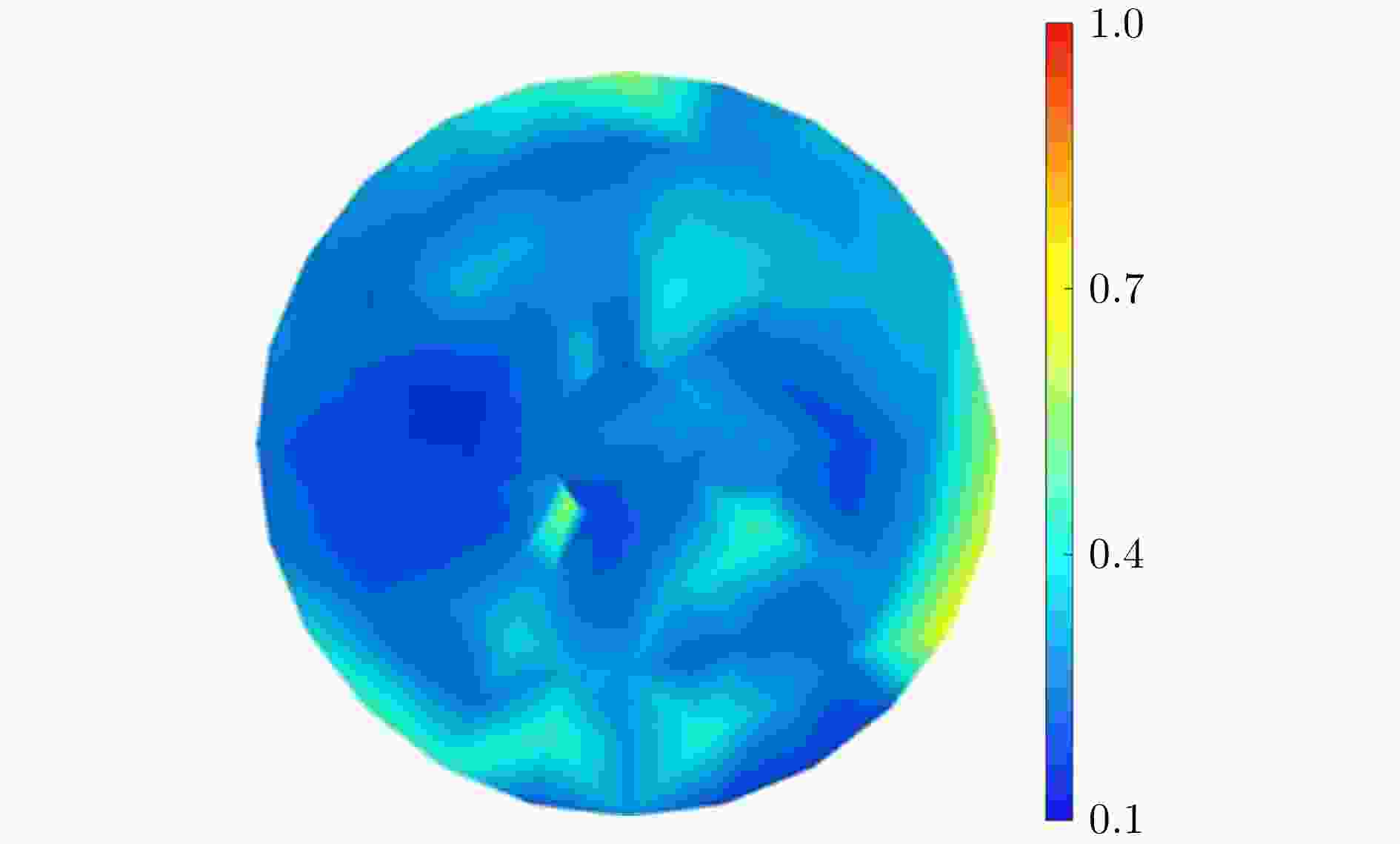
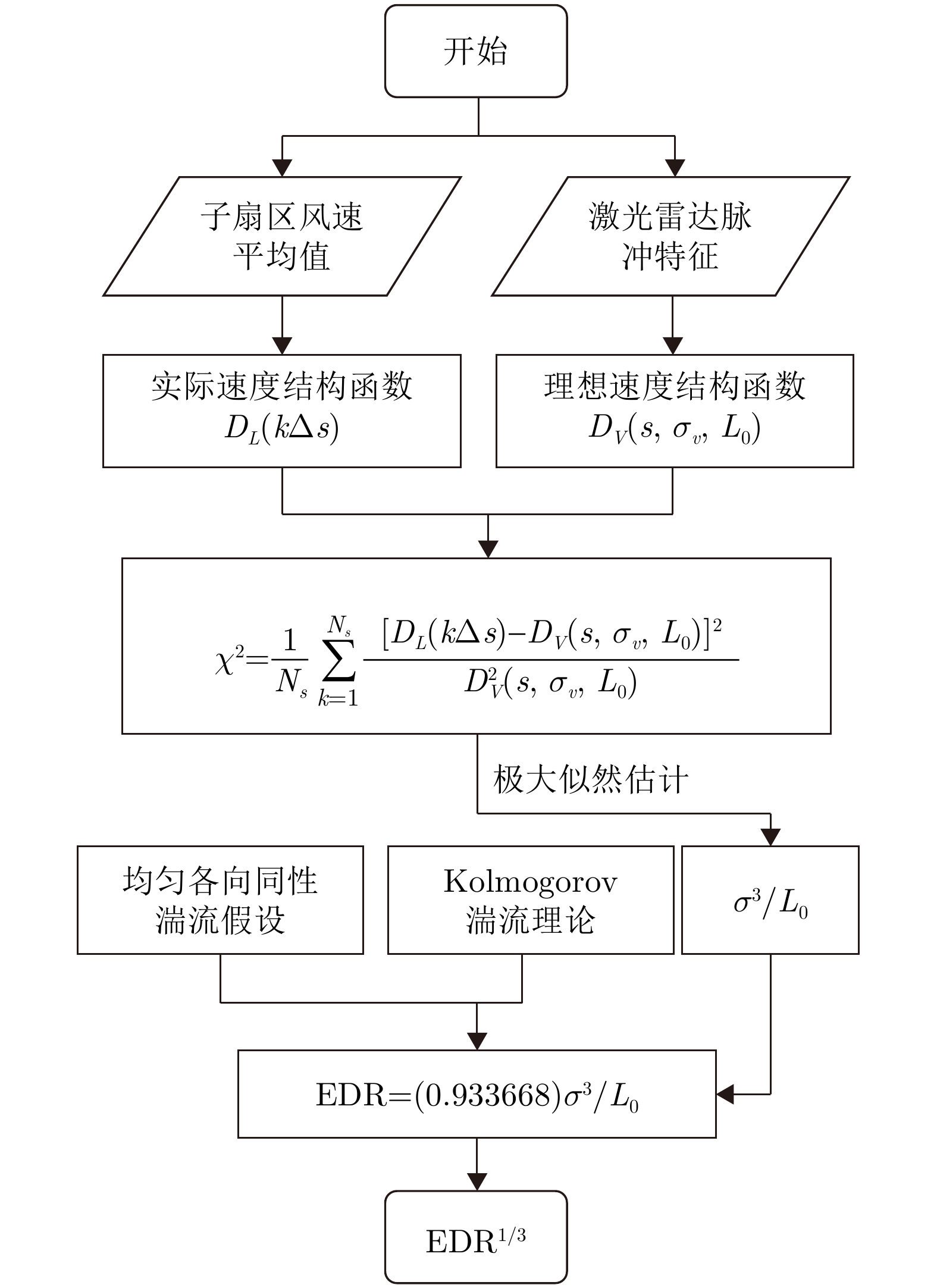
-
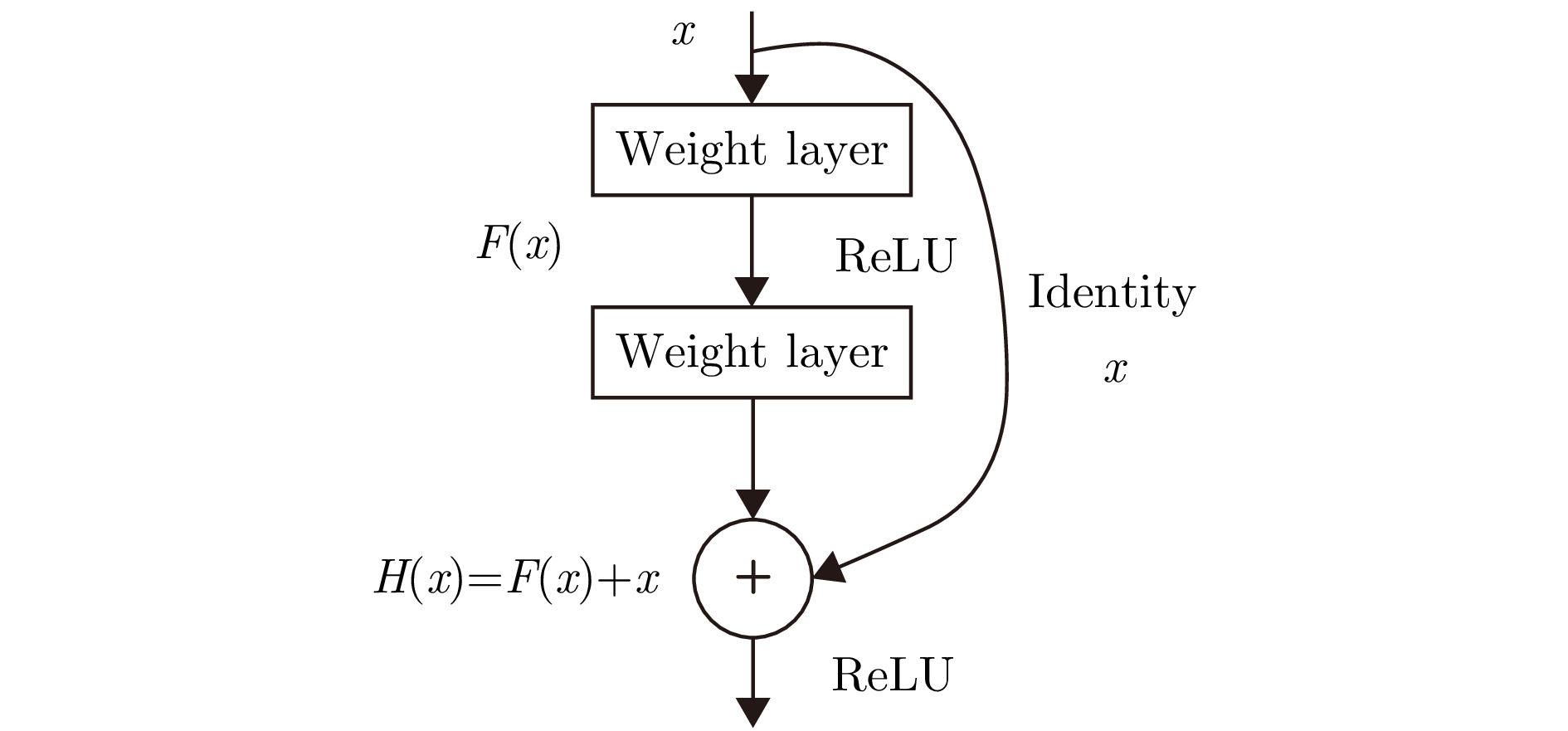
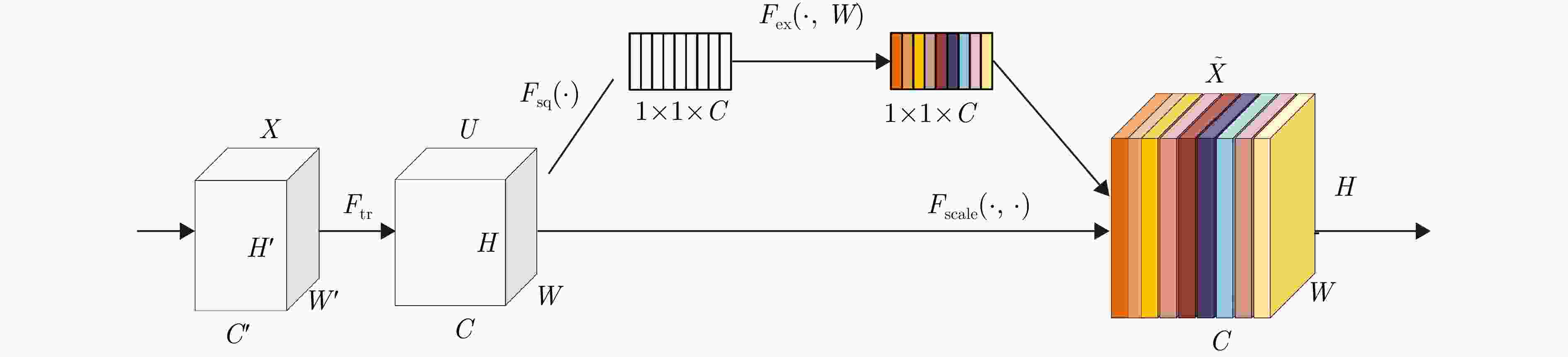
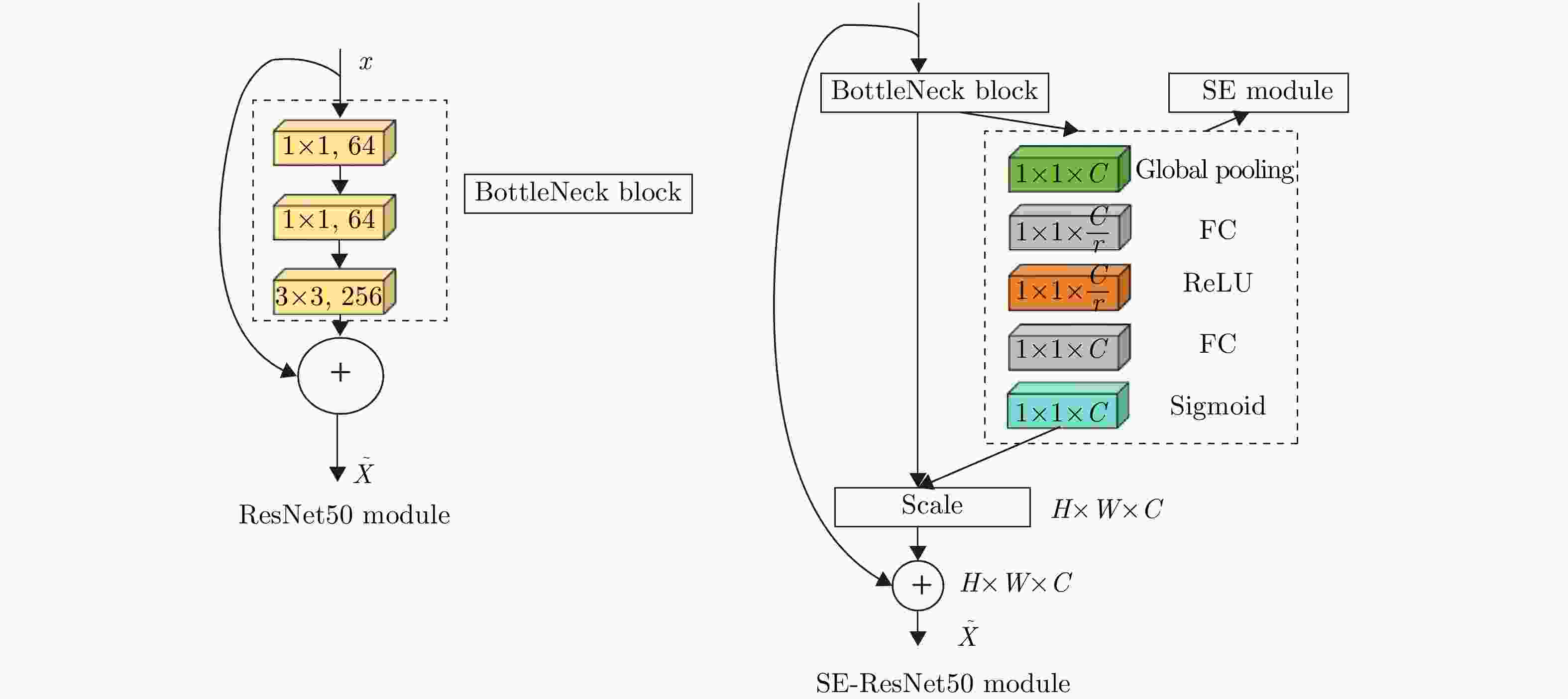
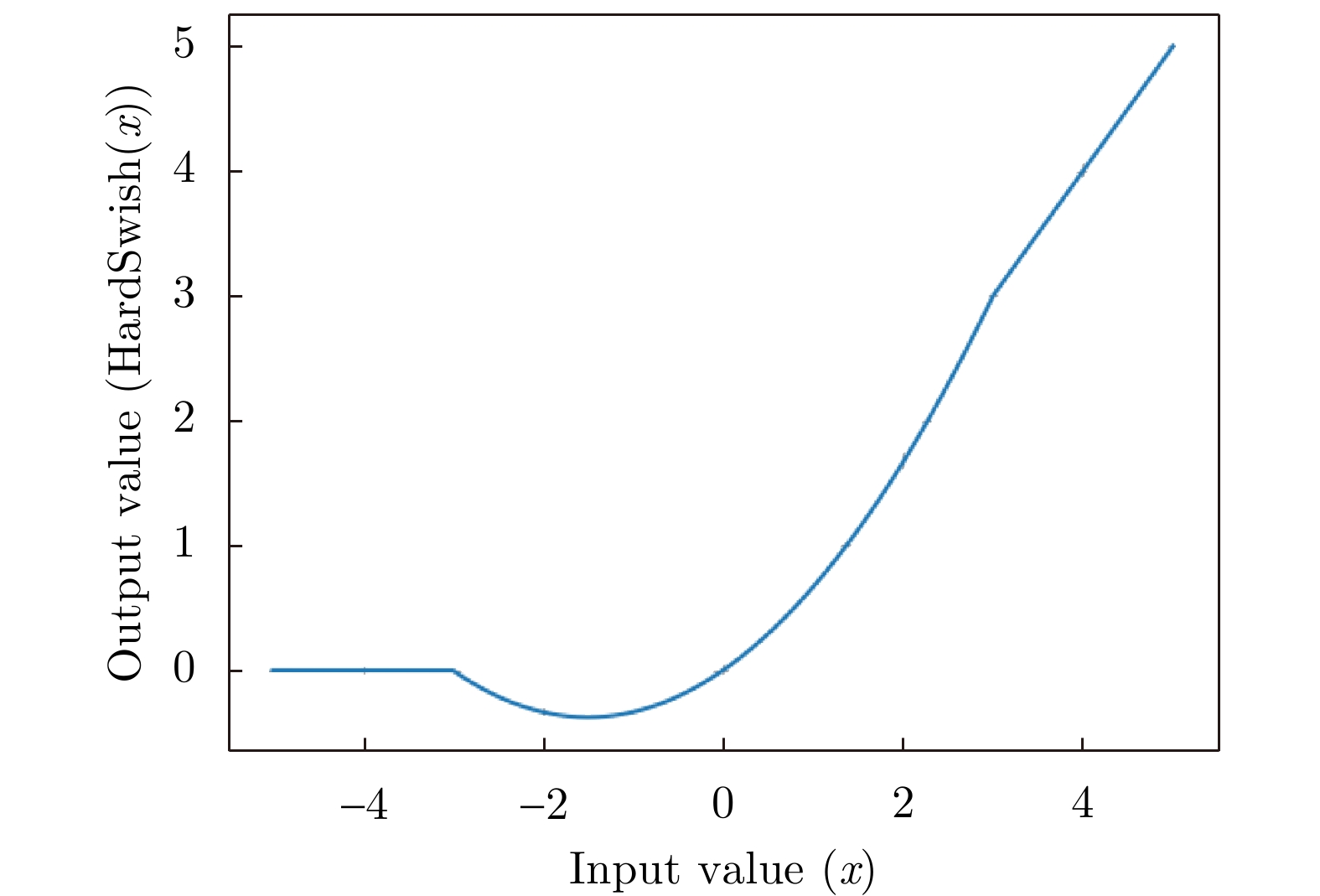
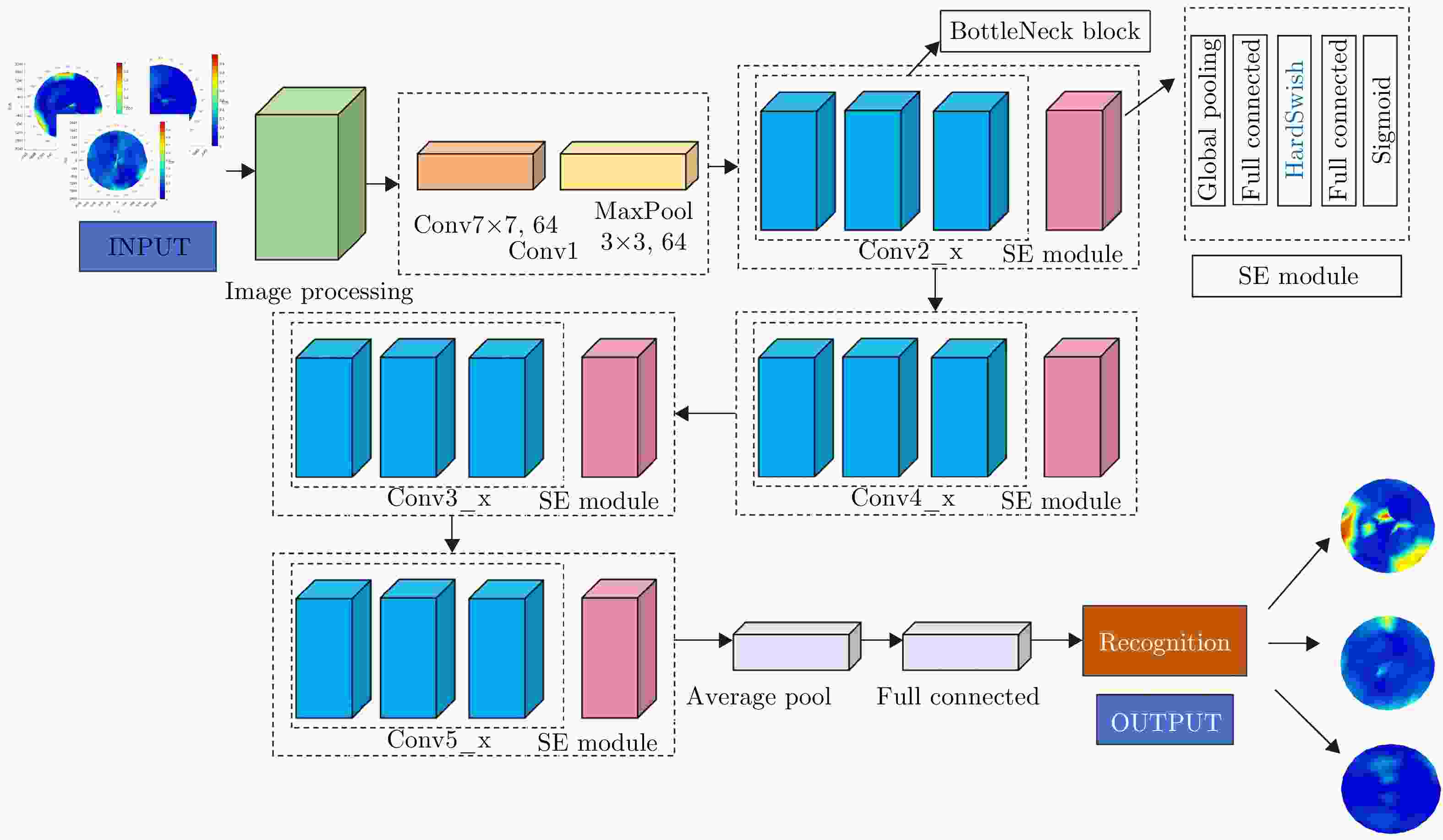
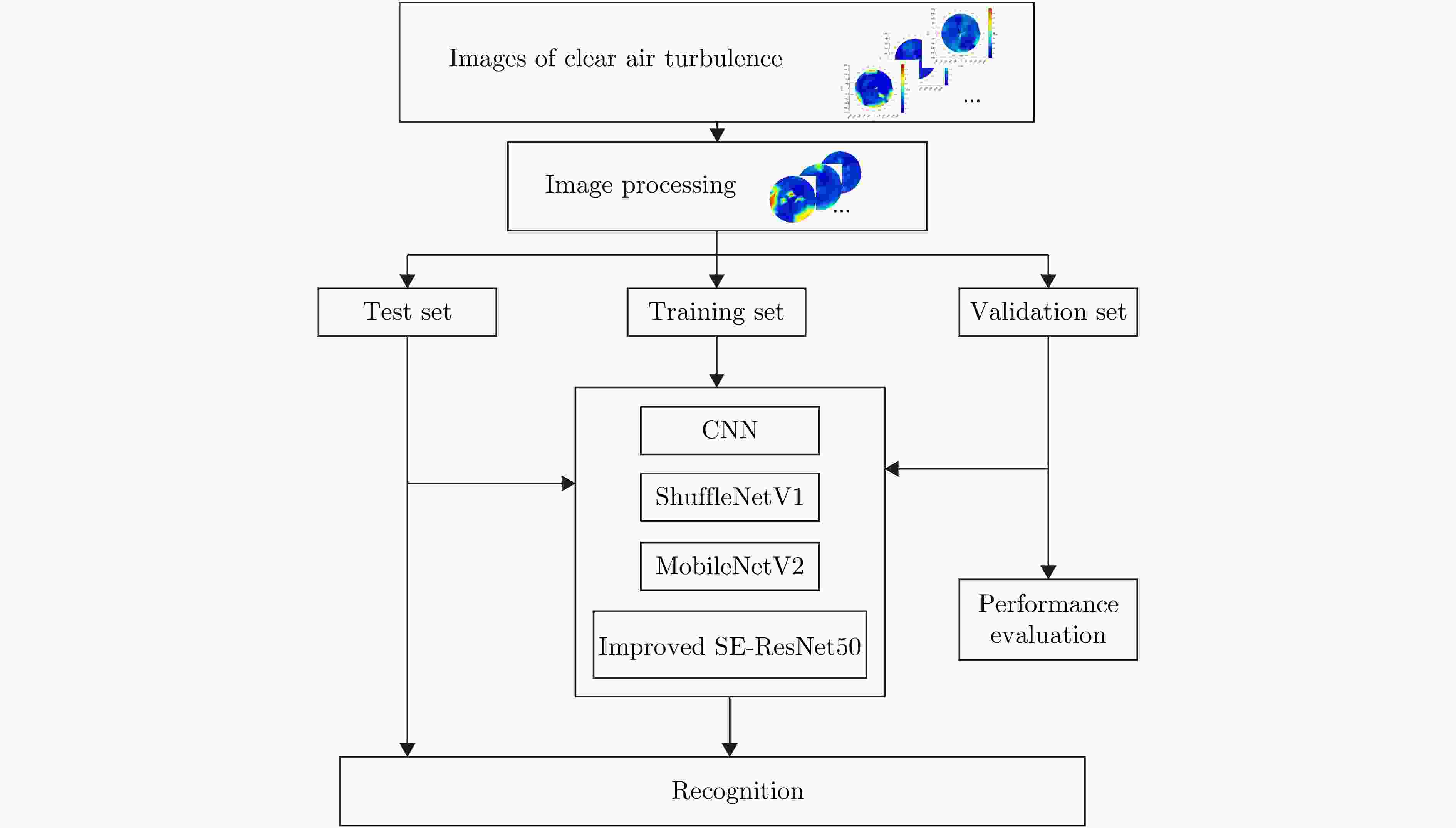
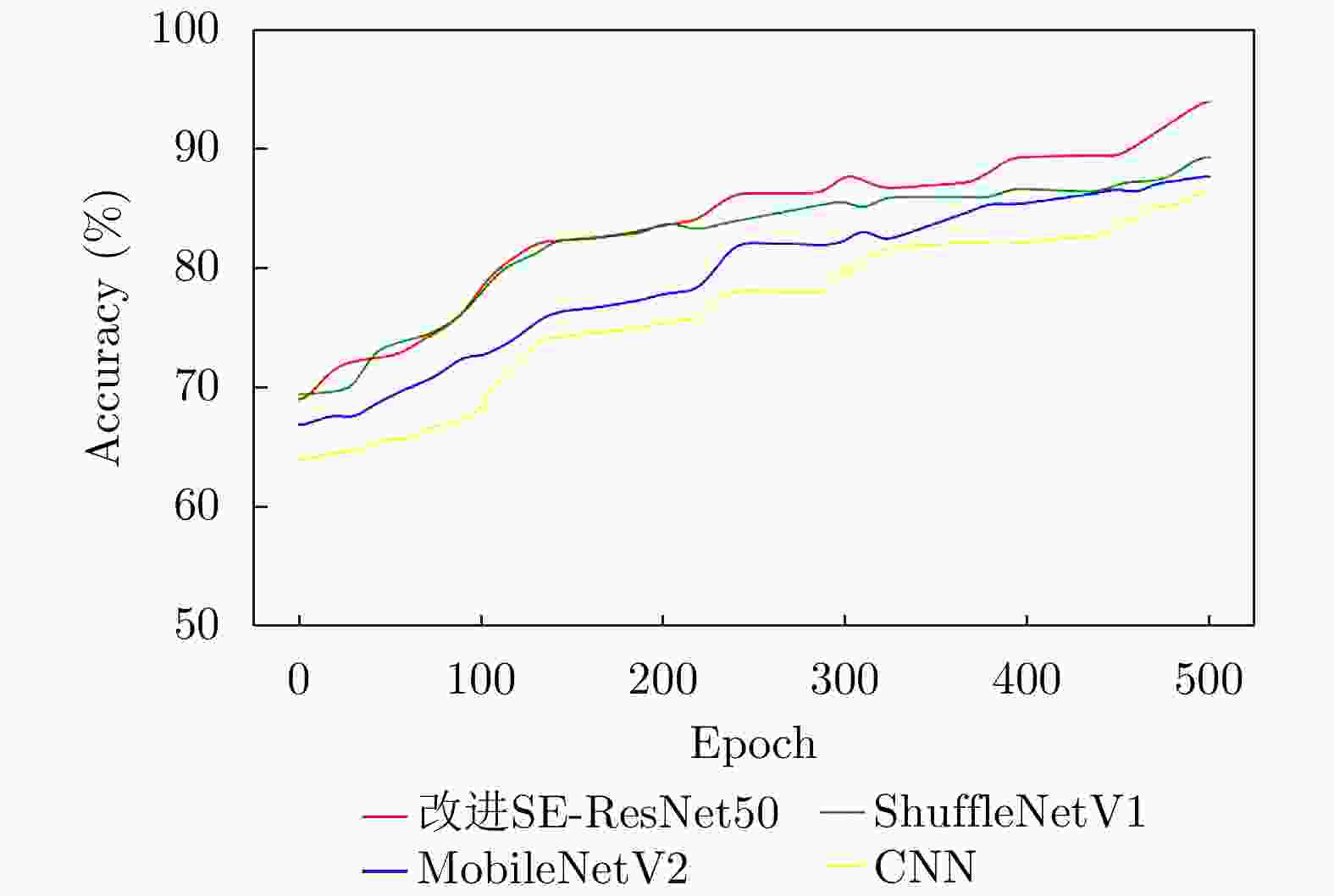
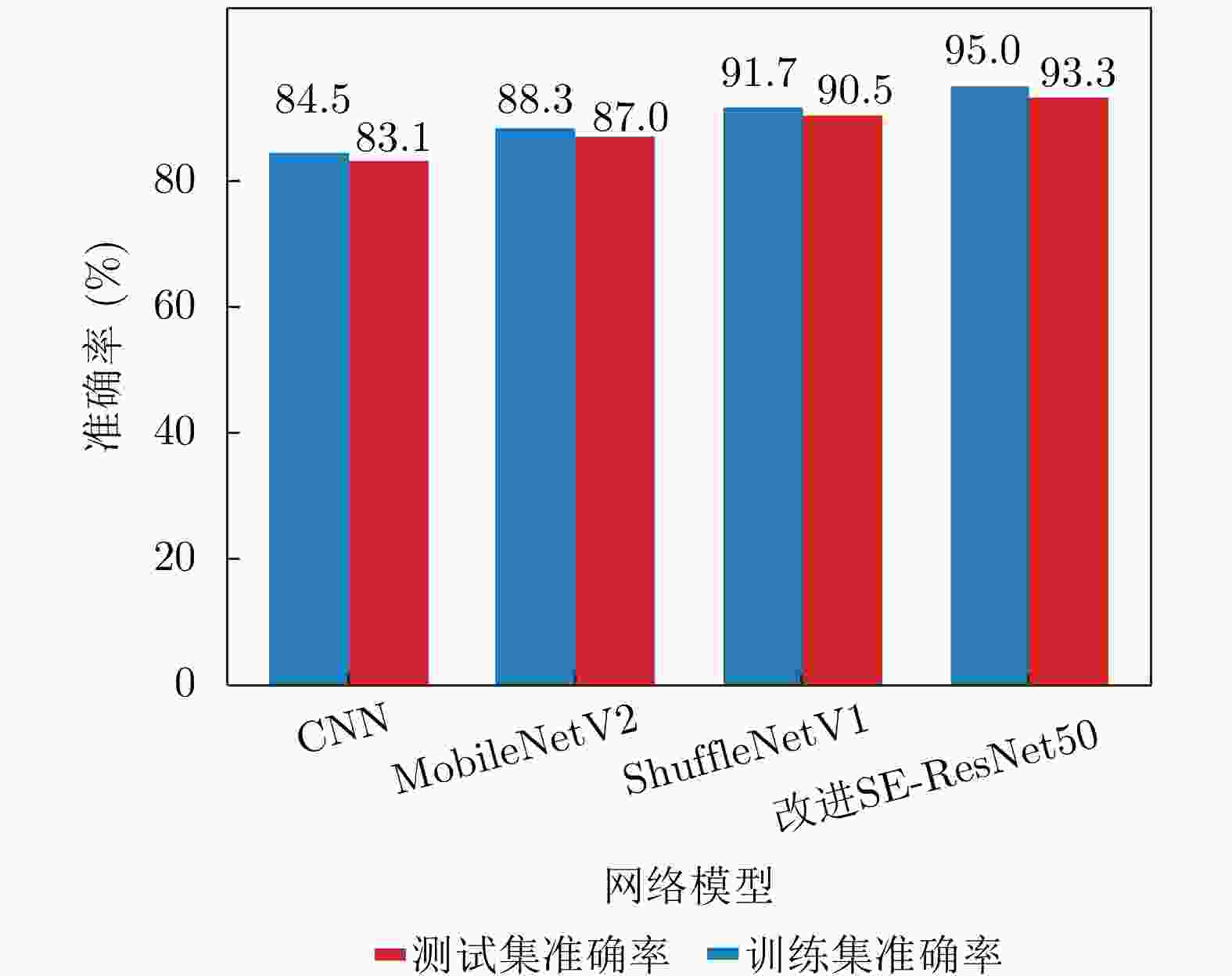
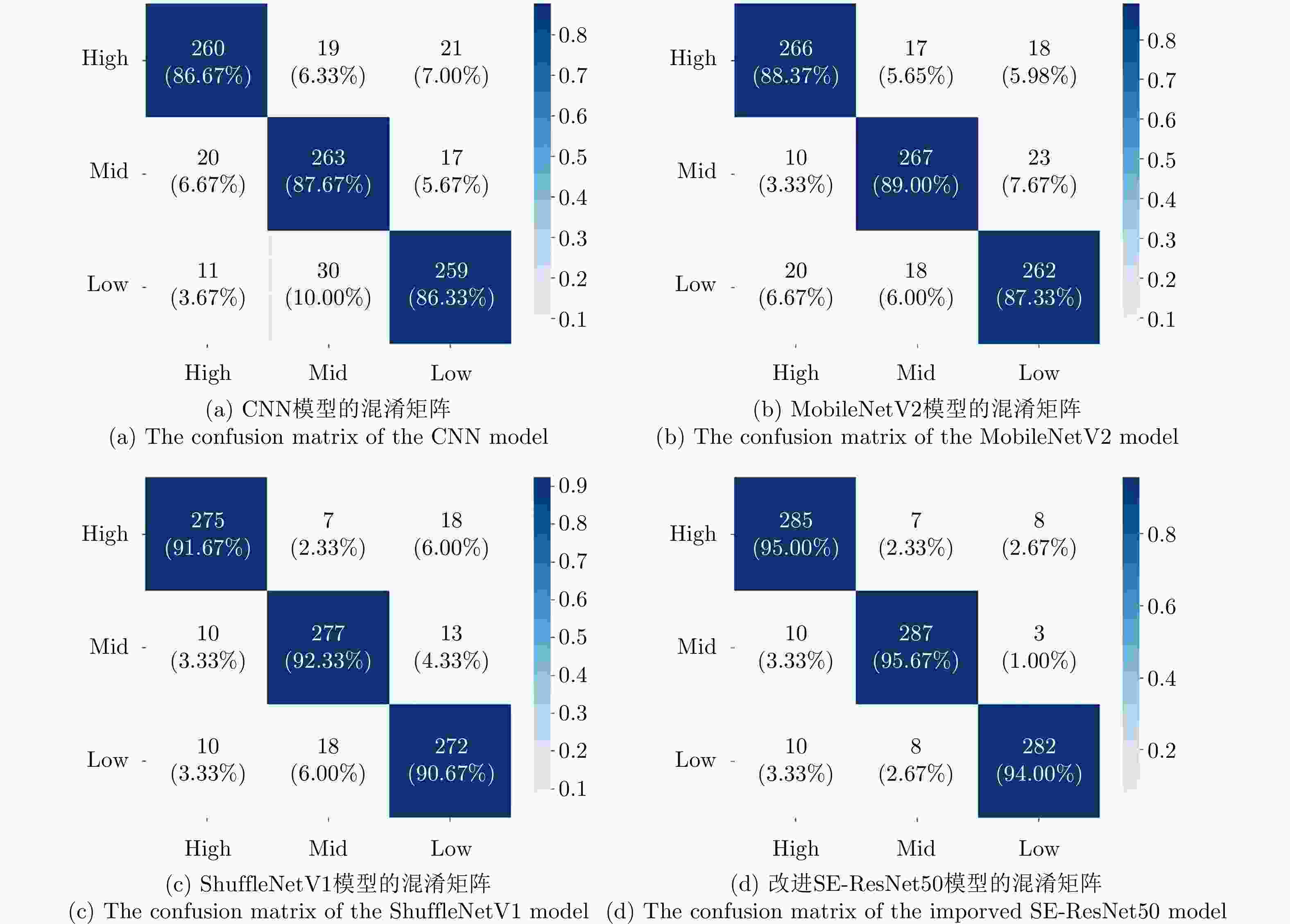
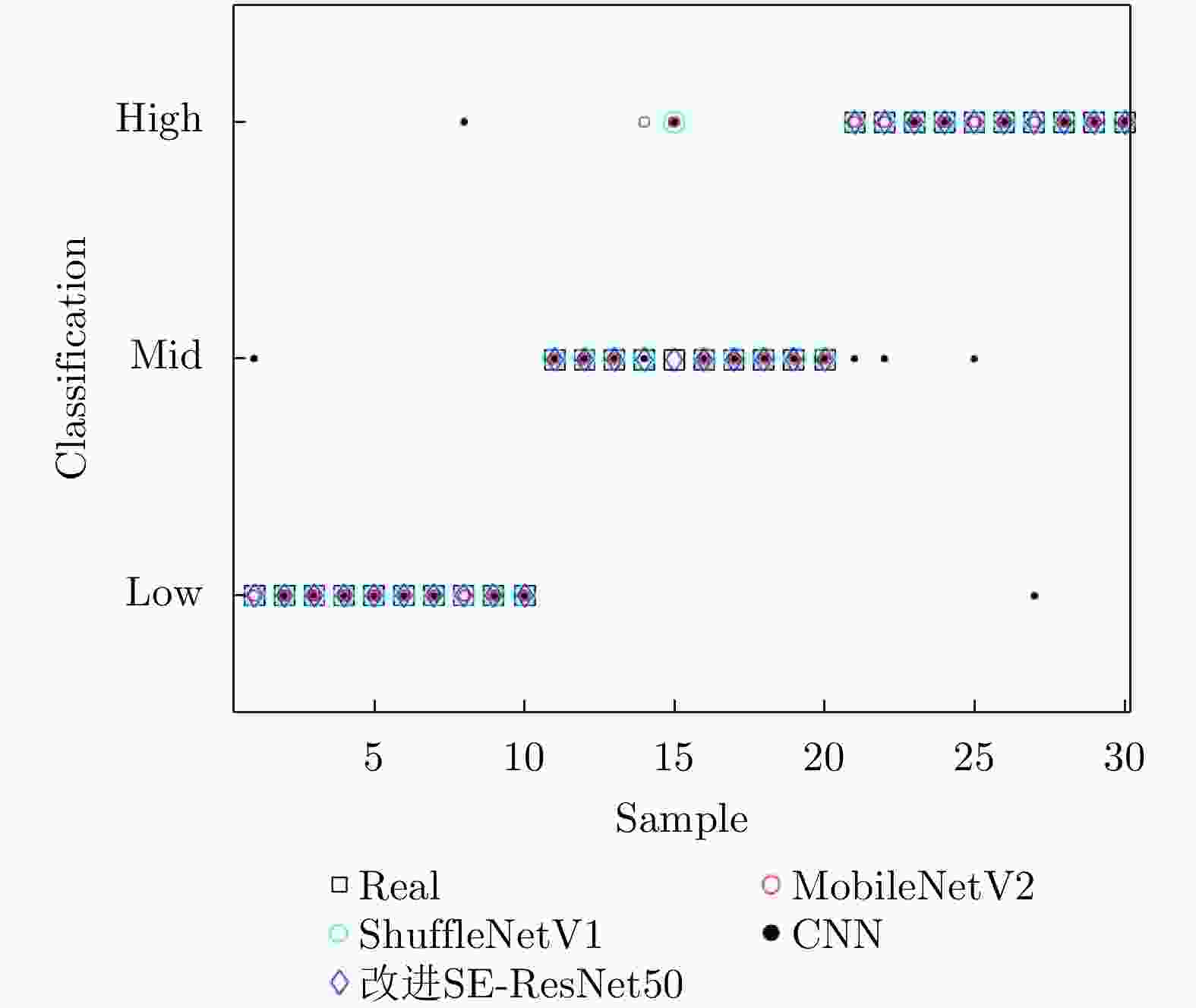
摘要: 针对机场低空区域采用激光雷达进行湍流识别时识别率低的问题,提出了使用一种改进50层挤压激励残差网络(SE-ResNet50)的晴空湍流识别方法。通过引入挤压激励模块,改进网络结构,降低了模型对特征定位的过度敏感,使网络在学习过程中选择性地突出有用的信息特征;以兰州中川国际机场的实测数据建立了样本数据集,依据湍流分类等级抽取弱、中、强3类等量颠簸数据建立平衡数据集进行模型训练。在相同的实验条件下,与卷积神经网络、MobileNetV2和ShuffleNetV1网络相比,改进SE-ResNet50的识别准确率分别提高了7.44%, 6.52%和4.11%,对比各个模型生成的混淆矩阵,表明该文方法的准确率达到了95%,验证了所提方法的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 激光雷达 /
- 涡流耗散率(EDR) /
- 晴空湍流 /
- 残差网络(ResNet) /
- 深度学习
Abstract: To address the issue of LiDAR’s low turbulence recognition rate at airports in low-altitude areas, a clear air turbulence recognition method based on an improved Squeeze-and-Excitation Residual Network with 50 layers (SE-ResNet50) is proposed. By introducing the squeeze-and-excitation module and improving the network structure, the model’s excessive sensitivity to feature location is reduced, thereby enabling the network to selectively highlight useful information features during the learning process. A sample dataset was established using measured data from Lanzhou Zhongchuan International Airport; for model training, a balanced dataset was created by extracting an equal amount of weak, moderate, and strong turbulence data based on the turbulence classification level. Under the same experimental conditions, the recognition accuracy of the improved SE-ResNet50 was increased by 7.44%, 6.52%, and 4.11% compared with the convolutional neural network, MobileNetV2, and ShuffleNetV1 networks, respectively. A comparison of the confusion matrices generated by each model showed that the accuracy of the proposed method reached 95%, verifying the feasibility of the proposed method. -
表 1 测风激光雷达主要技术指标
Table 1. Main technical indicators of LiDAR
参数 指标 扫描距离分辨率 15 m/30 m/50 m 数据刷新率 3 s 扫描角度分辨率 5° 俯仰角 3° 最大扫描高度 158 m 扫描方式 PPI 探测距离范围 45~ 3000 m表 2 湍流强度分级表
Table 2. Turbulence intensity classification table
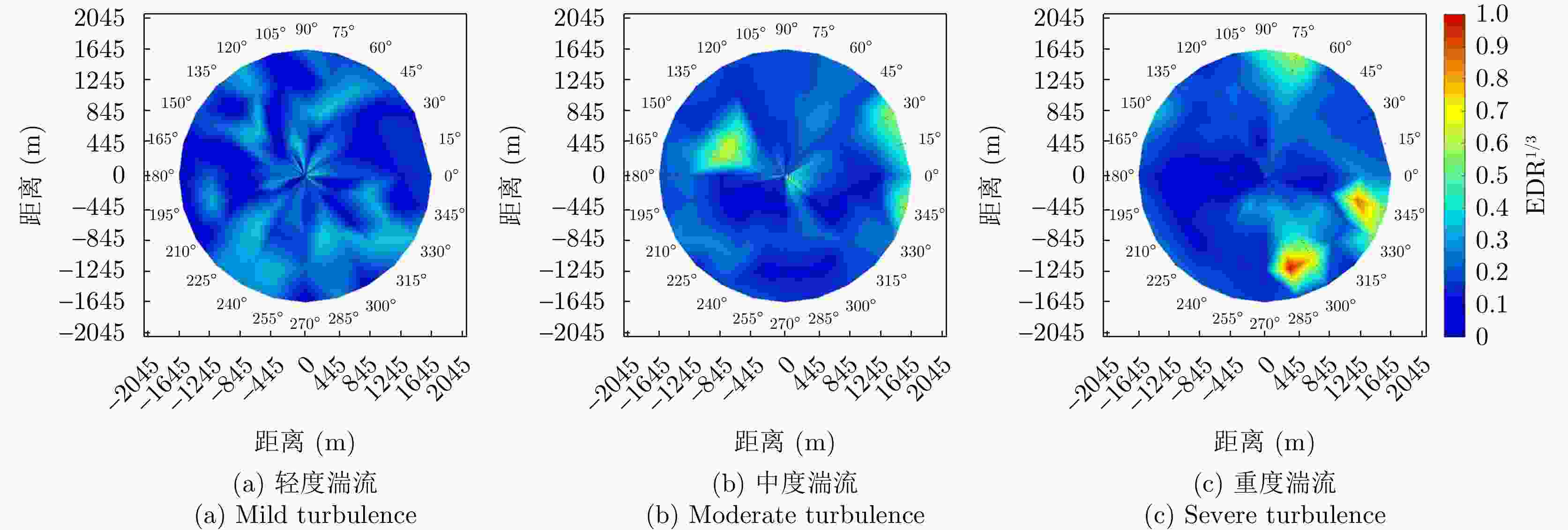
数值 湍流强度 ${{\rm{EDR}}^{1/3}} < 0.1$ 无湍流 $0.1 \le {{\rm{EDR}}^{1/3}} < 0.4$ 轻度湍流 $0.4 \le {{\rm{EDR}}^{1/3}} < 0.7$ 中度湍流 ${{\rm{EDR}}^{1/3}} \ge 0.7$ 严重湍流 表 3 ResNet50网络结构
Table 3. ResNet50 network structure
网络层名 输出大小 50层 Conv1 112×112 7×7, 64, stride 2 3×3 max pool, stride 2 Conv2_x 6×56 $ \left(\begin{array}{cc}1\times 1,& 64\\ 3\times 3,& 64\\ 1\times 1,& 256\end{array}\right) $ ×3 Conv3_x 28×28 $ \left(\begin{array}{cc}1\times 1,& 128\\ 3\times 3,& 128\\ 1\times 1,& 512\end{array}\right) $ ×4 Conv4_x 14×14 $ \left(\begin{array}{cc}1\times 1,& 256\\ 3\times 3,& 256\\ 1\times 1,& 1024\end{array}\right) $ ×6 Conv5_x 7×7 $ \left(\begin{array}{cc}1\times 1,& 512\\ 3\times 3,& 512\\ 1\times 1,& 2048\end{array}\right) $ ×3 1×1 Average pool, 1000 -dFc, softmax 表 4 每个模型的准确率、召回率、精确率、F1分数以及FPS
Table 4. Accuracy, Recall, Precision, F1-score and FPS for each model
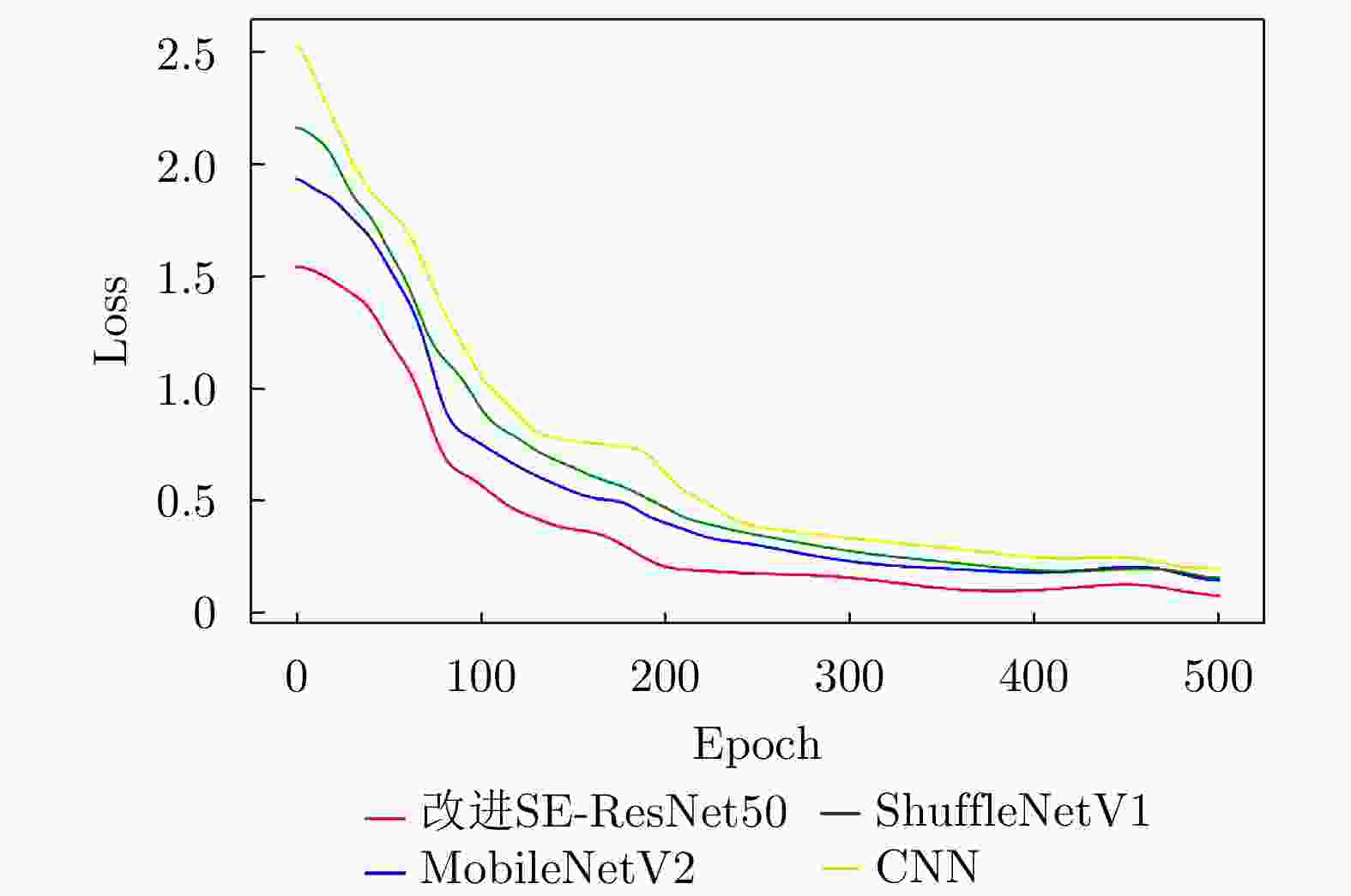
识别方法 准确率(%) 召回率(%) 精确率(%) F1分数 FPS CNN 86.82 88.22 92.55 0.9033 8.65 MobileNetV2 87.74 91.35 93.68 0.9250 20.13 ShuffleNetV1 90.15 93.41 95.21 0.9430 22.05 改进SE-ResNet50 94.26 96.47 98.42 0.9743 25.22 表 5 不同模块在晴空湍流图像数据集上的消融实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results of ablation of different modules on clear air turbulence image dataset
识别方法 Accuracy (%) ResNet50 90.13 SE-ResNet50 91.55 改进SE-ResNet50 94.32 -
[1] WANG Fazhi, DU Wenhe, YUAN Qi, et al. A survey of structure of atmospheric turbulence in atmosphere and related turbulent effects[J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(12): 1608. doi: 10.3390/atmos12121608. [2] 吴晓庆, 胡晓丹, 杨期科, 等. 低平流层长距离水平路径小尺度湍流首次测量及非Kolmogorov湍流特征参数研究[J/OL]. 中国科学: 物理 力学 天文学. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5848.N.20250326.1058.006.html, 2025.WU Xiaoqing, HU Xiaodan, YANG Qike, et al. First measurement of small-scale turbulence over long horizontal paths in the lower stratosphere and study of non-Kolmogorov turbulence characteristic parameters[J/OL]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronogy. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5848.N.20250326.1058.006.html, 2025. [3] PROSSER M C, WILLIAMS P D, MARLTON G J, et al. Evidence for large increases in clear-air turbulence over the past four decades[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(11): e2023GL103814. doi: 10.1029/2023GL103814. [4] STORER L N, WILLIAMS P D, and JOSHI M M. Global response of clear-air turbulence to climate change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(19): 9976–9984. doi: 10.1002/2017gl074618. [5] SMITH I H, WILLIAMS P D, and SCHIEMANN R. Clear-air turbulence trends over the North Atlantic in high-resolution climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2023, 61(7/8): 3063–3079. doi: 10.1007/s00382-023-06694-x. [6] 廉文超, 宋小全, 郝朝阳, 等. 双向长短期记忆网络在激光雷达风廓线预测的应用[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44(24): 2401004. doi: 10.3788/AOS240891.LIAN Wenchao, SONG Xiaoquan, HAO Zhaoyang, et al. Application of bidirectional long short-term memory network in Doppler Lidar wind profile prediction[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(24): 2401004. doi: 10.3788/AOS240891. [7] GUO Feng, MANN J, PEÑA A, et al. The space-time structure of turbulence for lidar-assisted wind turbine control[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 195: 293–310. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.05.133. [8] CHAN P W. LIDAR-based turbulence intensity calculation using glide-path scans of the Doppler LIght Detection And Ranging (LIDAR) systems at the Hong Kong International Airport and comparison with flight data and a turbulence alerting system[J]. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 2010, 19(6): 549–563. doi: 10.1127/0941-2948/2010/0471. [9] 蒋立辉, 陈红, 庄子波, 等. 小波不变矩的低空风切变识别[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(11): 3783–3787. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.048.JIANG Lihui, CHEN Hong, ZHUANG Zibo, et al. Recognition on low-level wind shear of wavelet invariant moments[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(11): 3783–3787. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.048. [10] SMALIKHO I N and BANAKH V A. Measurements of wind turbulence parameters by a conically scanning coherent Doppler lidar in the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2017, 10(11): 4191–4208. doi: 10.5194/amt-10-4191-2017. [11] BANAKH V A, SMALIKHO I N, and ZALOZNAYA I V. Possibility of clear air turbulence localization with lidar[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Optics, 2023, 36(2): 132–136. doi: 10.1134/S102485602303003X. [12] BALATTI D, HADDAD KHODAPARAST H, FRISWELL M I, et al. Aircraft turbulence and gust identification using simulated in-flight data[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 115: 106805. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106805. [13] 杨宏宇, 王峰岩. 基于深度卷积神经网络的气象雷达噪声图像语义分割方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098.YANG Hongyu and WANG Fengyan. Meteorological radar noise image semantic segmentation method based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2373–2381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190098. [14] 叶舒然, 张珍, 王一伟, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的深度学习流场特征识别及应用进展[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524736. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24736.YE Shuran, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Yiwei, et al. Progress in deep convolutional neural network based flow field recognition and its applications[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524736. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24736. [15] 王泽洋, 朱月, 安岩. 基于深度卷积生成对抗网络的大气湍流相位屏生成方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(21): 2101001. doi: 10.3788/LOP232738.WANG Zeyang, ZHU Yue, and AN Yan. Method for generating atmospheric turbulence phase screen based on deep convolutional generative-adversarial networks[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(21): 2101001. doi: 10.3788/LOP232738. [16] 侯宇超, 王洁, 李洪涛, 等. 基于多尺度胶囊Swin Transformer的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 通信学报, 2025, 46(3): 274–290. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025045.HOU Yuchao, WANG Jie, LI Hongtao, et al. Multi-scale capsule Swin Transformer-based method for SAR image target recognition[J]. Journal on Communications, 2025, 46(3): 274–290. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025045. [17] SHARMA A K, NANDAL A, DHAKA A, et al. HOG transformation based feature extraction framework in modified Resnet50 model for brain tumor detection[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2023, 84: 104737. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104737. [18] ZHU Qiming, ZHUANG Hongwei, ZHAO Mi, et al. A study on expression recognition based on improved mobilenetV2 network[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 8121. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58736-x. [19] 郭立民, 黄文青, 陈前, 等. 轻量化的ML-SNet雷达复合干扰识别算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(2): 418–427. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.02.09.GUO Limin, HUANG Wenqing, CHEN Qian, et al. Lightweight algorithm of ML-SNet radar compound jamming recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(2): 418–427. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.02.09. [20] KARADDI S H and SHARMA L D. Classification of lung disorders in chest multi-modal images using hyper-Parameter tuning and modified ResNet50[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024: 1–25. doi: 10.1007/s11042-024-20097-y. [21] 张洪玮, 吴松华, 尹嘉萍, 等. 基于短距相干测风激光雷达的机场低空风切变观测[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2018, 37(4): 468–476. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.04.015.ZHANG Hongwei, WU Songhua, YIN Jiaping, et al. Airport low-level wind shear observation based on short-range CDL[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(4): 468–476. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.04.015. [22] 李策, 赵培娥, 彭涛, 等. 3维激光测风雷达技术研究[J]. 激光技术, 2017, 41(5): 703–707. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2017.05.017.LI Ce, ZHAO Peie, PENG Tao, et al. Technical research of 3-D wind lidar[J]. Laser Technology, 2017, 41(5): 703–707. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2017.05.017. [23] 庄子波, 陈星, 台宏达, 等. 基于奇异值分解的激光雷达湍流预警算法[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(3): 671–679. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0671.ZHUANG Zibo, CHEN Xing, TAI Hongda, et al. Turbulence alerting algorithm based on singular value decomposition of Lidar[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 671–679. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0671. [24] CHAN P W and LEE Y F. Performance of LIDAR- and radar-based turbulence intensity measurement in comparison with anemometer-based turbulence intensity estimation based on aircraft data for a typical case of terrain-induced turbulence in association with a typhoon[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A, 2013, 14(7): 469–481. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1200236. [25] 陈小龙, 何肖阳, 邓振华, 等. 雷达微弱目标智能化处理技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160.CHEN Xiaolong, HE Xiaoyang, DENG Zhenhua, et al. Radar intelligent processing technology and application for weak target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160. [26] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [27] QIAO Weiliang, GUO Hongtongyang, HUANG Enze, et al. Two-phase flow pattern identification by embedding double attention mechanisms into a convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(4): 793. doi: 10.3390/jmse11040793. [28] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372. [29] WANG Hua, YING Jichong, LIU Jianlei, et al. Harnessing ResNet50 and SENet for enhanced ankle fracture identification[J]. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 2024, 25(1): 250. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07355-8. [30] YOO J, JIN Y, KO B, et al. k-labelsets method for multi-label ECG signal classification based on SE-ResNet[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(16): 7758. doi: 10.3390/app11167758. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
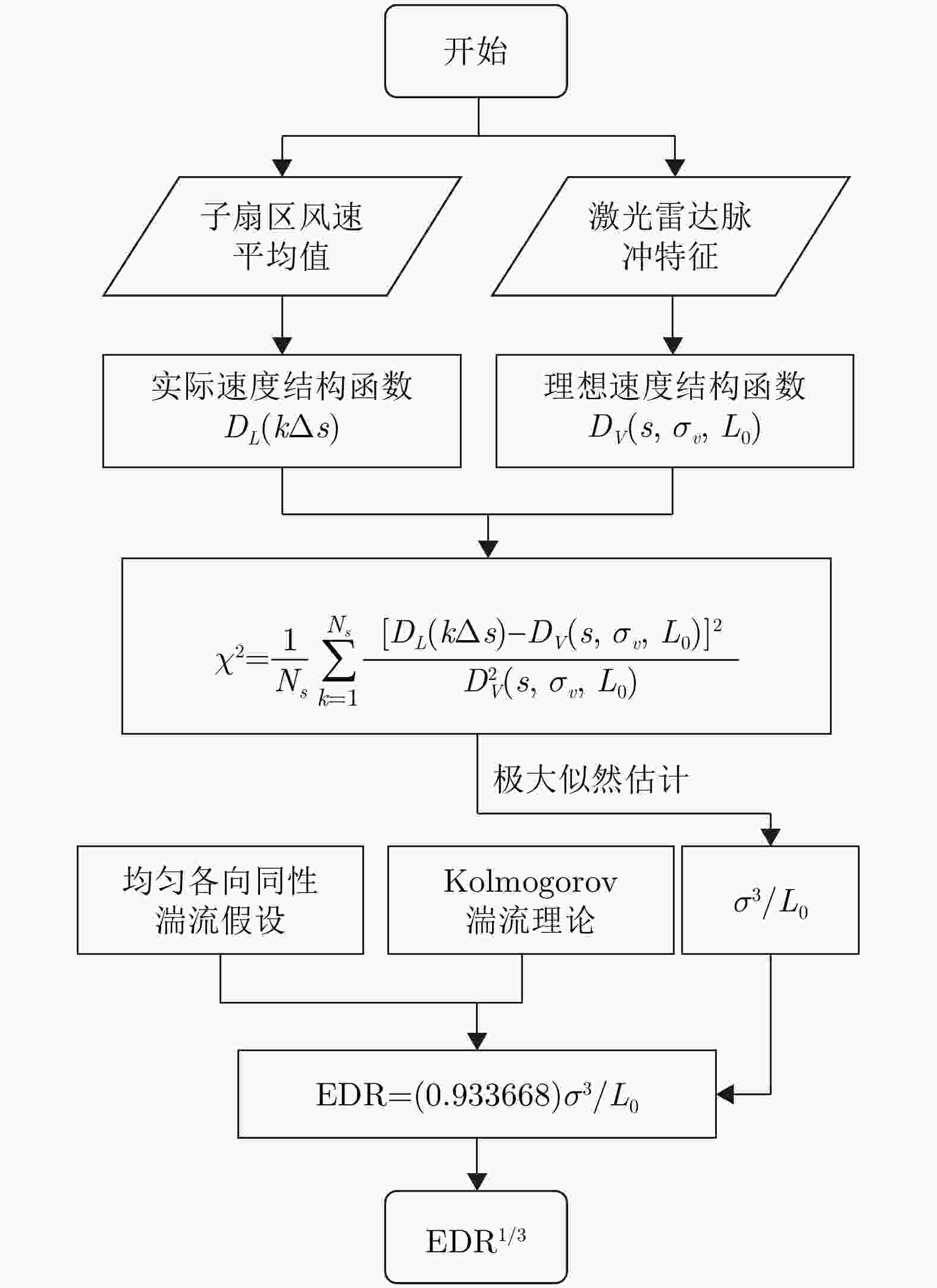
 下载:
下载: