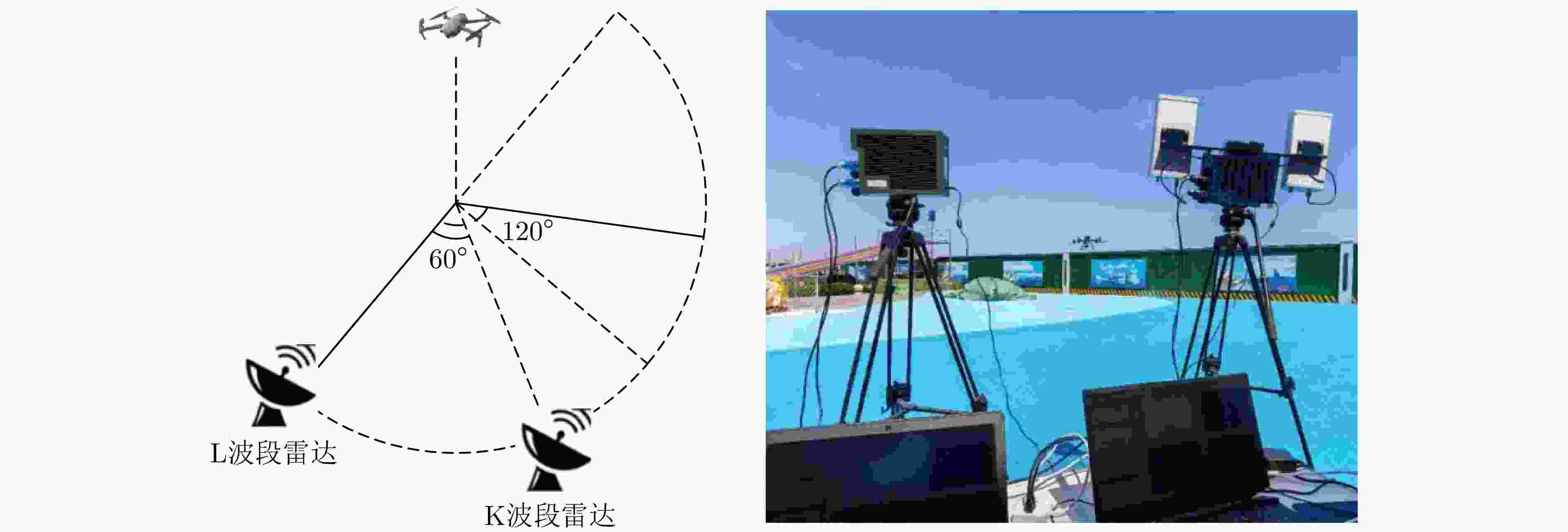
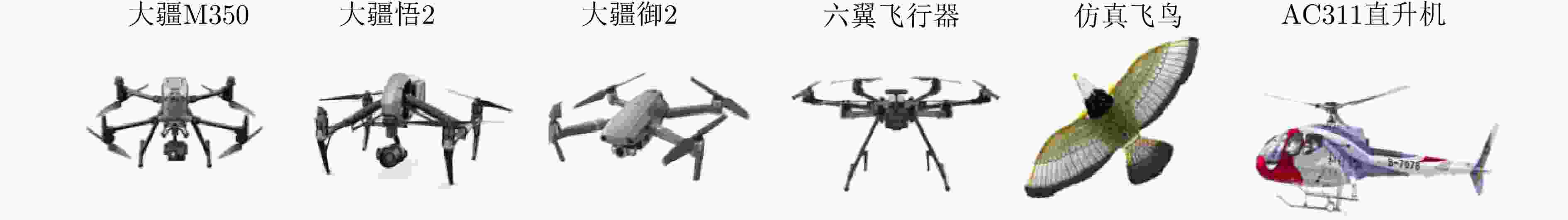
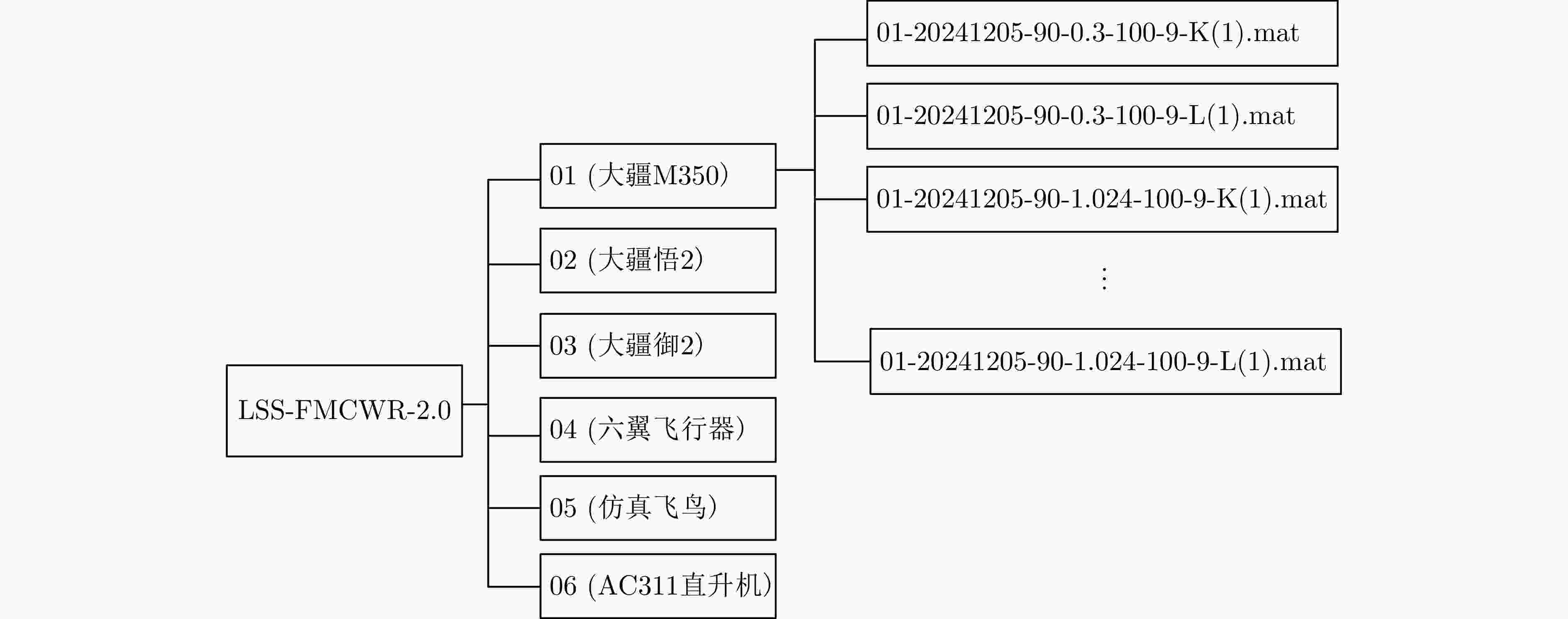
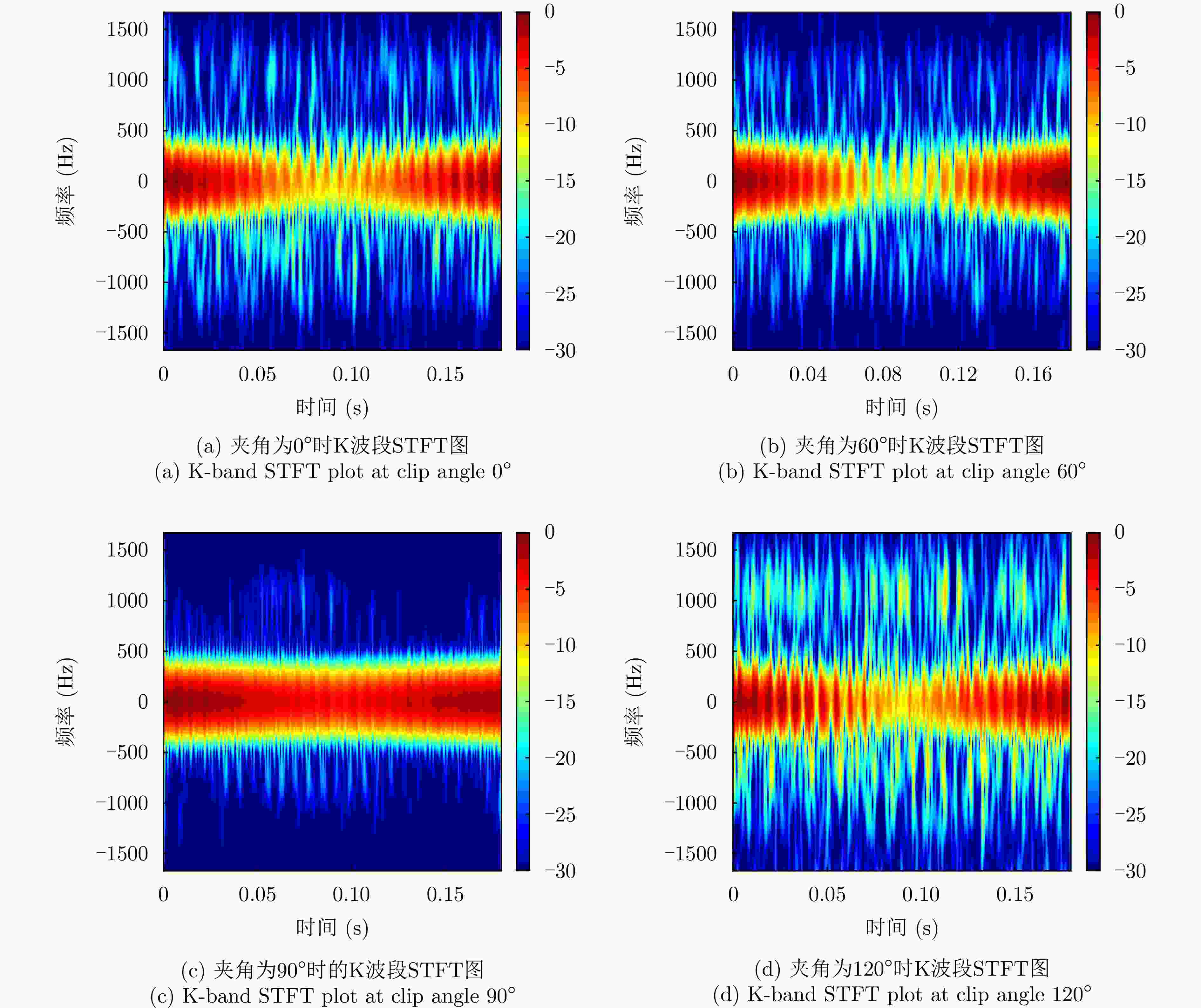
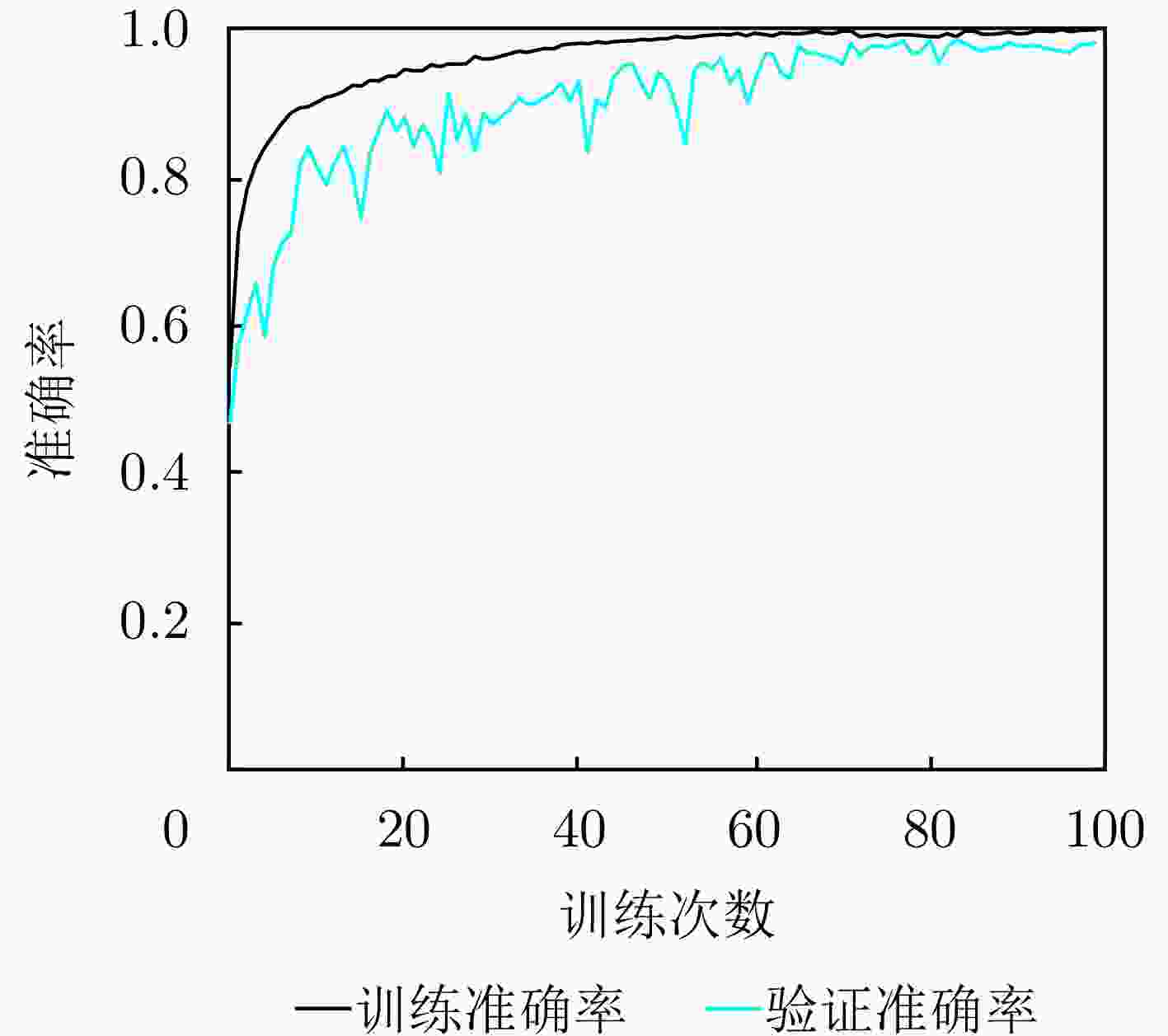
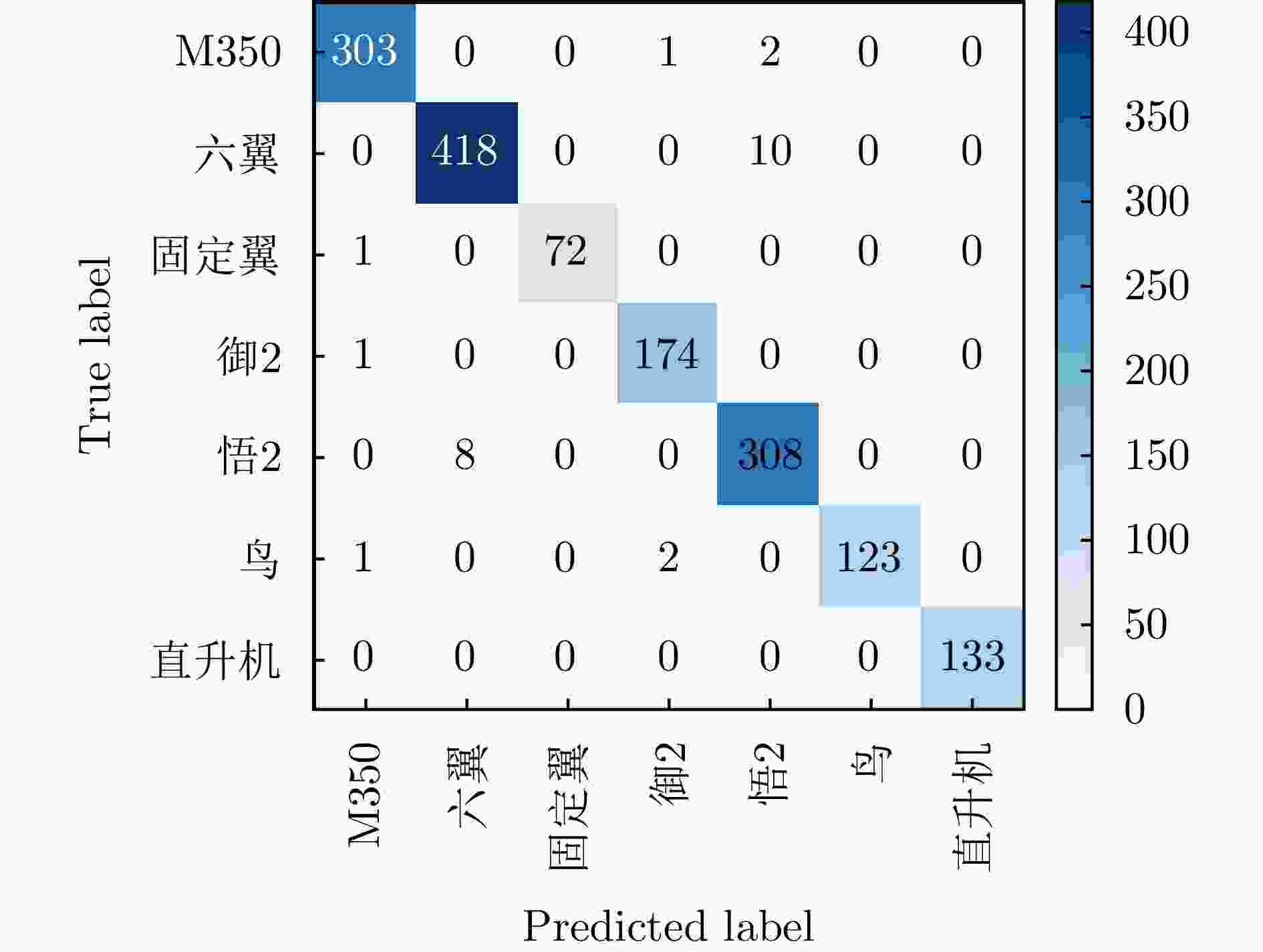
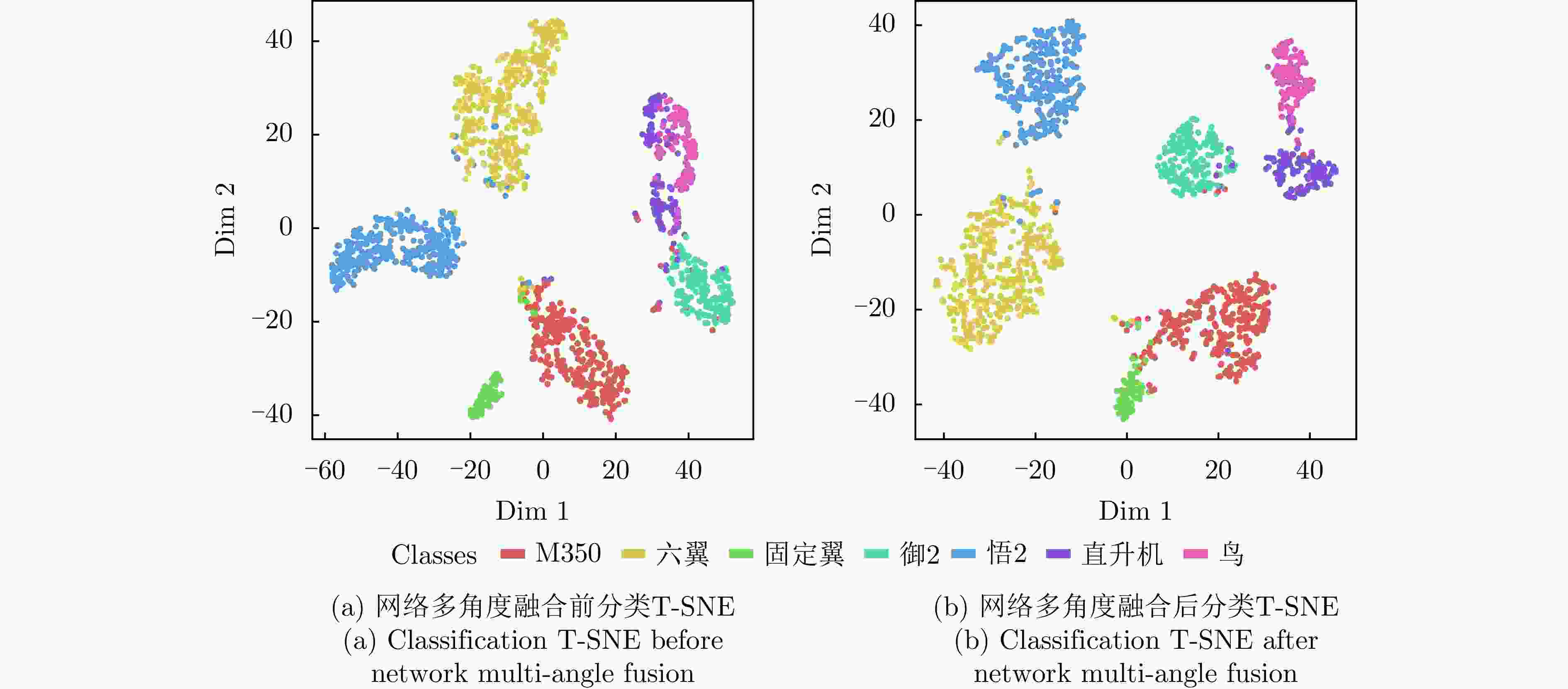
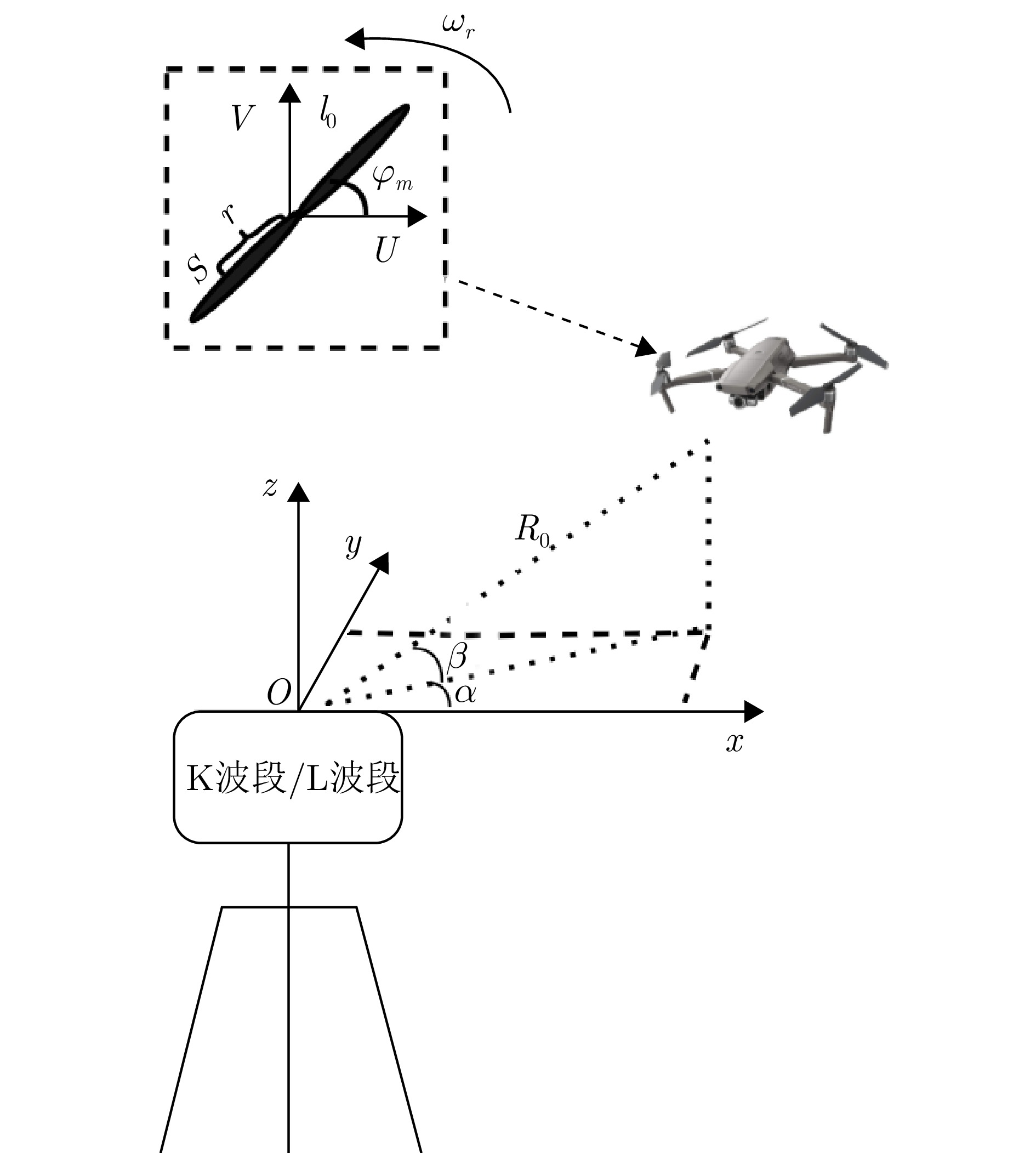
Multi-band Multi-angle FMCW Radar Low-Slow-Small Target Detection Dataset (LSS-FMCWR-2.0) and Feature Fusion Classification Methods
-
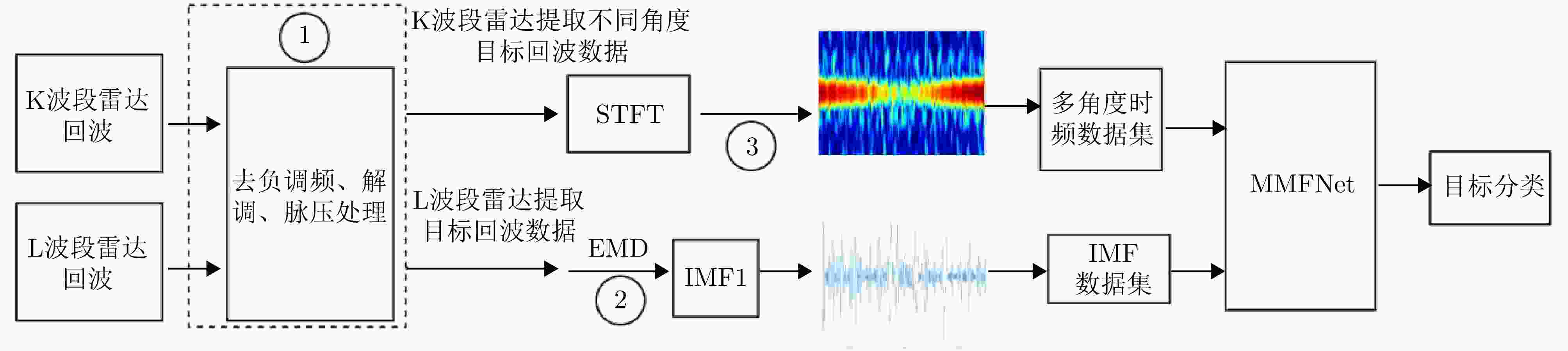
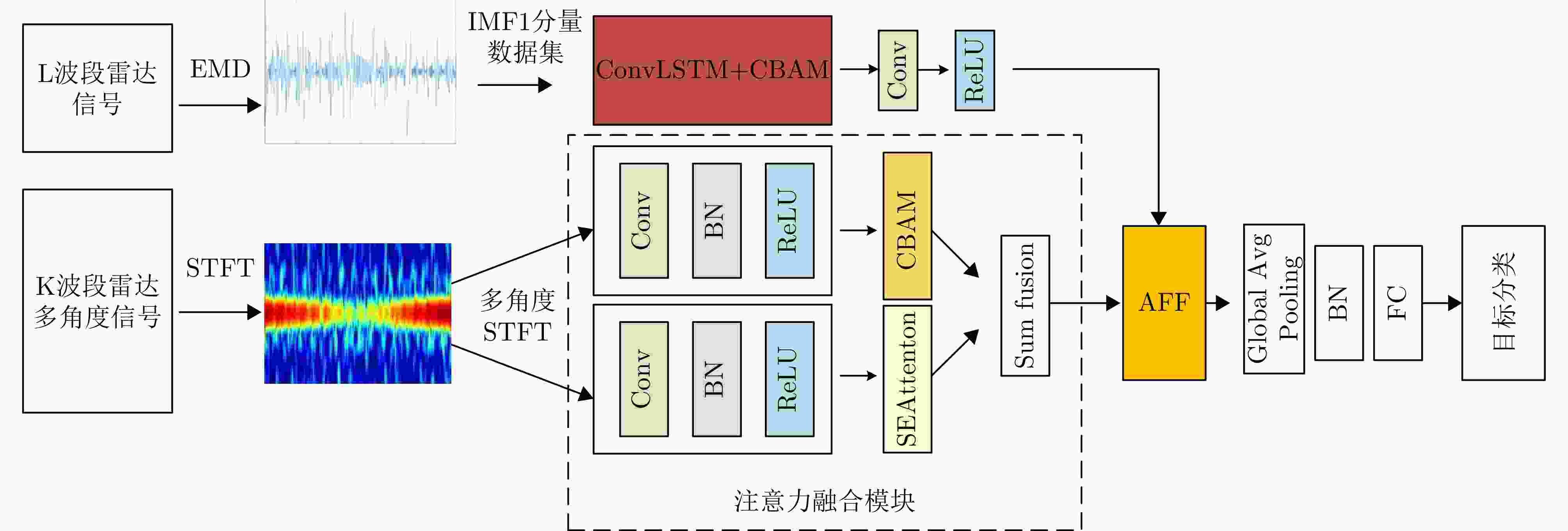
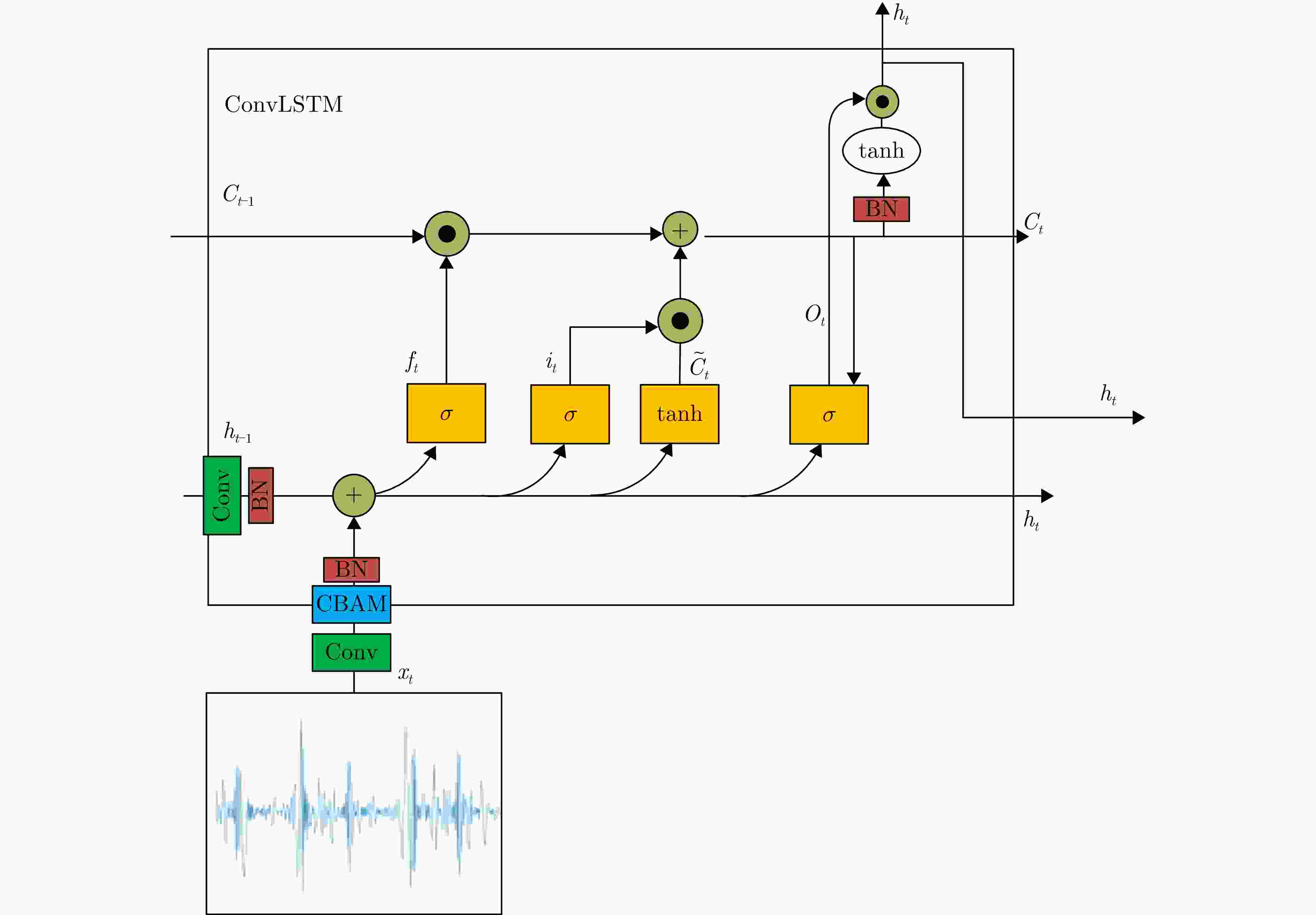
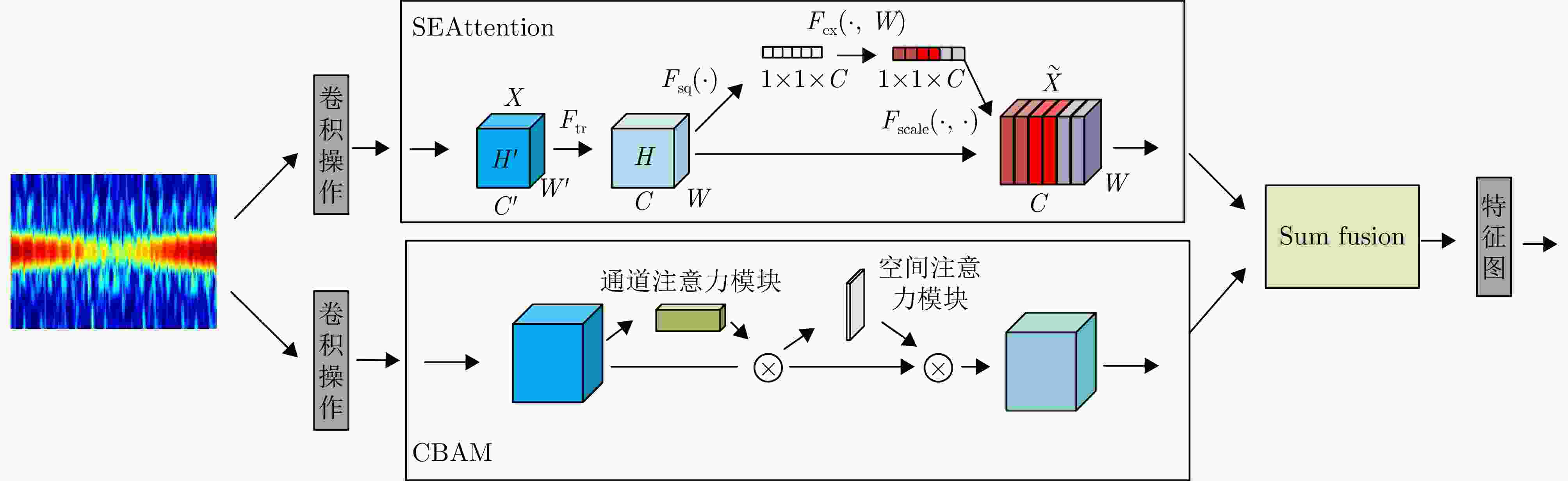
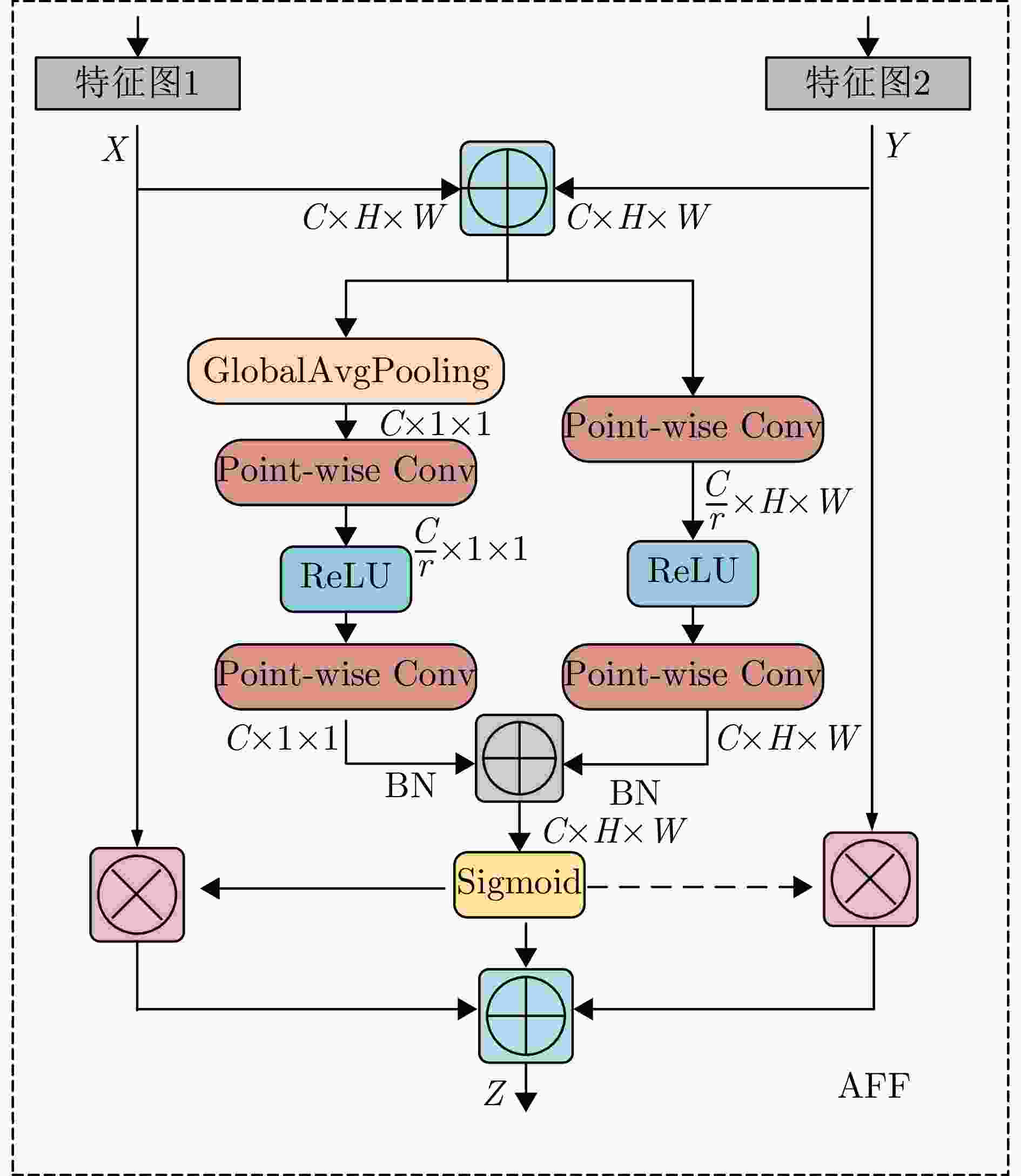
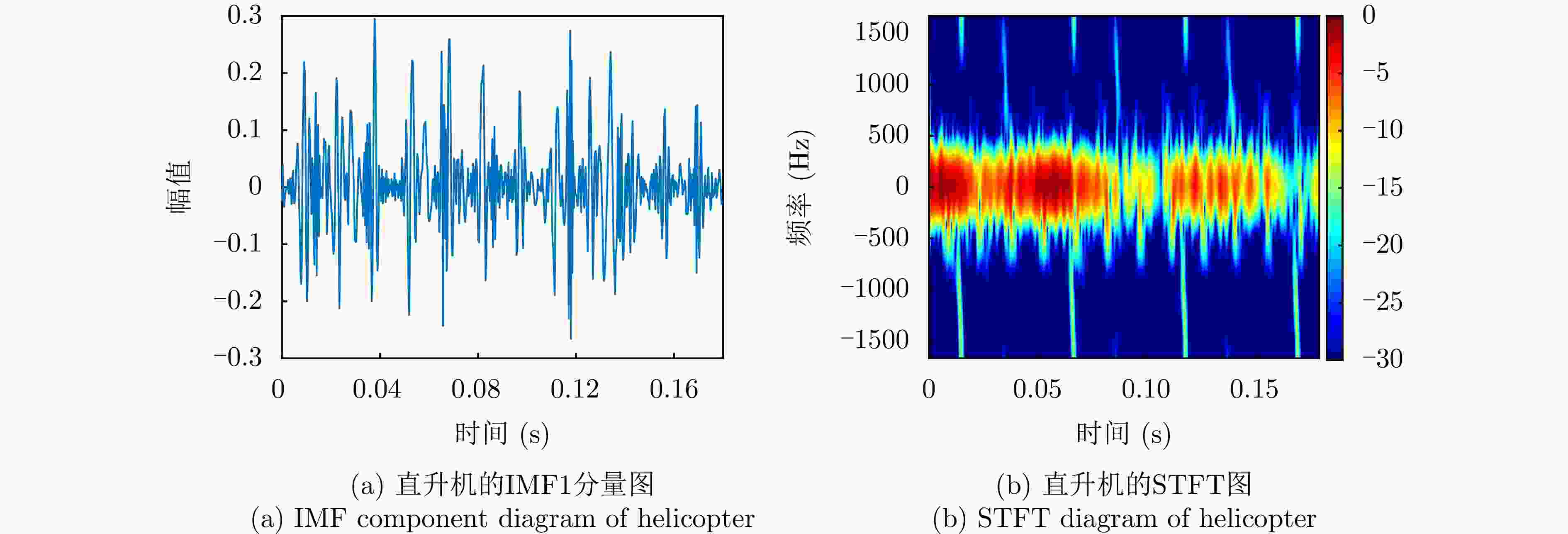
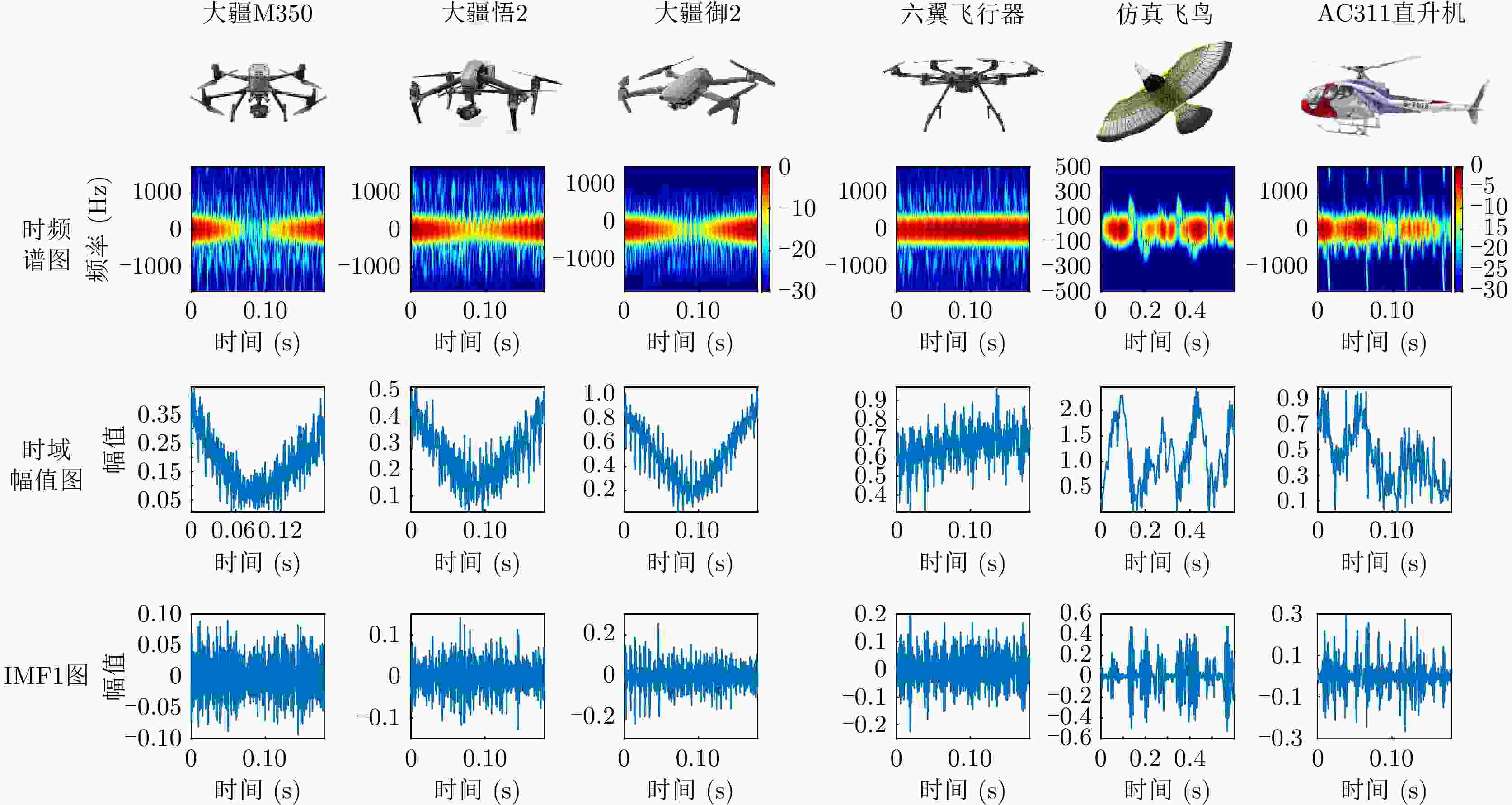
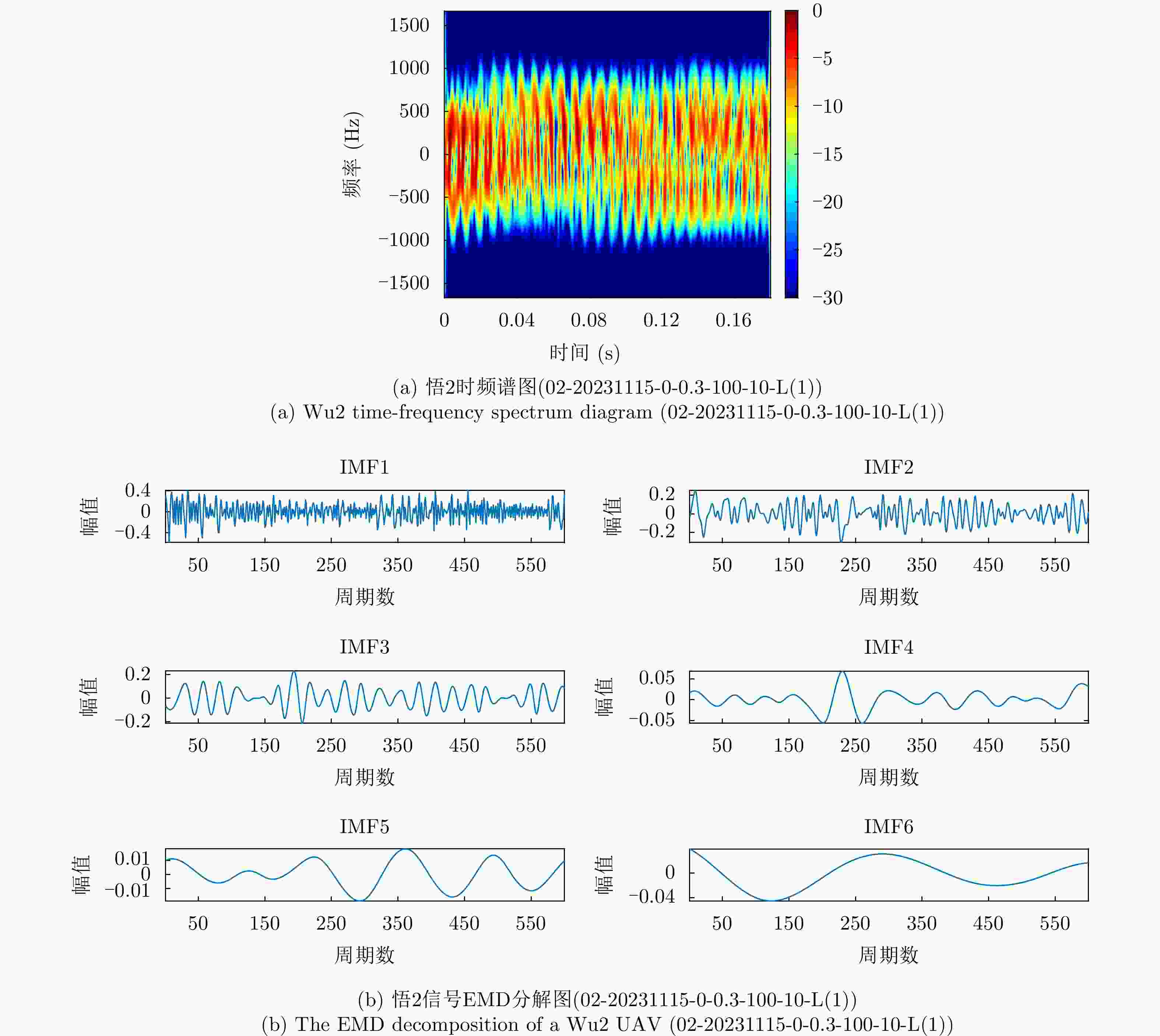
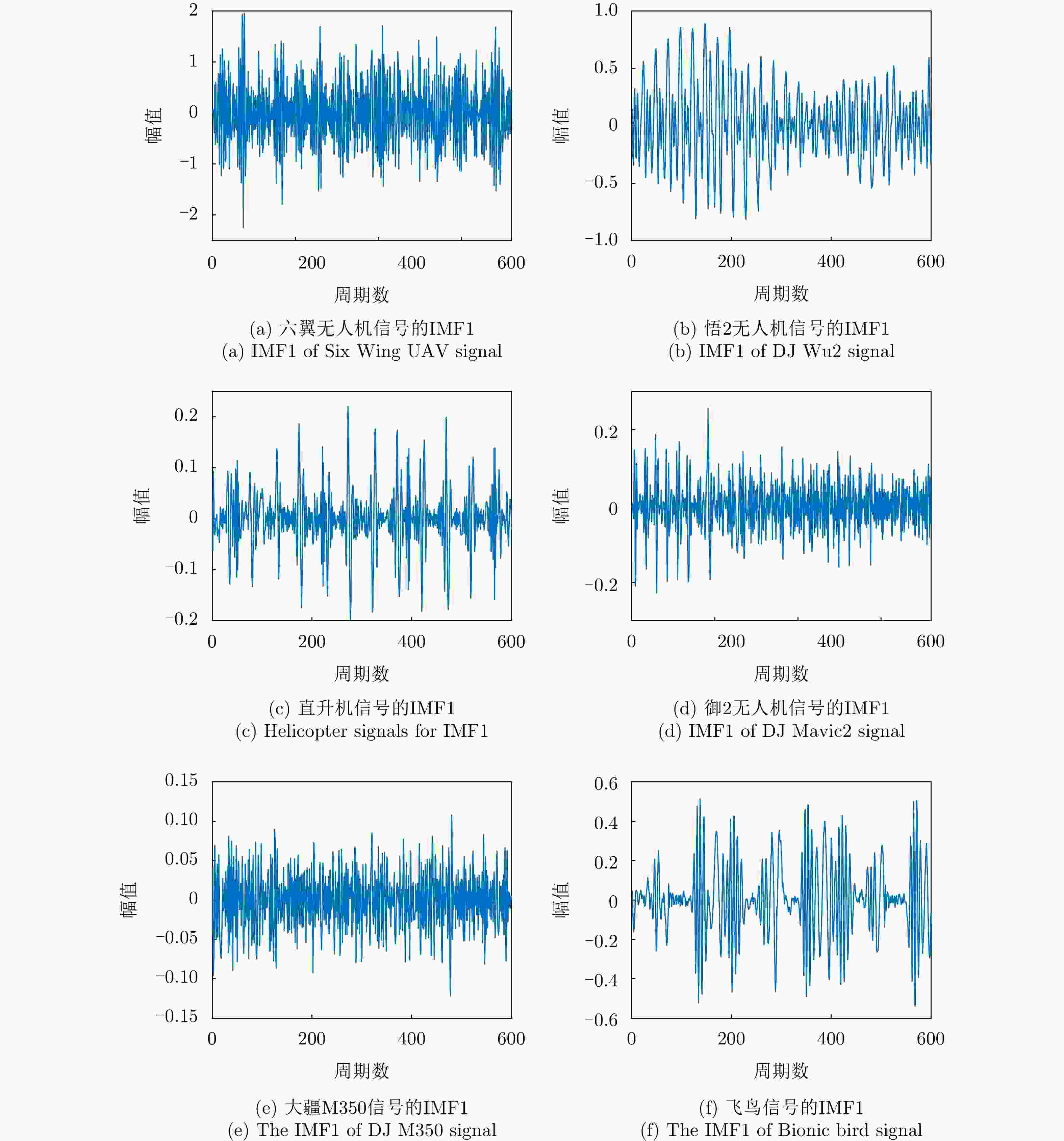
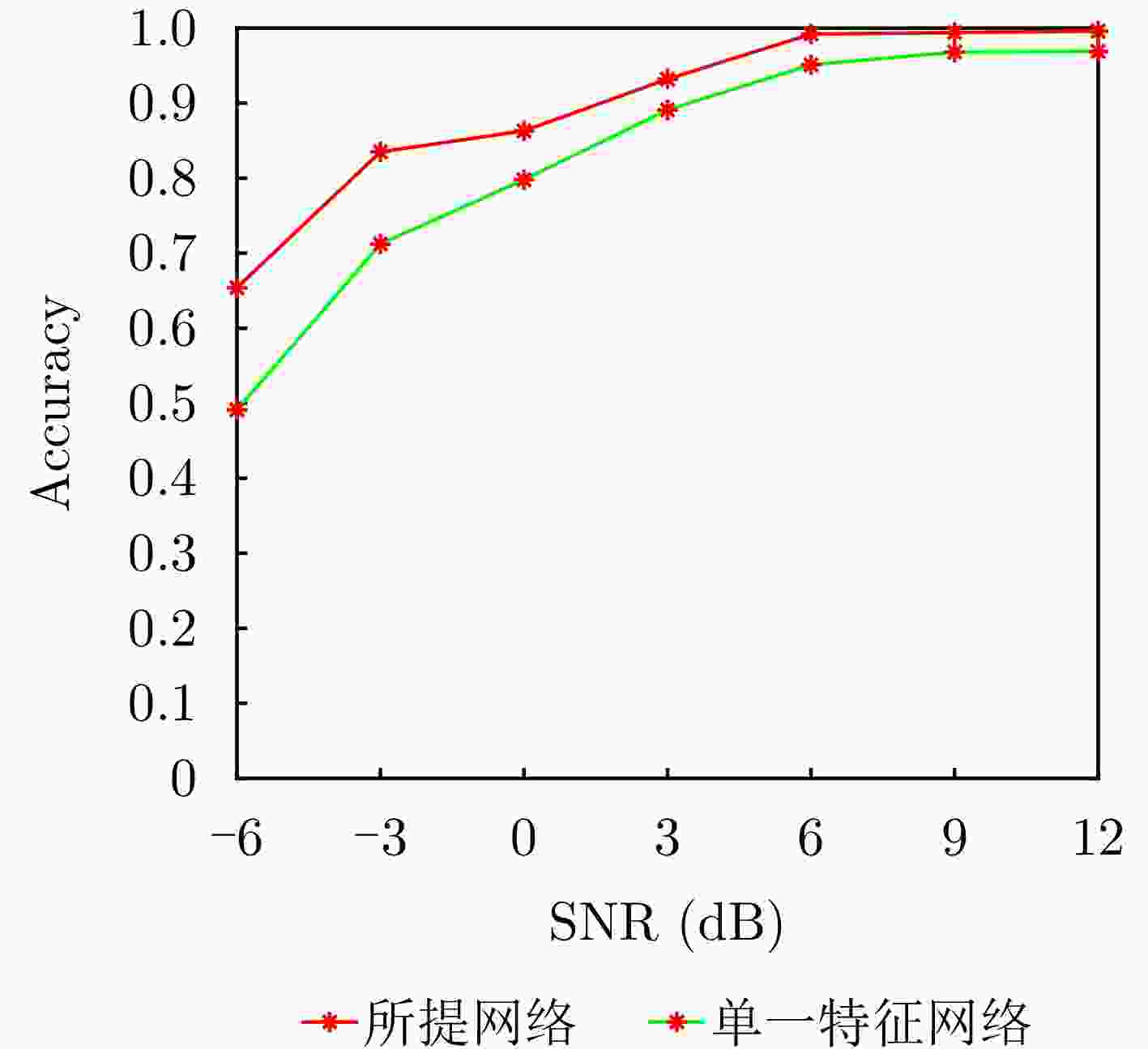
摘要: 该文针对飞鸟和无人机等低慢小目标精细化特征提取和分类问题,提出了一种多波段多角度特征融合分类方法。首先分别基于K波段和L波段调频连续波雷达从多个角度采集了5种类型旋翼无人机和飞鸟模型数据,构建低慢小探测数据集。其次,为了获取L波段目标信号的周期性振动特征,利用经验模态分解提取L波段信号中高频特征,抑制噪声影响;对K波段回波信号进行短时傅里叶变换,获得多角度高分辨微动特征。然后,设计了一种多波段多角度特征融合网络模型(MMFFNet),包含改进的卷积长短期记忆网络时序特征提取模块、注意力融合模块和多尺度特征融合模块,通过多波段多角度特征的融合提高了目标分类的准确率。通过实测数据集验证表明,与使用单一雷达特征分类方法相比,在高信噪比为5 dB和低信噪比为–3 dB条件下所提方法对7种类型的低慢小目标的正确分类准确率分别提高了3.1%和12.3%。Abstract: This study addresses the issue of fine-grained feature extraction and classification for Low-Slow-Small (LSS) targets, such as birds and drones, by proposing a multi-band multi-angle feature fusion classification method. First, data from five types of rotorcraft drones and bird models were collected at multiple angles using K-band and L-band frequency-modulated continuous-wave radars, forming a dataset for LSS target detection. Second, to capture the periodic vibration characteristics of the L-band target signals, empirical mode decomposition was applied to extract high-frequency features and reduce noise interference. For the K-band echo signals, short-time Fourier transform was applied to obtain high-resolution micro-Doppler features from various angles. Based on these features, a Multi-band Multi-angle Feature Fusion Network (MMFFNet) was designed, incorporating an improved convolutional long short-term memory network for temporal feature extraction, along with an attention fusion module and a multiscale feature fusion module. The proposed architecture improves target classification accuracy by integrating features from both bands and angles. Validation using a real-world dataset showed that compared with methods relying on single radar features, the proposed approach improved the classification accuracy for seven types of LSS targets by 3.1% under a high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of 5 dB and by 12.3% under a low SNR of −3 dB.
-
表 1 各类型无人机的数据参数
Table 1. Data parameters for each type of UAV
目标类型 尺寸大小(mm)
(长×宽×高)高度范围
(m)L波段
RCS (dBsm)K波段
RCS (dBsm)大疆M350 810×670×430 1~3 –23~–13 –13~–5 大疆悟2 605×588×315 1~3 –30~–23 –20~–13 大疆御2 322×242×84 1~3 –40~–30 –30~–20 六翼飞行器 800~ 1200 1~3 –13~–5 –5~3 仿真飞鸟 500~ 1500 1~2 <–40 <–30 表 2 L波段和K波段调频连续波雷达参数设置
Table 2. L-band and K-band FM continuous wave radar parameter settings
参数 K波段雷达 L波段雷达 工作频率(GHz) 23.7 0.145 Chirp重复周期(ms) 0.3 1.024 调制带宽(MHz) 100 100 采样频率(kHz) 500 500 表 3 低慢小目标采集参数设置
Table 3. Low-slow-small target acquisition parameter settings
无人机类型及编号 调制带宽(MHz) 角度(°) 调制周期(ms) 目标距离(m) 雷达波段(K/L) 大疆M350(01) 100 0 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 60 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 90 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 120 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 180 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 大疆悟2(02) 100 0 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 60 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 90 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 120 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 180 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 大疆御2(03) 100 0 0.300+1.024 6 K+L 60 0.300+1.024 6 K+L 90 0.300+1.024 6 K+L 120 0.300+1.024 6 K+L 180 0.300+1.024 6 K+L 六翼飞行器(04) 100 0 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 60 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 90 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 120 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 180 0.300+1.024 8 K+L 仿真飞鸟(05) 100 0 0.300+1.024 2 K+L 200 0 0.3 2 K AC311直升机(06) 100 0 0.300 32 L+K 500 0 4.096 30 K 1000 0 4.096 32 K 表 4 构建数据集的样本数
Table 4. The number of samples to build the dataset
无人机类型 训练集 验证集 测试集 大疆悟2 3506 328 316 固定翼 1126 96 73 大疆御2 1833 186 175 六翼飞行器 4820 462 428 大疆M350 3192 326 306 AC311直升机 1326 135 126 仿真飞鸟 1250 124 120 表 5 多波段多角度特征融合网络超参数
Table 5. Hyperparameters of multi-band multi-angle feature fusion network
参数 指标 优化器 AdamW 瞬时函数 Cross Entropy Loss 训练次数 100 Dropout 0.2 初始学习率 0.001 批处理大小 4 表 6 ConvLSTM改进前后对分类的影响
Table 6. Effect on classification before and after ConvLSTM improvement
特征提取结构 分类准确率(%) 所提方法(ConvLSTM) 98.2 所提方法(ConvLSTM+CBAM) 99.1 所提方法(CBAM) 98.6 所提方法(SEAttention) 97.6 表 7 在SNR=5 dB噪声下不同网络的性能比较
Table 7. Performance comparison of different networks at SNR=5 dB noise
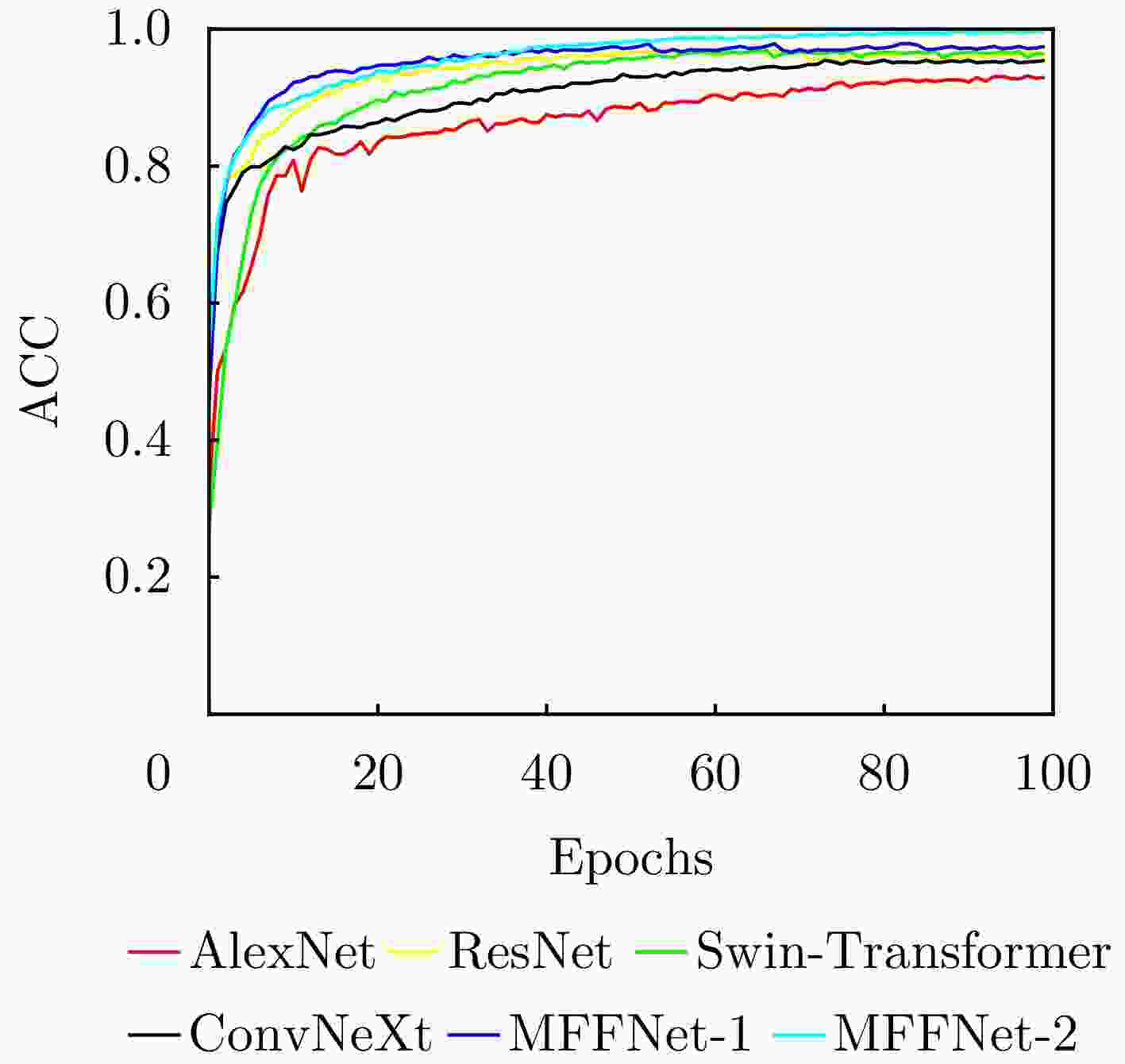
模型 数据集 ACC MAP MF1 KC FLOPs (G) AlexNet 数据集1 0.933 0.931 0.926 0.923 0.309 ResNet50 数据集1 0.946 0.943 0.937 0.929 4.132 Swin-transformer 数据集1 0.954 0.948 0.941 0.937 23.55 ConvNext 数据集1 0.943 0.938 0.933 0.931 15.354 所提网络_单角度 数据集1 0.956 0.953 0.948 0.942 30.129 MMFFNet 数据集1+数据集2 0.987 0.976 0.965 0.961 30.129 -
[1] AJAKWE S O, IHEKORONYE V U, KIM D S, et al. DRONET: Multi-tasking framework for real-time industrial facility aerial surveillance and safety[J]. Drones, 2022, 6(2): 46. doi: 10.3390/drones6020046. [2] 陈小龙, 南钊, 张海, 等. 飞鸟与旋翼无人机雷达微多普勒测量实验研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(5): 704–714. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020192.CHEN Xiaolong, NAN Zhao, ZHANG Hai, et al. Experimental research on radar micro-Doppler of flying bird and rotor UAV[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(5): 704–714. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020192. [3] 陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068.CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068. [4] YAN Jun, HU Huiping, GONG Jiangkun, et al. Exploring radar micro-Doppler signatures for recognition of drone types[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(4): 280. doi: 10.3390/drones7040280. [5] WU Jing, AI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Yuqing, et al. Micro-Doppler curve extraction based on reassociation Viterbi algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4295–4309. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3373719. [6] MA Xinyue, OH B S, SUN Lei, et al. EMD-based entropy features for micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification[C]. 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 2018: 1295–1300. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2018.8546180. [7] ZHAO Yichao and SU Yi. The extraction of micro-Doppler signal with EMD algorithm for radar-based small UAVs’ detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(3): 929–940. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2905751. [8] LI Ruoyu and HE D. Rotational machine health monitoring and fault detection using EMD-based acoustic emission feature quantification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(4): 990–1001. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2179819. [9] OH B S, GUO Xin, WAN Fangyuan, et al. An EMD-based micro-Doppler signature analysis for mini-UAV blade flash reconstruction[C]. 2017 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), London, UK, 2017. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICDSP.2017.8096105. [10] PATEL J S, FIORANELLI F, and ANDERSON D. Review of radar classification and RCS characterisation techniques for small UAVs or drones[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 911–919. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.0020. [11] LEONARDI M, LIGRESTI G, and PIRACCI E. Drones classification by the use of a multifunctional radar and micro-Doppler analysis[J]. Drones, 2022, 6(5): 124. doi: 10.3390/drones6050124. [12] CHEN Xu, MA Chunguang, ZHAO Chaofan, et al. UAV classification based on deep learning fusion of multidimensional UAV micro-Doppler image features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3503205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3371171. [13] KUMAWAT H C, CHAKRABORTY M, BAZIL RAJ A A, et al. DIAT-μSAT: Small aerial targets’ micro-Doppler signatures and their classification using CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 6004005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3102039. [14] WANG Chenxing, TIAN Jiangmin, CAO Jinwen, et al. Deep learning-based UAV detection in pulse-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3104907. [15] CHEN Tao, GAO Shuncheng, ZHENG Shilian, et al. EMD and VMD empowered deep learning for radio modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2023, 9(1): 43–57. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3218694. [16] ZHU Jianping, CHEN Haiquan, and YE Wenbin. A hybrid CNN-LSTM network for the classification of human activities based on micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24713–24720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971064. [17] SUN Yingxiang, ABEYWICKRAMA S, JAYASINGHE L, et al. Micro-Doppler signature-based detection, classification, and localization of small UAV with long short-term memory neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6285–6300. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3028654. [18] CHEN Xiaolong, ZHANG Hai, SONG Jie, et al. Micro-motion classification of flying bird and rotor drones via data augmentation and modified multi-scale CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1107. doi: 10.3309/rs14051107. [19] FU Rui, AL-ABSI M A, KIM K H, et al. Deep learning-based drone classification using radar cross section signatures at mmWave frequencies[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 161431–161444. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3115805. [20] MO Yongguang, HUANG Jianjun, and QIAN Gongbin. Deep learning approach to UAV detection and classification by using compressively sensed RF signal[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 3072. doi: 10.3390/s22083072. [21] CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. [22] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1.0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. [23] 陈小龙, 饶桂林, 关键, 等. 被动雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-PR-1.0)及多域特征提取和分析方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145.CHEN Xiaolong, RAO Guilin, GUAN Jian, et al. Passive radar low slow small detection dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) and multi-domain feature extraction and analysis methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145. [24] 章鹏飞, 李刚, 霍超颖, 等. 基于双雷达微动特征融合的无人机分类识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061.ZHANG Pengfei, LI Gang, HUO Chaoying, et al. Classification of drones based on micro-Doppler radar signatures using dual radar sensors[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061. doi: 10.12000/JR18061. [25] OH B S, GUO Xin, WAN Fangyuan, et al. Micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification using empirical-mode decomposition features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 227–231. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2781711. [26] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [27] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [28] DAI Yimian, GIESEKE F, OEHMCKE S, et al. Attentional feature fusion[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 3559–3568. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00360. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: