-
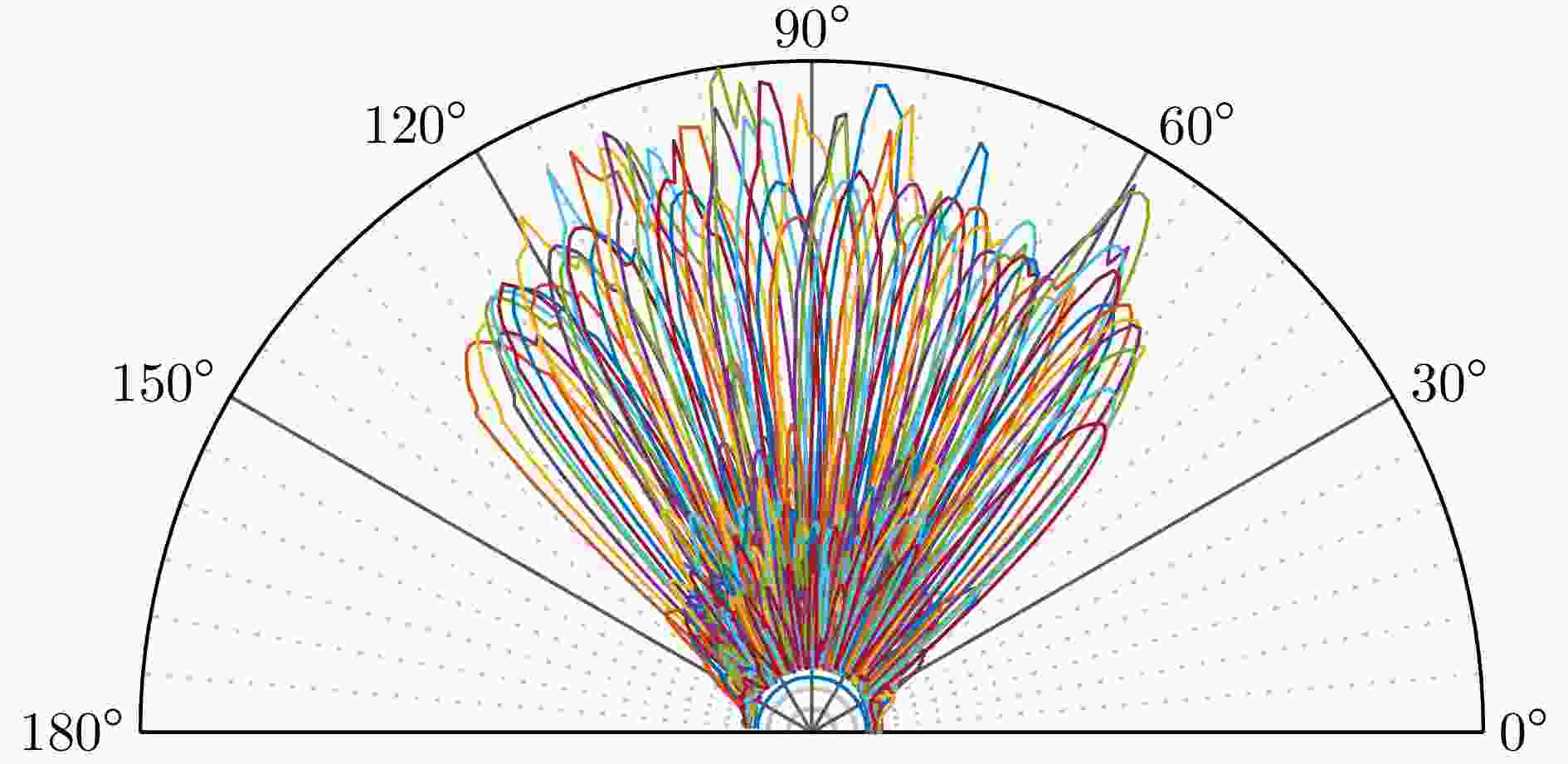
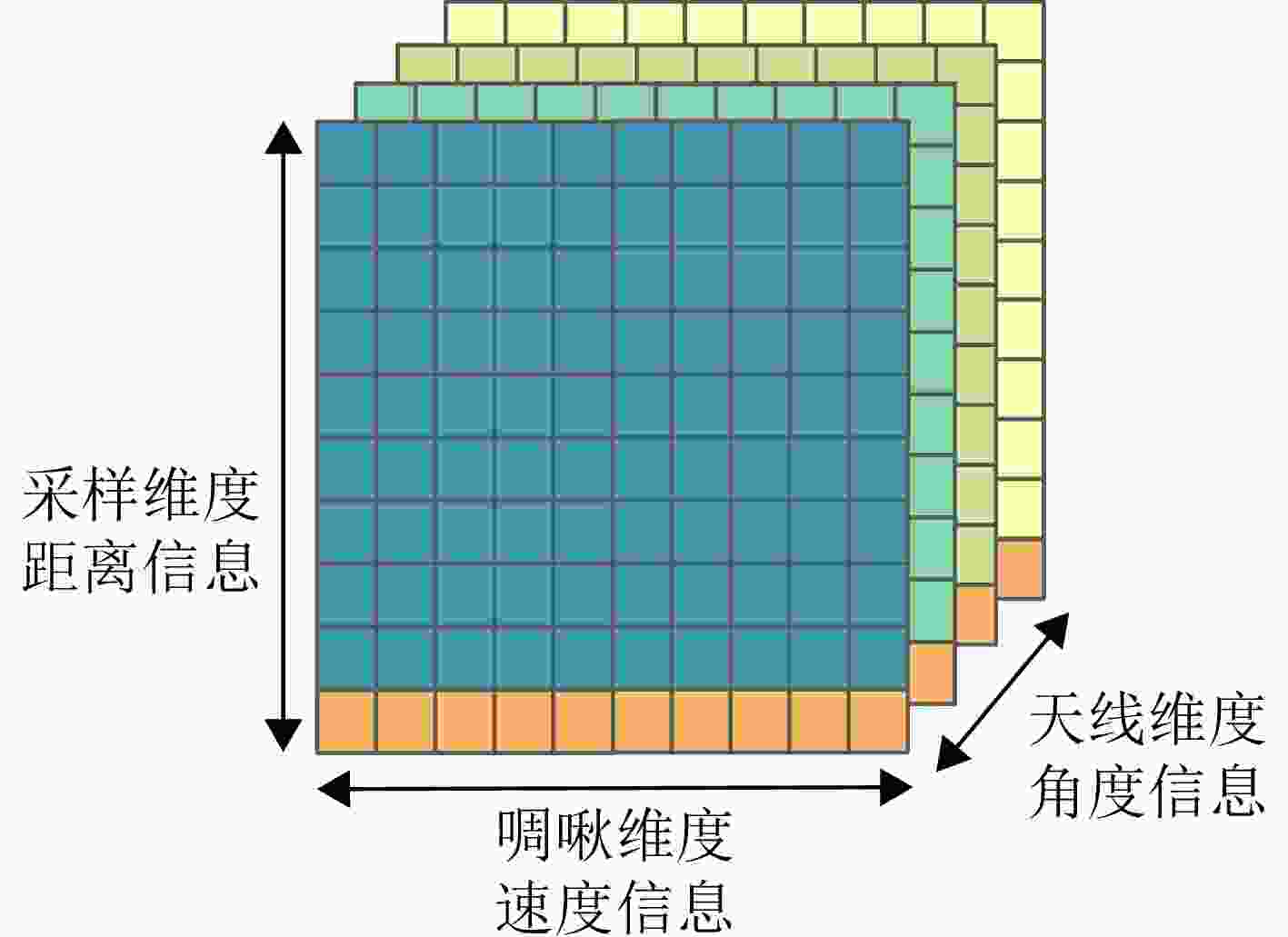
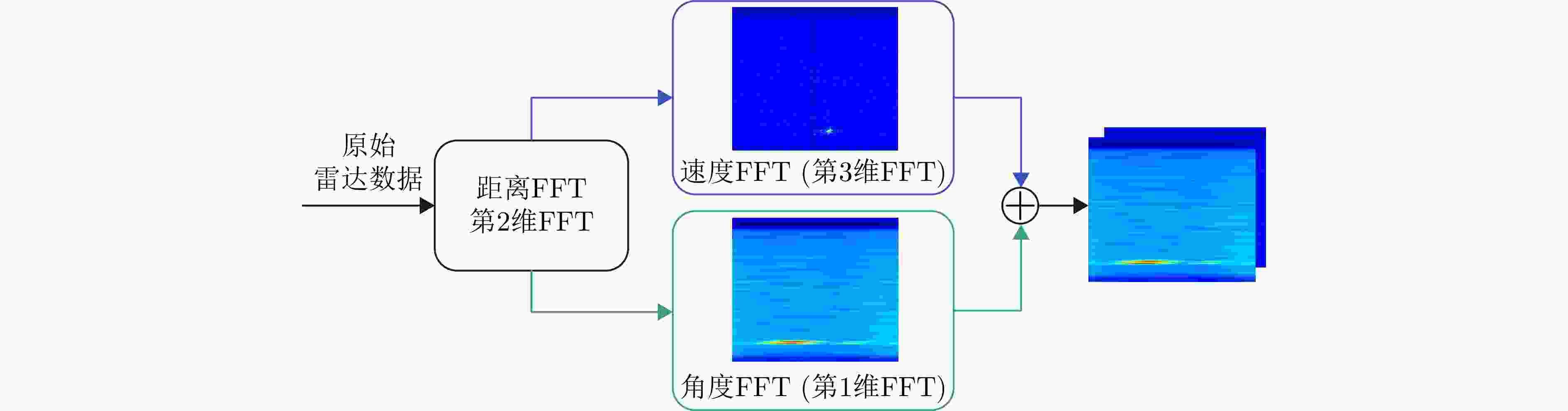
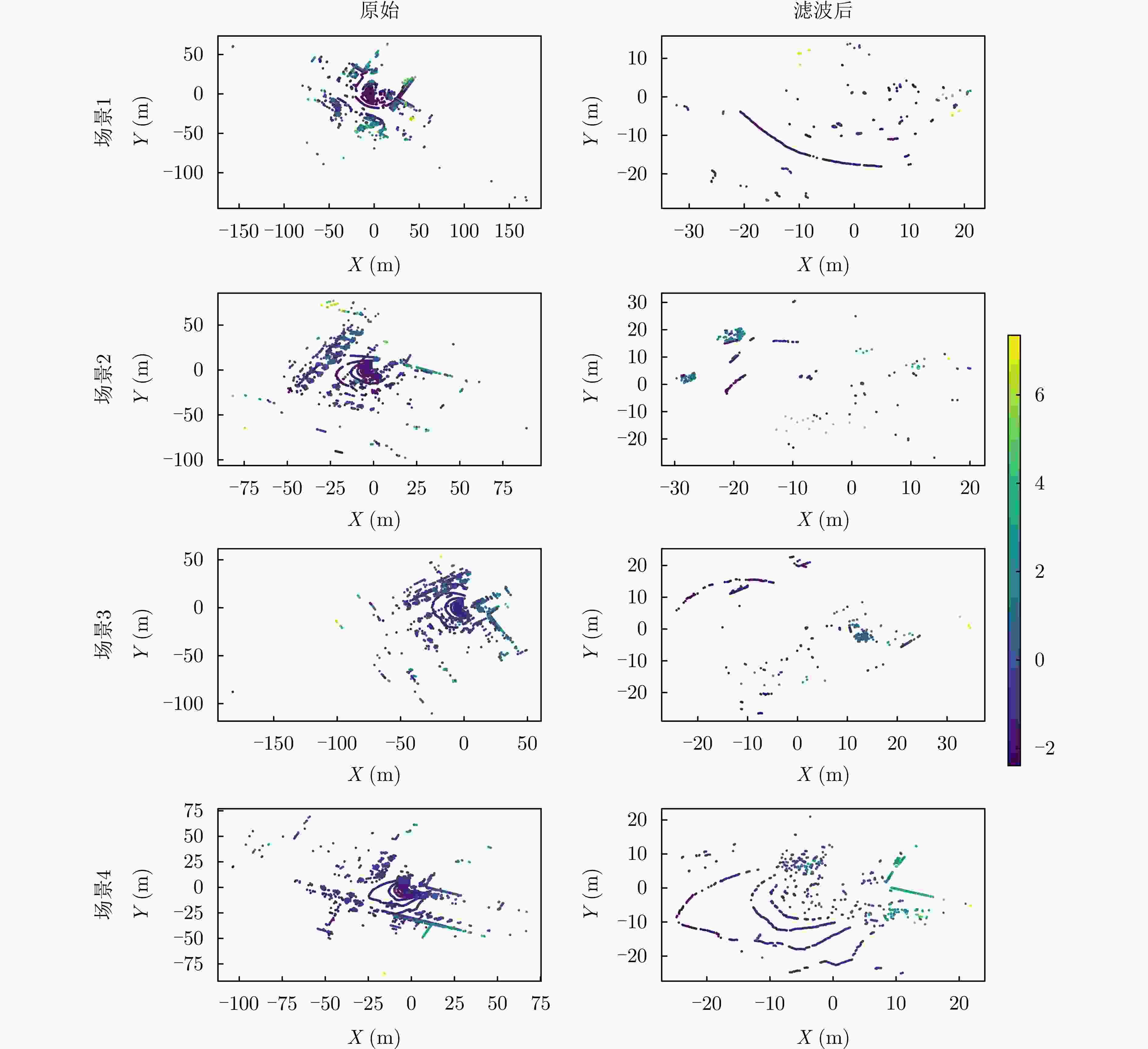
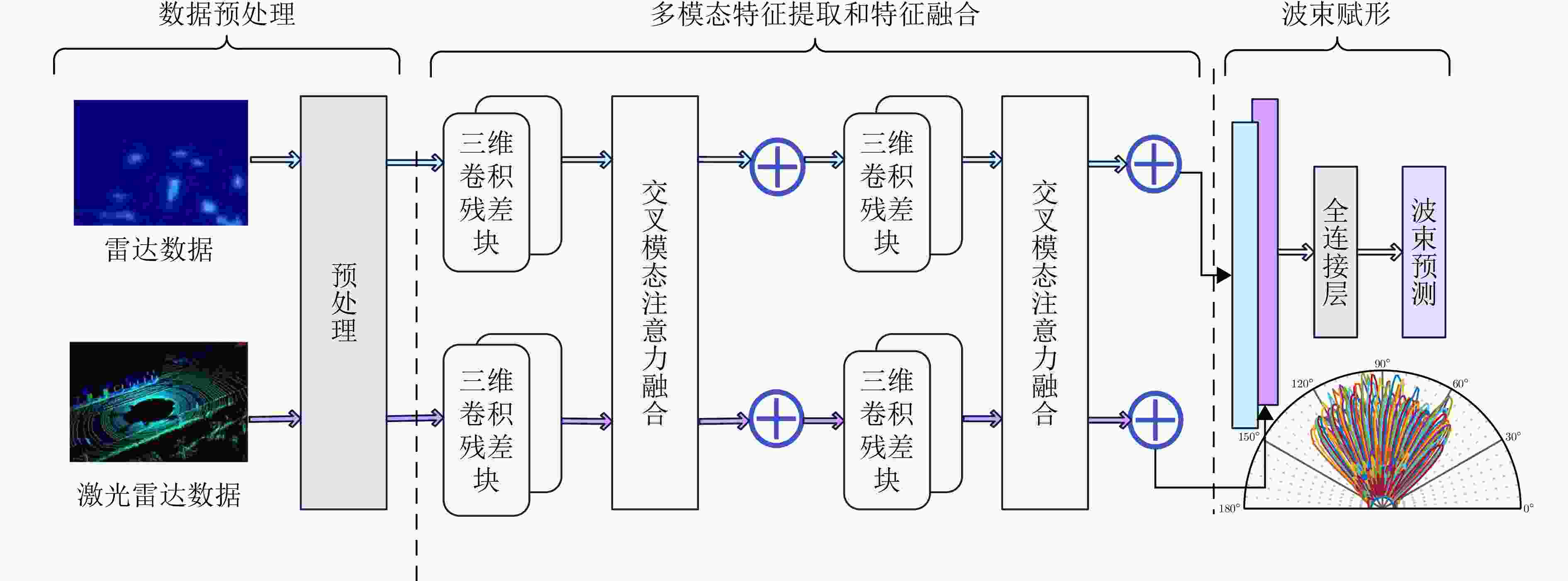
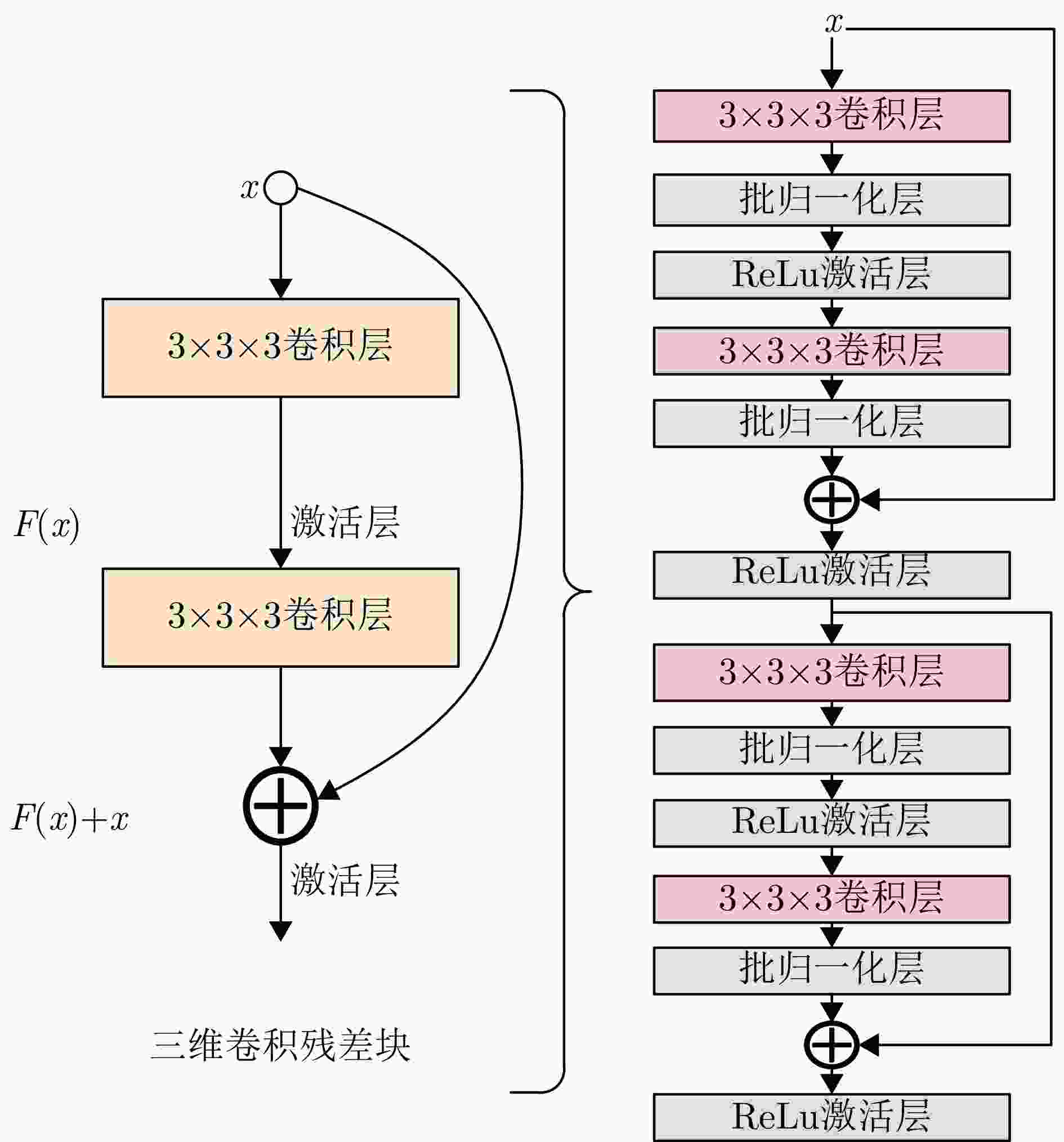
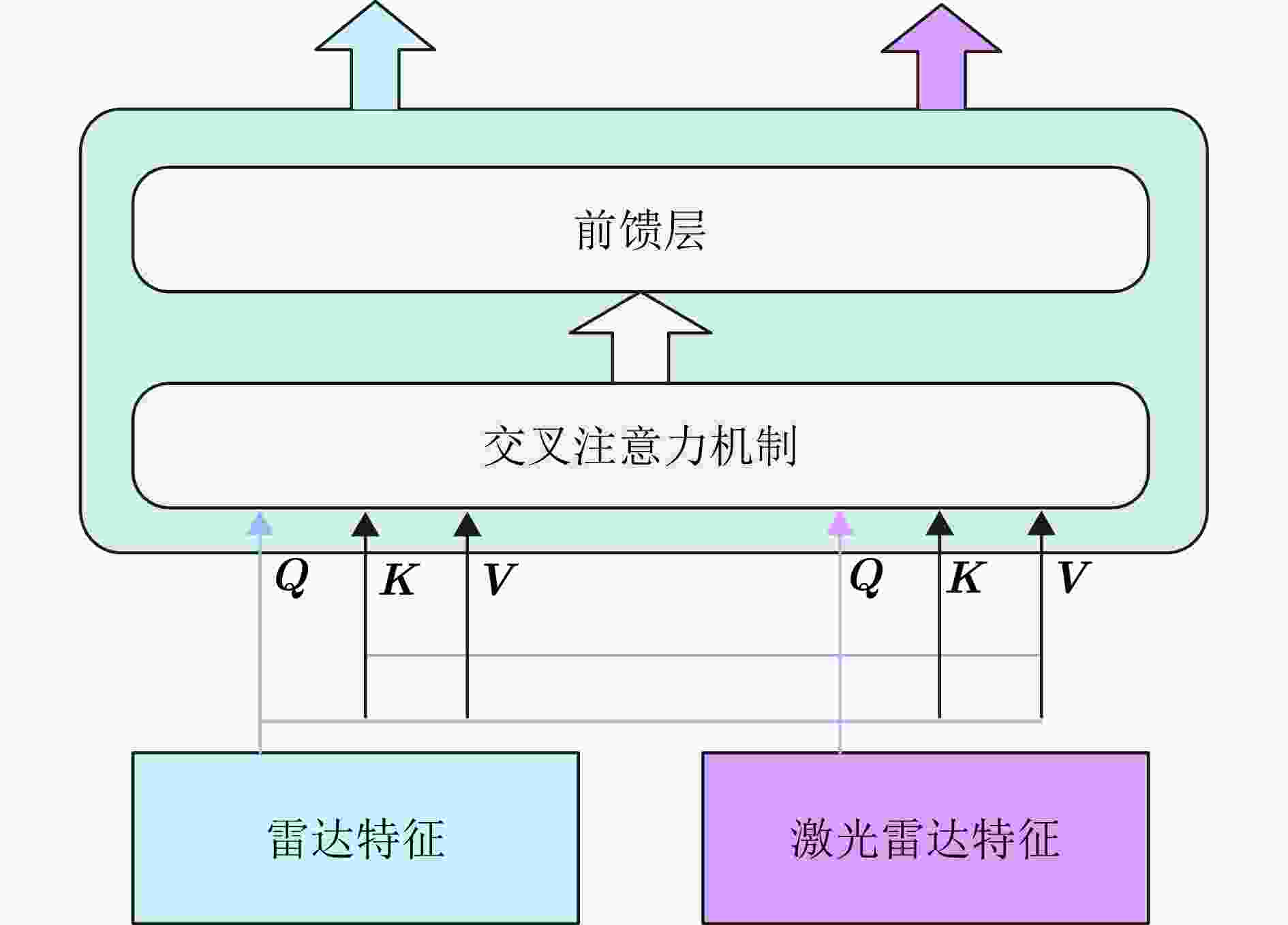
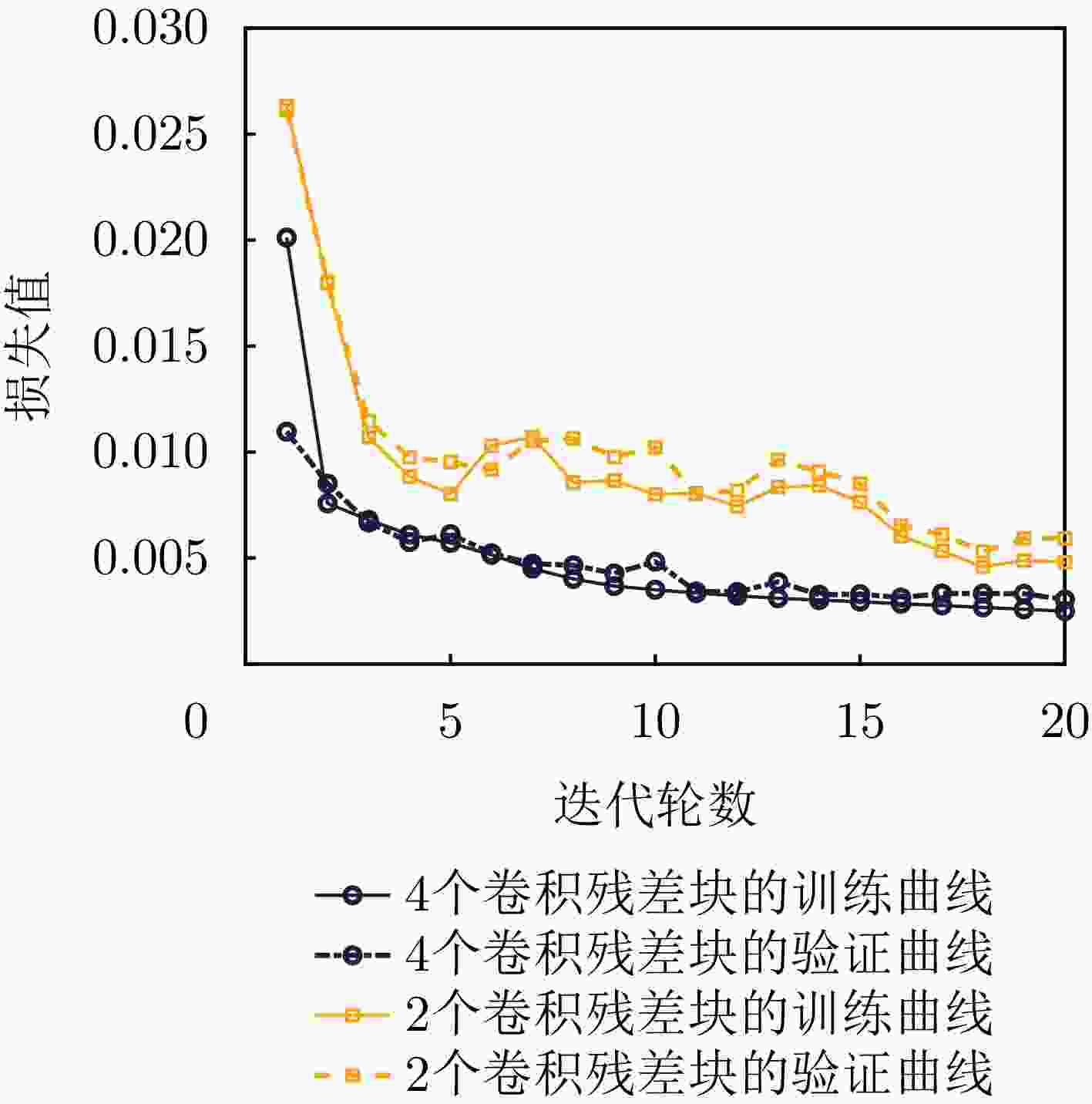
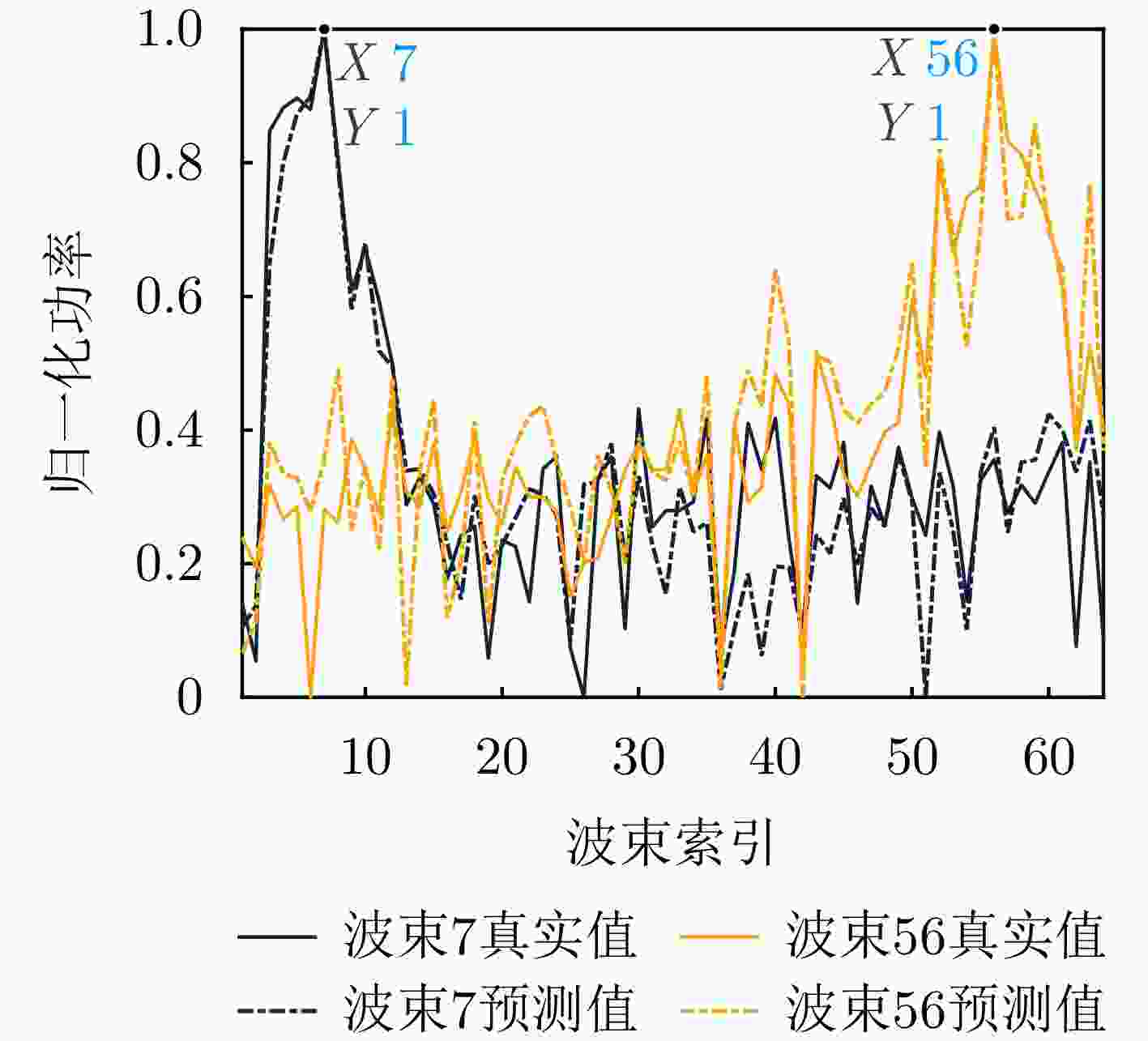
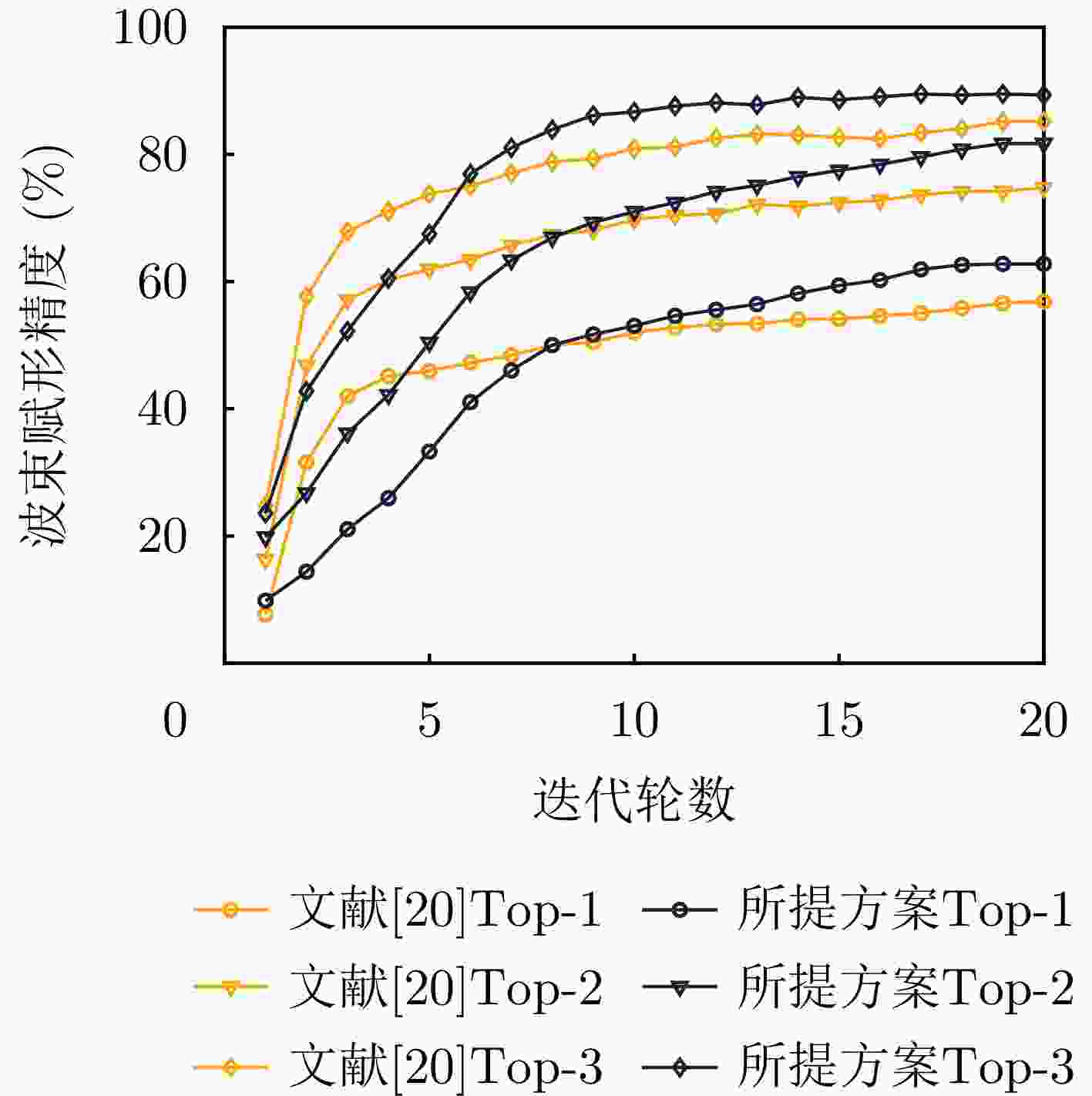
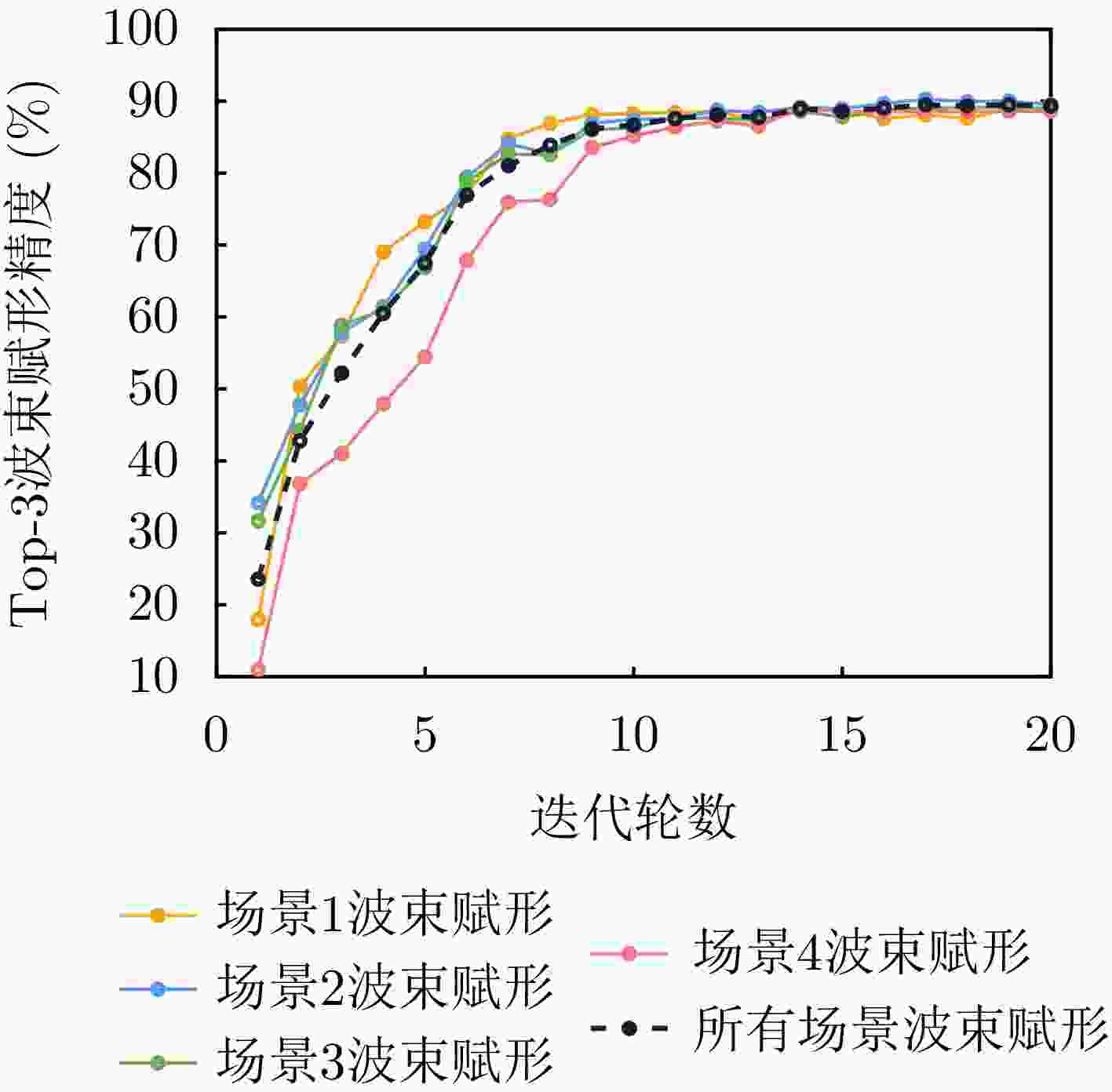
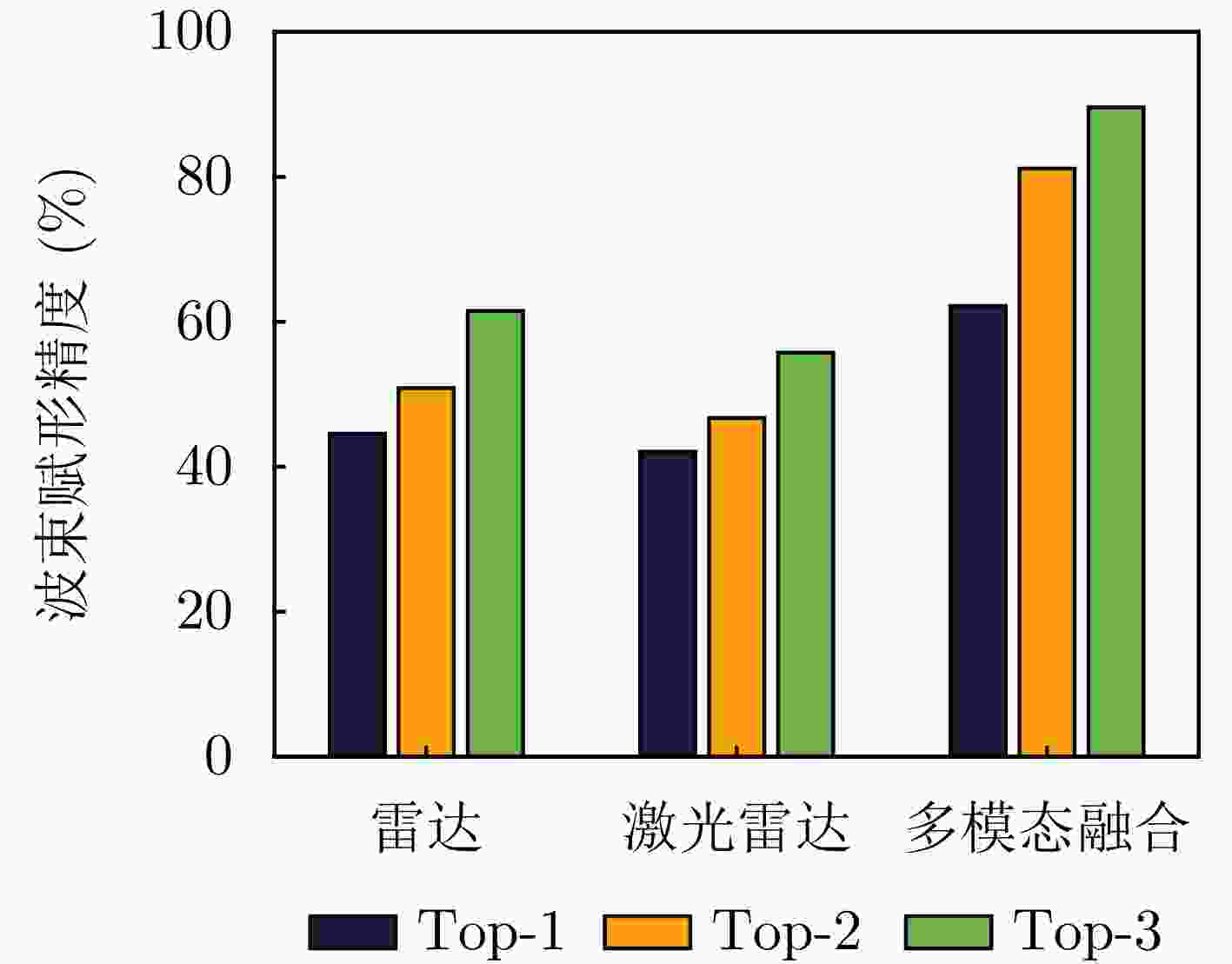
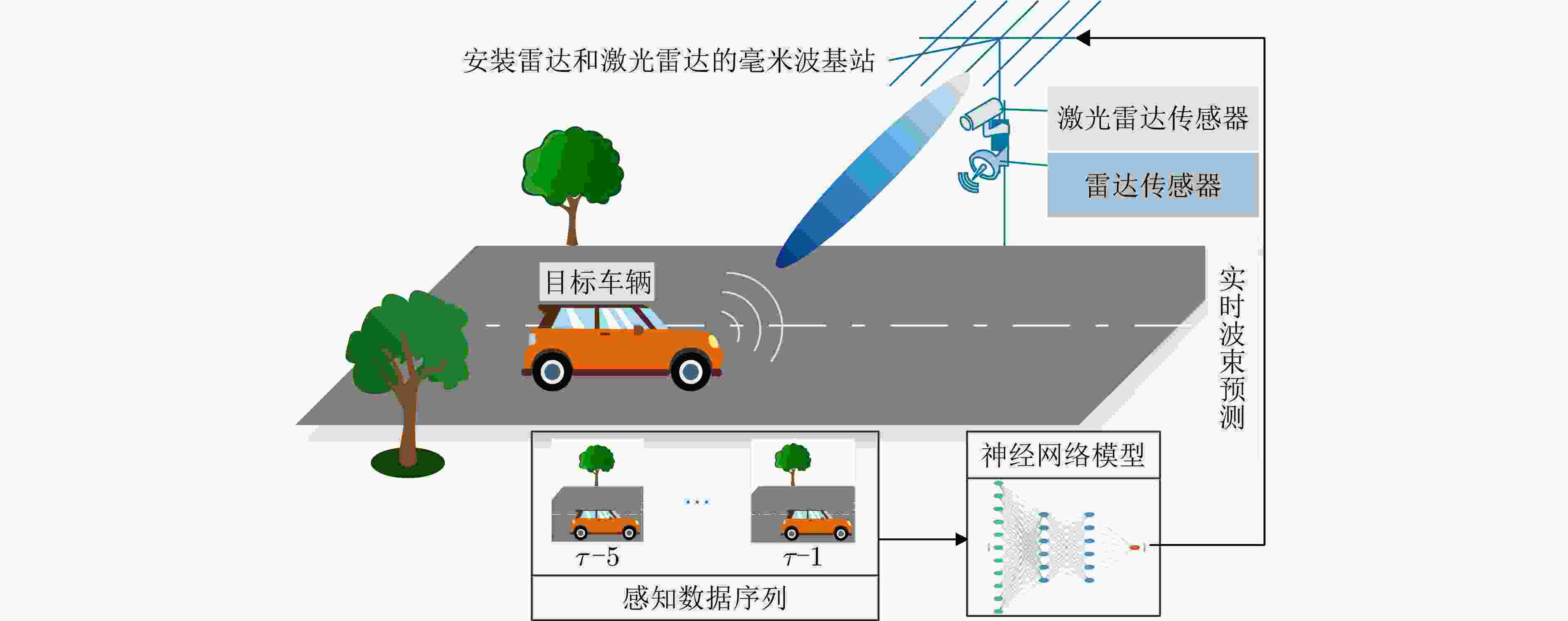
摘要: 波束赋形技术通过向特定方向发射信号,提高了接收信号的功率。然而,在高速动态的车辆网络场景下,频繁的信道状态更新与波束调整导致系统开销过大;波束与用户位置难以实时对齐,易出现错位现象,影响通信稳定性;复杂路况中的遮挡和信道衰落进一步限制了波束赋形的效果。为了解决上述问题,该文提出了一种基于卷积神经网络和注意力机制模型的多模态特征融合波束赋形方法,以实现感知辅助的高可靠通信。模型首先对传感器采集的雷达、激光雷达数据分别定制数据转换和标准化策略,解决数据异构问题。然后使用三维卷积残差块提取多层次高阶多模态特征后,利用注意力机制模型融合特征并预测最佳波束,实现通信性能的优化。实验结果表明,该文所提方法在高速场景下可达到接近90%的平均Top-3波束预测精度,相比单模态方案性能显著提升,验证了其在提升通信性能和可靠性方面的优越性。Abstract: Beamforming enhances the received signal power by transmitting signals in specific directions. However, in high-speed and dynamic vehicular network scenarios, frequent channel state updates and beam adjustments impose substantial system overhead. Furthermore, real-time alignment between the beam and user location becomes challenging, leading to potential misalignment that undermines communication stability. Obstructions and channel fading in complex road environments further constrain the effectiveness of beamforming. To address these challenges, this study proposes a multimodal feature fusion beamforming method based on a convolutional neural network and an attention mechanism model to achieve sensor-assisted high-reliability communication. Data heterogeneity is solved by customizing data conversion and standardization strategies for radar and lidar data collected by sensors. Three-dimensional convolutional residual blocks are employed to extract multimodal features, while the cross-attention mechanism integrates integrate these features for beamforming. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves an average Top-3 accuracy of nearly 90% in high-speed environments, which is substantially improved compared with the single-modal beamforming scheme.
-
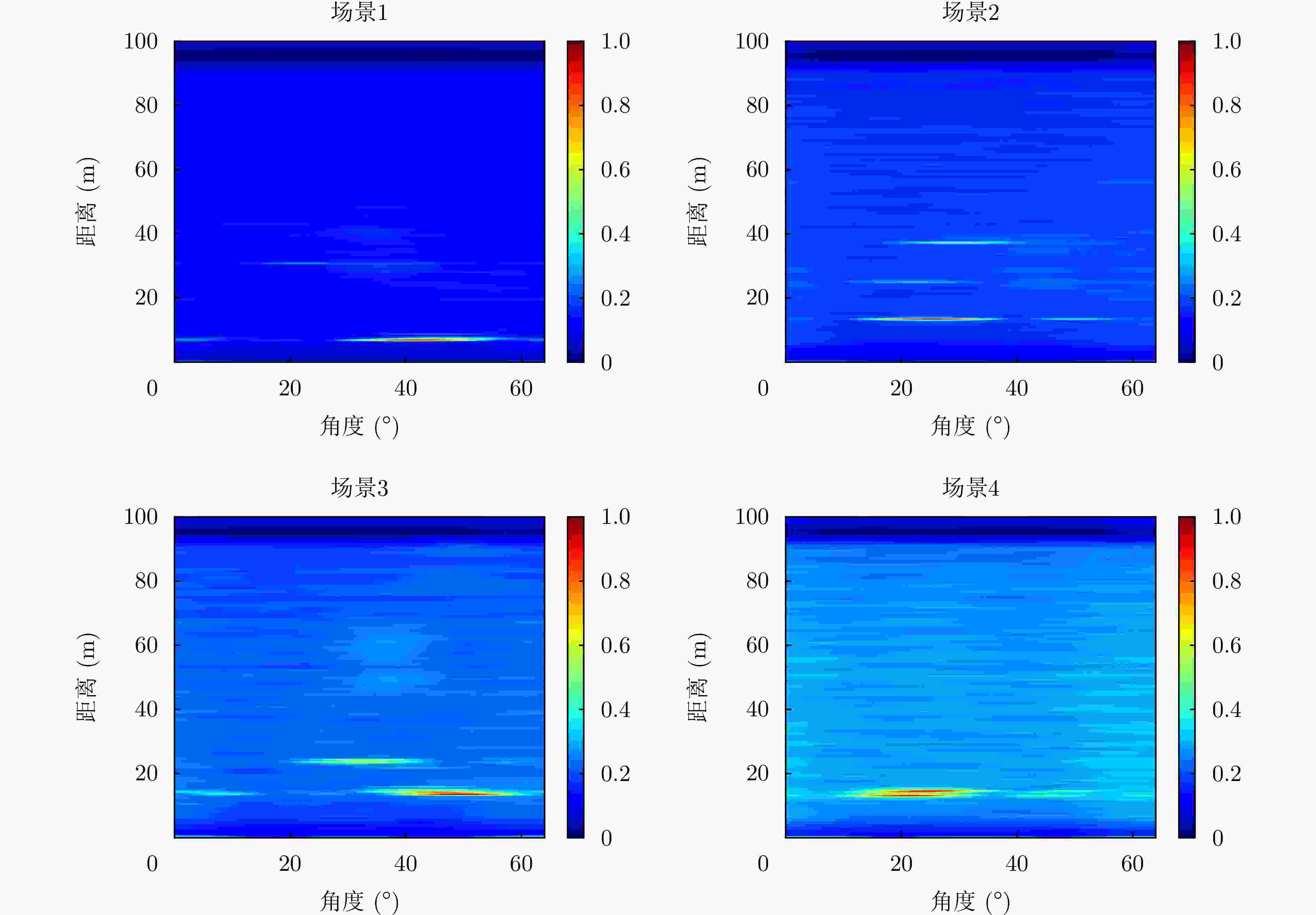
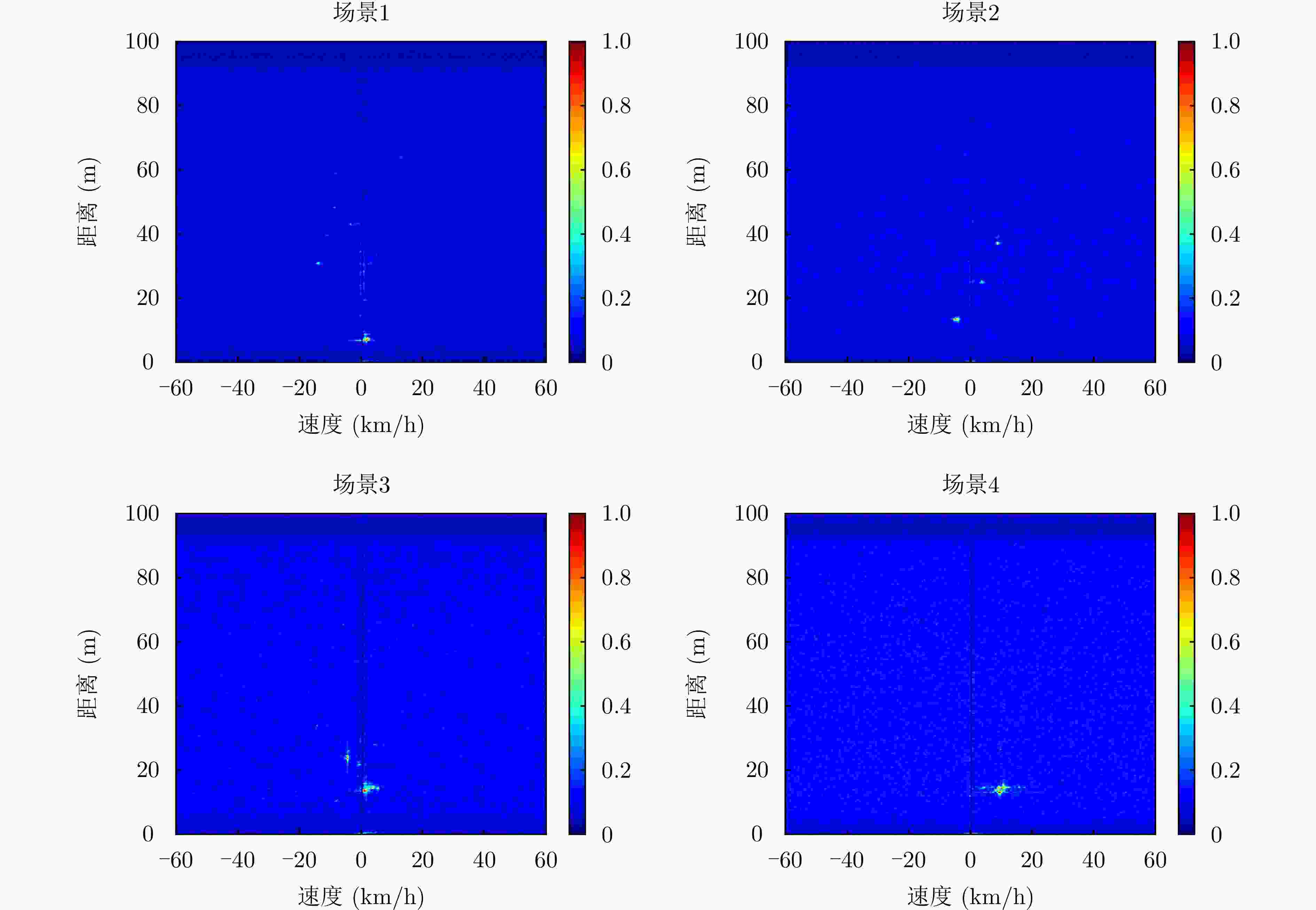
表 1 数据集描述
Table 1. Dataset description
场景 采样数 采集时间 场景1 3506 白天 场景2 3235 白天 场景3 3981 夜间 场景4 4431 夜间 -
[1] 王明哲. 5G移动通信发展趋势及关键技术研究[J]. 智慧中国, 2022(2): 68–69.WANG Mingzhe. Research on the development trend and key technologies of 5G mobile communication[J]. Wisdom China, 2022(2): 68–69. [2] CHEN Wanshi, LIN Xingqin, LEE J, et al. 5G-advanced toward 6G: Past, present, and future[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(6): 1592–1619. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3274037. [3] ZHANG Zhengquan, XIAO Yue, MA Zheng, et al. 6G wireless networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(3): 28–41. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2921208. [4] LIU Fan, ZHENG Le, CUI Yuanhao, et al. Seventy years of radar and communications: The road from separation to integration[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2023, 40(5): 106–121. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2023.3272881. [5] NIE Jiali, CUI Yuanhao, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Near-field beam training for extremely large-scale MIMO based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(1): 352–362. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3462960. [6] WEI Xiuhong, DAI Linglong, ZHAO Yajun, et al. Codebook design and beam training for extremely large-scale RIS: Far-field or near-field[J]. China Communications, 2022, 19(6): 193–204. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2022.06.015. [7] NOH S, ZOLTOWSKI M D, and LOVE D J. Multi-resolution codebook and adaptive beamforming sequence design for millimeter wave beam alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(9): 5689–5701. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2713357. [8] ABDELREHEEM A, MOHAMED E M, and ESMAIEL H. Location-based millimeter wave multi-level beamforming using compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(1): 185–188. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2766629. [9] CUI Yuanhao, LIU Fan, JING Xiaojun, et al. Integrating sensing and communications for ubiquitous IoT: Applications, trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(5): 158–167. doi: 10.1109/MNET.010.2100152. [10] LU Shihang, LIU Fan, LI Yunxin, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Recent advances and ten open challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(11): 19094–19120. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3361173. [11] CUI Yuanhao, CAO Xiaowen, ZHU Guangxu, et al. Edge perception: Intelligent wireless sensing at network edge[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2025, 63(3): 166–173. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2300660. [12] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, LI Ang, et al. MU-MIMO communications with MIMO radar: From co-existence to joint transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2755–2770. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2803045. [13] LIU Fan, YUAN Weijie, MASOUROS C, et al. Radar-assisted predictive beamforming for vehicular links: Communication served by sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7704–7719. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3015735. [14] NIE Jiali, ZHOU Quan, MU Junsheng, et al. Vision and radar multimodal aided beam prediction: Facilitating metaverse development[C]. The 2nd Workshop on Integrated Sensing and Communications for Metaverse, Helsinki, Finland, 13–18. doi: 10.1145/3597065.3597449. [15] LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, MASOUROS C, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Toward dual-functional wireless networks for 6G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1728–1767. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3156632. [16] VA V, CHOI J, SHIMIZU T, et al. Inverse multipath fingerprinting for millimeter wave V2I beam alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 4042–4058. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2787627. [17] XU Weihua, GAO Feifei, JIN Shi, et al. 3D scene-based beam selection for mmWave communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(11): 1850–1854. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3005983. [18] YING Ziqiang, YANG Haojun, GAO Jia, et al. A new vision-aided beam prediction scheme for mmWave wireless communications[C]. The 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2020: 232–237. doi: 10.1109/ICCC51575.2020.9344988. [19] SHEN L H, CHANG Tingwei, FENG K T, et al. Design and implementation for deep learning based adjustable beamforming training for millimeter wave communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2413–2427. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3058715. [20] NIE Jiali, CUI Yuanhao, YU Tiankuo, et al. An efficient nocturnal scenarios beamforming based on multi-modal enhanced by object detection[C]. 2023 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2023: 515–520. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps58843.2023.10464587. [21] SHI Binpu, LI Min, ZHAO Mingmin, et al. Multimodal deep learning empowered millimeter-wave beam prediction[C]. The 2024 IEEE 99th Vehicular Technology Conference, Singapore, Singapore, 2024: 1–6, doi: 10.1109/VTC2024-Spring62846.2024.10683225. [22] GU J, SALEHI B, ROY D, et al. Multimodality in mmWave MIMO beam selection using deep learning: Datasets and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(11): 36–41. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.002.2200028. [23] CHARAN G, OSMAN T, HREDZAK A, et al. Vision-position multi-modal beam prediction using real millimeter wave datasets[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 2022: 2727–2731. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771835. [24] CUI Yuanhao, NIE Jiali, CAO Xiaowen, et al. Sensing-assisted high reliable communication: A transformer-based beamforming approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2024, 18(5): 782–795. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2024.3405859. [25] ALKHATEEB A, CHARAN G, OSMAN T, et al. DeepSense 6G: A large-scale real-world multi-modal sensing and communication dataset[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(9): 122–128. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.006.2200730. [26] DEMIRHAN U and ALKHATEEB A. Radar aided 6G beam prediction: Deep learning algorithms and real-world demonstration[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 2022: 2655–2660. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771564. [27] ZHOU Bo, XIE Jiapeng, PAN Yan, et al. MotionBEV: Attention-aware online LiDAR moving object segmentation with bird’s eye view based appearance and motion features[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(12): 8074–8081. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3325687. [28] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [29] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [30] HAN Dongchen, PAN Xuran, HAN Yizeng, et al. FLatten transformer: Vision transformer using focused linear attention[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 5938–5948. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00548. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: