Weak Labeling-specific Emitter Identification Algorithm Based on the Weakly Supervised Wav-KAN Network
-
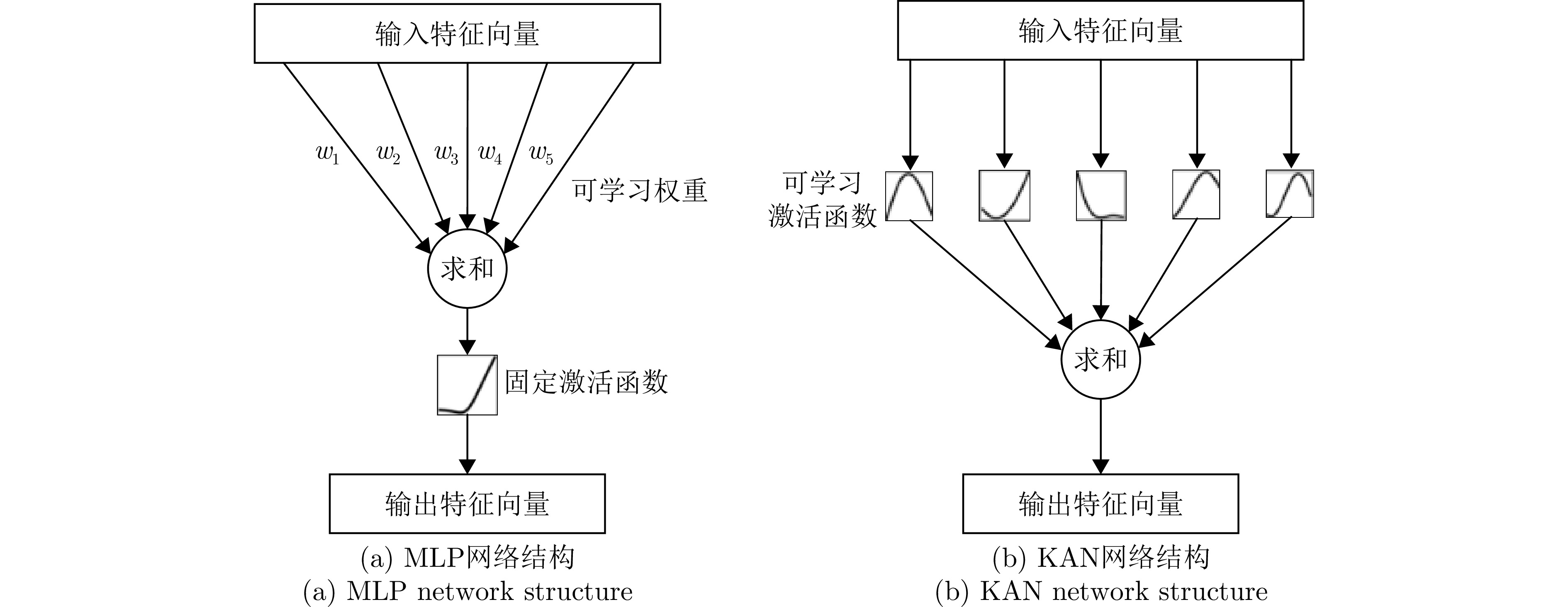
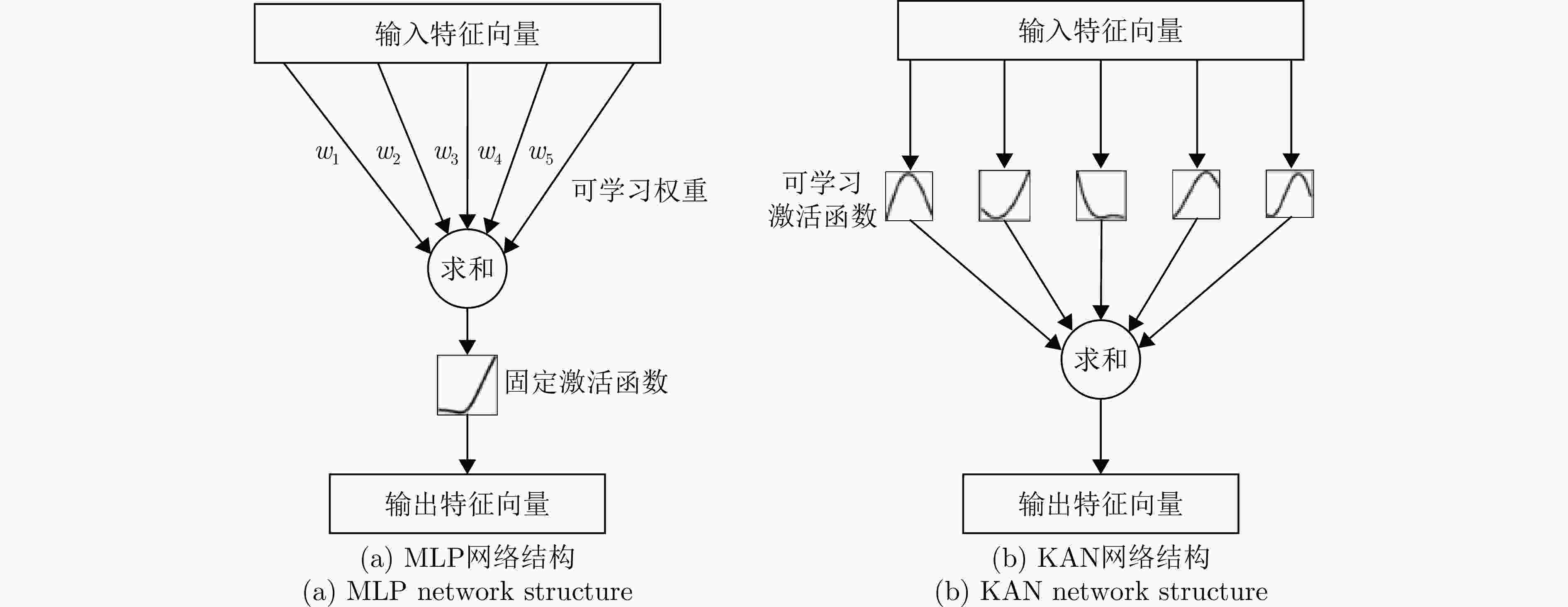
摘要: 当前辐射源个体识别技术多数基于有监督学习条件下开展,不适应由于采集环境(天气条件、地形和障碍物、干扰源)、器件性能(雷达分辨率、信号处理能力、硬件故障)、标注者水平等因素导致的大范围标签缺失的情形。该文提出了一种基于弱监督小波KAN (WSW-KAN)网络的弱标注辐射源识别算法。该算法首先结合KAN网络独有的边缘函数可学习特性和小波函数的多分辨率分析特性,构建WSW-KAN基线网络;然后将弱标注数据集拆分为小样本有标注数据集和大样本无标注数据集,利用小样本有标注数据集初步训练模型;最后在预训练模型基础上,基于自适应感知伪标签加权选择方法(APLWS),采用对比学习方法提取无标签数据特征并迭代训练,从而有效提高模型的泛化能力。基于真实采集雷达数据集验证,该文所提出的算法对特定辐射源个体识别精度达到95%左右,且算法效率高、参数规模小、适应能力强,能够满足实际场景的需求。Abstract: Most existing specific emitter identification technologies rely on supervised learning, making them unsuitable for scenarios with label loss due to factors such as the acquisition environment (e.g., weather conditions, terrain, obstacles, and interference sources), device performance (e.g., radar resolution, signal processing capabilities, and hardware failures), and tagger level. In this study, a weakly labeled specific emitter identification algorithm based on the Weakly Supervised Wav-KAN (WSW-KAN) network is proposed. First, a WSW-KAN baseline network is constructed by integrating the unique learnable edge function of the KAN network with the multiresolution analysis of the wavelet function. The weakly labeled dataset is then divided into a small labeled dataset and a large unlabeled dataset, with the small labeled dataset used for initial model training. Finally, based on the pretrained model, Adaptive Pseudo-Label Weighted Selection (APLWS) is used to extract features from the unlabeled data using a contrast learning method, followed by iterative training, thereby effectively improving the generalization capability of the model. Experimental validation using a real acquisition radar dataset demonstrates that the proposed algorithm achieves a recognition accuracy of approximately 95% for specific emitters while maintaining high efficiency, a small parameter scale, and strong adaptability, making it suitable for practical applications.
-
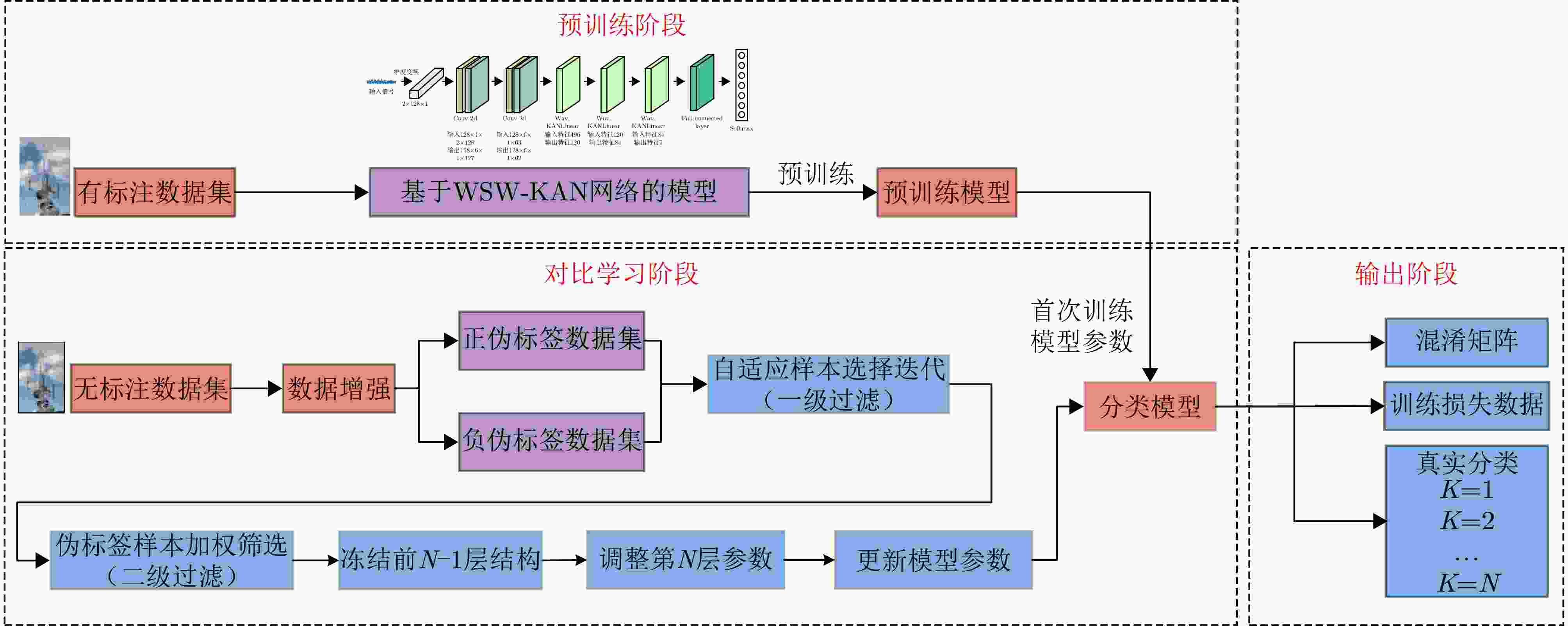
1 对比学习阶段自适应感知伪标签加权选择算法
1. Adaptive sensing pseudo label weighted selection algorithm in contrastive learning phase
1. 针对对比学习阶段数据流$ {D_{{\mathrm{U,unlabeled}}}} = \{ ({x^{(i)}})\} _{i = 1}^{{N_{{\mathrm{U,unlabeled}}}}} $
利用自适应感知伪标签加权选择算法调整代价函数。2. for $j = 1,2, \cdots ,50$ do 迭代条件 3. 对于每一类样本$ {x_t} $,计算特征空间中的成对余弦距离; 4. 构造相似样本对$ {N_t} $; 5. 计算样本类$ {x_t} $的后验概率${\hat p_t}$; 6. 更新样本临时伪标签$ {\hat y_t} $; 7. 计算置信度分数$ {q_t} $,并对置信度分数排序,依据所设定的
阈值比例过滤伪标签;8. 根据置信度分数$ {q_t} $计算动态权重$ {w^i} $; 9. 计算损失${l^i}$,并调整网络的代价函数; 10. end 表 1 雷达型号参数
Table 1. Radar type parameters
技术指标 参数值 工作频段 X 工作频段范围(GHz) 9.3~9.5 量程(nm) 0.0625 ~96.0000扫描带宽(MHz) 25 距离分辨率(m) 6 脉冲重复频率 1.6 K, 3.0 K, 5.0 K和10.0 K 发射峰值功率(W) 50 天线转速(r/min) 2, 12, 24, 48 天线长度(m) 1.8 天线工作模式 凝视、圆周扫描 天线极化方式 HH 天线水平波束宽度(°) 1.2 天线垂直波束宽度(°) 22 表 2 预训练阶段和对比学习阶段数据情况(表中为接收到的辐射源脉冲数量)
Table 2. Data of pre-training stage and comparative learning stage (the number of emitter pulses received is shown in the table)
类型 预训练阶段 对比学习阶段 辐射源A 5000 100000 辐射源B 4500 96890 辐射源C 4987 95678 辐射源D 4321 98978 辐射源E 3907 98765 辐射源F 4678 90780 辐射源G 4187 96789 表 3 不同网络参数设置情况
Table 3. Different network parameter settings
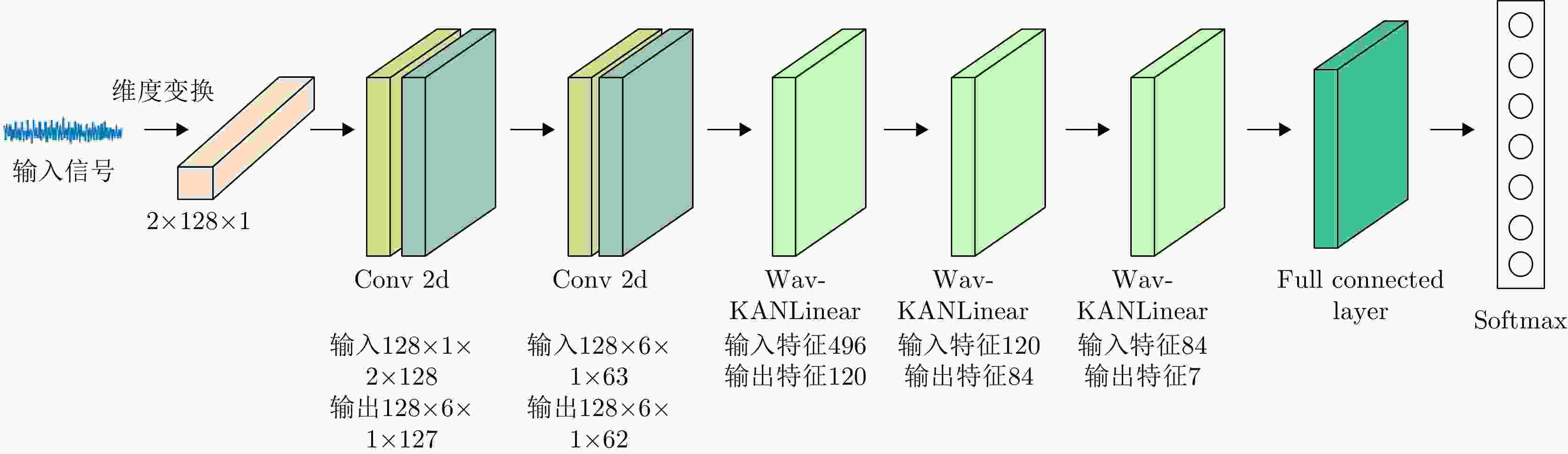
类别 网络层数 网络层类型 网络层设置 残差块 激活函数 批归一化 叠加层 小波变换 具体参数 Wav-KAN 5 Wav-KANLinear层、
叠加层小波变换、一维卷积核、
叠加函数无 ReLU 有 有 有 小波基选择(DOG),一维卷积核,滤波器数量64 KAN 5 KANLinear层、
叠加层一维卷积核、叠加
函数无 ReLU 有 有 无 一维卷积核,滤波器数量64 CNN-13 13 卷积层、池化层、
全连接层卷积核、激活函数 无 ReLU 有 无 无 3$ \times $3卷积核,滤波器64,步幅1 Wideresnet 15 卷积层、残差连接 残差块、宽卷积核、
激活函数有 ReLU 有 无 无 16-4 (16基本通道数,
宽度乘数4)表 4 预训练阶段不同识别网络识别性能
Table 4. Identification performance of different identification networks in pre-training stage
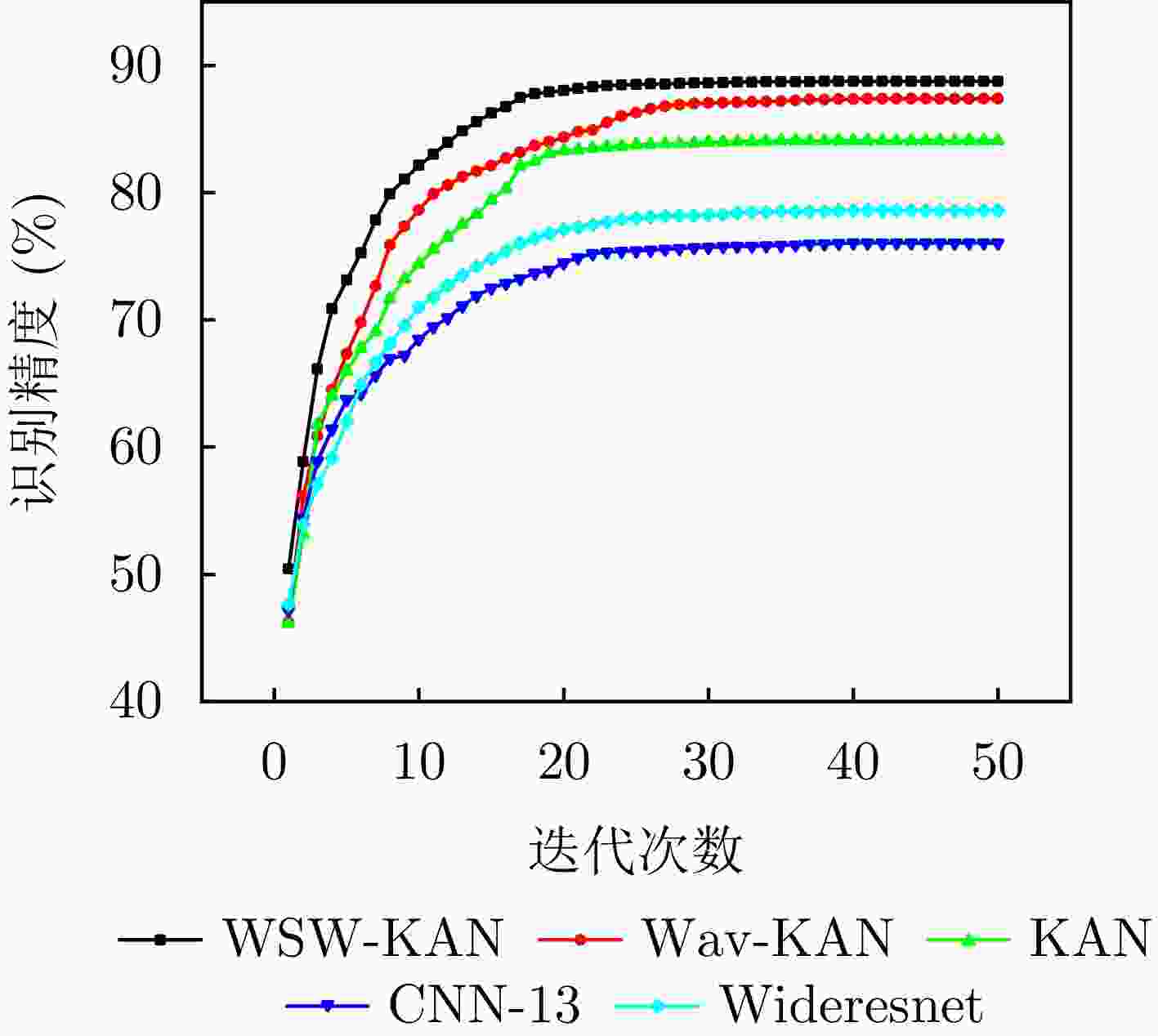
迭代次数 WSW-KAN (%) Wav-KAN (%) KAN (%) CNN-13 (%) Wideresnet (%) 1 50.44 46.23 46.14 47.16 47.62 2 58.87 56.11 53.14 54.37 53.88 3 66.14 60.87 61.77 58.89 57.10 4 70.88 64.50 63.99 61.41 59.14 5 73.11 67.34 65.98 63.76 62.02 6 75.27 69.78 67.77 64.18 64.89 7 77.84 72.66 69.08 65.66 66.67 8 79.91 75.90 71.67 66.94 68.11 9 81.07 77.36 73.20 67.20 69.56 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 46 88.74 87.36 84.09 76.05 78.60 47 88.74 87.36 84.09 76.05 78.60 48 88.75 87.36 84.09 76.05 78.60 49 88.75 87.36 84.09 76.05 78.60 50 88.75 87.36 84.09 76.05 78.60 表 5 对比学习阶段不同识别网络识别性能
Table 5. Identification performance of different identification networks in contrastive learning stage
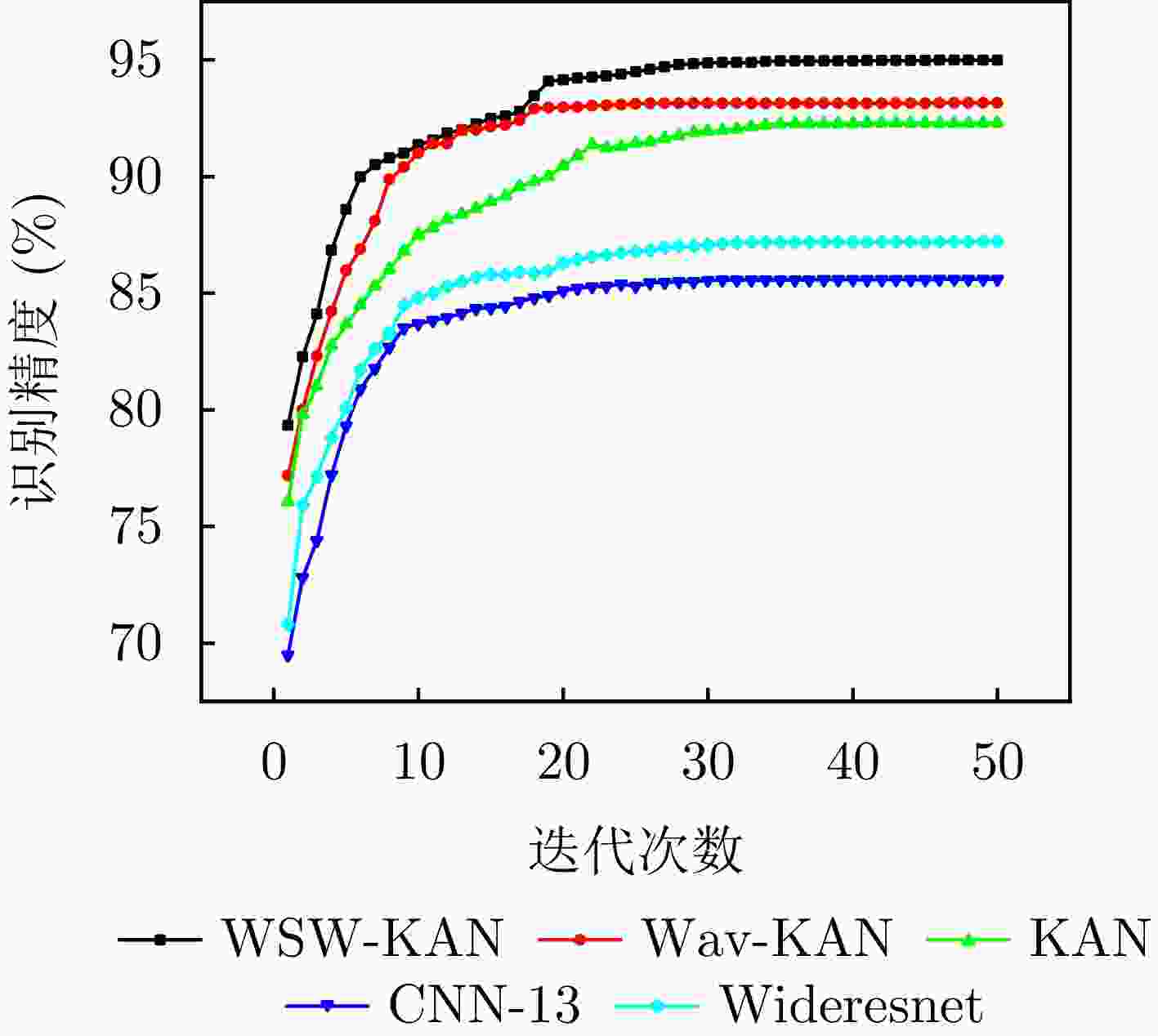
迭代次数 WSW-KAN (%) Wav-KAN (%) KAN (%) CNN-13 (%) Wideresnet (%) 1 79.33 77.18 76.08 69.49 70.80 2 82.27 80.00 79.80 72.81 75.91 3 84.11 82.30 81.01 74.40 77.14 4 86.84 84.23 82.77 77.21 78.81 5 88.58 85.98 83.66 79.31 80.10 6 89.98 86.89 84.49 80.90 81.71 7 90.50 88.10 85.31 81.77 82.61 8 91.21 89.87 86.02 82.68 83.27 9 91.61 90.40 86.80 83.51 84.50 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 46 94.98 93.16 92.29 85.59 87.20 47 94.99 93.16 92.29 85.59 87.21 48 94.99 93.16 92.29 85.59 87.21 49 94.99 93.16 92.29 85.59 87.21 50 94.99 93.16 92.29 85.59 87.21 表 6 自适应感知伪标签加权选择算法消融实验数据
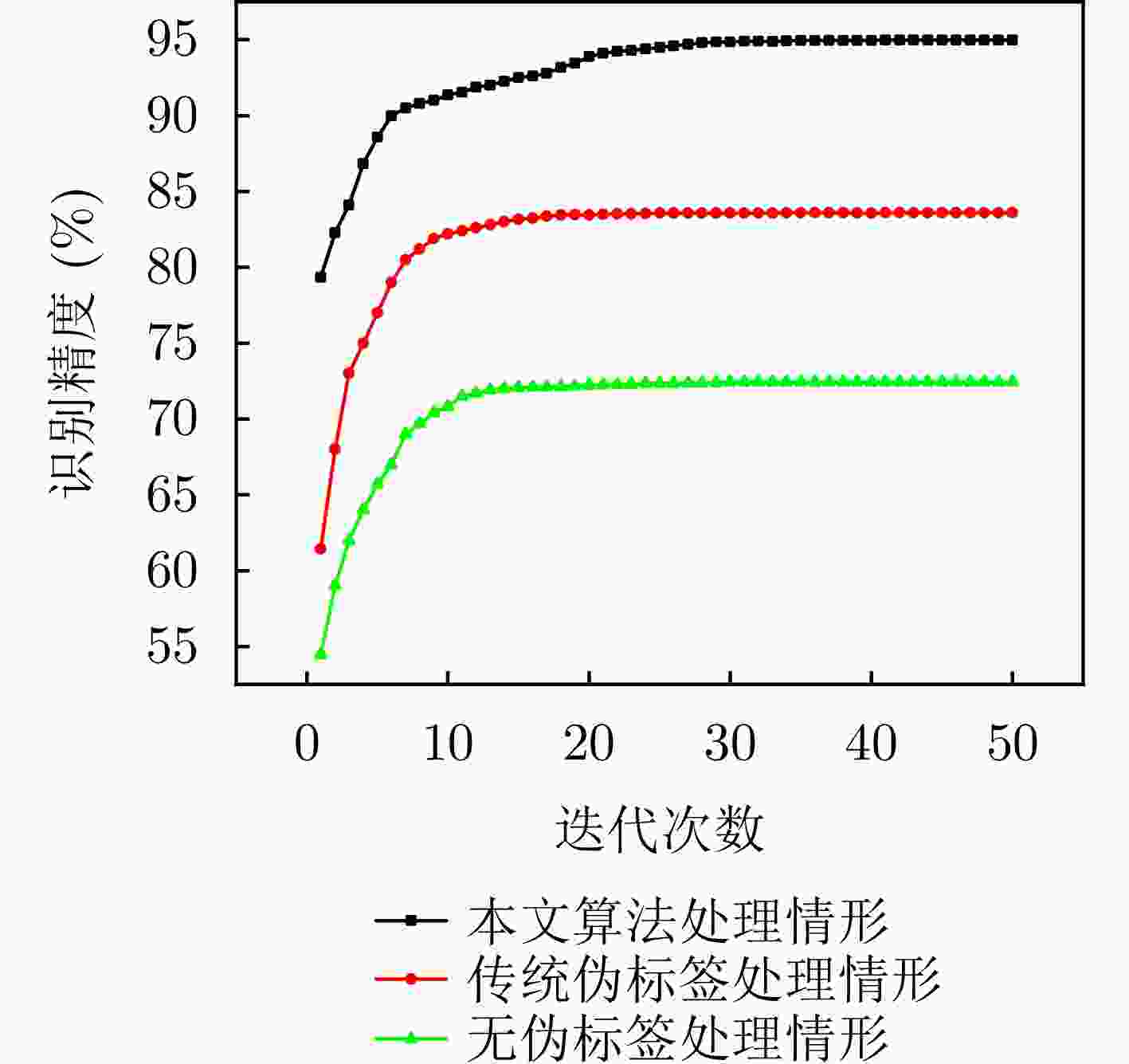
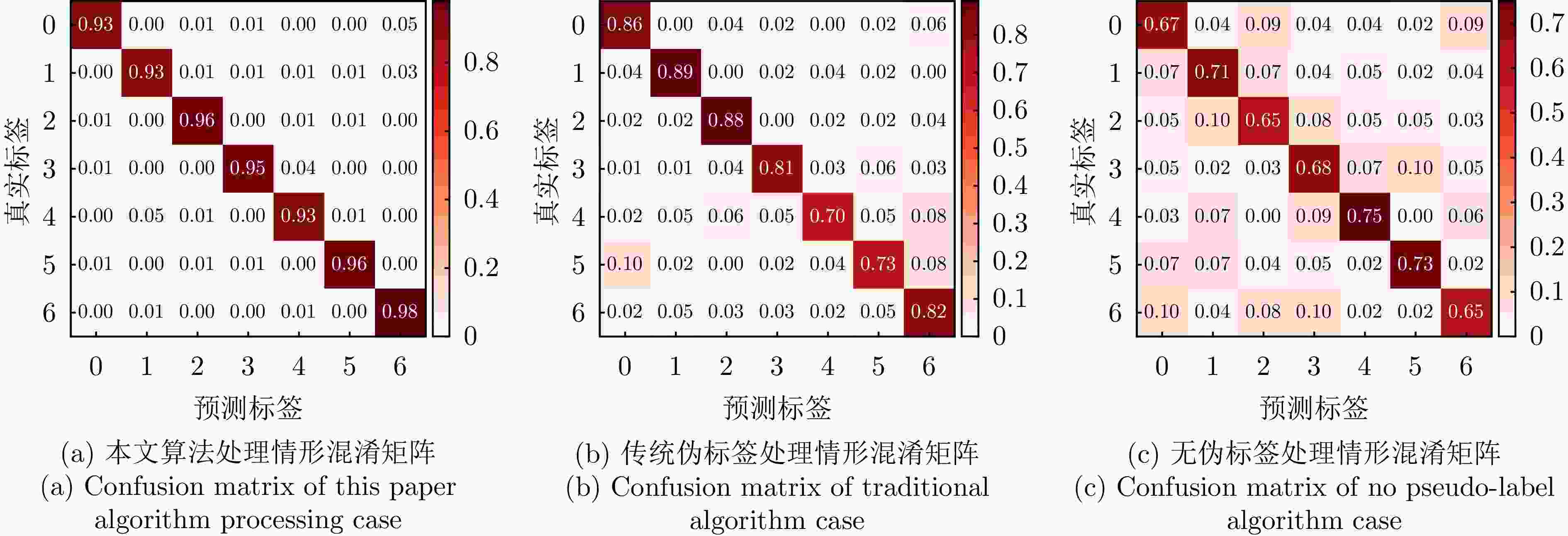
Table 6. Adaptive pseudo-label weighted selection algorithm ablation study data
迭代次数 本文算法处理
情形(%)传统伪标签处理
情形(%)无伪标签处理
情形(%)1 79.33 61.45 54.47 2 82.27 68.06 59.03 3 84.11 73.15 61.95 4 86.84 75.06 63.89 5 88.58 77.35 65.71 6 89.98 79.03 67.11 7 90.50 80.50 68.97 8 91.21 81.22 69.70 9 91.61 81.90 70.40 ··· ··· ··· ··· 46 94.98 83.60 72.45 47 94.99 83.60 72.45 48 94.99 83.60 72.45 49 94.99 83.60 72.45 50 94.99 83.60 72.45 表 7 预训练阶段不同识别网络算法复杂度对比
Table 7. Comparison of the complexity of different identification network algorithms in pre-training stage
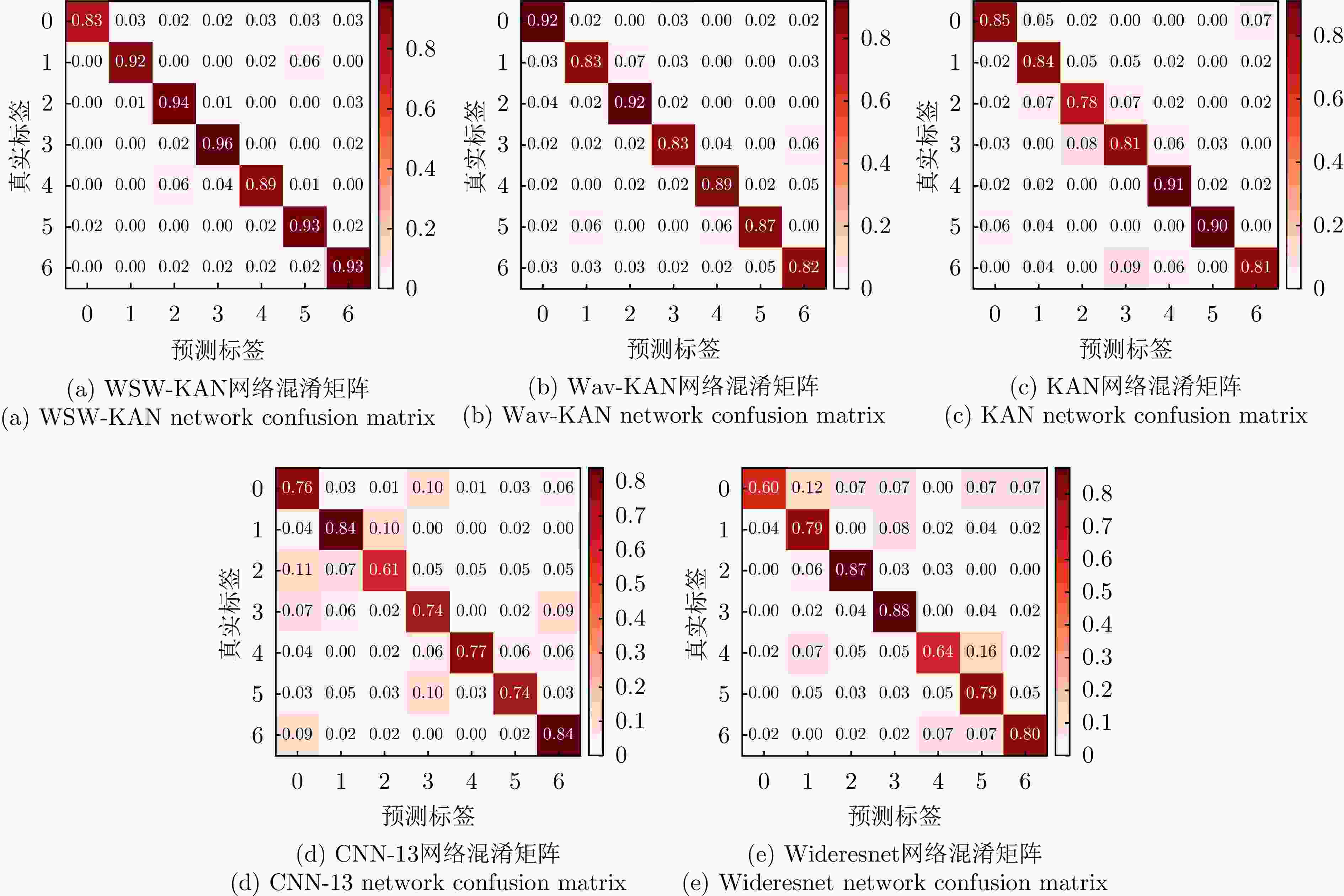
网络模型 耗时(s) 参数数量(个) 识别精度(%) WSW-KAN 246.56 419935 88.75 Wav-KAN 280.88 439978 87.36 KAN 312.73 702118 84.09 CNN-13 408.68 3150990 76.05 Wideresnet 379.03 1466935 78.60 表 8 对比学习阶段不同识别网络算法时间复杂度和空间复杂度对比
Table 8. Comparison of the complexity of different identification network algorithms in contrastive learning stage
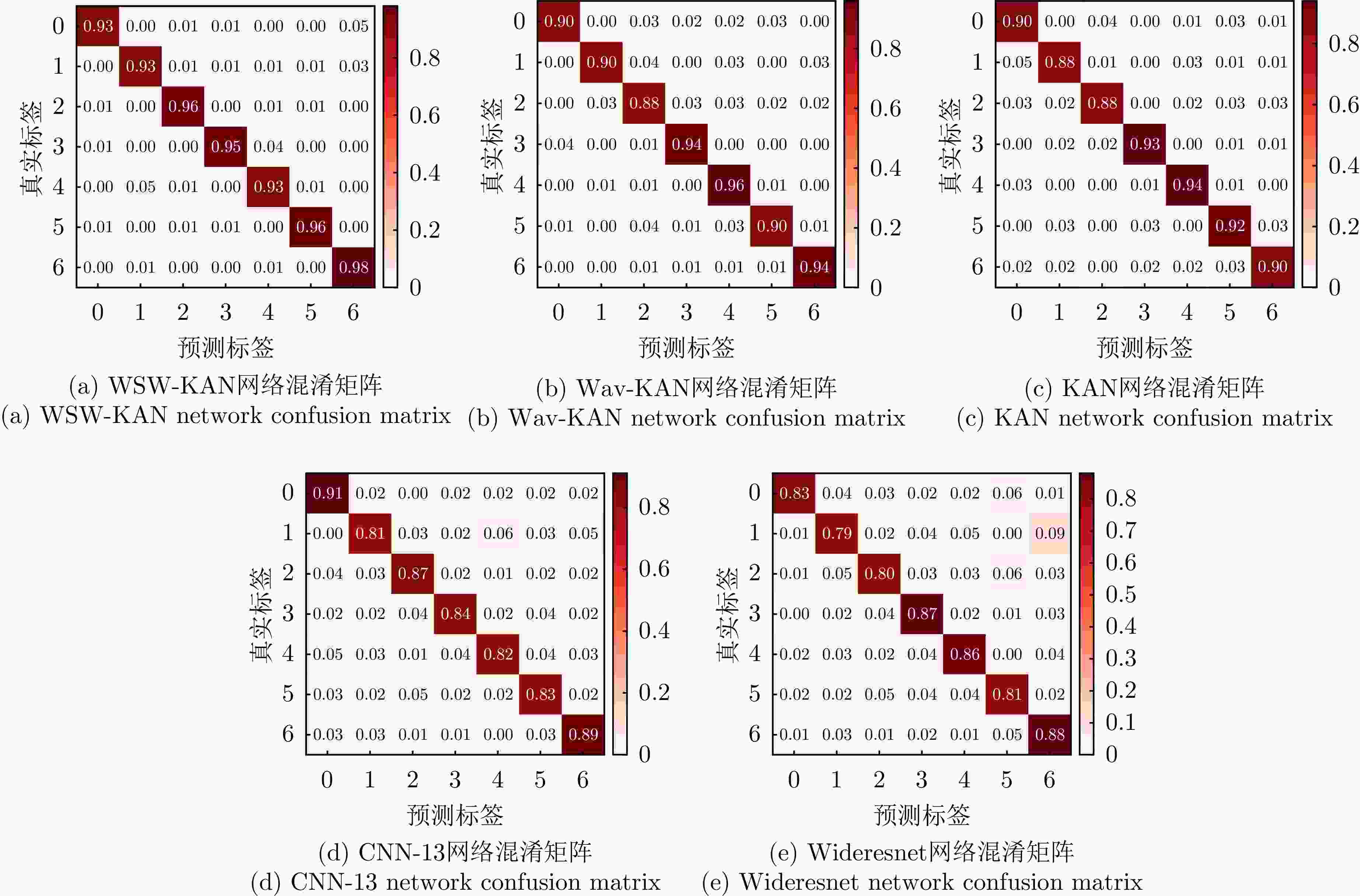
网络模型 耗时(s) 参数数量(个) 识别精度(%) WSW-KAN 356.78 419935 94.99 Wav-KAN 392.45 439978 93.16 KAN 430.98 702118 92.29 CNN-13 544.23 3150990 85.59 Wideresnet 487.78 1466935 87.21 表 9 小波基函数形式和参数对比
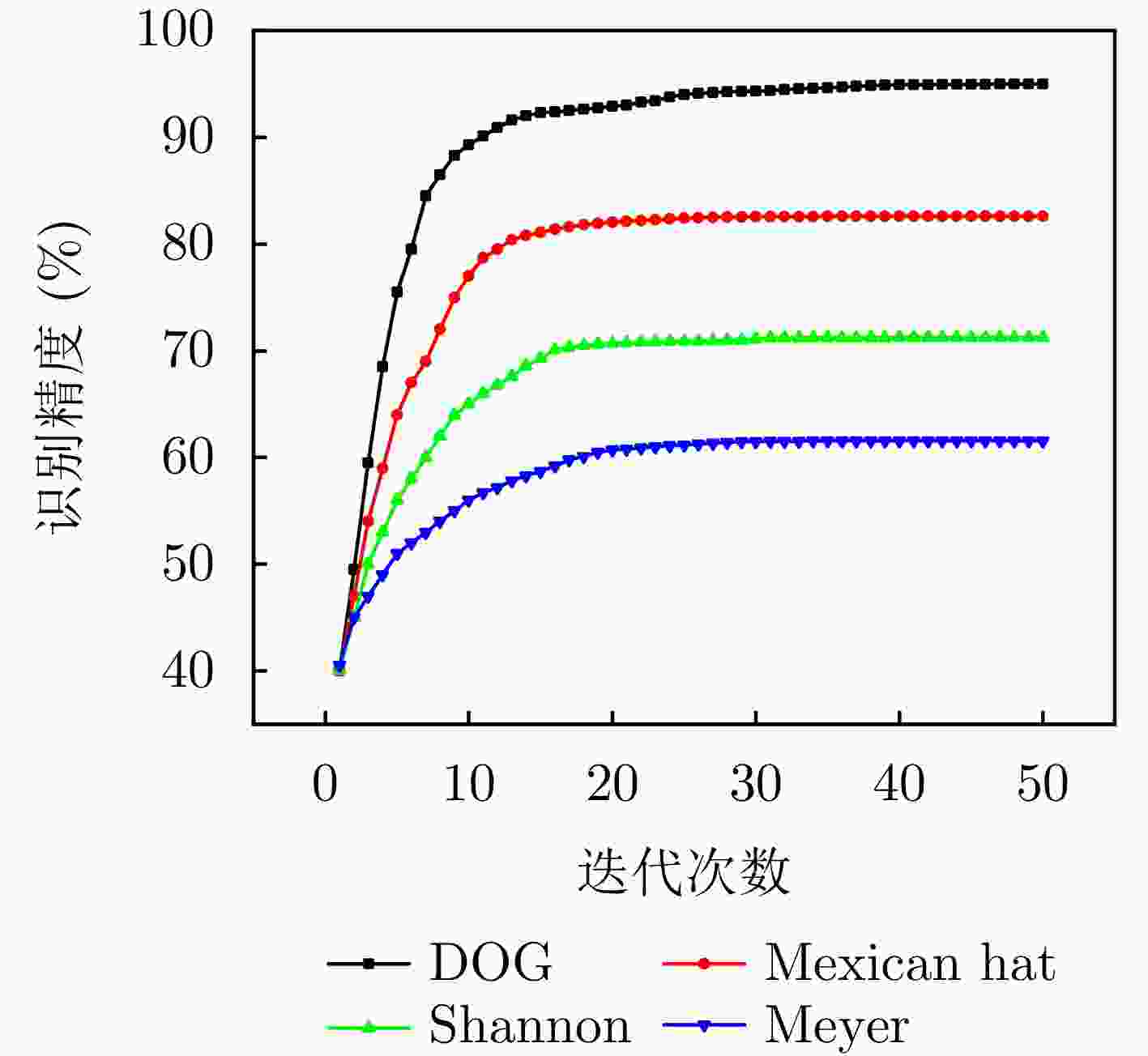
Table 9. The comparison of wavelet basis function form and parameters
类型 小波基函数形式 参数 Mexican hat $ \psi (t) = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 {p^{1/4}}}}({t^2} - 1){{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\textstyle\frac{{{t^2}}}{2}}}} $ $ \tau ,s $ Derivative of Gaussian (DOG) $ \psi (t) = - \dfrac{{\mathrm{d}}}{{{\mathrm{d}}t}}\left({{\mathrm{e}}^{ -\textstyle{ \frac{{{t^2}}}{2}}}}\right) $ $ \tau ,s $ Shannon $ \psi (t) = {\mathrm{sinc}}(t/p) \cdot \omega (t) $ $ \tau ,s,w(t):矩形窗 $ Meyer $ \psi (t) = \dfrac{1}{{2p}}\displaystyle\int_{ - \infty }^\infty {\hat \psi (\xi ){{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{i}}\xi t}}{\mathrm{d}}\xi } $ $ \tau ,s $ 表 10 不同伪标签阈值参数识别性能(%)
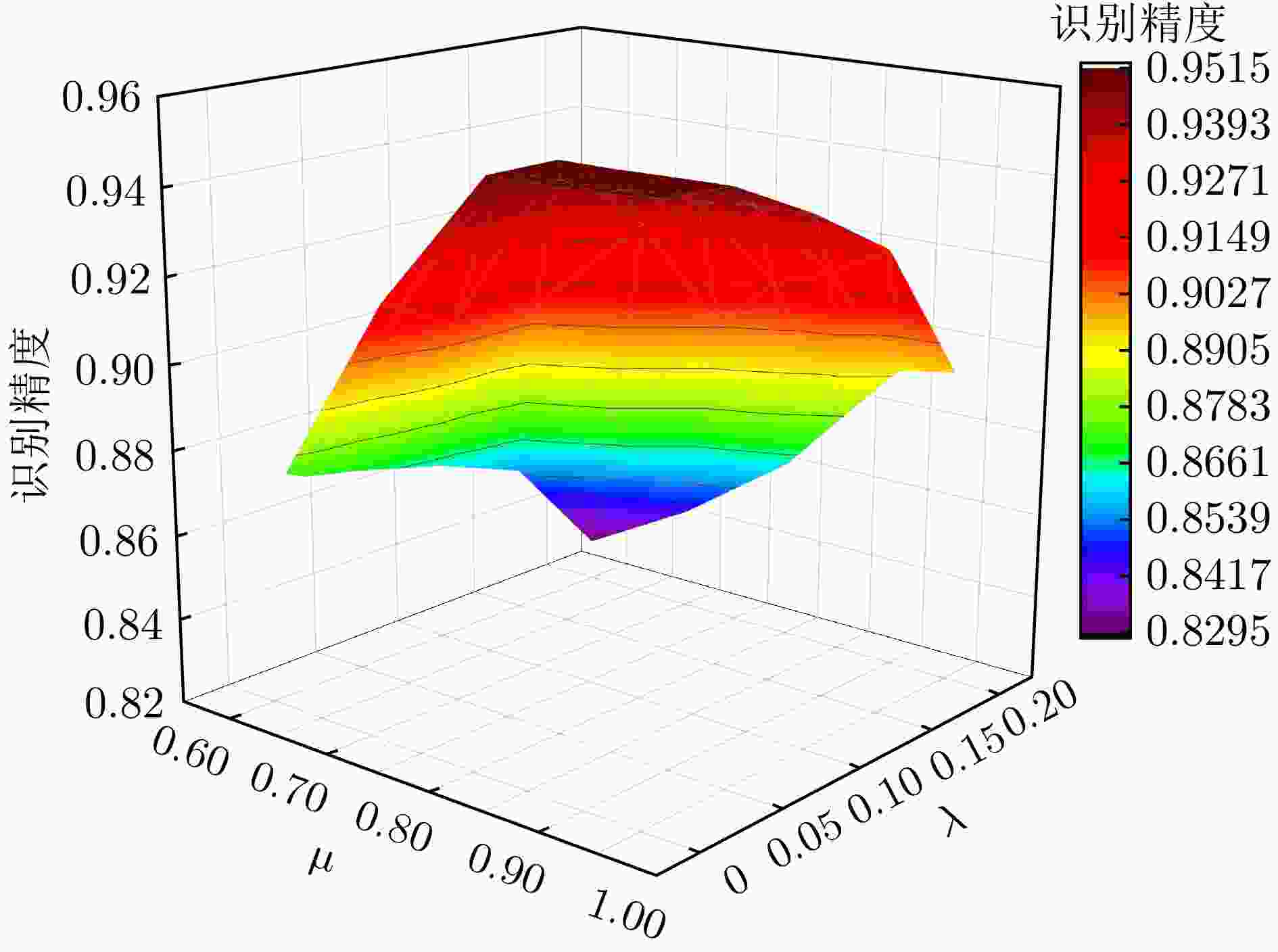
Table 10. The identification performance of different pseudo-label threshold parameters (%)
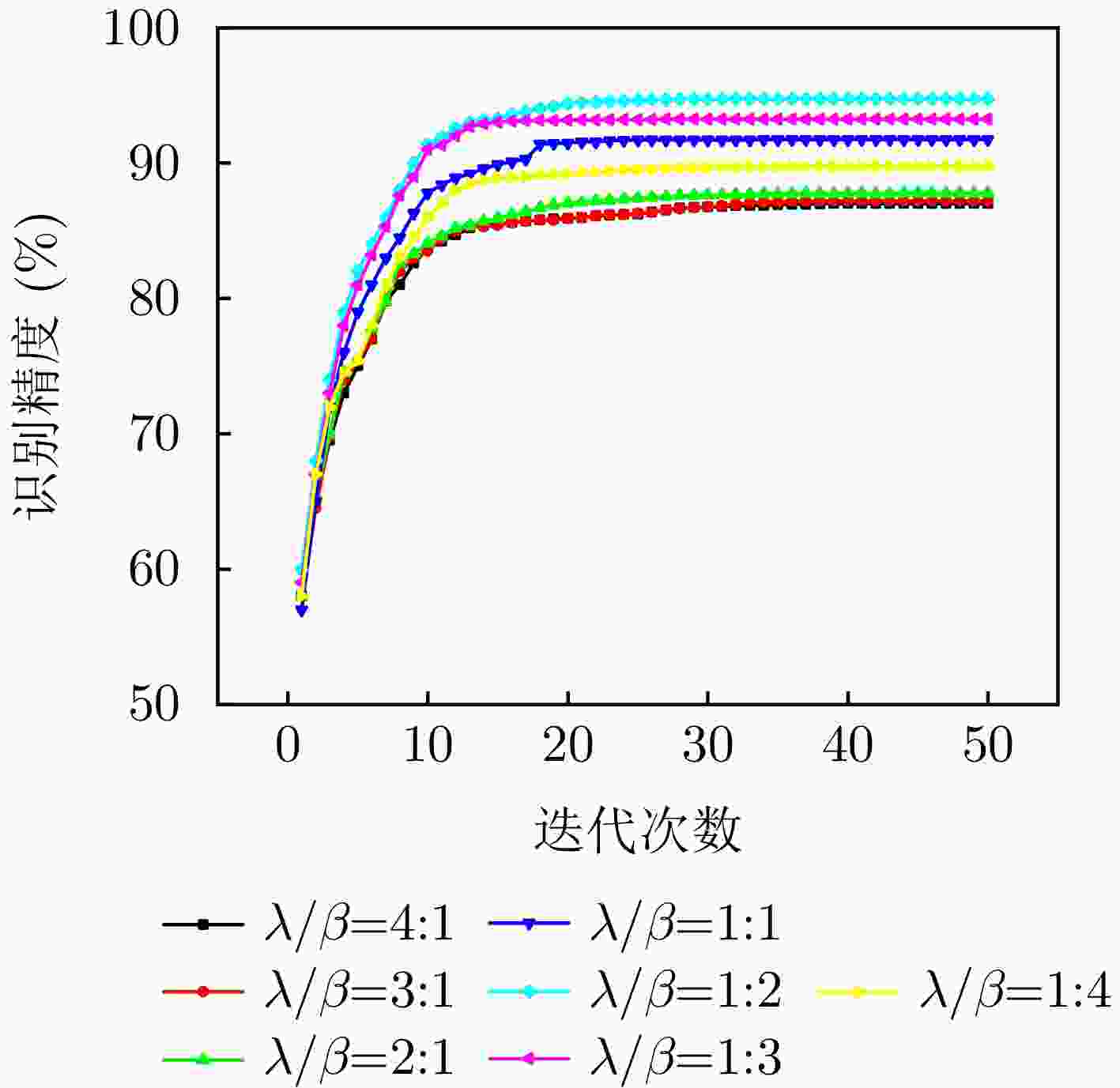
$\lambda $ $\mu $ 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.95 95.12 95.12 95.04 94.03 92.79 89.45 0.90 95.02 95.02 95.02 93.99 92.03 89.21 0.85 94.99 95.00 94.99 93.86 91.56 87.79 0.80 94.99 94.99 94.99 93.14 90.34 86.34 0.70 91.78 91.58 90.89 90.82 87.45 84.45 0.60 87.34 87.13 86.88 86.34 85.56 82.98 -
[1] 吴琼. 基于改进CNN的雷达辐射源识别算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.7666/d.D01905147.WU Qiong. Research on radar emitter recognition algorithm based on improved CNN[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.7666/d.D01905147. [2] TAN Kaiwen, YAN Wenjun, ZHANG Limin, et al. Specific emitter identification based on software-defined radio and decision fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 86217–86229. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3088542. [3] 王艺卉, 闫文君, 凌青, 等. 基于置信学习的低标注率辐射源个体识别算法[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2024, 45(5): 267–275. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2024.05.037.WANG Yihui, YAN Wenjun, LING Qing, et al. Low labeling rate specific emitter identification algorithm based on confidence learning[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2024, 45(5): 267–275. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2024.05.037. [4] 张顺生, 丁宦城, 王文钦. 面向辐射源识别的多尺度特征提取与特征选择网络[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2024, 46(6): 141–148. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202406015.ZHANG Shunsheng, DING Huancheng, and WANG Wenqin. Multi-scale feature extraction and feature selection network for radiation source identification[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2024, 46(6): 141–148. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202406015. [5] XING Yuexiu, HU Aiqun, ZHANG Junqing, et al. Design of a robust radio-frequency fingerprint identification scheme for multimode LFM radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 10581–10593. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3003692. [6] 李昕. 基于无监督学习的通信辐射源个体识别技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2019: 1–10. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2019.000718.LI Xin. Research on individual communication transmitter identification based on unsupervised learning[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2019: 1–10. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2019.000718. [7] CHEN Qi, YANG Lingxiao, LAI Jianhuang, et al. Self-supervised image-specific prototype exploration for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4278–4288. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00425. [8] DU Ye, FU Zehua, LIU Qingjie, et al. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation by pixel-to-prototype contrast[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4310–4319. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00428. [9] JIANG Pengtao, YANG Yuqi, HOU Qibin, et al. L2G: A simple local-to-global knowledge transfer framework for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 16865–16875. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01638. [10] LEE J, KIM E, and YOON S. Anti-adversarially manipulated attributions for weakly and semi-supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 4070–4078. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00406. [11] LEE S, LEE M, LEE J, et al. Railroad is not a train: Saliency as pseudo-pixel supervision for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 5491–5501. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00545. [12] ZHOU Tianfei, ZHANG Meijie, ZHAO Fand, et al. Regional semantic contrast and aggregation for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4289–4299. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00426. [13] HE Kaiming, FAN Haoqi, WU Yuxin, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 9726–9735. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00975. [14] PENG Yang, HOU Changbo, ZHANG Yibin, et al. Supervised contrastive learning for RFF identification with limited samples[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(19): 17293–17306. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3272628. [15] CHEN Jun, WONG W K, and HAMDAOUI B. Unsupervised contrastive learning for robust RF device fingerprinting under time-domain shift[C]. ICC 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Denver, USA, 2024: 3567–3572. doi: 10.1109/ICC51166.2024.10622173. [16] ZHAN Mengqi, LI Yang, CUI Huajun, et al. MCRFF: A meta-contrastive learning-based RF fingerprinting method[C]. MILCOM 2023 - 2023 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Boston, USA, 2023: 391–396. doi: 10.1109/MILCOM58377.2023.10356211. [17] DU Mingyang, PAN Jifei, and BI Daping. A contrastive learner for automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, in press. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3532438. [18] LIU Ziming, WANG Yixuan, VAIDYA S, et al. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756, 2024. [19] BOZORGASL Z and CHEN Hao. Wav-KAN: Wavelet Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.12832, 2024. [20] PERSONS J B, WONG L J, MOORE M O, et al. Classification of radio signals using truncated Gaussian discriminant analysis of convolutional neural network-derived features[C]. MILCOM 2022 - 2022 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Rockville, USA, 2022: 304–310. doi: 10.1109/MILCOM55135.2022.10017724. [21] ZHENG Qinghe, ZHAO Penghui, LI Yang, et al. Spectrum interference-based two-level data augmentation method in deep learning for automatic modulation classification[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(13): 7723–7745. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05514-1. [22] CHEN Xi, YANG Haosen, ZHANG Huicong, et al. Uncertainty-aware pseudo-label filtering for source-free unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 575: 127190. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.127190. [23] 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011.LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. [24] ALBATINEH A N, BOUBAKARI I, and KIBRIA B M G. New confidence interval estimator of the signal-to-noise ratio based on asymptotic sampling distribution[J]. Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods, 2017, 46(2): 574–590. doi: 10.1080/03610926.2014.1000498. [25] ZAGORUYKO S and KOMODAKIS N. Wide residual networks[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2016, York, UK, 2016. [26] 谭凯文, 张立民, 闫文君, 等. 面向非均衡类别的半监督辐射源识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 713–727. doi: 10.12000/JR22043.TAN Kaiwen, ZHANG Limin, YAN Wenjun, et al. A semi-supervised emitter identification method for imbalanced category[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 713–727. doi: 10.12000/JR22043. [27] 王程昱, 凌青, 闫文君. 基于DCGAN的雷达辐射源信号个体识别算法[J]. 测控技术, 2024, 43(7): 17–22, 64. doi: 10.19708/j.ckjs.2024.04.222.WANG Chengyu, LING Qing, and YAN Wenjun. Individual identification algorithm for radar emitter signal based on DCGAN[J]. Measurement and Control Technology, 2024, 43(7): 17–22, 64. doi: 10.19708/j.ckjs.2024.04.222. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: