Beamforming Design for Dual-functional Radar-communication Systems with Holographic Metasurface Antennas
-
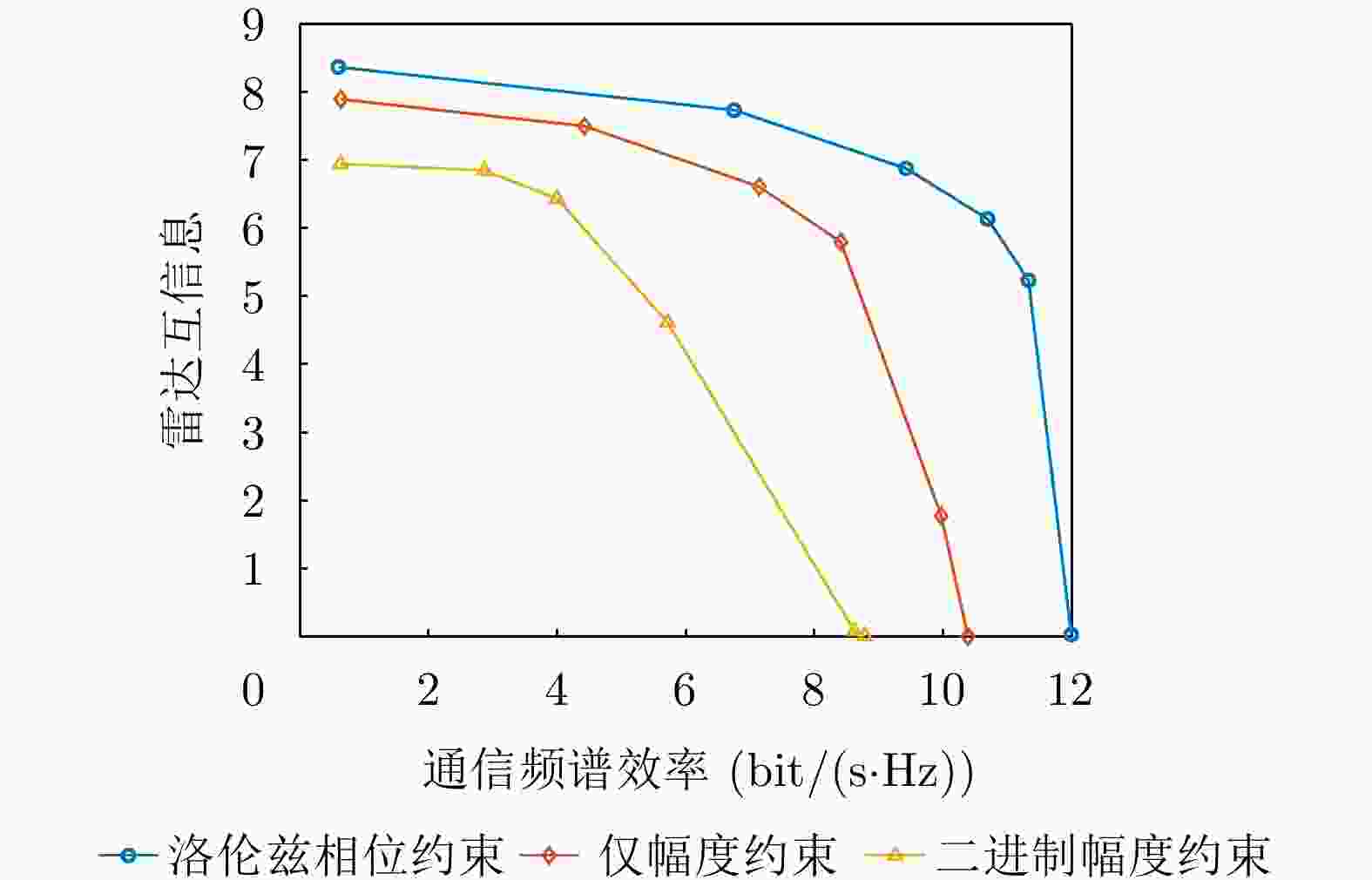
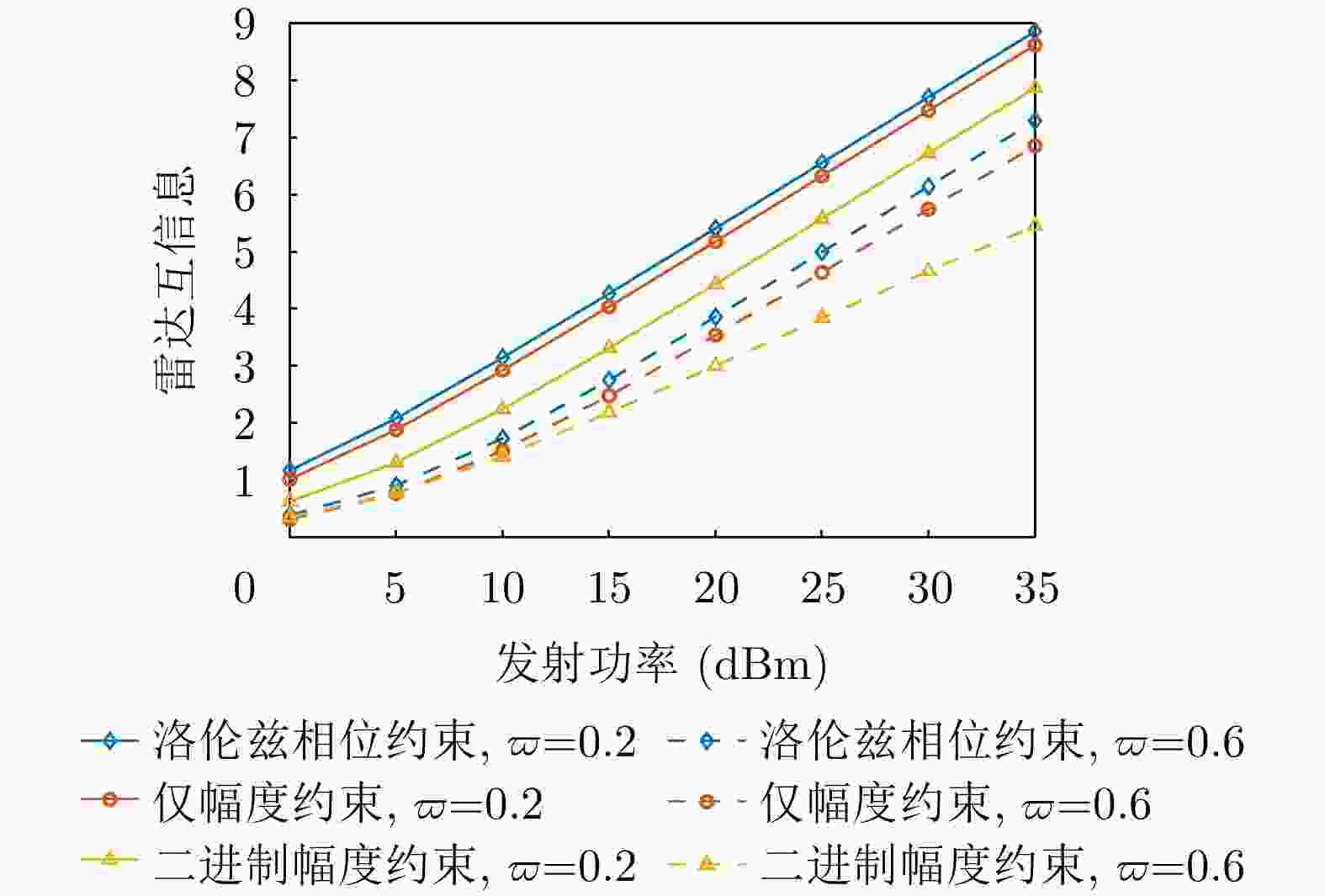
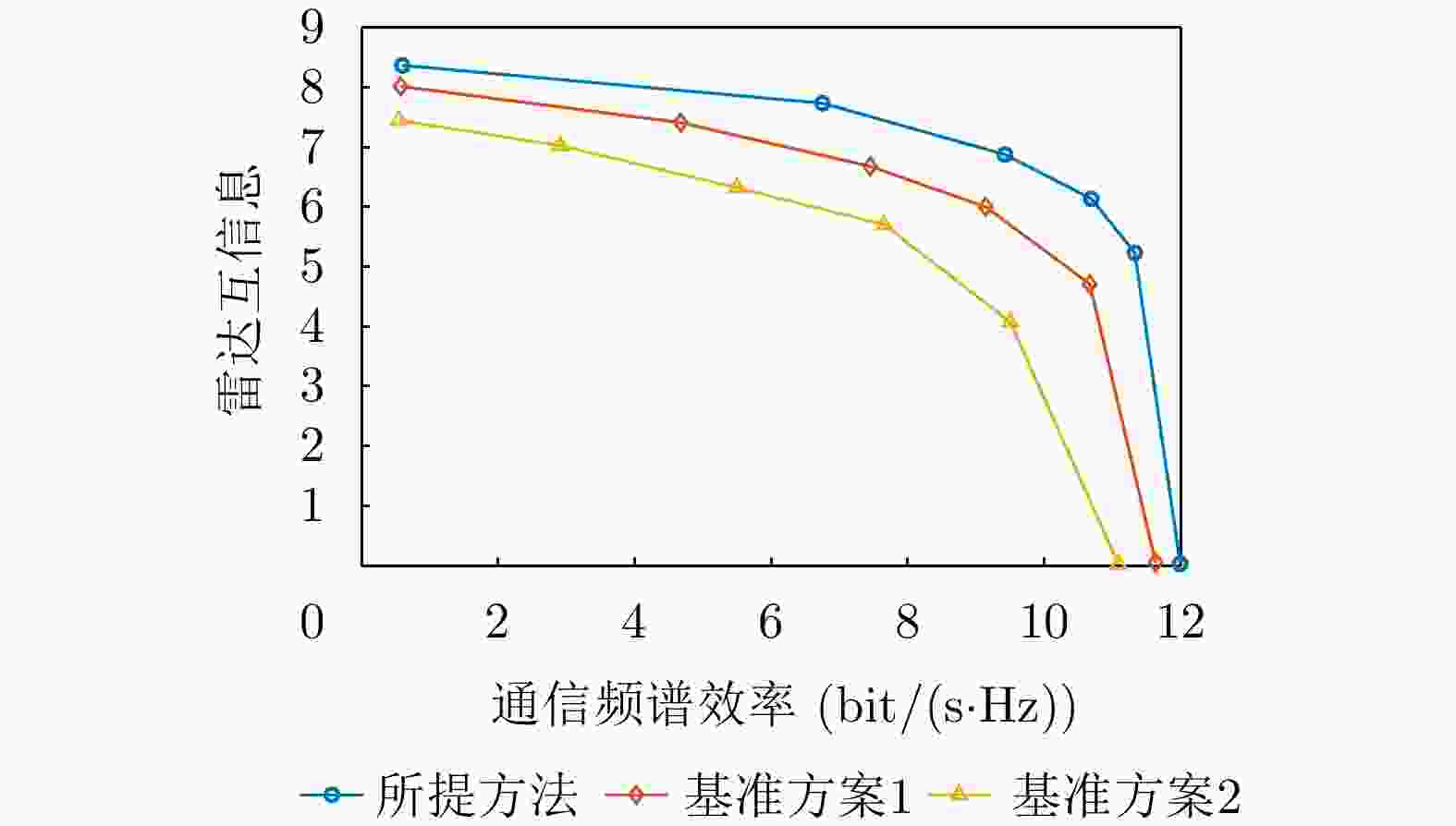
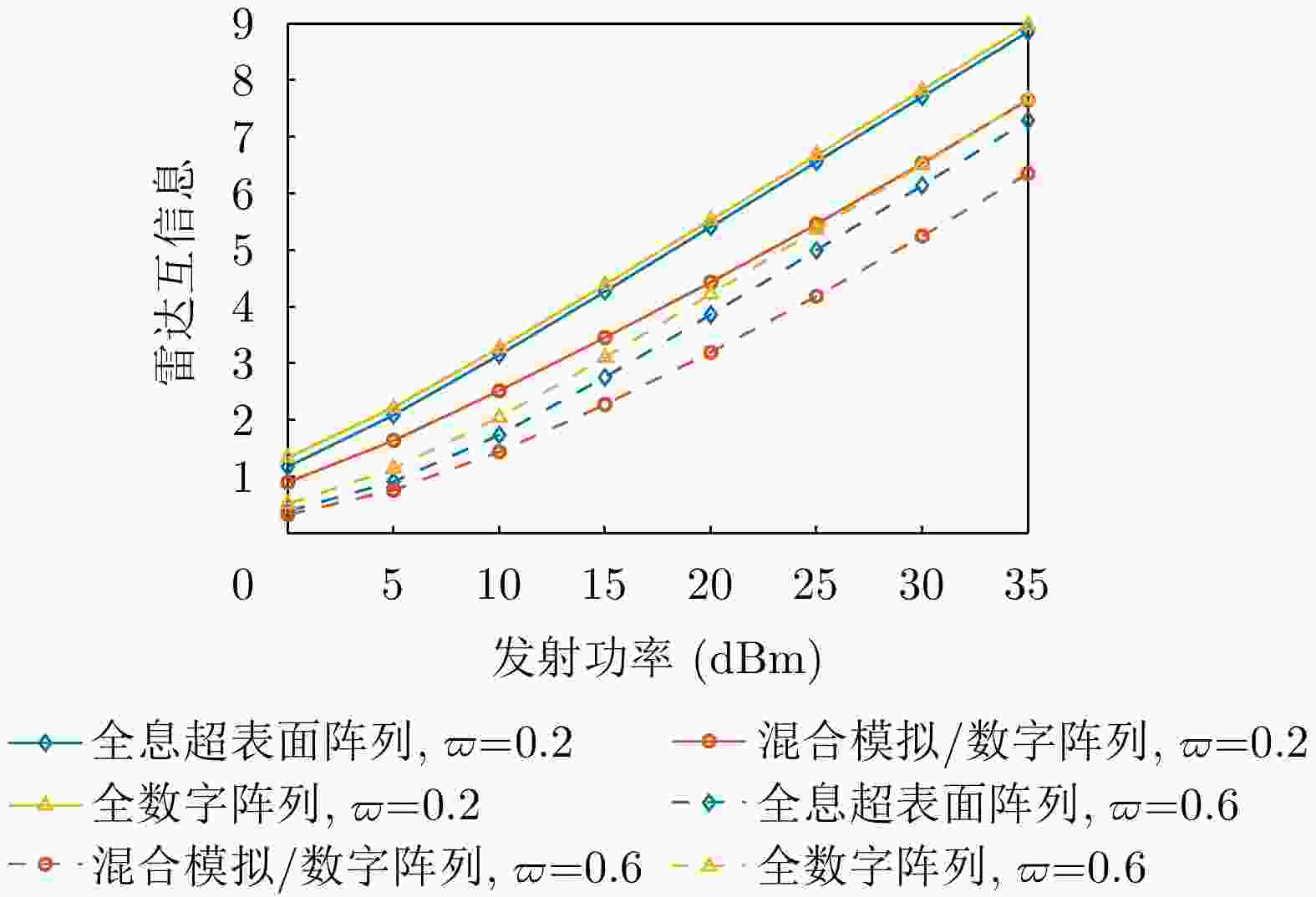
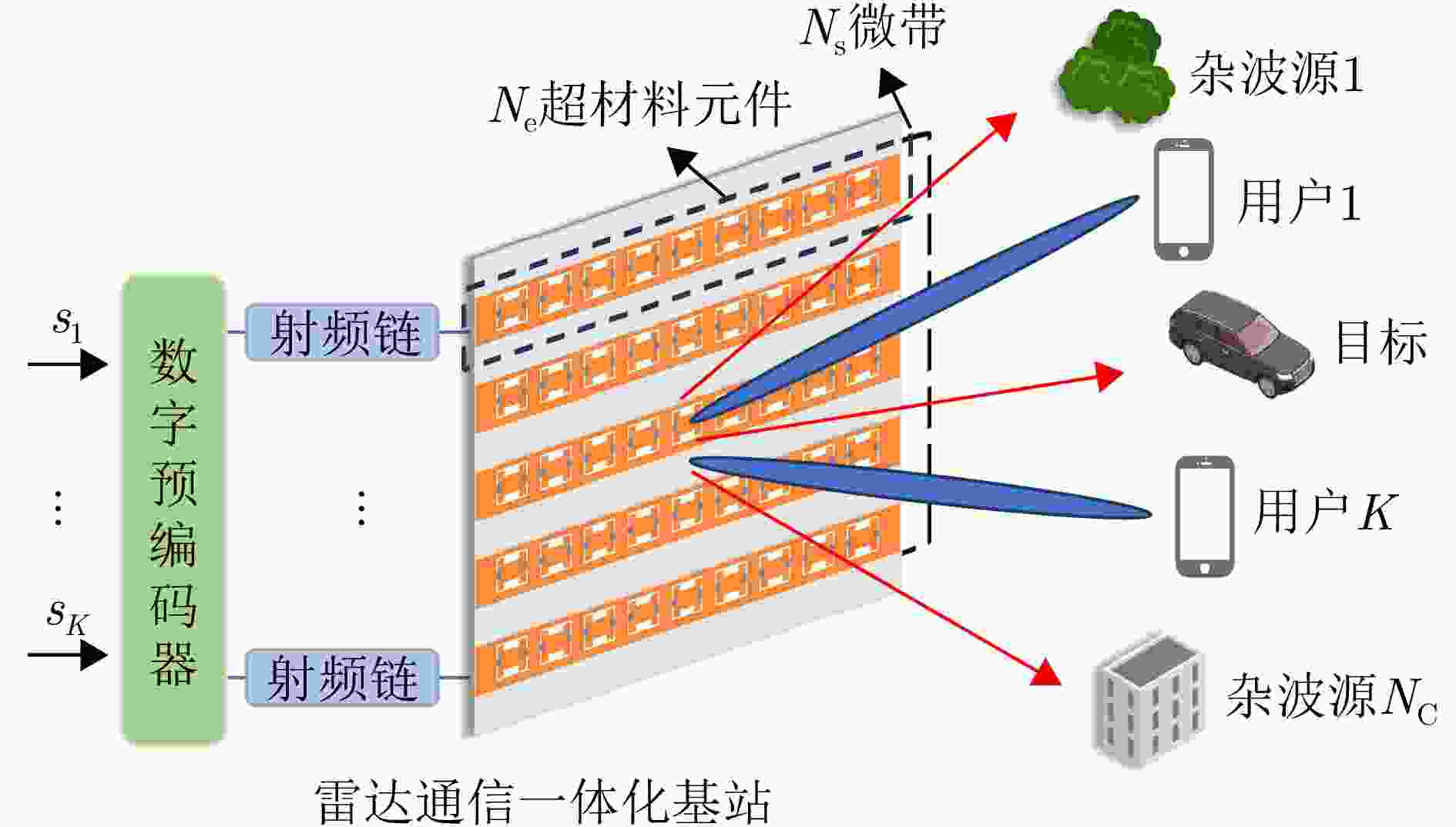
摘要: 无线通信设备在新兴场景(例如,如车联网、低轨卫星等)的大量应用使得通信用频逐渐向更高频段扩展,进而导致其与雷达用频的重叠现象日益突出。雷达通信一体化凭借其联合信号处理能力和低功耗特性,被视为一种解决频谱拥挤问题的有效途径。相比于传统的天线阵列架构,全息超表面天线(HMA)通过嵌入紧密排列的超材料单元,可以灵活配置各单元的状态以调控频率响应,从而实现可控且高能效的波束成形,为雷达通信一体化系统提供了潜在可行选择。考虑一个基于全息超表面的雷达通信一体化系统,在杂波环境下进行目标感知的同时能够为多个单天线用户提供通信服务。接下来,该文在满足发射功率和HMA频率响应约束的前提下,构建了最大化通信频谱效率和雷达互信息加权和的问题,通过联合优化数字预编码器、HMA权重矩阵和接收滤波器,实现基于HMA的雷达通信一体化波束成形设计。为求解这一非凸优化问题,该文提出一种基于分式规划的交替优化算法。该算法首先利用分式规划技术将原始问题转化为更易于处理的子问题,然后通过拉格朗日对偶分解和流形优化等方法对子问题进行交替优化求解。仿真结果表明,HMA阵列架构的波束成形设计在通信频谱效率与雷达互信息性能间取得了灵活的平衡,并且其性能接近全数字阵列架构。Abstract: The widespread application of wireless communication devices in emerging scenarios (e.g., Vehicle-to-Everything, Low Earth Orbit Satellites) has gradually pushed communication frequencies toward higher bands, resulting in an increasingly prominent overlap with radar frequency bands. A Dual-Functional Radar-Communication (DFRC) system, with its joint signal processing capabilities and low-power characteristics, is regarded as effective in alleviating spectrum congestion. Unlike traditional antenna array architectures, Holographic Metasurface Antennas (HMAs) embed closely arranged metamaterial units, enabling the flexible configuration of each unit’s state to regulate frequency responses. This facilitates controllable and energy-efficient beamforming, offering potential for application in DFRC systems. Considering an HMA-based DFRC system that performs target sensing in a cluttered environment while providing communication services to multiple single-antenna users, this paper formulates an optimization problem to maximize the weighted sum of communication spectral efficiency and radar mutual information, subject to constraints on the transmission power and HMA frequency response. It jointly optimizes the involved digital precoder, HMA weight matrix, and receive filter to realize an HMA-based DFRC beamforming design. To tackle this nonconvex optimization challenge, we propose an alternating optimization algorithm based on fractional programming. This algorithm first employs fractional programming techniques to transform the original problem into more manageable subproblems, which are then alternately solved using methods such as Lagrangian dual decomposition and manifold optimization. Simulation results show that the beamforming design with the HMA array architecture achieves a flexible tradeoff between communication spectral efficiency and radar mutual information performance, approaching the performance of a fully digital array architecture.
-
1 搜索对偶变量$\lambda $的二分法
1. Bisection method for searching dual variable $\lambda $
输入:初始化上下界${\lambda _{{\text{max}}}}$, ${\lambda _{{\text{min}}}}$和容差$\varepsilon $。 输出:最优对偶变量${\lambda ^ \star }$。 步骤: 1:设置$\lambda = ({\lambda _{{\text{max}}}} + {\lambda _{{\text{max}}}})/2$。 2:如果$ {\displaystyle \sum _{k=1}^{K}\Vert {{\boldsymbol{HQf}}}_{k}{\Vert }^{2}}\le {P}_{\text{max}} $,则${\lambda _{{\text{max}}}} = \lambda $;否则,
${\lambda _{{\text{min}}}} = \lambda $。3:计算${\text{res}} = |{\lambda _{{\text{max}}}} - {\lambda _{{\text{max}}}}|$。 4:如果$ \text{res} \gt \varepsilon$,则返回步骤1;否则,${\lambda ^ \star } = \lambda $。 2 基于流形优化算法求解问题${\mathcal{P}_{4.4}}$
2. Solving problem ${\mathcal{P}_{4.4}}$ based on MO algorithm
输入:V, ${\boldsymbol{\tau }}$, ${{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_0}$和$t = 0$。 输出:${\boldsymbol{\theta }}$。 步骤: 1:$t = t + 1$。 2:选择Armijo步长${\delta _t}$。 3:根据式(43)找到下一个点${{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_t}$。 4:根据式(39)计算${{\mathrm{grad}}}_{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_t}f$。 5:更新Polak-Ribiere参数${\kappa_t}$。 6:如果目标函数梯度为零的临界点,则输出${\boldsymbol{\theta }}$;否则,返回步
骤1。3 基于分式规划的交替优化算法
3. Alternating optimization algorithm based on fractional programming
输入:${{\boldsymbol{g}}_k},\forall k$, H, ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_0}$和${{\boldsymbol{A}}_c},\forall c$。随机初始化Q, F, ${{\boldsymbol{\mu }}^{\text{c}}}$, ${\mu ^{\text{s}}}$,
${{\boldsymbol{\xi }}^{\text{c}}}$, ${{\boldsymbol{\xi }}^{\text{s}}}$和w。输出:Q, F和w。 步骤:
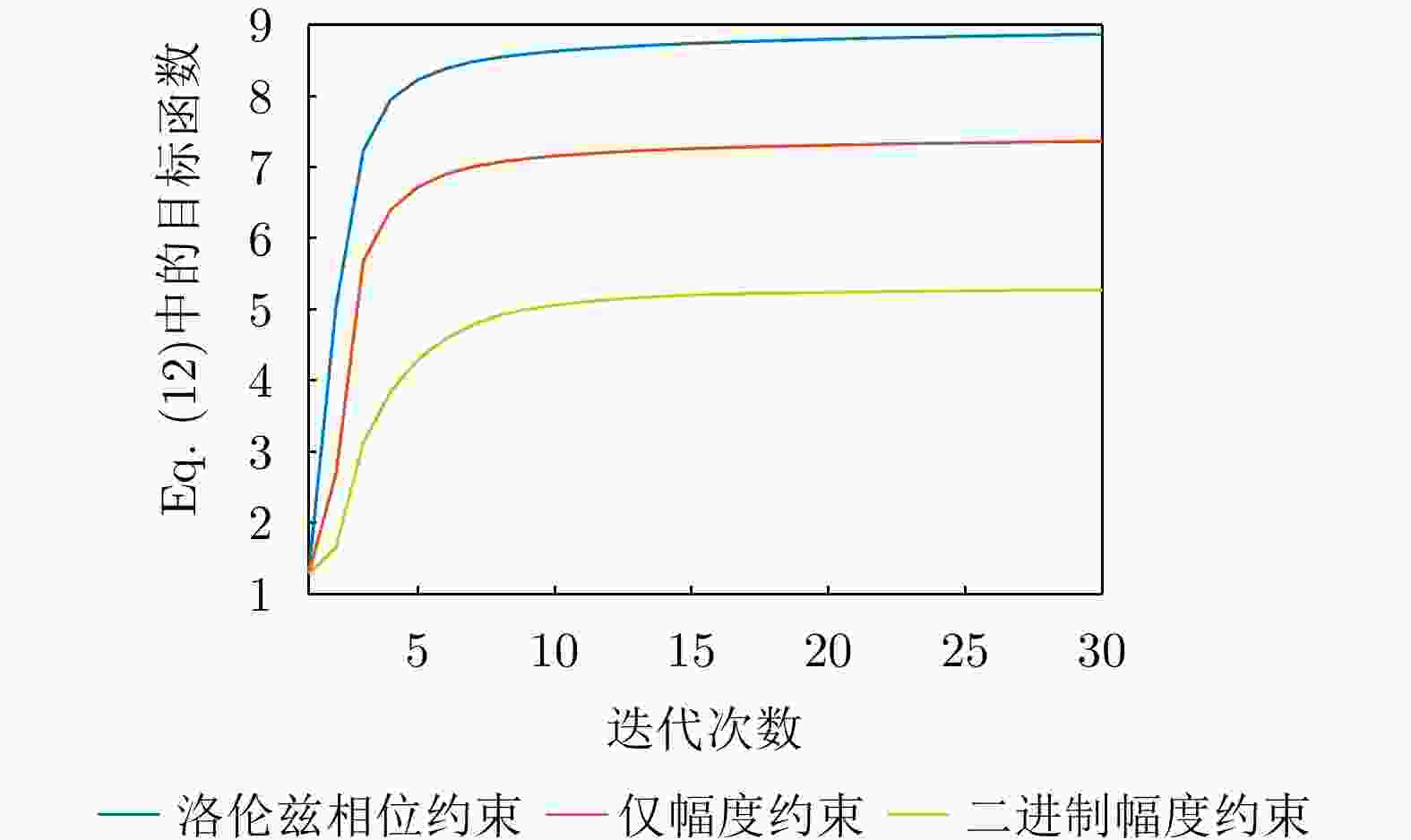
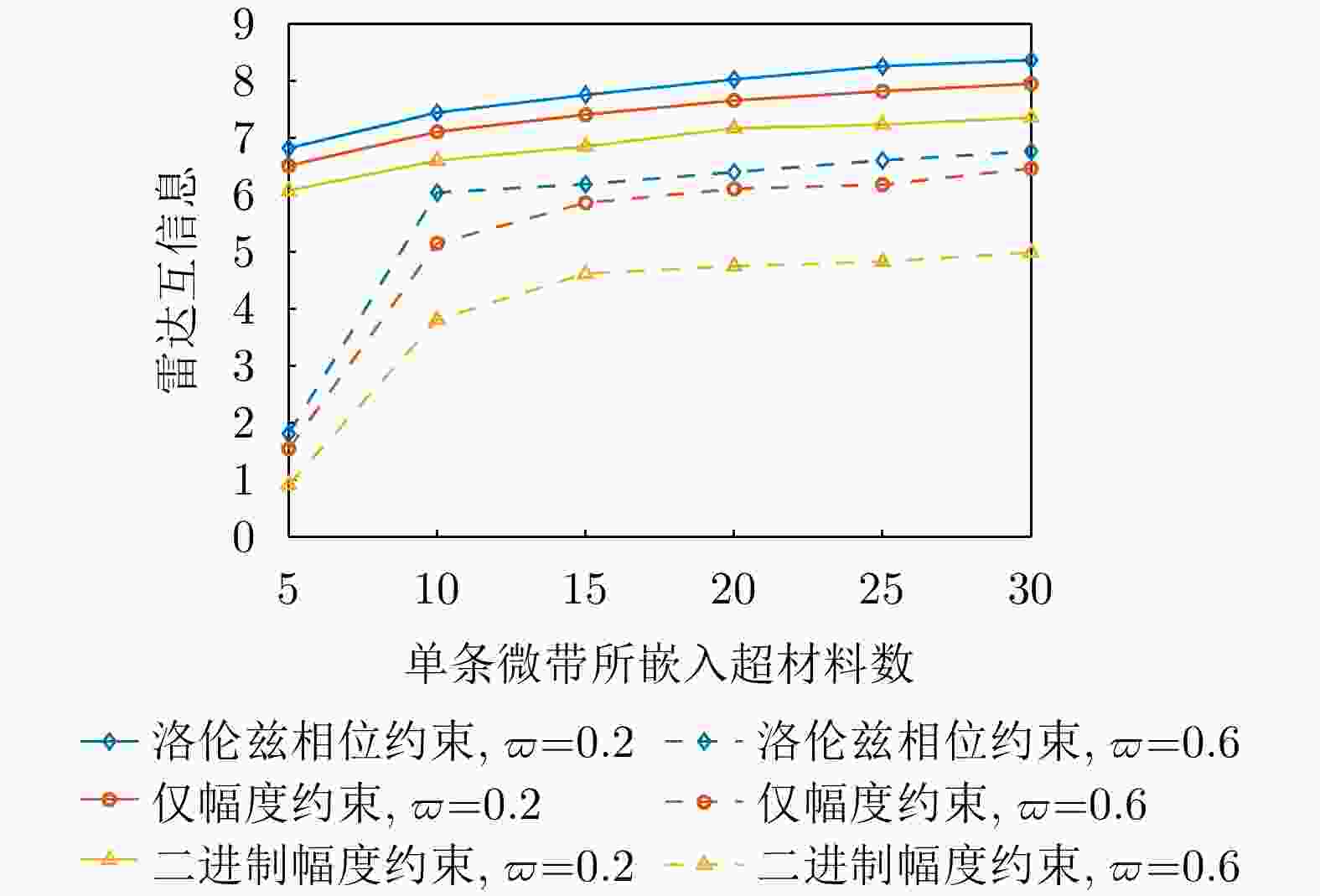
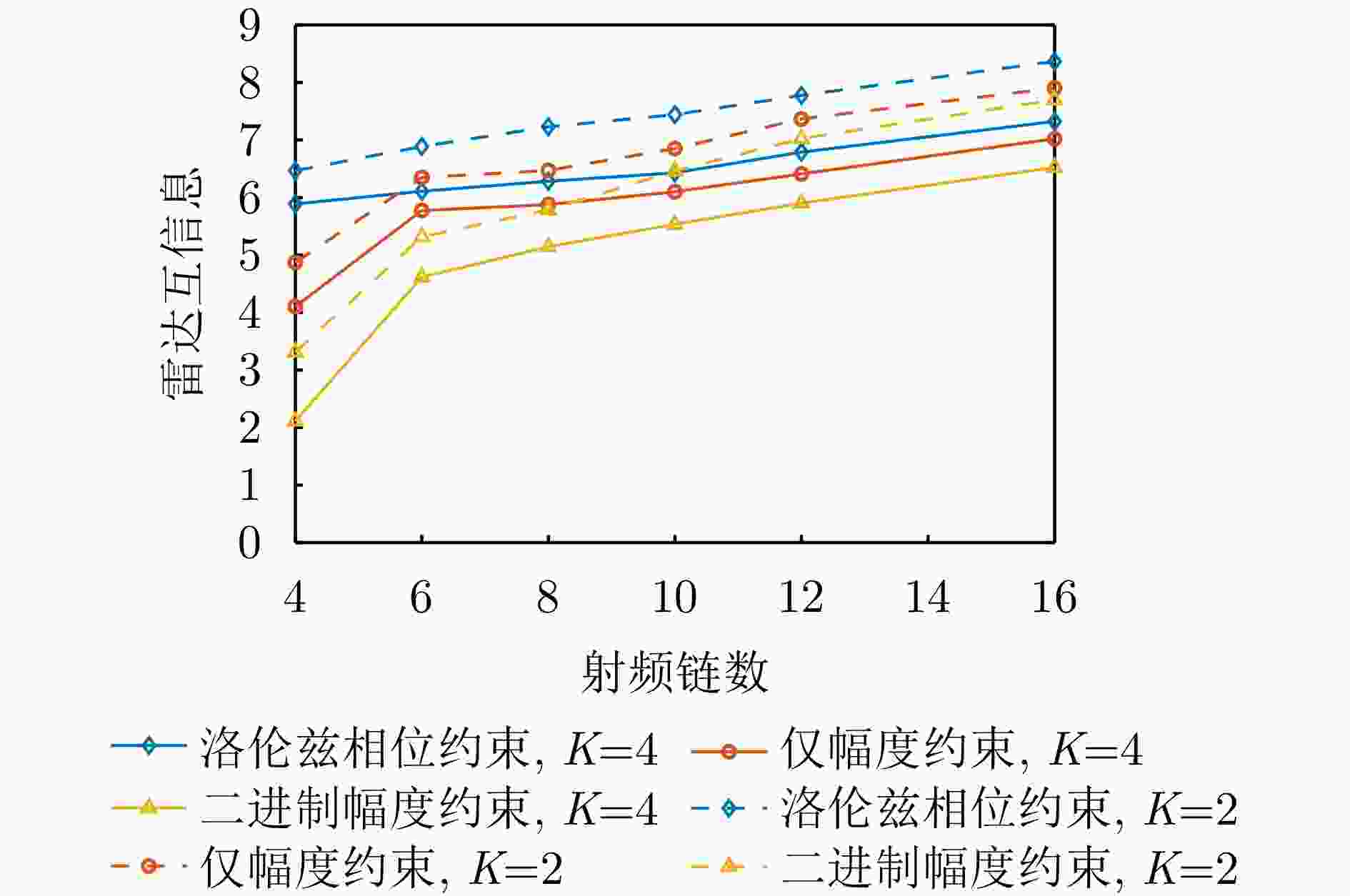
1:根据式(18)—式(21)更新辅助变量${{\boldsymbol{\mu }}^{\text{c}}}$, ${{\boldsymbol{\xi }}^{\text{s}}}$, ${\mu ^{\text{s}}}$和${{\boldsymbol{\xi }}^{\text{c}}}$。2:根据式(28)更新数字预编码器${\boldsymbol{F}} = [{{\boldsymbol{f}}_1},{{\boldsymbol{f}}_2}, \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{f}}_K}]$。 3:HMA权重矩阵Q的优化: 4:若为仅幅度响应约束,则根据式(33)更新q。 5:若为二进制幅度响应约束,则根据式(36)更新q。 6:若为洛伦兹相位约束响应约束,则根据式(37)更新q。 7:重塑${\boldsymbol{Q}} = {\text{diag}}\{ {\boldsymbol{q}}\} {\boldsymbol{B}}$。 8:根据式(44)更新接收滤波器w。 9:如果目标函数(12)收敛,则输出Q, F和w;否则,重复步骤1—
步骤8。 -
[1] 刘凡, 袁伟杰, 原进宏, 等. 雷达通信频谱共享及一体化: 综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113.LIU Fan, YUAN Weijie, YUAN Jinhong, et al. Radar-communication spectrum sharing and integration: Overview and prospect[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 467–484. doi: 10.12000/JR20113. [2] 张若愚, 袁伟杰, 崔原豪, 等. 面向6G的大规模MIMO通信感知一体化: 现状与展望[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(6): 17–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.003.ZHANG Ruoyu, YUAN Weijie, CUI Yuanhao, et al. Integrated sensing and communications with massive MIMO for 6G: Status and prospect[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(6): 17–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.06.003. [3] ZHOU Wenxing, ZHANG Ruoyu, CHEN Guangyi, et al. Integrated sensing and communication waveform design: A survey[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 1930–1949. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3215683. [4] ZHANG Ruoyu, CHENG Lei, WANG Shuai, et al. Integrated sensing and communication with massive MIMO: A unified tensor approach for channel and target parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(8): 8571–8587. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3351856. [5] LIU Xiang, HUANG Tianyao, and LIU Yimin. Transmit design for joint MIMO radar and multiuser communications with transmit covariance constraint[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1932–1950. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155512. [6] CHEN Guangyi, ZHANG Ruoyu, REN Hong, et al. Hybrid beamforming design with overlapped subarrays for massive MIMO-ISAC systems[C]. 2023 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2023: 528–533. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM54140.2023.10437590. [7] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, PETROPULU A P, et al. Joint radar and communication design: Applications, state-of-the-art, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(6): 3834–3862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2973976. [8] CHEN Li, WANG Zhiqin, DU Ying, et al. Generalized transceiver beamforming for DFRC with MIMO radar and MU-MIMO communication[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1795–1808. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155515. [9] ZHAO Zongyao, ZHANG Long, JIANG Rui, et al. Joint beamforming scheme for ISAC systems via Robust Cramér-Rao bound optimization[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(3): 889–893. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2024.3349488. [10] LI Jin, ZHOU Gui, GONG Tantao, et al. A framework for mutual information-based MIMO integrated sensing and communication beamforming design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(6): 8352–8366. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3355899. [11] QI Chenhao, CI Wei, ZHANG Jinming, et al. Hybrid beamforming for millimeter wave MIMO integrated sensing and communications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(5): 1136–1140. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3157751. [12] SHLEZINGER N, DICKER O, ELDAR Y C, et al. Dynamic metasurface antennas for uplink massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(10): 6829–6843. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2927213. [13] SMITH D R, YURDUSEVEN O, MANCERA L P, et al. Analysis of a waveguide-fed metasurface antenna[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2017, 8(5): 054048. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.054048. [14] SHLEZINGER N, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, IMANI M F, et al. Dynamic metasurface antennas for 6G extreme massive MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(2): 106–113. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000267. [15] KIMARYO S F and LEE K. Downlink beamforming for dynamic metasurface antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(7): 4745–4755. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3228272. [16] CHEN Guangyi, ZHANG Ruoyu, ZHANG Haiyang, et al. Energy-efficient beamforming for downlink multi-user systems with dynamic metasurface antennas[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2025, 29(2): 284–288. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2024.3513554. [17] YOU Li, XIONG Jiayuan, NG D W K, et al. Energy efficiency and spectral efficiency tradeoff in RIS-aided multiuser MIMO uplink transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1407–1421. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047474. [18] REZVANI M and ADVE R. Channel estimation for dynamic metasurface antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(6): 5832–5846. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3328496. [19] HUANG Wei, ZHANG Haiyang, SHLEZINGER N, et al. Joint microstrip selection and beamforming design for mmWave systems with dynamic metasurface antennas[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10096260. [20] YOU Li, XU Jie, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Energy efficiency maximization of massive MIMO communications with dynamic metasurface antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(1): 393–407. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3194070. [21] 高克, 张海洋, 王保云. 基于动态超表面天线的雷达通信一体化设计[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2023, 49(5): 946–952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2023.05.021.GAO Ke, ZHANG Haiyang, and WANG Baoyun. Beamforming design for dual-functional radar-communication systems with dynamic metasurface antennas[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2023, 49(5): 946–952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2023.05.021. [22] ZHANG Haiyang, SHLEZINGER N, GUIDI F, et al. Beam focusing for near-field multiuser MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 7476–7490. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3158894. [23] LI Yihan, GONG Shiqi, LIU Heng, et al. Near-field beamforming optimization for holographic XL-MIMO multiuser systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(4): 2309–2323. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3338737. [24] WANG Bowen, LI Hongyu, and CHENG Ziyang. Dynamic hybrid beamforming design for dual-function radar-communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(2): 2842–2847. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3312759. [25] 吴文俊, 唐波, 汤俊, 等. 杂波环境中雷达通信一体化系统波形设计算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 570–580. doi: 10.12000/JR22105.WU Wenjun, TANG Bo, TANG Jun, et al. Waveform design for dual-function radar-communication systems in clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 570–580. doi: 10.12000/JR22105. [26] SHEN Kaiming and YU Wei. Fractional programming for communication systems-part I: Power control and beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(10): 2616–2630. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2812733. [27] PONTRYAGIN L S. Smooth manifolds and their applications in homotopy theory[J]. American Mathematical Society Translations, Ser, 1976, 2: 1, 114. [28] BERTSEKAS D P. Nonlinear Programming[M]. 3rd ed. Belmont, USA: Athena Scientific, 2016: 120–125. [29] ABSIL P A, MAHONY R, and SEPULCHRE R. Optimization Algorithms on Matrix Manifolds[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2008: 105–106. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: