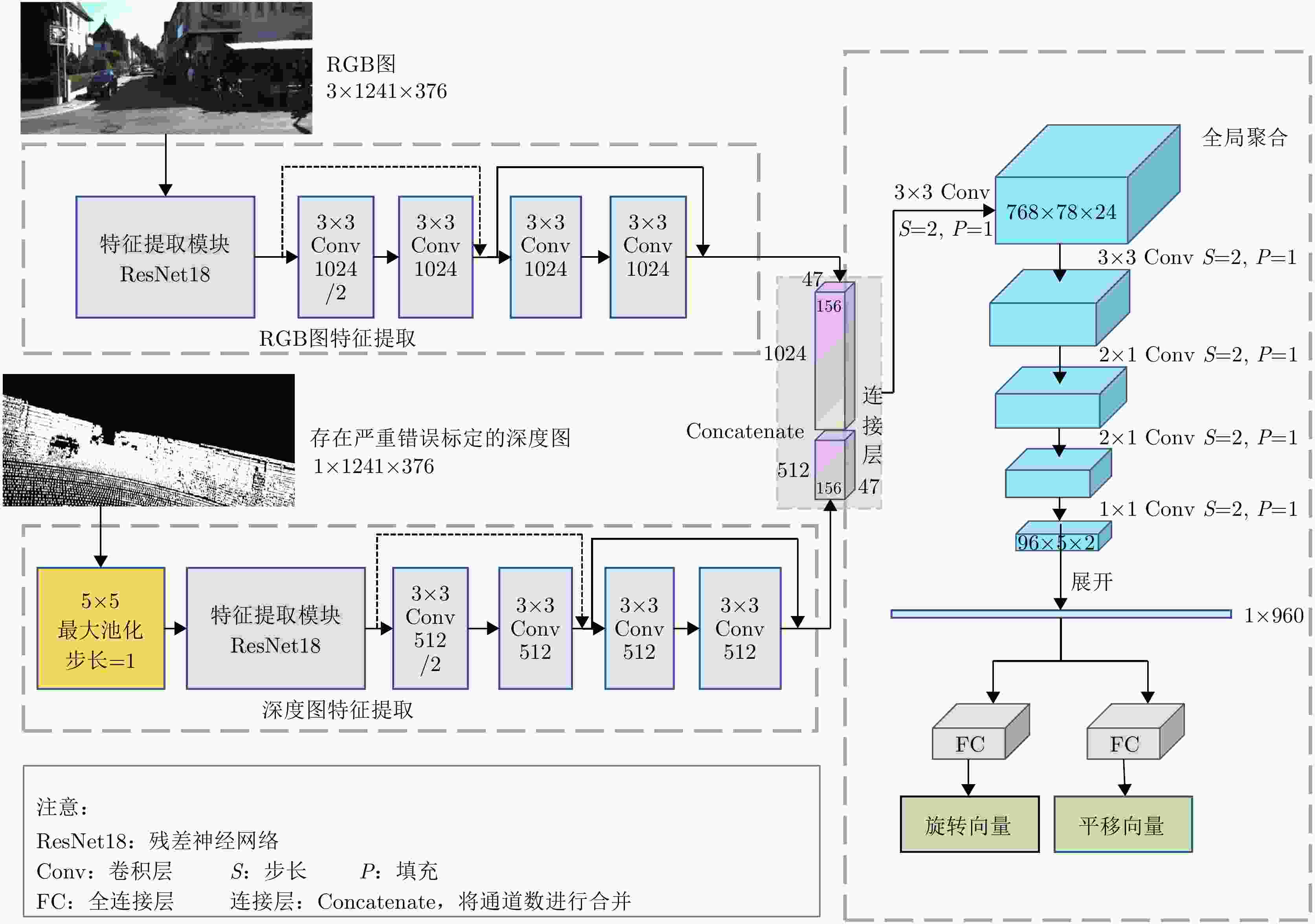
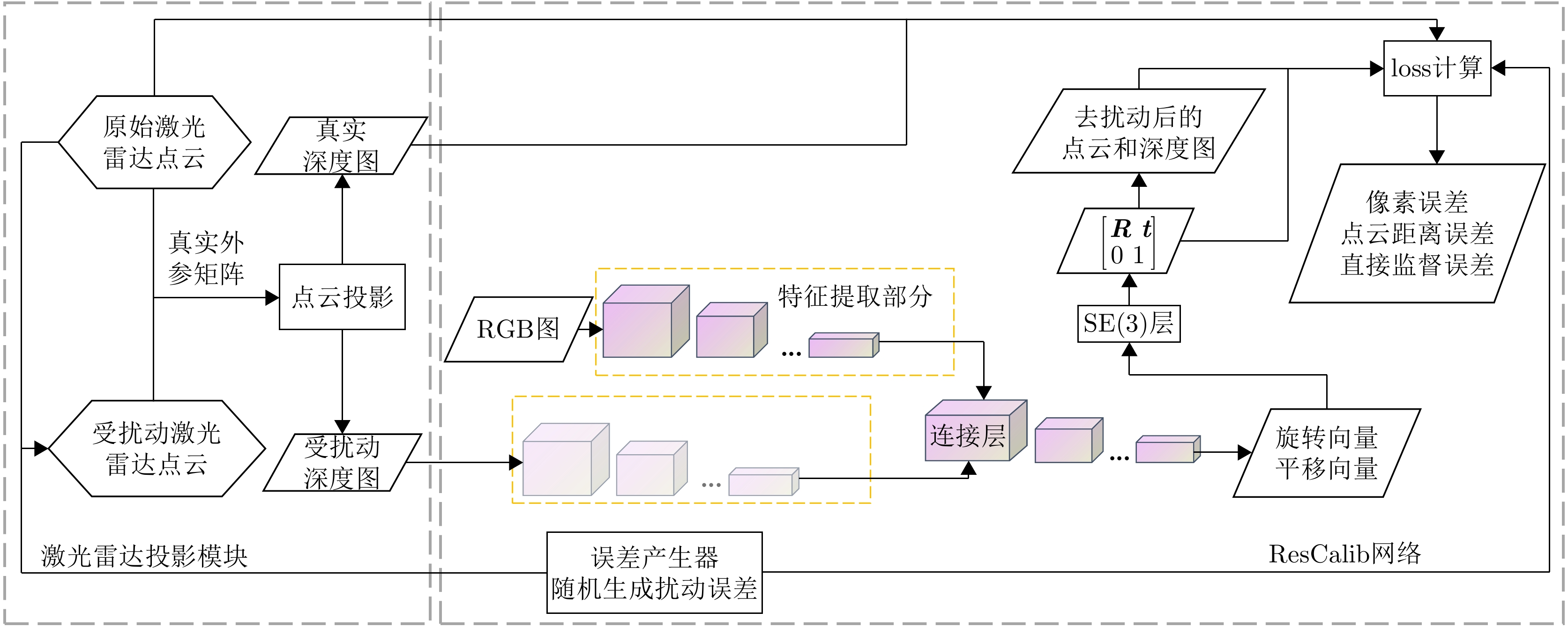
ResCalib: Joint LiDAR and Camera Calibration Based on Geometrically Supervised Deep Neural Networks
-
摘要: 激光雷达缺乏纹理色彩信息,相机缺乏深度信息,激光雷达和相机的信息具有高度的互补性,融合二者能获得丰富的观测数据,能提高环境感知的精准度和稳定性。而对两类传感器的外部参数进行精确的联合标定是数据融合的前提。目前,绝大多数的联合标定方法需要借助校准靶标物和人工选点的方式处理,导致其无法在动态的应用场景中使用。该文提出一种ResCalib深度神经网络模型用于解决激光雷达与相机的在线联合标定问题,该方法以激光雷达点云、单目图像和相机内参数矩阵作为输入以实现参数解算,而方法对外部特征物或靶标的依赖度低。ResCalib是一个几何监督深度神经网络,通过实施监督学习使输入图像和点云的几何及光度一致性最大化,利用单次迭代网络,自动估计激光雷达和相机之间的6自由度外参关系。实验表明该文方法能够纠正旋转±10°和平移±0.2 m的错误标定,标定解算结果的旋转分量的平均绝对误差为0.35°,平移分量为0.032 m,且单组标定所需时间为0.018 s,为实现动态环境下的自动化联合标定提供了技术支撑。Abstract: Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) systems lack texture and color information, while cameras lack depth information. Thus, the information obtained from LiDAR and cameras is highly complementary. Therefore, combining these two types of sensors can obtain rich observation data and improve the accuracy and stability of environmental perception. The accurate joint calibration of the external parameters of these two types of sensors is the premise of data fusion. At present, most joint calibration methods need to be processed through target calibration and manual point selection. This makes it impossible to use them in dynamic application scenarios. This paper presents a ResCalib deep neural network model, which can be used to solve the problem of the online joint calibration of LiDAR and a camera. The method uses LiDAR point clouds, monocular images, and in-camera parameter matrices as the input to achieve the external parameters solving of LiDAR and cameras; however, the method has low dependence on external features or targets. ResCalib is a geometrically supervised deep neural network that automatically estimates the six-degree-of-freedom external parameter relationship between LiDAR and cameras by implementing supervised learning to maximize the geometric and photometric consistencies of input images and point clouds. Experiments show that the proposed method can correct errors in calibrating rotation by ±10° and translation by ±0.2 m. The average absolute errors of the rotation and translation components of the calibration solution are 0.35° and 0.032 m, respectively, and the time required for single-group calibration is 0.018 s, which provides technical support for realizing automatic joint calibration in a dynamic environment.
-
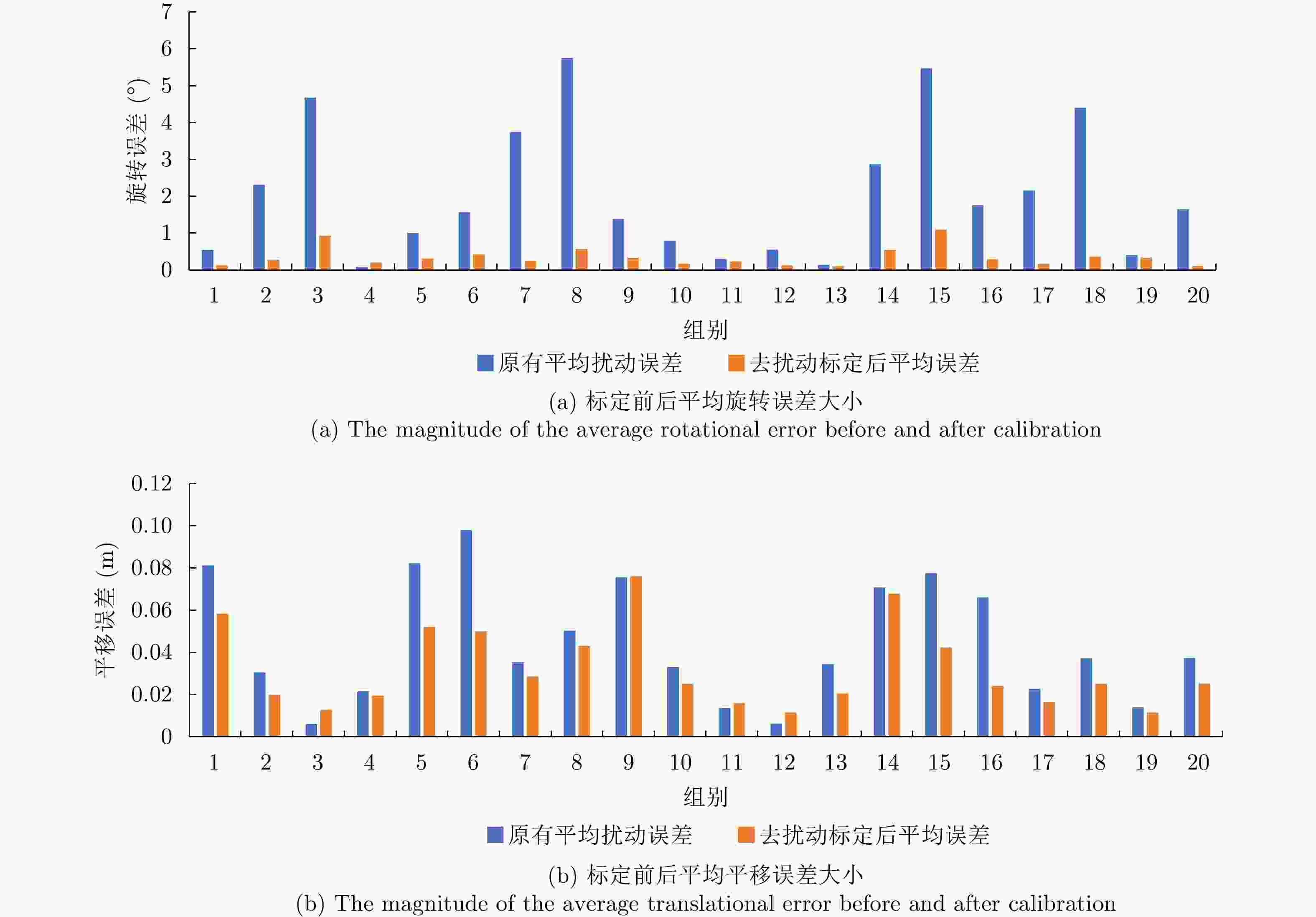
表 1 标定前后旋转误差的数学统计(°)
Table 1. Mathematical statistics of rotation error before and after calibration (°)
数据类型 平均值 标准差 原有旋转误差 2.0820 1.8200 联合标定后旋转误差 0.3505 0.2655 表 2 标定前后平移误差的数学统计(m)
Table 2. Mathematical statistics of translation error before and after calibration (m)
数据类型 平均值 标准差 原有平移误差 0.0447 0.0284 联合标定后平移误差 0.0324 0.0195 表 3 不同场景下算法的标定效果比较(±0.2 m, ±10°)
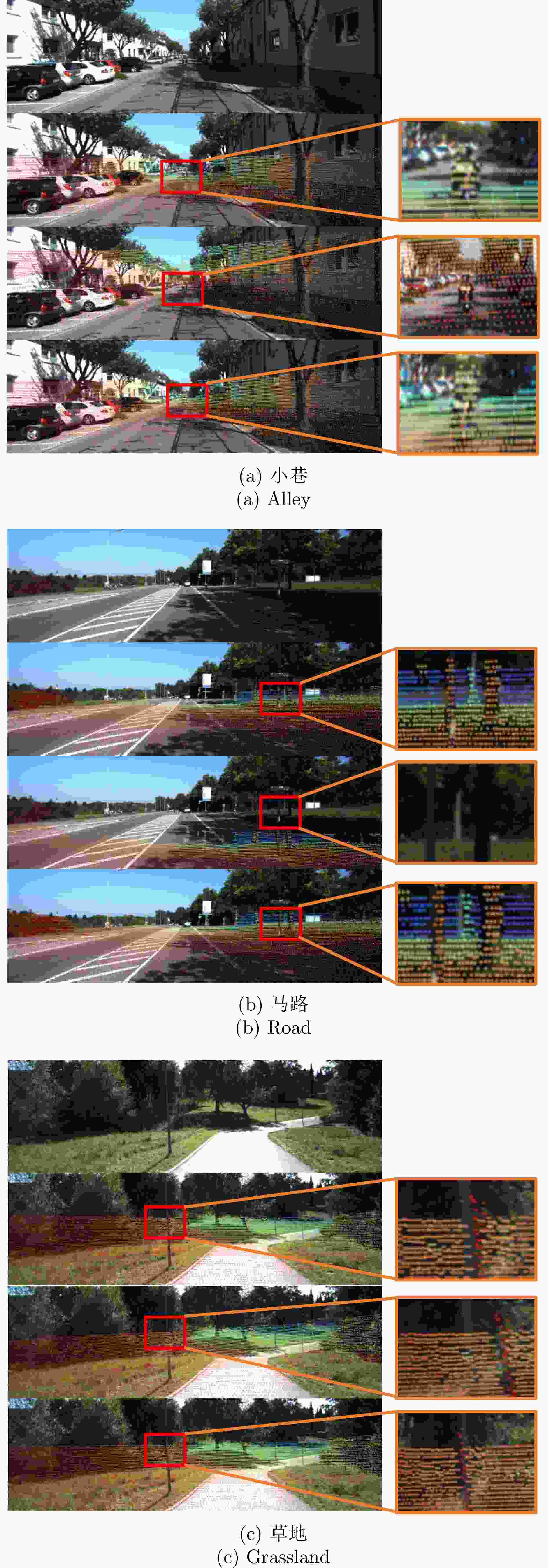
Table 3. Comparison of the calibration effects of the algorithms in different scenarios (±0.2 m, ±10°)
场景 联合标定后
旋转误差平均值(°)联合标定后
平移误差平均值(m)街道 0.35 0.03 小巷 0.32 0.04 草地 0.44 0.05 住宅区 0.37 0.04 草地(大雾) 0.44 0.05 表 4 多种深度学习网络标定效果对比
Table 4. Comparison of calibration effects of multiple deep learning networks
原始误标定范围 深度学习网络 标定后旋转绝对误差(°) 标定后平移绝对误差(cm) 俯仰 滚动 偏航 平均值 X Y Z 平均值 ±0.2 m, ±10° CalibNet[31] 0.15 0.90 0.18 0.41 4.20 1.60 7.22 4.34 ResCalib 0.14 0.72 0.19 0.35 4.35 1.69 3.68 3.24 ±0.2 m, ±2° NetCalib[30] 0.33 0.55 0.47 0.45 6.83 7.57 5.47 6.62 ResCalib 0.17 0.27 0.12 0.18 2.51 1.48 3.02 2.33 ±0.1 m, ±1° ResCalib 0.16 0.19 0.11 0.16 1.11 1.11 1.37 1.19 表 5 多种深度学习网络单次迭代时间对比
Table 5. Comparison of single iteration time of multiple deep learning networks
表 6 不同损失权重下的网络去扰动标定效果(±0.2 m, ±10°)
Table 6. Calibration effect of network de-perturbation under different loss weights (±0.2 m, ±10°)
损失权重 标定后旋转绝对
误差平均值(°)标定后平移绝对
误差平均值(cm)1.0:1.0:1.0 0.351 3.24 0.5:1.0:1.5 0.350 3.26 0.5:1.5:1.0 0.513 5.03 1.0:0.5:1.5 0.911 4.99 1.0:1.5:0.5 0.614 5.09 1.5:1.0:0.5 0.453 5.06 1.5:0.5:1.0 0.612 5.10 -
[1] AZIMIRAD E, HADDADNIA J, and IZADIPOUR A. A comprehensive review of the multi-sensor data fusion architectures[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 2015, 71(1): 33–42. [2] 王世强, 孟召宗, 高楠, 等. 激光雷达与相机融合标定技术研究进展[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(8): 20230427. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230427.WANG Shiqiang, MENG Zhaozong, GAO Nan, et al. Advancements in fusion calibration technology of lidar and camera[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(8): 20230427. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230427. [3] 熊超, 乌萌, 刘宗毅, 等. 激光雷达与相机联合标定进展研究[J]. 导航定位学报, 2024, 12(2): 155–166. doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20240218.XIONG Chao, WU Meng, LIU Zongyi, et al. Review of joint calibration of LiDAR and camera[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2024, 12(2): 155–166. doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20240218. [4] PANDEY G, MCBRIDE J, SAVARESE S, et al. Extrinsic calibration of a 3D laser scanner and an omnidirectional camera[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2010, 43(16): 336–341. doi: 10.3182/20100906-3-IT-2019.00059. [5] WANG Weimin, SAKURADA K, and KAWAGUCHI N. Reflectance intensity assisted automatic and accurate extrinsic calibration of 3D LiDAR and panoramic camera using a printed chessboard[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 851. doi: 10.3390/rs9080851. [6] GONG Xiaojin, LIN Ying, and LIU Jilin. 3D LiDAR-camera extrinsic calibration using an arbitrary trihedron[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(2): 1902–1918. doi: 10.3390/s130201902. [7] PARK Y, YUN S, WON C S, et al. Calibration between color camera and 3D LiDAR instruments with a polygonal planar board[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(3): 5333–5353. doi: 10.3390/s140305333. [8] PUSZTAI Z and HAJDER L. Accurate calibration of LiDAR-camera systems using ordinary boxes[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 2017: 394–402. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW.2017.53. [9] DHALL A, CHELANI K, RADHAKRISHNAN V, et al. LiDAR-camera calibration using 3D-3D point correspondences[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.09785. 2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1705.09785. [10] ZHANG Juyong, YAO Yuxin, and DENG Bailin. Fast and robust iterative closest point[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(7): 3450–3466. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054619. [11] 徐思雨, 祝继华, 田智强, 等. 逐步求精的多视角点云配准方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1486–1494. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170556.XU Siyu, ZHU Jihua, TIAN Zhiqiang, et al. Stepwise refinement approach for registration of multi-view point sets[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1486–1494. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170556. [12] 谢婧婷, 蔺小虎, 王甫红, 等. 一种点线面约束的激光雷达和相机标定方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(12): 1916–1923. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20210313.XIE Jingting, LIN Xiaohu, WANG Fuhong, et al. Extrinsic calibration method for LiDAR and camera with joint point-line-plane constraints[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(12): 1916–1923. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20210313. [13] BELTRÁN J, GUINDEL C, DE LA ESCALERA A, et al. Automatic extrinsic calibration method for LiDAR and camera sensor setups[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(10): 17677–17689. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3155228. [14] PEREIRA M, SILVA D, SANTOS V, et al. Self calibration of multiple LiDARs and cameras on autonomous vehicles[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2016, 83: 326–337. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2016.05.010. [15] TÓTH T, PUSZTAI Z, and HAJDER L. Automatic LiDAR-camera calibration of extrinsic parameters using a spherical target[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Paris, France, 2020: 8580–8586. doi: 10.1109/ICRA40945.2020.9197316. [16] LEVINSON J and THRUN S. Automatic online calibration of cameras and lasers[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems IX, Berlin, Germany, 2013: 1–8. doi: 10.15607/RSS.2013.IX.029. [17] PANDEY G, MCBRIDE J R, SAVARESE S, et al. Automatic targetless extrinsic calibration of a 3D LiDAR and camera by maximizing mutual information[C]. 26th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, 2012: 2053–2059. [18] KANG J and DOH N L. Automatic targetless camera-LiDAR calibration by aligning edge with Gaussian mixture model[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2020, 37(1): 158–179. doi: 10.1002/rob.21893. [19] CASTORENA J, KAMILOV U S, and BOUFOUNOS P T. Autocalibration of LiDAR and optical cameras via edge alignment[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 2862–2866. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472200. [20] ISHIKAWA R, OISHI T, and IKEUCHI K. LiDAR and camera calibration using motions estimated by sensor fusion odometry[C]. 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 2018: 7342–7349. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8593360. [21] HUANG Kaihong and STACHNISS C. Extrinsic multi-sensor calibration for mobile robots using the Gauss-Helmert model[C]. 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017: 1490–1496. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2017.8205952. [22] QIU Kejie, QIN Tong, PAN Jie, et al. Real-time temporal and rotational calibration of heterogeneous sensors using motion correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(2): 587–602. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2020.3033698. [23] 赵亮, 胡杰, 刘汉, 等. 基于语义分割的深度学习激光点云三维目标检测[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(17): 1710004. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1710004.ZHAO Liang, HU Jie, LIU Han, et al. Deep learning based on semantic segmentation for three-dimensional object detection from point clouds[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(17): 1710004. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1710004. [24] LI Shengyu, LI Xingxing, CHEN Shuolong, et al. Two-step LiDAR/camera/IMU spatial and temporal calibration based on continuous-time trajectory estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(3): 3182–3191. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3270506. [25] 仲训杲, 徐敏, 仲训昱, 等. 基于多模特征深度学习的机器人抓取判别方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1022–1029. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150661.ZHONG Xungao, XU Min, ZHONG Xunyu, et al. Multimodal features deep learning for robotic potential grasp recognition[J] Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1022–1029. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150661. [26] KENDALL A, GRIMES M, and CIPOLLA R. PoseNet: A convolutional network for real-time 6-Dof camera relocalization[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2938–2946. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.336. [27] QI C R, SU Hao, MO Kaichun, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. [28] QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017: 5105–5114. [29] SCHNEIDER N, PIEWAK F, STILLER C, et al. RegNet: Multimodal sensor registration using deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017: 1803–1810. doi: 10.1109/IVS.2017.7995968. [30] WU Shan, HADACHI A, VIVET D, et al. NetCalib: A novel approach for LiDAR-camera auto-calibration based on deep learning[C]. The 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Milan, Italy, 2021: 6648–6655. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.13266.79048. [31] IYER G, RAM R K, MURTHY J K, et al. CalibNet: Geometrically supervised extrinsic calibration using 3D spatial transformer networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 2018: 1110–1117. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8593693. [32] LV Xudong, WANG Shuo, and YE Dong. CFNet: LiDAR-camera registration using calibration flow network[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(23): 8112. doi: 10.3390/s21238112. [33] LV Xudong, WANG Boya, DOU Ziwen, et al. LCCNet: LiDAR and camera self-calibration using cost volume network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, TN, USA, 2021: 2888–2895. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW53098.2021.00324. [34] JING Xin, DING Xiaqing, XIONG Rong, et al. DXQ-Net: Differentiable LiDAR-camera extrinsic calibration using quality-aware flow[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.09385, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2203.09385. [35] ZHOU Tinghui, BROWN M, SNAVELY N, et al. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 6612–6619. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.700. [36] LI Ruihao, WANG Sen, LONG Zhiqiang, et al. UnDeepVO: Monocular visual odometry through unsupervised deep learning[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2018: 7286–7291. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2018.8461251. [37] 张重生, 陈杰, 李岐龙, 等. 深度对比学习综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 15–39. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220421.ZHANG Chongsheng, CHEN Jie, LI Qilong, et al. Deep contrastive learning: A survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 15–39. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220421. [38] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [39] WU T, PAN L, ZHANG J, et al. Density-aware chamfer distance as a comprehensive metric for point cloud completion[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12702. 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2111.12702. [40] GEIGER A, LENZ P, STILLER C, et al. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231–1237. doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297. [41] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. 2014. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. [42] YE Chao, PAN Huihui, and GAO Huijun. Keypoint-based LiDAR-camera online calibration with robust geometric network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 2503011. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3129882. [43] 刘辉, 蒙丽雯, 段一戬, 等. 基于4D相关性金字塔的激光雷达-视觉传感器外参在线标定方法[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(17): 1704003. doi: 10.3788/CJL231290.LIU Hui, MENG Liwen, DUAN Yijian, et al. Online calibration method of lidar-visual sensor external parameters based on 4D correlation pyramid[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(17): 1704003. doi: 10.3788/CJL231290. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: