A Hyperparameter-free Total Variation Regularization Method for Real Aperture Radar Angular Super-resolution
-
摘要: 受平台物理空间限制,实孔径雷达天线波束宽、角分辨率低下。基于稀疏重建的角超分辨方法,在正则化框架下引入目标稀疏先验约束并通过迭代优化求解对目标散射分布进行反演,是提升实孔径雷达角分辨率的重要途径。然而,现有稀疏重建方法仅考虑了强点目标的稀疏分布特性,未考虑扩展目标的轮廓信息,存在目标边缘恢复失真的问题;同时,现有稀疏重建方法对代价函数中引入的超参数敏感,实际应用中依赖人工精细调整,难以根据不同场景进行自适应选取。针对上述两个问题,该文提出一种无超参数全变差(TV)正则化角超分辨方法,首先建立一种均方根LASSO代价函数,用于表征扫描回波序列与目标散射分布的拟合残差,以及目标边缘梯度的稀疏约束,从而将目标轮廓重建问题重转化为TV正则化约束下的非平滑凸优化问题;然后基于协方差拟合准则,导出了无超参数TV正则化约束的解析表达;最后提出一种广义迭代重加权最小二乘(GIRLS)求解策略,实现了均方根LASSO非平滑凸优化问题的迭代优化求解。仿真和实测结果表明,该文提出的方法能够在改善分辨率的同时保持目标的轮廓信息,且无需人工调整超参数。Abstract: A real aperture radar has physical space limitations that result in a wide antenna beam, leading to low angular resolution. The angular super-resolution method based on sparse reconstruction introduces sparse prior constraints of the target under a regularization framework and reconstructs the target reflectivity function through iterative optimization, thereby significantly enhancing the angular resolution of the radar. However, existing sparse reconstruction methods primarily consider the sparse distribution characteristics of strong point targets, neglecting the contour information of extended targets, which results in distortion in the recovery of target edges. Additionally, these methods are sensitive to one or more hyperparameters introduced into the cost function. Thus, meticulous manual adjustments are essential in practical applications, and they pose challenges in terms of the adaptive selection of hyperparameters in dynamic scenarios. To address these issues, this paper proposes a hyperparameter-free Total Variation (TV) regularization angular super-resolution method. First, a square-root Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) cost function was established to characterize the fitting residuals between the scan echo sequence and target reflectivity function and to characterize the sparse constraints on the target edge gradients. Using this function, the target contour reconstruction problem was transformed into a non-smooth convex optimization problem under TV regularization constraints. The analytical expression of the hyperparameter-free TV regularization term was derived based on the covariance fitting criterion. Finally, a Generalized Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares (GIRLS) strategy was proposed, and an iterative optimization method for solving the non-smooth convex optimization problem of square-root LASSO was derived. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method improves angular resolution of the radar while preserving the contour information of the target without requiring manual adjustment of the hyperparameters.
-
1 基于GIRLS的迭代优化求解方法流程
1. Flowchart of the GIRLS-based iterative optimization solving method
1. 根据天线方向图向量h构造字典矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{B}} = {\boldsymbol{H}}{\nabla ^{ - 1}} $ 2. 根据式(24)构造加权矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}} $ 3. 初始化$ {\boldsymbol{\hat s}} = {\left( {{{\boldsymbol{H}}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{H}}} \right)^{ - 1}}{{\boldsymbol{H}}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{y}} $ 4. $ {\lambda _1} = \dfrac{1}{{{{\left\| {{\boldsymbol{y}} - {\boldsymbol{H\hat s}}} \right\|}_2}}} $ 5. 根据式(46)构造${{\boldsymbol{U}}_2}$ 6. $ {\boldsymbol{\hat s}} = {\lambda _1}{\left[ {{\lambda _1}{{\boldsymbol{H}}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{H}} + {M^{ - 1/2}}{\nabla ^{\text{H}}}{{\left( {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{1/2}} \right)}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{U}}_2^{\text{H}}{{\boldsymbol{U}}_2}{\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{1/2}\nabla } \right]^{ - 1}} $
${{\boldsymbol{H}}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{y}} $7. 重复迭代步骤4—步骤6,直至收敛 表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
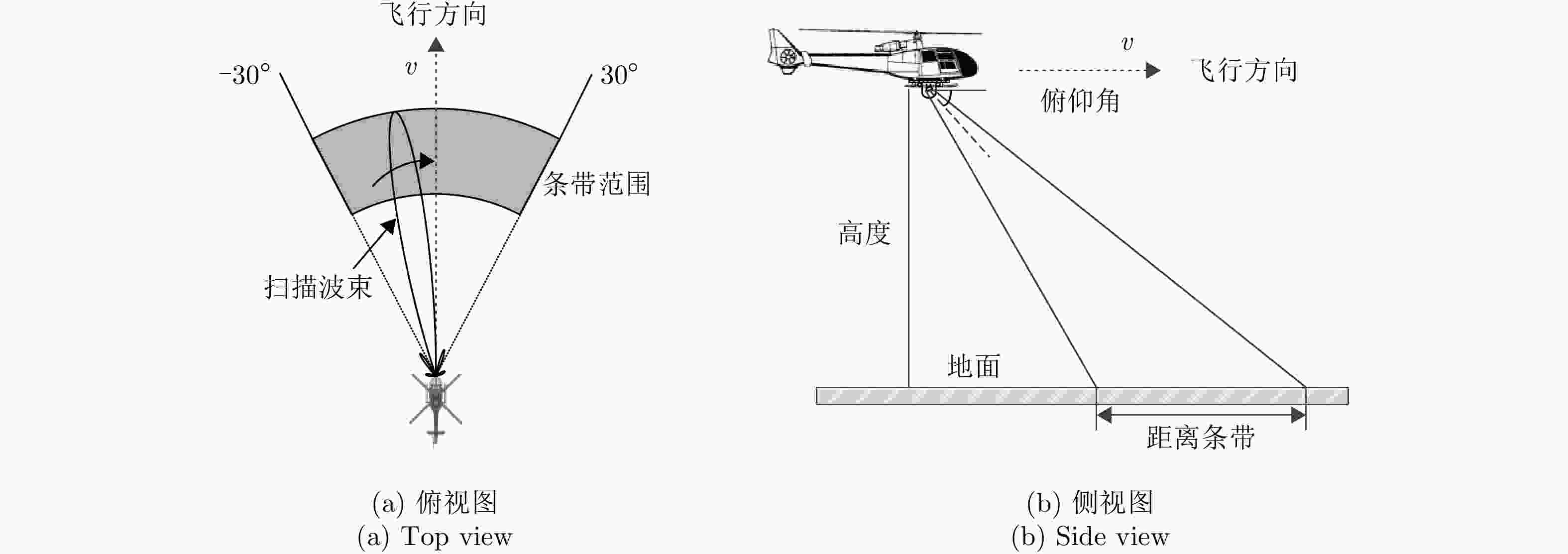
参数 数值 载频 10 GHz 信号带宽 40 MHz 信号时宽 2 μs PRF 500 Hz 扫描速度 60°/s 作用距离 3 km 波束宽度 3° 表 2 机载雷达试验参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters for airborne radar
参数 数值 载频 30.75 GHz 信号时宽 1 μs 信号带宽 200 MHz PRF 4000 Hz俯仰角 20° 波束宽度 4° 扫描速度 60°/s 扫描范围 –30°~30° 平台速度 37 m/s 飞行高度 300 m 表 3 试验结果图像熵对比
Table 3. Comparison of image Entropy for experimental results
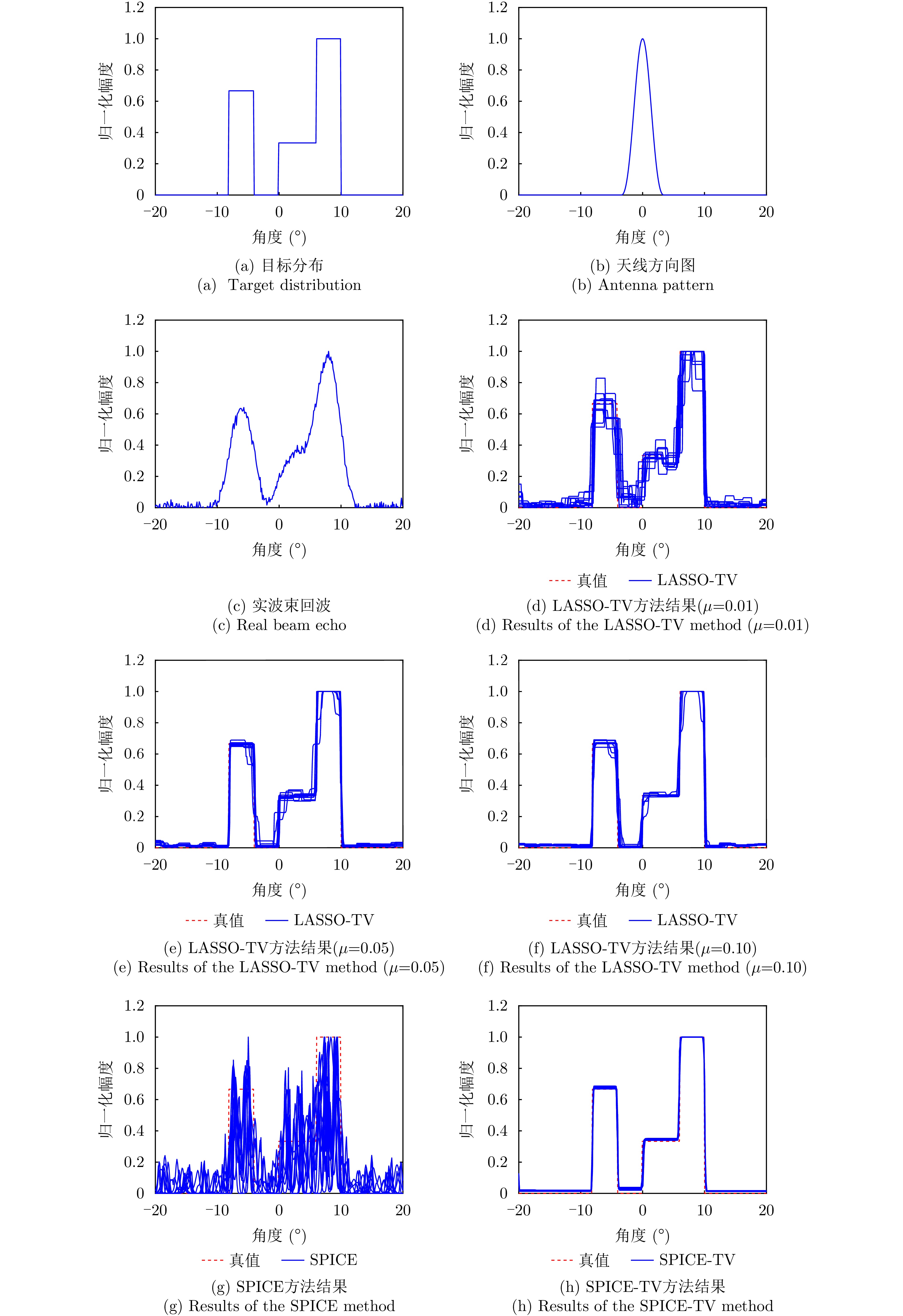
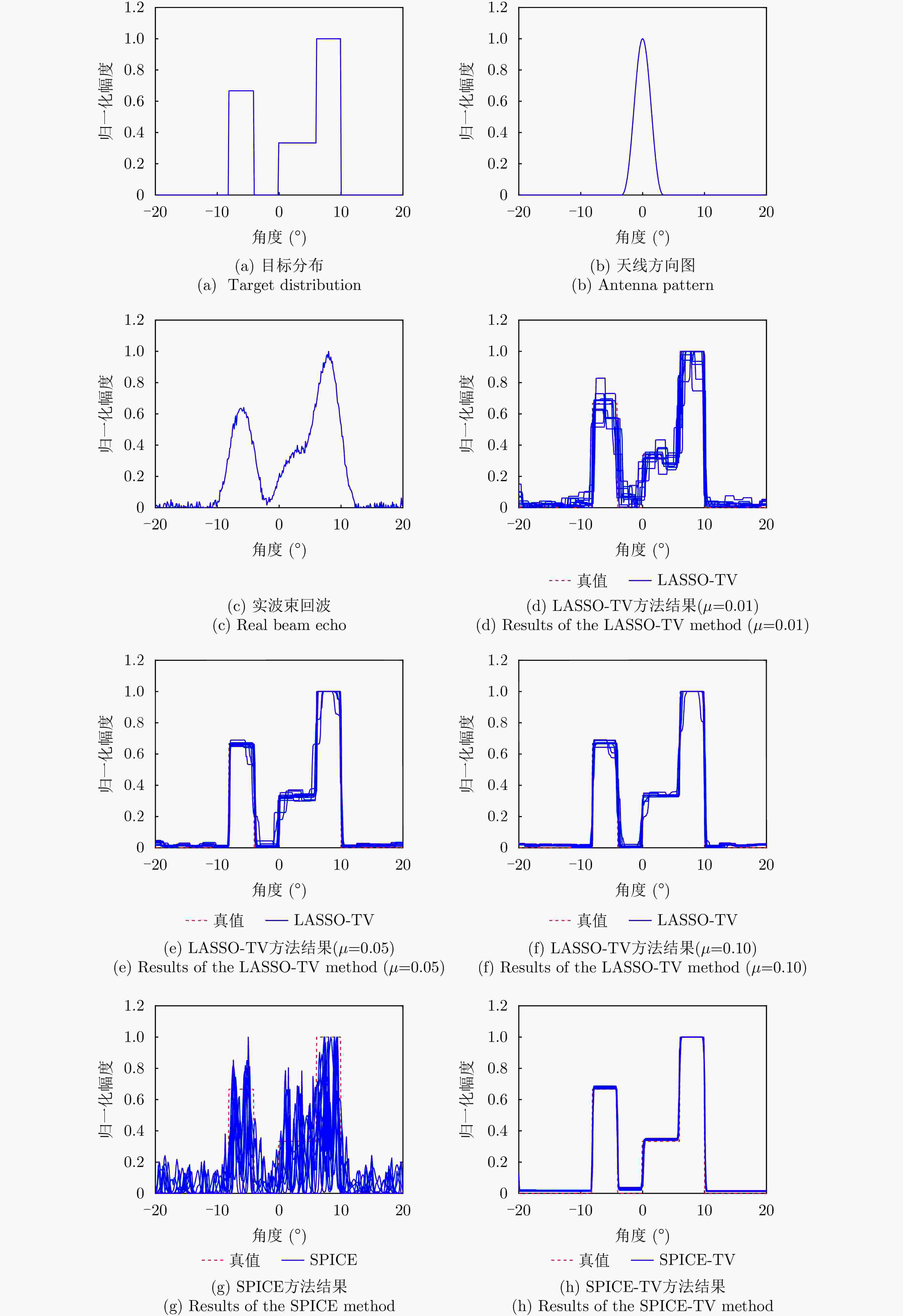
超分辨方法 图像熵 LASSO-TV方法 2.7645 本文方法(SPICE-TV) 0.9721 -
[1] STIMSON G W. Introduction to Airborne Radar[M]. 2nd ed. Mendham, USA: SciTech, 1998. [2] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099. [3] 李亚超, 王家东, 张廷豪, 等. 弹载雷达成像技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119.LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Present situation and prospect of missile-borne radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119. [4] 陈洪猛, 余继周, 张文杰, 等. 基于概率模型驱动的机载贝叶斯前视超分辨多目标成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1125–1137. doi: 10.12000/JR23080.CHEN Hongmeng, YU Jizhou, ZHANG Wenjie, et al. Probability model-driven airborne Bayesian forward-looking super-resolution imaging for multitarget scenario[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1125–1137. doi: 10.12000/JR23080. [5] 丁义元, 杨建宇, 张卫华, 等. 改进实孔径雷达角分辨力的广义逆滤波方法[J]. 电子学报, 1993, 21(9): 15–19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1993.09.003.DING Yiyuan, YANG Jianyu, ZHANG Weihua, et al. Improvement of angular resolution of real aperture radar via generalized inverse filtering[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1993, 21(9): 15–19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1993.09.003. [6] ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, LI Wenchao, et al. Super-resolution surface mapping for scanning radar: Inverse filtering based on the fast iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 127–144. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743263. [7] 李悦丽, 梁甸农, 黄晓涛. 一种单脉冲雷达多通道解卷积前视成像方法[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(5): 699–703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.05.013.LI Yueli, LIANG Diannong, and HUANG Xiaotao. A multi-channel deconvolution based on forword-looking imaging method in monopulse radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 23(5): 699–703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.05.013. [8] ZHANG Yongchao, LUO Jiawei, ZHANG Yongwei, et al. Resolution enhancement for large-scale real beam mapping based on adaptive low-rank approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3202073. [9] MIGLIACCIO M and GAMBARDELLA A. Microwave radiometer spatial resolution enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(5): 1159–1169. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.844099. [10] TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. Fast sparse-TSVD super-resolution method of real aperture radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6609–6620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027053. [11] GAMBARDELLA A and MIGLIACCIO M. On the superresolution of microwave scanning radiometer measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 796–800. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2006285. [12] ZHANG Qiping, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. TV-sparse super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6534–6549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977719. [13] JOHNSTON P R and GULRAJANI R M. Selecting the corner in the L-curve approach to Tikhonov regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2000, 47(9): 1293–1296. doi: 10.1109/10.867966. [14] GOLUB G H, HEATH M, and WAHBA G. Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter[J]. Technometrics, 1979, 21(2): 215–223. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1979.10489751. [15] STOICA P, BABU P, and LI Jian. New method of sparse parameter estimation in separable models and its use for spectral analysis of irregularly sampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(1): 35–47. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2086452. [16] MAO Deqing, YANG Jianyu, TUO Xing, et al. Angular superresolution of real aperture radar for target scale measurement using a generalized hybrid regularization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5109314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3315310. [17] TIBSHIRANI R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO: A retrospective[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1996, 58(1): 267–288. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x. [18] STOICA P, ZACHARIAH D, and LI Jian. Weighted SPICE: A unifying approach for hyperparameter-free sparse estimation[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 33: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2014.06.010. [19] TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. A fast sparse azimuth super-resolution imaging method of real aperture radar based on iterative reweighted least squares with linear sketching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2928–2941. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3061430. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: