Low-altitude Secure Communication Driven by Deep Reinforcement Learning: An Integrated Sensing and Communication Design
-
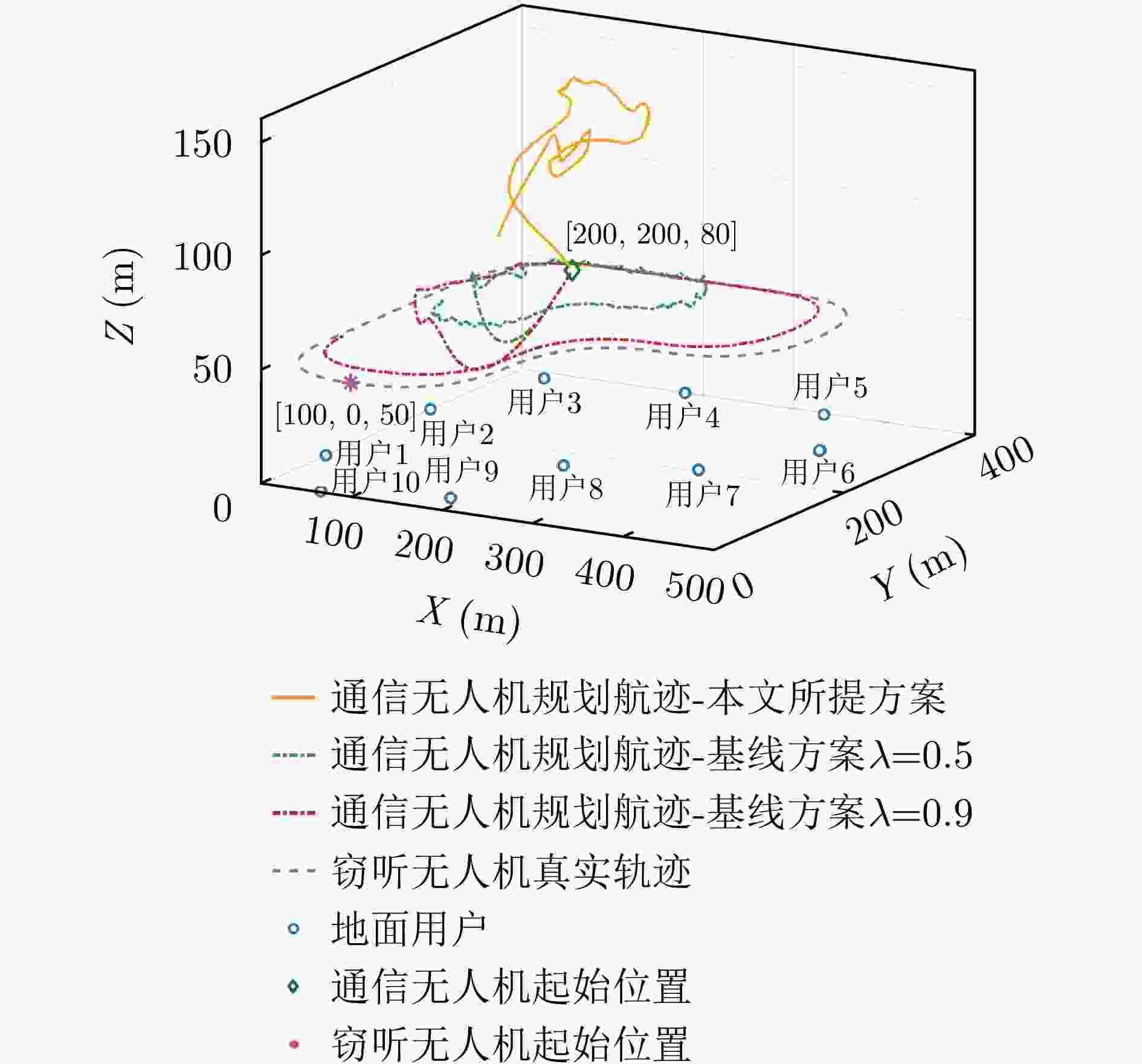
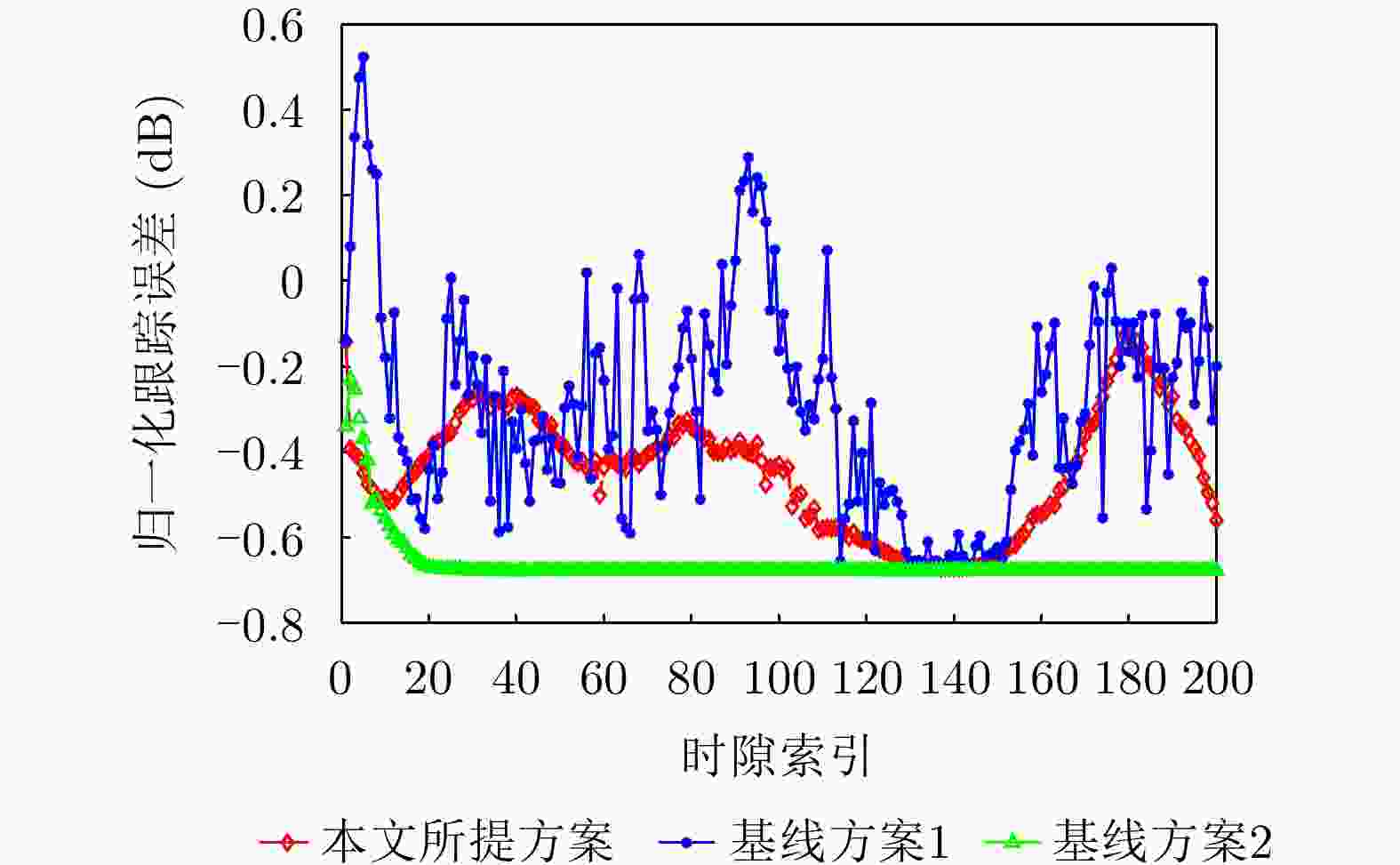
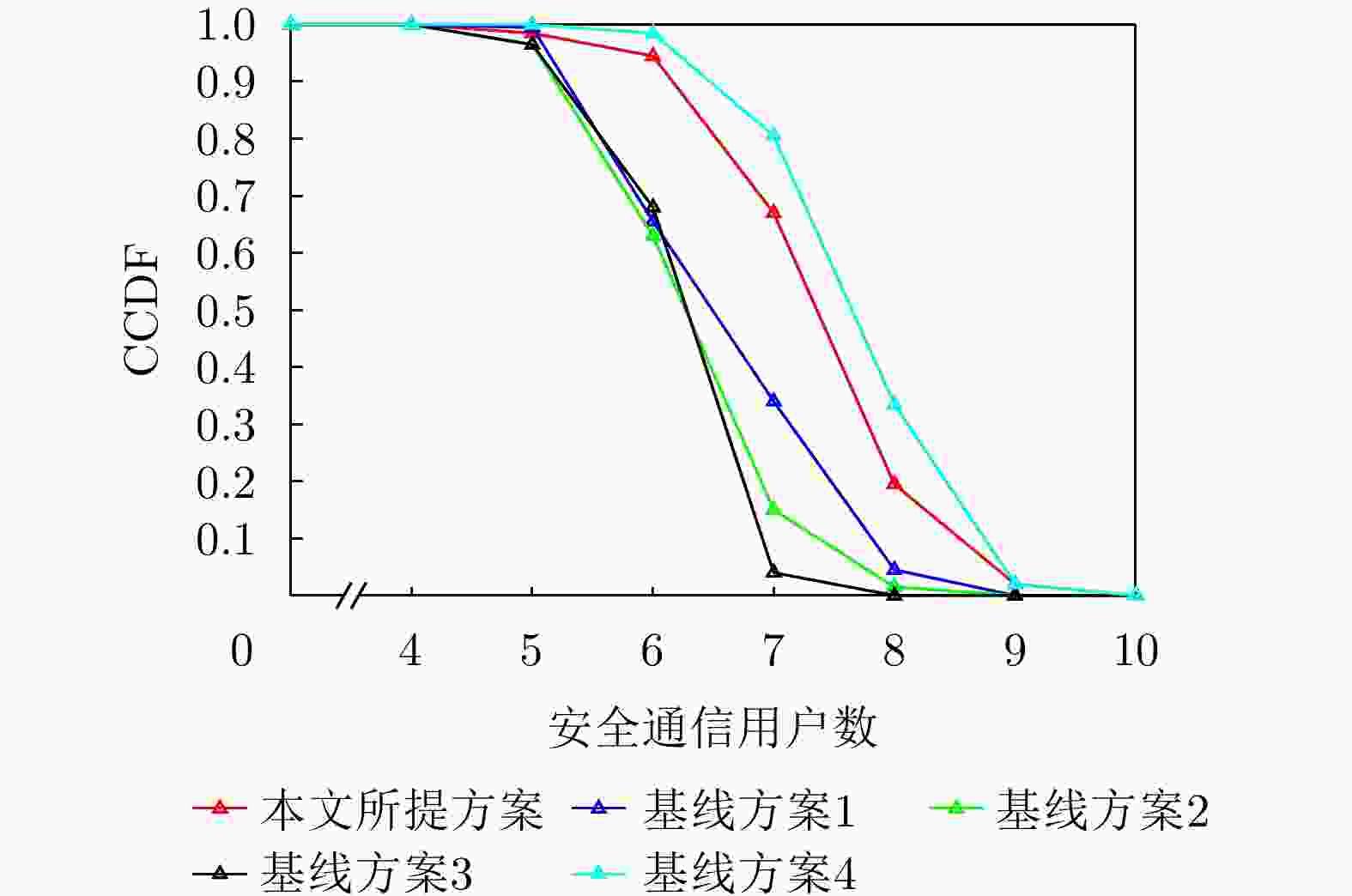
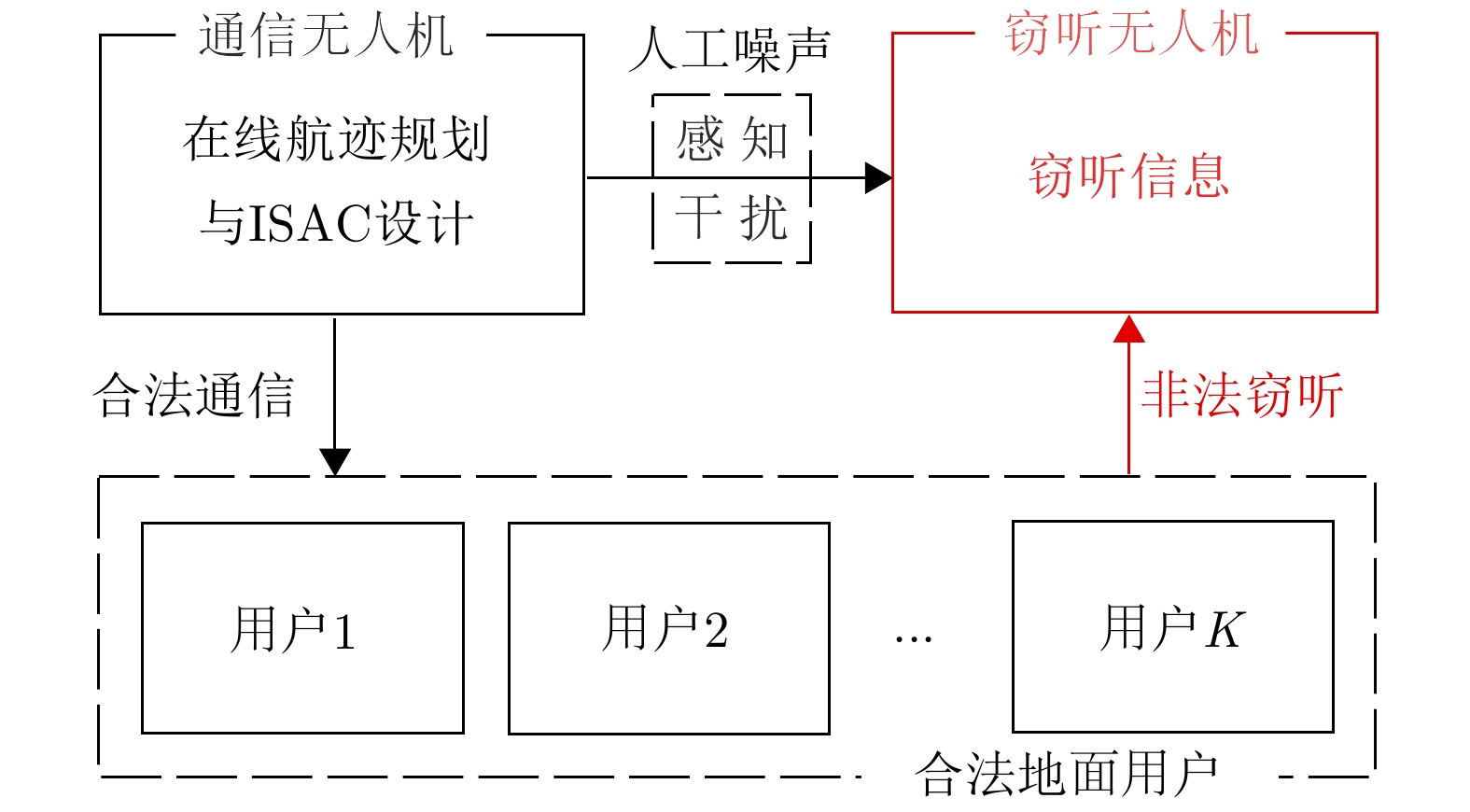
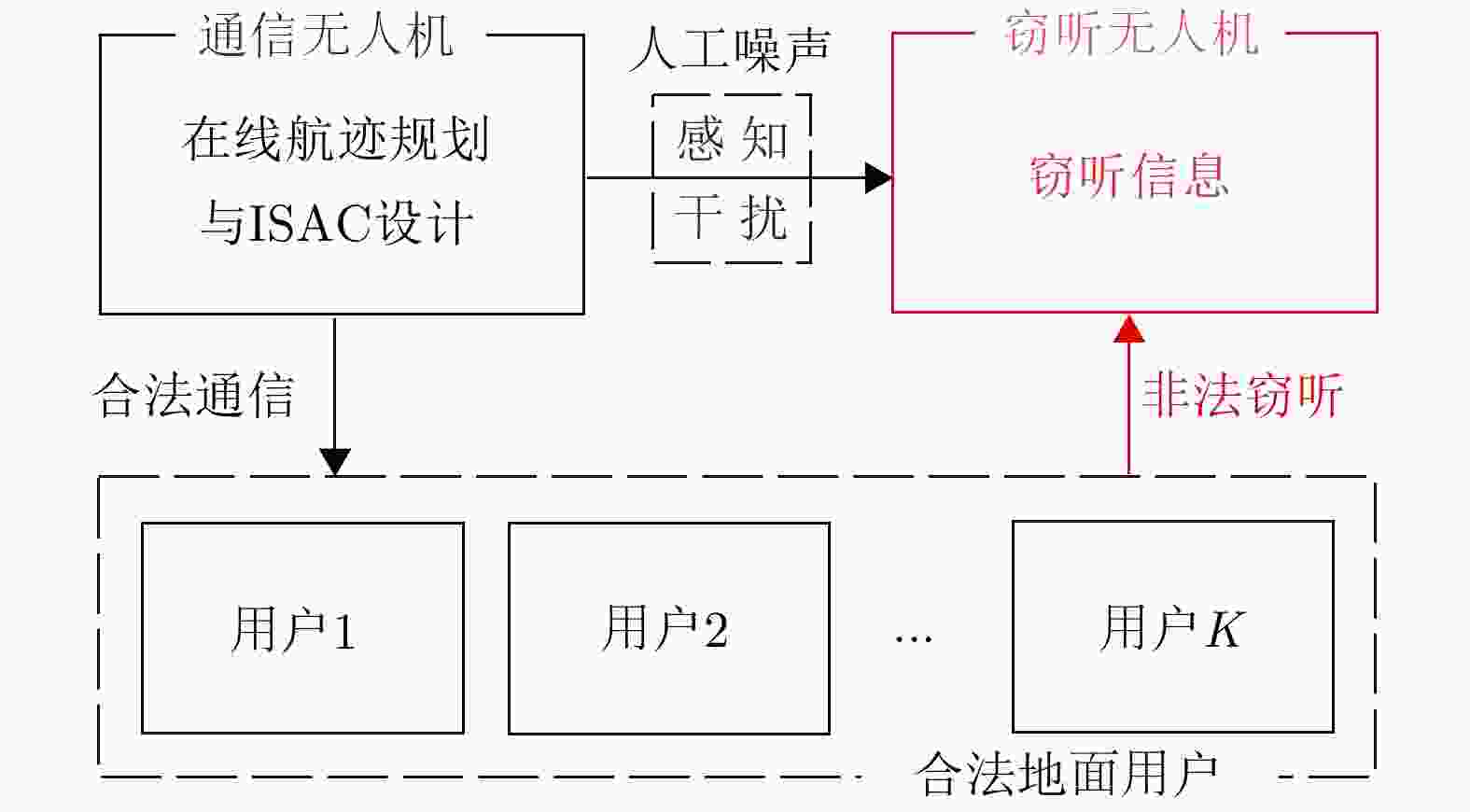
摘要: 针对低空无人机通信中的物理层安全挑战,该文提出了一种感通一体化(ISAC)方案,并据此基于深度强化学习(DRL)方法在线优化通信无人机的航迹和通信资源分配策略。所提方案通过复用通信无人机传输的人工噪声,同时实现对窃听无人机的感知与干扰,保障地面用户的安全通信服务。基于对窃听无人机的状态估计和预测,该文将在线无人机航迹和通信资源分配联合设计建模为马尔可夫决策过程,基于深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)方法,逐步学习最优策略,动态优化通信无人机的航迹与通信资源分配策略,最大化系统的长期感知和安全通信性能。仿真结果表明,该文所提方案和优化方法在感知性能不损失的前提下,安全通信性能上优于基线方案,在感知和安全通信性能之间实现更好的折中,验证了感知和在线航迹规划的增益,也验证了深度强化学习优化方法在感知、通信和航迹规划联合设计问题中的可行性和先进性。Abstract: To address the physical layer security challenges in low-altitude Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) communications, this paper proposes an Integrated Sensing And Communication (ISAC) scheme. For the proposed ISAC scheme, an online optimization framework for UAV trajectory and communication resource allocation is developed using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). In the proposed scheme, artificial noise transmitted by a communication UAV is reused to simultaneously sense and jam a potential eavesdropping UAV, thereby enhancing secure communications for ground users. By estimating and predicting the state of the eavesdropping UAV, the trajectory and resource allocation design problem is reformulated as a Markov decision process. Using the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm, the optimal framework is learned over time, dynamically optimizing the communication UAV’s trajectory and resource allocation to maximize long-term sensing and secure communication performance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme achieves a superior trade-off between sensing and security without degrading sensing performance and outperforms baseline methods in terms of secure communication performance. This validates the performance gains achieved through sensing and online trajectory design, as well as the potential and superior performance of applying DRL to the integrated design of sensing, communication, and trajectory.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 参数 数值 参数 数值 K 10 $ \left[{M}_{\rm e}^{x},{M}_{\rm e}^{y}\right] $ $ \left[\mathrm{4,4}\right] $ $ {c}_{{\theta }_{{\mathrm{be}}}} $ 0.1 $ {V}_{\max} $ $ 30\;\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s} $ $ \delta $ 1 s $ \left[{M}_{\rm b}^{{\mathrm{t}}x},{M}_{\rm b}^{{\mathrm{t}}y}\right] $ $ \left[\mathrm{4,4}\right] $ $ {c}_{{\phi }_{{\mathrm{be}}}} $ 0.1 $ {p}_{\max} $ 30 dBm $ {\beta }_{0}^{2} $ –40 dBW $ \left[{M}_{\rm b}^{{\mathrm{r}}x},{M}_{\rm b}^{{\mathrm{r}}y}\right] $ $ \left[\mathrm{4,4}\right] $ $ {c}_{{\tau }_{\rm e}} $ $ {10}^{-7} $ N 200 $ {R}_{\min} $ 3 bit/(s·Hz) $ {R}_{{\mathrm{Leakage}}} $ 0.1 bit/(s·Hz) $ {c}_{{\nu}_{\rm e}} $ 1 $ {f}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $ 3 GHz $ {\sigma }_{\rm e}^{2},{\sigma }_{k}^{2} $ –90 dBm $ {{\boldsymbol{q}}}_{\min} $ $ {\left[\mathrm{0,0},50\right]}^{\rm T} $ c $ 3\times {10}^{8}\;\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s} $ $ {G}_{{\mathrm{MF}}} $ $ {10}^{4} $ $ {\sigma }_{\rm b}^{2} $ –50 dBm $ {{\boldsymbol{q}}}_{\max} $ $ {\left[\mathrm{500,500,100}\right]}^{\rm T} $ $ {\upsilon }_{\rm e} $ $ 0.1\;{{\mathrm{m}}}^{2} $ $ \left[{A}_{{\mathrm{cc}}}^{x},{A}_{{\mathrm{cc}}}^{y},{A}_{{\mathrm{cc}}}^{z}\right] $ $ \left[\mathrm{4,4},2\right] $ -
[1] MUKHERJEE A, FAKOORIAN S A A, HUANG Jing, et al. Principles of physical layer security in multiuser wireless networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(3): 1550–1573. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2014.012314.00178. [2] LIU Chenxi, LEE J, and QUEK T Q S. Safeguarding UAV communications against full-duplex active eavesdropper[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 2919–2931. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2906177. [3] WANG Qian, CHEN Zhi, MEI Weidong, et al. Improving physical layer security using UAV-enabled mobile relaying[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2017, 6(3): 310–313. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2680449. [4] ZHANG Guangchi, WU Qingqing, CUI Miao, et al. Securing UAV communications via joint trajectory and power control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(2): 1376–1389. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2892461. [5] ZHOU Xiaobo, WU Qingqing, YAN Shihao, et al. UAV-enabled secure communications: Joint trajectory and transmit power optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 4069–4073. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900157. [6] CUI Miao, ZHANG Guangchi, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust trajectory and transmit power design for secure UAV communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(9): 9042–9046. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2849644. [7] CAI Yuanxin, WEI Zhiqiang, LI Ruide, et al. Joint trajectory and resource allocation design for energy-efficient secure UAV communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(7): 4536–4553. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2982152. [8] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, PETROPULU A P, et al. Joint radar and communication design: Applications, state-of-the-art, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(6): 3834–3862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2973976. [9] ZHANG J A, RAHMAN M L, WU Kai, et al. Enabling joint communication and radar sensing in mobile networks-A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(1): 306–345. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3122519. [10] WEI Zhongxiang, LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, et al. Toward multi-functional 6G wireless networks: Integrating sensing, communication, and security[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(4): 65–71. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.002.2100972. [11] SU Nanchi, LIU Fan, WEI Zhongxiang, et al. Secure dual-functional radar-communication transmission: Exploiting interference for resilience against target eavesdropping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 7238–7252. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3156893. [12] SU Nanchi, LIU Fan, and MASOUROS C. Secure radar-communication systems with malicious targets: Integrating radar, communications and jamming functionalities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 83–95. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3023164. [13] HUANG Chongwen, YANG Zhaohui, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Multi-Hop RIS-empowered terahertz communications: A DRL-based hybrid beamforming design[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(6): 1663–1677. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3071836. [14] SUN Yan, XU Dongfang, NG D W K, et al. Optimal 3D-trajectory design and resource allocation for solar-powered UAV communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(6): 4281–4298. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2900630. [15] YOU Changsheng and ZHANG Rui. Hybrid offline-online design for UAV-enabled data harvesting in probabilistic LoS channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(6): 3753–3768. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2978073. [16] WEI Zhiqiang, LIU Fan, LIU Chang, et al. Integrated sensing, navigation, and communication for secure UAV networks with a mobile eavesdropper[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(7): 7060–7078. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3337148. [17] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.5602, 2013. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1312.5602. [18] LILLICRAP T P, HUNT J J, PRITZEL A, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1509.02971, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1509.02971. [19] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.06347, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1707.06347. [20] HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, ABBEEL P, et al. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.01290, 2018. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1801.01290. [21] GAN Xu, HUANG Chongwen, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Bayesian learning for double-RIS aided ISAC systems with superimposed pilots and data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2024, 18(5): 766–781. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2024.3408071. [22] QIN Yunhui, ZHANG Zhongshan, LI Xulong, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based resource allocation and trajectory planning in integrated sensing and communications UAV network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(11): 8158–8169. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3260304. [23] ZHU Yuqian, LI Ming, LIU Yang, et al. DRL-based joint beamforming and BS-RIS-UE association design for RIS-assisted mmWave networks[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, USA, 2022: 345–350. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771607. [24] DONG Runze, WANG Buhong, TIAN Jiwei, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based UAV for securing mmWave communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5429–5434. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3224959. [25] ZENG Yong, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. Accessing from the sky: A tutorial on UAV communications for 5G and beyond[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(12): 2327–2375. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2952892. [26] YOU Changsheng and ZHANG Rui. 3D trajectory optimization in Rician fading for UAV-enabled data harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 3192–3207. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2911939. [27] NASIR A A, DURRANI S, MEHRPOUYAN H, et al. Timing and carrier synchronization in wireless communication systems: A survey and classification of research in the last 5 years[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2016, 180(2016): 1–38. doi: 10.1186/s13638-016-0670-9. [28] SKOLNIK M I. Introduction to Radar Systems[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1980: 581. [29] LIU Fan, YUAN Weijie, MASOUROS C, et al. Radar-assisted predictive beamforming for vehicular links: Communication served by sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7704–7719. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3015735. [30] KAY S M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing[M]. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: PTR Prentice-Hall, 1993. [31] MONTAVON G, ORR G B, and MÜLLER K R. Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 769. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: