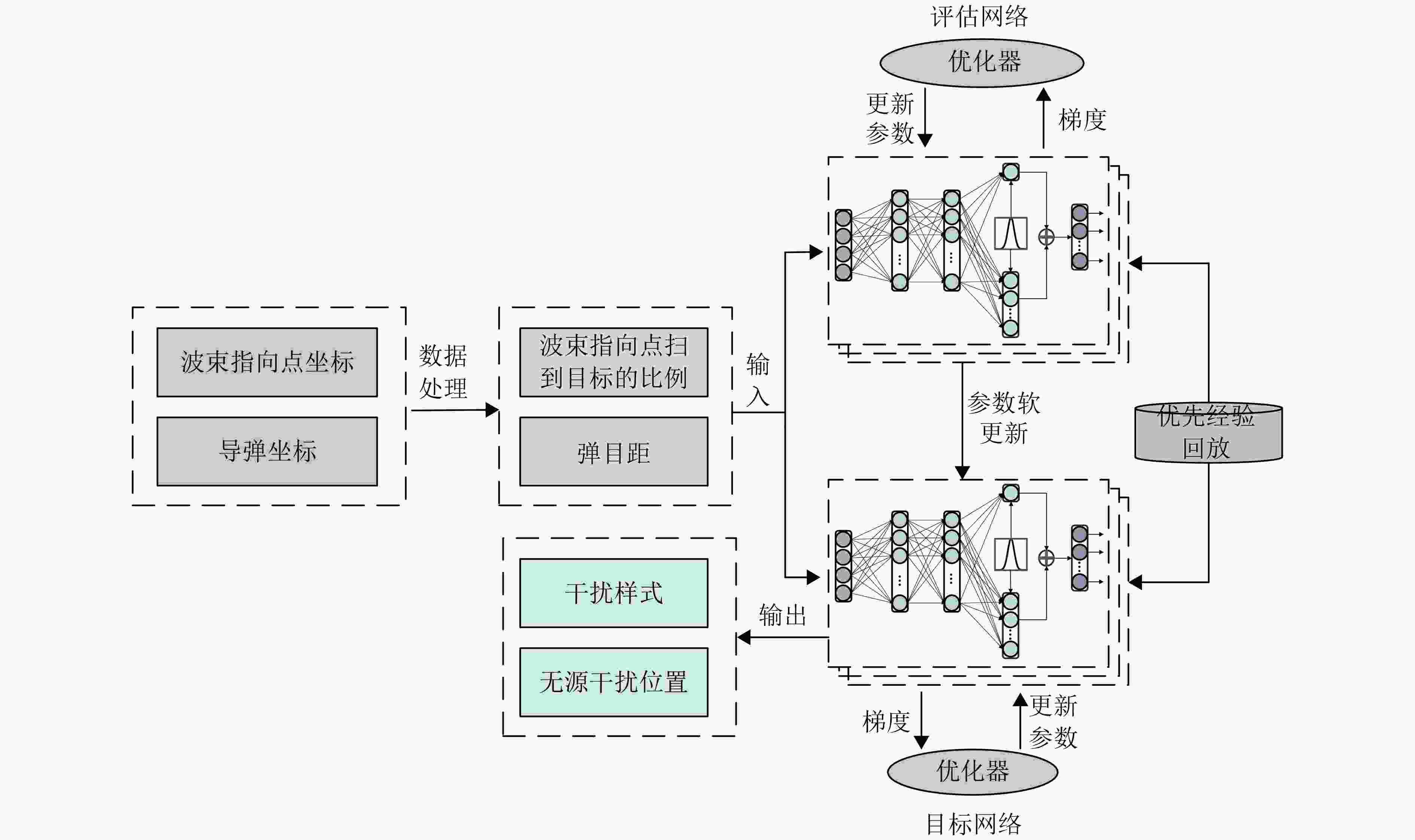
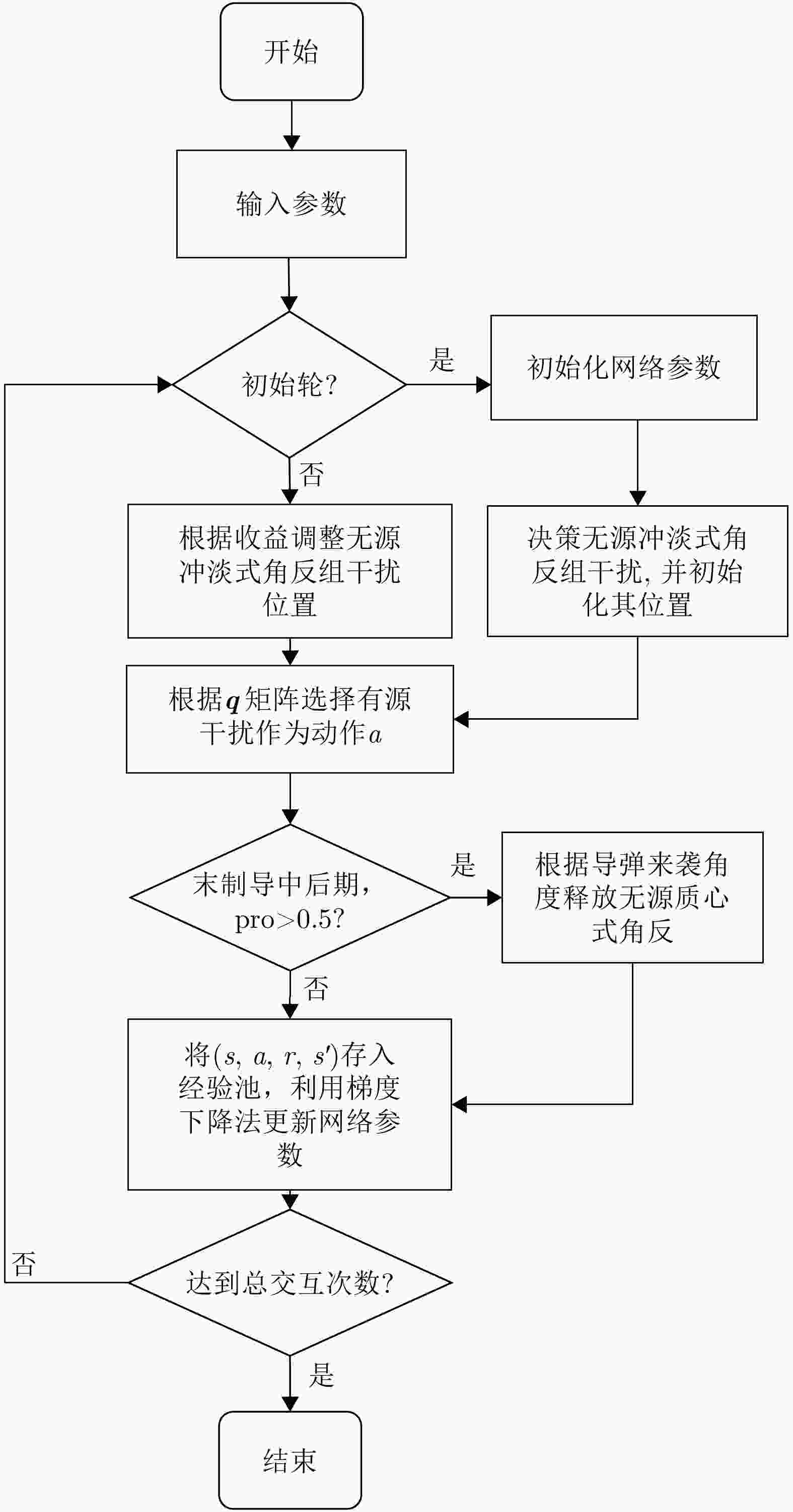
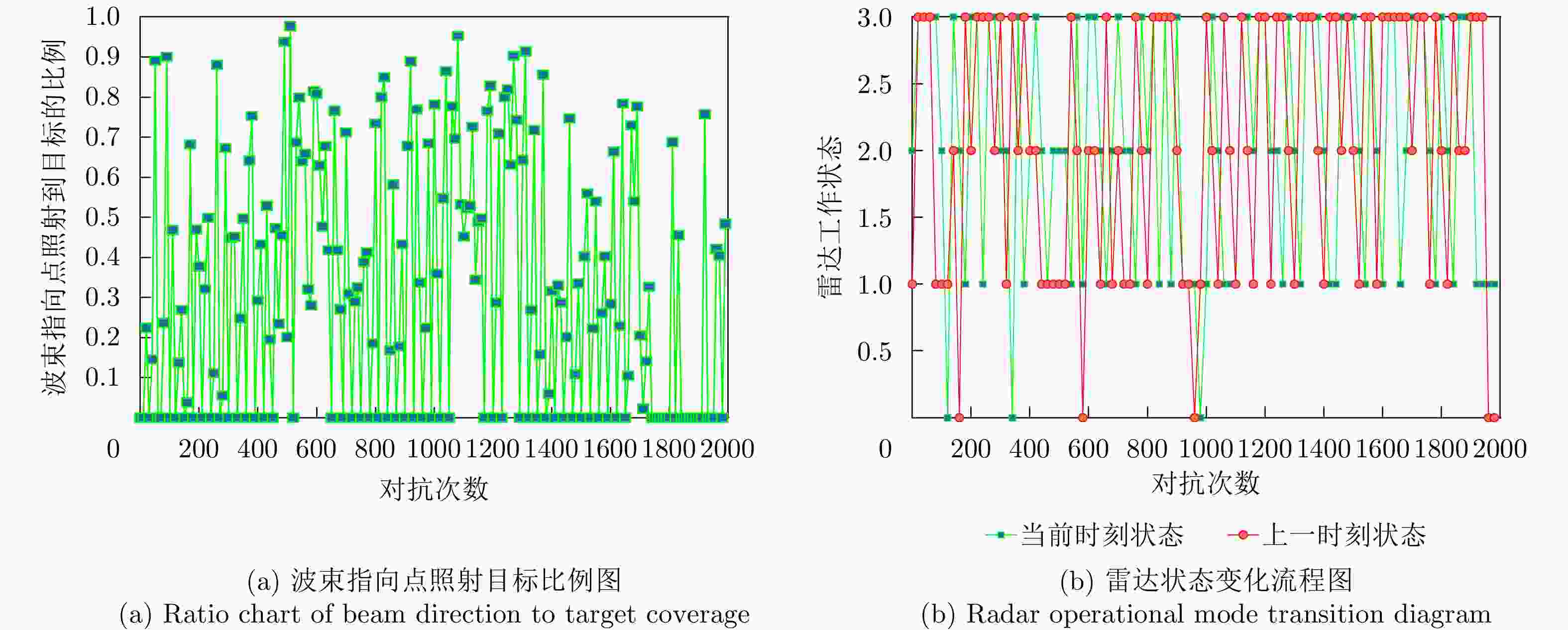
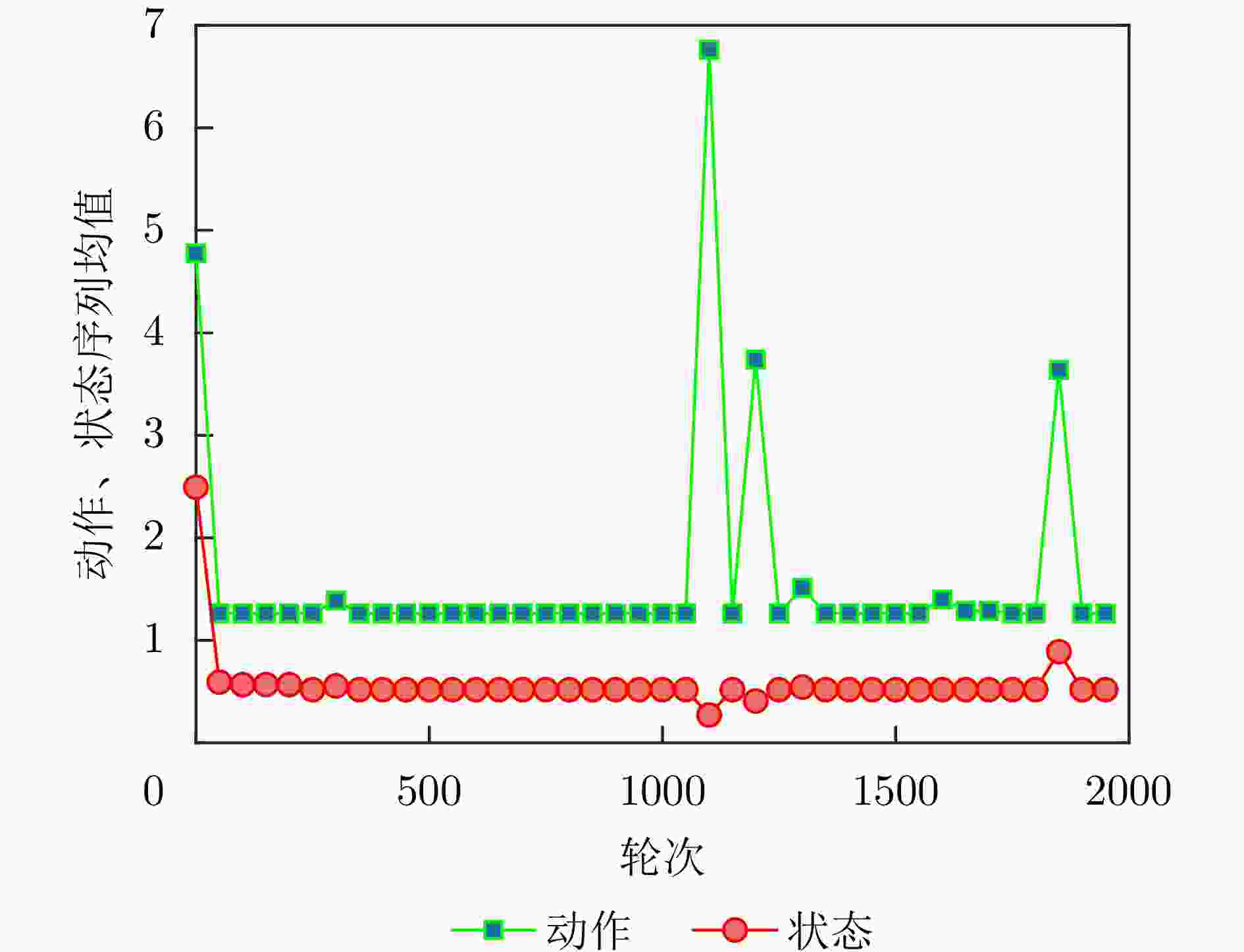
步骤1:初始化:设置${\mathrm{batch}}\_{\mathrm{size}}$,学习率${\mathrm{lr}}$,衰减率$\gamma $,初始化
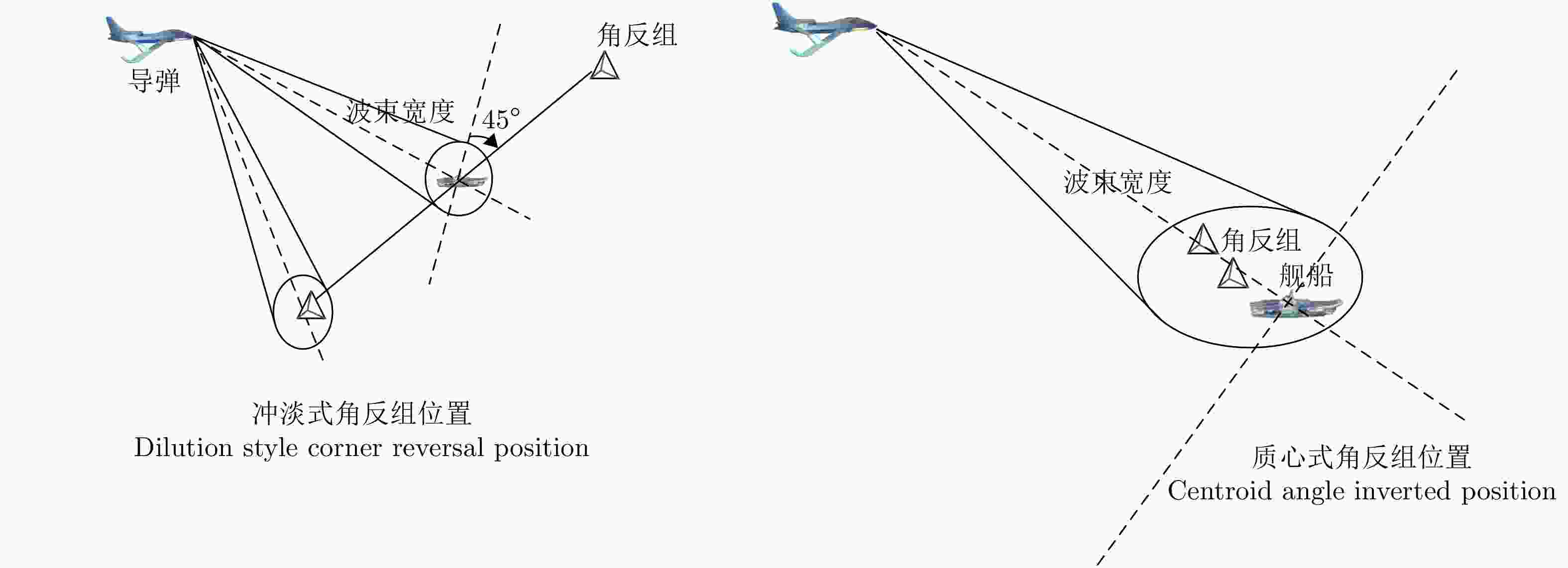
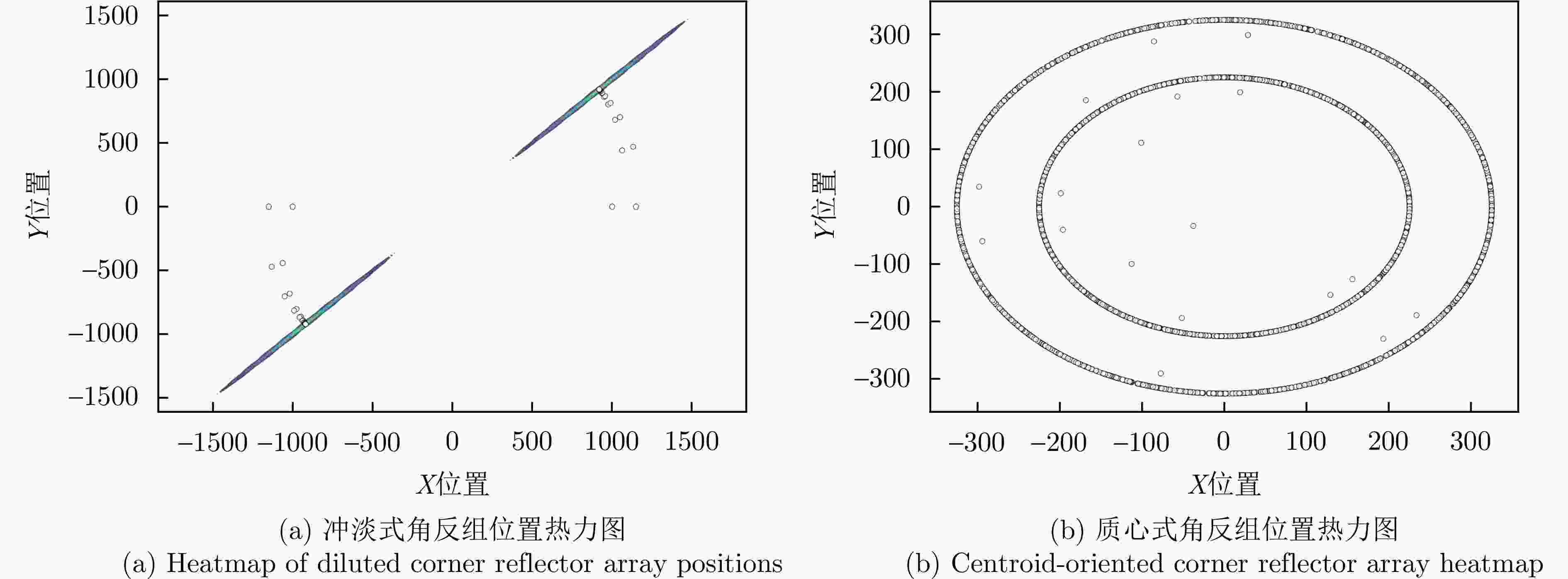
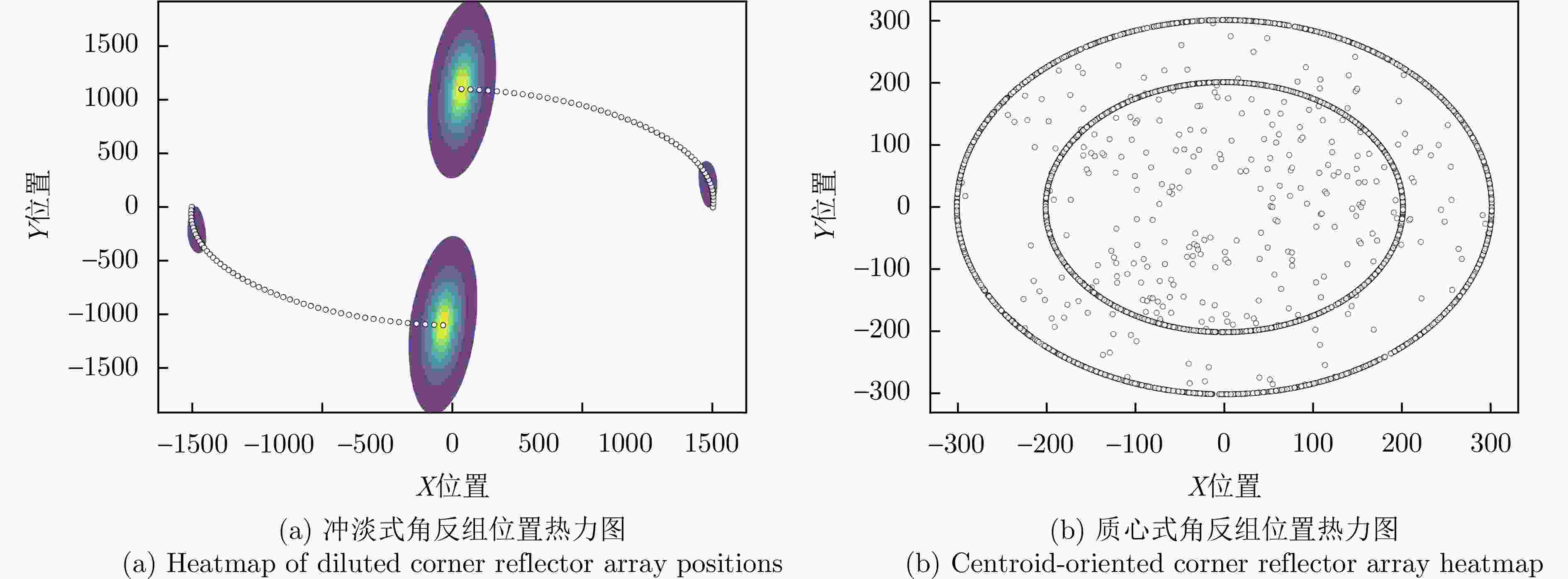
输入状态为搜索,初始化动作为无干扰;步骤2:是否为初始轮: 是,初始化冲淡式角反组干扰,抛掷位置为$(1\;{\mathrm{km}},45^\circ ) $,
$(1\;{\mathrm{km}},225^\circ )$;否,根据收益,利用二分法调整冲淡式角反组干扰的位置: $ ({r_t},{\theta _t}) = \left\{ \begin{gathered} \left( {\frac{{{r_{t - 1}} + {r_{t - 2}}}}{2},{\theta _{t - 1}}} \right),{J_t} \gt {J_{t - 1}} \\ \left( {{r_{t - 1}},\frac{{{\theta _{t - 1}} + {\theta _{t - 2}}}}{2}} \right),{J_t} \le {J_{t - 1}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ 步骤3:选择干扰动作a,根据奖励函数式(8),计算当前动作的
奖励r;步骤4:判断雷达是否处于探测的中后期,并且是否跟踪到目标: 是,投放质心式角反组干扰,投放极坐标为$(200\;{\mathrm{m}},\theta ) $,
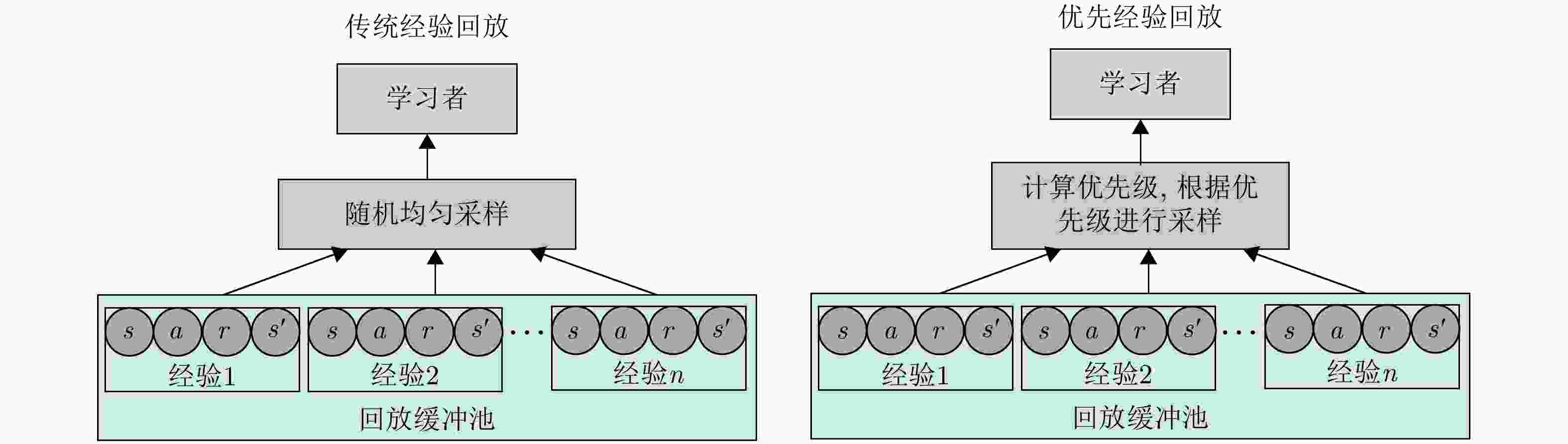
$(300\;{\mathrm{m}},\theta )$;否,根据收益,利用二分法调整质心式角反组干扰的位置: $ ({r_t},{\theta _t}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{r_{t - 1}} + {r_{t - 2}}}}{2},{\theta _d}} \right),{J_t} \gt {J_{t - 1}} $ 步骤5:将$(s,a,r,s')$存入到经验池D中; 步骤6:利用损失误差的反向传播,不断更新当前网络的参数,
执行步骤2—步骤5;步骤7:重复步骤6,直至式(7)收敛,此时将会得到最佳干扰序
列和最佳无源干扰位置。表 1 雷达任务状态转移概率矩阵
Table 1. Radar mission state transfer probability matrix
动作 状态 s1 s2 s3 s4 ${a_1}$ $p_{11}^n$ $p_{12}^n$ $p_{13}^n$ $p_{14}^n$ ${a_2}$ $p_{21}^n$ $p_{22}^n$ $p_{23}^n$ $p_{24}^n$ ${a_3}$ $ p_{31}^n $ $p_{32}^n$ $p_{33}^n$ $p_{34}^n$ ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 表 2 随着工作模式的变化波束指向点的变化
Table 2. Changes in beam pointing points with changes in operating mode
工作模式 波束指向点变化范围 搜索 以目标为圆心,以m为半径的圆 跟踪 以目标为圆心,以$m/2$为半径的圆 成像 以目标为圆心,以$m/4$为半径的圆 制导 以目标为圆心,以$m/8$为半径的圆 表 3 算法参数设计
Table 3. Algorithm parameter design
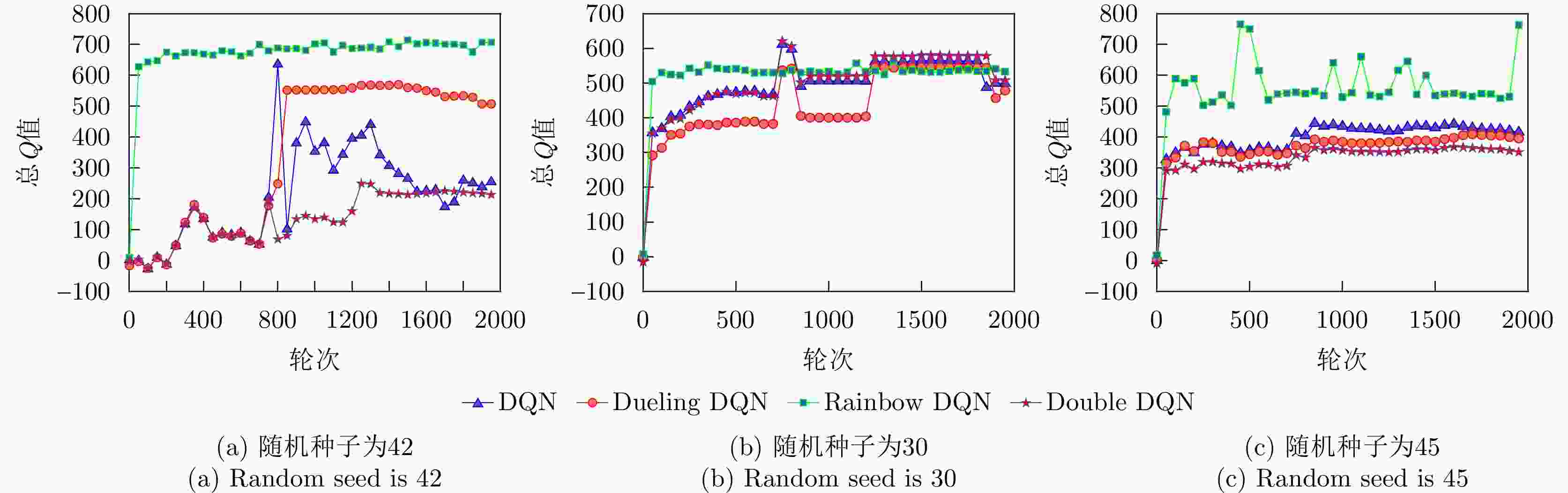
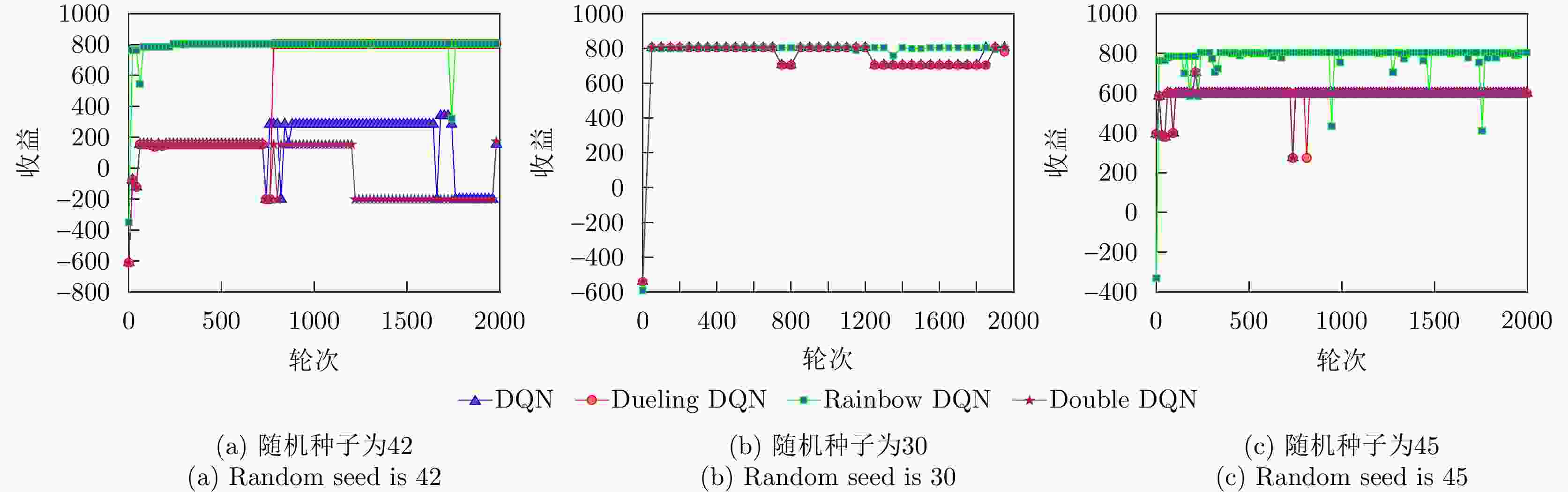
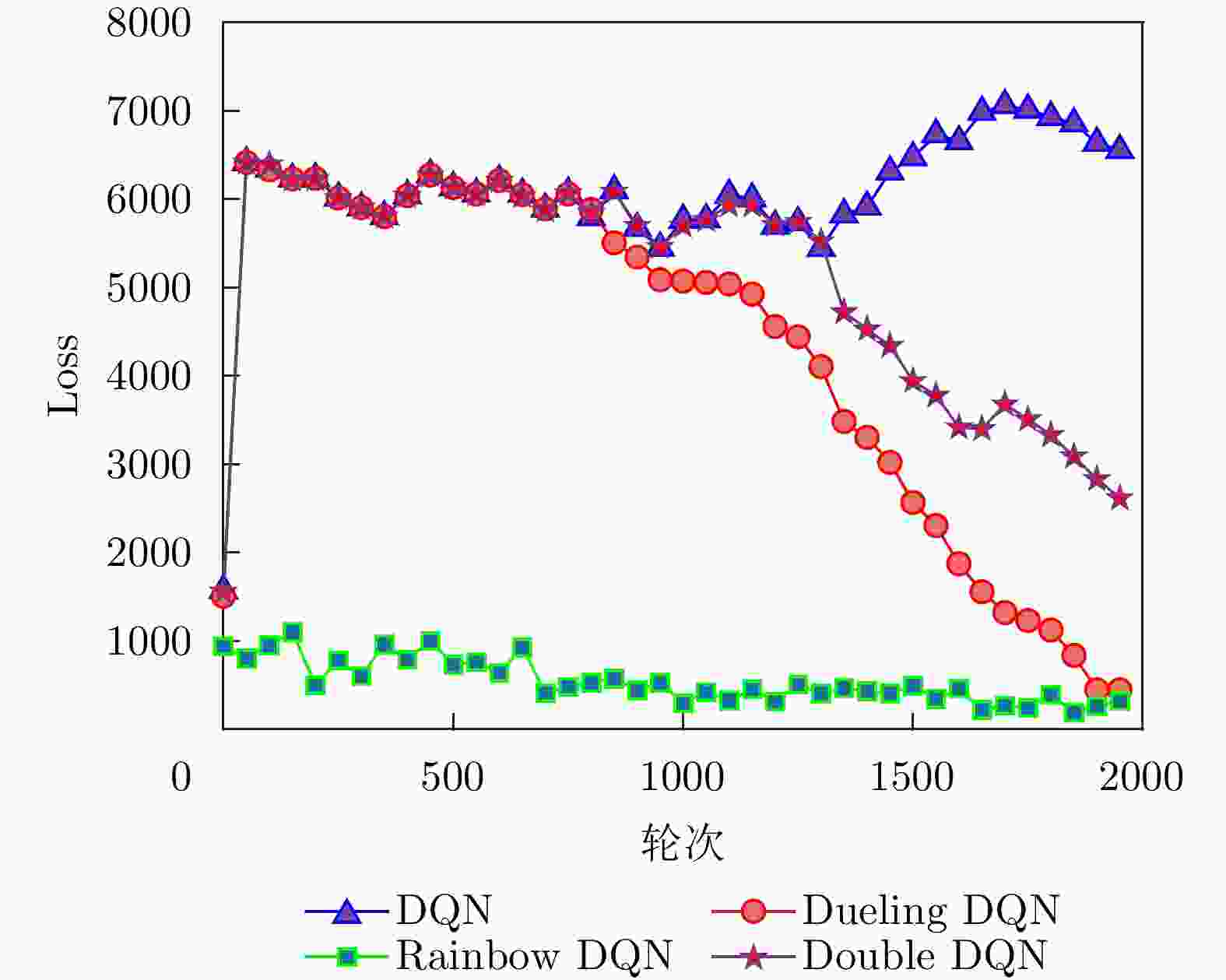
参数 学习率 优化器 批输入 折扣系数 奖励缩放 探索率 Rainbow DQN 1×10–4 Adam 64 0.99 1.0 0.5 DQN 1×10–4 Adam 64 0.99 1.0 0.5 Dueling DQN 1×10–4 Adam 64 0.99 1.0 0.5 Double DQN 1×10–4 Adam 64 0.99 1.0 0.5 表 4 各算法结果表格
Table 4. Table of results for each algorithm
参数 达到最优的
步数收敛后的
奖励值收敛Q值
均值总训练
时间测试选到
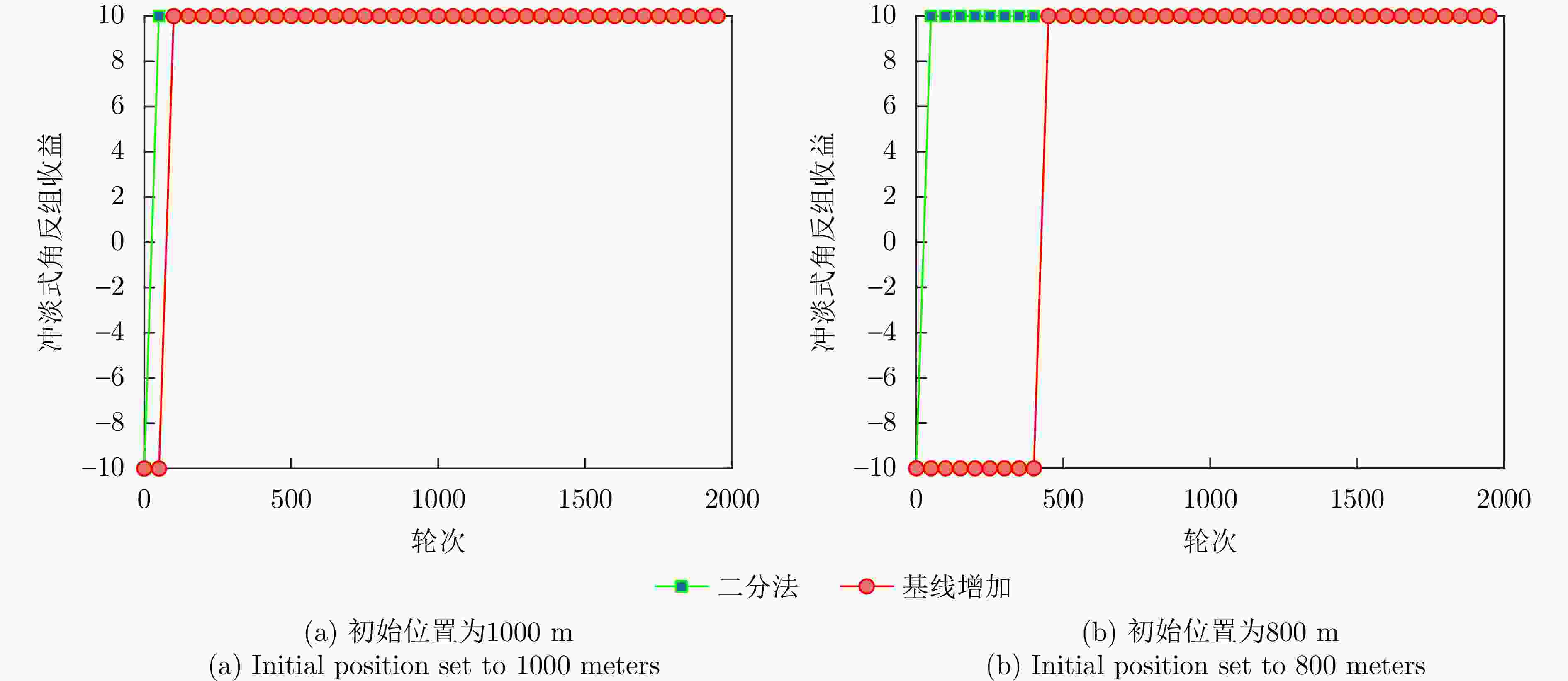
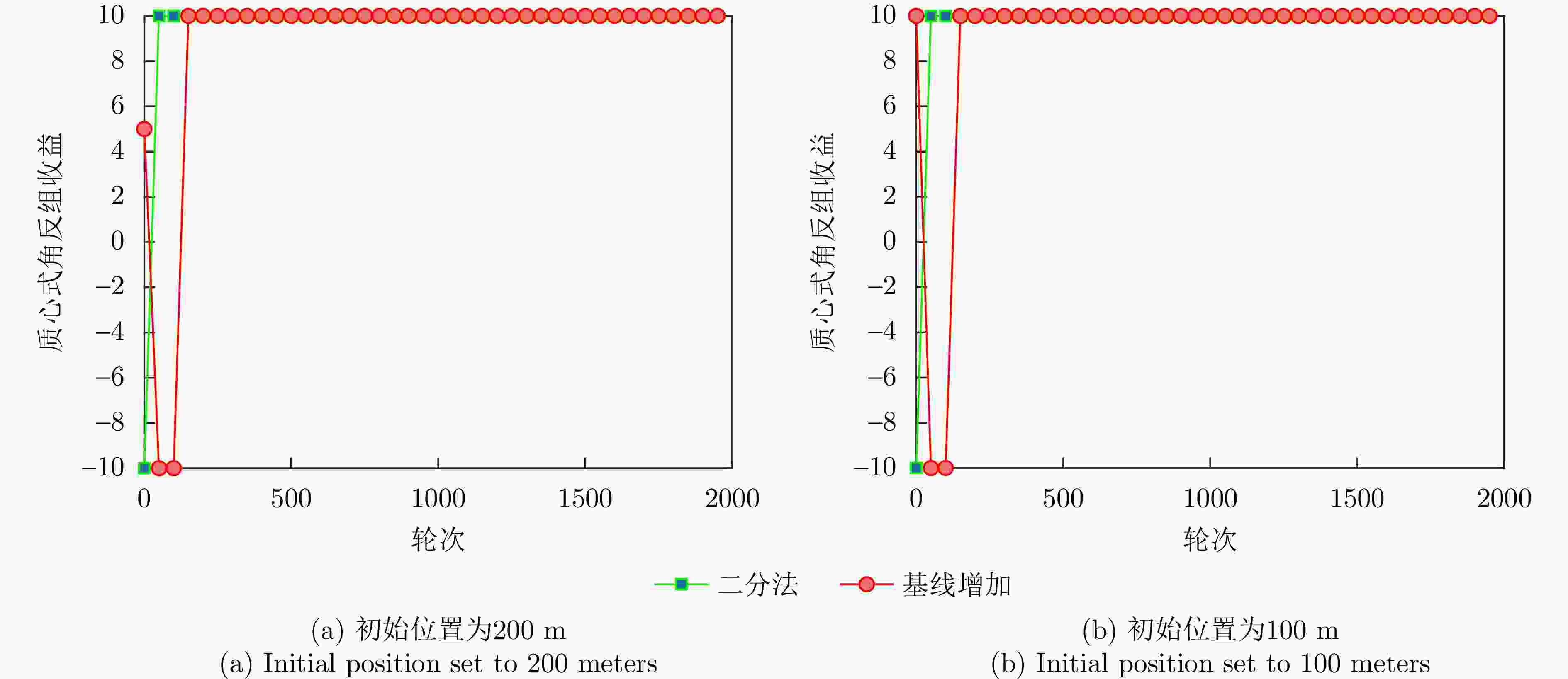
最优点时间Rainbow DQN 20 810 680 6.65 s 0.022 s DQN 760 280 310 4.19 s 0.418 s Dueling DQN 780 810 510 4.25 s 0.585 s Double DQN 60 150 180 4.30 s 0.039 s 表 5 二分法与基线增加对比表
Table 5. Comparison of dichotomous and itemised searches
收敛步数 基线增加 二分法 冲淡式角反组 152 70 质心式角反组 160 3 -
[1] 黄知涛, 王翔, 赵雨睿. 认知电子战综述[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2023, 45(5): 1–11. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202305001.HUANG Zhitao, WANG Xiang, and ZHAO Yurui. Overview of cognitive electronic warfare[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1–11. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202305001. [2] 刘松涛, 雷震烁, 温镇铭, 等. 认知电子战研究进展[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2020, 42(5): 1–15.LIU Songtao, LEI Zhenshuo, WEN Zhenming, et al. A development review on cognitive electronic warfare[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2020, 42(5): 1–15. [3] LI Nengjing and ZHANG Yiting. A survey of radar ECM and ECCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(3): 1110–1120. doi: 10.1109/7.395232. [4] FARINA A and TIMMONERI T. Live data test of Electronic Counter Counter Measures (ECCM) on a multifunctional prototype radar[C]. 2016 IEEE Metrology for Aerospace (MetroAeroSpace), Florence, Italy, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/MetroAeroSpace.2016.7573176. [5] 黄岩, 赵博, 陶明亮, 等. 合成孔径雷达抗干扰技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113.HUANG Yan, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. Review of synthetic aperture radar interference suppression[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113. [6] 韩朝赟, 岑熙, 崔嘉禾, 等. 纹理异常感知SAR自监督学习干扰抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168.HAN Zhaoyun, CEN Xi, CUI Jiahe, et al. Self-supervised learning method for SAR interference suppression based on abnormal texture perception[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168. [7] 解烽, 刘环宇, 胡锡坤, 等. 基于复数域深度强化学习的多干扰场景雷达抗干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1290–1304. doi: 10.12000/JR23139.XIE Feng, LIU Huanyu, HU Xikun, et al. A radar anti-jamming method under multi-jamming scenarios based on deep reinforcement learning in complex domains[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1290–1304. doi: 10.12000/JR23139. [8] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [9] ZHANG Tinghao, LI Yachao, WANG Jun, et al. A modified range model and extended Omega-K algorithm for high-speed-high-squint SAR with curved trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5204515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3255518. [10] 张嘉翔, 张凯翔, 梁振楠, 等. 一种基于深度强化学习的频率捷变雷达智能频点决策方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 227–239. doi: 10.12000/JR23197.ZHANG Jiaxiang, ZHANG Kaixiang, LIANG Zhennan, et al. An intelligent frequency decision method for a frequency agile radar based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 227–239. doi: 10.12000/JR23197. [11] LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, WANG Yu, et al. Random frequency coded waveform optimization and signal coherent accumulation against compound deception jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4434–4449. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3243884. [12] SONG Xuan, LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Focusing high-maneuverability bistatic forward-looking SAR using extended azimuth nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5240814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3228803. [13] ZHANG Tinghao, LI Yachao, YUAN Mingze, et al. Focusing highly squinted FMCW-SAR data using the modified wavenumber-domain algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 1999–2011. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3266886. [14] KAWANISHI T, KUROZUMI T, KASHINO K, et al. A fast template matching algorithm with adaptive skipping using inner-subtemplates’ distances[C]. The 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004, Cambridge, UK, 2004: 654–657. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2004.1334614. [15] VANDERBRUG and ROSENFELD. Two-stage template matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 1977, C-26(4): 384–393. doi: 10.1109/TC.1977.1674847. [16] XING Qiang, ZHU Weigang, CHI Zhou, et al. Jamming decision under condition of incomplete jamming rule library[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7449–7454. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0486. [17] 刘清, 王兴华, 王星, 等. 干扰方式选择方法的研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2011, 39(4): 50–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2011.04.011.LIU Qing, WANG Xinghua, WANG Xing, et al. Study on jamming choosing measures[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2011, 39(4): 50–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2011.04.011. [18] 周脉成. 基于博弈论的雷达干扰决策技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014. doi: 10.7666/d.D551732.ZHOU Maicheng. Research on radar jamming decision technology based on game theory[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014. doi: 10.7666/d.D551732. [19] 唐文龙, 张剑云, 王冰川, 等. 干扰样式选择方法研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(1): 72–76. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.01.017.TANG Wenlong, ZHANG Jianyun, WANG Bingchuan, et al. A study on jamming style selecting[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(1): 72–76. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.01.017. [20] MOUSAVI S S, SCHUKAT M, and HOWLEY E. Deep Reinforcement Learning: An Overview[M]. BI Yaxin, KAPOOR S, and BHATIA R. Proceedings of SAI Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys) 2016. Cham: Springer, 2016: 426–440. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56991-8_32. [21] 邢强, 贾鑫, 朱卫纲. 基于Q-学习的智能雷达对抗[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(5): 1031–1035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.11.XING Qiang, JIA Xin, and ZHU Weigang. Intelligent radar countermeasure based on Q-learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(5): 1031–1035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.11. [22] 李云杰, 朱云鹏, 高梅国. 基于Q-学习算法的认知雷达对抗过程设计[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2015, 35(11): 1194–1199. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.11.017.LI Yunjie, ZHU Yunpeng, and GAO Meiguo. Design of cognitive radar jamming based on Q-learning algorithm[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(11): 1194–1199. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.11.017. [23] 张柏开, 朱卫纲. 基于Q-Learning的多功能雷达认知干扰决策方法[J]. 电讯技术, 2020, 60(2): 129–136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2020.02.001.ZHANG Bokai and ZHU Weigang. A cognitive jamming decision method for multi-functional radar based on Q-Learning[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2020, 60(2): 129–136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2020.02.001. [24] DUAN Xueying. Abnormal behavior recognition for human motion based on improved deep reinforcement learning[J]. International Journal of Image and Graphics, 2024, 24(1): 2550029. doi: 10.1142/S0219467825500299. [25] ZHANG Wenxu, MA Dan, ZHAO Zhongkai, et al. Design of cognitive jamming decision-making system against MFR based on reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(8): 10048–10062. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3261318. [26] 张柏开, 朱卫纲. 对多功能雷达的DQN认知干扰决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(4): 819–825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.04.12.ZHANG Bokai and ZHU Weigang. DQN based decision-making method of cognitive jamming against multifunctional radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(4): 819–825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.04.12. [27] 曹舒雅, 张文旭, 赵桐, 等. 基于DQN的雷达智能干扰决策方法[J]. 制导与引信, 2024, 45(2): 11–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0576.2024.02.002.CAO Shuya, ZHANG Wenxu, ZHAO Tong, et al. Radar intelligent jamming decision method based on DQN[J]. Guidance & Fuze, 2024, 45(2): 11–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0576.2024.02.002. [28] GAN L, XIONG K, LIAO M, et al. Cognitive jammer time resource scheduling with imperfect information via fuzzy Q-Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 15: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/taes.2025.3540050. [29] 赵知劲, 朱家晟, 叶学义, 等. 基于多智能体模糊深度强化学习的跳频组网智能抗干扰决策算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2814–2823. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210608.ZHAO Zhijin, ZHU Jiasheng, YE Xueyi, et al. Intelligent anti-jamming decision algorithm for frequency hopping network based on multi-agent fuzzy deep reinforcemnet learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2814–2823. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210608. [30] 辛京钰, 谷继红, 杨婕, 等. 角反射器阵列排布设计及其散射特性研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2025, 40(1): 63–71. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2024196.XIN Jingyu, GU Jihong, YANG Jie, et al. Design of corner reflector array arrangement and study of its scattering characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2025, 40(1): 63–71. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2024196. [31] XIA Le, WANG Fulai, PANG Chen, et al. An identification method of corner reflector array based on mismatched filter through changing the frequency modulation slope[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(12): 2114. doi: 10.3390/rs16122114. [32] VAN HASSELT H, GUEZ A, and SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-Learning[C]. The 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 2094–2100. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10295. [33] WANG Ziyu, SCHAUL T, HESSEL M, et al. Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning[C]. The 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2015: 1995–2003. [34] SCHAUL T, QUAN J, ANTONOGLOU I, et al. Prioritized experience replay[C]. The 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016: 1–21. [35] HESSEL M, MODAYIL J, VAN HASSELT H, et al. Rainbow: Combining improvements in deep reinforcement learning[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 3215–3222. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11796. [36] 李艺春, 刘泽娇, 洪艺天, 等. 基于多智能体强化学习的博弈综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 540–558. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240478.LI Yichun, LIU Zejiao, HONG Yitian, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning based game: A survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 540–558. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240478. [37] 李明, 任清华, 吴佳隆. 无人机多域联合抗干扰智能决策算法研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2021, 39(2): 367–374. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213920367.LI Ming, REN Qinghua, and WU Jialong. Exploring UAV’s multi-domain joint anti-jamming intelligent decision algorithm[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021, 39(2): 367–374. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213920367. [38] 廖艳苹, 谢榕浩. 基于双层强化学习的多功能雷达认知干扰决策方法[J]. 应用科技, 2023, 50(6): 56–62. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202302004.LIAO Yanping and XIE Ronghao. Multi-function radar cognitive jamming decision-making method based on two-layer reinforcement learning[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2023, 50(6): 56–62. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202302004. [39] ZHANG Chudi, SONG Yunqi, JIANG Rundong, et al. A cognitive electronic jamming decision-making method based on Q-Learning and ant colony fusion algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(12): 3108. doi: 10.3390/rs15123108. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: