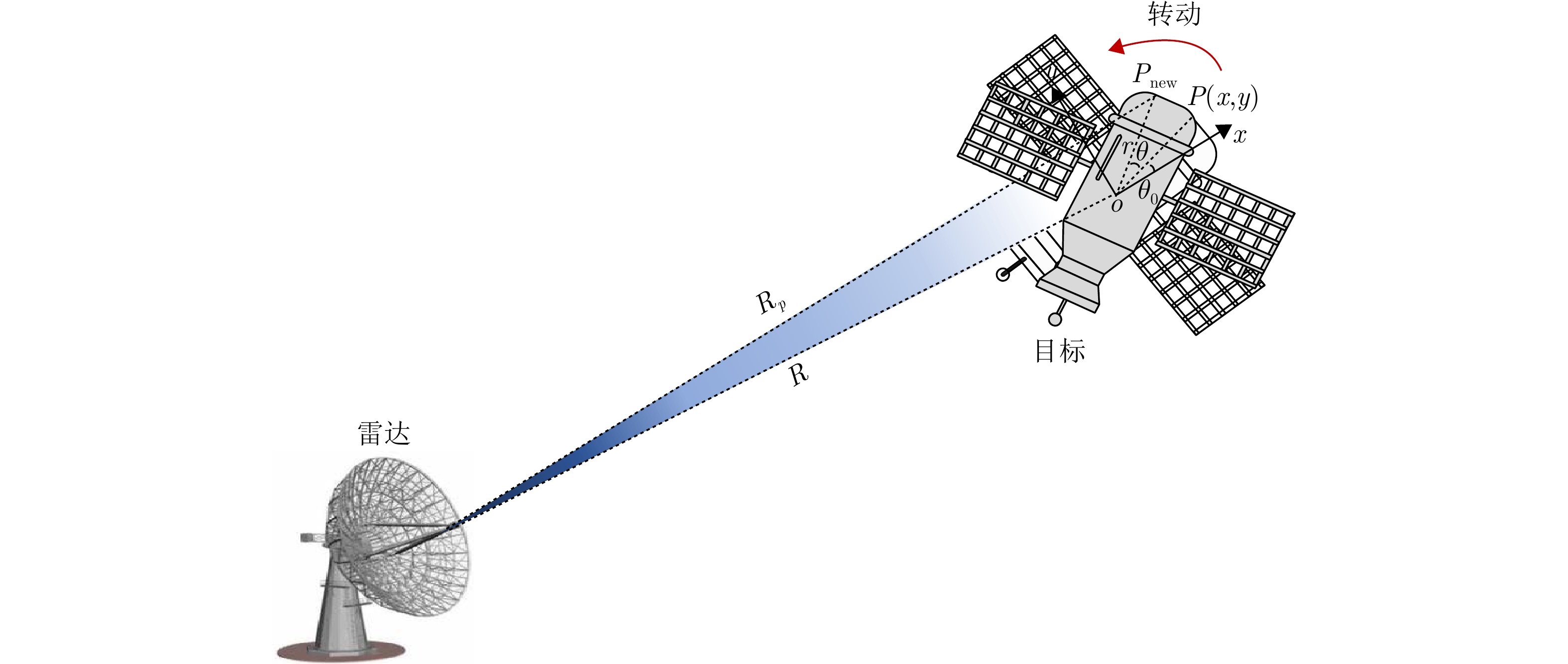
A ISAR Imaging Method for Space Targets Based on Fast Estimation of Joint Motion Parameters
-
摘要: 逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)是空间目标成像和监测的重要手段之一,大转角下空间目标成像结果的越分辨单元徙动(MTRC)现象加剧,严重影响ISAR成像的性能。为快速估计和补偿空间目标运动产生的回波相位误差,结合BFGS优化算法效率高与极坐标格式变换算法(PFA)补偿精度高的优势,该文提出了一种基于联合运动参数快速估计的空间目标ISAR成像方法。所提方法建立了目标平动和转动参数联合估计的最小化图像熵优化模型;为降低优化陷入局部最优的可能,设计了目标参数粗估计和精估计的高效BFGS求解子步骤,实现了目标转动参数的快速估计与大转角情况下MTRC的补偿。点目标仿真和实测民航客机数据成像结果表明,相比PSO-PFA算法,所提方法在低信噪比条件下的运动参数估计精度更高,运算时间缩短为原来的五分之一,具有显著优势。Abstract: Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) is an important tool for imaging and monitoring space targets. The large rotation angle of space targets can exacerbate the phenomenon of Migration Through Resolution Cells (MTRC), seriously affecting the ISAR imaging performance. For the fast estimation and compensation of echo phase errors caused by the motion of space targets, this paper proposes an ISAR space-target imaging method based on the rapid estimation of joint motion parameters. This method combines the advantages of the high efficiency of the Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS) optimization algorithm and the high compensation accuracy of the Polar Format Algorithm (PFA) algorithm. The proposed method formulates an image entropy minimization model considering the joint estimation of the translation and rotation parameters of the target. To reduce the possibility of optimization falling into local optima, the proposed method solves sub-steps, which comprise rough and fine estimations of the target motion parameters, using the BFGS optimization algorithm. The proposed method rapidly estimates target rotation parameters and performs quick MTRC compensation under large rotation angles. The simulation of point targets and imaging results of actual civil aircraft data show that compared with the Particle Swarm Optimization-Polar Format Algorithm (PSO-PFA) algorithm, the proposed method estimates motion parameters with a higher accuracy under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Further, the computational efficiency is improved by more than five times, which is significantly advantageous.
-
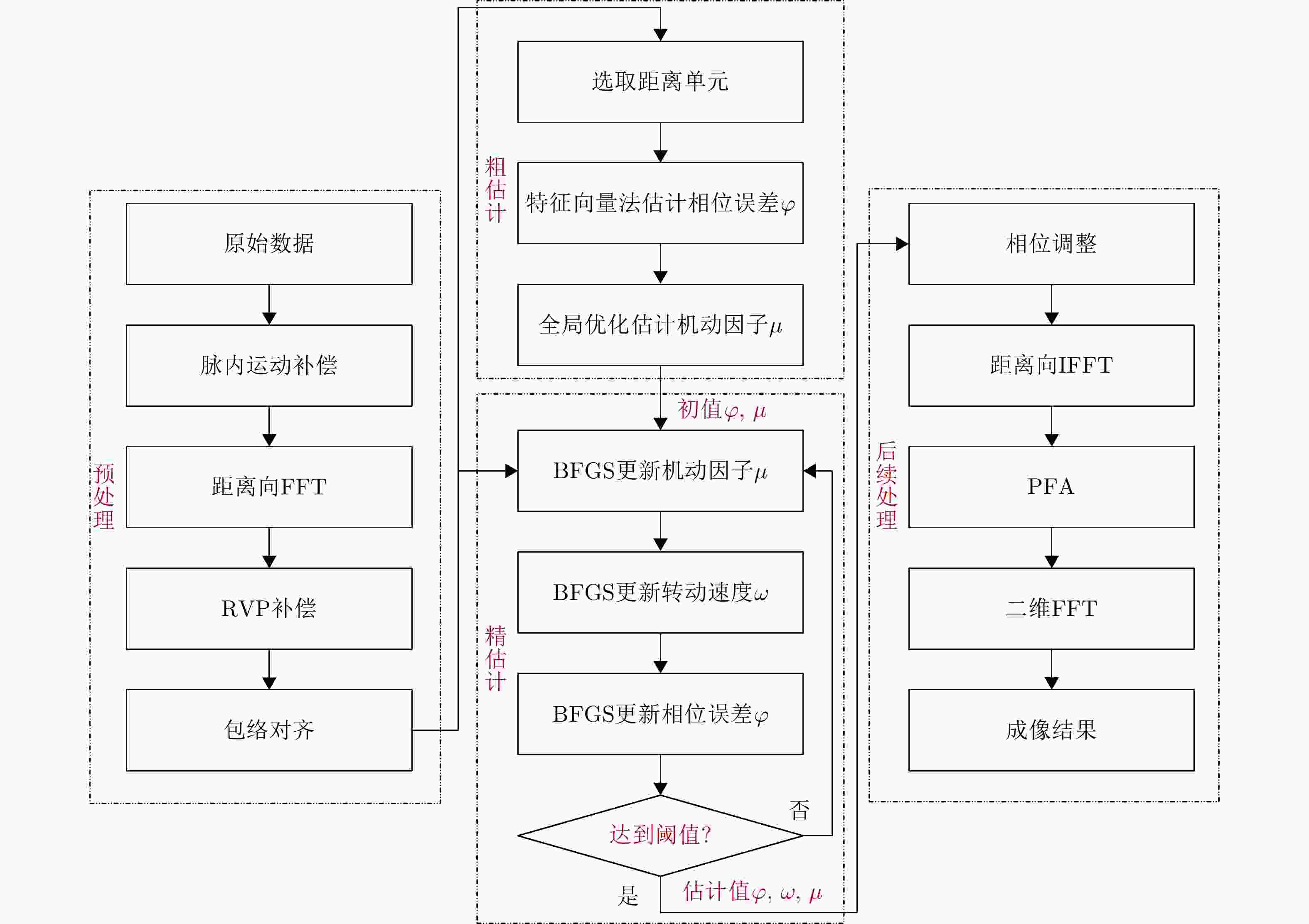
1 BFGS算法伪代码
1. Pseudocode for the BFGS algorithm.
输入:待估计值$ {k_i} $,目标函数$ {H_z}{(}{k_i}{)} $ 初始化:粗估计值$ {k^0_i} $,黑塞矩阵$ {H^0}{ = }{\bf{I}} $,步长$ {\alpha ^j} $,迭代次数$ j = 0 $。 开始迭代: 1. 更新变量: $ k_i^{j + 1}{ = }k_i^j - {\alpha ^j}{H^j}\dfrac{{\partial {H_z}}}{{\partial k_i^j}} $ (33) $ {x^j}{ = }k_i^{j + 1}{ - }k_i^j $ (34) $ {y^j}{ = }\dfrac{{\partial {H_z}}}{{\partial k_i^{j + 1}}}{ - }\dfrac{{\partial {H_z}}}{{\partial k_i^j}} $ (35) 2. 更新黑塞矩阵: $ {\rho ^j}{ = }\dfrac{1}{{{{{(}{x^j}{)}}^{\mathrm{T}}}{y^j}}} $ (36) $ {H^{j + 1}}{ = [}{\bf{I}}{ - }{\rho ^j}{y^j}{{(}{x^j}{)}^{\mathrm{T}}}{{]}^{\mathrm{T}}}{H^j}{[}{\bf{I}}{ - }{\rho ^j}{y^j}{{(}{x^j}{)}^{\mathrm{T}}}{] + }{\rho ^j}{x^j}{{(}{x^j}{)}^{\mathrm{T}}} $ (37) $ j{ = }j{ + }1 $ (38) 3. 判断是否达到阈值 输出:完成迭代后,输出估计值 表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1. Simulation parameter table
仿真参数 数值 中心频率 20 GHz 脉冲宽度 200 μs 带宽 4 GHz 脉冲重复频率 100 Hz 去斜后距离向采样率 20 MHz 表 2 不同信噪比下各算法运算时间和转动参数估计质量比较
Table 2. Comparison of algorithm calculation time and rotation parameter estimation quality under different SNR
信噪比(dB) 算法 运算时间(s) 转动速度
(rad/s)转动速度估计误差
(rad/s)转动加速度
(rad/s2)转动加速度
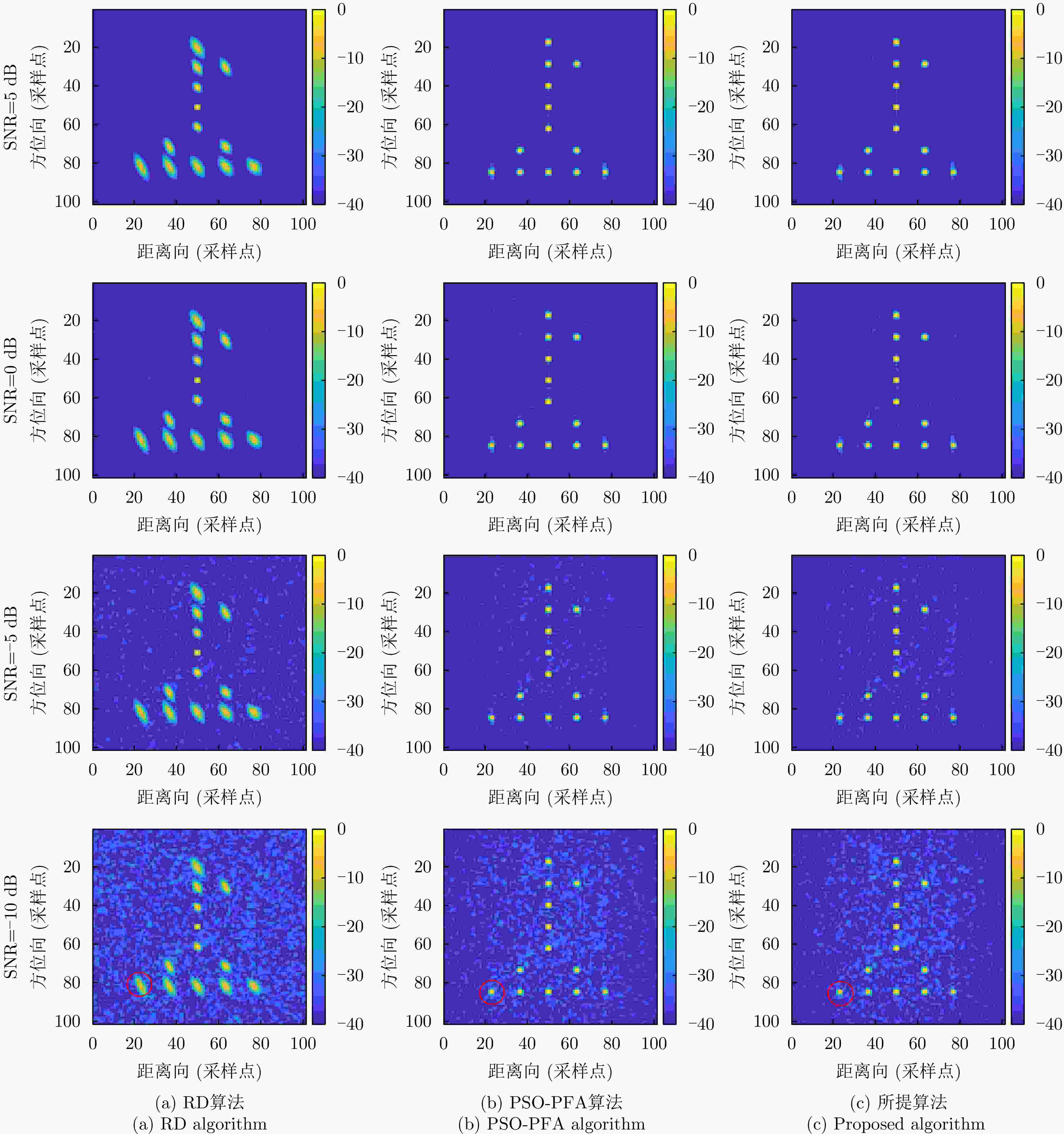
估计误差(rad/s2)理论值 0.0800 0.0100 5 PSO-PFA算法 48.09 0.0779 0.0021 0.0096 0.0004 所提算法 10.40 0.0784 0.0016 0.0094 0.0006 0 PSO-PFA算法 49.85 0.0750 0.0050 0.0095 0.0005 所提算法 10.88 0.0780 0.0020 0.0093 0.0007 –5 PSO-PFA算法 59.64 0.0696 0.0104 0.0082 0.0018 所提算法 11.01 0.0771 0.0029 0.0092 0.0008 –10 PSO-PFA算法 32.75 0.0714 0.0086 0.0083 0.0017 所提算法 12.25 0.0781 0.0019 0.0093 0.0007 表 3 点目标成像结果性能对比
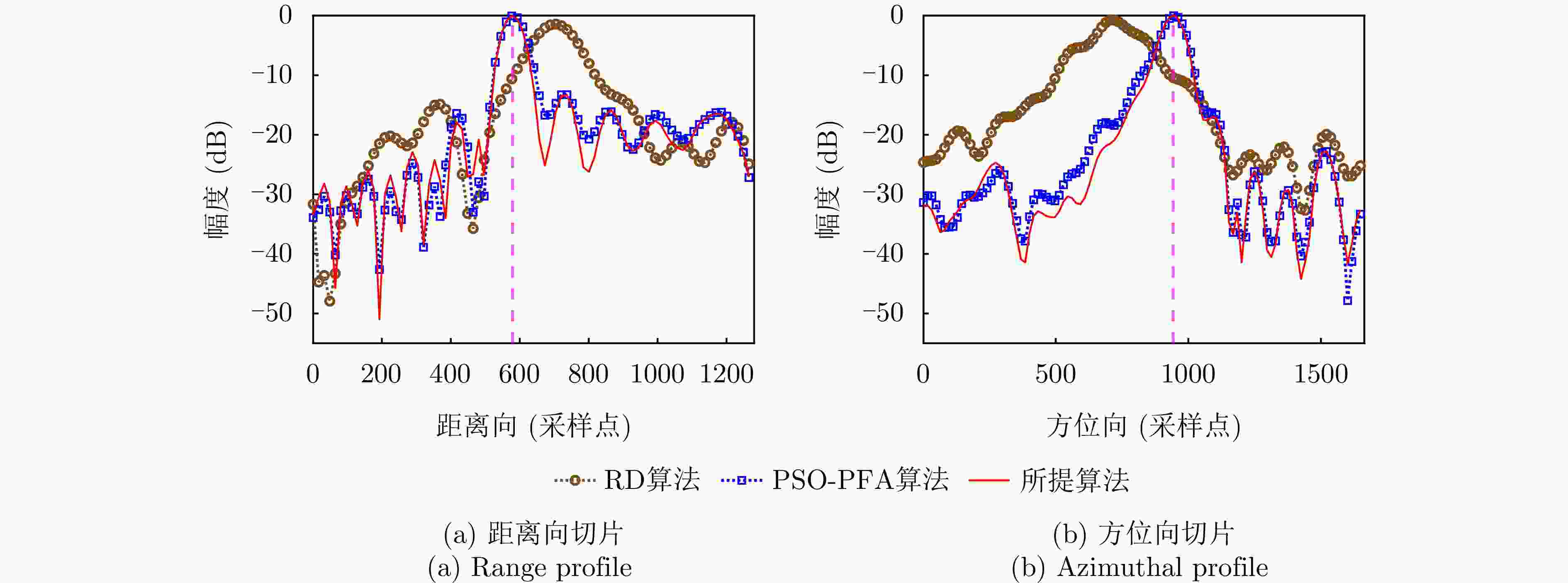
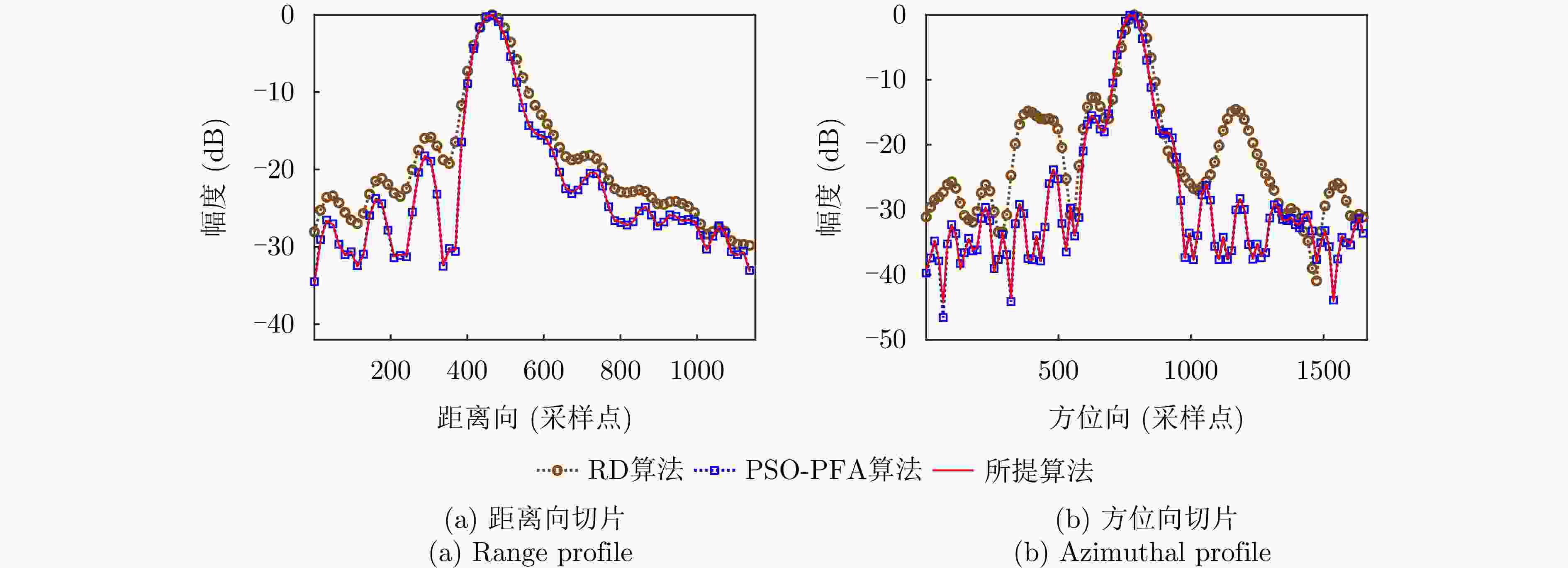
Table 3. Comparison of imaging results in point
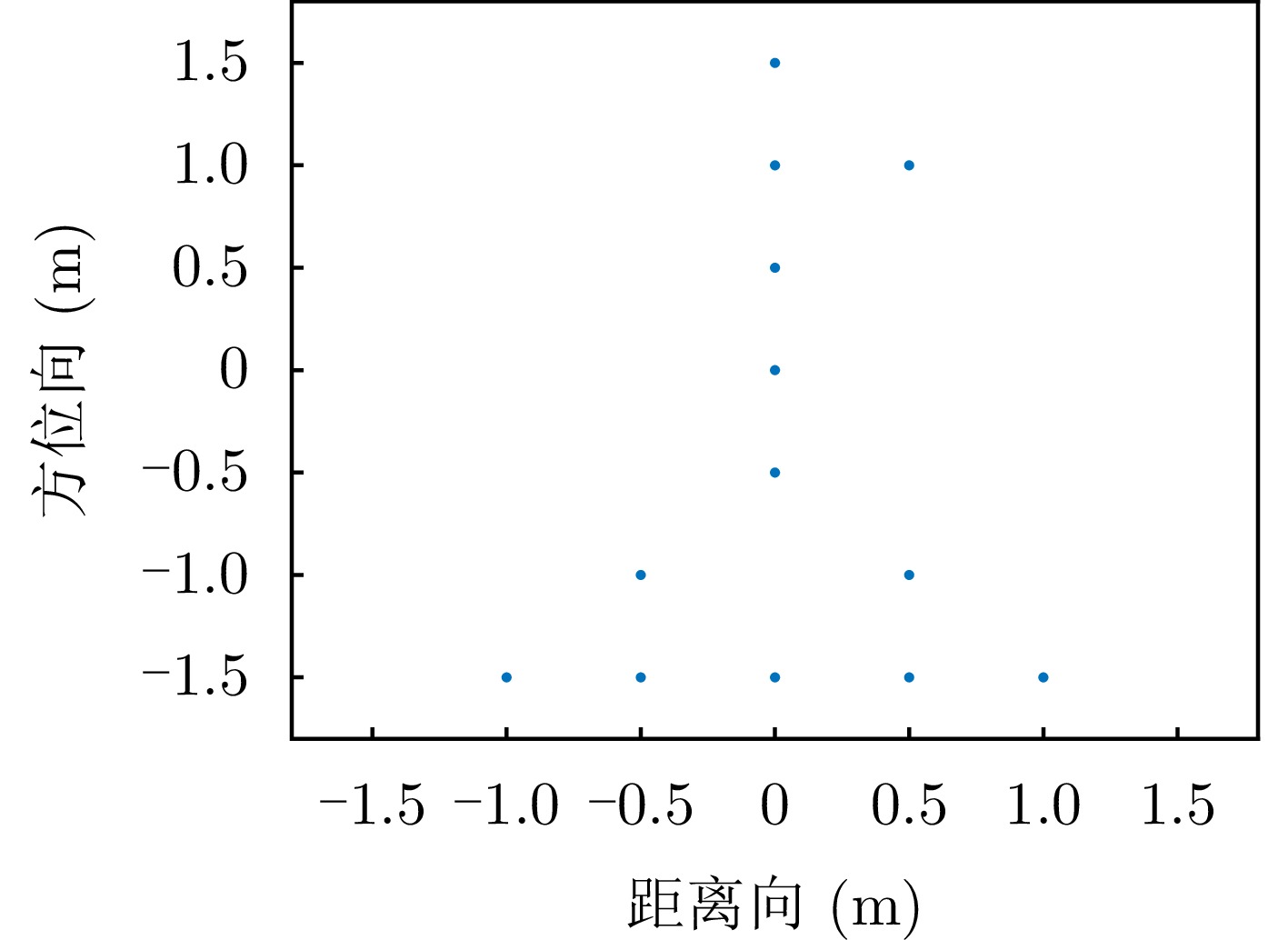
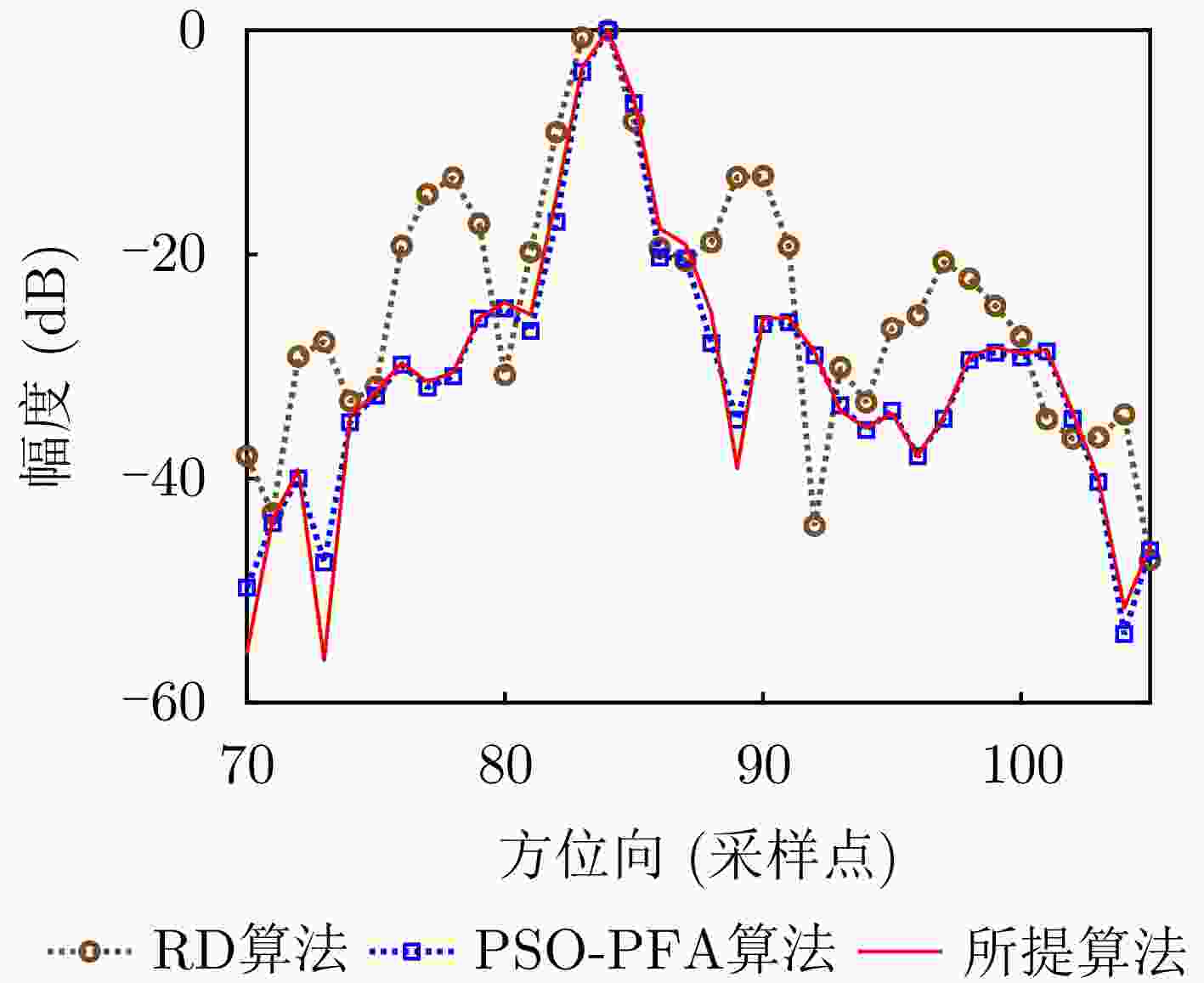
方向 算法 ISLR (dB) PSLR (dB) IRW(采样点) 距离向 RD算法 – 12.6383 – 13.3929 2.0172 PSO-PFA算法 – 7.9669 – 13.0756 1.0804 所提算法 – 8.3111 – 13.1223 1.0031 方位向 RD算法 – 16.0624 – 16.2671 2.9232 PSO-PFA算法 – 14.5834 – 16.2696 1.4372 所提算法 – 16.4953 – 16.9167 1.3865 表 4 实测实验参数表
Table 4. Experimental parameter table
参数 数值 中心频率 14.6 GHz 脉冲宽度 500 μs 带宽 600 MHz 脉冲重复频率 2000 Hz 去斜后距离向采样率 25 MHz 表 5 实测数据成像结果指标
Table 5. Indicators for imaging results based on actual measurement data
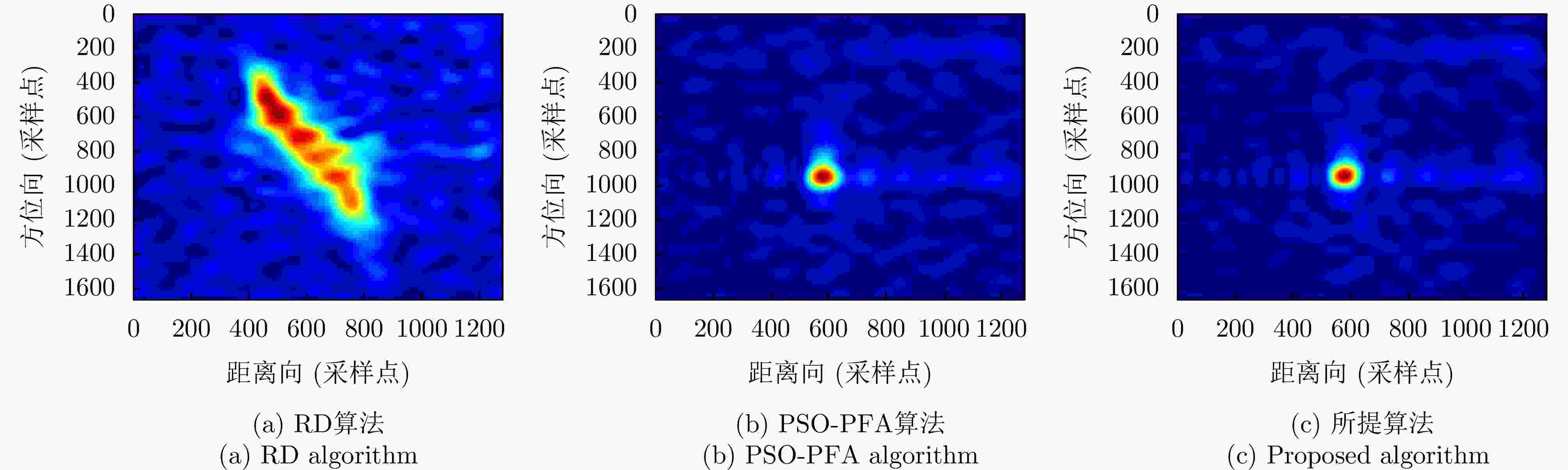
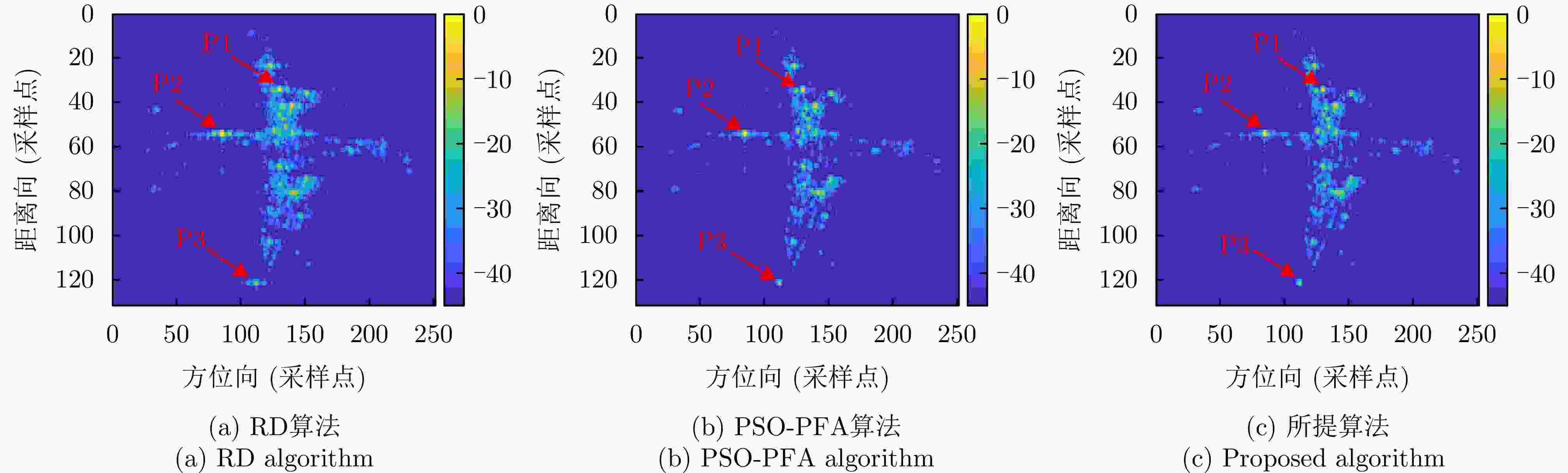
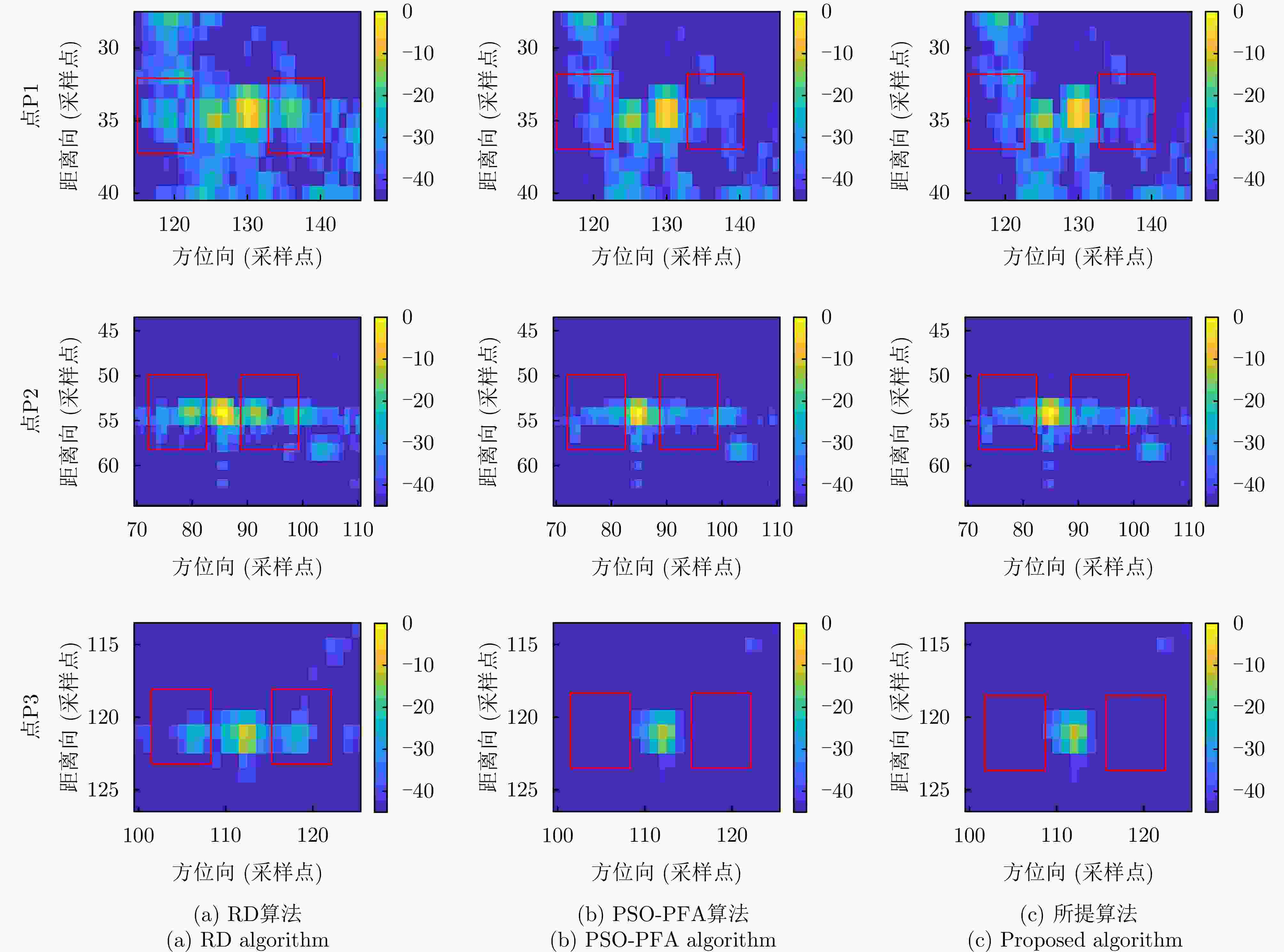
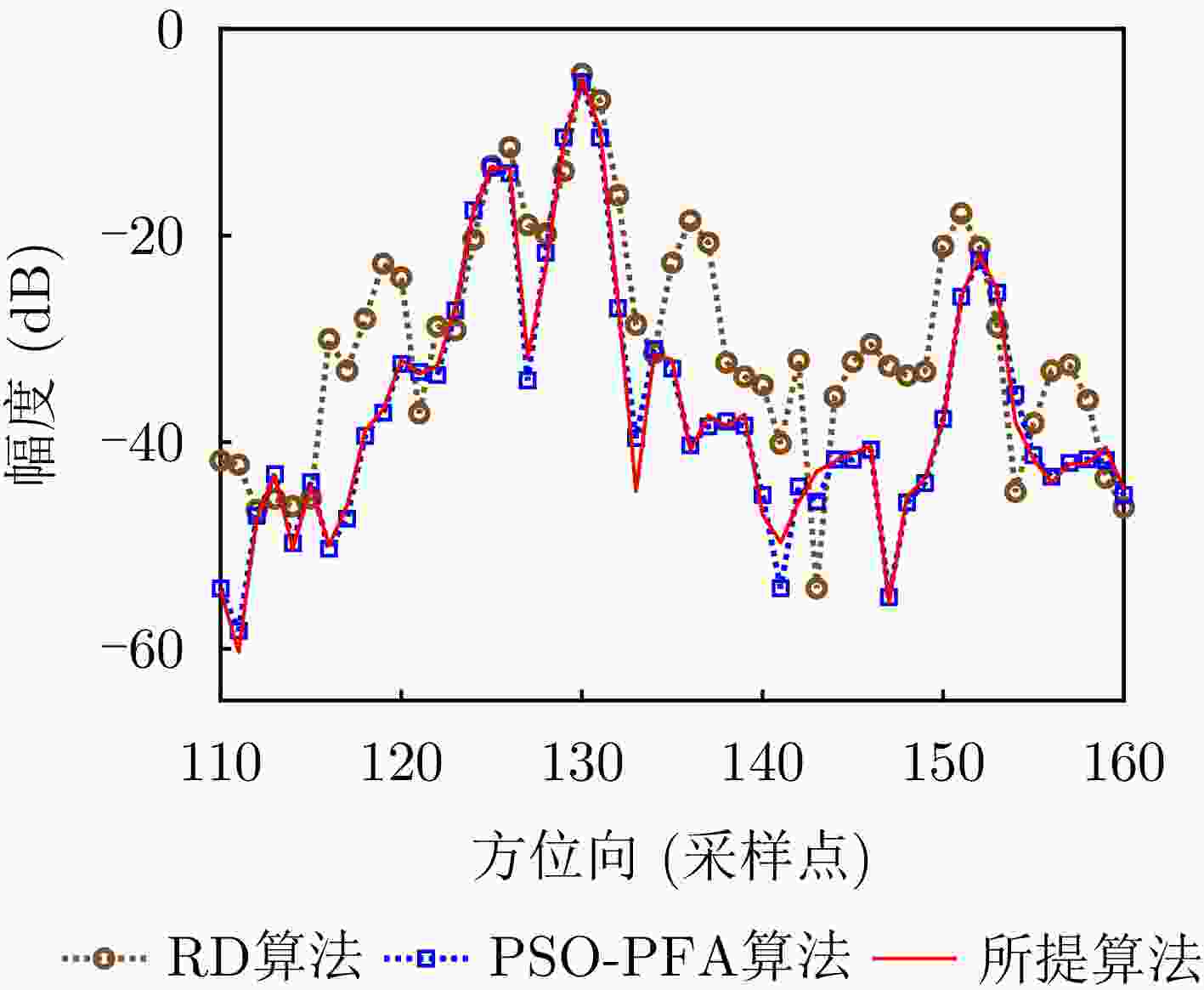
算法 运算时间(s) 图像熵 图像对比度 RD算法 5.5604 22.3463 PSO-PFA算法 296.38 5.1896 26.7782 所提算法 41.11 5.1950 26.1366 表 6 点P3成像指标
Table 6. Comparison of imaging results in point P3
方向 算法 ISLR (dB) PSLR (dB) IRW(采样点) 距离向 RD算法 – 12.5781 – 15.7136 1.3516 PSO-PFA算法 – 15.1908 – 18.1396 1.1771 所提算法 – 15.1643 – 18.1401 1.1788 方位向 RD算法 – 8.2897 – 12.5406 1.2609 PSO-PFA算法 – 14.1262 – 15.5056 1.1882 所提算法 – 14.1223 – 15.4902 1.1891 -
[1] ANGER S, JIROUSEK M, DILL S, et al. High-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of satellites in space[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2024, 18(4): 544–563. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12505. [2] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 6–70.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 6–70. [3] ANGER S, JIROUSEK M, Dill S, et al. Research on advanced space surveillance using the IoSiS radar system[C]. The 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Online, Germany, 2021: 1–4. [4] 田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060.TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. Review of high-resolution imaging techniques of wideband inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. [5] 田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 1–18.TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. High-resolution Imaging Techniques of Wideband Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022: 1–18. [6] 夏靖远, 杨志雄, 周治兴, 等. 一种基于元学习的稀疏孔径ISAR成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121.XIA Jingyuan, YANG Zhixiong, ZHOU Zhixing, et al. A metalearning-based sparse aperture ISAR imaging method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121. [7] 李中余, 桂亮, 海宇, 等. 基于变分模态分解与优选的超高分辨ISAR成像微多普勒抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043.LI Zhongyu, GUI Liang, HAI Yu, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution ISAR micro-Doppler suppression methodology based on variational mode decomposition and mode optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043. [8] XING Mengdao, WU Renbiao, LAN Jinqiao, et al. Migration through resolution cell compensation in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(2): 141–144. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.824766. [9] KARAMANAVIS V, DIRKS H, FUHRMANN L, et al. Characterization of deorbiting satellites and space debris with radar[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(8): 3269–3281. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.07.033. [10] PERRY R P, DIPIETRO R C, and FANTE R L. SAR imaging of moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(1): 188–200. doi: 10.1109/7.745691. [11] LIPPS R and KERR D. Polar reformatting for ISAR imaging[C]. 1998 IEEE Radar Conference, RADARCON’98 Challenges in Radar Systems and Solutions, Dallas, USA, 1998: 275–280. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1998.678014. [12] HUANG Penghui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Ground maneuvering target imaging and high-order motion parameter estimation based on second-order keystone and generalized hough-HAF Transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 320–335. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606436. [13] LI Xiaolong, CUI Guolong, YI Wei, et al. Range migration correction for maneuvering target based on generalized keystone transform[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 95–99. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130977. [14] 杨利超, 高悦欣, 邢孟道, 等. 基于广义keystone和频率变标的微波光子ISAR高分辨实时成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 215–223. doi: 10.12000/JR18120.YANG Lichao, GAO Yuexin, XING Mengdao, et al. High resolution microwave photonics radar real-time imaging based on generalized keystone and frequency scaling[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 215–223. doi: 10.12000/JR18120. [15] 卢光跃, 保铮. ISAR成像中散射点越分辨单元走动校正算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1999, 26(4): 487–492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.1999.04.022.LU Guangyue and BAO Zheng. Analysis of the MTRC compensation algorithm in ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1999, 26(4): 487–492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.1999.04.022. [16] GONG Rui, WANG Ling, and ZHU Daiyin. Three-dimensional high-resolution space-borne ISAR imaging with compact antenna configuration for large rotational angle[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 7422–7435. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3379584. [17] 吴熙芃. W波段雷达高分辨ISAR目标的运动补偿[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021: 43–57. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001254.WU Xipeng. Motion compensation for W-band radar’s high-resolution ISAR targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021: 43–57. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001254. [18] 杜荣震. 基于多视角ISAR图像的空间目标在轨状态反演方法[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2022: 27–44. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003472.DU Rongzhen. On-orbit state estimation methods of space targets utilizing multi-view ISAR images[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2022: 27–44. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003472. [19] LIU Yifei, YU Weidong, YANG Shenghui, et al. An effective space-borne ISAR high-resolution imaging approach for satellite on-orbit based on minimum entropy optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 4523–4537. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3359264. [20] SHAO Shuai, LIU Hongwei, ZHANG Lei, et al. Ultrawideband ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets with joint high-order motion compensation and azimuth scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5214621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3113007. [21] WANG Jiadong, LI Yachao, SONG Ming, et al. Noise robust high-speed motion compensation for ISAR imaging based on parametric minimum entropy optimization[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2178. doi: 10.3390/rs14092178. [22] ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, TAO Qingnian, et al. ISAR range alignment by minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631897. [23] ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562. [24] WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752. [25] LI Xi, LIU Guosui, and NI Jinlin. Autofocusing of ISAR images based on entropy minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(4): 1240–1252. doi: 10.1109/7.805442. [26] 王盛利, 李士国, 倪晋麟, 等. 一种新的变换—匹配傅里叶变换[J]. 电子学报, 2001, 29(3): 403–405. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.03.030.WANG Shengli, LI Shiguo, NI Jinlin, et al. A new transform—match fourier transform[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 29(3): 403–405. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.03.030. [27] LI Yuanyuan, FU Yaowen, and ZHANG Wenpeng. Distributed ISAR subimage fusion of nonuniform rotating target based on matching fourier transform[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(6): 1806. doi: 10.3390/s18061806. [28] RONG Jiajia, WANG Yong, and HAN Tao. Iterative optimization-based ISAR imaging with sparse aperture and its application in interferometric ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(19): 8681–8693. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2019.2923447. [29] CHEN Chen, XU Zhiyong, and TIAN Sirui. An efficient sparse aperture ISAR imaging framework for maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2024, 72(2): 1873–1886. doi: 10.1109/tap.2023.3344877. [30] XU Gang, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. High-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging and scaling with sparse aperture[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 4010–4027. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2439266. [31] 刘浩洋, 户将, 李勇锋, 等. 最优化: 建模、算法与理论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2020: 254–262.LIU Haoyang, HU Jiang, LI Yongfeng, et al. Optimization: Modeling, Algorithm and Theory[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2020: 254–262. [32] LI Ruoming, LI Wangzhe, DING Manlai, et al. Demonstration of a microwave photonic synthetic aperture radar based on photonic-assisted signal generation and stretch processing[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(13): 14334–14340. doi: 10.1364/oe.25.014334. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: