Dual Function Radar and Communication Waveform Design Based on Sub-pulse Hybrid Modulation
-
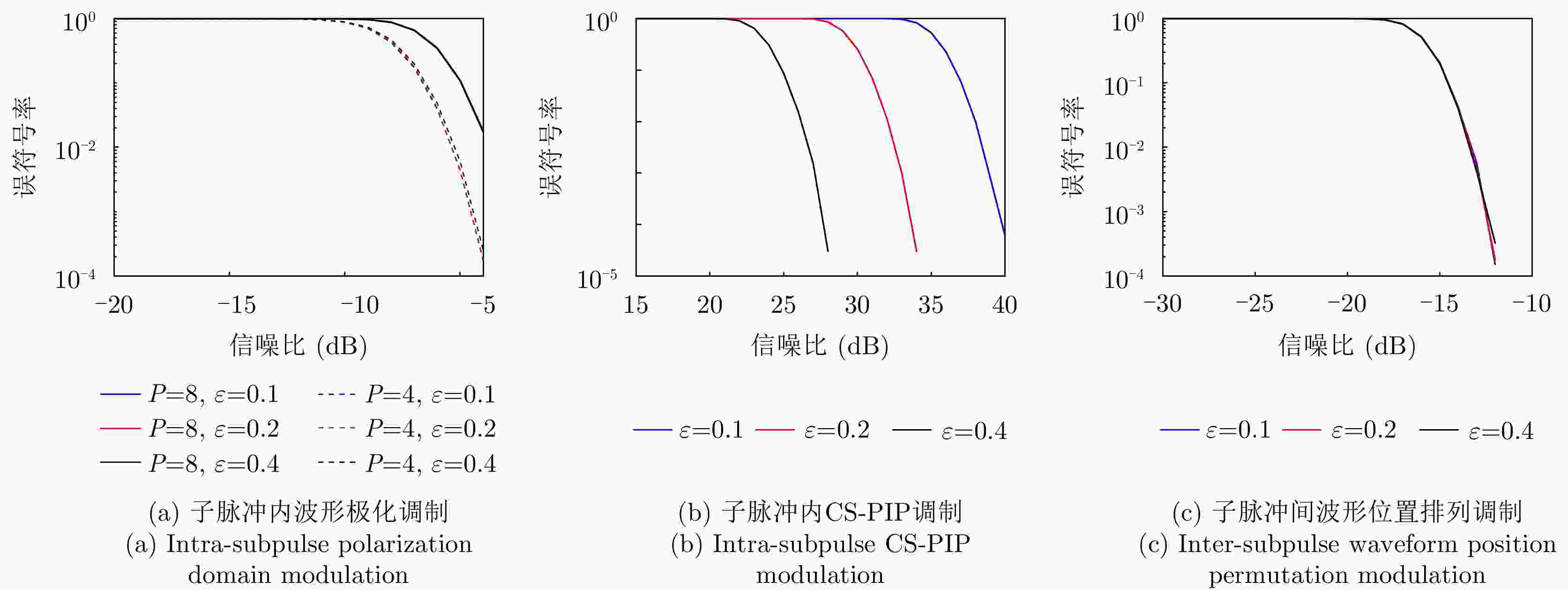
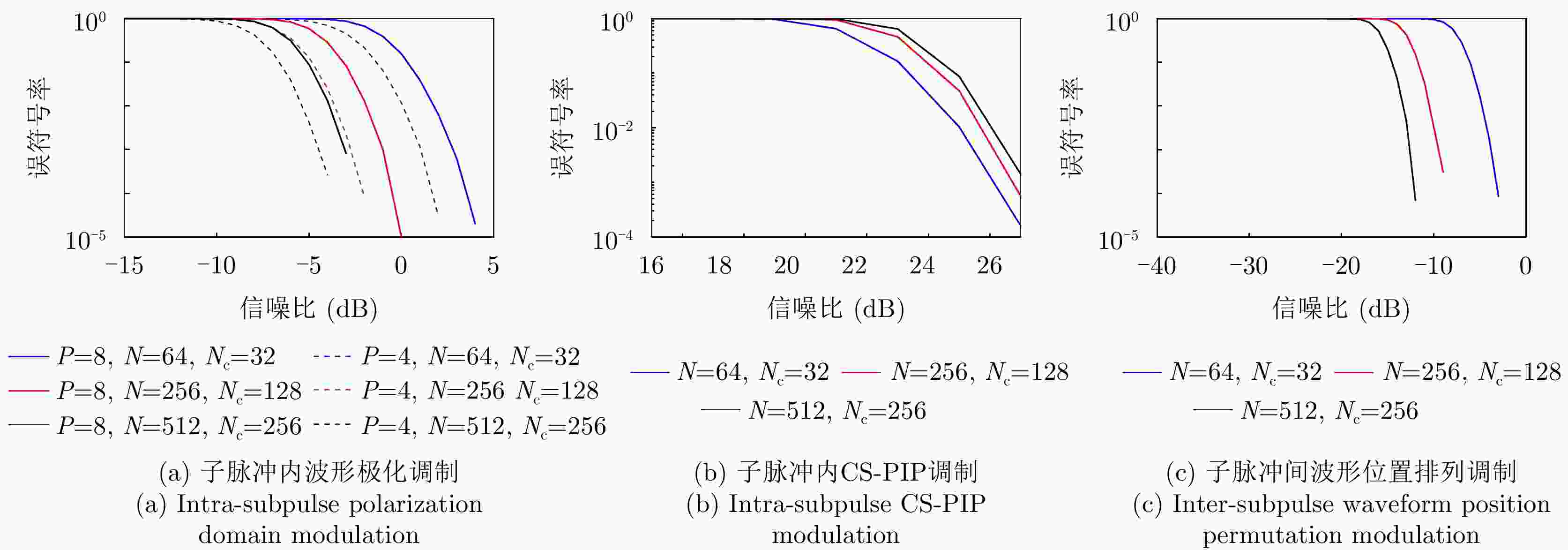
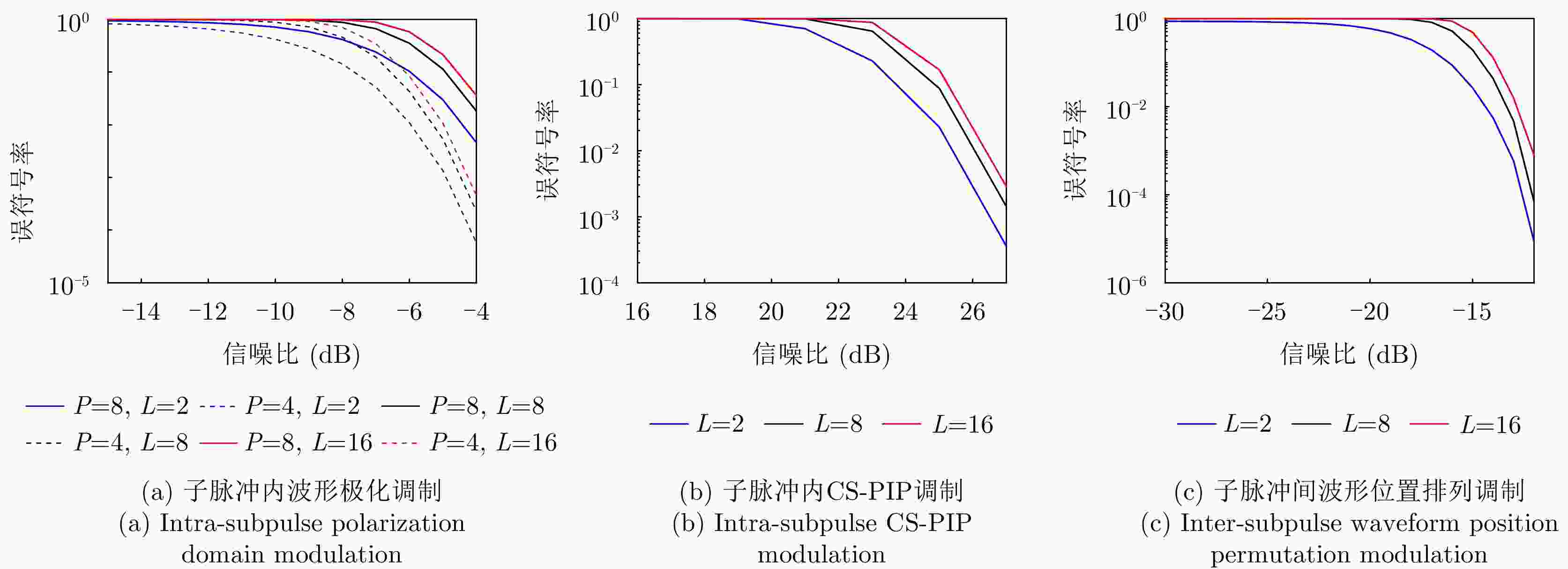
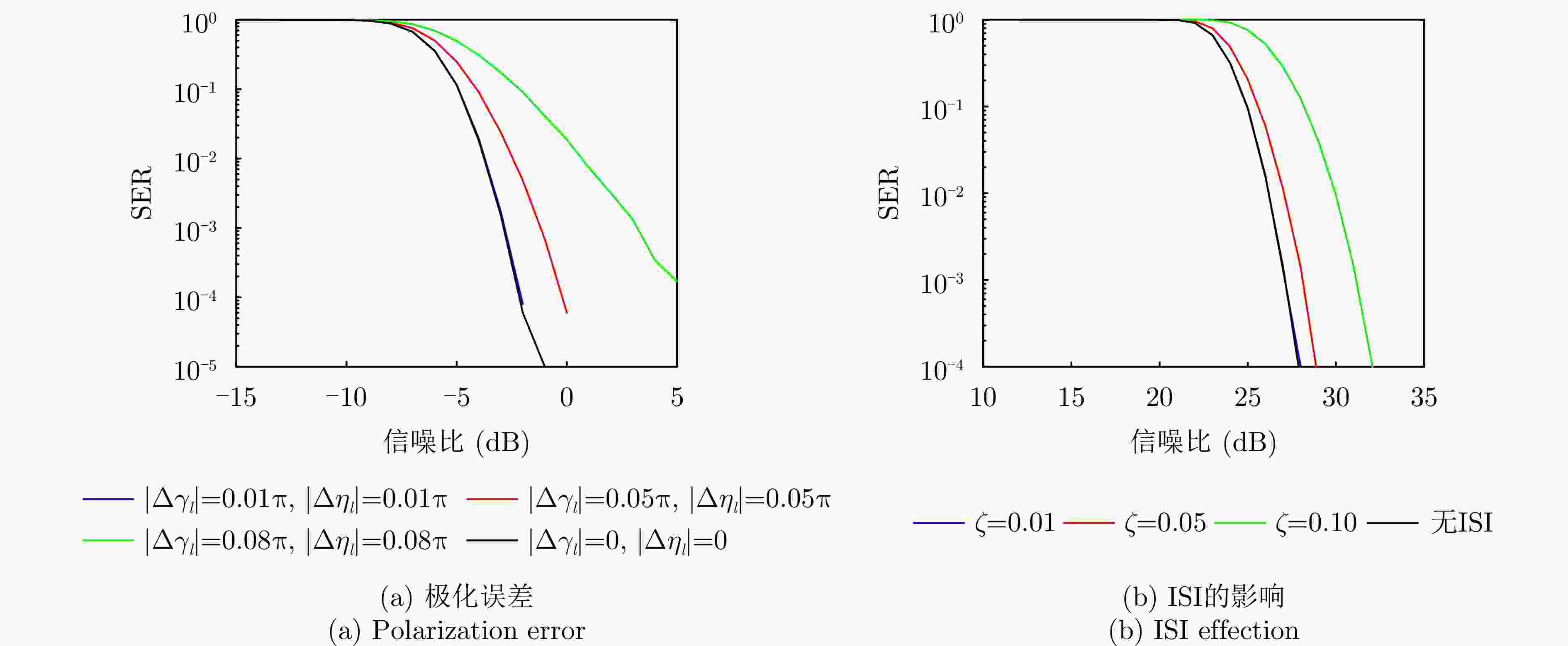
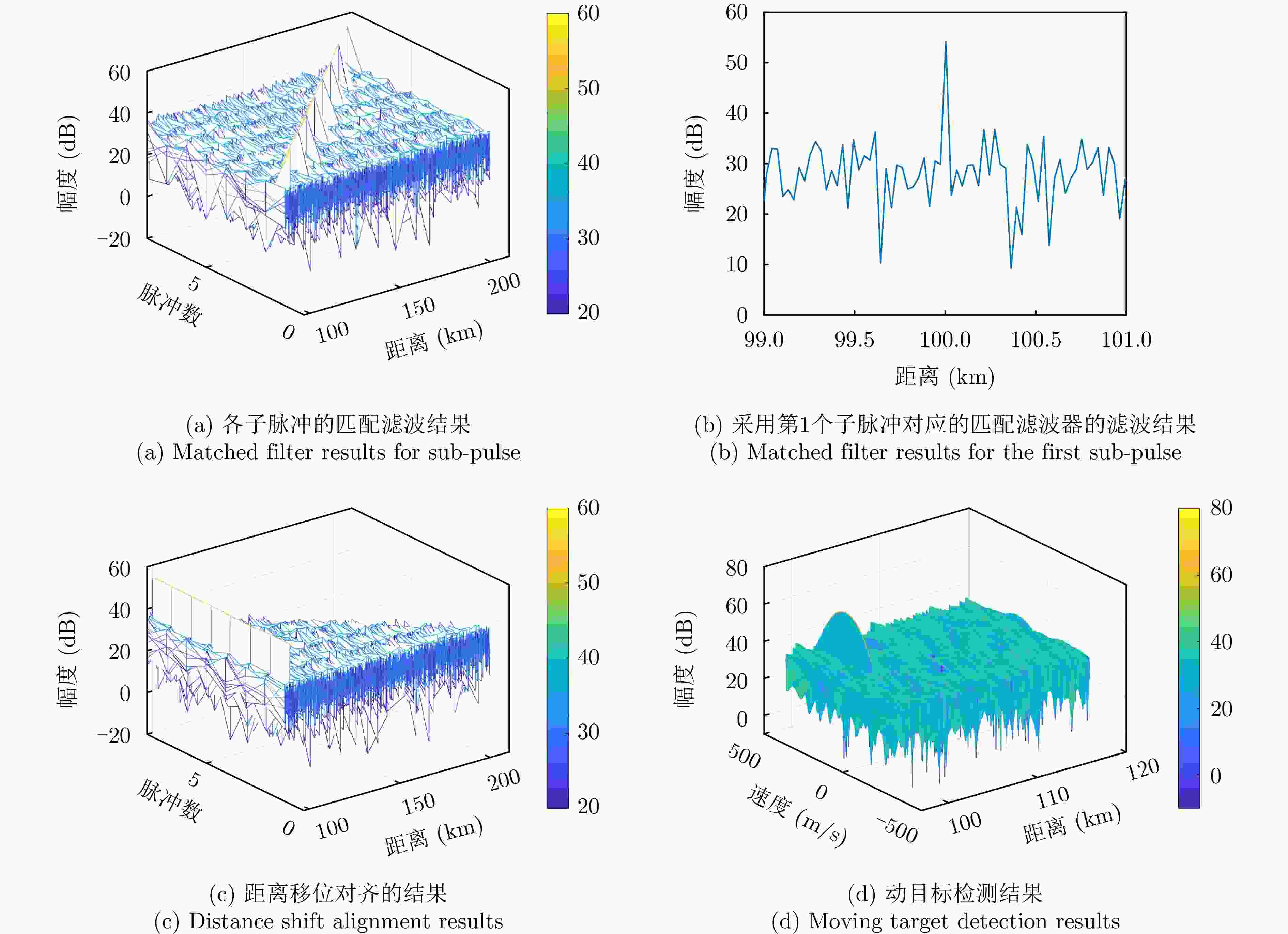
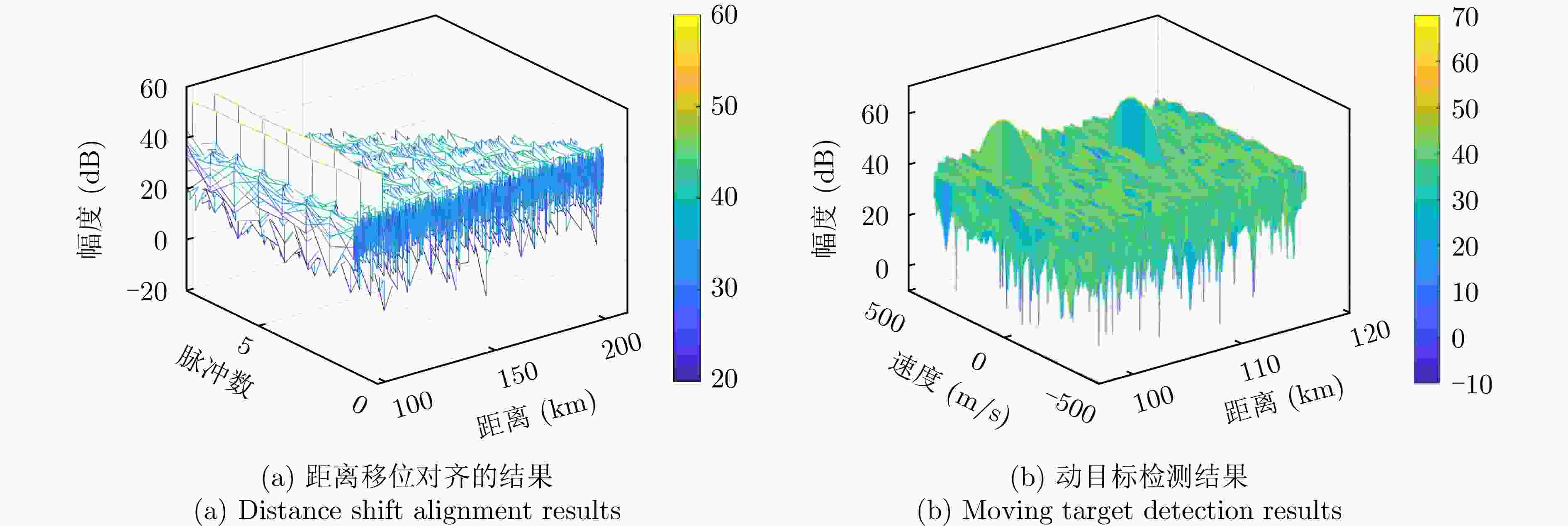
摘要: 针对以雷达探测为首要功能的探通一体(DFRC)波形设计中通信速率低的问题,该文提出了一种基于子脉冲混合调制(SHM)的探通一体波形设计方法,利用波形子脉冲内/间时域、频域和极化域资源进行多维调制,实现了通信速率的有效提升。构建了以最小化正交波形簇自/互相关函数的峰值旁瓣电平(PSL)为准则,考虑SHM信息调制约束和波形恒模约束的一体化波形设计优化问题,并提出了频域主分量最小化(SMM)算法快速求解上述非凸优化问题。此外,提出了一种基于单脉冲的探通一体回波处理方法,使模糊函数零延时截线的第1个零点处多普勒频率变为传统波形的L(子脉冲数)倍,保证了一体化波形的高多普勒容忍度,实现了对高速目标的有效探测。Abstract: To address the low data rate issue in the design of Dual-Function Radar-Communication (DFRC) waveforms with radar detection as the primary function, this paper proposes an information modulation method for multiple sub-pulse structure waveforms called Sub-pulse Hybrid Modulation (SHM). The proposed SHM method utilizes time-, spectral-, and polarization-domain features from inter-subpulse and intra-subpulse sources to convey information. The DFRC waveform design problem is formulated based on minimizing cross- and auto-correlation Peak Sidelobe Levels (PSL), while considering constant envelope and SHM constraints. To tackle the resulting nonconvex and nondeterministic polynomial-hard optimization problem, the Spectral Majorization Minimization (SMM) algorithm is employed to monotonically decrease the objective function value. Furthermore, this paper explores an echo processing method that makes the Doppler frequency at the first zero point of the zero-delay intercept of the fuzzy function $ L - 1 $ times higher than that of the conventional waveform, where L is the number of sub-pulses. This enhancement ensures high Doppler tolerance for the DFRC waveform and enables effective detection of high-speed targets.
-
表 1 信息解调方法步骤总结
Table 1. Summary of information demodulation methods
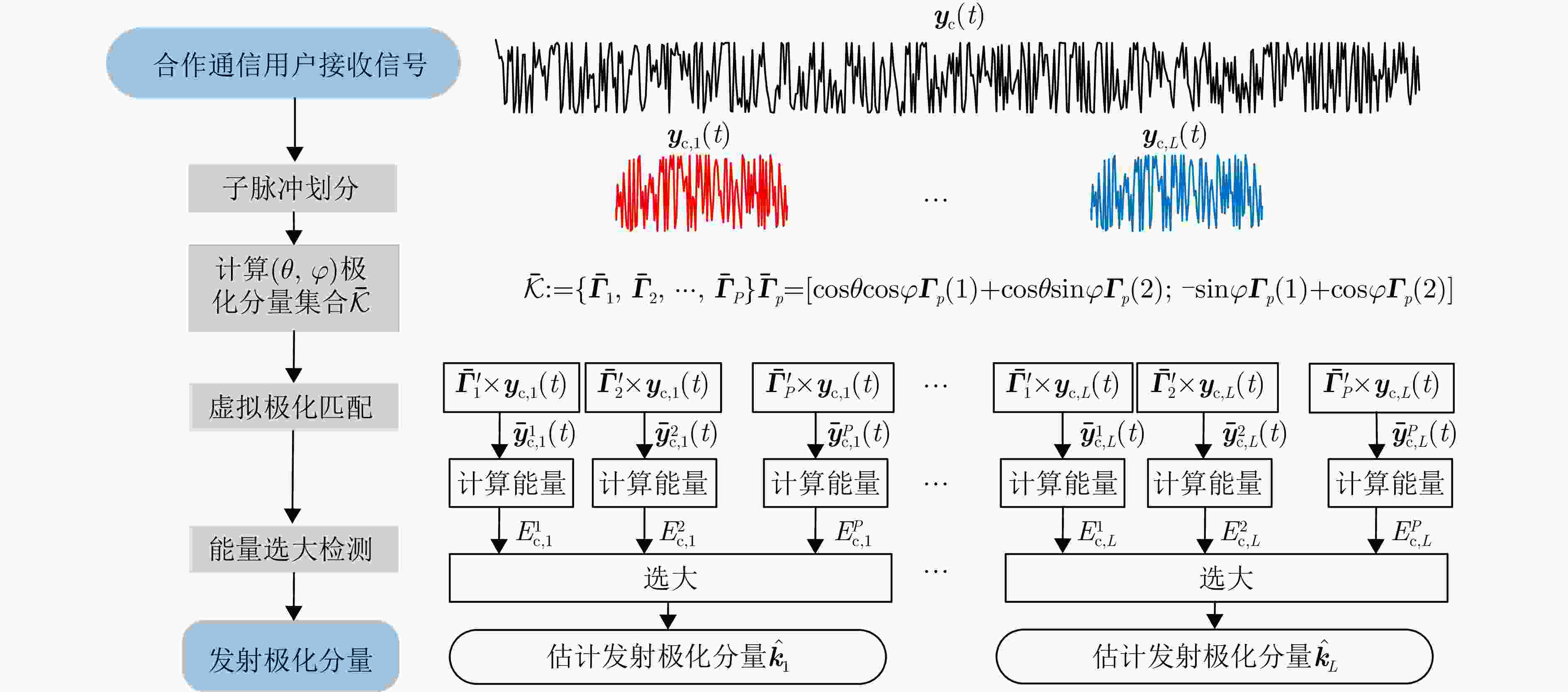
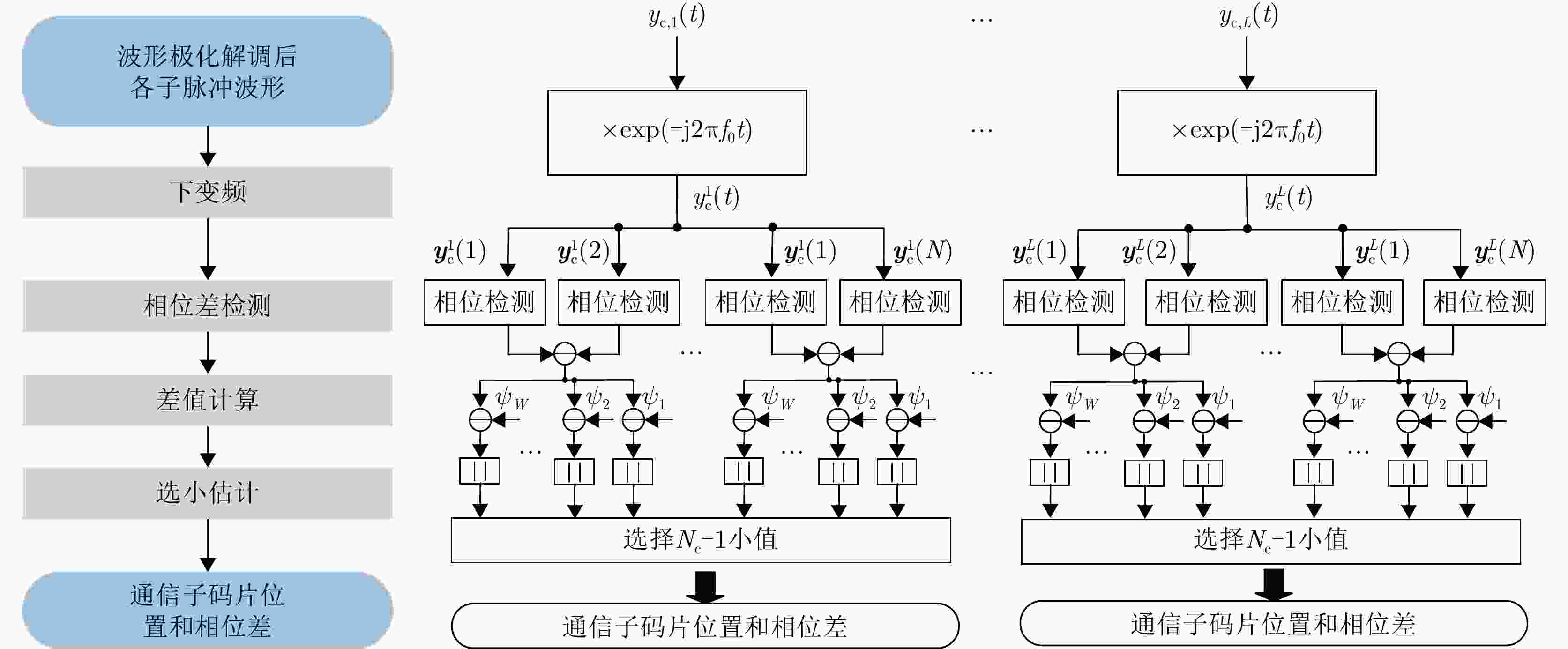
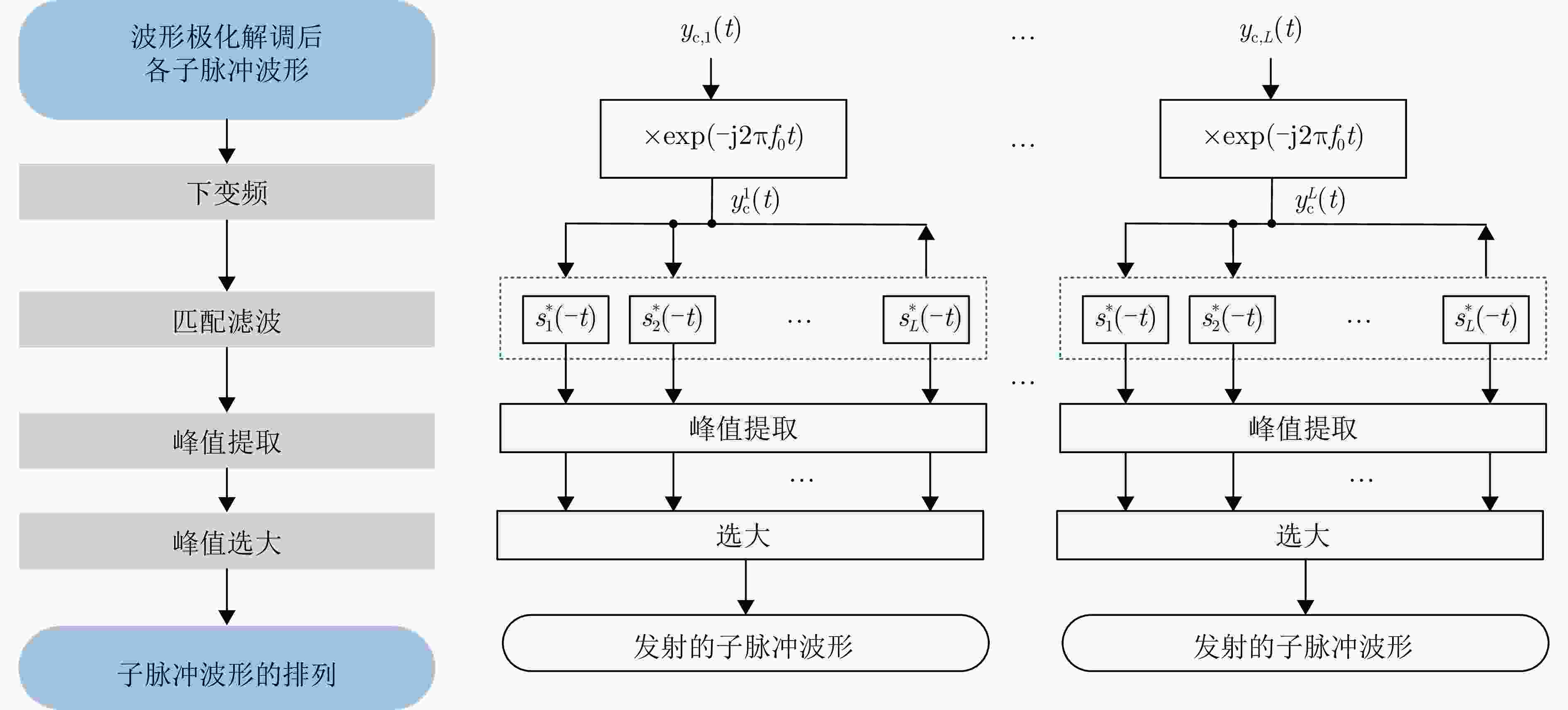
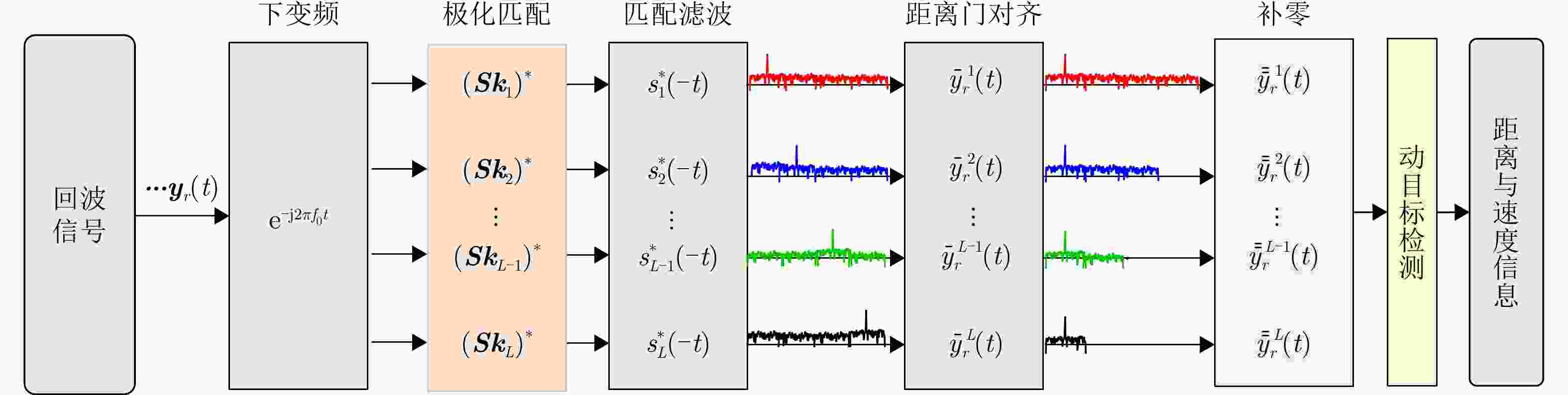
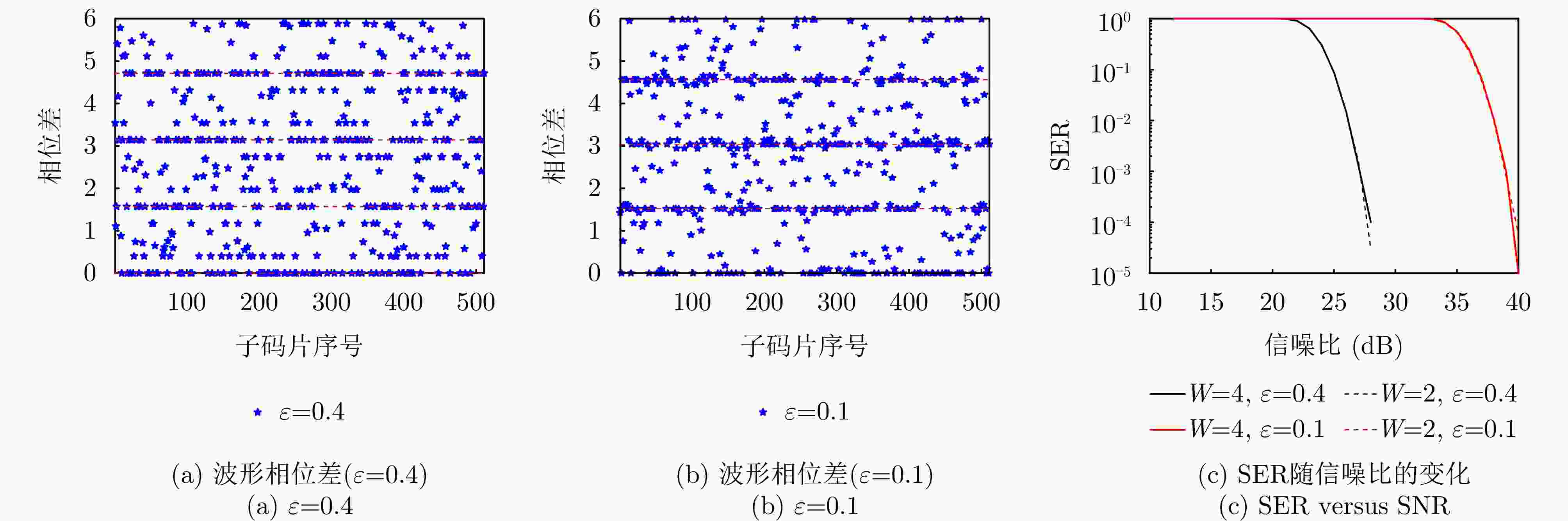
信息调制方法 解调步骤1 解调步骤2 解调步骤3 解调步骤4 解调步骤5 子脉冲内波形极化调制 子脉冲划分 计算空间方位$\left( {\theta ,\varphi } \right)$极化分量集合 虚拟极化匹配 子脉冲内CS-PIP调制 子脉冲内波形极化解调 下变频 相位差检测 差值计算 选小估计 子脉冲间波形位置排列调制 子脉冲内波形极化解调 下变频 匹配滤波 峰值提取 峰值选大 1 SMM算法求解优化问题$ {P_1} $
1. SMM algorithm for solving optimization problems $ {P_1} $
输入:$N,L,{{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( 0 \right)}},p,{\mathrm{tol}},{N_{\rm c}},{l_{\rm c}},{U_1},\varepsilon ,{U_2}$; 输出:优化问题$ {P_1} $的次优解$ {{\boldsymbol{q}}^ \star } $; 1:$t = 0$,初始化${{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( t \right)}} = {{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( 0 \right)}}$; 2:$t = t + 1$; 3:计算$ {\boldsymbol{d}}_{l,\hat l}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)},\tilde {\boldsymbol{d}}_{l,\hat l}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)},\tilde {\tilde {\boldsymbol{d}}}_{l,\hat l}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)},\bar {\boldsymbol{d}} _{l,\hat l}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)},\bar {\bar {\boldsymbol{d}} } _{l,\hat l}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)} $; 4:根据式(35)顺序求解$\phi _l^{\left( t \right)}\left( {{h_e}} \right),l = 1,2, \cdots ,L$; 5:若$ \left\| {{{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( {t - 1} \right)}} - {{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( t \right)}}} \right\| \le {\mathrm{tol}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{q}}^ \star } = {{\boldsymbol{q}}^{\left( t \right)}} $并退出,否则返回步
骤2。表 2 仿真分析信息调制主要参数设置
Table 2. Parameters setting for information modulation simulation
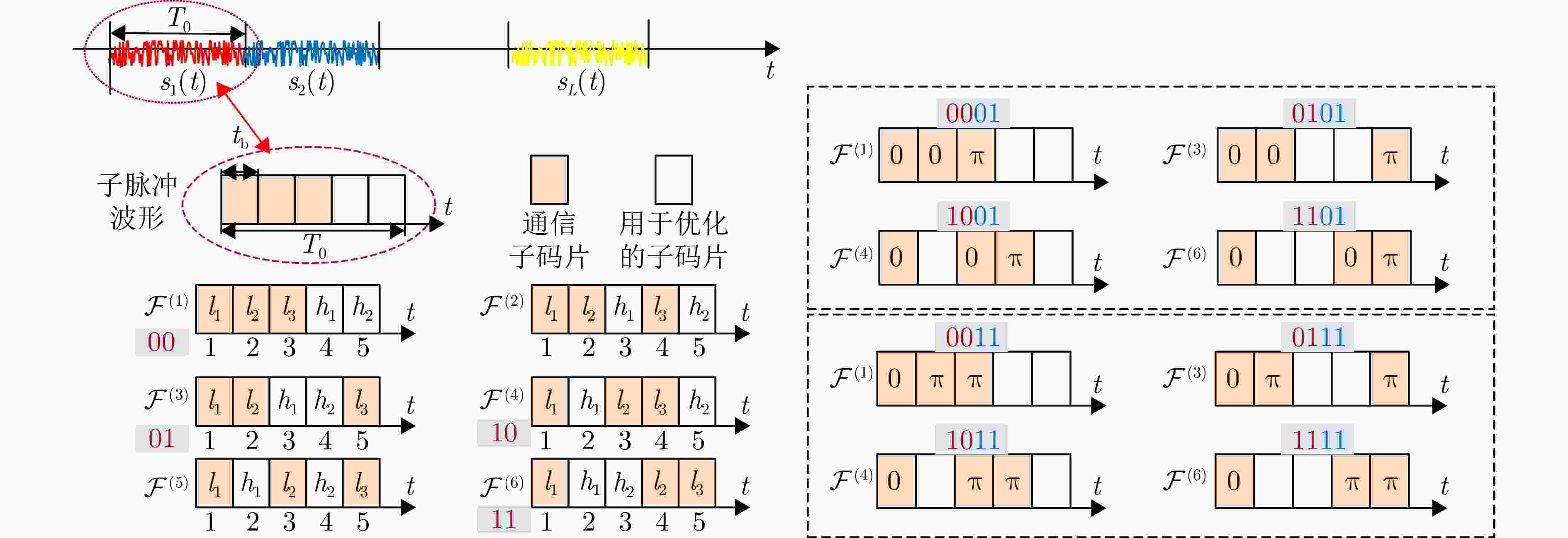
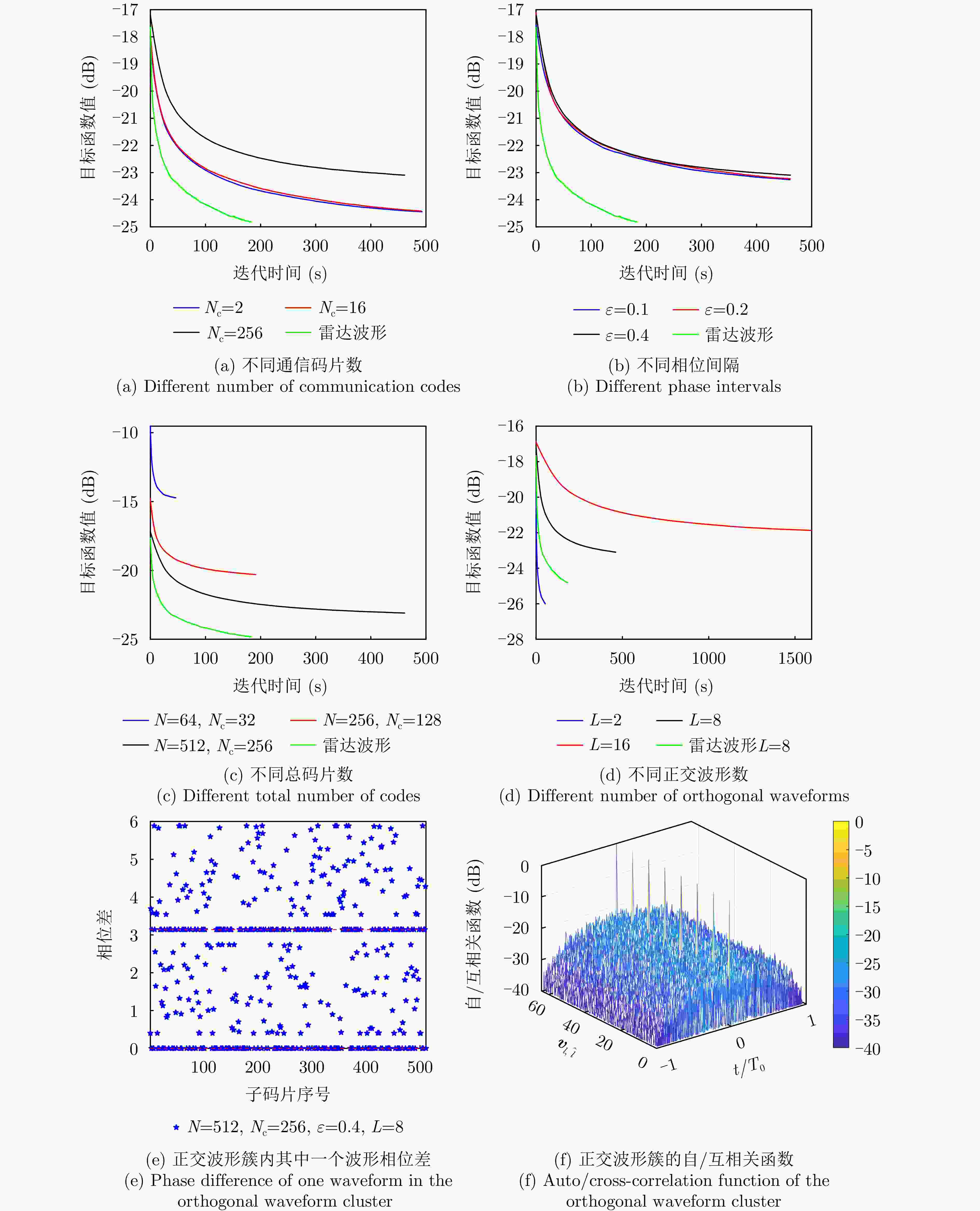
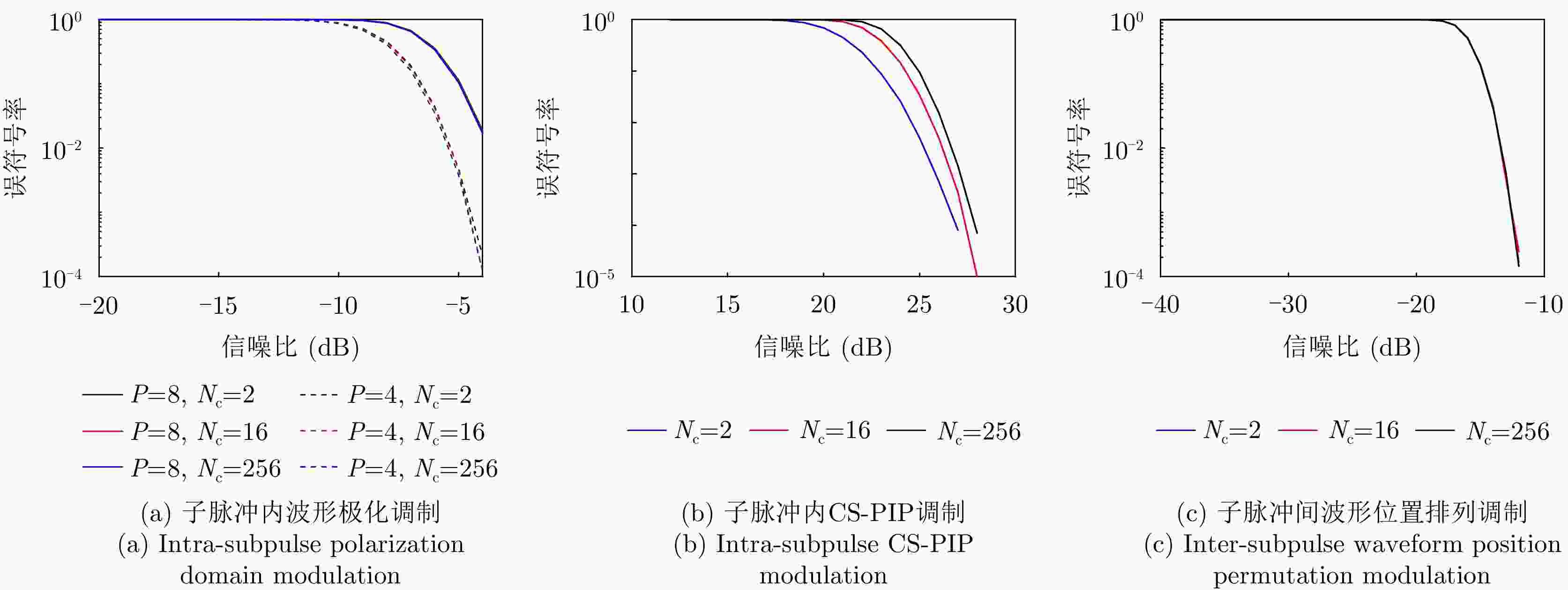
变量类型 变量名 变量取值 变量名 变量取值 子脉冲内CS-PIP调制 子脉冲波形码片数 $N = 512$ 子脉冲内通信码片数 ${N_{\rm c}} = 256$ 相位保护间隔 $\varepsilon = 0.4$ 子脉冲内通信码片相位差集合 $ {U_1}: = \left\{ {0,\pi } \right\} $ 子脉冲间波形排列调制 子脉冲个数 $L = 8$ 子脉冲内波形极化调制 发射极化分量集合
($P = 4$)$ \mathcal{K} : = \left\{ \begin{gathered} [\cos0.0157;\cos0.0157{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}0.0628}}] \\ [\cos0.8796;\cos0.8796{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}0.0628}}] \\ [\cos0.8796;\cos0.8796{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}2.1363}}] \\ [\cos0.8796;\cos0.8796{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}4.2097}}] \\ \end{gathered} \right\} $ 发射极化分量集合
($P = 8$)$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} [\cos0.1885;\cos0.1885{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}1.4451{\text{ }}}}],[\cos0.5341;\cos0.5341{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}4.2097}}] \\ [\cos0.5341;\cos0.5341{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}5.5920}}],[\cos0.7069;\cos0.7069{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}2.8274}}] \\ [\cos0.8796;\cos0.8796{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}1.4451}}],[\cos1.0524;\cos1.0524{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}0.0628}}] \\ [\cos1.0524;\cos1.0524{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}4.9009}}],[\cos1.3980;\cos1.3980{\text{ }}{{\rm e}^{{\text{j}}2.8274}}] \\ \end{gathered} \right\} $ 表 3 仿真分析基础参数设置
Table 3. Basic parameters setting for simulation
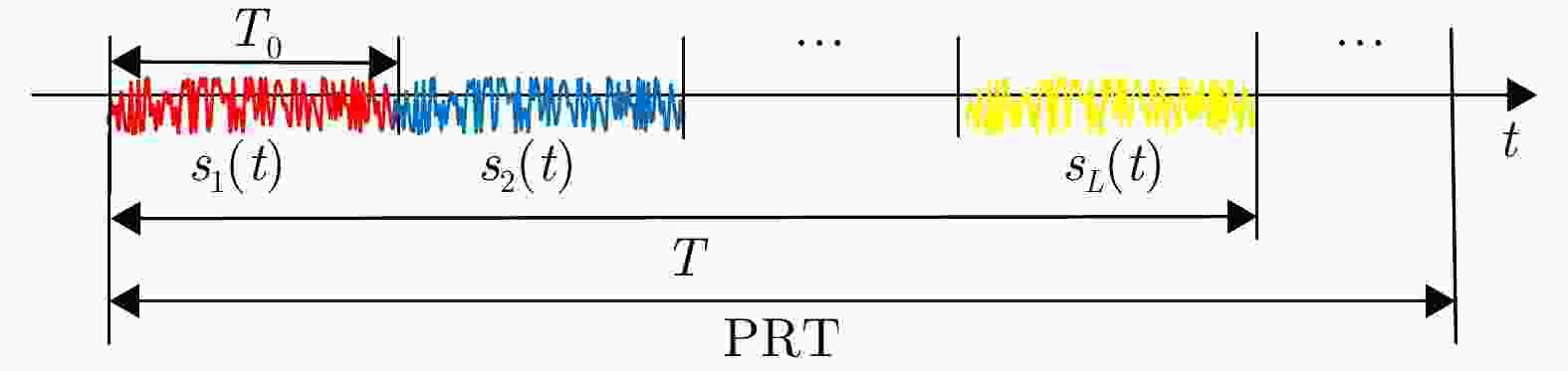
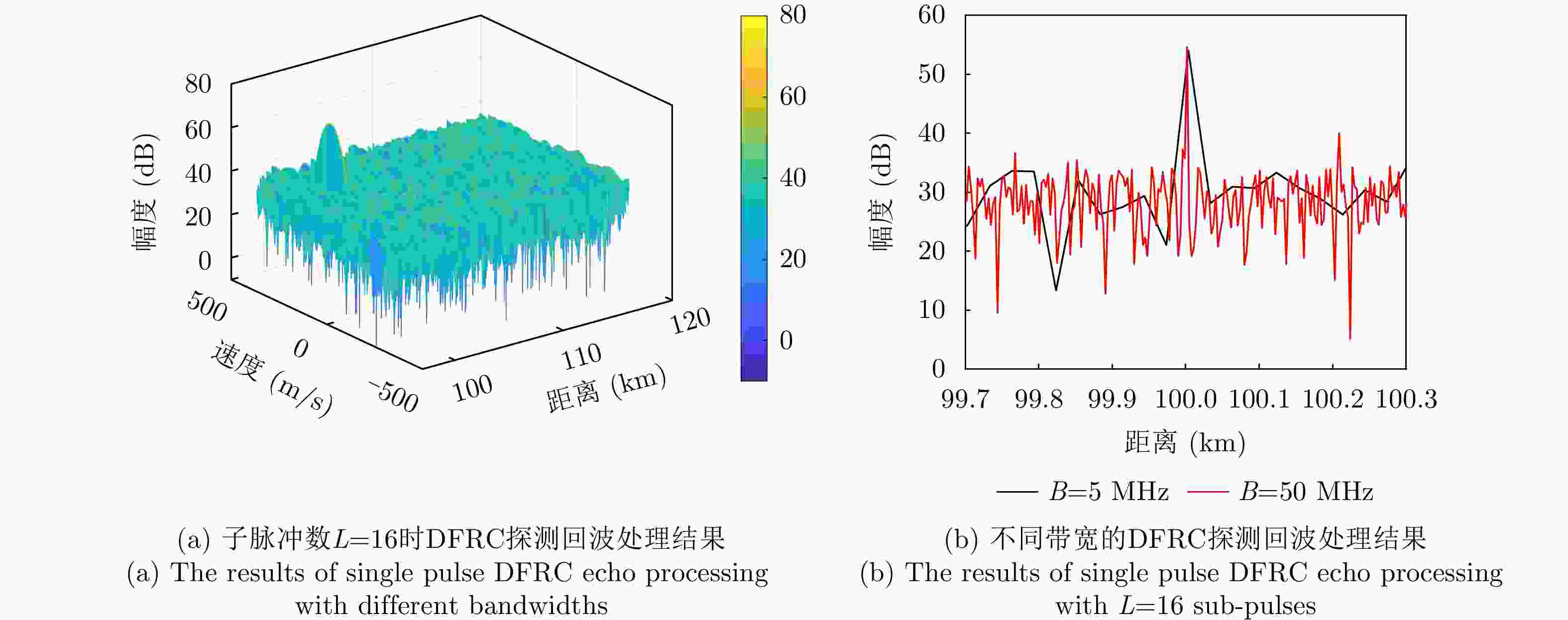
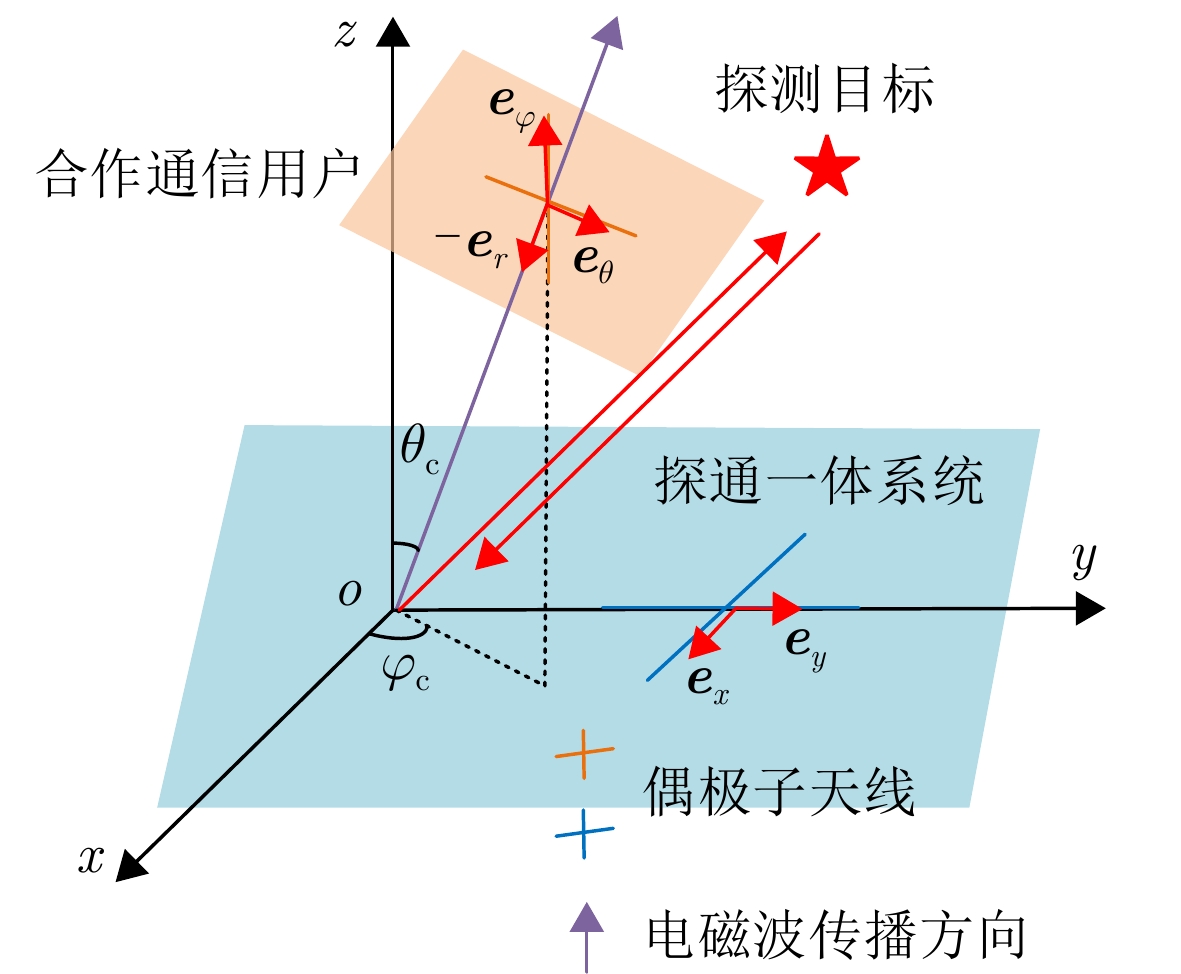
变量 取值 变量名 取值 带宽 B = 5 MHz 子脉冲宽度 $ {T_0} $= 102.4 μs 脉冲宽度 T = 819.2 μs 基带信号采样率 ${f_{\mathrm{s}}} $= 5 MHz 子码片宽度 ${t_{\mathrm{b}}}$ = 0.2 μs 目标回波SNR 0 dB 载频 ${f_0} $= 2 GHz 目标距离 ${R_0} $ = 100 km 目标速度 v = 150 m/s 通信用户方位 $\left( {\theta ,\varphi } \right) = \left( {{{30}^ \circ },{{10}^ \circ }} \right)$ 表 4 一些典型参数下的通信比特数(1个PRT时间)
Table 4. Communication bits for some typical parameters (1 PRT time)
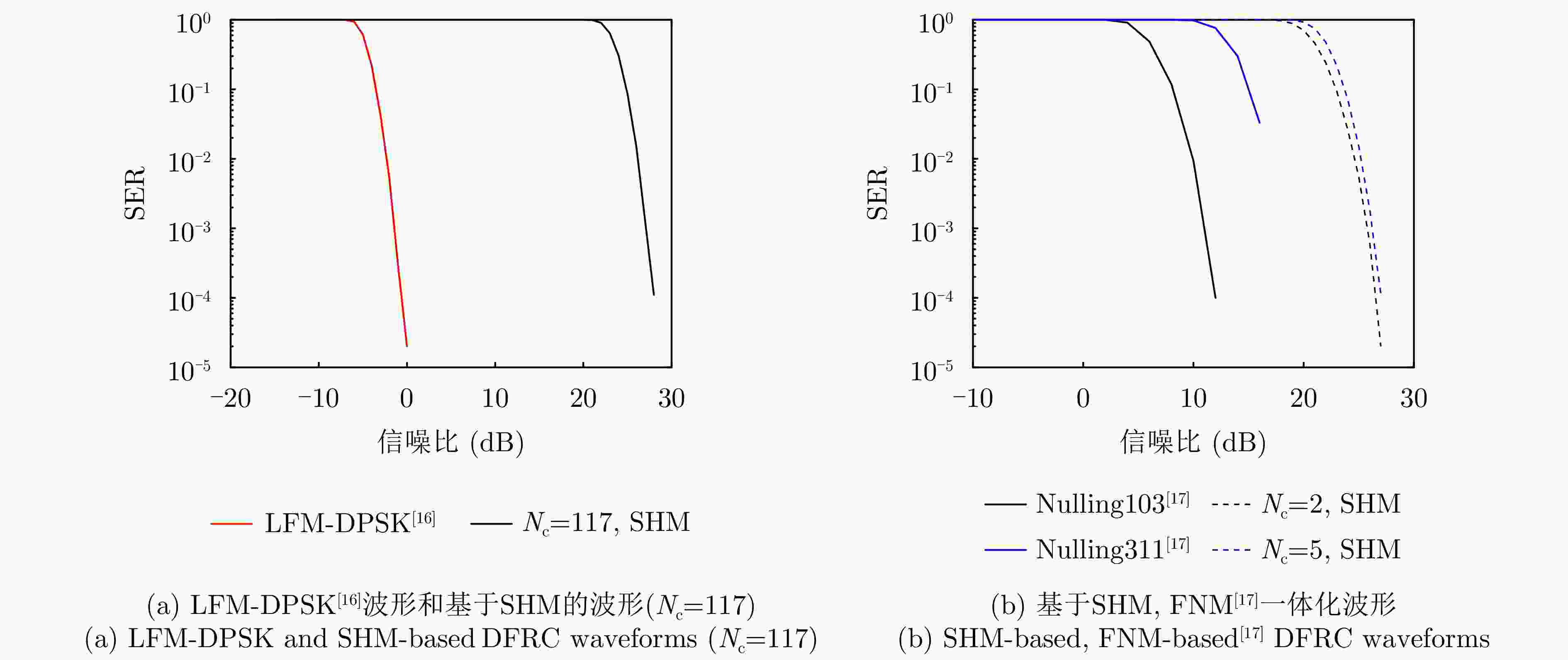
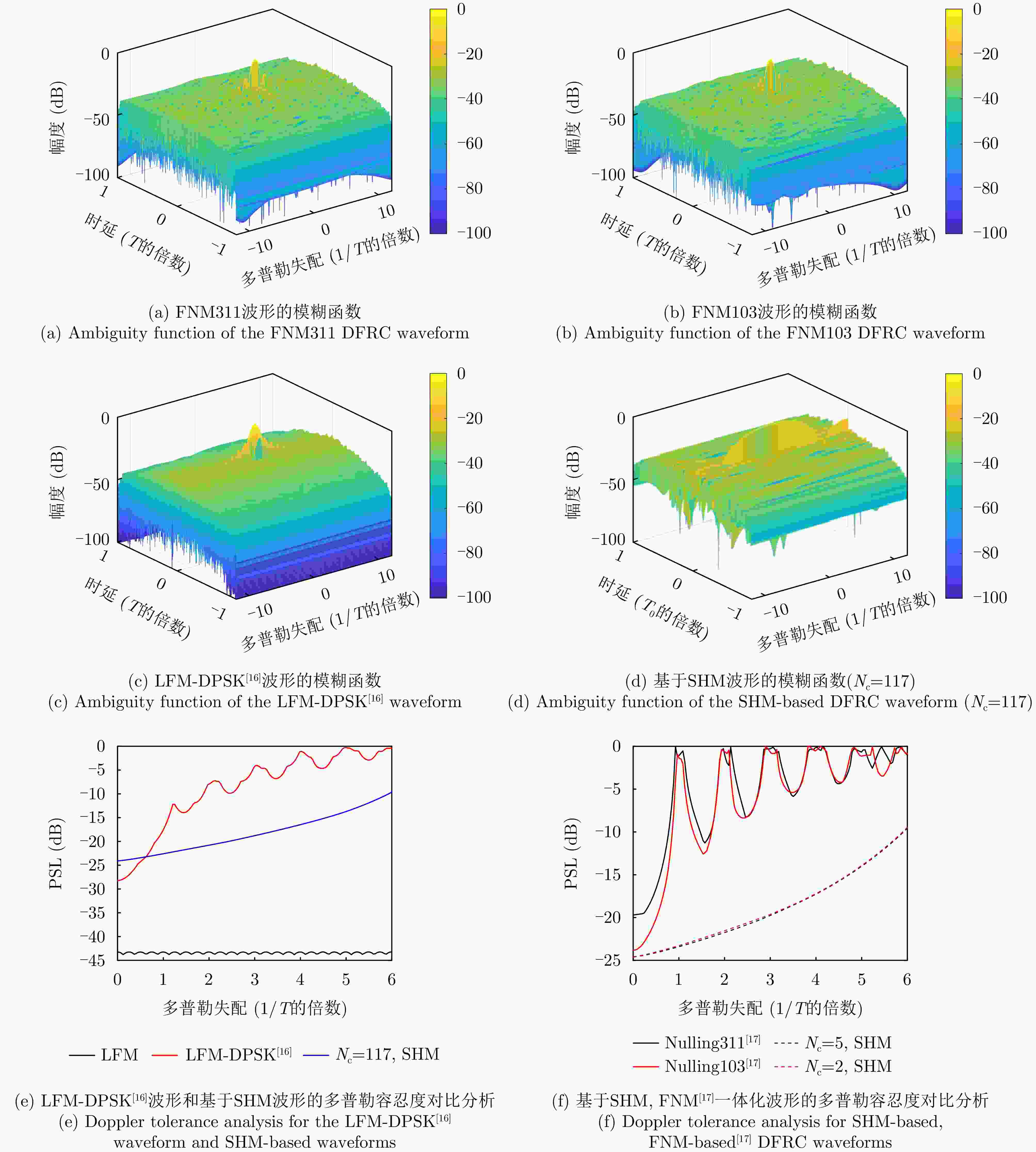
序号 参数设置 SHM LFM-DPSK[16] FNM103[17] FNM311[17] ① $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 256,L = 8,P = 4$ 6119 4088 103 311 ② $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 117,L = 8,P = 4$ 4079 4088 103 311 ③ $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 2,L = 8,P = 4$ 103 4088 103 311 ④ $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 5,L = 8,P = 4$ 311 4088 103 311 ⑤ $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 256,L = 16,P = 4$ 12252 4088 103 311 ⑥ $N = 512,{N_{\text{c}}} = 256,L = 8,P = 8$ 6127 4088 103 311 -
[1] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, PETROPULU A P, et al. Joint radar and communication design: Applications, state-of-the-art, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(6): 3834–3862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2973976. [2] HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, ABOUTANIOS E, et al. Dual-function radar communication systems: A solution to the spectrum congestion problem[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(5): 115–126. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2900571. [3] 刘永军, 廖桂生, 李海川, 等. 电磁空间分布式一体化波形设计与信息获取[J]. 中国科学基金, 2021, 35(5): 701–707. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2021.05.005.LIU Yongjun, LIAO Guisheng, LI Haichuan, et al. Distributed integrated waveform design and information acquisition in electromagnetic space[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2021, 35(5): 701–707. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2021.05.005. [4] WU Kai, ZHANG J A, HUANG Xiaojing, et al. Reliable frequency-hopping MIMO radar-based communications with multi-antenna receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(8): 5502–5513. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3079270. [5] TSINOS C G, ARORA A, CHATZINOTAS S, et al. Joint transmit waveform and receive filter design for dual-function radar-communication systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1378–1392. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3112295. [6] LIU Rang, LI Ming, LIU Qian, et al. Joint waveform and filter designs for STAP-SLP-based MIMO-DFRC systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1918–1931. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155501. [7] HASSANIEN A, AMIN M G, ZHANG Y D, et al. Dual-function radar-communications: Information embedding using sidelobe control and waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(8): 2168–2181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2505667. [8] YU Xianxiang, YAO Xue, YANG Jing, et al. Integrated waveform design for MIMO radar and communication via spatio-spectral modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 2293–2305. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3170687. [9] TANG Bo and STOICA P. MIMO multifunction RF systems: Detection performance and waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4381–4394. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3202315. [10] BAXTER W, ABOUTANIOS E, and HASSANIEN A. Joint radar and communications for frequency-hopped MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 729–742. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3142909. [11] HUANG Tianyao, SHLEZINGER N, XU Xingyu, et al. MAJoRCom: A dual-function radar communication system using index modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3423–3438. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2994394. [12] XU Jing, WANG Xiangrong, ABOUTANIOS E, et al. Hybrid index modulation for dual-functional radar communications systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(3): 3186–3200. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3219888. [13] YAO Xue, YANG Jing, XIONG Kui, et al. Integrated signal design for MIMO DFRC with intrapulse index modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1490–1504. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3339118. [14] 刘志鹏. 雷达通信一体化波形研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京理工大学, 2015.LIU Zhipeng. Waveform research on integration of radar and communication[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Technology, 2015. [15] SAHIN C, JAKABOSKY J, MCCORMICK P M, et al. A novel approach for embedding communication symbols into physical radar waveforms[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 1498–1503. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944444. [16] CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, LU Shuping, et al. Dual-use unimodular sequence design via frequency nulling modulation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 62470–62481. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2876644. [17] YANG Jing, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Dual-use signal design for radar and communication via ambiguity function sidelobe control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9781–9794. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3002773. [18] YAO Xue, LIU Yu, QIU H, et al. Dual-use baseband signal design for radCom with position index and phase modulation[J]. Signal Processing, 2023, 209: 109015. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109015. [19] YANG Jing, TAN Youshan, YU Xianxiang, et al. Waveform design for watermark framework based DFRC system with application on joint SAR imaging and communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5200214. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3232528. [20] GUO Caili, LIU Fangfang, CHEN Shuo, et al. Advances on exploiting polarization in wireless communications: Channels, technologies, and applications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(1): 125–166. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2606639. [21] HU Yaoyue, PAN Zhiwen, LIU Xiaobei, et al. Sliding window soft-SCL decoders for asynchronous polar-coded modulation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(1): 60–64. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3213854. [22] ZHANG Bo, LIU Wei, and LAN Xiang. Directional modulation design based on crossed-dipole arrays for two signals with orthogonal polarizations[C]. 12th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, London, UK, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp.2018.0428. [23] ZHANG Qiaoyu, YANG Zhaoyang, WANG Wen, et al. A dual-polarized antennas based directional modulation scheme[C]. 26th International Conference on Telecommunications, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2019: 468–473. doi: 10.1109/ICT.2019.8798807. [24] 倪吉华. 基于虚拟极化的目标增强与杂波抑制技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2006. doi: 10.7666/d.Y915593.NI Jihua. Research on target enhancement and clutter suppression techniques based on virtual polarization[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2006. doi: 10.7666/d.Y915593. [25] ZHAO Licheng, SONG Junxiao, BABU P, et al. A unified framework for low autocorrelation sequence design via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(2): 438–453. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2620113. [26] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence design to minimize the weighted integrated and peak sidelobe levels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(8): 2051–2064. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2510982. [27] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, CHEN Zihao, et al. Spectrally compatible aperiodic sequence set design with low cross- and auto-correlation PSL[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 183: 107960. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107960. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: