Dual-channel Clutter Cancellation Processing Method via Space-time Decoupling for Airborne BiSAR
-
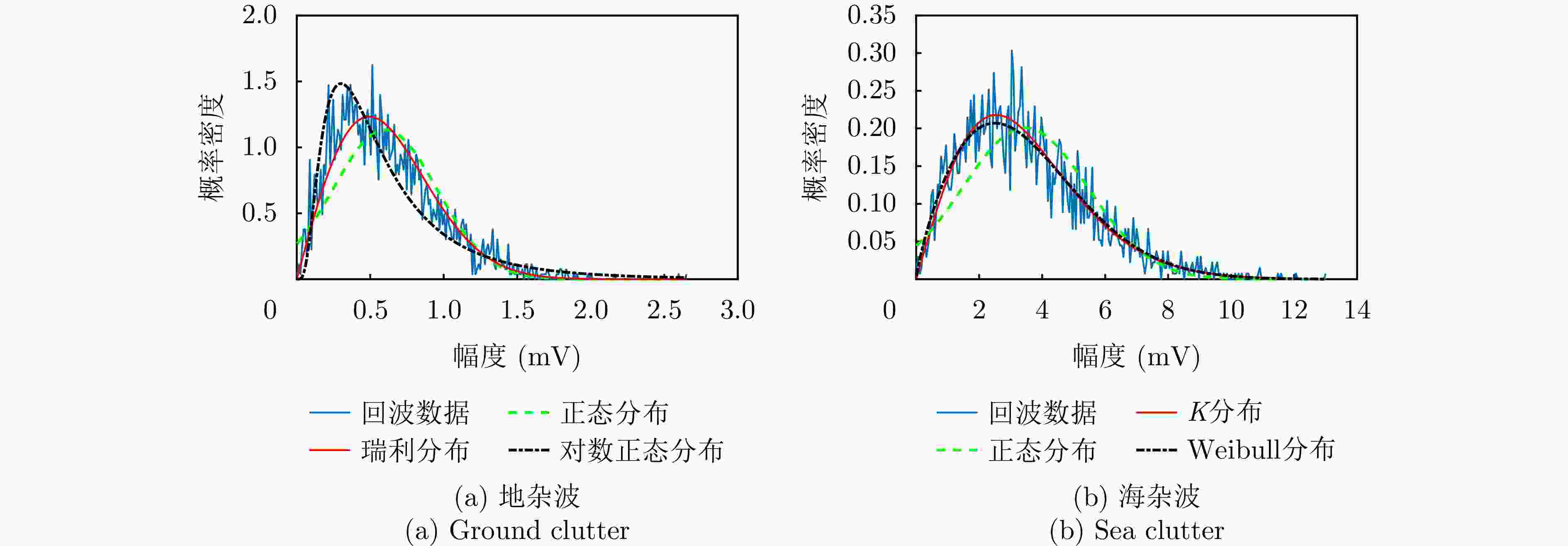
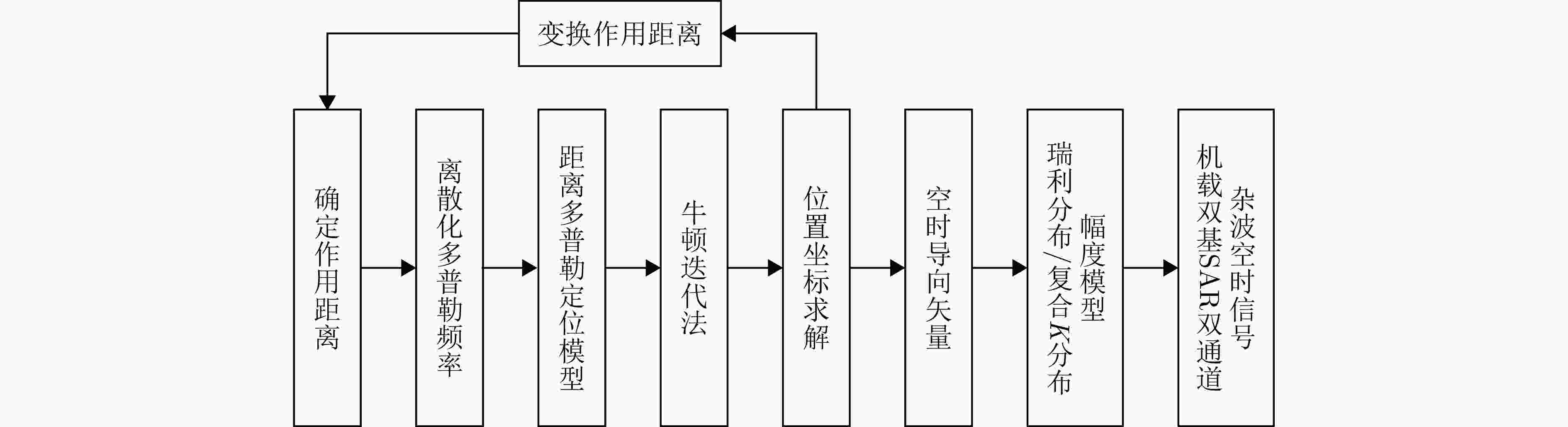
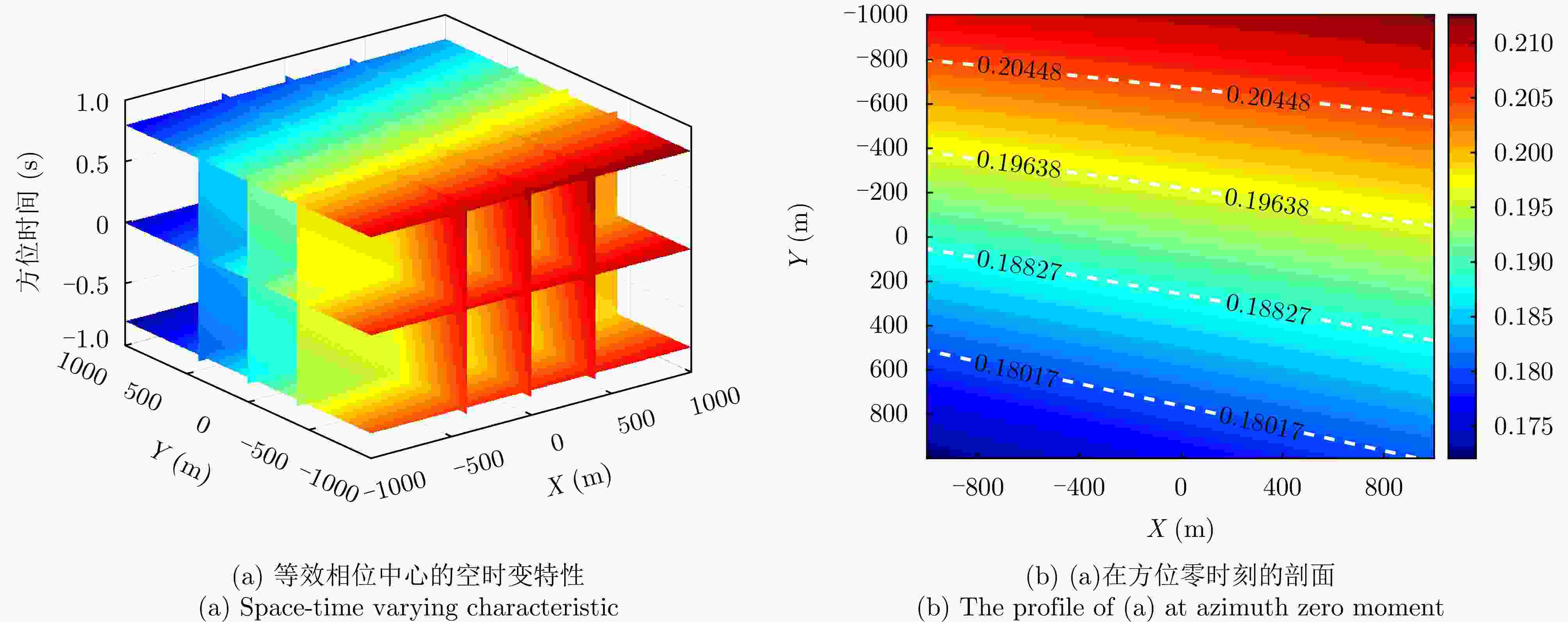
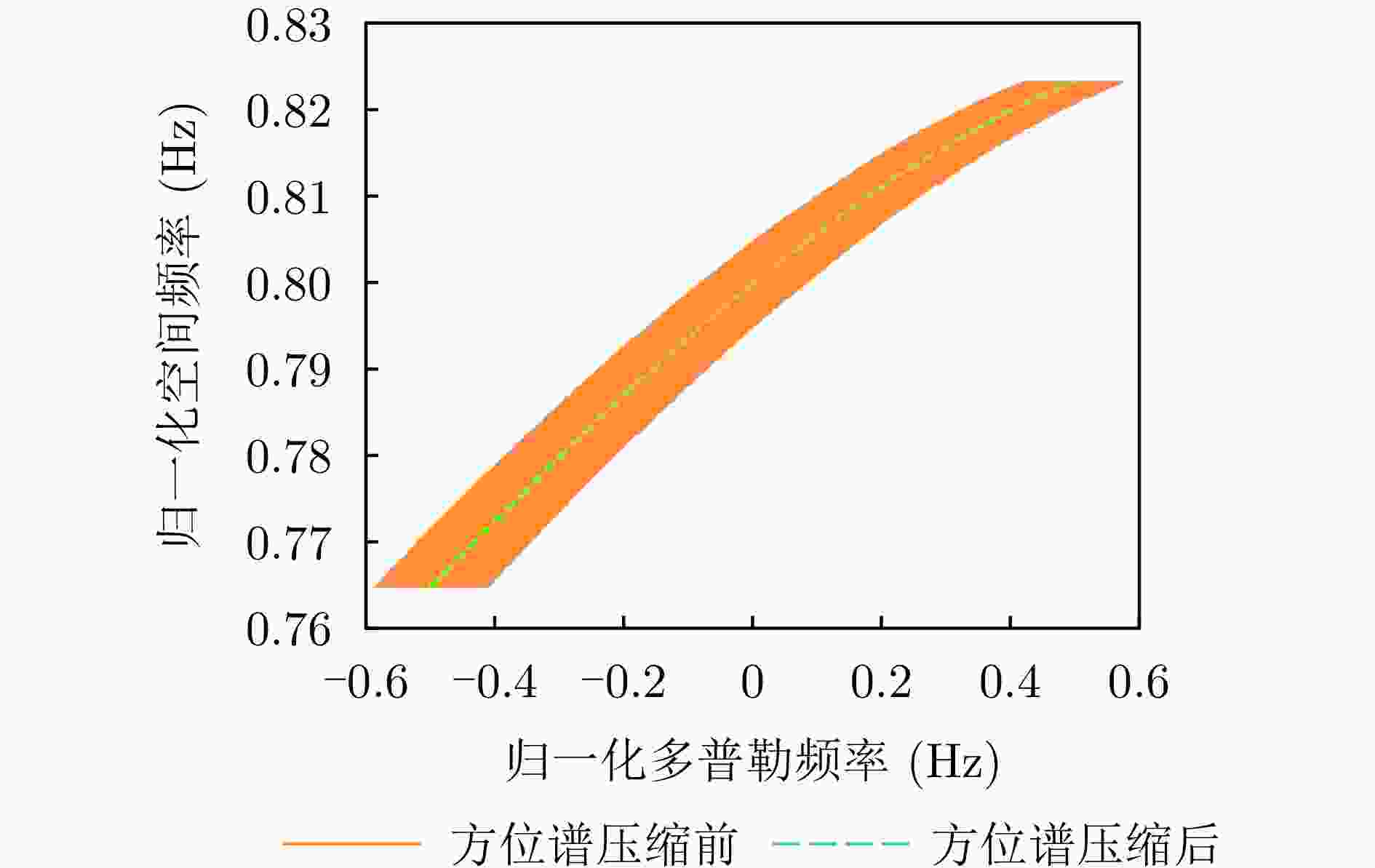
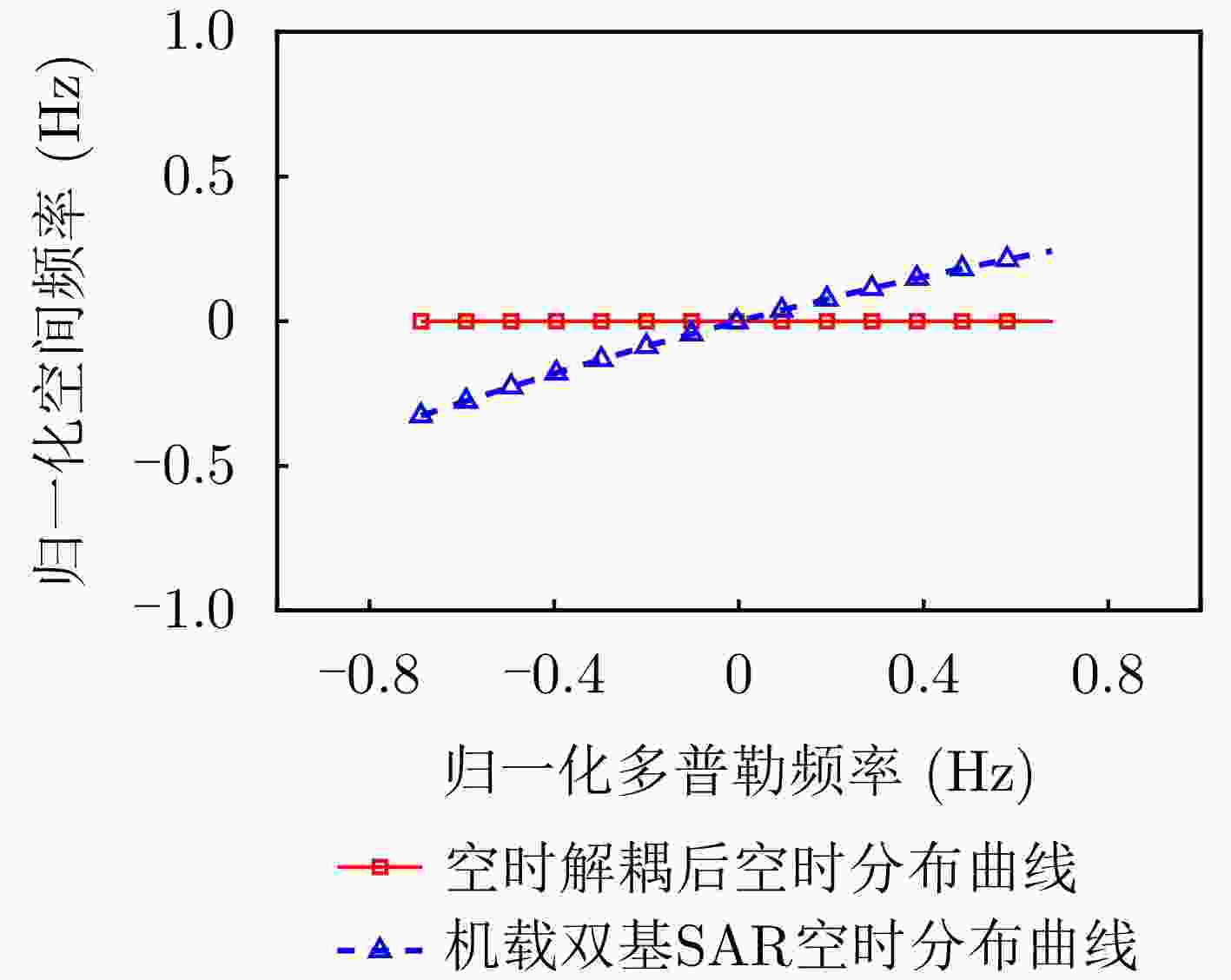
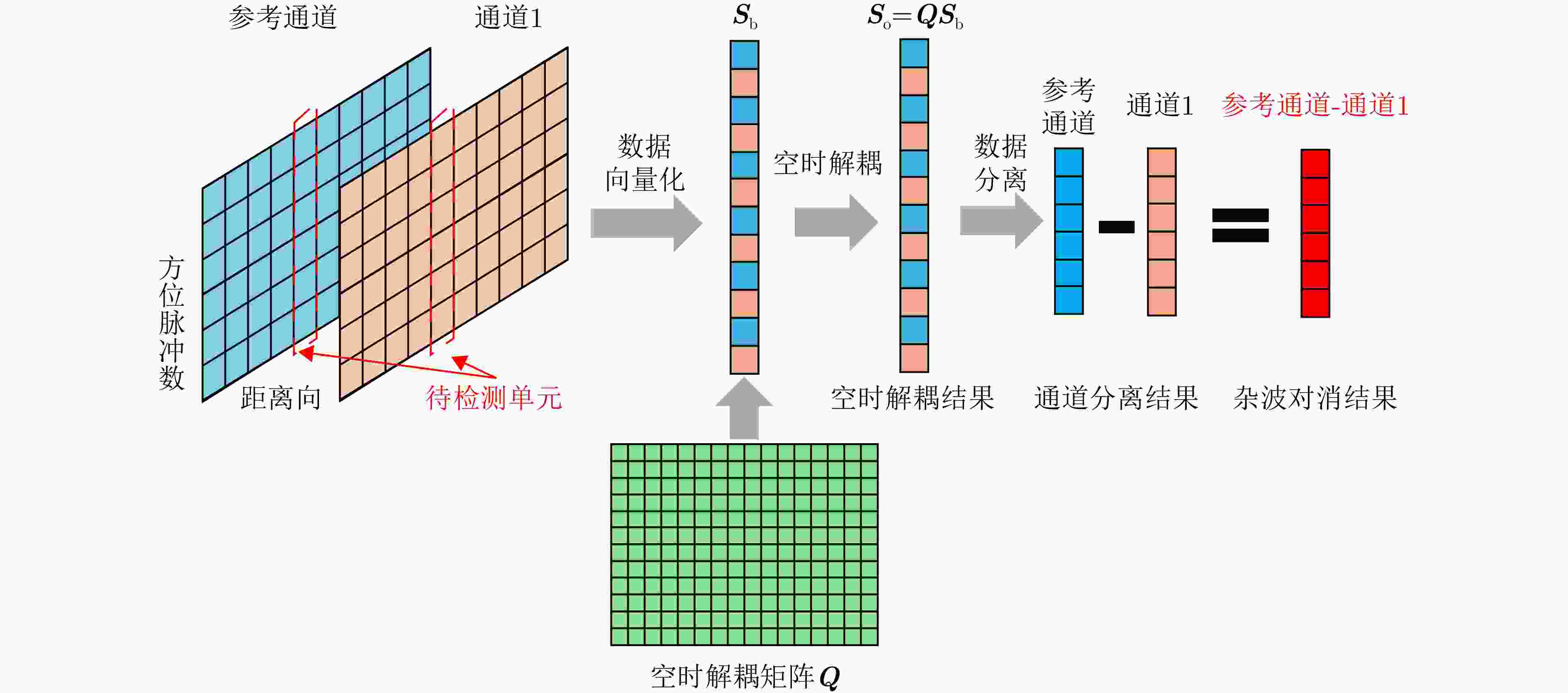
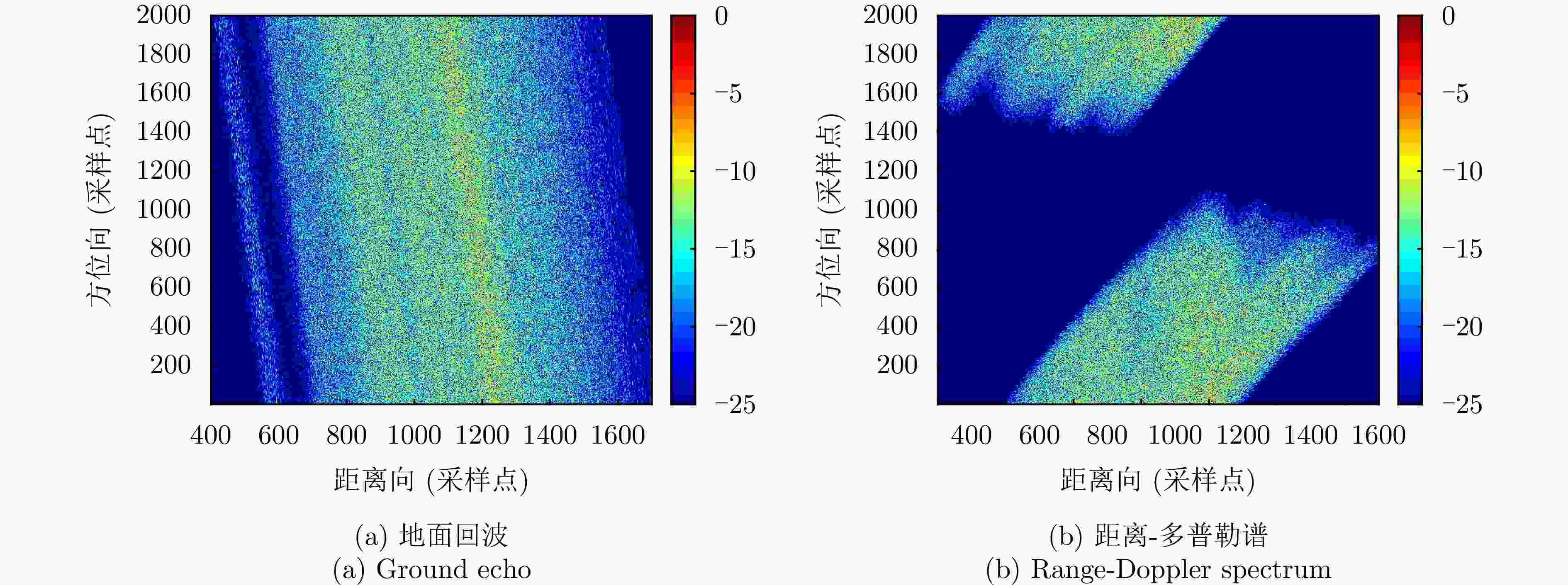
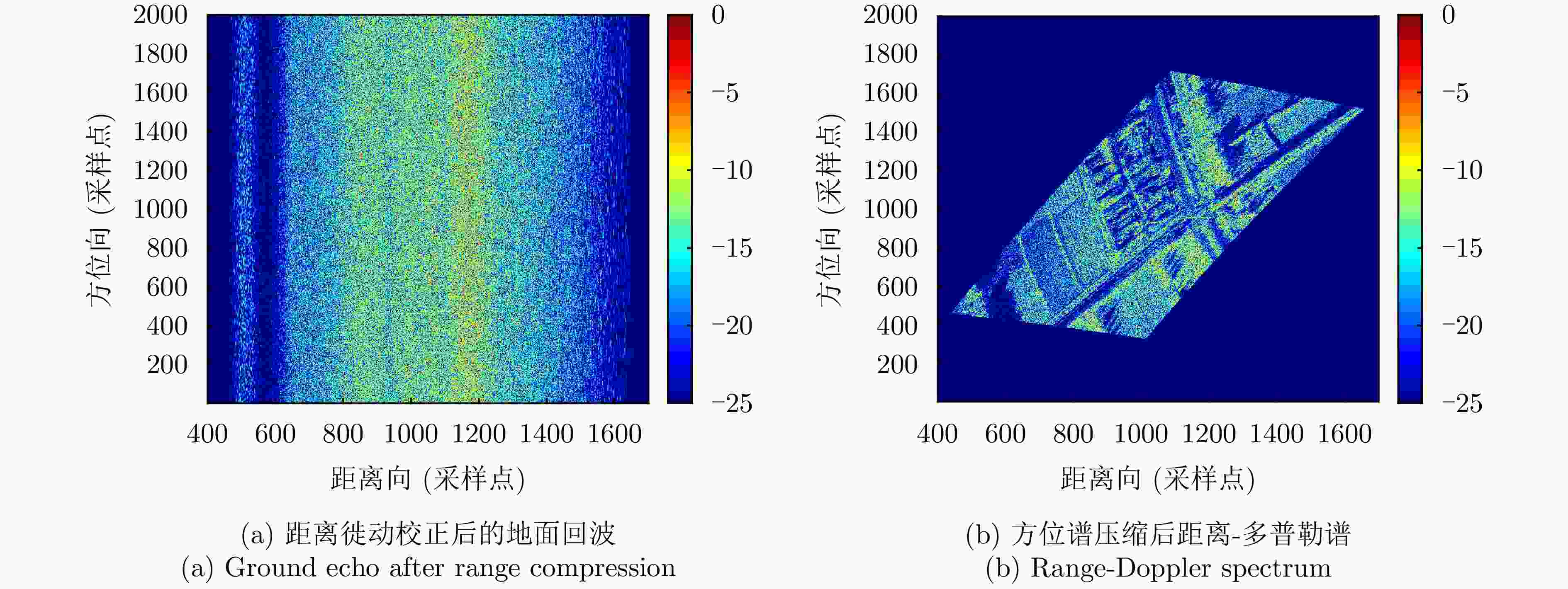
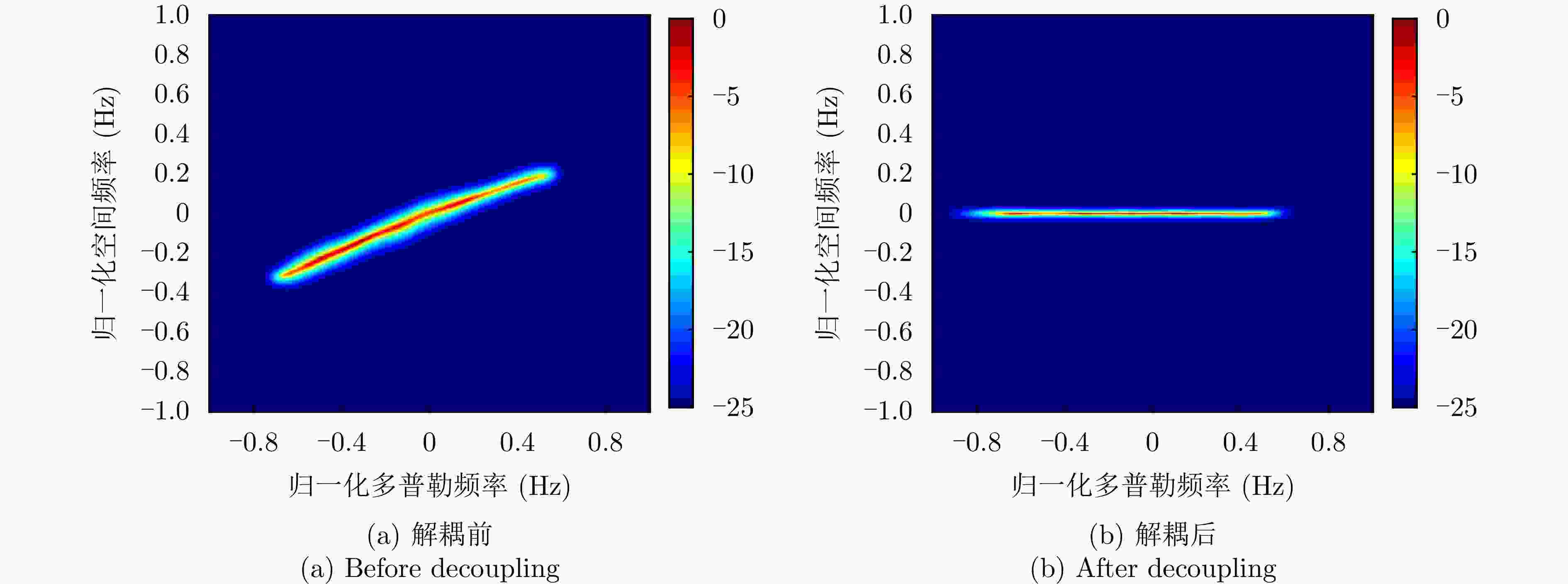
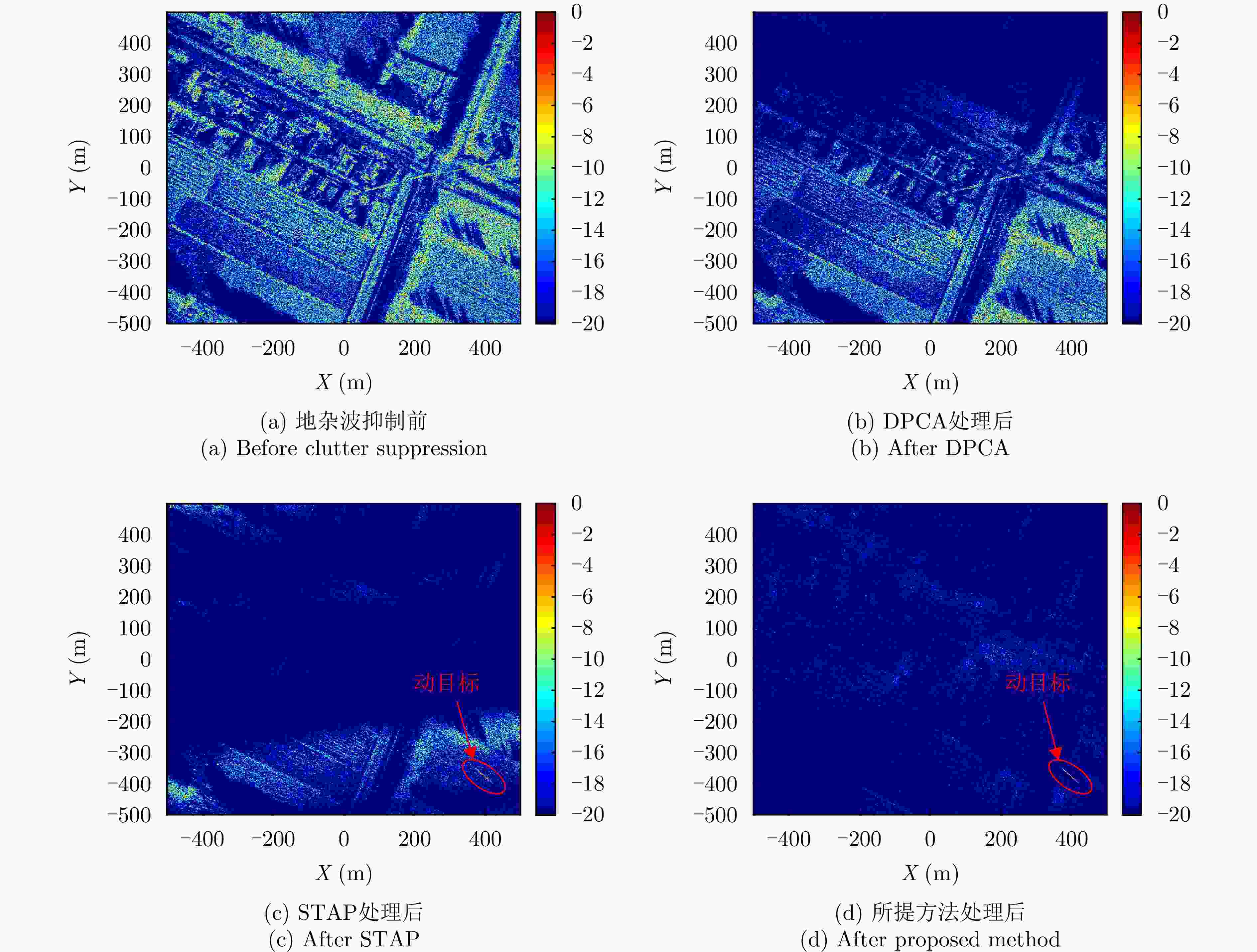
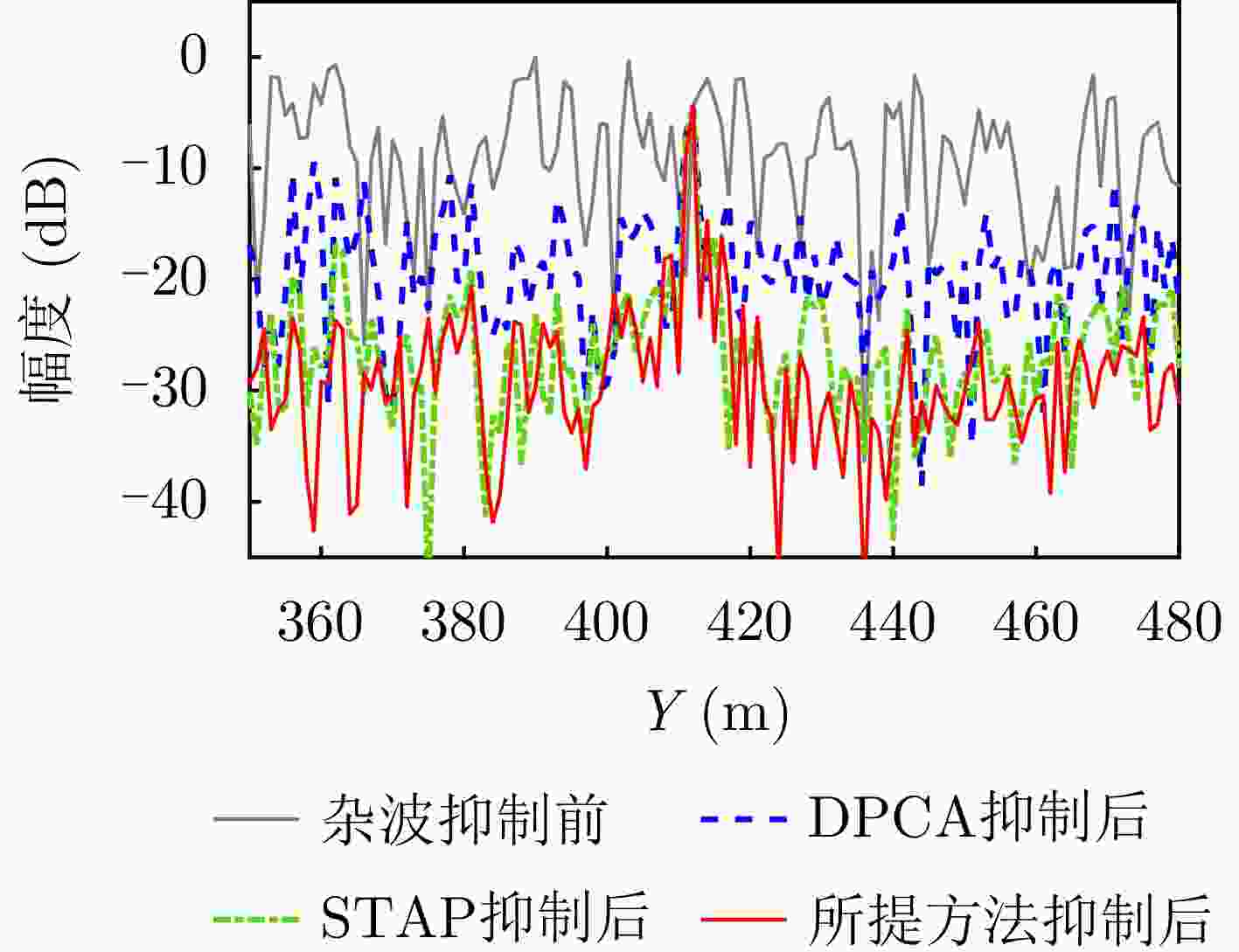
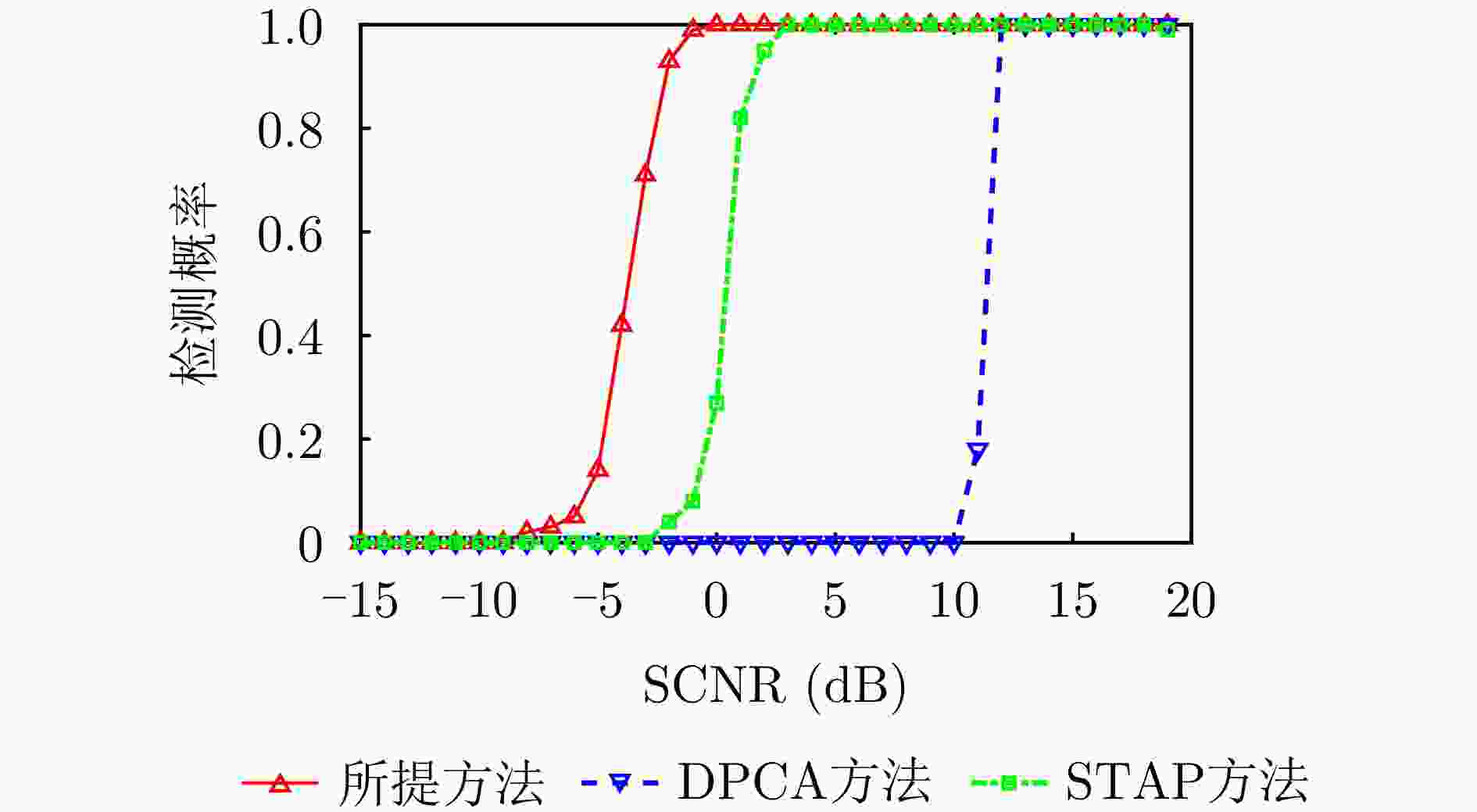
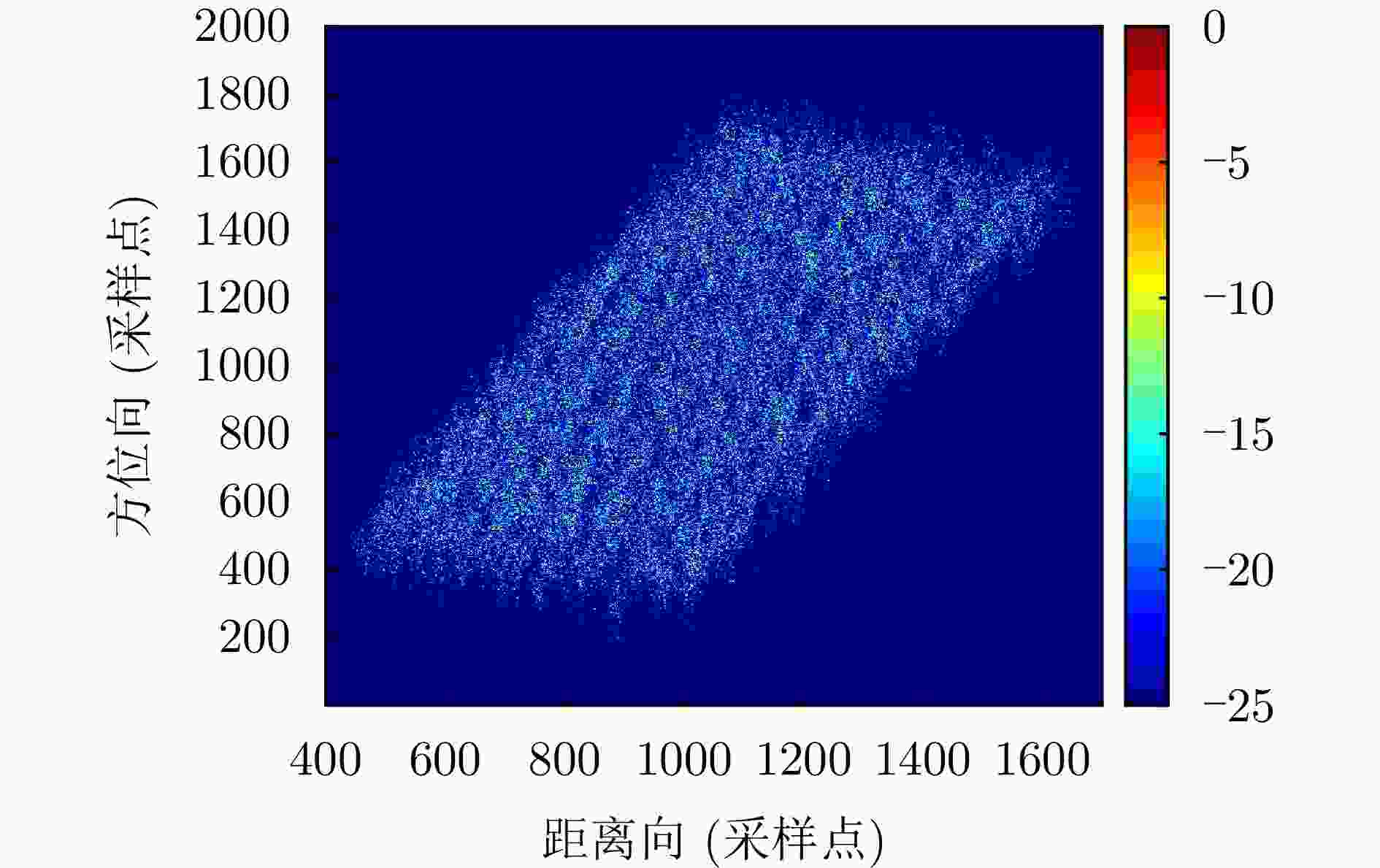
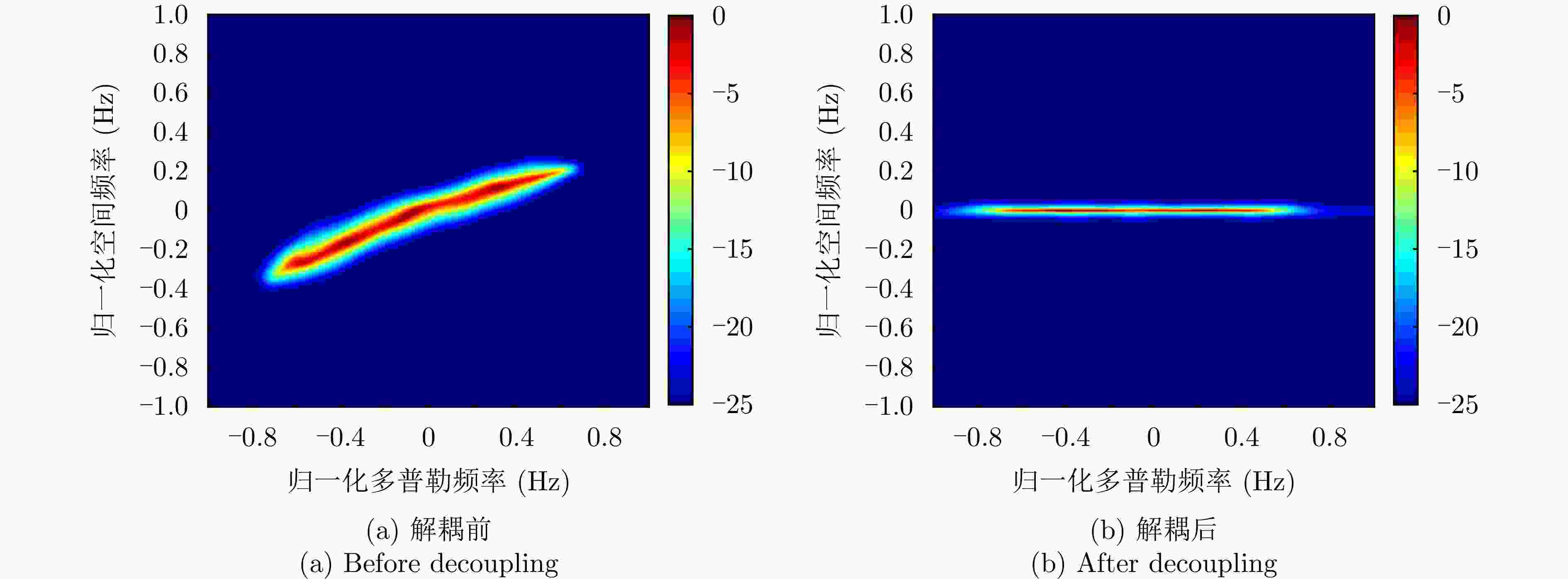
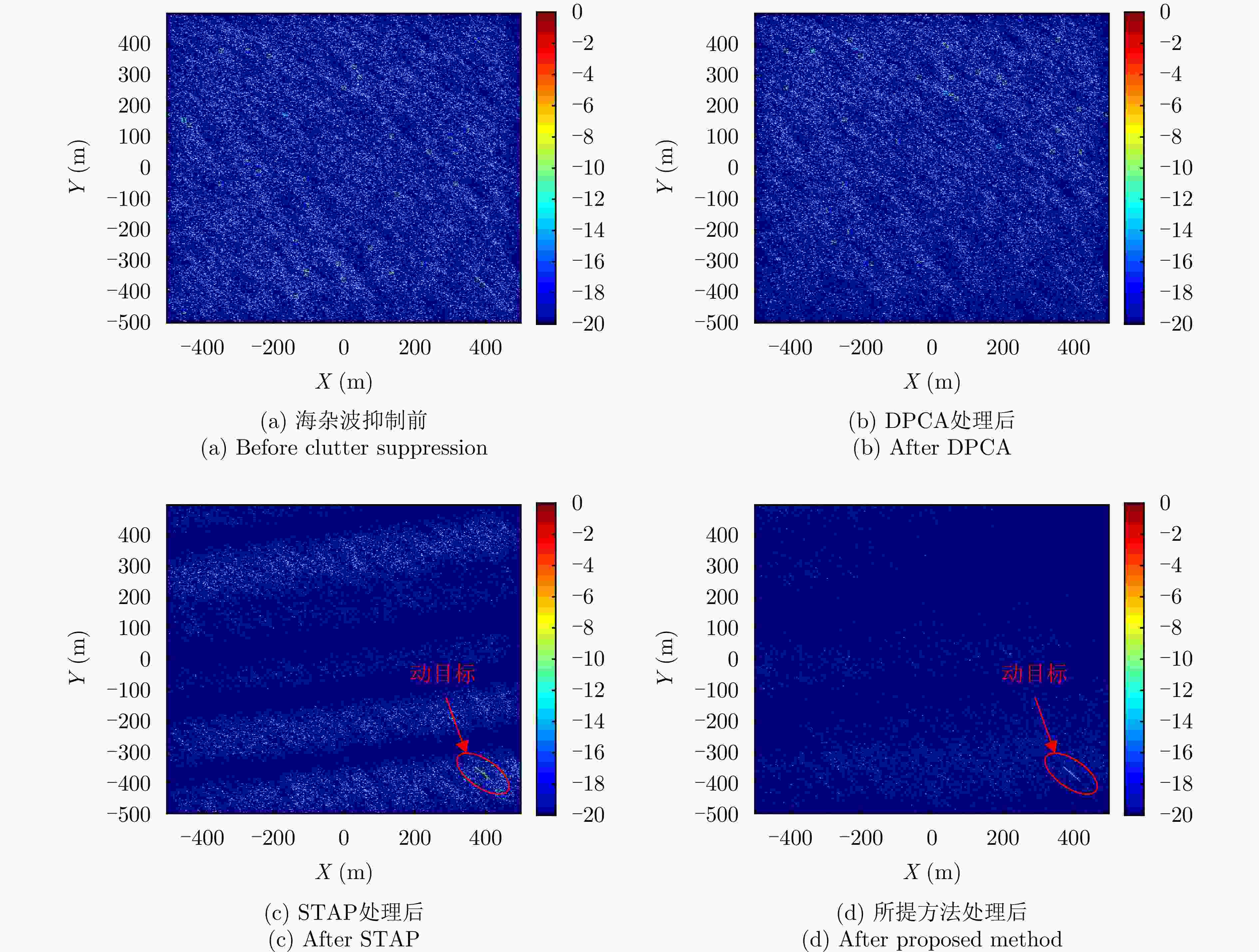
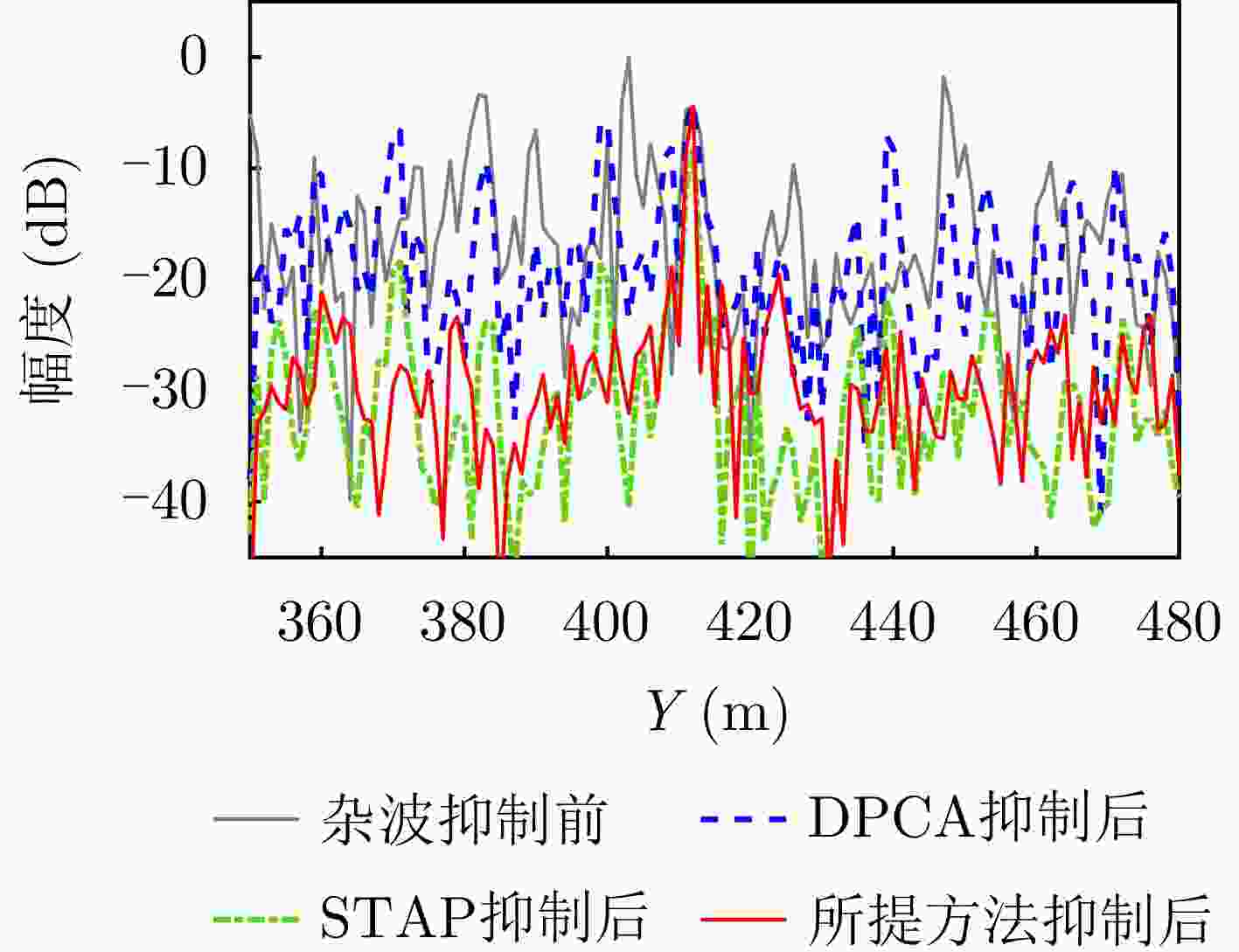
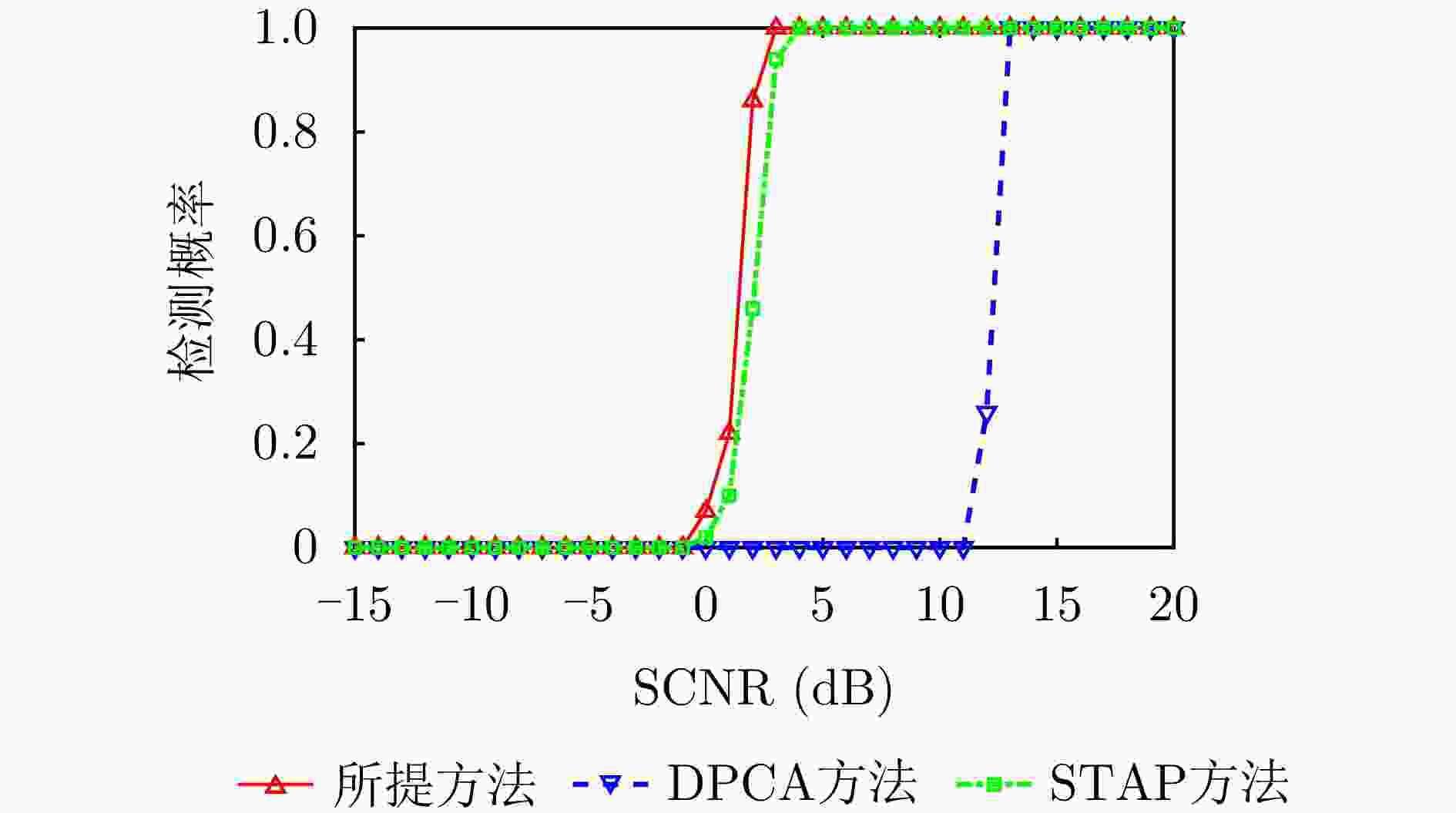
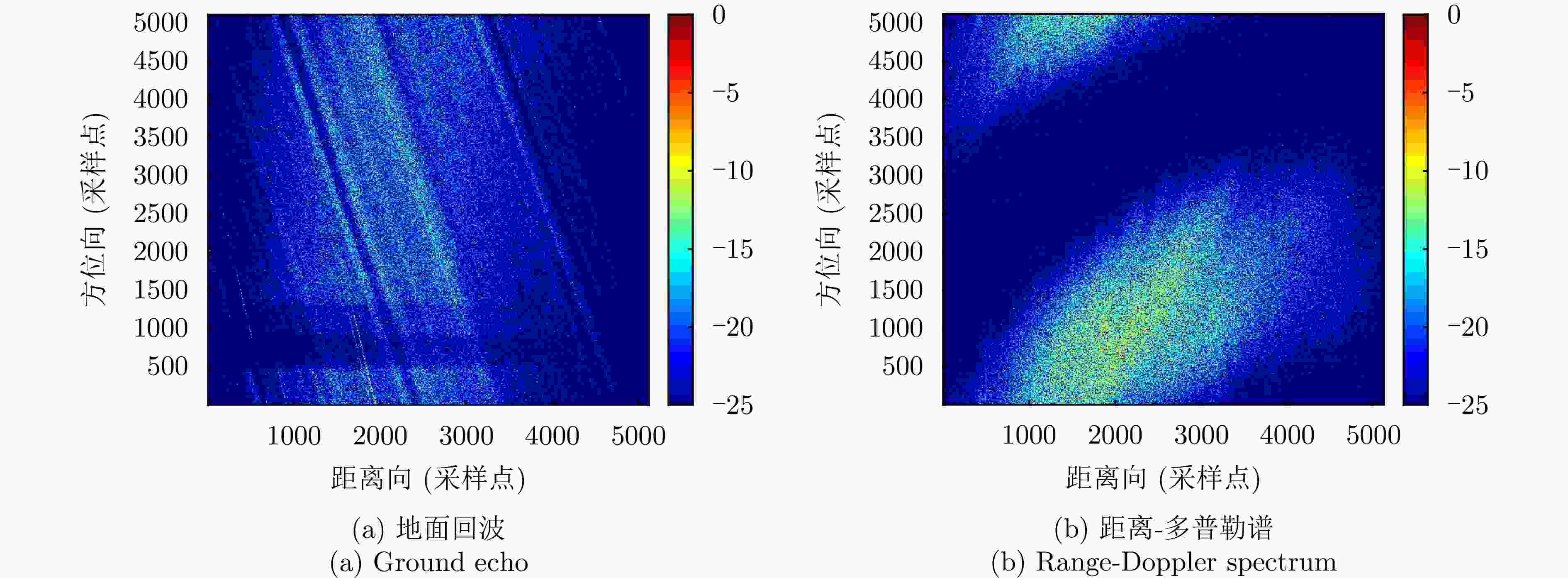
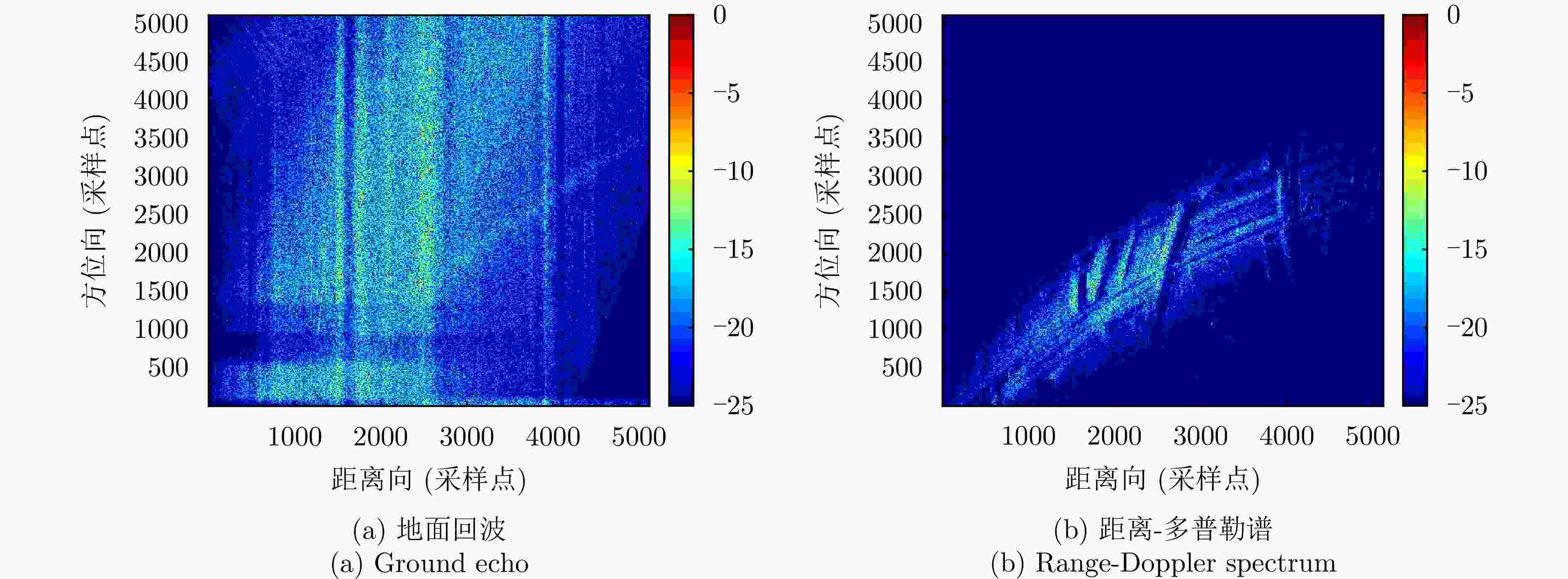
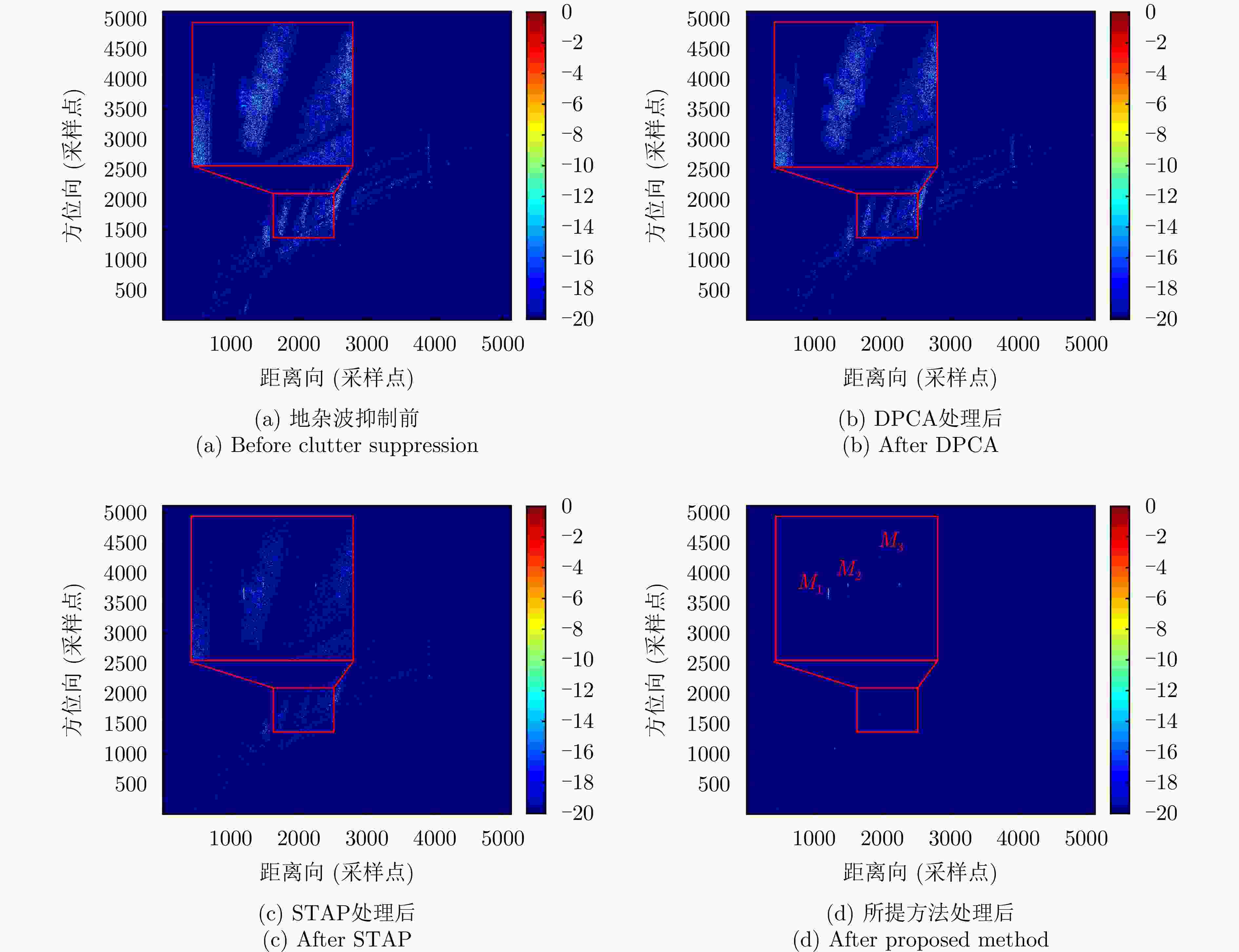
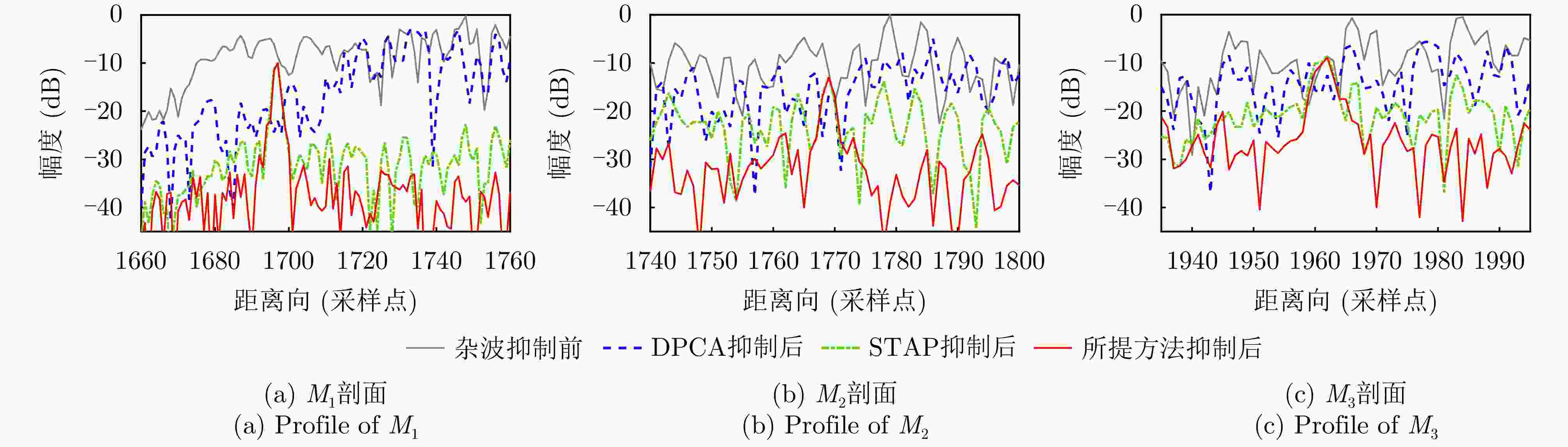
摘要: 杂波抑制是实现动目标指示的一项重要技术手段。然而,在机载双基合成孔径雷达(SAR)动目标指示中,受限于杂波的空时强耦合非线性和非平稳性,传统的空时自适应滤波、偏置相位中心方法不能获得期望的杂波抑制性能。为解决上述难题,该文提出了一种基于空时解耦的机载双基SAR双通道杂波对消处理方法。其核心在于建立空时解耦矩阵,将机载双基SAR强耦合非线性的空时谱解耦为空间频率保持一致的空时谱。所提方法主要分为以下3个步骤:(1)为提高目标信杂噪比,应用一阶Keystone变换和高阶距离徙动校正函数,使得目标信号能量集中在同一个距离单元;(2)为削弱双基平台运动造成的方位谱扩展效应,逐距离单元补偿多普勒调频率项;(3)为实现通道间杂波对消处理,引入空时解耦矩阵,在保持机载双基SAR同一距离单元内各杂波点归一化多普勒频率不变的情况下,将对应的空间频率均衡到零频,再利用通道间回波对消处理,实现杂波的有效抑制。通过仿真和实测数据处理,证明了所提方法进行机载双基SAR杂波抑制的有效性。Abstract: Clutter suppression is an important technology for moving target indication. However, for Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar (BiSAR) moving target indication, traditional space-time adaptive processing and displaced phase center antenna methods cannot achieve the expected clutter suppression because of the strong coupling nonlinearity and nonstationarity of clutter. To address the aforementioned challenge, this study proposes a dual-channel clutter cancellation processing method via space-time decoupling for airborne BiSAR. The core lies in establishing the space-time decoupling matrix, which converts the strongly coupled nonlinear two-dimensional space-time spectrum of airborne BiSAR into that with consistent spatial frequency. The proposed method mainly consists of the following steps: (1) To improve the signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio of moving targets, the first-order Keystone transformation and high-order range migration correction function are applied to concentrate the energy of moving targets in the same range cell. (2) To weaken the azimuth spectrum expansion effect caused by the motion of bistatic platforms, the Doppler frequency rate term is compensated for each range cell. (3) To achieve clutter cancellation, the space-time decoupling matrix is introduced. The normalized Doppler frequency remains unchanged, and the clutter atoms on the airborne BiSAR space-time plane are linearly transformed into atomic positions with the same normalized spatial frequency. Then, the echo signals of dual channels are subtracted for effective clutter suppression. The effectiveness of the proposed method for airborne BiSAR clutter suppression is demonstrated through simulation and real data processing.
-
表 1 BiSAR系统参数
Table 1. The system parameters of BiSAR
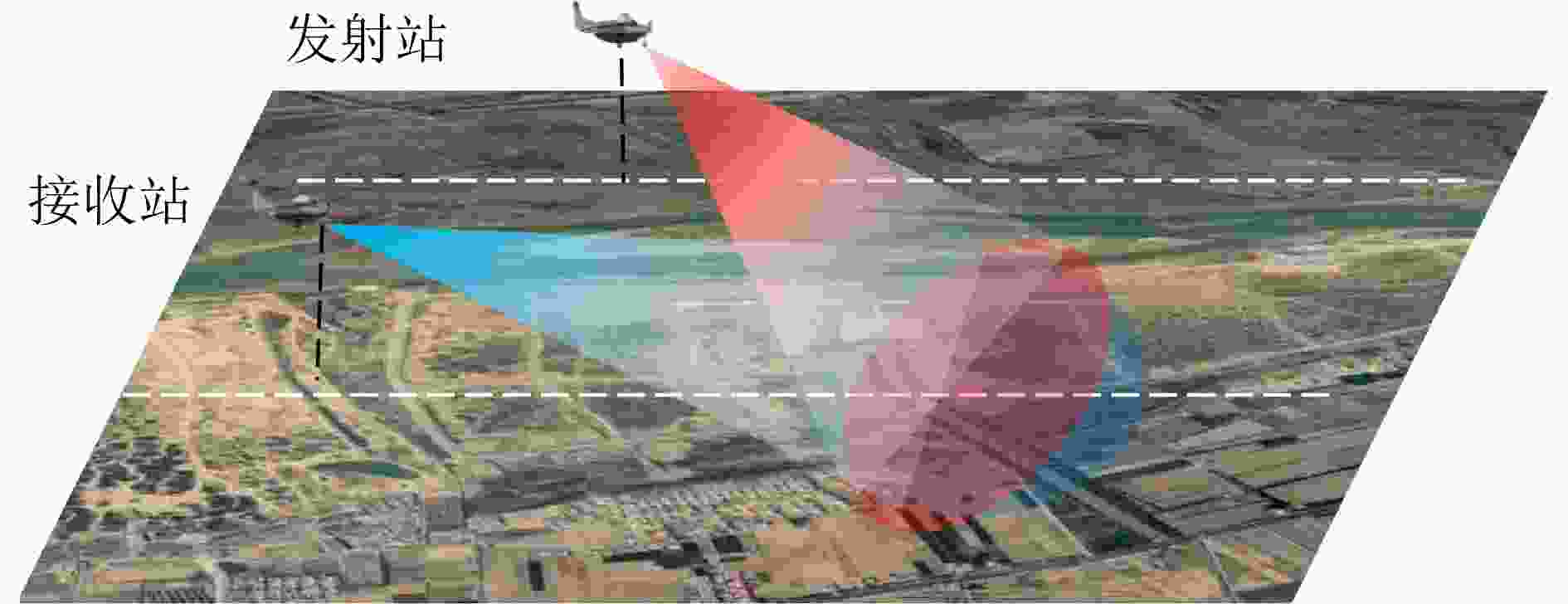
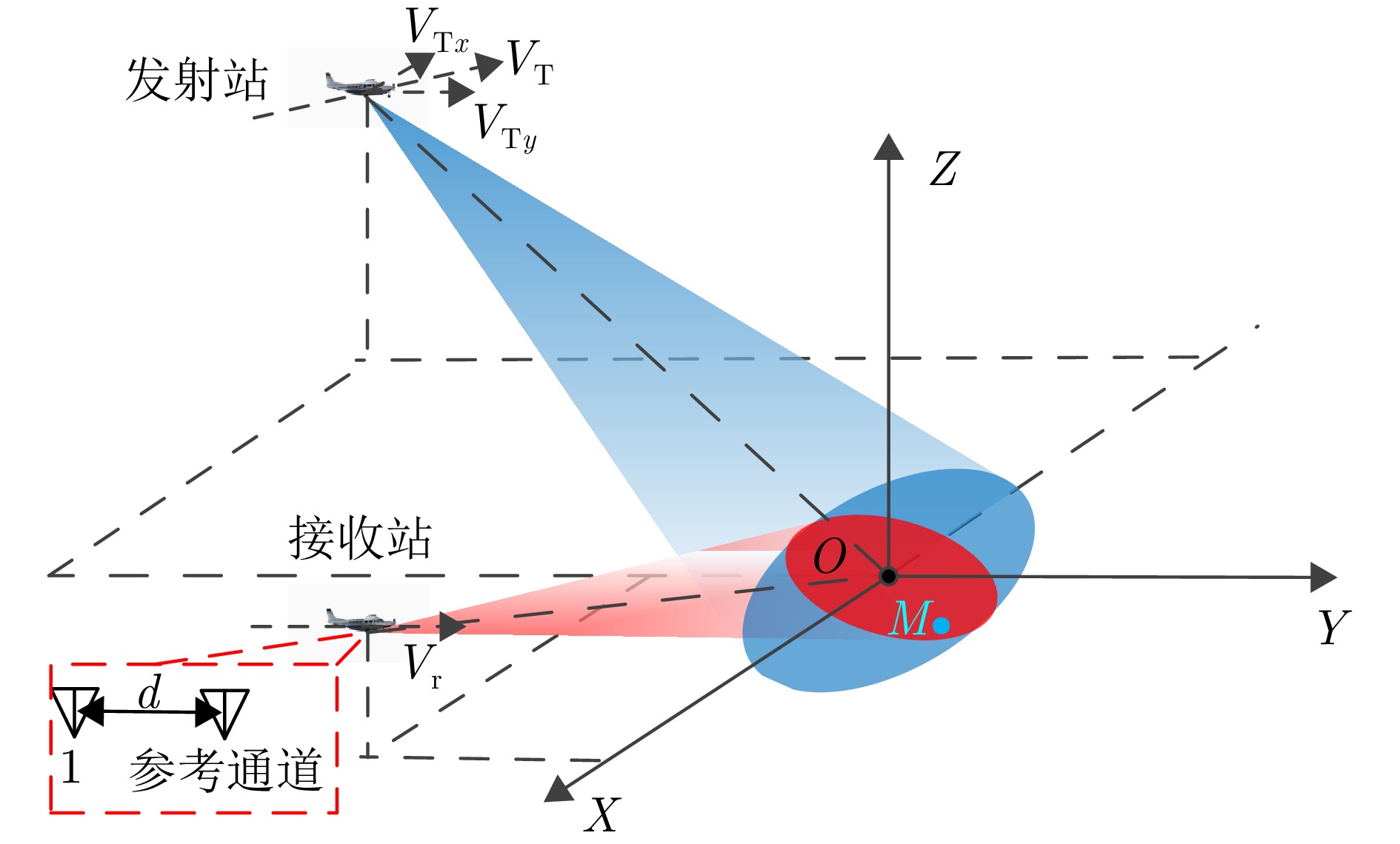
参数 符号 数值 发射站位置 $ T $ (– 8000 , –1000 ,6000 ) m接收站位置 $ {R} $ (0, – 8000 ,6000 ) m发射站速度 $ {V}_{\mathrm{T}} $ (–50, 150, 0) m/s 接收站速度 $ {V}_{\mathrm{R}} $ (0, 200, 0) m/s 载频 $ f_{{\mathrm{c}}} $ 10 GHz 带宽 $ B_{\mathrm{r}} $ 200 MHz 合成孔径时间 $ T_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 1 s 脉冲重复频率 $ \text { PRF } $ 1200 Hz通道数量 $ N $ 2 脉冲数量 $ M $ 10 -
[1] 杨建宇. 雷达技术发展规律和宏观趋势分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010.YANG Jianyu. Development laws and macro trends analysis of radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010. [2] 胡克彬. SAR高精度成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.HU Kebin. Research on high-precision imaging methods for synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [3] 张强辉. 高速机动平台双基前视SAR成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2019.000037.ZHANG Qianghui. Imaging method research for bistatic forward-looking SAR mounted on high-speed maneuvering platform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2019.000037. [4] 李中余. 双基地合成孔径雷达动目标检测与成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.LI Zhongyu. Research on bistatic SAR moving target detection and imaging technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [5] XIONG Tao, LI Yachao, LI Qi, et al. Using an equivalence-based approach to derive 2-D spectrum of BiSAR data and implementation into an RDA processor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(6): 4765–4774. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3011420. [6] ZHAO Ye, ZHANG Ming, ZHAO Yanwei, et al. A bistatic SAR image intensity model for the composite ship-ocean scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(8): 4250–4258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2393915. [7] LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, et al. Bistatic SAR Clutter Suppression: Theory, Method, and Experiment[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2022, 1–137. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-0159-1. [8] LI Junao, LI Zhongyu, YANG Qing, et al. Joint clutter suppression and moving target indication in 2-D azimuth rotated time domain for single-channel bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5202516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3237553. [9] NOHARA T J, WEBER P, PREMJI A, et al. Airborne ground moving target indication using non-side-looking antennas[C]. 1998 IEEE Radar Conference, RADARCON’98. Challenges in Radar Systems and Solutions (Cat. No.98CH36197), Dallas, USA, 1998: 269–274. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1998.678013. [10] KLEMM R. Adaptive airborne MTI: An auxiliary channel approach[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Communications, Radar and Signal Processing), 1987, 134(3): 269–276. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-1.1987.0054. [11] YANG Zhaocheng, LI Xiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. On clutter sparsity analysis in space-time adaptive processing airborne radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(5): 1214–1218. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2236639. [12] KAN Qingyun, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Clutter characteristics analysis and range-dependence compensation for space-air bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5101615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3347547. [13] 李中余, 皮浩卓, 李俊奥, 等. 双基SAR空时自适应ANM-ADMM-Net杂波抑制技术[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1196–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR24032.LI Zhongyu, PI Haozhuo, LI Jun’ao, et al. Clutter suppression technology based space-time adaptive ANM-ADMM-Net for bistatic SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1196–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR24032. [14] LI Zhongyu, YE Hongda, LIU Zhutian, et al. Bistatic SAR clutter-ridge matched STAP method for nonstationary clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5216914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3125043. [15] 穆慧琳. 多通道SAR地面运动目标检测与成像研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.000177.MU Huilin. Research on ground moving target detection and imaging in multichannel SAR system[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.000177. [16] 张文鹏. 复杂条件下多通道SAR运动目标检测与参数估计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2018. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2018.000417.ZHANG Wenpeng. Research of moving target detection and parameter estimation methods for multichannel SAR in complicated conditions[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2018. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2018.000417. [17] YANG Taoli, LI Zhenfang, SUO Zhiyong, et al. Performance analysis for multichannel HRWS SAR systems based on STAP approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1409–1413. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2258889. [18] GUERCI J R, GOLDSTEIN J S, REED I S. Optimal and adaptive reduced-rank STAP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(2): 647–663. doi: 10.1109/7.845255. [19] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, BAO Zhonghua, et al. Detection and extraction of target with micromotion in spiky sea clutter via short-time fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1002–1018. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2246574. [20] CERUTTI-MAORI D and SIKANETA I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 560–572. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201260. [21] HOU Yingjie, WANG Junfeng, LIU Xingzhao, et al. An automatic SAR-GMTI algorithm based on DPCA[C]. 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 592–595. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946492. [22] XU Jia, HUANG Zuzhen, YAN Liang, et al. SAR ground moving target indication based on relative residue of DPCA processing[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1676. doi: 10.3390/s16101676. [23] LI Zhongyu, LI Shanchuan, LIU Zhutian, et al. Bistatic forward-looking SAR MP-DPCA method for space-time extension clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6565–6579. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977982. [24] WARD J. Space-time adaptive processing for airborne radar[C]. IEE Colloquium on Space-Time Adaptive Processing (Ref. No.1998/241), London, UK, 1998: 2/1–2/6. doi: 10.1049/ic:19980240. [25] HUANG Penghui, YANG Hao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A novel sea clutter rejection algorithm for spaceborne multichannel radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5117422. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3204324. [26] HUANG Penghui, ZOU Zihao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Multichannel sea clutter modeling for spaceborne early warning radar and clutter suppression performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(10): 8349–8366. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3039495. [27] HUANG Penghui, ZOU Zihao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A novel dimension-reduced space-time adaptive processing algorithm for spaceborne multichannel surveillance radar systems based on spatial-temporal 2-D sliding window[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5109721. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3144668. [28] LV Mingjie and ZHOU Chen. Study on sea clutter suppression methods based on a realistic radar dataset[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(23): 2721. doi: 10.3390/rs11232721. [29] ZHANG Tianfu, DENG Yunkai, and WANG Yongliang. A novel joint dimensionality-reduced adaptive clutter suppression method for space-based early warning radar utilizing frequency diversity array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2024, 2: 1123–1134. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2024.3483772. [30] WANG Yumiao, ZHAO Wenjing, WANG Xiang, et al. Nonhomogeneous sea clutter suppression using complex-valued U-Net model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4027705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3214633. [31] JI Yuanzheng, LIU Aijun, SONG Zhen, et al. HFSWR clutter suppression and target detection method based on RRN and exponential weight control[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3507305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3417486. [32] HUA Qinglong, YUN Zhang, MU Huilin, et al. An approach of sea clutter suppression for SAR images by self-supervised complex-valued deep learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4512505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3183582. [33] 邓云凯, 王宇. 先进双基SAR技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026.DENG Yunkai and WANG Yu. Exploration of advanced bistatic SAR experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026. [34] 陈士超, 邢孟道, 张双喜, 等. 一种串行双基SAR的SIFT成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 14–22. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.13018.CHEN Shichao, XING Mengdao, ZHANG Shuangxi, et al. A SIFT algorithm for bistatic SAR imaging in spaceborne constant-offset configuration[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 14–22. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.13018. [35] 刘裕洲, 蔡天倚, 李亚超, 等. 联合距离方位二维NCS的星弹双基前视SAR成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1202–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR23144.LIU Yuzhou, CAI Tianyi, LI Yachao, et al. A range and azimuth combined two-dimensional NCS algorithm for spaceborne-missile bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1202–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR23144. [36] 武俊杰, 孙稚超, 吕争, 等. 星源照射双/多基地SAR成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 13–35. doi: 10.12000/JR22213.WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LV Zheng, et al. Bi/multi-static synthetic aperture radar using spaceborne illuminator[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 13–35. doi: 10.12000/JR22213. [37] LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, YI Qingying, et al. Bistatic forward-looking SAR ground moving target detection and imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1000–1016. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130539. [38] LIU Zhutian, YE Hongda, LI Zhongyu, et al. Optimally matched space-time filtering technique for BFSAR nonstationary clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3090462. [39] LI Junao, LI Zhongyu, YANG Qing, et al. Efficient matrix sparse recovery STAP method based on Kronecker transform for BiSAR sea clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5103218. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3362844. [40] ZHU Daiyin, LI Yong, and ZHU Zhaoda. A keystone transform without interpolation for sar ground moving-target imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(1): 18–22. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.882147. [41] WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LI Zhongyu, et al. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 840. doi: 10.3390/rs8100840. [42] WONG F H, CUMMING I G, and NEO Y L. Focusing bistatic SAR data using the nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(9): 2493–2505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.917599. [43] SCHöNEMANN P H. A generalized solution of the orthogonal procrustes problem[J]. Psychometrika, 1966, 31(1): 1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02289451. [44] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. New York: McGraw, 1970, 262–304. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: