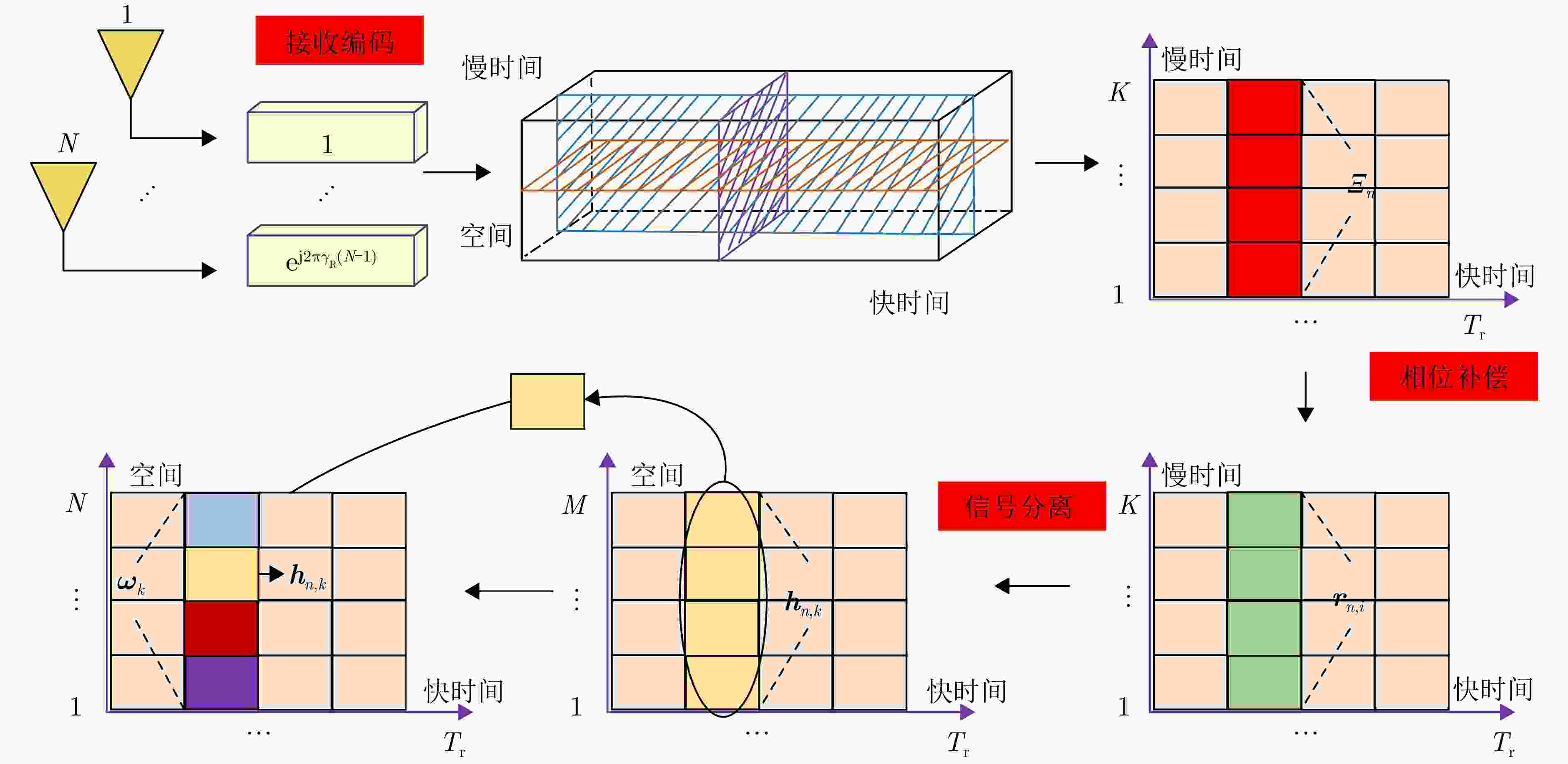
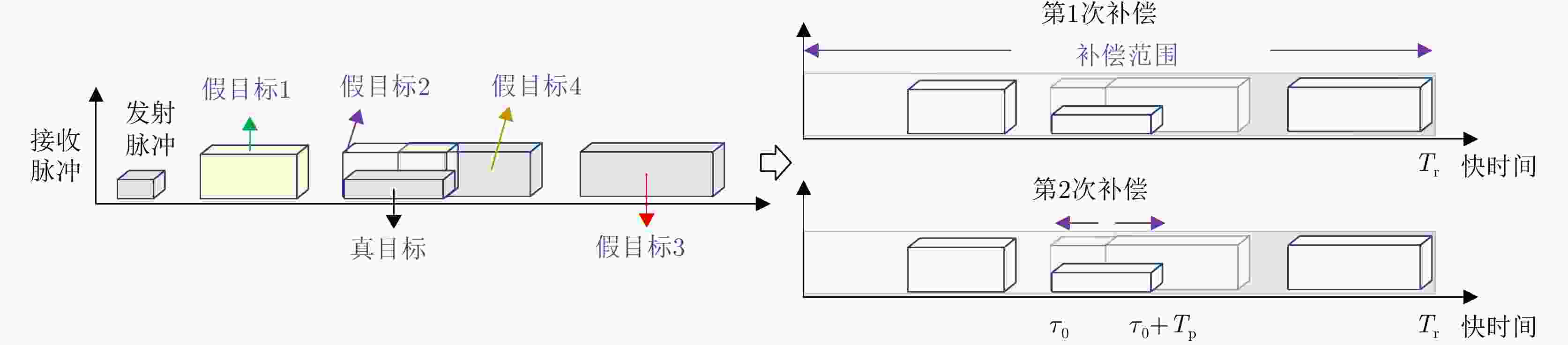
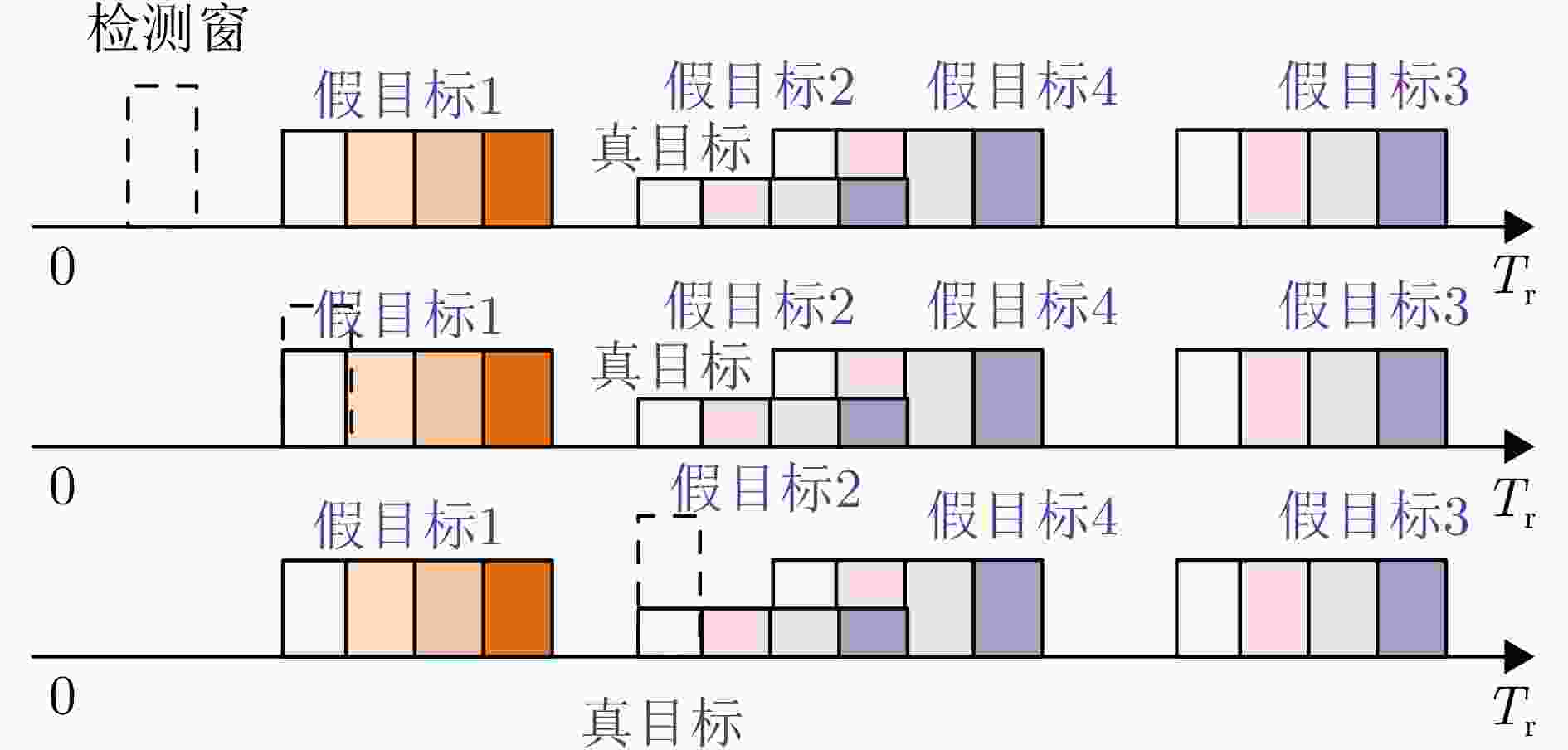
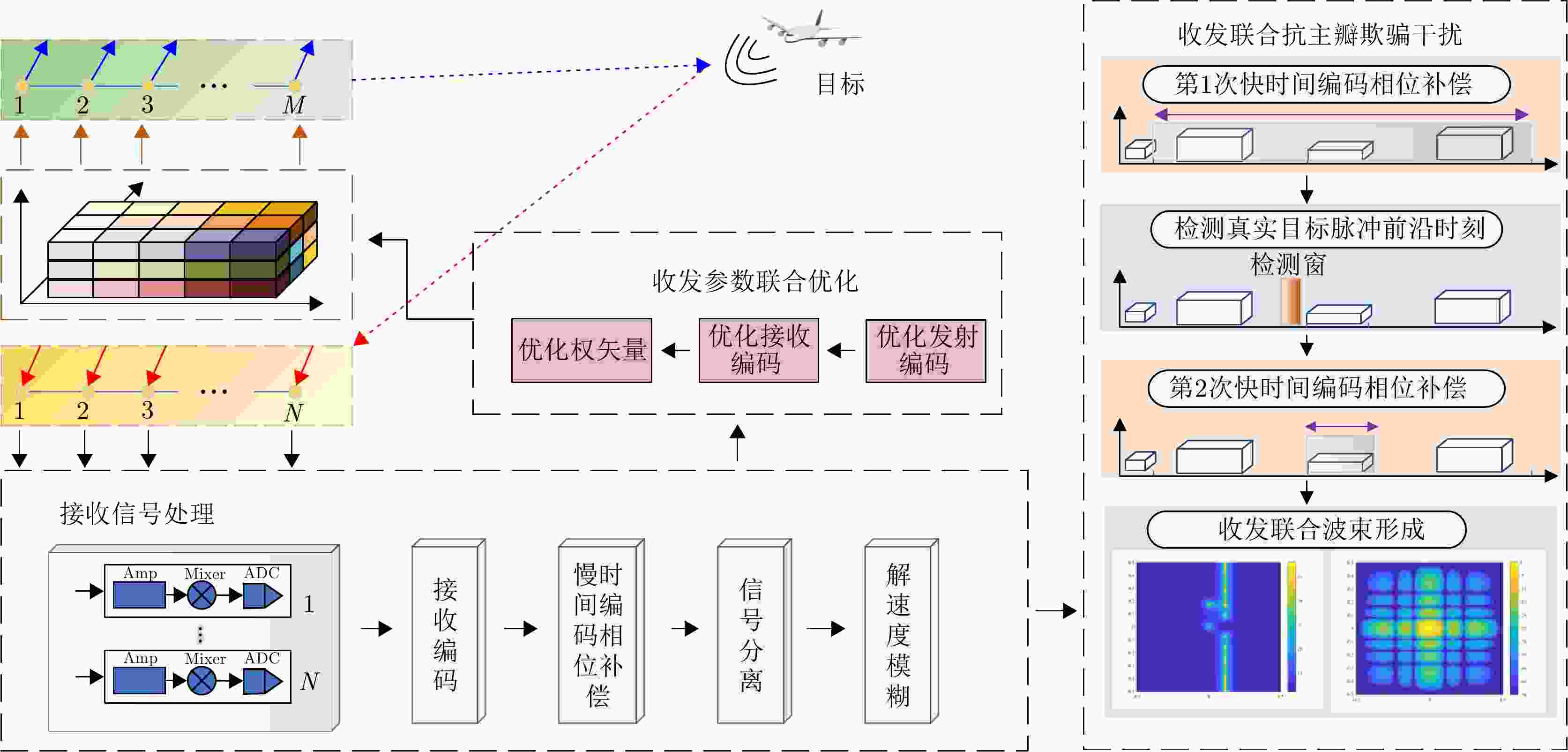
Main-lobe Deceptive Jammers with Array Radars Using Space-time Multidimensional Coding
-
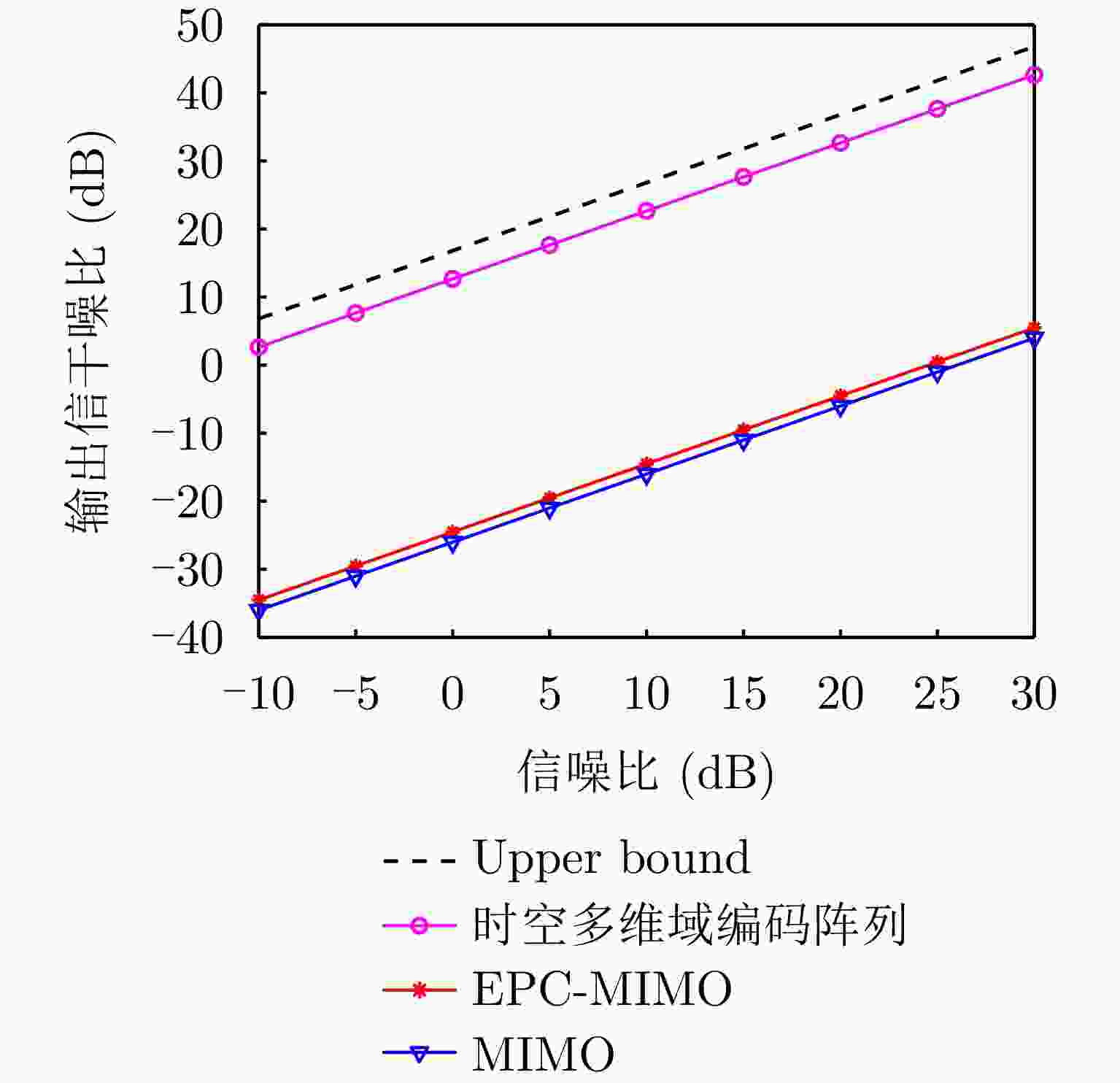
摘要: 随着电子技术的快速发展,雷达面临的电磁环境日益复杂。当存在主瓣有源欺骗干扰时,传统相控阵雷达自适应波束形成抗干扰失效,主瓣干扰抑制已成为雷达领域亟待解决的共性难题。该文针对来自主瓣的自卫式转发干扰,提出了一种时空多维域编码抗主瓣欺骗式干扰方法。首先,设计发射通道-脉冲-子脉冲编码,在接收端采用多普勒分多址方法实现了发射信号分离。针对目标高速运动导致的分离错位现象,提出一种基于波束形成能量差的移位数估计方法。随后,利用目标与干扰的延时相位差,设计收发联合的双重编码相位补偿方法,在发射空间频率域实现对真实目标、跨脉冲转发干扰、脉内转发干扰的区分,并且通过构建联合发射-接收权矢量,对主瓣欺骗式干扰进行空域滤波抑制。针对实际中波达角度(DOA)误差造成的抗干扰性能下降问题,构建了以最大化输出信干噪比(SINR)为目标函数的约束优化问题,基于交替迭代算法对接收权矢量,发射编码系数、接收编码系数分别进行优化。仿真实验验证了所提方法相比于其他雷达体制在抗主瓣欺骗干扰方面的有效性,其中相比于传统MIMO雷达,所提阵列时空多维域编码技术在4个主瓣干扰存在的情况下SINR可提升34 dB。Abstract: With the rapid development of electronic technology, the electromagnetic environment is becoming increasingly complex. For instance, adaptive beamforming cannot suppress main-lobe jammers for traditional phased array radars; therefore, developing measures to tackle this common problem is an urgent need in radar technology. This study addresses the problem of main-lobe deceptive jammer suppression using space-time multidimensional coding. The first step is to design a three-dimensional phase coding scheme applicable across transmit channels, pulses, and subpulses. A Doppler division multiple access technique is employed at the receiver to separate the transmit signals. To solve the problem of waveform misalignment caused by high-speed moving targets, a novel approach is proposed to estimate the compensation index according to differences in beamforming energy. Subsequently, a dual-phase compensation method that leverages the phase differences between the main-lobe deceptive jammers and the target is proposed; this method can distinguish the true target, pulse-delayed jammers, and rapidly generated jammers in the transmit spatial frequency domain. Moreover, spatial filtering is applied to suppress all the main-lobe deceptive jammers by designing an appropriate transmit-receive weight vector. Additionally, an optimization problem aiming to maximize the output Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) is formulated to address the problem of performance degradation due to the Direction of Arrival (DOA) Errors. Further, to solve this problem, an alternating optimization method is utilized to obtain the optimized weight vector and transmit and receive coding coefficients iteratively to improve the SINR. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method suppresses the main-lobe deceptive jammers more effectively than other radar frameworks. Specifically, compared to the conventional multiple-input multiple-output radar, the proposed method achieves an SINR improvement of 34 dB in the presence of four main-lobe deceptive jammers.
-
表 1 目前主瓣干扰抑制技术对比
Table 1. Comparison of current main-lobe jammer suppression techniques
分类 方法 抗干扰原理 局限性 空域 单脉冲技术[7,8] 构建4通道单脉冲系统,分两级抗干扰 对系统误差稳健性差,低快拍时性能差 数据预处理[9,10] 采用阻塞矩阵、正交投影矩阵、特征投影矩阵等预处理矩阵抑制主瓣干扰 子空间技术[11] 将主瓣干扰斜投影到旁瓣干扰子空间抑制 时域 盲源分离[12,13] 利用基于矩阵联合对角化/特征矩阵近似联合对角化方法
分离出主瓣干扰和目标不适用于目标和干扰信号具有部分
相关特性的场景稀疏恢复[14] 将信号模型转换为欠定矩阵方程,然后通过稀疏分解基追踪算法来求解 脉冲分集[15,16] 改变信号慢时间域参数,构造脉间的信息差异来区分真、
假目标频域 频率捷变[3−5] 结合Hough变换、参差重频、压缩感知、交替迭代、脉冲变换等方法设计抗干扰捷变波形 相参积累难 极化域 极化滤波[17−19] 通过雷达收发系统极化方式与干扰信号极化方式正交,
抑制了主瓣压制干扰真、假目标间互扰对极化抗干扰
性能影响很大极化分集[20] 采用发射端极化分集、收发二维极化分集、极化编码等
方法抑制主瓣干扰分布式组网 组网/分布式[21−24] 通过数据级/信号级信息融合,进行多站协同对抗 系统时间和空间同步、目标配对、
资源调度管理难表 2 第1次和第2次补偿后的目标发射、接收空间频率
Table 2. Transmit and receive spatial frequencies of targets after first and second compensation
目标 第1次补偿后发射空间频率 第1次补偿后接收空间频率 第2次补偿后发射空间频率 第2次补偿后接收空间频率 真实目标 $ f_{{\theta _0},{p_0},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _0} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ f_{{\theta _0}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _0} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _0},{p_0},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _0} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _0}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _0} $ 假目标1 $ \begin{gathered} f_{{\theta _1},{p_1},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _1} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}\left( {{p_1} - {p_0}} \right) \\ - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) \\ \end{gathered} $ $ f_{{\theta _1}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _1} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ \begin{gathered} {{\bar f}_{{\theta _1},{p_1},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _1} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}\left( {{p_1} - {p_0}} \right) \\ - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) \\ \end{gathered} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _1} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ 假目标2 $ \begin{gathered} f_{{\theta _2},{p_2},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _2} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}\left( {{p_2} - {p_0}} \right) \\ - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) \\ \end{gathered} $ $ f_{{\theta _2}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _2} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _2},{p_2},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _2} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}\left( {{p_2} - {p_0}} \right) $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _2}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _2} $ 假目标3 $ f_{{\theta _3},{p_3},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _3} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ f_{{\theta _3}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _3} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _3},{p_3},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _3} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _3}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _3} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ 假目标4重叠
部分$ f_{{\theta _4},{p_4},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ f_{{\theta _4}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _4},{p_4},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}l' $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _4}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} $ 假目标4非
重叠部分$ f_{{\theta _4},{p_4},l}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ f_{{\theta _4}}^{} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _4},{p_4},l}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{T}}}(l - 1) $ $ {\bar f_{{\theta _4}}} = \dfrac{d}{\lambda }\sin {\theta _4} - {\gamma _{\text{R}}} $ 1 交替迭代的收发编码及方向图联合优化方法
1. The joint optimization of transceiver coding and beampattern using alternating iteration
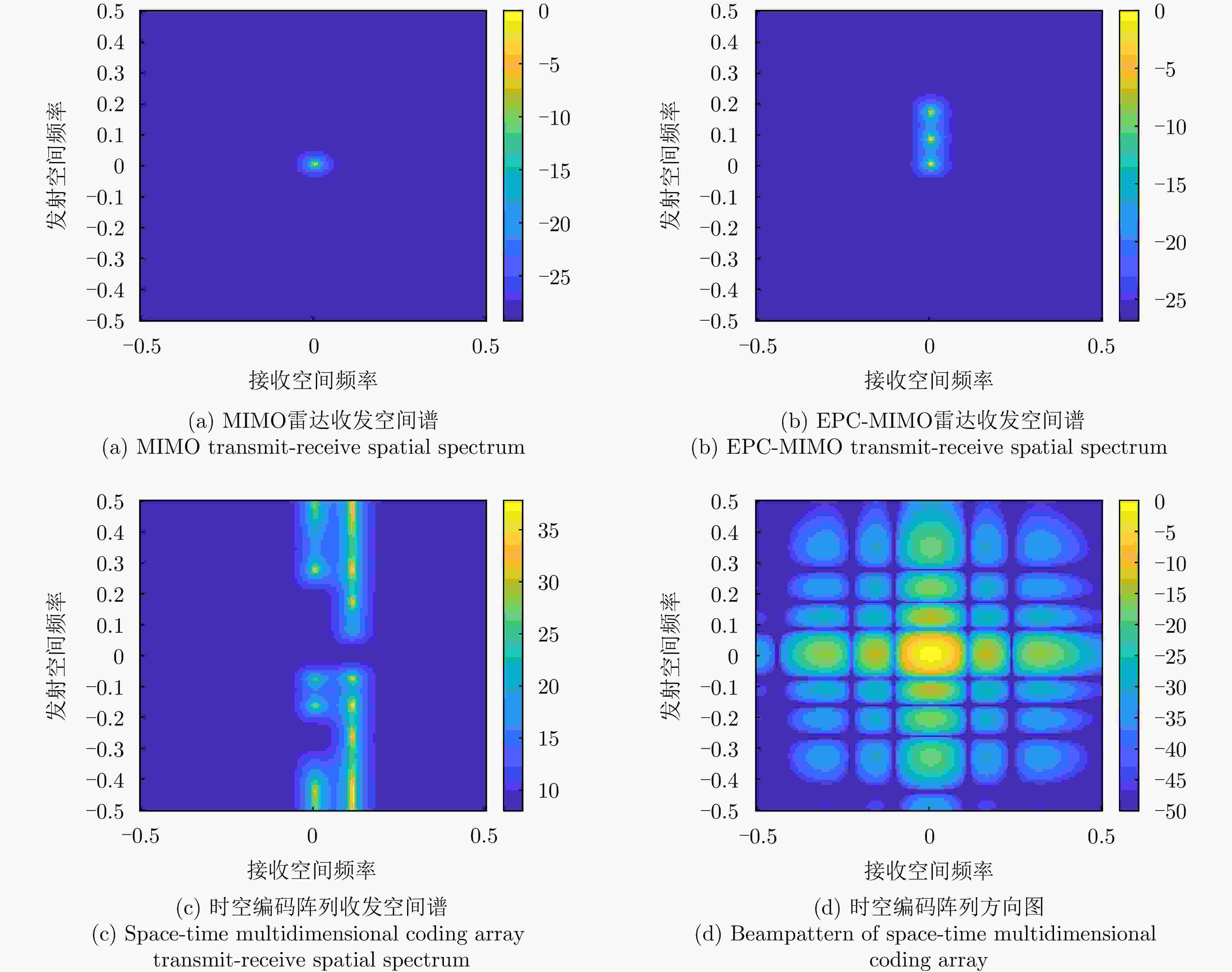
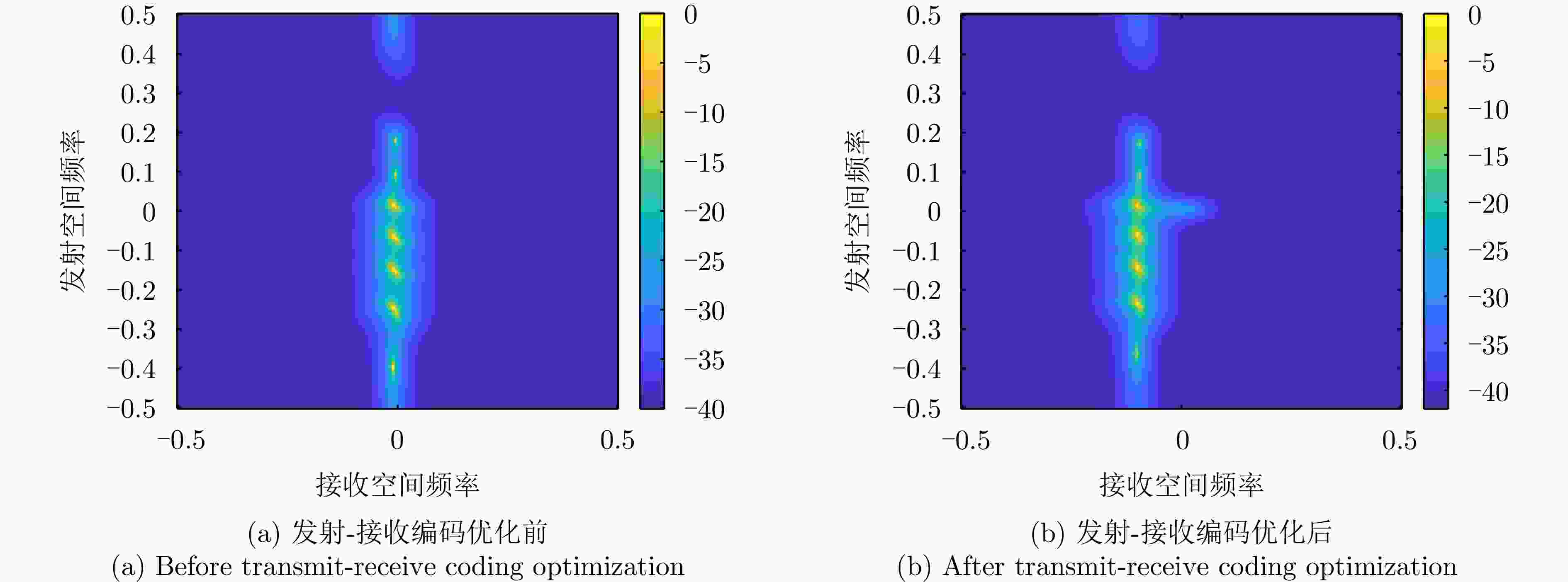
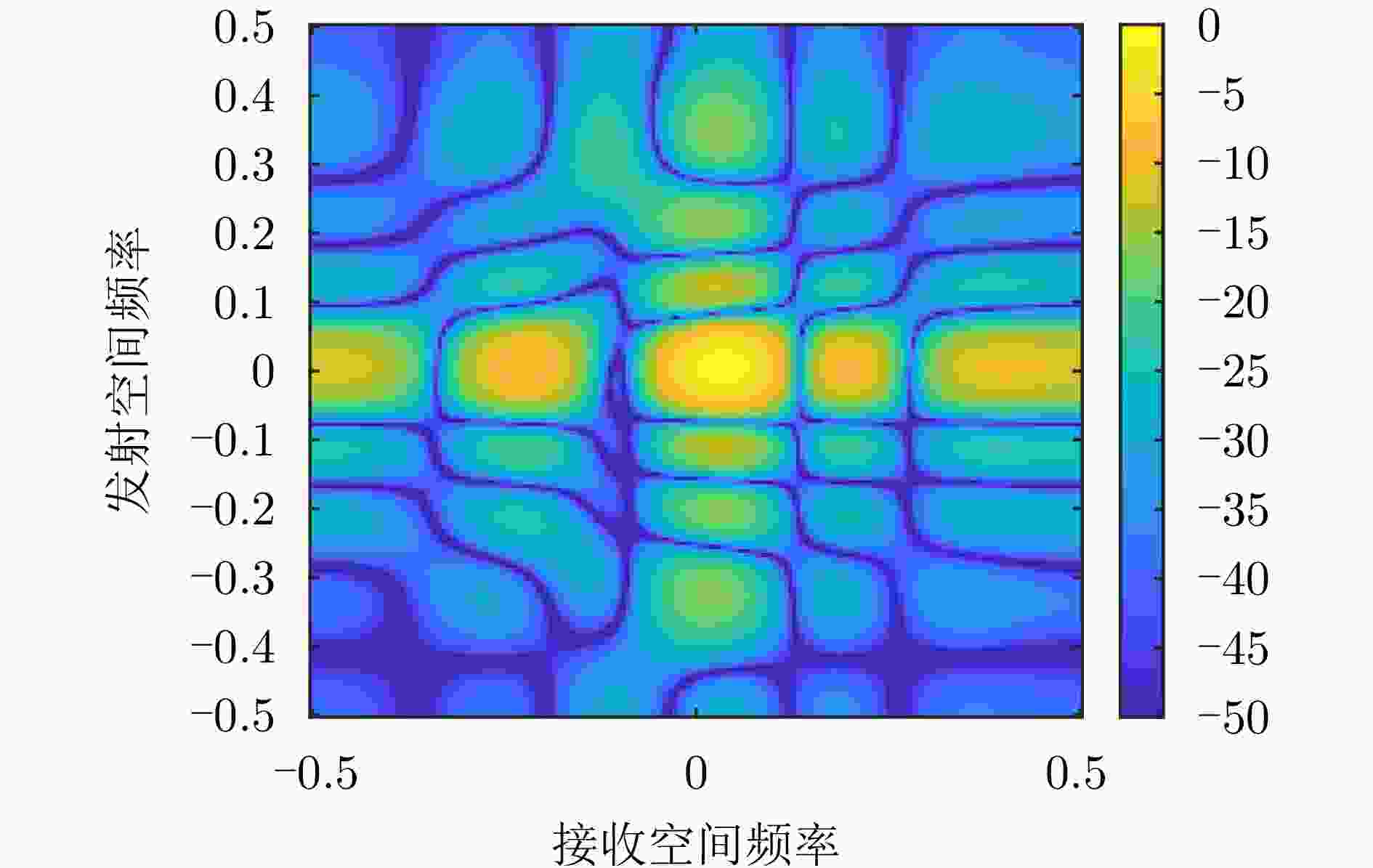
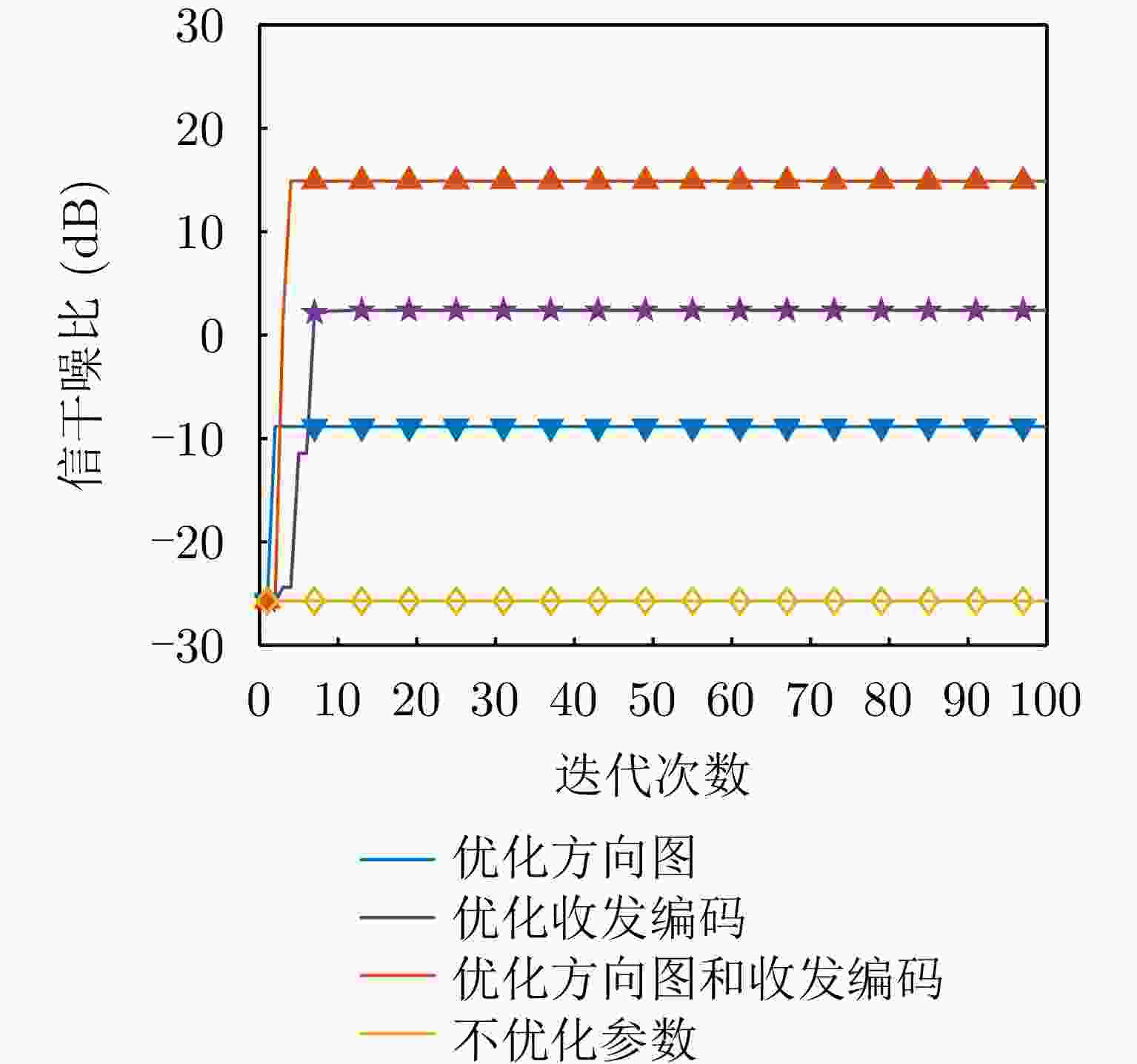
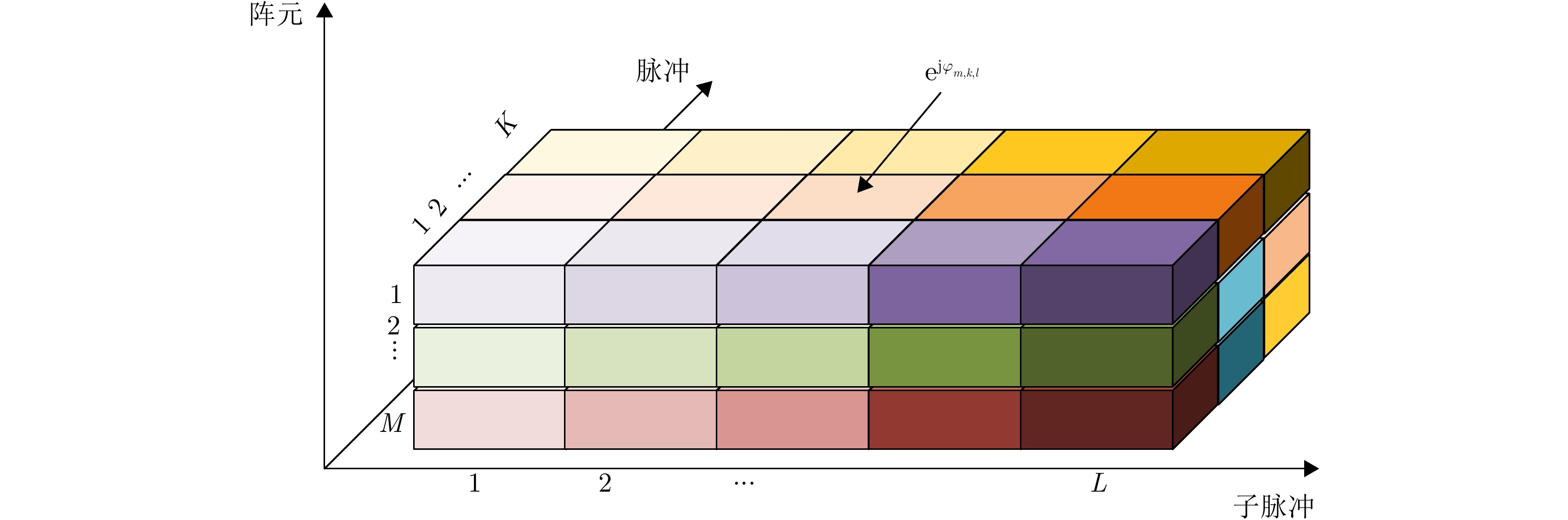
输入:M, N, L, K, $ {p_0} $, $ {p_q} $, $ {\sigma _q} $, $ {\sigma _n} $ 初始化:$i = 1$, $ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(i - 1)}} $, $ \gamma _{\text{T}}^{(i - 1)} $, $ \gamma _{\text{R}}^{(i - 1)} $, ${\text{ }}I$ while ${{i < }}I$ 1. 依据$ \gamma _{\text{T}}^{(i - 1)} $, $ \gamma _{\text{R}}^{(i - 1)} $,通过求解优化问题$ \mathcal{P}_{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(i)} $搜索$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(i)}} $; 2. 依据$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(i)}} $, $ \gamma _{\text{R}}^{(i - 1)} $,通过求解优化问题$ \mathcal{P}_{{\gamma _{\text{T}}}}^{(i)} $搜索$ \gamma _{\text{T}}^{(i)} $; 3. 依据$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(i)}} $, $ \gamma _{\text{T}}^{(i)} $,通过求解优化问题$ \mathcal{P}_{{\gamma _{\text{R}}}}^{(i)} $搜索$ \gamma _{\text{R}}^{(i)} $; 4. 计算当前${{\mathrm{SINR}}^{(i)}}$; 5. if $ \left| {{{\mathrm{SINR}}^{(i)}} - {{\mathrm{SINR}}^{(i - 1)}}} \right| < \varepsilon $ then 6. 令$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}}^{\ast }={{\boldsymbol{w}}}^{(i)},\;{\gamma }_{\text{T}}^{\ast }={\gamma }_{\text{T}}^{(i)},\;{\gamma }_{\text{R}}^{\ast }={\gamma }_{\text{R}}^{(i)} $,停止迭代; 7. end if 8 $i = i + 1$; end while 输出:$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^ * } $, $ \gamma _{\text{T}}^ * $, $ \gamma _{\text{R}}^ * $. 表 3 系统仿真参数
Table 3. System simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 发射阵元数M 8 接收阵元数N 6 载频${f_0}$ 8 GHz 脉冲重复频率${f_{\mathrm{r}}}$ 20 kHz 脉冲数K 64 发射编码系数$ {\gamma _{\text{T}}} $ 1/M 接收编码系数${\gamma _{\text{R}}}$ 1/N 脉宽${T_{\mathrm{p}}}$ 5 μs 子脉冲数L 5 带宽B 5 MHz 表 4 真假目标参数设置
Table 4. Simulation parameters of true and false targets
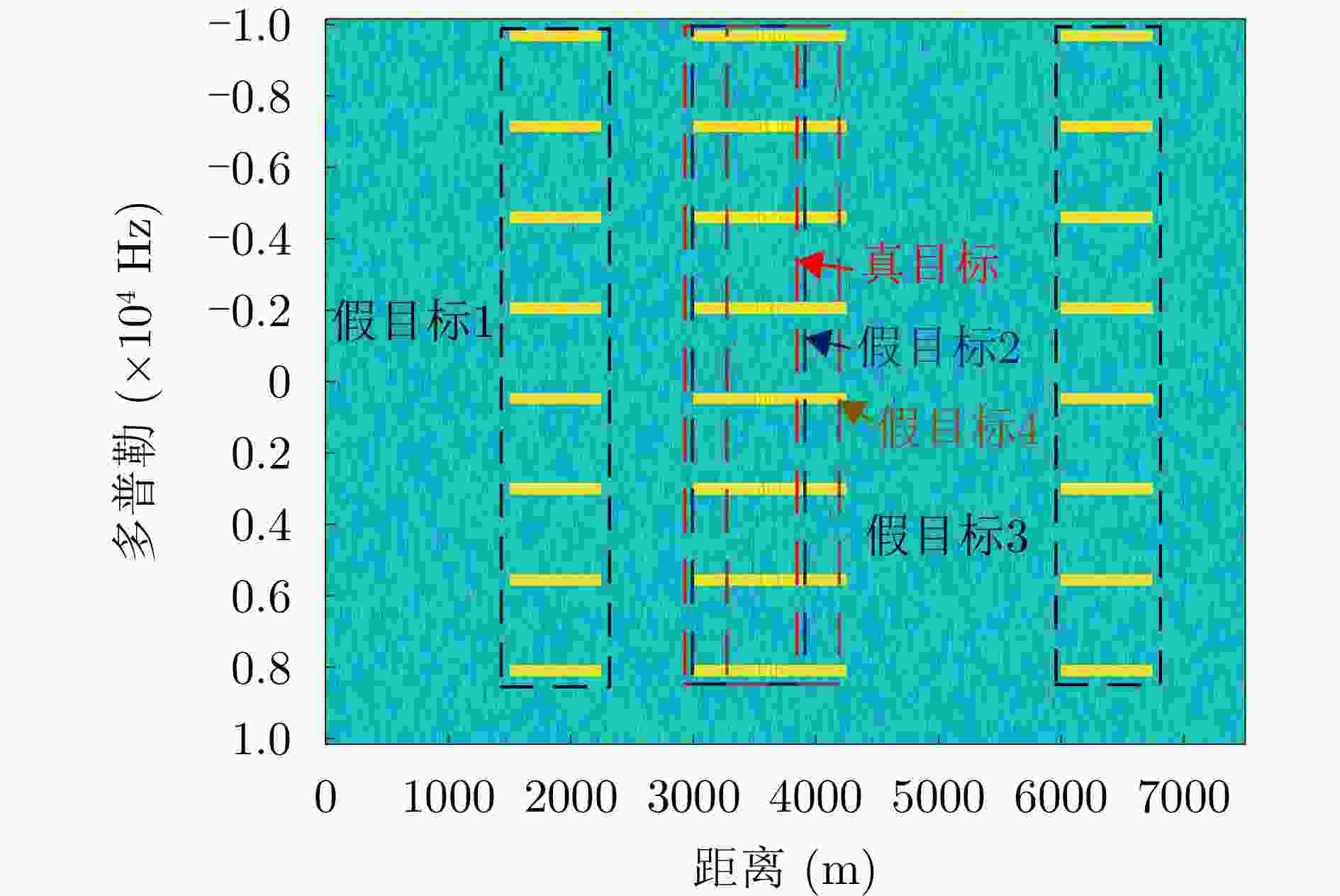
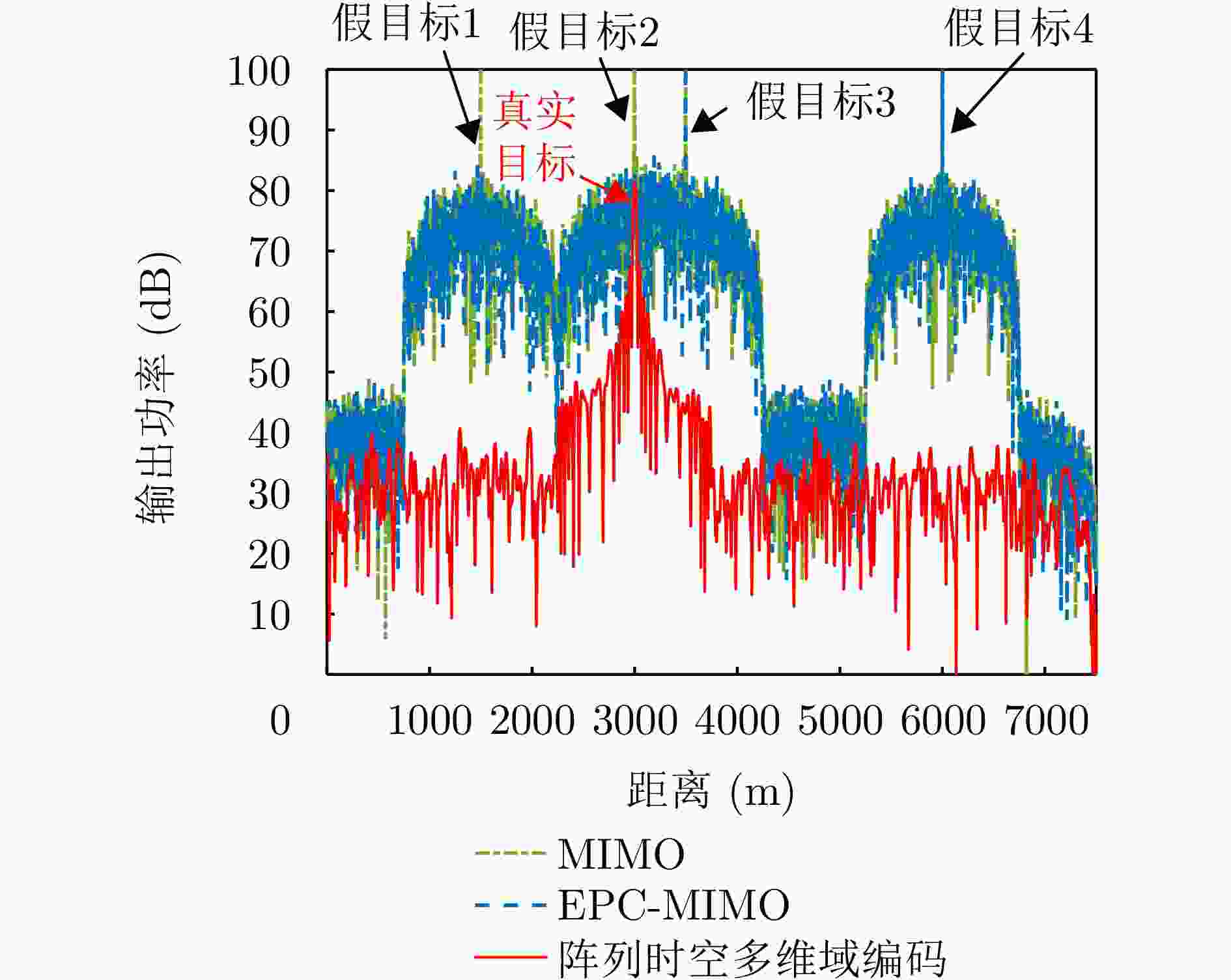
参数 数值 参数 数值 真目标角度($^ \circ $) 1 真目标主值距离(km) 3 信噪比SNR (dB) 0 真目标脉冲延迟数 0 目标速度(m/s) 80 假目标角度($^ \circ $) 1, 1, 1, 1 假目标主值
距离(km)1.5, 3.0, 3.5, 6.5 假目标脉冲延迟数 2, 1, 0, 0 假目标JNR (dB) 20, 20, 20, 20 -
[1] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [2] 刘强, 张敏, 郭福成, 等. 基于迭代二次优化算法的低截获波形序列设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 2048–2056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231333.LIU Qiang, ZHANG Min, GUO Fucheng, et al. Low-intercept waveform sequence design based on iterative quadratic optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 2048–2056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231333. [3] 全英汇, 方文, 沙明辉, 等. 频率捷变雷达波形对抗技术现状与展望[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11.QUAN Yinghui, FANG Wen, SHA Minghui, et al. Present situation and prospects of frequency agility radar waveform countermeasures[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11. [4] 王晓戈, 李槟槟, 陈辉, 等. 基于脉内频率编码联合调频斜率捷变波形的ISRJ对抗方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(5): 1019–1036. doi: 10.12000/JR24046.WANG Xiaoge, LI Binbin, CHEN Hui, et al. Anti-ISRJ method based on intrapulse frequency-coded joint frequency modulation slope agile radar waveform[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(5): 1019–1036. doi: 10.12000/JR24046. [5] AKHTAR J and OLSEN K E. Frequency agility radar with overlapping pulses and sparse reconstruction[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 61–66. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378531. [6] 高宇航, 张凯翔, 范花玉, 等. 基于脉间码型捷变波形的距离-多普勒二维干扰重构算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 187–199. doi: 10.12000/JR23196.GAO Yuhang, ZHANG Kaixiang, FAN Huayu, et al. Range-Doppler two-dimensional jamming reconstruction algorithm based on interpulse code agile waveform[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 187–199. doi: 10.12000/JR23196. [7] WU Hao, LIU Rang, GUO Yu, et al. Performance analysis of mainlobe canceller for monopulse at subarray level in the presence of amplitude-phase error[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 2461–2473. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3354224. [8] WANG Jianlu, XU Xiong, DAI Huanyao, et al. Method for four-channel monopulse radar to resist dual-source angle deception jamming[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7493–7497. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0464. [9] 王明, 郭山红, 丛潇雨, 等. 一种主瓣保形的主副瓣联合空域抗干扰算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2025, 47(1): 71–78. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2025.01.012.WANG Ming, GUO Shanhong, CONG Xiaoyu, et al. A joint anti-jamming algorithm in space-domain of mainlobe and sidelobe for mainlobe shape-preserving[J]. Modern Radar, 2025, 47(1): 71–78. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2025.01.012. [10] MENG Haoyu, QU Xiaodong, ZHANG Xingyu, et al. Mainlobe interference suppression method based on blocking matrix preprocessing with low sidelobe constraint[C]. 2022 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2022: 2065–2070. doi: 10.23919/APSIPAASC55919.2022.9980066. [11] YANG Xiaopeng, ZHANG Zongao, ZENG Tao, et al. Mainlobe interference suppression based on eigen-projection processing and covariance matrix reconstruction[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 1369–1372. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2339224. [12] GE Mengmeng, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Main lobe jamming suppression via blind source separation sparse signal recovery with subarray configuration[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(3): 431–438. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0500. [13] 房津辉, 宋宝军, 朱明哲. 基于改进的盲源分离算法抗主瓣SMSP干扰[J]. 现代雷达, 2023, 45(2): 8–15. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.02.002.FANG Jinhui, SONG Baojun, and ZHU Mingzhe. Anti-mainlobe SMSP interference based on improved blind source separation algorithm[J]. Modern Radar, 2023, 45(2): 8–15. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.02.002. [14] WANG Jie, ZHU Qiuming, LIN Zhipeng, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning-based 3-D radio environment map construction-sampling optimization, scenario-dependent dictionary construction, and sparse recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(1): 80–93. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3319539. [15] DAI Gane, HUAN Sha, and ZHANG Lei. Integrating agile waveforms with DBF for HRWS SAR imagery and adaptive jamming suppression[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 4080–4095. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3268526. [16] 刘智星, 杜思予, 吴耀君, 等. 脉间-脉内捷变频雷达抗间歇采样干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001.LIU Zhixing, DU Siyu, WU Yaojun, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming method for interpulse and intrapulse frequency-agile radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001. [17] MA Jiazhi, SHI Longfei, LI Yongzhen, et al. Estimation of extended targets in main-lobe interference with polarization filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(1): 169–189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2649783. [18] 陈焱, 王占领, 庞晨, 等. 基于极化时变调控表面的有源欺骗干扰辨识方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 929–940. doi: 10.12000/JR24028.CHEN Yan, WANG Zhanling, PANG Chen, et al. Radar active deception jamming recognition method based on the time-varying polarization-conversion metasurface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 929–940. doi: 10.12000/JR24028. [19] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039.WANG Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039. [20] XIANG Zhe, CHEN Baixiao, and YANG Minglei. Transmitter/receiver polarisation optimisation based on oblique projection filtering for mainlobe interference suppression in polarimetric multiple-input-multiple-output radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 137–144. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0648. [21] HAN Xiaofei, HE Huafeng, ZHANG Qi, et al. Main-lobe jamming suppression method for phased array netted radar based on MSNR-BSS[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(23): 22972–22984. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3213986. [22] 张林让, 赵珊珊, 周宇, 等. 网络化雷达协同抗欺骗式干扰技术研究进展[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2014, 29(4): 516–525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.005.ZHANG Linrang, ZHAO Shanshan, ZHOU Yu, et al. Research advance on cooperative anti-deception jamming in netted radar[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2014, 29(4): 516–525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.005. [23] 黄大通, 崔国龙, 孔令讲. 一种多基地雷达抗距离欺骗干扰技术[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(3): 83–90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.03.018.HUANG Datong, CUI Guolong, and KONG Lingjiang. A suppression technique for range deception jamming in multistatic radar system[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(3): 83–90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.03.018. [24] 陈静, 李晗, 张洪纲, 等. 分布式雷达主瓣间歇采样转发干扰抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(11): 1368–1376. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.013.CHEN Jing, LI Han, ZHANG Honggang, et al. Main-lobe interrupted sampling repeater jamming suppression method in distributed radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(11): 1368–1376. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.013. [25] LIU Qi, XU Jingwei, DING Zhi, et al. Target localization with jammer removal using frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11685–11696. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3016948. [26] LAN Lan, ZHANG Yitao, XU Jingwei, et al. Suppressing mainlobe deceptive jammers via two-low-rank matrix decomposition in FDA-MIMO Radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3480030. [27] 兰岚, 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 等. 波形分集阵列雷达抗干扰进展[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(6): 1437–1451. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.01.LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Advances in anti-jamming using waveform diverse array radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(6): 1437–1451. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.01. [28] 王文钦, 陈慧, 郑植, 等. 频控阵雷达技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029.WANG Wenqin, CHEN Hui, ZHENG Zhi, et al. Advances on frequency diverse array radar and its applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029. [29] 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 廖桂生, 等. 频率分集阵雷达技术探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023.XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, LIAO Guisheng, et al. An overview of frequency diverse array radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023. [30] 兰岚, 廖桂生, 许京伟, 等. 基于频率分集阵列的多功能一体化波形设计与信号处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 850–870. doi: 10.12000/JR22163.LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Waveform design and signal processing method of a multifunctional integrated system based on a frequency diverse array[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 850–870. doi: 10.12000/JR22163. [31] 许京伟, 廖桂生, 张玉洪, 等. 波形分集阵雷达抗欺骗式干扰技术[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(3): 545–551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.005.XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHANG Yuhong, et al. On anti-jamming technique with waveform diverse array radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(3): 545–551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.005. [32] 兰岚, 廖桂生, 许京伟, 等. FDA-MIMO雷达主瓣距离欺骗式干扰抑制方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(5): 997–1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.06.LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Main-beam range deceptive jamming suppression approach with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(5): 997–1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.06. [33] LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Suppression approach to main-beam deceptive jamming in FDA-MIMO radar using nonhomogeneous sample detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34582–34597. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2850816. [34] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Deceptive jamming suppression with frequency diverse MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 113: 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.01.014. [35] LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Suppression of mainbeam deceptive jammer with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11584–11598. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014689. [36] LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Mainlobe deceptive jammer suppression using element-pulse coding with MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 182: 107955. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107955. [37] RABIDEAU D J. MIMO radar waveforms and cancellation ratio[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1167–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178055. [38] SUN Ying, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 794–816. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2601299. [39] YAO Yu, LI Zeqing, LIU Haitao, et al. Robust transceiver optimization against echo eclipsing via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 2464–2479. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3215113. [40] QIAO Yuchuan, VAN LEW B, LELIEVELDT B P F, et al. Fast automatic step size estimation for gradient descent optimization of image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(2): 391–403. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2476354. [41] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, ZAPPONE A, et al. A new sequential optimization procedure and its applications to resource allocation for wireless systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(24): 6518–6533. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2868265. [42] HE Hao, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Designing unimodular sequence sets with good correlations—including an application to MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(11): 4391–4405. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2025108. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
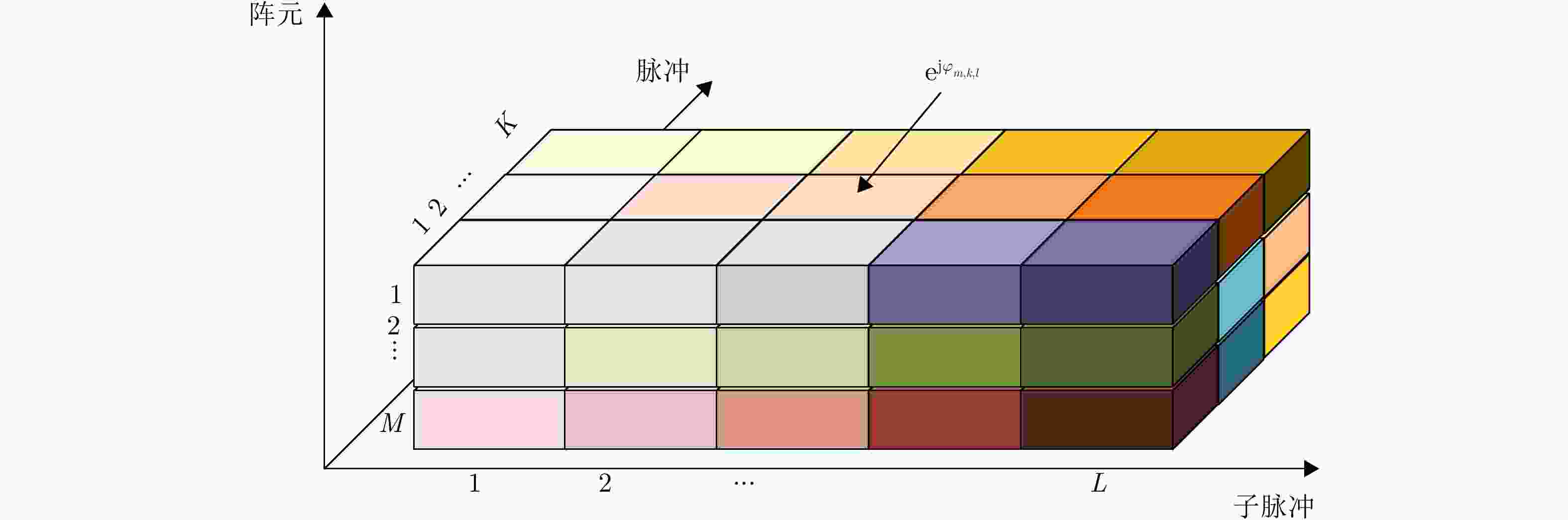
 下载:
下载: