Information Metasurface Technology-enabled Integrated Passive Wireless Communication System Based on Synthetic Aperture Radar
-
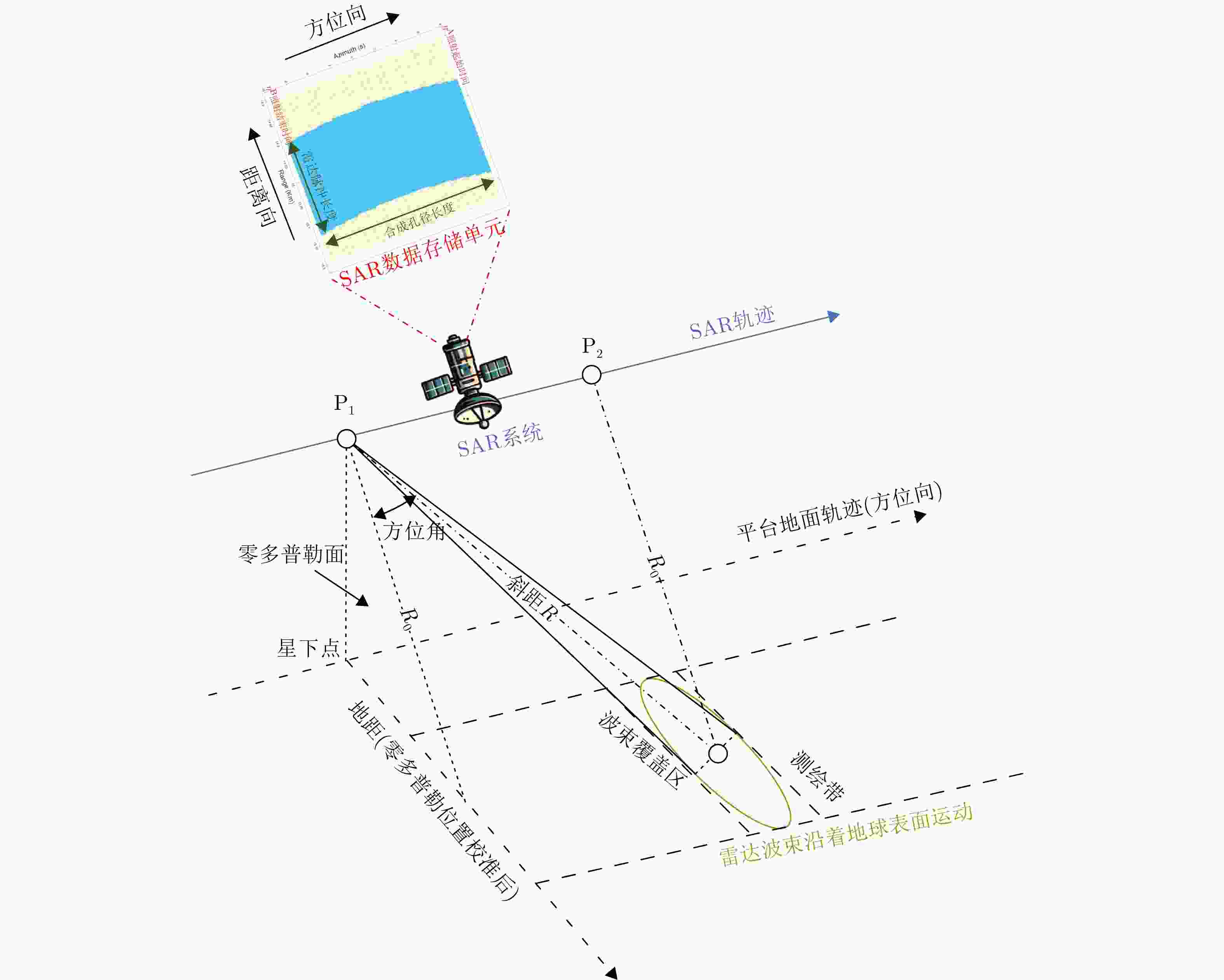
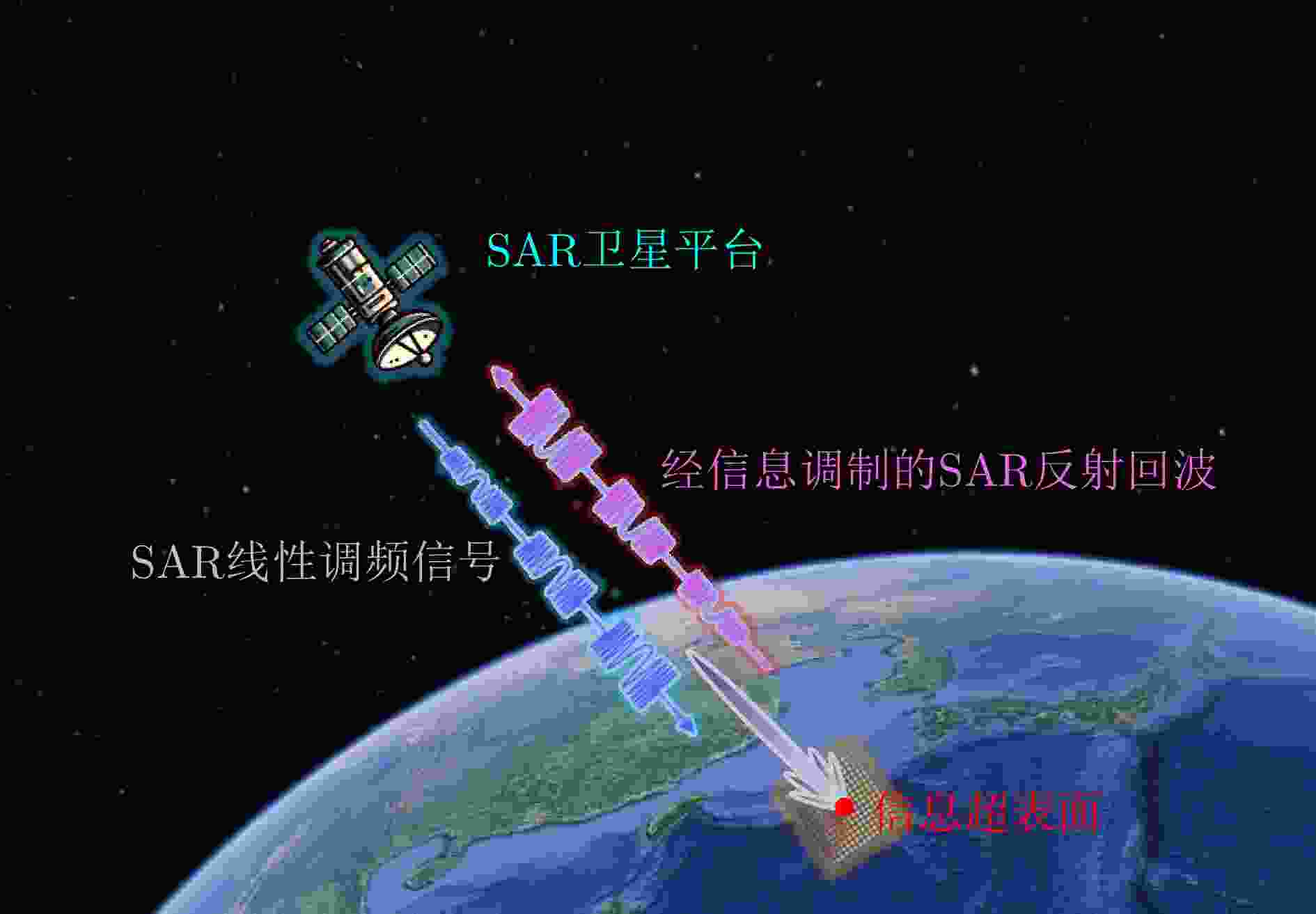
摘要: 卫星通信与星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)遥感探测的一体化技术旨在融合通信与遥感功能,实现数据传输与遥感成像的同步进行,以满足对高效、隐蔽和安全信息传输的需求,提升系统的多用途能力。然而,由于二者在波形特性、收发器设计及信号处理算法等方面存在显著差异,实现星载通信与遥感一体化系统面临诸多挑战。该研究提出了一种基于信息超表面技术的无源无线通信系统,结合SAR回波调制方法,创新性地实现了地星通信与星载SAR遥感探测的深度融合。该系统通过精确调制其SAR散射回波参数,在维持SAR遥感探测质量约束条件下实现了无源无线通信功能。在此基础上,利用电磁反向散射特性替代主动发射机制,有效保障了通信链路的电磁隐蔽性与信息安全特性。场景仿真实验与星载SAR数据实验结果验证了系统的可行性与有效性。实验结果表明,在兼容传统SAR波形体制的前提下,该系统成功实现了地星数据传输与星载SAR成像的同步运行。该研究的核心目标是推动星载SAR遥感探测系统与无线通信技术的深度融合,旨在实现频谱资源的高效利用,并探索如何将信息超表面技术有效应用于通信与遥感一体化系统中,而为该领域提供新的研究视角与技术潜力。Abstract: The integration technology of satellite communications and spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) remote sensing aims to combine communication and remote sensing functionalities, enabling simultaneous data transmission and remote sensing imaging to meet the demands of efficient, covert, and secure information transfer, enhancing system multifunctionality. However, due to significant differences between the waveform characteristics, transceiver design, and signal processing algorithms of the technologies, integrating communication and remote sensing in spaceborne systems presents numerous challenges. This study proposes a passive wireless communication system based on information metasurface technology, combined with SAR echo modulation methods, to innovatively achieve the deep integration of ground-to-space communication and spaceborne SAR remote sensing. The system precisely modulates the scattering parameters of SAR echoes to enable passive wireless communication without affecting the quality of SAR imaging. Additionally, by leveraging electromagnetic backscatter properties instead of active transmission mechanisms, the system effectively ensures the electromagnetic concealment and information security of the communication link. A series of scene simulation experiments and spaceborne SAR data experiments were performed, which validated the system’s feasibility and effectiveness. Results indicate that while maintaining compatibility with traditional SAR waveform structures, the proposed system successfully achieved the synchronous operation of ground-to-space data transmission and spaceborne SAR imaging. The core objective of this research was to promote the deep integration of spaceborne SAR remote sensing systems and wireless communication technologies, aiming for the efficient utilization of spectrum resources and exploring the application of information metasurface technology in integration of communication and remote sensing systems, providing new research perspectives and technological potential in this field.
-
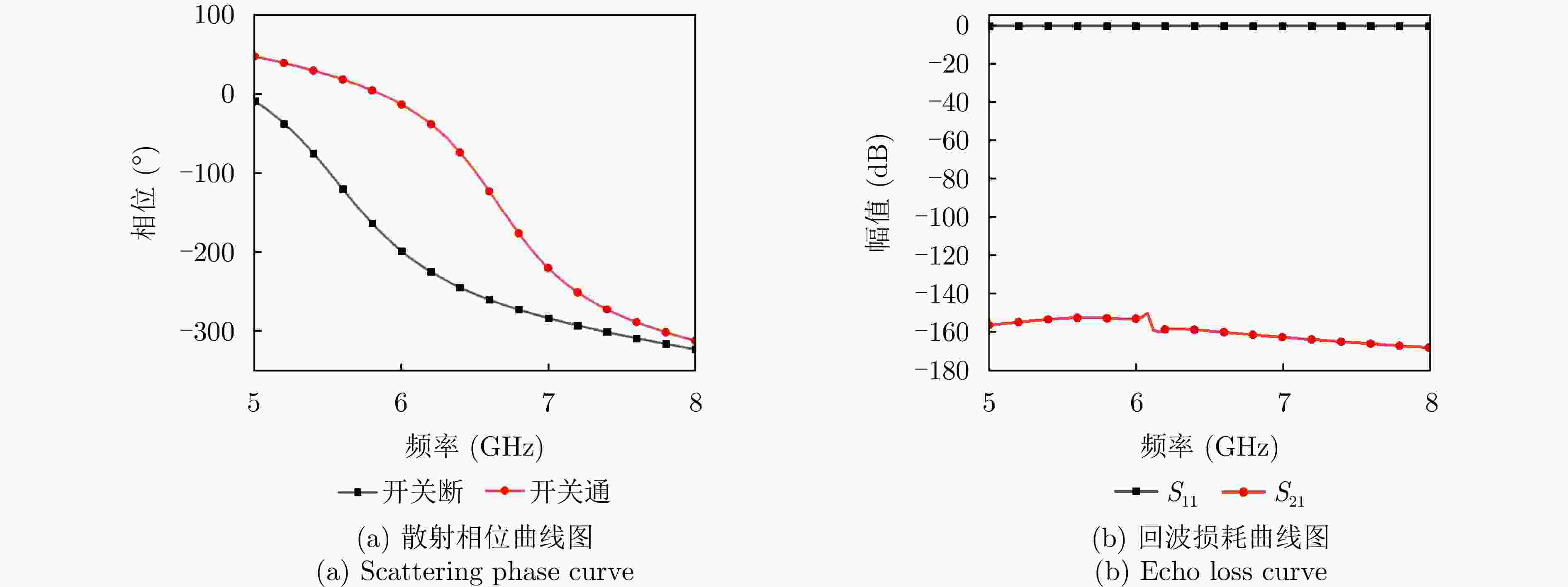
表 1 不同编码的C波段信息超表面散射系数幅值和相位
Table 1. Scattering coefficient magnitude and phase of C-band information metasurface with different encodings
编码序列 幅值(dB) 相位(°) 1111111 ···1111111 26.25 187.0 0111111··· 1111110 24.33 177.0 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 0001110···0111000 15.27 69.0 0111011···0111110 19.89 51.0 0000000···0000000 32.92 0.1 表 2 高分3号卫星轨道参数
Table 2. Orbital parameters of Gaofen-3 satellite
参数 数值 偏心率 0.0015 升交点 0° 倾角 98.4° 半长轴 7126.4 km近地点俯角 270° 表 3 高分3号卫星雷达系统参数
Table 3. SAR system parameters of Gaofen-3 satellite
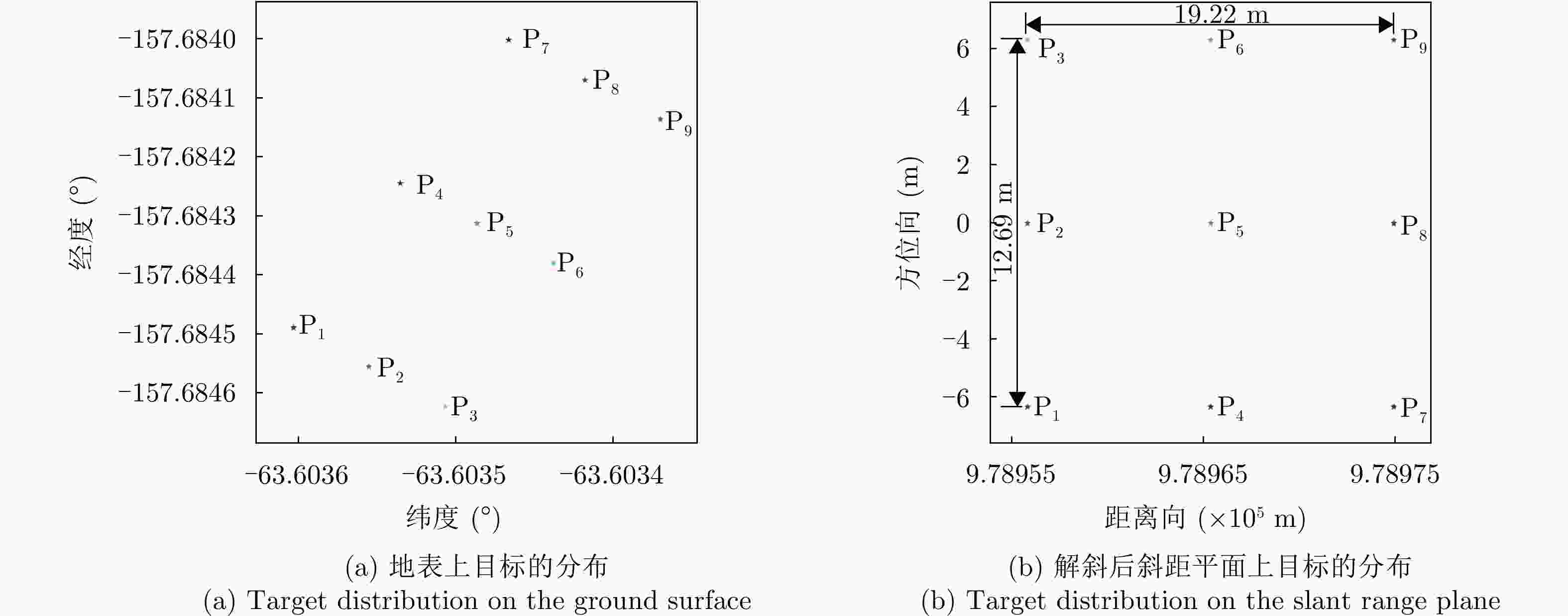
参数 数值 波长 5.55 cm 传输带宽 120 MHz 采样率 133.33 MHz 孔径中心斜视角 0° 中心观测角 32.57° 等效地面速度 6735.52 m/s标称多普勒质心 16.857 kHz 脉冲重复频率 1.996 kHz 场景中心分辨率(距离 × 方位) 2.5 m × 3.0 m 表 4 不同相位编码模式下点目标成像指标
Table 4. Imaging metrics of point targets under different phase encoding modes
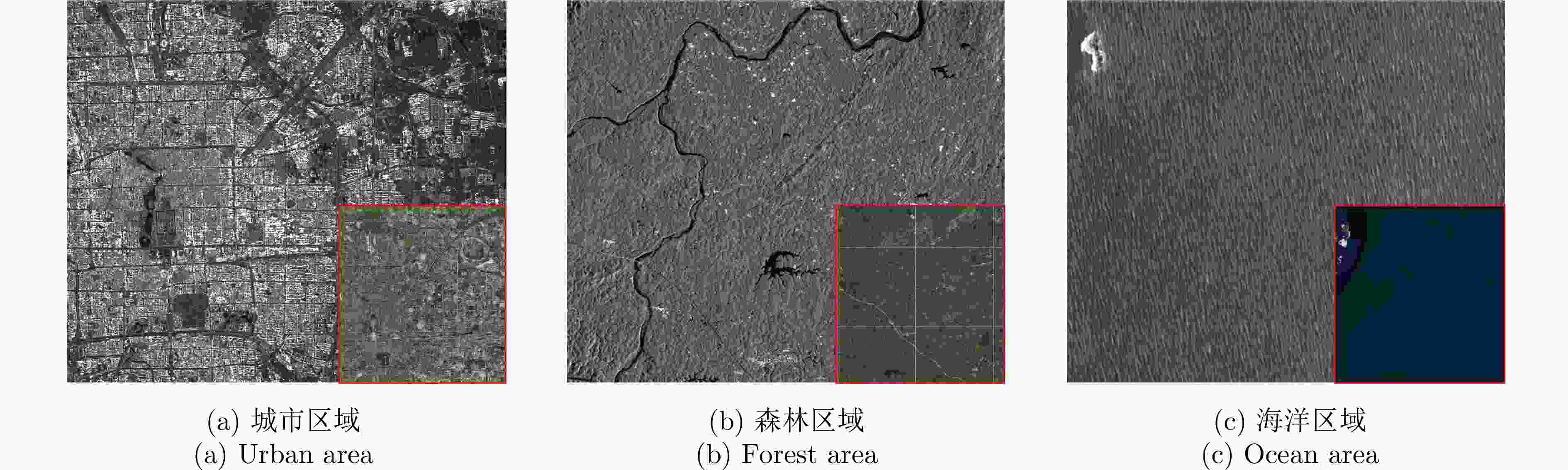
表 5 不同SAR散射背景下的系统通信性能分析结果
Table 5. System communication analysis for different SAR scattering backgrounds
场景类型 RCS均值($ {\sigma _{{\text{env}}}} $) BER1 $ {\varGamma _{{\text{com1}}}} $ $ {P_{{\text{clutter}}}}/{{P_{\inf 1}}} $ BER2 $ {\varGamma _{{\text{com2}}}} $ $ P_{{\text{clutter}}}/{{P_{\inf 2}}} $ 海洋区域 –7.4 dBsm 0.17% 1.117 30.15 – – – 城市区域 14.7 dBsm 5.83% 0.103 299.46 2.77% 0.649 122.70 森林区域 2.2 dBsm 1.08% 0.931 34.73 0.89% 1.022 31.50 -
[1] ULABY F T and LONG D D. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing[M]. Ann Arbor, USA: University of Michigan Press, 2014: 65–72. [2] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, JÄGER M, et al. Staggered SAR: Performance analysis and experiments with real data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6617–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731047. [3] CAI Yonghua, LI Junfeng, YANG Qingyue, et al. First demonstration of RFI mitigation in the phase synchronization of LT-1 bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5217319. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3310613. [4] JIN Guodong, LIU Kaiyu, LIU Dacheng, et al. An advanced phase synchronization scheme for LT-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1735–1746. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2948219. [5] 李涛, 唐新明, 李世金, 等. L波段差分干涉SAR卫星基础形变产品分类[J]. 测绘学报, 2023, 52(5): 769–779. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20220050.LI Tao, TANG Xinming, LI Shijin, et al. Classification of basic deformation products of L-band differential interfero-metric SAR satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2023, 52(5): 769–779. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20220050. [6] HUBER S, DE ALMEIDA F Q, VILLANO M, et al. Tandem-L: A technical perspective on future spaceborne SAR sensors for earth observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4792–4807. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2837673. [7] CHIRIYATH A R, PAUL B, and BLISS D W. Radar-communications convergence: Coexistence, cooperation, and co-design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2017, 3(1): 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2017.2666266. [8] SADDIK G N, SINGH R S, and BROWN E R. Ultra-wideband multifunctional communications/radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2007, 55(7): 1431–1437. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.900343. [9] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Joint wireless communication and radar sensing systems—State of the art and future prospects[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2013, 7(11): 876–885. doi: 10.1049/iet-map.2012.0450. [10] YOUNIS M, FISCHER C, and WIESBECK W. Digital beamforming in SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(7): 1735–1739. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.815662. [11] CURRIE A and BROWN M A. Wide-swath SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1992, 139(2): 122–135. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0016. [12] STURM C and WIESBECK W. Waveform design and signal processing aspects for fusion of wireless communications and radar sensing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2011, 99(7): 1236–1259. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2131110. [13] JACYNA G M, FELL B, and MCLEMORE D. A high-level overview of fundamental limits studies for the DARPA SSPARC program[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 3558–3561. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485100. [14] CHIRIYATH A R, PAUL B, and BLISS D W. Joint radar-communications information bounds with clutter: The phase noise menace[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 2256–2260. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485311. [15] RICHMOND C D, BASU P, LEARNED R E, et al. Performance bounds on cooperative radar and communication systems operation[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1887–1891. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485101. [16] KIM J H, YOUNIS M, MOREIRA A, et al. Spaceborne MIMO synthetic aperture radar for multimodal operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5): 2453–2466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2360148. [17] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. First demonstration of joint wireless communication and high-resolution SAR imaging using airborne MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6619–6632. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2907561. [18] PENDRY J B, SCHURIG D, and SMITH D R. Controlling electromagnetic fields[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5781): 1780–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1125907. [19] WEI Menglin, ZHAO Hanting, GALDI V, et al. Metasurface-enabled smart wireless attacks at the physical layer[J]. Nature Electronics, 2023, 6(8): 610–618. doi: 10.1038/s41928-023-01011-0. [20] ENGHETA N and ZIOLKOWSKI R W. Metamaterials: Physics and Engineering Explorations[M]. Hoboken, USA: Wiley, 2006: 155–173. [21] LI Lianlin, CUI Tiejun, JI Wei, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9. [22] WANG Xin, HAN Jiaqi, LI Guanxuan, et al. High-performance costefficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6002. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41763-z. [23] YANG Bo, CHEN Xiaojie, CHU Jie, et al. A 5.8-GHz phased array system using power-variable phase-controlled magnetrons for wireless power transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(11): 4951–4959. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3007187. [24] ALALI B, ZELENCHUK D, and FUSCO V. A 2D reflective metasurface augmented Luneburg lens antenna for 5G communications[C]. 2022 International Workshop on Antenna Technology, Dublin, Ireland, 2022: 136–138. doi: 10.1109/iWAT54881.2022.9811041. [25] LIANG Qiuyan and LAU B K. Beam reconfigurable reflective metasurface for indoor wireless communications[C]. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, Singapore, Singapore, 2021: 4358–4359. doi: 10.1109/APS/URSI47566.2021.9703707. [26] ZHANG Lei, CHEN Xiaoqing, CHENG Qiang, et al. Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces for new-architecture wireless communications[C]. 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Madrid, Spain, 2022: 684–688. doi: 10.23919/EuCAP53622.2022.9769603. [27] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [28] WATTS S. Modeling and simulation of coherent sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3303–3317. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324707. [29] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. Joint wireless communication and high resolution SAR imaging using airborne mimo radar system[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 2511–2514. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8897826. [30] PROAKIS J G and SALEHI M. Digital Communications[M]. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2007: 273–301. [31] GOLDSMITH A. Wireless Communications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005: 157–166. [32] RICHARDS M A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014: 314–333. [33] TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887. [34] DAI Junyan, TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, et al. Wireless communication based on information metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(3): 1493–1510. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3054662. [35] 丁昊, 朱晨光, 刘宁波, 等. 高海况条件下海面漂浮小目标特征提取与分析[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2023, 38(4): 301–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2023.04.001.DING Hao, ZHU Chenguang, LIU Ningbo, et al. Feature extraction and analysis of small floating targets in high sea conditions[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2023, 38(4): 301–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2023.04.001. [36] BROSCHAT S L. Reflection loss from a “Pierson-Moskowitz” sea surface using the nonlocal small slope approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(1): 632–634. doi: 10.1109/36.739134. [37] SHI Shuo, ZHANG Heng, DENG Yunkai, et al. Increase the coherent processing interval for SAR focusing of maneuvering ships by data resampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3390790. [38] WANG Peng, LI Zhenning, WEI Zhaohui, et al. Space-time-coding digital metasurface element design based on state recognition and mapping methods with CNN-LSTM-DNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2024, 72(6): 4962–4975. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2024.3349778. [39] WANG Di, YIN Lizheng, HUANG Tiejun, et al. Design of a 1 bit broadband space-time-coding digital metasurface element[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(4): 611–615. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2020.2973424. [40] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995: 217–219. [41] ROSENBERG L, OUELLETTE J D, and DOWGIALLO D J. Passive bistatic sea clutter statistics from spaceborne illuminators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 56(5): 3971–3984. [42] ARMSTRONG B C and GRIFFITHS H D. CFAR detection of fluctuating targets in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1991, 138(2): 139–152. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0020. [43] TULINO A M and VERDÚ S. Random matrix theory and wireless communications[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Communications and Information Theory, 2004, 1(1): 1–182. doi: 10.1561/0100000001. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: