Research on Super-resolution Methods for Radar Targets Based on Bat-inspired Spectrogram Correlation and Transformation Models(in English)
-
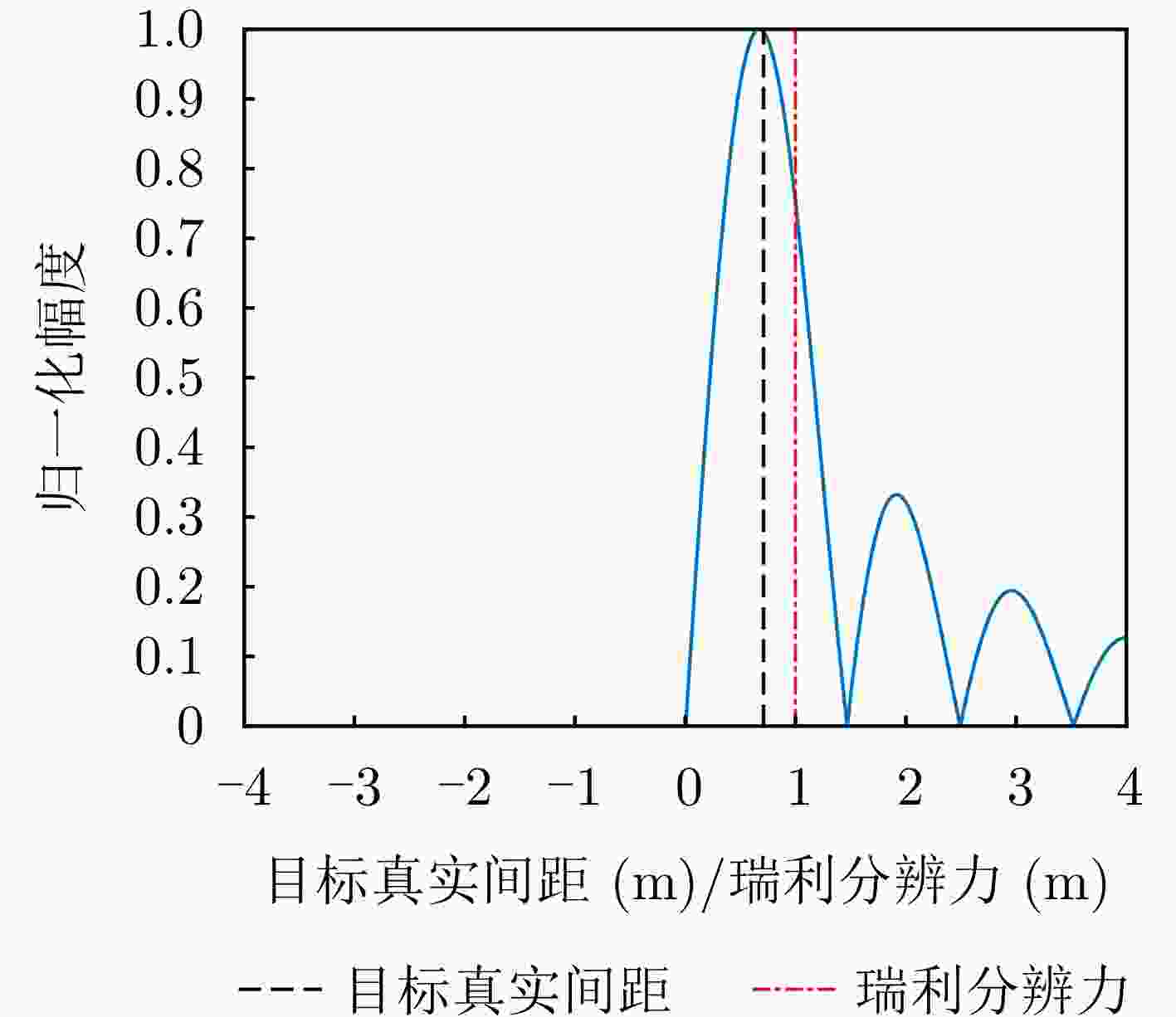
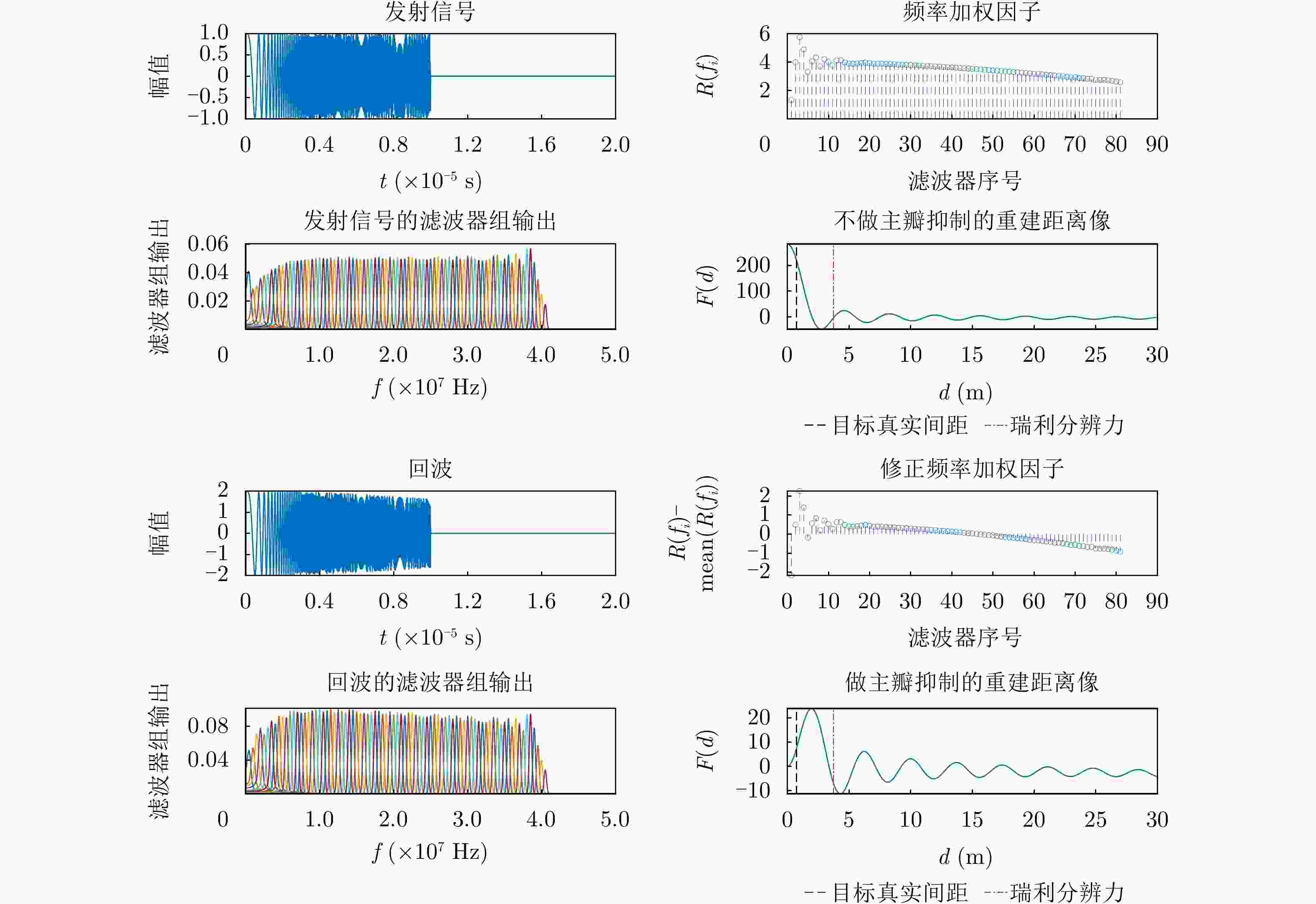
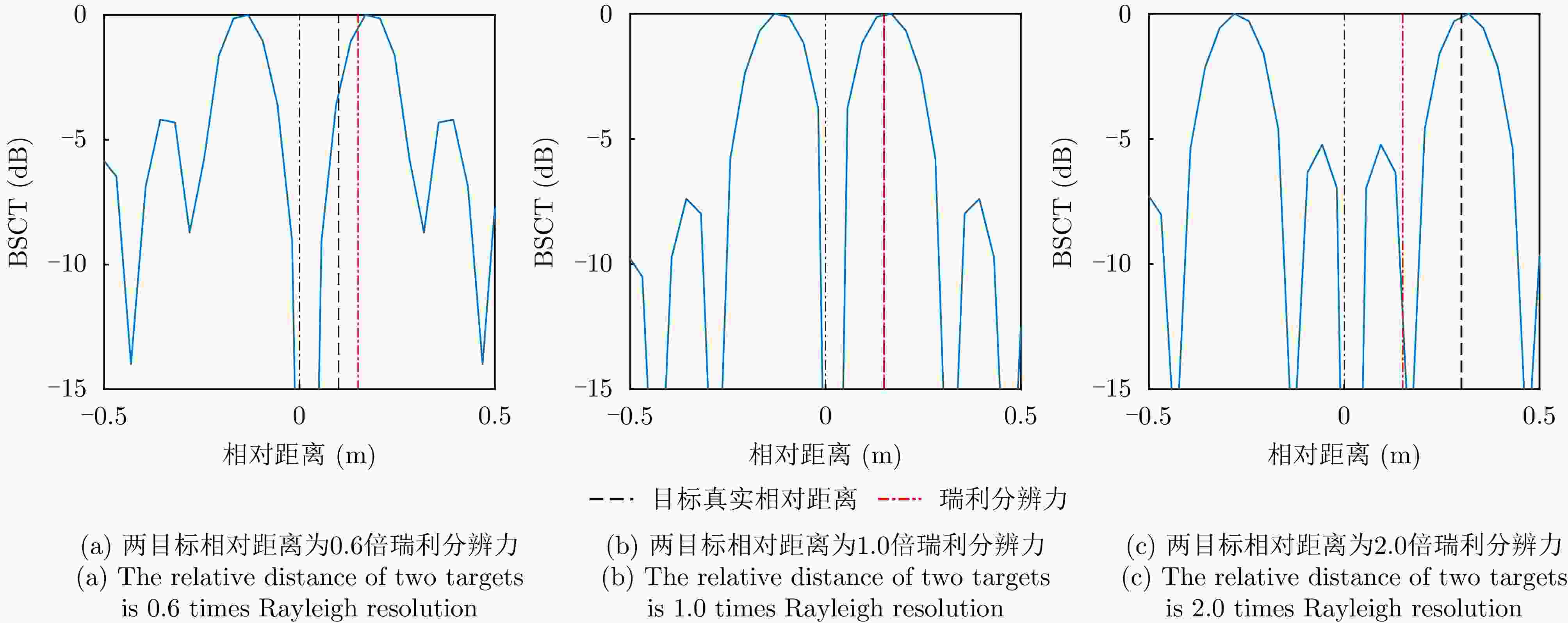
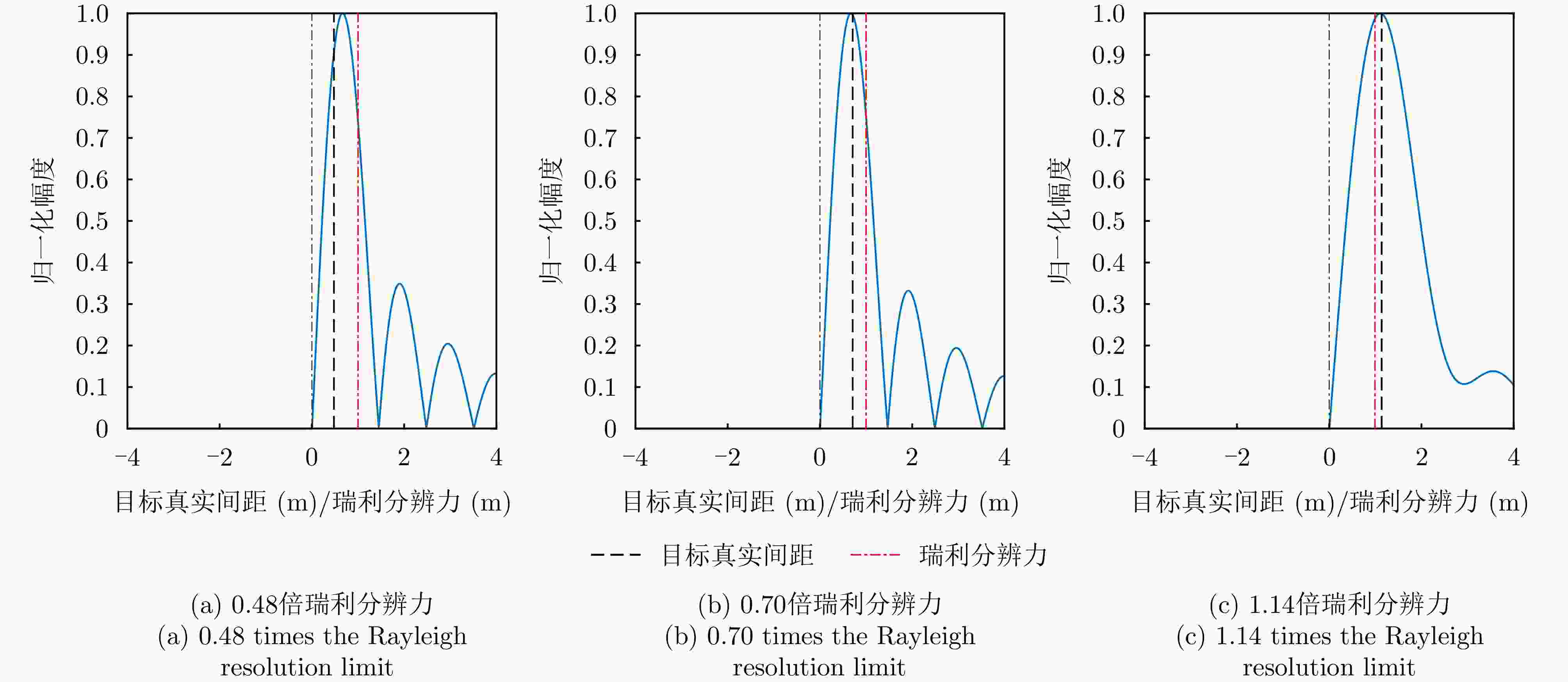
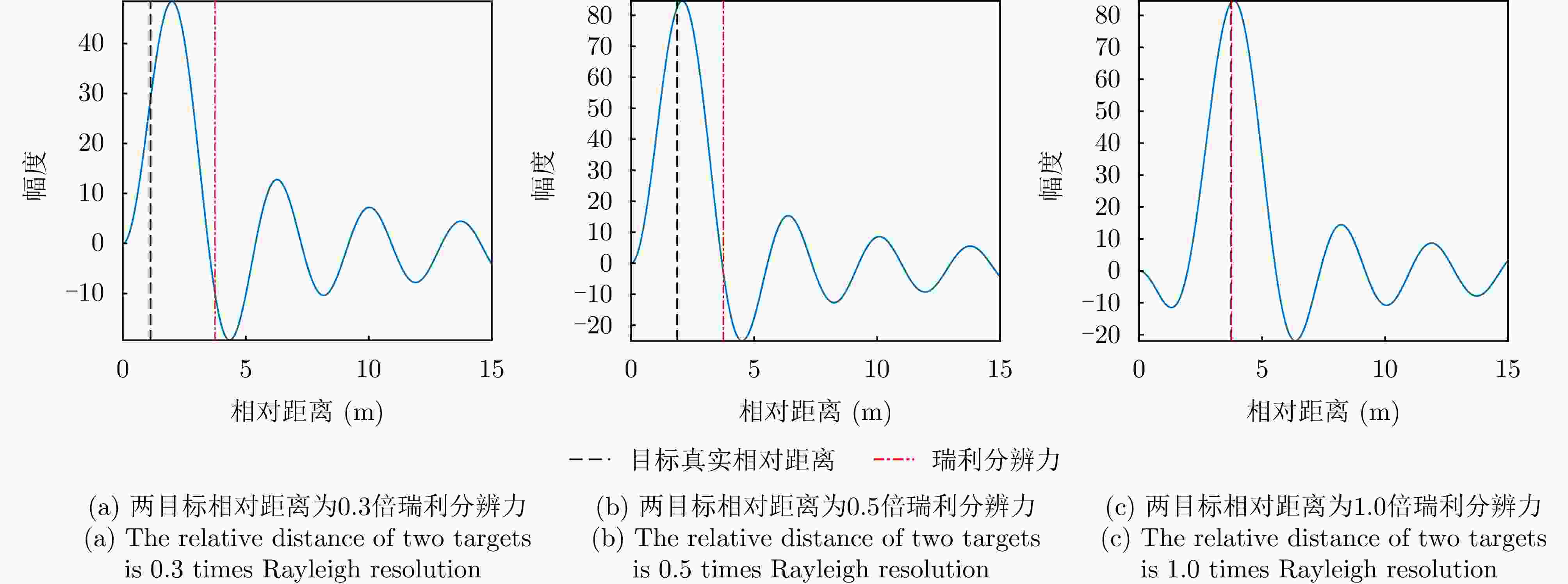
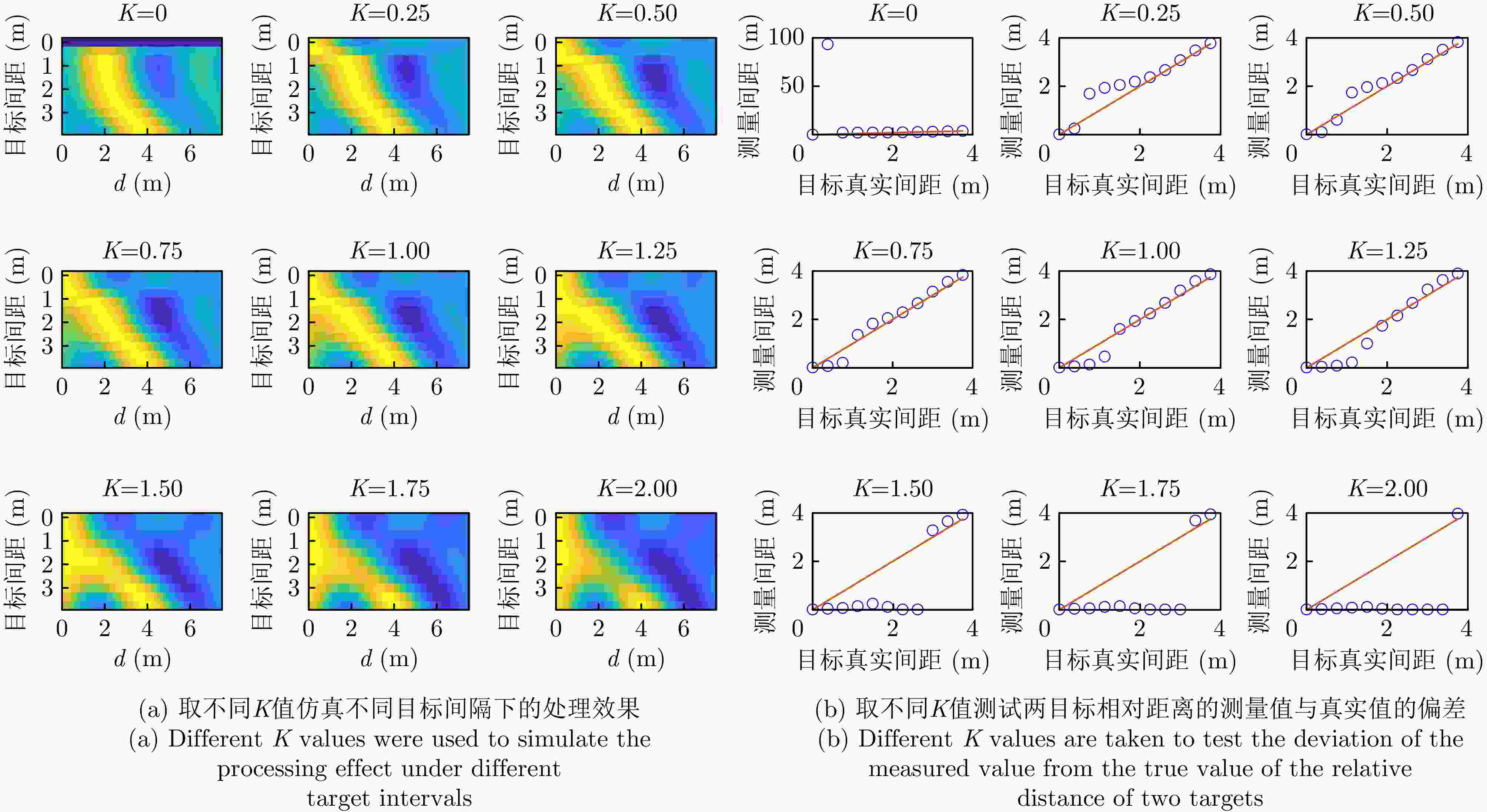
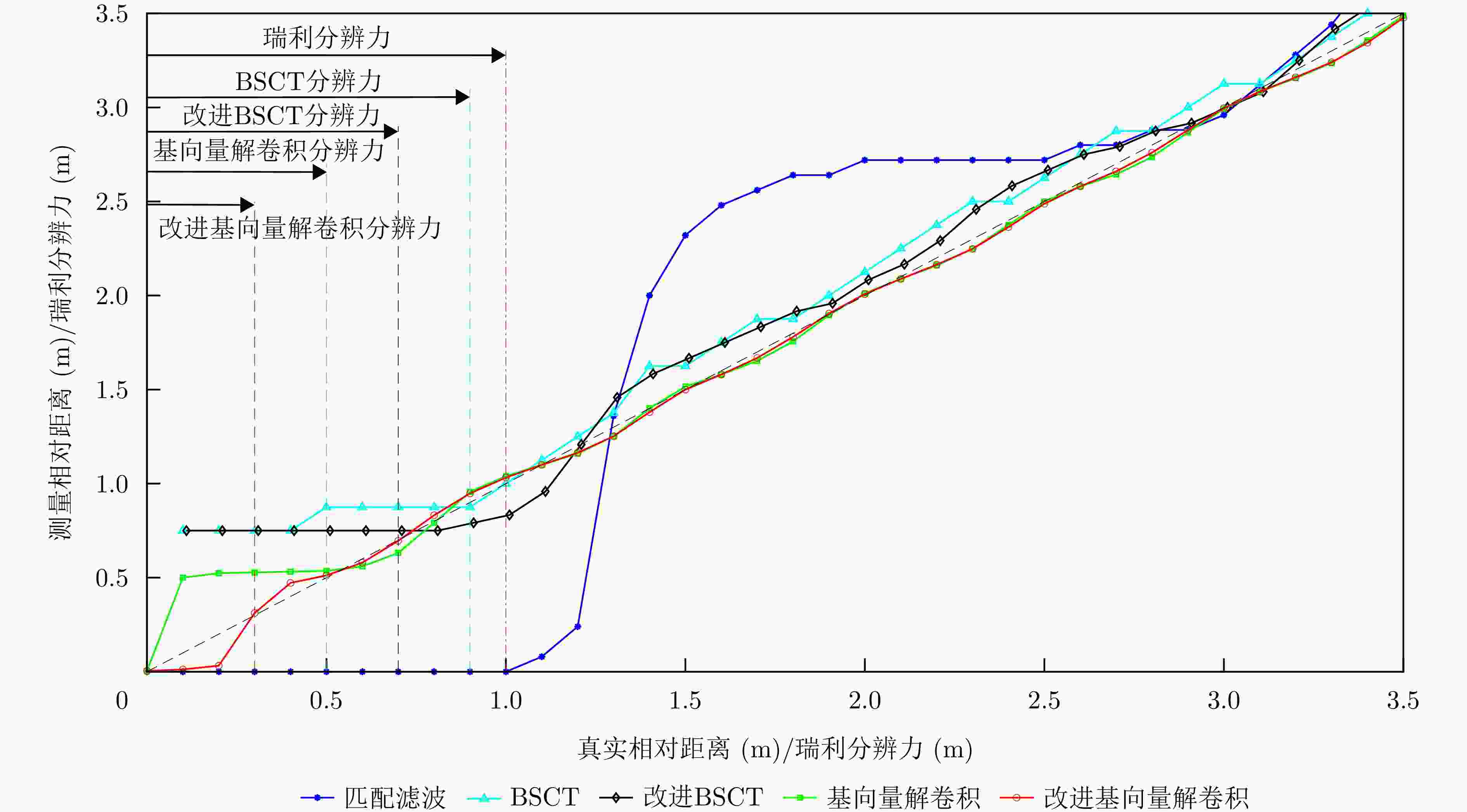
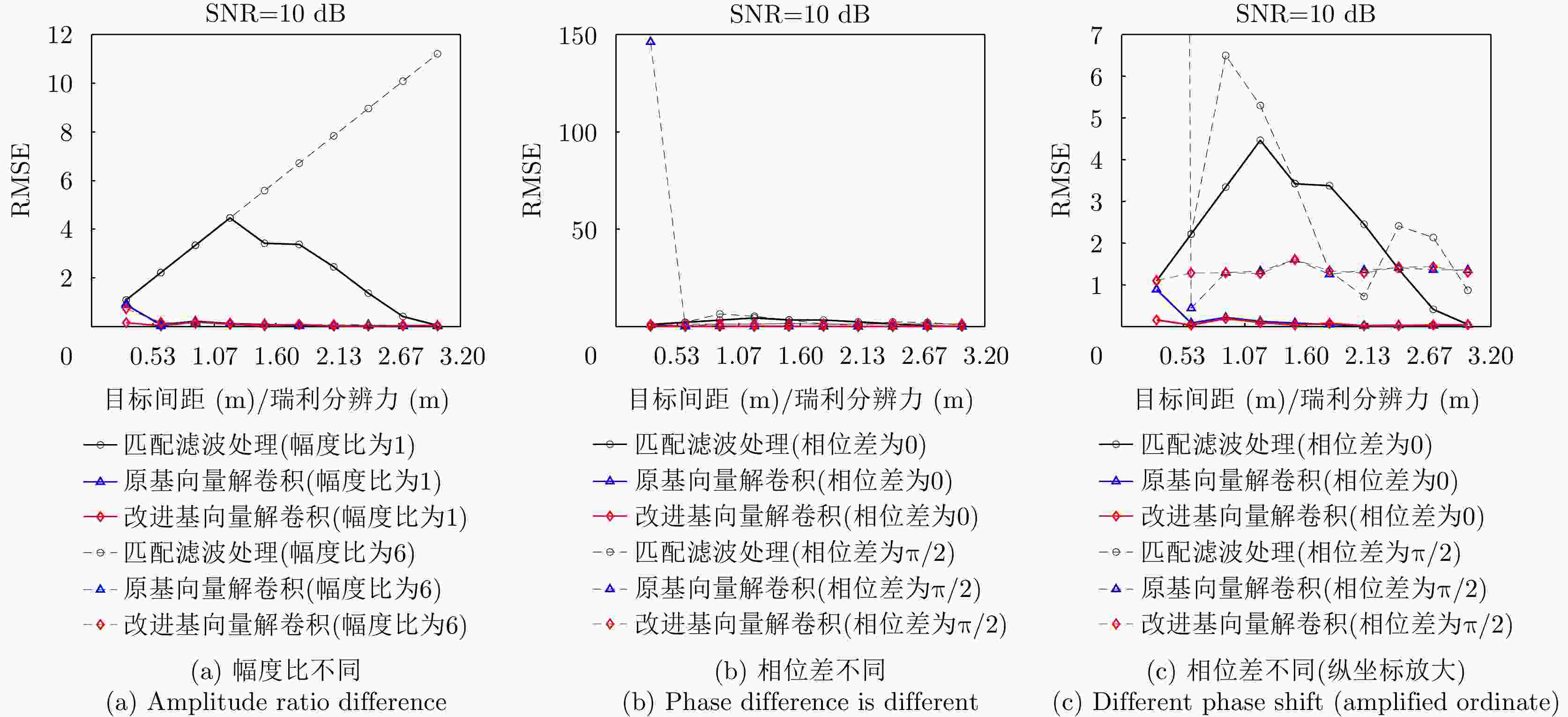
摘要: 传统雷达分辨能力主要利用模糊函数来进行分析,其极限分辨力一般用瑞利限表征。自然界中蝙蝠具有相当敏锐的听觉系统,学者提出谱相关及变换(SCAT)模型对蝙蝠听觉系统建模,探索了蝙蝠的超分辨原理,为突破雷达目标常规(瑞利)分辨力提供了一个可能的途径。为了进一步提高SCAT模型的分辨性能,通过抑制距离像负半轴和原点处多余的波瓣,改进了基向量解卷积法和基带SCAT (BSCT)两种蝙蝠超分辨模型,同时提出可靠分辨力概念及计算方法,统一了SCAT分辨力与瑞利分辨力的衡量标准,对比验证了可靠分辨力概念的合理性以及改进算法的有效性。仿真与实测实验表明,改进超分辨算法均获得了可观的分辨力提升,其中改进基向量解卷积法性能最佳,将原基向量解卷积法的分辨力提高约2 dB,同时将匹配滤波分辨力提高约5 dB。Abstract: The resolving power of traditional radar is mainly analyzed using the ambiguity function, and its limit is generally characterized by the Rayleigh limit. Bats have a rather sensitive auditory system. Researchers have proposed the Spectrogram Correlation And Transformation (SCAT) model to represent the auditory system of bats, explored their super-resolution principle, and provided a possible means to break through the conventional (Rayleigh) resolving power limit of radar targets. To further enhance the discriminative performance of the SCAT model, two bat-auditory-system-based super-resolution models, namely the base vector deconvolution method and Baseband SCAT (BSCT), are improved by suppressing redundant wave flaps at the negative semiaxis of the range profile and at the origin. Meanwhile, the concept and computation method of reliable discriminative power are proposed to unify the measurements of SCAT and Rayleigh discriminative powers. Further, a comparison is made to validate the rationality of the concept of reliable discriminative power, and the effectiveness of the improved models is verified. Simulation and real experiments show that the improved super-resolution models achieve a sizable increase in the resolving power. Notably, the improved base vector deconvolution method performs the best, improving the resolving power of the original method by ~2 dB while enhancing the matched filtering resolving power by ~5 dB.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameter settings
参数 数值 脉冲脉宽${T_{\text{p}}}$ 10 μs 脉冲带宽${B_{\text{c}}}$ 40 ${\text{MHz}}$ 耳蜗单元滤波器组数目N 81 相邻滤波器中心频率差异$\Delta {f_i}$ 0.5 ${\text{MHz}}$ 滤波器阶数 128 滤波器带通宽度B 1 ${\text{MHz}}$ 表 2 不同信号处理方法的对比
Table 2. Comparison of different signal processing methods
信号处理方法 无相位差 有相位差 幅度差异对分辨的影响 分辨力 可靠分辨力 分辨力 可靠分辨力 匹配滤波处理 ${1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ 与相位差有关,等幅反相时为无穷小 与相位差有关,大于瑞利分辨力 幅度差越大,分辨效果越差 BSCT $ < {1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ $ < {1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ 无影响 改进BSCT $ < {{0.7} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.7} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ $ < {{0.7} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.7} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ 无影响 基向量解卷积 $ < {{0.5} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.5} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ 效果变差 无影响 改进基向量解卷积 $ < {{0.31} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}} $ $ {{0.31} / {{B_{\text{c}}}}} $ 效果变差 无影响 表 3 实测雷达参数
Table 3. Measured radar parameters
参数 数值 脉冲脉宽${T_{\text{p}}}$ 1 μs 脉冲带宽${B_{\text{c}}}$ 100 MHz 中心频率${f_0}$ 19 GHz 采样率${f_{\text{s}}}$ 80 GHz 耳蜗单元滤波器组数目N 81 相邻滤波器中心频率差异$\Delta {f_i}$ 1.25 MHz 滤波器阶数 128 滤波器带通宽度B 2.5 MHz 表 1 Simulation parameter settings
Parameters Value Pulse width ${T_{\text{p}}}$ 10 μs Bandwidth ${B_{\text{c}}}$ 40 MHz Number of cochlear unit filter banks N 81 Difference in the center frequency of adjacent filters $\Delta {f_i}$ 0.5 MHz Filter order 128 Filter bandpass width B 1 MHz 表 2 Comparison of different signal processing methods
Signal processing methods No phase difference Phase difference Effect of amplitude differences on discrimination Resolution Reliable resolution Resolution Reliable resolution Matched filtering ${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ Related to the phase difference, infinitesimal for equal amplitude inverse phase Related to the phase difference, greater than the Rayleigh resolution The larger the difference in amplitude, the worse the resolution BSCT $ < {1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ $ < {1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ Unaffected Improved BSCT $ < {{0.7} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.7} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.7} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.7} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ $ < {{0.7} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.7} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.7} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.7} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ Unaffected Basis-vector deconvolution $ < {{0.5} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.5} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ ${{0.5} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.5} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}}$ Effect worsened Unaffected Improved basis-vector deconvolution $ < {{0.31} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.31} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}} $ $ {{0.31} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{0.31} {{B_{\text{c}}}}}} \right. } {{B_{\text{c}}}}} $ Effect worsened Unaffected 表 3 Measured radar parameters
Parameters Value Pulse width ${T_{\text{p}}}$ 1 μs Bandwidth ${B_{\text{c}}}$ 100 MHz Center frequency ${f_0}$ 19 GHz Sampling rate ${f_{\text{s}}}$ 80 GHz Number of cochlear unit filter banks N 81 Difference in the center frequency of
adjacent filters $\Delta {f_i}$1.25 MHz Filter order 128 Filter bandpass width B 2.5 MHz -
[1] 陈岁新. 雷达群目标超分辨技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.001266.CHEN Suixin. Study on super-resolution for radar detection of group targets[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.001266. [2] FENG Junjie, SUN Yinan, and JI Xiuxia. High-resolution ISAR imaging based on improved sparse signal recovery algorithm[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021, 2021: 5541116. doi: 10.1155/2021/5541116. [3] 倪晋麟, 储晓彬, 林幼权. 基于去卷积距离超分辨方法的机理及限制条件[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2000, 22(3): 62–64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.03.019.NI Jinlin, CHU Xiaobin, and LIN Youquan. The principle and limitation of the range super-resolution algorithms based on deconvolution[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2000, 22(3): 62–64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.03.019. [4] 王永良. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 18–52, 306–336.WANG Yongliang. Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithms[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 18–52, 306–336. [5] DING Shanshan, TONG Ningning, ZHANG Yongshun, et al. Super-resolution 3D imaging in MIMO radar using spectrum estimation theory[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(2): 304–312. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0233. [6] 王璟琛. 密集群目标分辨方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.001665.WANG Jingchen. Research on target discrimination method of dense cluster[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.001665. [7] 陈希信. 基于LFM信号频域去斜和压缩感知的雷达距离超分辨[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(12): 70–73. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.010.CHEN Xixin. Radar range super-resolution based on LFM frequency dechirp and compressive sensing[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(12): 70–73. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.010. [8] WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, WANG Mou, et al. 3DRIED: A high-resolution 3-D millimeter-wave radar dataset dedicated to imaging and evaluation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3366. doi: 10.3390/rs13173366. [9] 康乐, 张群, 李涛泳, 等. 基于贝叶斯学习的下视三维合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0611003.KANG Le, ZHANG Qun, LI Taoyong, et al. Imaging method of downward-looking three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar based on bayesian learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0611003. [10] SIMMONS J A, FERRAGAMO M, MOSS C F, et al. Discrimination of jittered sonar echoes by the echolocating bat, Eptesicus fuscus: The shape of target images in echolocation[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 1990, 167(5): 589–616. doi: 10.1007/BF00192654. [11] SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, WOTTON J M, et al. Composition of biosonar images for target recognition by echolocating bats[J]. Neural Networks, 1995, 8(7/8): 1239–1261. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(95)00059-3. [12] SCHMIDT S. Perception of structured phantom targets in the echolocating bat, Megaderma lyra[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1992, 91(4): 2203–2223. doi: 10.1121/1.403654. [13] 杨琳. 镫骨、耳蜗及其Corti器的建模与生物力学研究[D]. [博士论文], 复旦大学, 2009: 17–34. doi: 10.7666/d.y1970550.YANG Lin. Modeling and biomechanical analysis of the stapes, cochlea and organ of Corti[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Fudan University, 2009: 17–34. doi: 10.7666/d.y1970550. [14] CHI T, RU Powen, and SHAMMA S A. Multiresolution spectrotemporal analysis of complex sounds[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(2): 887–906. doi: 10.1121/1.1945807. [15] 秦晓瑜. 基于听觉仿生的听觉谱生成方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 东北师范大学, 2013: 1–18.QIN Xiaoyu. Study on the generation method of auditory spectrum based on auditory bionics[D]. [Master dissertation], Northeast Normal University, 2013: 1–18. [16] SAILLANT P A, SIMMONS J A, DEAR S P, et al. A computational model of echo processing and acoustic imaging in frequency-modulated echolocating bats: The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1993, 94(5): 2691–2712. doi: 10.1121/1.407353. [17] MATSUO I, KUNUGIYAMA K, and YANO M. An echolocation model for range discrimination of multiple closely spaced objects: Transformation of spectrogram into the reflected intensity distribution[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 115(2): 920–928. doi: 10.1121/1.1642626. [18] MATSUO I and YANO M. An echolocation model for the restoration of an acoustic image from a single-emission echo[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 116(6): 3782–3788. doi: 10.1121/1.1811411. [19] WIEGREBE L. An autocorrelation model of bat sonar[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 2008, 98(6): 587–595. doi: 10.1007/s00422-008-0216-2. [20] PEREMANS H and HALLAM J. The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver, revisited[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 104(2): 1101–1110. doi: 10.1121/1.423326. [21] SIMON R, KNÖRNSCHILD M, TSCHAPKA M, et al. Biosonar resolving power: Echo-acoustic perception of surface structures in the submillimeter range[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2014, 5: 64. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00064. [22] PARK M and ALLEN R. Pattern-matching analysis of fine echo delays by the spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 128(3): 1490–1500. doi: 10.1121/1.3466844. [23] SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, FERRAGAMO M J, et al. Auditory Computations for Biosonar Target Imaging in Bats[M]. HAWKINS H L, MCMULLEN T A, POPPER A N, et al. Auditory Computation. New York: Springer, 1996: 401–468. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-4070-9_9. [24] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Baseband version of the bat-inspired spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485152. [25] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired two target resolution at radio frequencies[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 2017: 436–440. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944242. [26] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired processing of radar target echoes[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1402–1409. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5241. [27] 成彬彬. 自适应雷达波形的仿生处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 清华大学, 2009.CHENG Binbin. Research on bionic processing for auto-adaptive radar waveform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2009. [28] 苏梦娜, 梁红, 杨长生. 基于SCAT模型的水下多目标高分辨仿生成像方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(2): 189–193. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-1509.2019.02.010.SU Mengna, LIANG Hong, and YANG Changsheng. Bionic imaging of underwater multiple targets with high resolution based on SCAT model[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(2): 189–193. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-1509.2019.02.010. [29] CHEN Ming, BATES M E, and SIMMONS J A. How frequency hopping suppresses pulse-echo ambiguity in bat biosonar[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(29): 17288–17295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001105117. [30] CHEN Ming, HARO S, SIMMONS A M, et al. A comprehensive computational model of animal biosonar signal processing[J]. PLOS Computational Biology, 2021, 17(2): e1008677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008677. [31] BALLERI A, GRIFFITHS H, and BAKER C. Biologically-Inspired Radar and Sonar: Lessons from Nature[M]. Edison: SciTech Publishing, 2017: 1–81. [32] 丁鹭飞, 耿富禄, 陈建春. 雷达原理[M]. 6版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2020: 210–211, 348–360.DING Lufei, GENG Fulu, and CHEN Jianchun. Radar Principles[M]. 6th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2020: 210–211, 348–360. [33] 王罗胜斌, 王雪松, 徐振海. 雷达极化域调控超分辨的原理与方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141.WANG Luoshengbin, WANG Xuesong, and XU Zhenhai. Principle and approach to polarization modulation for radar super-resolution[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141. [34] WANG Luoshengbin, XU Zhenhai, DONG Wei, et al. A scheme of polarimetric superresolution for multitarget detection and localization[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 439–443. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3058007. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: