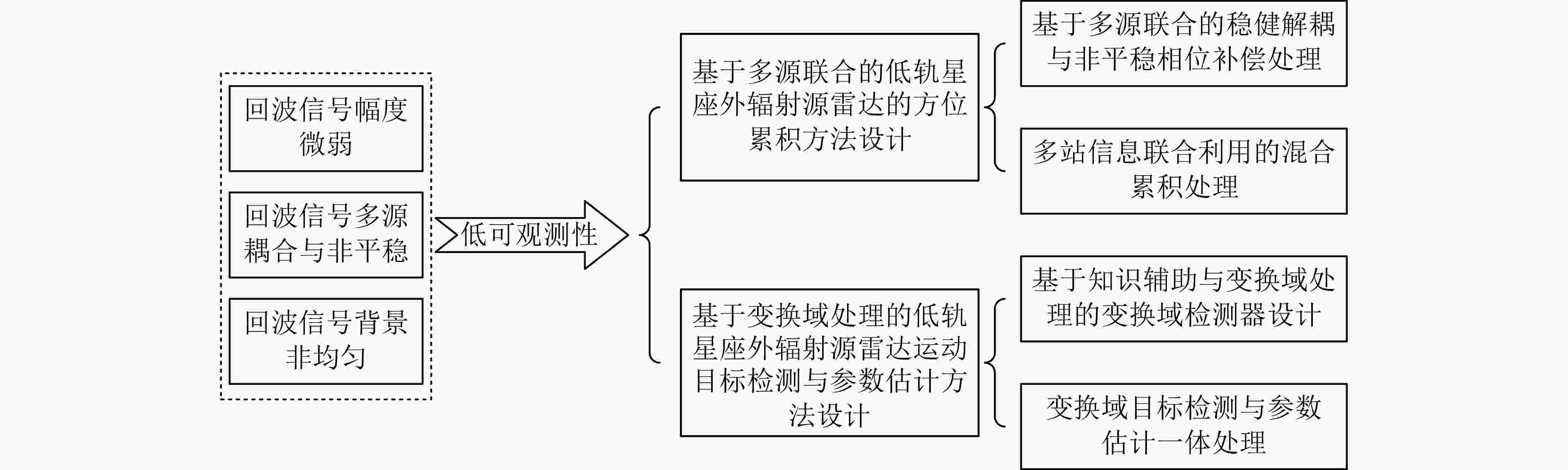
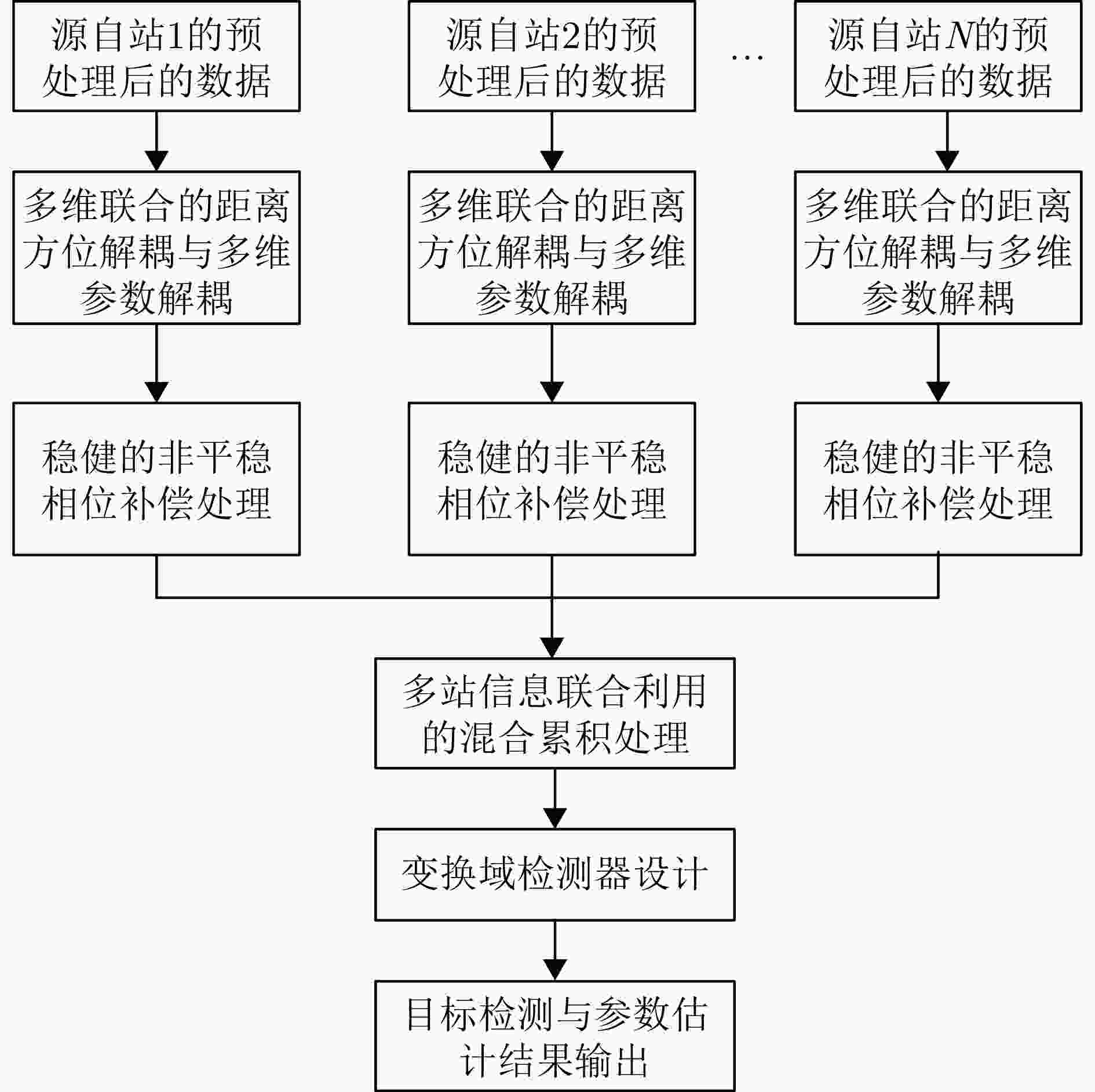
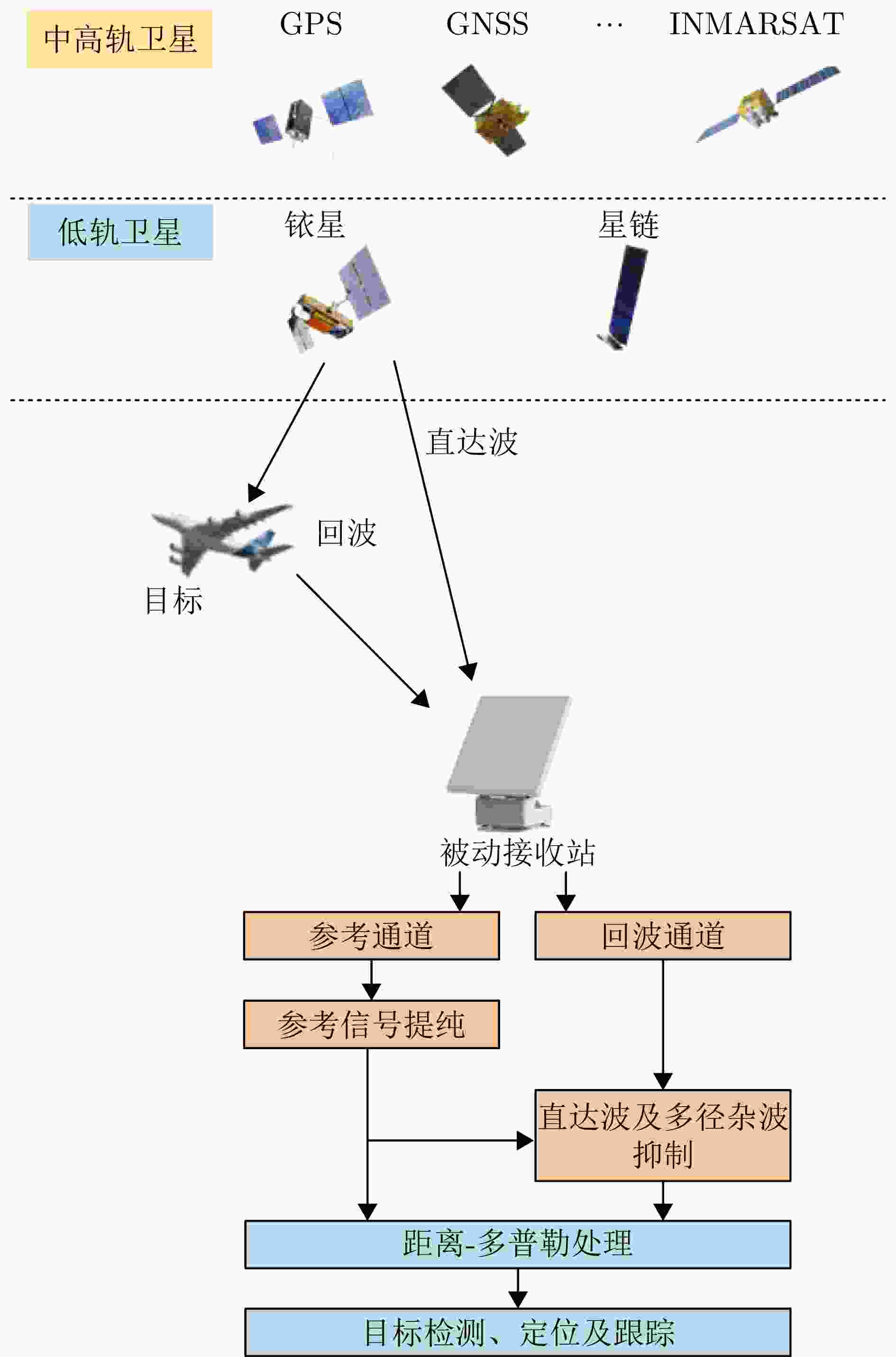
-
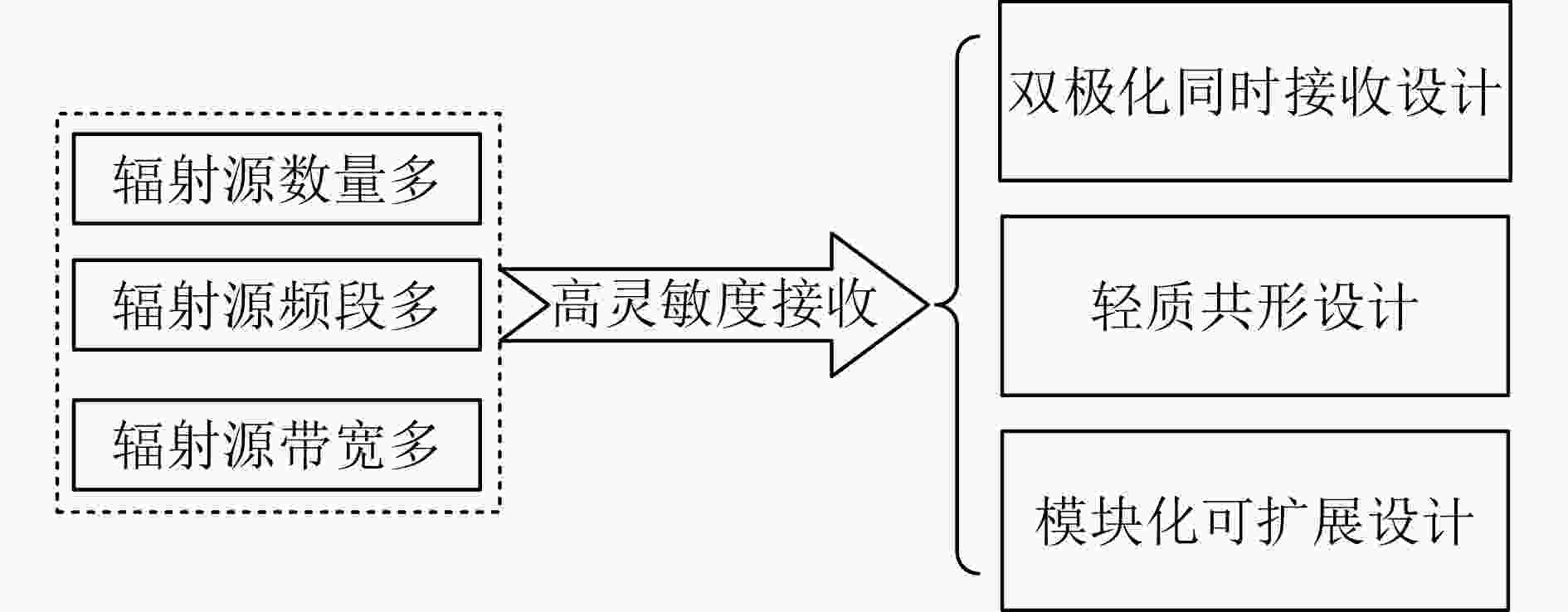
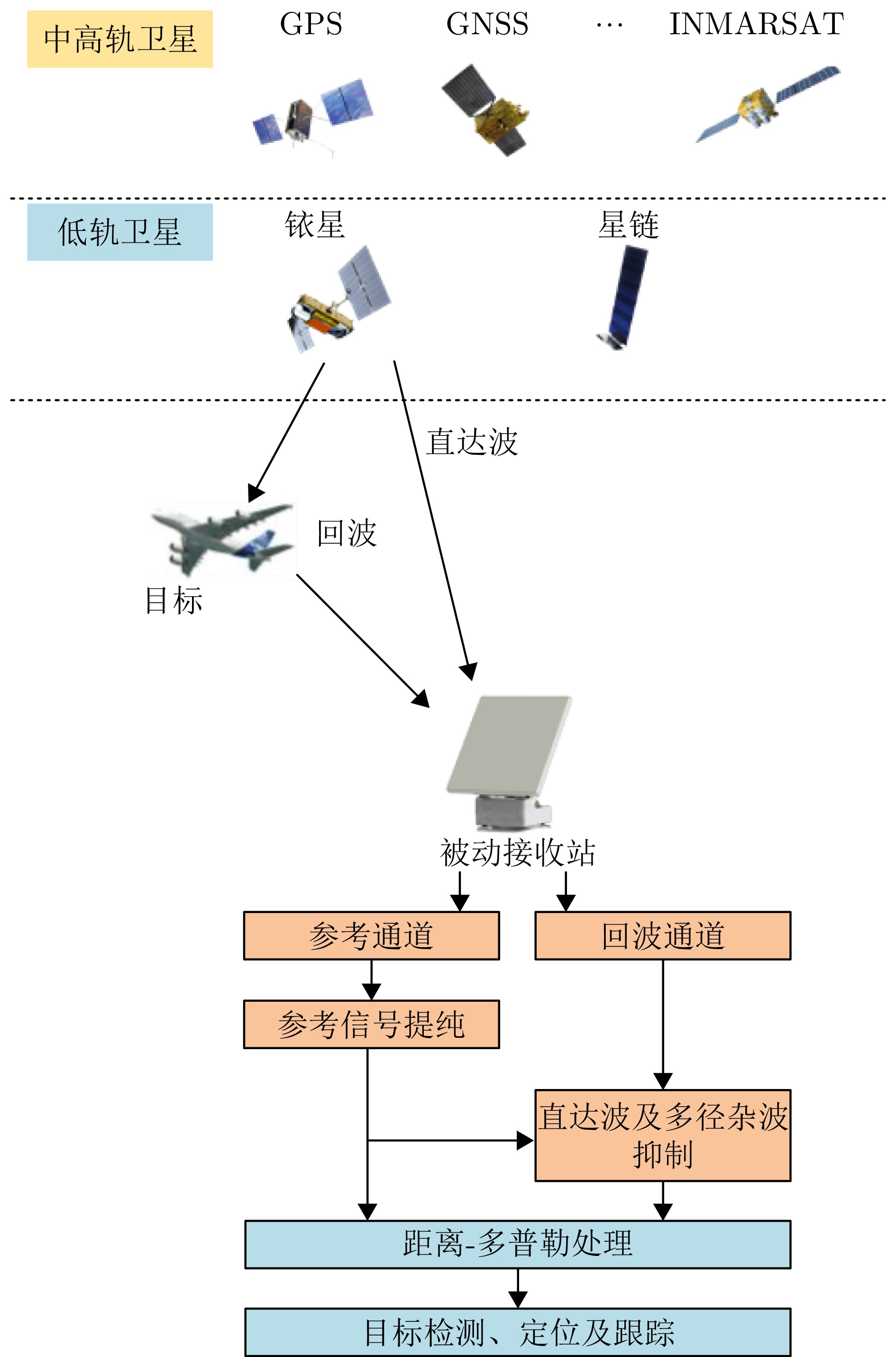
摘要: 相较于地基外辐射源雷达,基于卫星信号的外辐射源雷达(即卫星信号外辐射源雷达)具有全球、全时、全天候覆盖等优势,可弥补地基外辐射源雷达在海上覆盖范围不足的限制;相较于中高轨卫星信号,低轨通信卫星信号具有接收功率强、卫星数目多等优势,可为海上目标无源探测提供可观的探测距离与探测精度。面向未来发展需求,该文详细论述了卫星信号外辐射源雷达研究现状与应用前景,给出了以铱星、星链两类低轨通信卫星系统构建高低频宽窄带融合的低轨通信卫星信号外辐射源雷达系统的可行性分析,据此总结了研发低轨通信卫星信号外辐射源雷达系统面临的技术挑战与候选解决思路。上述研究可为广域范围内,外辐射源雷达探测提供重要参考。Abstract: Compared to ground-based external radiation source radar, satellite signal-based external radiation source radar (i.e., satellite signal external radiation source radar) offers advantages such as global, all-time, and all-weather coverage, which can compensate for the limitations of ground-based external radiation source radar in terms of maritime coverage. In contrast to medium and high-altitude satellite signals, Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) communication satellite signals have advantages such as strong reception power and a large number of satellites, which can provide substantial detection range and accuracy for passive detection of maritime targets. In response to future development needs, this paper provides a detailed discussion of the research status and application prospects of satellite signal external radiation source radar, and presents a feasibility analysis for constructing a low-earth orbit communication satellite signal external radiation source radar system using Iridium and Starlink, two types of LEO communication satellite systems, which integrates high and low frequencies with both wide and narrow bandwidths. Based on this, the paper summarizes the technical challenges and potential solutions in the development of low-earth orbit communication satellite signal external radiation source radar systems. The aforementioned research can serve as an important reference for wide-area external radiation source radar detection.
-
表 1 基于GNSS信号的外辐射源雷达研究现状
Table 1. Research status of passive radar using GNSS signals
参考文献 年份 第一作者研究机构 外辐射源 研究内容 备注 [29] 1995 德国 GPS, GLONASS 验证卫星信号与目标回波信号相关性 实验 [30] 1999 昆士兰科技大学 GPS, GLONASS 提取目标三维轨迹实现目标探测 实验 [31] 2002 昆士兰科技大学 GPS 空中目标探测距离理论计算 理论 [32] 2011 保加利亚IICT GPS 功率预算和最大目标探测距离分析 理论 [33,34] 2018 伯明翰大学 Galileo 提出长短时相干-非相关积累融合的长时积累算法 实验 [35] 2019 圣彼得堡国立电子工程技术大学 GPS, GLONASS 几何模型估计及空中目标探测范围计算 理论 [36,37] 2023 罗马大学 Galileo 改进目标探测与定位算法,同时进行实验验证 实验 [38] 2001 解放军电子工程学院 GPS 利用4颗卫星经过目标散射后的时间差估计目标信息 理论 [39,40] 2004 西安电子科技大学 GPS 通过对回波信号进行多普勒补偿提升微弱目标探测能力 理论 [41] 2005 北京理工大学 GNSS 热噪声及同频干扰下目标探测性能分析 理论 [42] 2009 北京航空航天大学 GPS 提出利用导航卫星信号实现空间飞行器的远程定位方法 实验 [43] 2010 国防科技大学 GPS, 北斗 探测距离、模糊函数等对比分析 理论 [44] 2014 南京电子技术研究所 GPS 可探测时间、直达波抑制、辐射源数多角度探测性能分析 理论 [45] 2015 中国空间技术研究院 GPS 多发单收的双基地雷达新体制 理论 [46] 2017 西安电子科技大学 GPS 多星数据融合的微弱回波信号检测算法 理论 [47] 2019 西安电子科技大学 GPS 基于北斗二代卫星信号外辐射源雷达系统的信号处理方法 理论 [48] 2020 香港理工大学 GPS 研究了利用目标运动特点聚焦目标回波能量的目标探测方法 实验 [49−51] 2022 电子科技大学 北斗 世界上第1个基于北斗的无源雷达舰艇目标探测海上实验 实验 [52] 2022 北京航空航天大学 GPS 改进的多帧长时积累算法与空中动目标探测 实验 [53] 2023 香港理工大学 GPS 融合图像处理与多普勒历史的长时间移动目标检测处理技术 理论 [54] 2023 国防科技大学 GPS 搭建软件无线电接收平台并对接收的参考信号进行重构 实验 [55] 2024 北京航空航天大学 GPS 两阶段由粗到细的多普勒频移补偿提升长时间积累能力 实验 [56] 2024 北京航空航天大学 GNSS 提出针对GNSS的基于高度角随机模型的定位算法 实验 [57] 2024 北京卫星信息工程研究所 GNSS、北斗 提出多颗北斗卫星协同的相干合成孔径成像方法 实验 表 2 基于DVB-S信号的外辐射源雷达研究现状
Table 2. Research status of passive radar using DVB-S signals
参考文献 年份 第一作者研究机构 外辐射源 研究内容 备注 [58] 1992 伦敦大学 DVB-S 研究了基于马可波罗1号卫星信号的外辐射源雷达回波信号信噪比 实验 [59] 2011 里斯本高等教育学院 DVB-S 测试了DVB-S作为辐射源的探测性能与自适应滤波算法去噪性能 实验 [60,61] 2019 弗劳恩霍夫高频物理和雷达技术研究所 DVB-S 探索了DVB-S作为辐射源时极化分集对ISAR目标探测能力的提升 实验 [62,63] 2020 罗马大学 DVB-S 搭建了基于DVB-S信号的外辐射源雷达试验系统,研究了非相干
积累、相干长时积累与极化分集的探测性能实验 [64] 2022 意大利RaSS国家实验室 DVB-S/S2 探索了基于DVB-S/S2信号的外辐射源雷达探测低轨道空间驻留
目标的可行性理论 [65] 2024 华沙理工大学 DVB-S2 探索了DVB-S作为辐射源时极化分集对探测概率的提升 实验 [66] 2012 中国科学院 DVB-S 基于DVB-S信号的外辐射源雷达几何结构、信号模糊函数及分辨特性 理论 [67,68] 2013 中国科学技术大学 DVB-S 利用APStar-5卫星信号进行外场实验,初步实现了目标回波信号检测 实验 [69] 2014 中国科学技术大学 DVB-S 探究了最大探测距离和距离分辨率性能 实验 [70] 2016 西安电子科技大学 DVB-S 基于多个异构卫星信息融合的微弱回波信号检测 理论 [71,72] 2019 浙江大学 DVB-S 基于加权融合的多信道联合检测方法 理论 [73] 2021 电子科技大学 DVB-S 基于Radon-Fourier变换的多频道积累检测算法 理论 [74] 2023 武汉大学 DVB-S 搭建DVB-S信号接收系统成功接收信号并探测到2 km外的目标 实验 表 3 基于铱星、星链信号的外辐射源雷达研究现状
Table 3. Research status of passive radar using Iridium and Starlink signals
参考文献 年份 第一作者研究机构 外辐射源 研究内容 备注 [79] 2002 伯明翰大学 铱星 利用模拟的铱星信号开展空中目标探测实验 理论 [80,81] 2016 伯明翰大学 铱星 模糊函数特性分析 理论 [82] 2019 伯明翰大学 星链 基于雷达方程的探测威力分析 理论 [27,83] 2022 华沙理工大学 星链 基于雷达方程的探测威力分析与软件无线电接收机设计方案 理论 [84−86] 2022 弗劳恩霍夫高频物理和雷达技术研究所 星链
一网基于雷达方程的探测威力与模糊函数特性分析、
软件无线电接收机设计方案理论 [87] 2023 国防科技大学 星链 基于雷达方程的探测威力、可观测时间与距离-多普勒徙动分析 理论 [88,89] 2024 电子科技大学 OFDM 基于低轨星座OFDM信号的外辐射源雷达信号处理算法仿真验证 理论 [90] 2024 华沙理工大学 星链 无源SAR成像试验验证 试验 [91] 2024 武汉大学 星链 验证了在低轨卫星照射源前向散射区进行目标探测的有效性 试验 [92] 2024 重庆大学 铱星 基于雷达方程的探测威力与模糊函数特性分析、改进的杂波抑制算法 理论 表 4 国内外典型低轨星座的轨道参数概述
Table 4. System parameters of typical LEO constellations
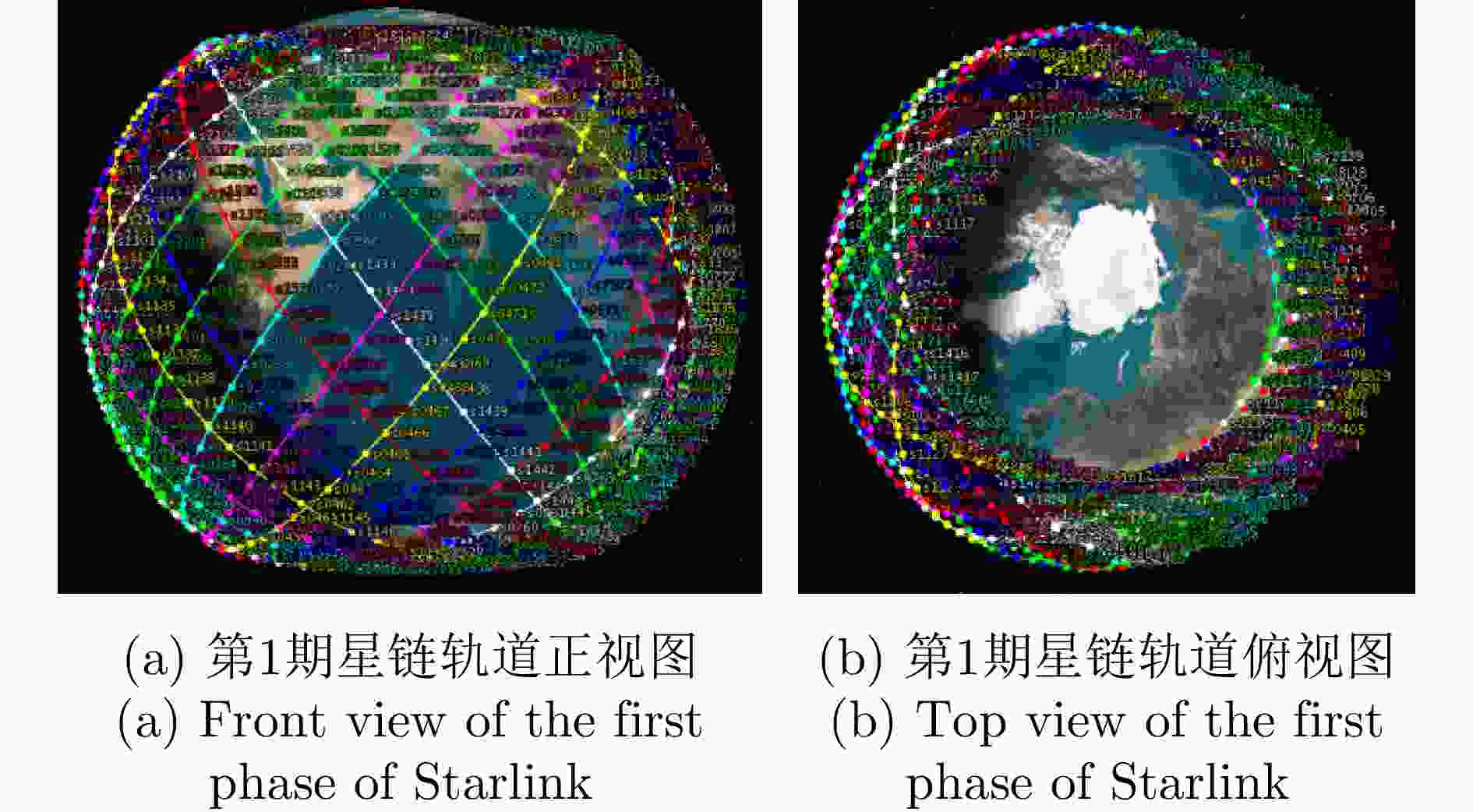
时间 星座名称 运营单位 轨道高度(km) 星座构型 卫星数量(计划) 星间链路 应用场景 2015 星链 美国太空探索技术公司 328~614 独特轨道 40000 +有 宽带互联网
物联网2016 铱星 美国铱星公司 780 近极轨道 66 有 物联网 2016 轨道通信 美国卫星通信公司 800~ 1000 倾斜轨道 100+ 有 宽带互联网
物联网2016 哨兵 欧洲航天局 693 倾斜轨道 12 有 国防 2016 一网 一网卫星公司 1200 近极轨道 1980 无 高速电信网络 2018 行云工程 中国航天科技集团 800, 1400 倾斜轨道 80 有 窄带物联网 2018 虹云工程 中国航天科工集团 1040 倾斜轨道 156 有 天基WiFi 2018 鸿雁星座 中国航天科工集团 1100 近极轨道 360 有 宽带互联网
物联网2019 柯伊伯 美国亚马逊 610/630 倾斜轨道 3236 有 宽带互联网
物联网表 5 国内外典型卫星星座的信号参数概述
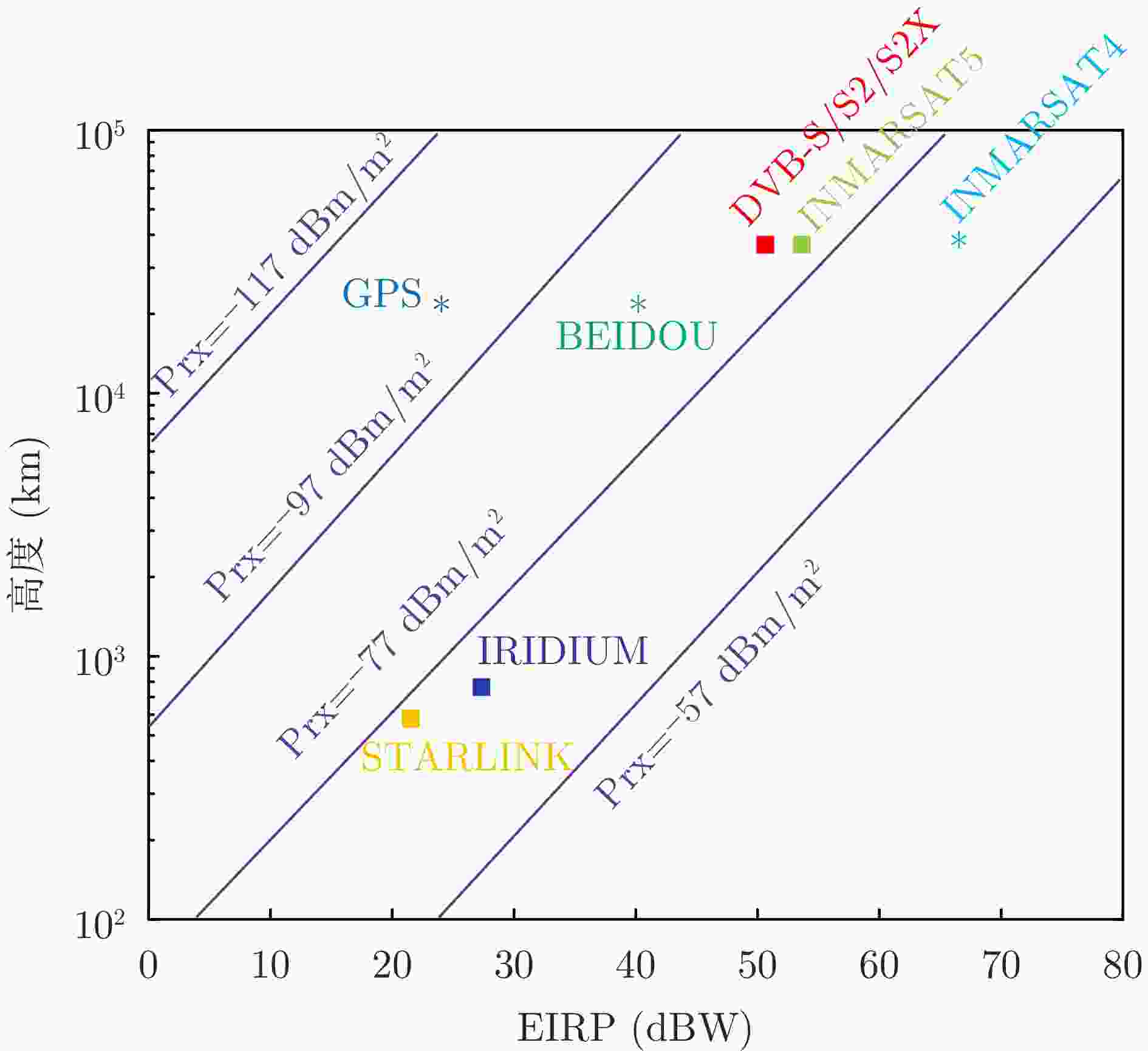
Table 5. System parameters for typical satellite signals
低轨星座
(建设时间)轨道高度
(km)工作频段
(用户下行链路)信号带宽 通信体制 调制方式 单波束覆
盖范围是否全球
覆盖有效全向辐射功率
(dBW)铱星
(2019年)780 L: 1616.0 ~1626.5 MHz31.50 kHz TDMA, FDMA BPSK, QPSK 480~
670 km是 28~45 星链
(2016年)550 X: 10.7~12.7 GHz 250 MHz MF-TDMA, OFDMA 16-256APSK 20~50 km 是 27.6~32.3 GPS
(1993年)20200 L: 1575.42 MHz,1227.60 MHzL1: 2.046 MHz
L5: 10.23 MHzCDMA BPSK 38%地表 是 28 北斗
(2020年)21500
(MEO)L: 1561.098 MHzB1I: 4.092 MHz
B3I: 20.46 MHzCDMA BPSK 38%地表 是 40 DVB-S
(1994年)36000 X: 10.7~12.7 GHz 7 MHz, 36 MHz
54 MHz, 72 MHzMF-TDMA QPSK 40%地表 否,仅陆地或近海 51~54 DVB-S2
(2005年)36000 X: 10.7~12.7 GHz 54 MHz MF-TDMA 4/8PSK,
16/32APSK40%地表 否,仅陆地或近海 52 DVB-S2X
(2014年)36000 X: 10.7~12.7 GHz 250~
500 MHzMF-TDMA 2-8PSK,
16-256APSK40%地表 否,仅陆地或近海 52 INMARSAT4
(2012年)36000 L: 1525 ~1559 MHz200 kHz MF-TDMA QPSK, 16QAM 40%地表 否,+/–75o 67 INMARSAT5
(2013年)36000 Ka: 19.7~20.2 GHz 40 MHz MF-TDMA 4/8PSK, 16/32APSK 40%地表 否,+/–75o 51~54 表 6 铱星轨道参数
Table 6. Iridium orbit parameters
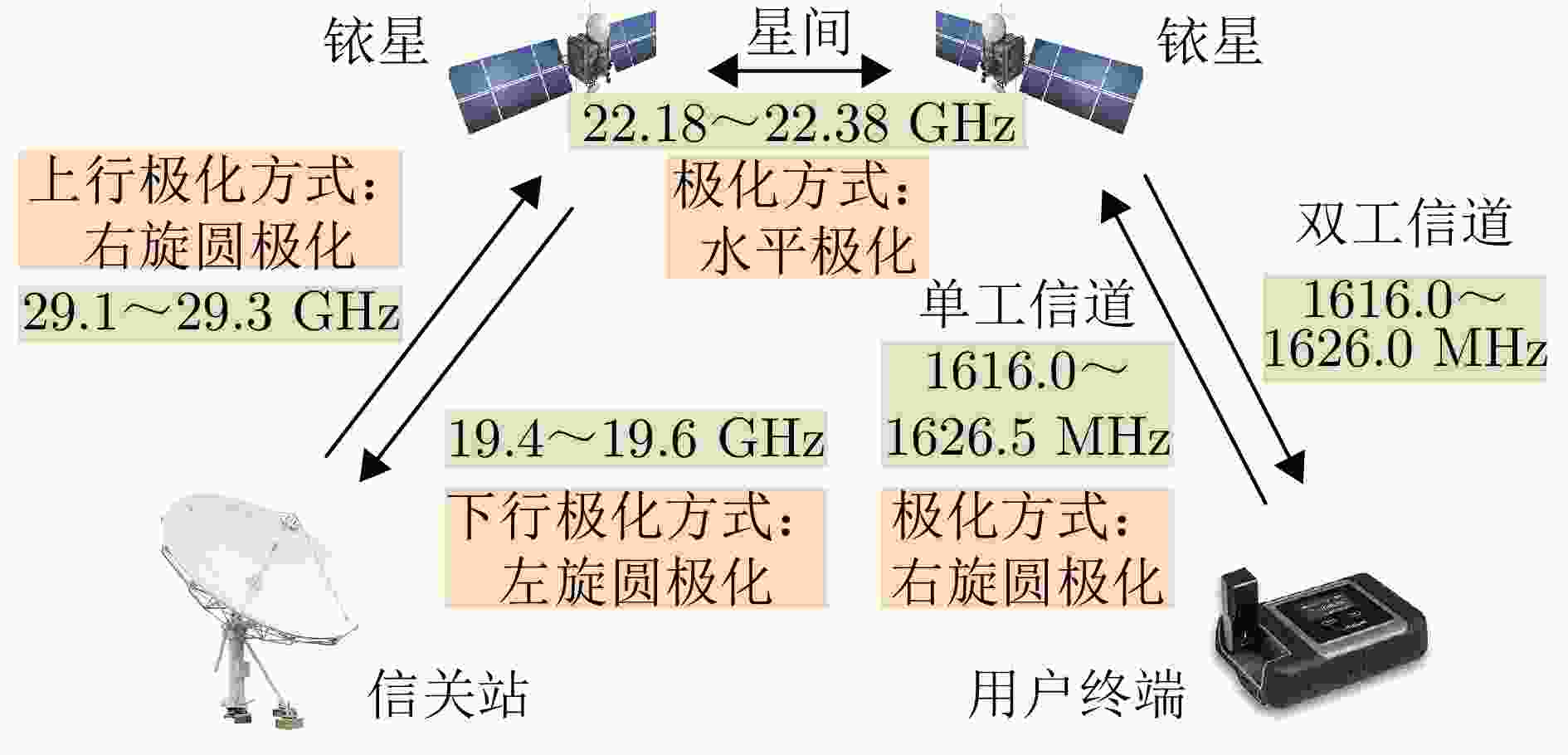
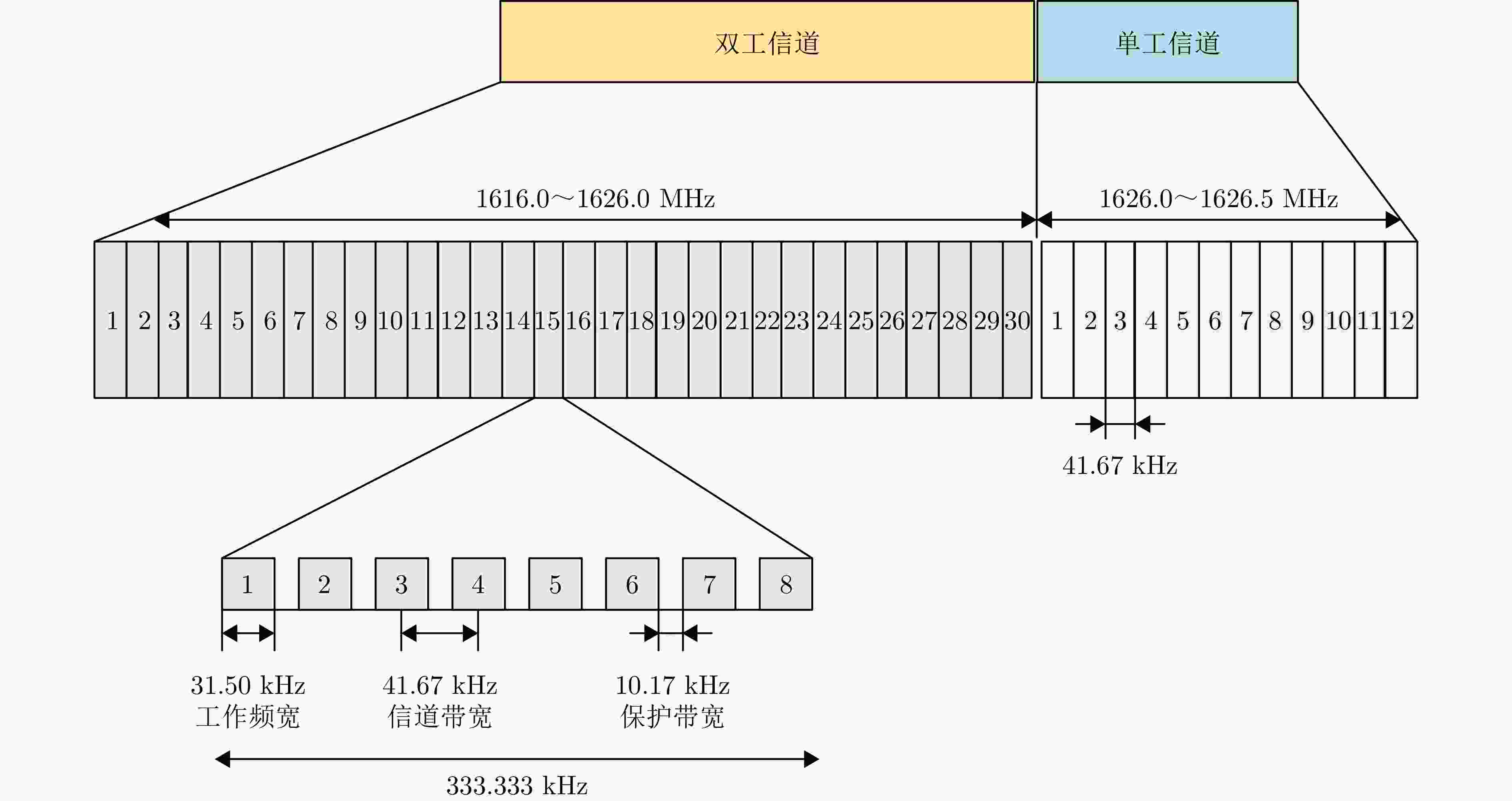
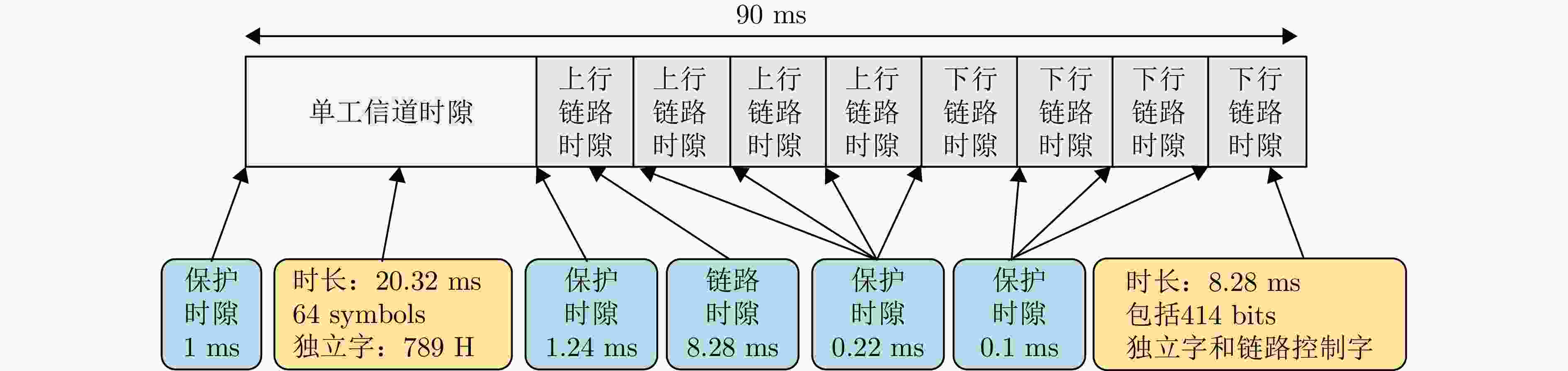
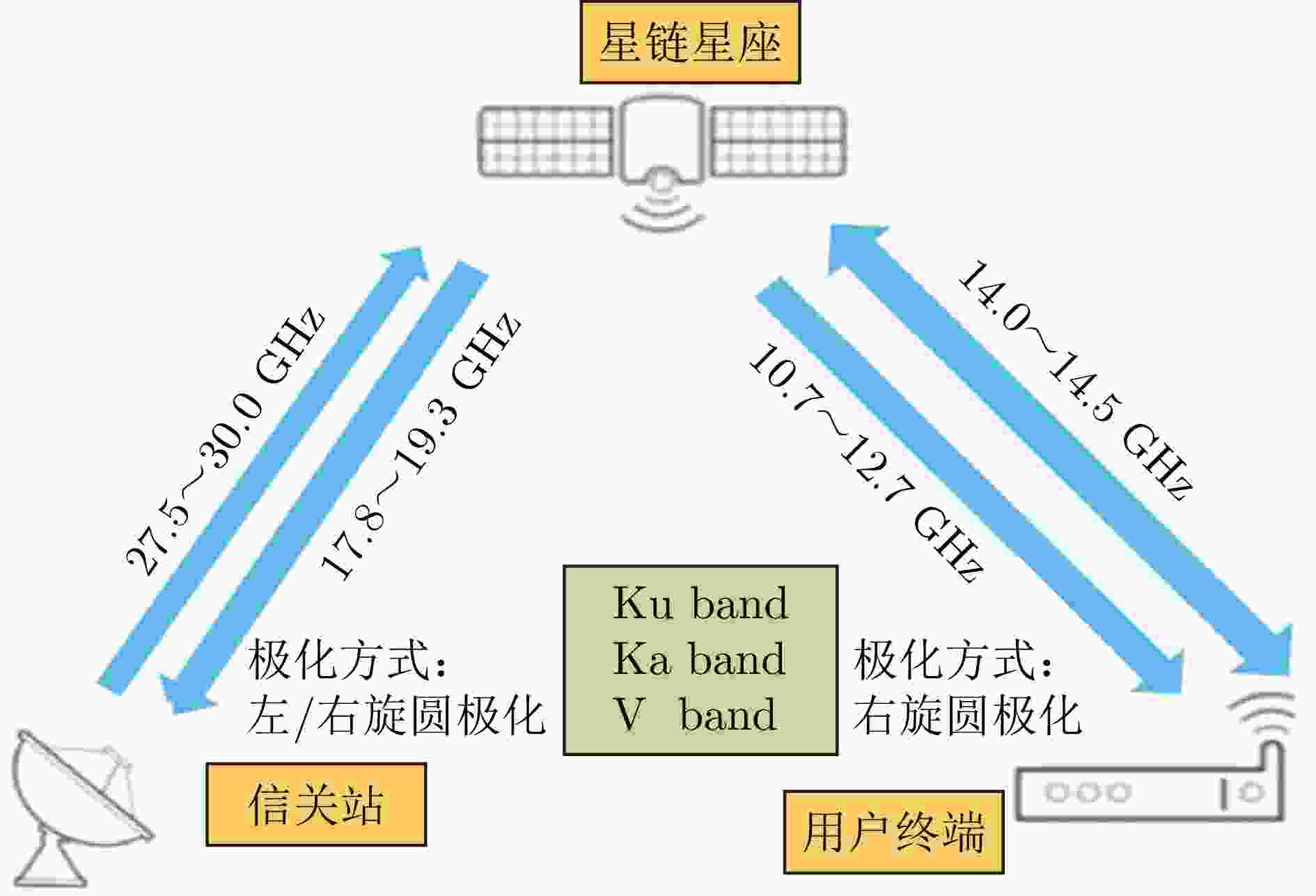
轨道信息 参数 轨道平面数量 6个 每个轨道面卫星数量 11(+1)颗 地面备份卫星数量 9颗 轨道周期 101 min 轨道高度 780 km 轨道倾角 86.4° 相邻轨道夹角 31.6°/22° 运行速度 277088 km/h最大可视时间 15 min 卫星飞行速度 7.46 km/s 可见半角 27° 最大斜高 3249 km最大斜距 6498 km最大地表范围 5940 km表 7 铱星用户链路通信体制
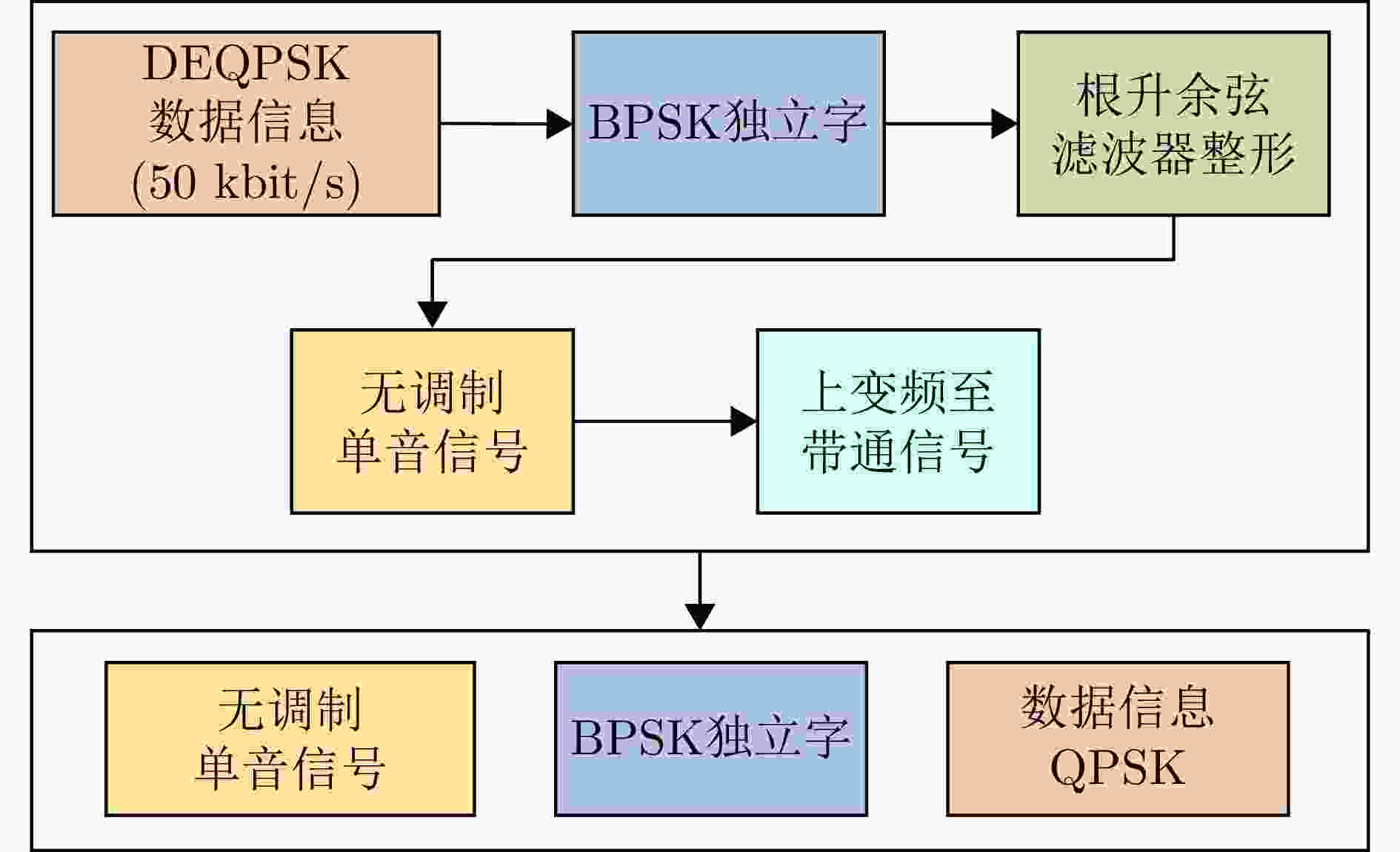
Table 7. Iridium service links communication parameters
参数 技术指标 带宽 31.5 kHz 功率 200 W 速率 128 kbit/s (星-移动端)、1.5 Mbit/s (星-Iridium OpenPort终端)、8 Mbit/s (高速Ka-Band服务将可用于较大的固定和可移动终端) 调制方式 QPSK (DEQPSK) 波束 高椭圆形波束(固定) 单卫星波束覆盖 4700 km (直径) 极化方式 右旋圆极化 多址方式 FDMA/TDMA/SDMA/TDD 纠错编码方式 FEC卷积码 脉冲成型方式 40%均方根升余弦脉冲成型 表 8 星链通信体制
Table 8. Starlink communication parameters
参数 技术指标(上行) 技术指标(下行) 用户链路带宽 125 MHz×4 250 MHz×8 调制方式 256APSK (编码率3/4) 16APSK (编码率3/4) 功率 66.89 dBm (卫星段天线最大发射功率)
2.44 W (用户终端天线)波束 圆形波束(可单独成形与控制) 卫星波束覆盖 2800 km2 极化方式 右旋圆极化 表 9 符号解释
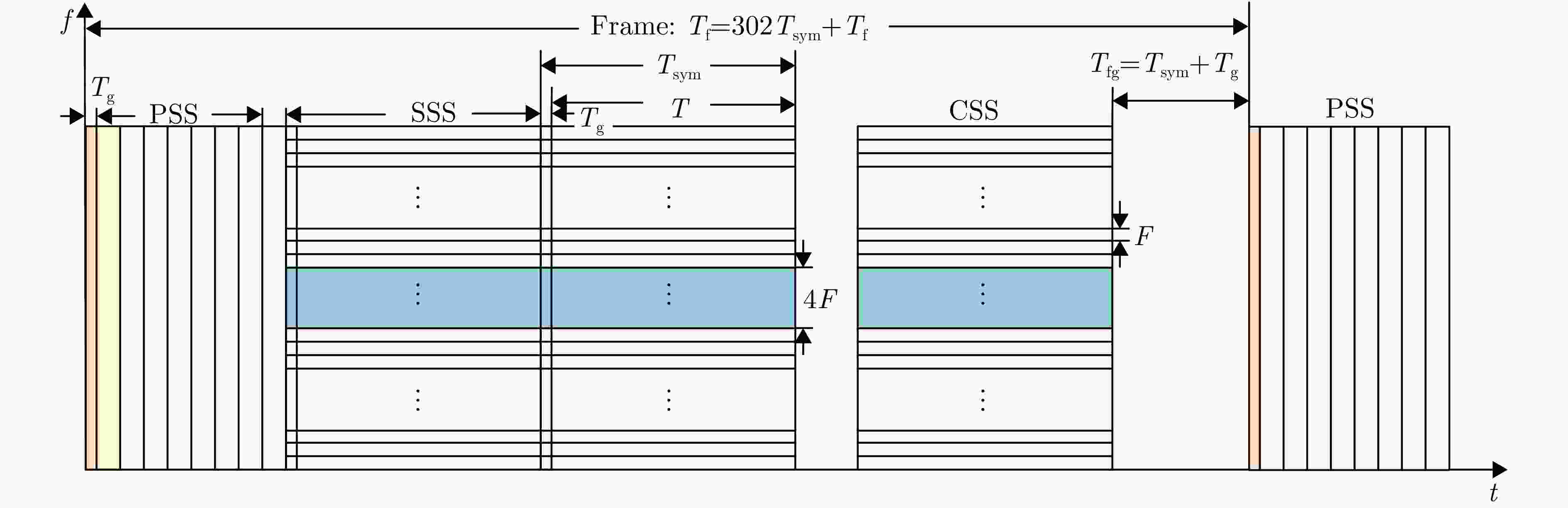
Table 9. Symbol definition
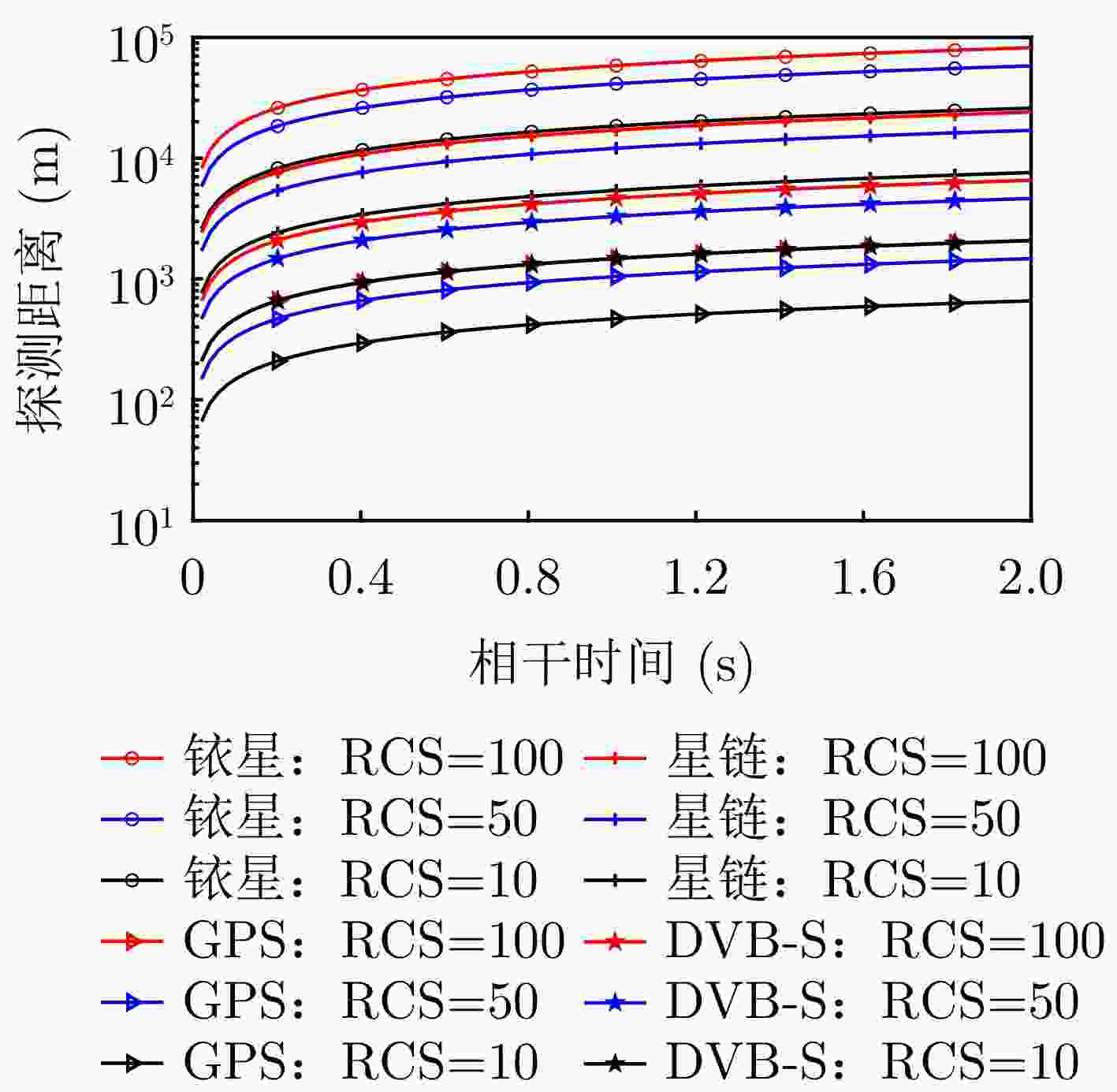
参数 含义 $ {D_{{\text{dir}}}} $ 卫星信号照射到直达波接收天线时的功率密度 $ {P_{\mathrm{t}}} $ 卫星信号发射功率 $ {G_{\mathrm{t}}} $ 卫星天线方向增益 $ {R_0} $ 卫星距离地面的高度 $ {L_{\mathrm{t}}} $ 传输损耗 $ {\text{EIRP}} $ 卫星等效全向辐射功率 A 接收天线等效面积 $ \lambda $ 卫星信号载波波长 G 接收天线增益 $ {P_{{\text{dir}}}} $ 直达波信号功率 $ {G_{{\text{proc}}}} $ 相干处理增益 $ {P_{\text{N}}} $ 接收机噪声功率 K 玻尔兹曼常数 T 接收机噪声温度 B 接收机带宽 F 接收机噪声系数 $ {\text{SN}}{{\text{R}}_{{\text{dir}}}} $ 直达波信噪比 f 载波频率 $ {D_{{\text{re}}}} $ 目标回波信号的功率密度 R 目标到接收天线的距离 表 10 卫星信号外辐射源雷达系统链路参数
Table 10. Link budget parameters of passive radar using satellite signals
系统组成 外辐射源 接收系统 目标
$ \sigma \;({{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}) $EIRP (dBW) $ {R_0}\;({\text{km}}) $ $ f \;({\text{GHz}}) $ $ G\;({\text{dB}}) $ $ K\;({\mathrm{J}}/^\circ) $ $ T\;({\text{K}}) $ $ B $ $ F\;({\text{dB}}) $ $ {\text{Loss}}\;({\text{dB}}) $ $ {T_{\rm{int} }}\;({\text{s}} )$ $ {\text{SN}}{{\text{R}}_{{\text{min}}}}\;({\text{dB}}) $ 一网 37.0 1200 11.700 25 1.38×10–23 290 250 MHz 3 5 0~2 8.2 10/50/100 铱星II 28.0 780 1.626 25 1.38×10–23 290 31.5 kHz 3 5 0~2 8.2 10/50/100 星链 22.0 330 11.700 30 1.38×10–23 290 250 MHz 3 5 0~2 8.2 10/50/100 GPS 24.0 20200 1.560 25 1.38×10–23 290 10.23 MHz 3 5 0~2 8.2 10/50/100 DVB-S 51.7 36000 12.000 30 1.38×10–23 290 36 MHz 3 5 0~2 8.2 10/50/100 表 11 卫星信号外辐射源雷达系统直达波功率
Table 11. SNR of direct wave of passive radar using satellite signals
外辐射源(卫星) 直达波功率$ {P_{{\text{dir}}}}\;{\text{(dBm}}) $ 一网 –88.4 铱星 –76.5 星链 –87.2 GPS –108.4 DVB-S –98.5 表 12 回波通道的信号特性
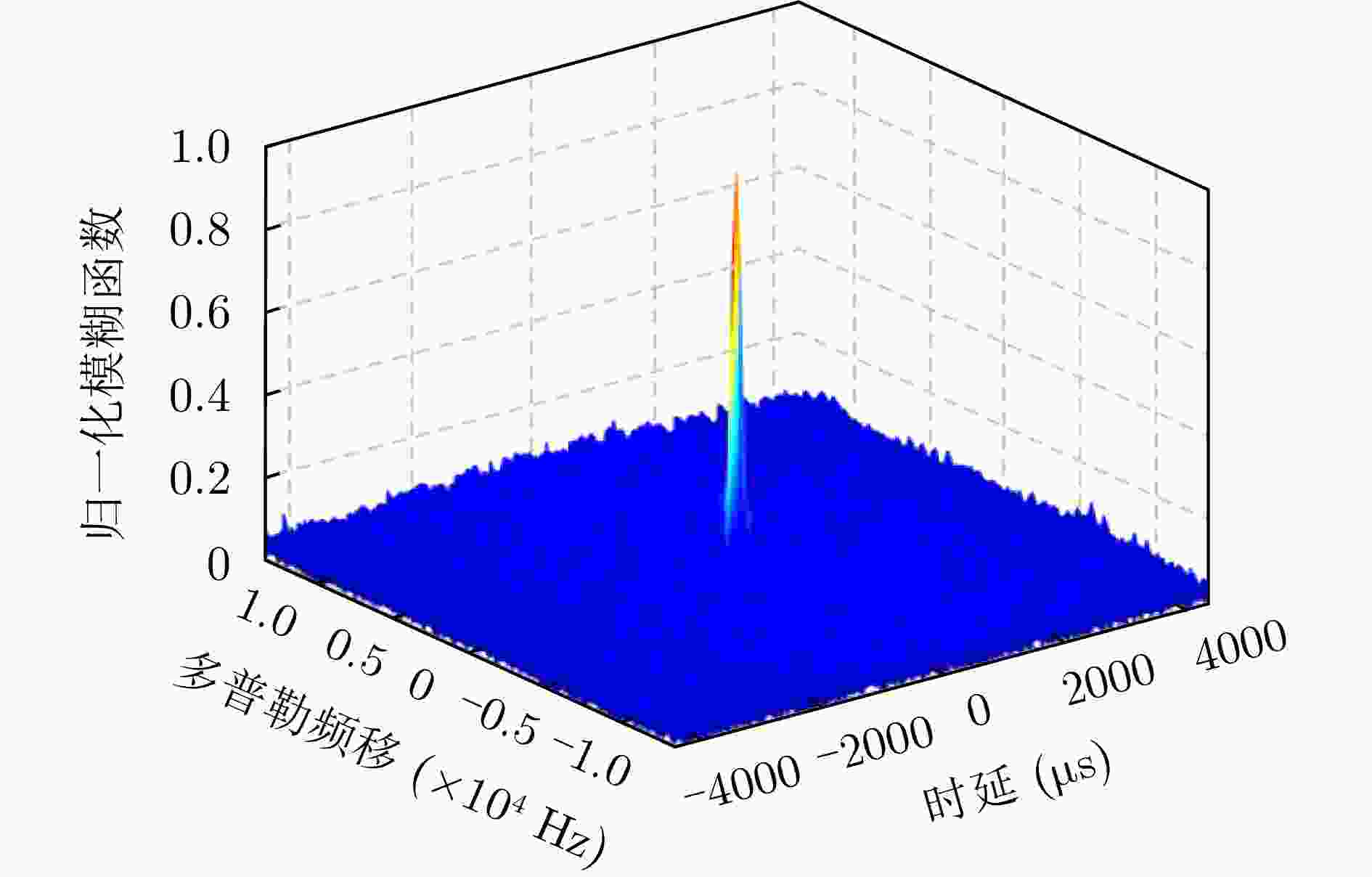
Table 12. Simulate the signal characteristics of the echo channel
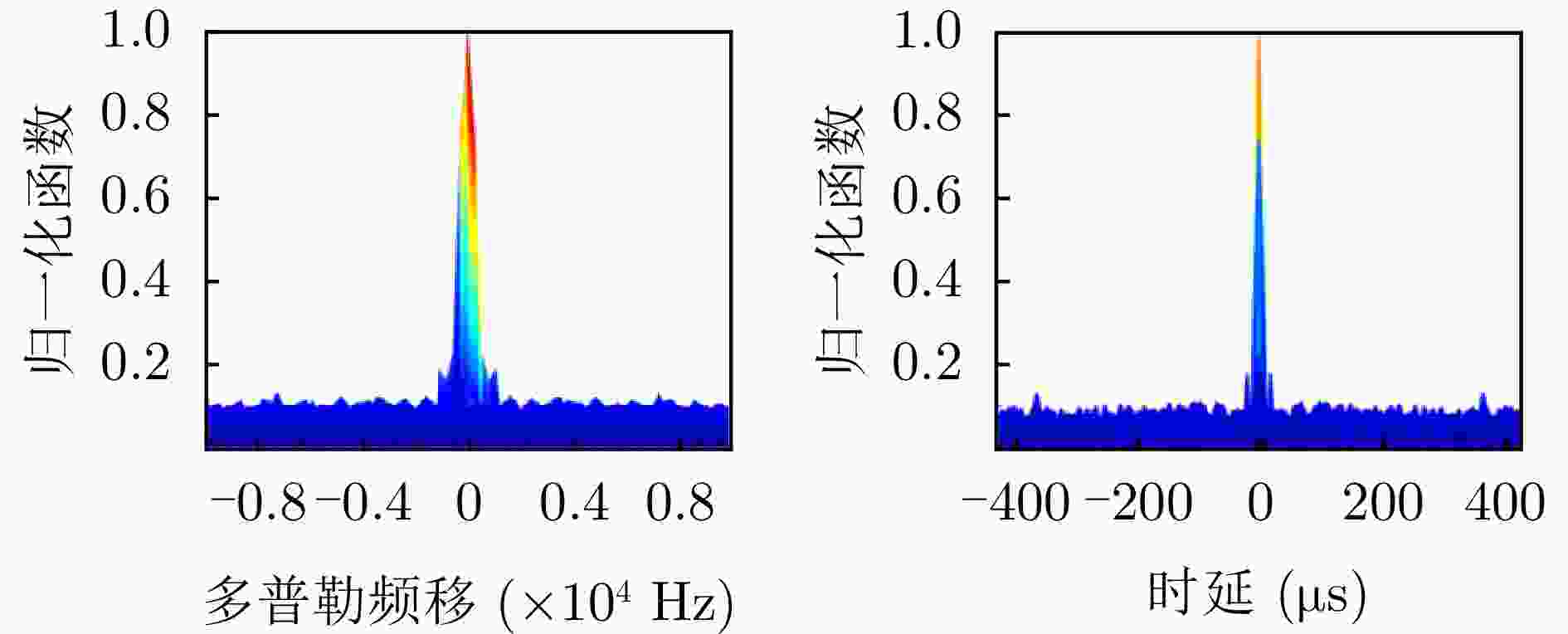
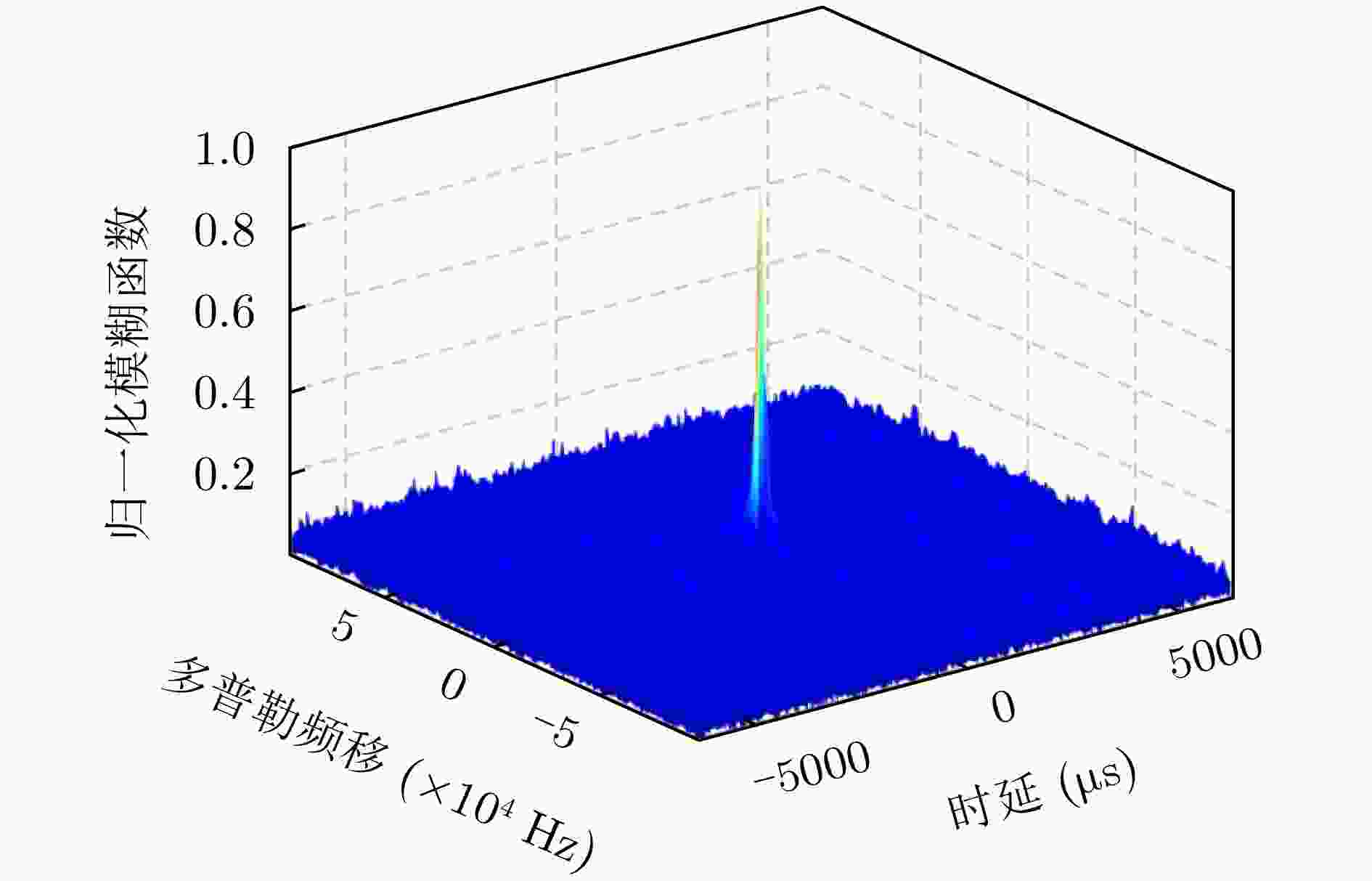
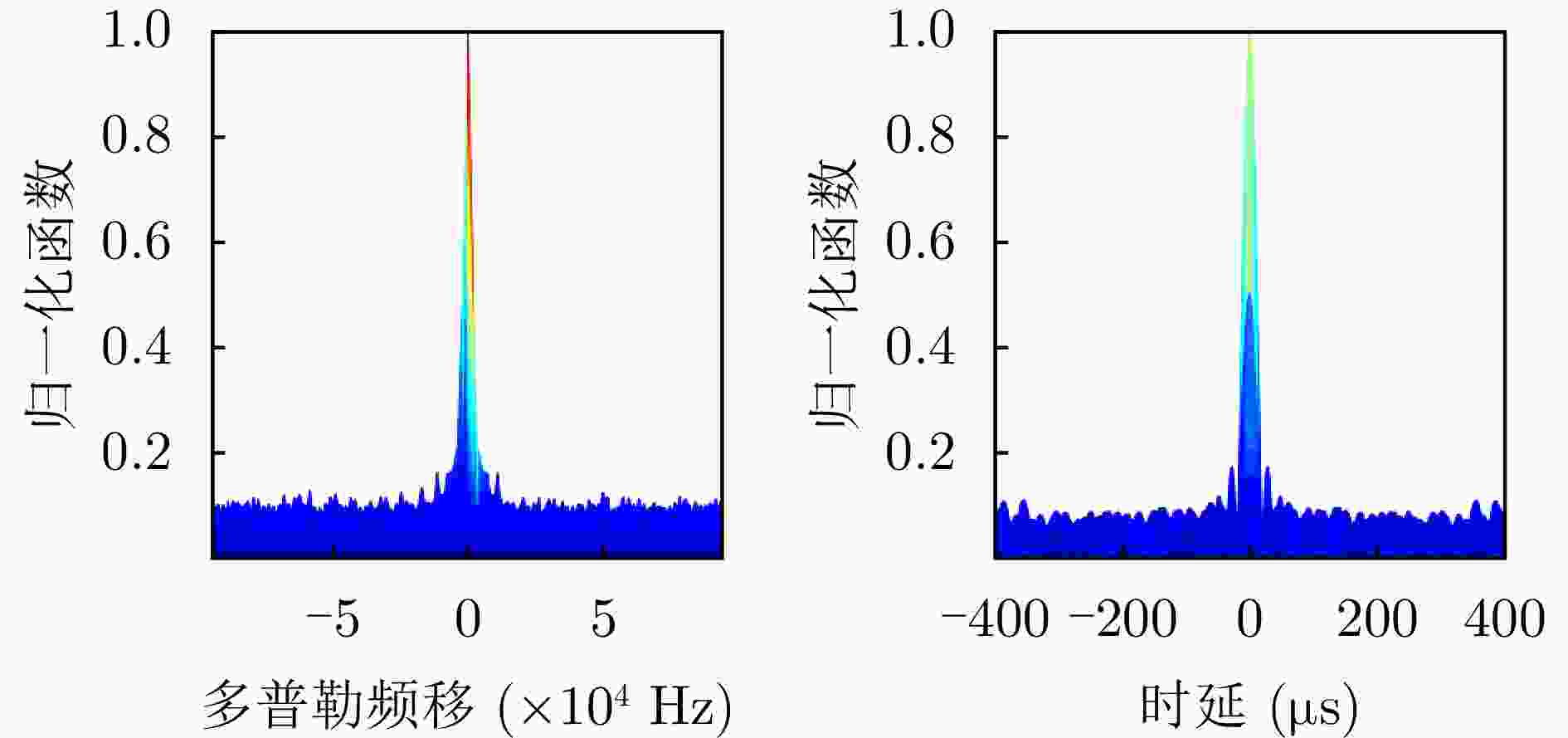
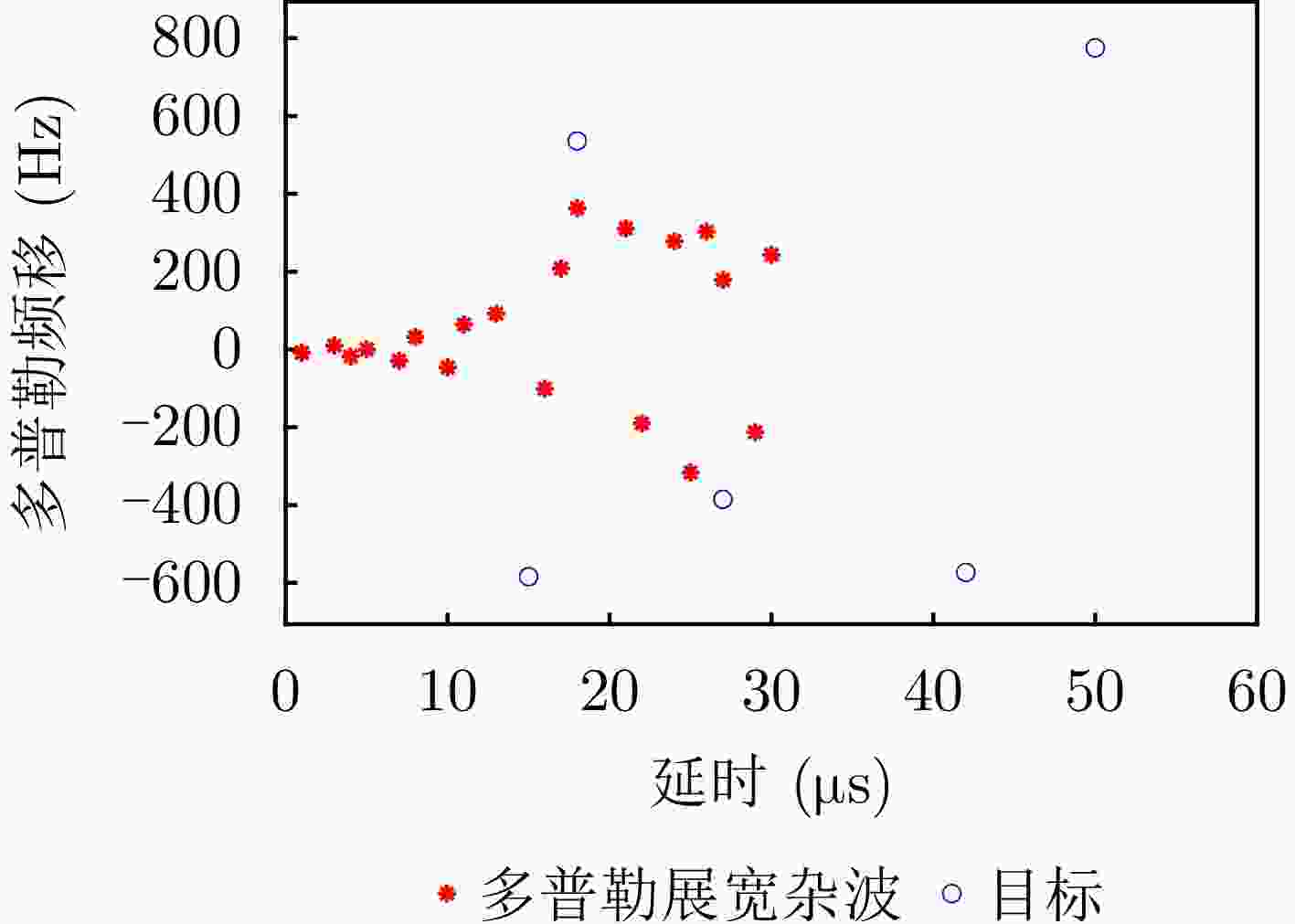
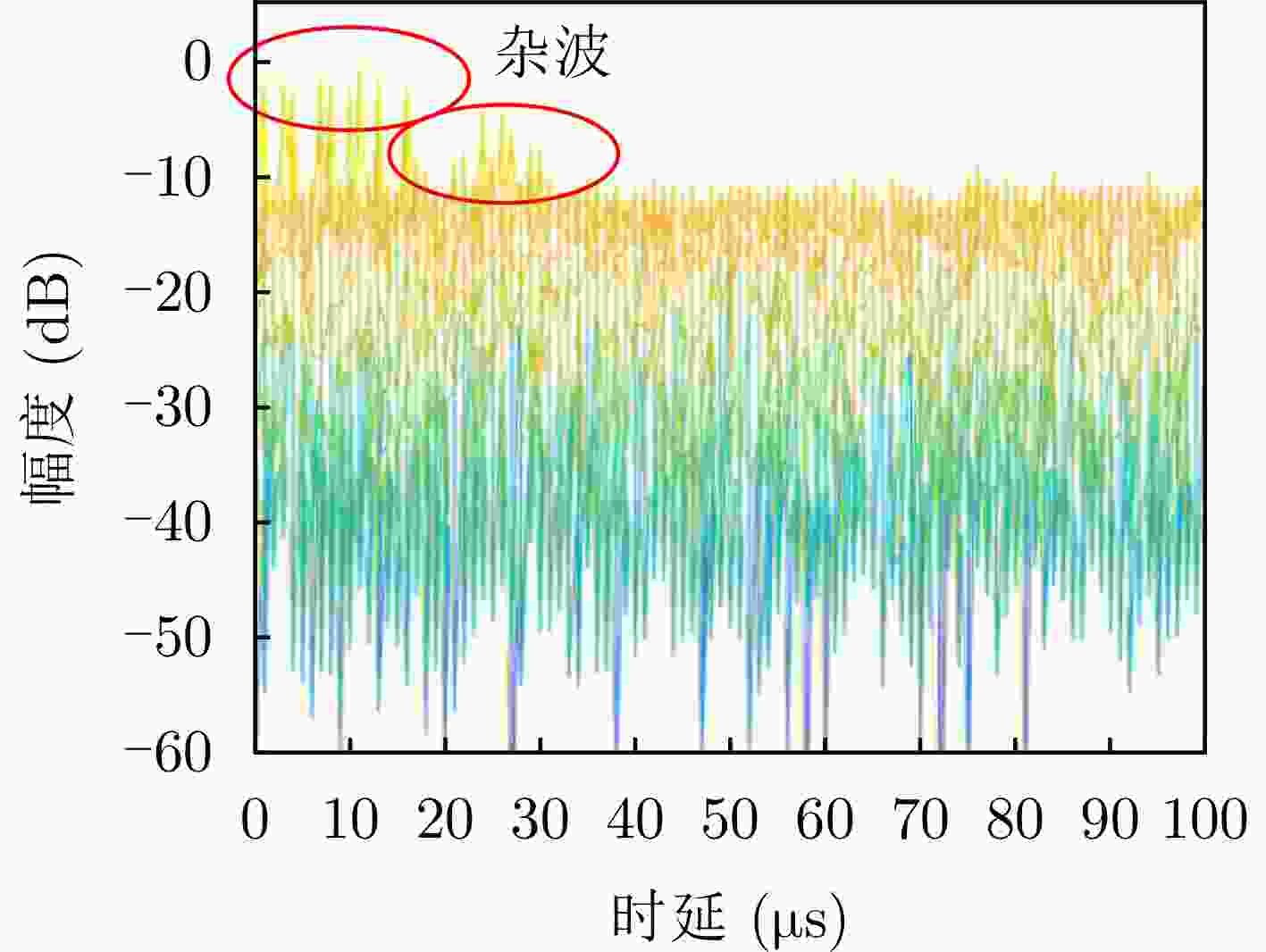
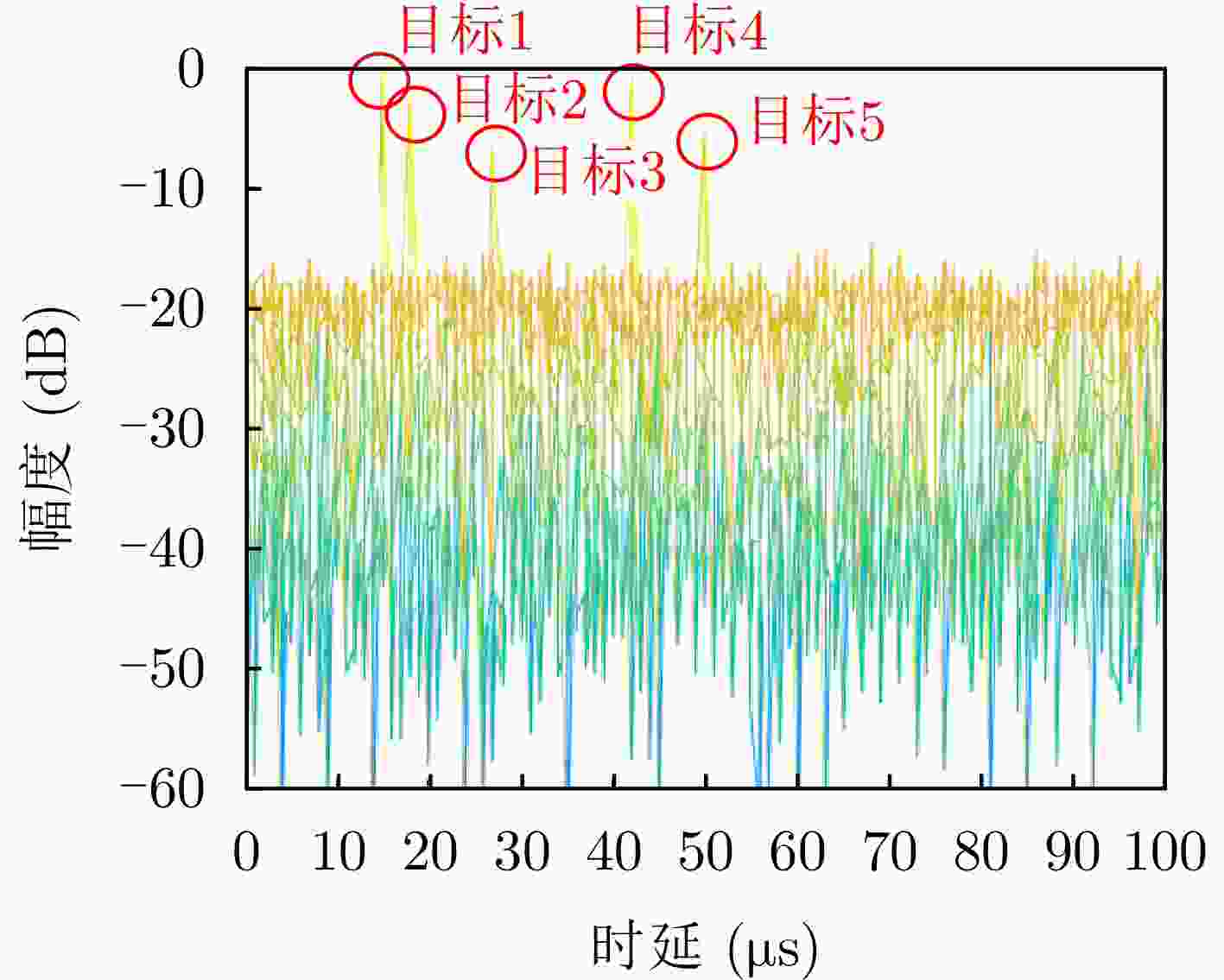
类型 时延范围(μs) 多普勒范围(Hz) 杂噪比(dB) 多普勒杂波 0~30 –400~400 –5~30 目标 25~60 –800~–300, 300~800 –20~–10 -
[1] KUSCHEL H. Approaching 80 years of passive radar[C]. 2013 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2013: 213–217. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6651987. [2] 宋杰, 何友, 蔡复青, 等. 基于非合作雷达辐射源的无源雷达技术综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(9): 2151–2156, 2180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.09.028.SONG Jie, HE You, CAI Fuqing, et al. Overview of passive radar technology based on non-cooperative radar illuminator[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(9): 2151–2156, 2180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.09.028. [3] 郑恒, 王俊, 江胜利, 等. 外辐射源雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 1–10.ZHENG Heng, WANG Jun, JIANG Shengli, et al. Passive Bistatic Radar[M]. Beijing, China: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 1–10. [4] 万显荣, 易建新, 占伟杰, 等. 基于多照射源的被动雷达研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143.WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, ZHAN Weijie, et al. Research progress and development trend of the multi-illuminator-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143. [5] WILLIS N J and GRIFFITHS H D. Advances in bistatic radar (Willis, NJ and Griffiths, HD, Eds.; 2007) [Book Review][J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2008, 23(7): 46–46. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2008.4579292. [6] GRIFFITHS H and WILLIS N. Klein Heidelberg-the first modern bistatic radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(4): 1571–1588. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5595580. [7] GRIFFITHS H D and LONG N R W. Television-based bistatic radar[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Communications, Radar and Signal Processing), 1986, 133(7): 649–657. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-1.1986.0104. [8] 王小谟, 吴曼青, 王政. 未来战争中的“沉默哨兵”——外辐射源目标探测与跟踪雷达[J]. 现代军事, 2000(10): 10–12.WANG Xiaomo, WU Manqing, and WANG Zhen. ‘Silence Sentinel’ in future wars—external radiation source target detection and tracking radar[J]. Modern Military, 2000(10): 10–12. [9] HOWLAND P E, MAKSIMIUK D, and REITSMA G. FM radio based bistatic radar[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(3): 107–115. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045077. [10] EDRICH M, SCHROEDER A, and MEYER F. Design and performance evaluation of a mature FM/DAB/DVB-T multi-illuminator passive radar system[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(2): 114–122. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0162. [11] O’HAGAN D W, KUSCHEL H, UMMENHOFER M, et al. A multi-frequency hybrid passive radar concept for medium range air surveillance[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2012, 27(10): 6–15. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2012.6373907. [12] BIČÍK P. Passive radar: Here comes the new generation VERA-NG[C]. The 11-th International Radar Symposium, Vilnius, Lithuania, 2010: 1–4. [13] 贾玉贵. 现代对空情报雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2004: 169.JIA Yugui. Modern Air Surveillance Radar[M]. Beijing, China: National Defense Industry Press, 2004: 169. [14] 吴翼虎. 外辐射源雷达目标检测与定位技术[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2010. doi: 10.7666/d.Y1706760.WU Yihu. Target detection and location technology in external illuminator based passive radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2010. doi: 10.7666/d.Y1706760. [15] 杨广平. 外辐射源雷达关键技术研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2008, 30(8): 5–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2008.08.002.YANG Guangping. A study on key technology of passive radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2008, 30(8): 5–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2008.08.002. [16] 郑雨晴, 艾小锋, 王满喜, 等. 以全球导航卫星系统为辐射源的前向散射雷达发展综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(8): 3073–3093. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231255.ZHENG Yuqing, AI Xiaofeng, WANG Manxi, et al. Global navigation satellite system forward scatter radar: A review[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(8): 3073–3093. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231255. [17] 李中余, 黄川, 武俊杰, 等. 基于GNSS的无源雷达海面目标检测技术综述[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(4): 404–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.04.009.LI Zhongyu, HUANG Chuan, WU Junjie, et al. Overview of maritime target detection techniques using GNSS-based passive radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(4): 404–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.04.009. [18] HUANG Chuan, LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, et al. A long-time integration method for GNSS-based passive radar detection of marine target with multi-stage motions[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 2815–2818. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9324042. [19] 陈江宁. 基于高轨卫星外辐射源微弱目标检测技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2021.001367.CHEN Jiangning. Research on dim target detection technology based on external transmitter of geostationary earth orbit satellite[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2021.001367. [20] 李唐, 王峰, 杨新宇, 等. GNSS外辐射源空中目标探测研究现状及发展[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(7): 1639–1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.07.018.LI Tang, WANG Feng, YANG Xinyu, et al. Development and status of air target detection from GNSS-based passive radar[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(7): 1639–1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.07.018. [21] LYU Xiaoyong, STOVE A, GASHINOVA M, et al. Ambiguity function of Inmarsat BGAN signal for radar application[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(18): 1557–1559. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.1400. [22] FOSSA C E, RAINES R A, GUNSCH G H, et al. An overview of the IRIDIUM (R) Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite system[C]. IEEE 1998 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference. NAECON 1998. Celebrating 50 Years (Cat. No.98CH36185), Dayton, USA, 1998: 152–159. doi: 10.1109/NAECON.1998.710110. [23] 梁健. 铱星STL系统定位方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华中科技大学, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002798.LIANG Jian. Investigation on Iridium STL positioning method[D]. [Master dissertation], Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002798. [24] 秦红磊, 张宇. 星链机会信号定位方法[J]. 导航定位学报, 2023, 11(1): 67–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2023.01.010.QIN Honglei and ZHANG Yu. Positioning technology based on Starlink signal of opportunity[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2023, 11(1): 67–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2023.01.010. [25] 秦红磊, 武宁, 赵超. 基于视向矢量修正的铱星机会信号多普勒差分定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(3): 748–756. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0378.QIN Honglei, WU Ning, and ZHAO Chao. Differential positioning with doppler measurements from Iridium satellite signals of opportunity based on lines of sight correction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(3): 748–756. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0378. [26] 崔志颖, 岳富占, 田润, 等. 基于铱星突发信号的导航定位技术研究[J]. 全球定位系统, 2021, 46(2): 77–85. doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2020121503.CUI Zhiying, YUE Fuzhan, TIAN Run, et al. Research on positioning technology based on Iridium burst signal[J]. GNSS World of China, 2021, 46(2): 77–85. doi: 10.12265/j.gnss.2020121503. [27] GOMEZ-DEL-HOYO P, GRONOWSKI K, and SAMCZYNSKI P. The STARLINK-based passive radar: Preliminary study and first illuminator signal measurements[C]. 2022 23rd International Radar Symposium (IRS), Gdansk, Poland, 2022: 350–355. doi: 10.23919/IRS54158.2022.9905046. [28] KHALIFE J, NEINAVAIE M, and KASSAS Z M. The first carrier phase tracking and positioning results with Starlink LEO satellite signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(2): 1487–1491. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3113880. [29] KOCH V and WESTPHAL R. New approach to a multistatic passive radar sensor for air/space defense[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1995, 10(11): 24–32. doi: 10.1109/62.473409. [30] MCINTOSH J C. Passive three dimensional track of non-cooperative targets through opportunistic use of global positioning system (GPS) and GLONASS signals[EB/OL]. https://www.freepatentsonline.com/6232922.html, 2001. [31] MOJARRABI B, HOMER J, KUBIK K, et al. Power budget study for passive target detection and imaging using secondary applications of GPS signals in bistatic radar systems[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 449–451. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1025069. [32] BEHAR V and KABAKCHIEV C. Detectability of air targets using bistatic radar based on GPS L5 signals[C]. 2011 12th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Leipzig, Germany, 2011: 212–217. [33] MA Hui, ANTONIOU M, PASTINA D, et al. Maritime moving target indication using passive GNSS-based bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 115–130. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2739900. [34] PASTINA D, SANTI F, PIERALICE F, et al. Maritime moving target long time integration for GNSS-based passive bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(6): 3060–3083. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2840298. [35] VEREMYEV V I, VOROBEV E N, and KOKORINA Y V. Feasibility study of air target detection by passive radar using satellite-based transmitters[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), Saint Petersburg and Moscow, Russia, 2019: 154–157. doi: 10.1109/EIConRus.2019.8656630. [36] NASSO I and SANTI F. A centralized approach for ship target detection and localization with multi-transmitters GNSS-based passive radar[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems (RADAR 2022), Edinburgh, UK, 2022: 202–207. doi: 10.1049/icp.2022.2316. [37] NASSO I and SANTI F. Maritime moving target detection and localisation technique for Global Navigation Satellite Signals-based passive multistatic radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2024, 18(1): 93–106. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12438. [38] 戴剑华, 尹成友. 利用GPS星际照射源的无源侦察定位系统研究[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2001(4): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2001.04.003.DAI Jianhua and YIN Chengyou. Research on passive reconnaissance and positioning system using GPS interstellar irradiation source[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2001(4): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2001.04.003. [39] 袁伟明, 刘立东, 吴顺君, 等. 一种新的基于GPS照射源的天基雷达信号处理算法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2004, 19(2): 219–222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.02.019.YUAN Weiming, LIU Lidong, WU Shunjun, et al. An novel signal processing algorithm for SBR based on GPS illumination[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2004, 19(2): 219–222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.02.019. [40] 刘立东, 袁伟明, 吴顺君, 等. 基于GPS照射源的天地双基地雷达探测系统[J]. 电波科学学报, 2004, 19(1): 109–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.01.024.LIU Lidong, YUAN Weiming, WU Shunjun, et al. Bistatic radar system based on GPS illumination[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2004, 19(1): 109–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.01.024. [41] HE X, CHERNIAKOV M, and ZENG T. Signal detectability in SS-BSAR with GNSS non-cooperative transmitter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(3): 124–132. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045042. [42] 杨东凯, 路勇, 张波. 基于导航卫星反射信号的空间飞行器探测定位方法[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(1): 143–147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.01.023.YANG Dongkai, LU Yong, and ZHANG Bo. Space vehicle detection and positioning based on reflected signal of navigation satellite[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(1): 143–147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.01.023. [43] 范梅梅, 廖东平, 丁小峰. 基于北斗卫星信号的无源雷达可行性研究[J]. 信号处理, 2010, 26(4): 631–636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.04.028.FAN Meimei, LIAO Dongping, and DING Xiaofeng. Feasibility research of passive radar based on Beidou navigation and position system[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2010, 26(4): 631–636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.04.028. [44] 蒋铁珍, 肖文书, 李大圣, 等. 基于星载机会源的空间目标外辐射源雷达探测技术可行性研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 711–719. doi: 10.12000/JR14080.JIANG Tiezhen, XIAO Wenshu, LI Dasheng, et al. Feasibility study on passive-radar detection of space targets using spaceborne illuminators of opportunity[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 711–719. doi: 10.12000/JR14080. [45] 何征, 蒙继东, 尚社. 基于GPS照射源的双基地新体制雷达探测系统[J]. 电子设计工程, 2015, 23(21): 32–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2015.21.010.HE Zheng, MENG Jidong, and SHANG She. New bistatic radar system based on GPS illumination[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2015, 23(21): 32–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2015.21.010. [46] 李雨亭. 基于多个GPS卫星信息融合的信号检测[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2017. doi: 10.7666/d.D01385181.LI Yuting. Signal detection based on multiple GPS satellites information fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2017. doi: 10.7666/d.D01385181. [47] 郭丹丹. 基于北斗二代卫星信号的外辐射源雷达目标探测技术[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2019.000758.GUO Dandan. Target detection method in passive bistatic radar based on Beidou II satellite signals[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2019.000758. [48] 何振宇, 陈武, 杨扬. GPS天-地无源双基地雷达探测海面移动目标[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(12): 1523–1534. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20190487.HE Zhenyu, CHEN Wu, and YANG Yang. GPS-based space-surface passive bistatic radar technique for maritime moving target detection[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(12): 1523–1534. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20190487. [49] HUANG Chuan, LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, et al. Multistatic Beidou-based passive radar for maritime moving target detection and localization[C]. IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 2175–2177. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8900548. [50] LI Zhongyu, HUANG Chuan, WU Junjie, et al. Investigation and first experiment of BeiDou-based passive radar vessel target imaging[C]. 2022 3rd URSI Atlantic and Asia Pacific Radio Science Meeting (AT-AP-RASC), Gran Canaria, Spain, 2022: 1–4. doi: 10.23919/AT-AP-RASC54737.2022.9814205. [51] LI Zhongyu, HUANG Chuan, SUN Zhichao, et al. BeiDou-based passive multistatic radar maritime moving target detection technique via space-time hybrid integration processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5802313. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3128650. [52] HE Zhenyu, YANG Yang, CHEN Wu, et al. Moving target imaging using GNSS-based passive bistatic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(20): 3356. doi: 10.3390/rs12203356. [53] HE Zhenyu, CHEN Wu, YANG Yang, et al. Maritime ship target imaging with GNSS-based passive multistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5800918. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3270182. [54] ZHENG Hui, CHENG Shuiying, and ZHANG Maoyi. Reference signal reconstruction for GPS-based passive radar based on software radio platform[C]. 2023 IEEE 6th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chongqing, China, 2023: 732–736. doi: 10.1109/ITNEC56291.2023.10082494. [55] TANG Tao, WANG Pengbo, ZENG Hongcheng, et al. An efficient coarse-to-fine Doppler parameter search method for moving target detection using GNSS-based passive bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3509105. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3450209. [56] 杨东凯, 谭传瑞, 王峰, 等. 基于高度角随机模型的GNSS外辐射源雷达定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1373–1381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230462.YANG Dongkai, TAN Chuanrui, WANG Feng, et al. GNSS elevation-dependent stochastic localization algorithm for gnss-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1373–1381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230462. [57] GAO Wenning, YUE Fuzhan, XIA Zhenghuan, et al. Multistatic collaborative imaging for shipborne GNSS-S radar: Method and experimental verification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4009805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3398577. [58] GRIFFITHS H D, GARNETT A J, BAKER C J, et al. Bistatic radar using satellite-borne illuminators of opportunity[C]. 92 International Conference on Radar, Brighton, UK, 1992: 276–279. [59] MARQUES P, FERREIRA A, FORTES F, et al. A pedagogical passive RADAR using DVB-S signals[C]. 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Seoul, Korea (South), 2011: 1–4. [60] PISCIOTTANO I, PASTINA D, and CRISTALLINI D. DVB-S based passive radar imaging of ship targets[C]. The 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8768097. [61] PISCIOTTANO I, SANTI F, PASTINA D, et al. DVB-S based passive polarimetric ISAR—Methods and experimental validation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 6056–6070. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3037091. [62] MARTELLI T, CABRERA O, COLONE F, et al. Exploitation of long coherent integration times to improve drone detection in DVB-S based passive radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266624. [63] CABRERA O, BONGIOANNI C, COLONE F, et al. Non-coherent DVB-S passive radar demonstrator[C]. 2020 21st International Radar Symposium (IRS), Warsaw, Poland, 2020: 228–231. doi: 10.23919/IRS48640.2020.9253805. [64] GENTILE L, CAPRIA A, SAVERINO A L, et al. DVB-S2 passive bistatic radar for resident space object detection: Preliminary results[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 607–611. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114746. [65] GRONOWSKI K, ALMODOVAR-HERNANDEZ A, GUTIERREZ-SERRANO S, et al. Preliminary results of detection utilizing DVB-S2 based polarimetric passive radar[C]. 2024 International Radar Symposium (IRS), Wroclaw, Poland, 2024: 414–419. [66] 金威, 吕晓德, 向茂生. 基于DVB-S信号的外辐射源雷达的模糊函数及分辨特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 380–386. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20077.JIN Wei, LÜ Xiaode, and XIANG Maosheng. Ambiguity function and resolution characteristic analysis of DVB-S signal for passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 380–386. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20077. [67] SUN Zeyue, WANG Tianyun, JIANG Tao, et al. Analysis of the properties of DVB-S signal for passive radar application[C]. 2013 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2013: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/WCSP.2013.6677172. [68] 孙泽月. 基于DVB-S信号特性分析的无源检测技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2014.SUN Zeyue. Research on passive detection based on the analysis of the properties of DVB-S signal[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2014. [69] 冯斌. DVB-S信号的无源雷达接收处理技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2014.FENG Bin. Research on DVB-S signal processing of passive radar system[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2014. [70] 刘明骞, 高修会, 李兵兵. 一种多个不同体制卫星下微弱回波信号联合检测方法[P]. 中国, 201610344683.1, 2016.LIU Mingqian, GAO Xiuhui, and LI Bingbing. Joint detection method for weak echo signals under satellites of multiple different systems[P]. CN, 201610344683.1, 2016. [71] 李凌. 基于DVB-S信号的无源雷达检测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2019.LI Ling. A study on detection techniques for passive radar based on DVB-S signal[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2019. [72] LI Junjie, WEI Junkang, CAO Zhihui, et al. A DVB-S-based multichannel passive radar system for vehicle detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 2900–2912. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047525. [73] 谢进文. 基于外辐射源的高速运动目标探测技术[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018.XIE Jinwen. High velocity targets detection technology based on opportunity illumination[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018. [74] 童云, 万显荣, 周昕, 等. 基于DVB-S信号的被动雷达舰船目标探测实验研究[C]. 第十八届全国电波传播年会, 青岛, 中国, 2023: 4. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2023.050938.TONG Yun, WAN Xianrong, ZHOU Xin, et al. Experimental research of ship target detection with DVB-S based passive radar[C]. Chinese National Symposium on Radio Propagation (CNSRP2023), Qingdao, China, 2023: 4. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2023.050938. [75] DANIEL L, HRISTOV S, LYU Xiaoyong, et al. Design and validation of a passive radar concept for ship detection using communication satellite signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 3115–3134. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2728978. [76] STOVE A G, GASHINOVA M S, HRISTOV S, et al. Passive maritime surveillance using satellite communication signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2987–2997. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2722598. [77] STOVE A G, GASHINOVA M S, HRISTOV S, et al. Passive maritime surveillance using satellite communication signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2987–2997. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2722598. [78] DANIEL L, HRISTOV S, LYU Xiaoyong, et al. Design and validation of a passive radar concept for ship detection using communication satellite signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 3115–3134. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2728978. [79] CHERNIAKOV M, NEZLIN D, and KUBIK K. Air target detection via bistatic radar based on LEOs communication signals[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2002, 149(1): 33–38. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20020129. [80] LYU Xiaoyong, STOVE A, GASHINOVA M, et al. Ambiguity function of Iridium signal for radar application[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(19): 1631–1633. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.1404. [81] LYU Xiaoyong, HRISTOV S, GASHINOVA M, et al. Ambiguity function analysis of the Inmarsat I-4 and Iridium signals[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems, Belfast, UK, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1049/cp.2017.0510. [82] SAYIN A, CHERNIAKOV M, and ANTONIOU M. Passive radar using Starlink transmissions: A theoretical study[C]. 2019 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8768105. [83] GOMEZ-DEL-HOYO P, SAMCZYNSKI P, and MICHALAK F. Analysis of Starlink Users’ downlink for passive radar applications: Signal characteristics and ambiguity function performance[C]. 2023 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf23), San Antonia, US, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2351548.2023.10149600. [84] BLÁZQUEZ-GARCÍA R, UMMENHOFER M, CRISTALLINI D, et al. Passive radar architecture based on broadband LEO communication satellite constellations[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764342. [85] BLÁZQUEZ-GARCÍA R, CRISTALLINI D, UMMENHOFER M, et al. Experimental comparison of Starlink and OneWeb signals for passive radar[C]. 2023 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf23), San Antonio, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2351548.2023.10149580. [86] BLÁZQUEZ-GARCÍA R, CRISTALLINI D, SEIDEL V, et al. Experimental acquisition of Starlink satellite transmissions for passive radar applications[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems, Edinburgh, UK, 2022: 130–135. doi: 10.1049/icp.2022.2304. [87] ZHANG Maoyi, CHENG Shuiying, and ZHENG Hui. Feasibility of Starlink transmissions for passive airborne targets detection[C]. 2022 5th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 656–661. doi: 10.1109/ICICSP55539.2022.10050607. [88] ZHU Hanqing, ZHOU Dajiang, LI Zhongyu, et al. Moving target detection method for passive radar using LEO communication satellite constellation[C]. IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 8090–8093. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10283174. [89] QIU Xingye, LI Aocheng, LI Zhongyu, et al. The low-earth-orbit communication satellites-based passive radar target detection via blind signal identification[C]. IGARSS 2024-2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 6685–6688. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10642614. [90] GOMEZ-DEL-HOYO P and SAMCZYNSKI P. Starlink-based passive radar for Earth’s surface imaging: First experimental results[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 13949–13965. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3437179. [91] 周昕, 易建新, 万显荣, 等. 基于低轨卫星机会照射源的无人机目标前向散射探测方法与实验[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(12): 2105–2115. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2024.12.001.ZHOU Xin, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Methods and experiments for forward scattering detection of UAV targets based on opportunistic illumination from low-orbit satellites[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(12): 2105–2115. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2024.12.001. [92] 李江林. 铱星外辐射源雷达非均匀多普勒抽取杂波抑制技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆: 重庆大学, 2024.LI Jianglin. Research on Doppler extraction clutter suppression technology based on iridium passive bistatic radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2024. [93] 田润, 崔志颖, 张爽娜, 等. 基于低轨通信星座的导航增强技术发展概述[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2021, 8(1): 66–81. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.01.007.TIAN Run, CUI Zhiying, ZHANG Shuangna, et al. Overview of navigation augmentation technology based on LEO[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2021, 8(1): 66–81. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2021.01.007. [94] 蒙艳松, 边朗, 王瑛, 等. 基于“鸿雁”星座的全球导航增强系统[J]. 国际太空, 2018(10): 20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.10.005.MENG Yansong, BIAN Lang, WANG Ying, et al. Global navigation augmentation system based on Hongyan satellite constellation[J]. Space International, 2018(10): 20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.10.005. [95] 宋奕辰, 徐小涛, 宋文婷. 国内外卫星移动通信系统发展现状综述[J]. 电信快报, 2019(8): 37–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1339.2019.08.008.SONG Yichen, XU Xiaotao, and SONG Wenting. Overview of the development of satellite mobile communication systems at home and abroad[J]. Telecommunications Information, 2019(8): 37–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1339.2019.08.008. [96] WANG Qing, ZHU Minjiong, ZHOU Jie, et al. Terminal-to-terminal calling for GEO broadband mobile satellite communication[J]. ZTE Communications, 2015, 13(2): 46–52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5188.2015.02.009. [97] PRESS L. A new Chinese broadband satellite constellation[EB/OL]. https://circleid.com/posts/20201002-a-new-chinese-broadband-satellite-constellation/, 2020. [98] 《2021中国的航天》白皮书发布[EB/OL]. https://www.cnsa.gov.cn/n6758823/n6758844/n6760320/index.html, 2021.China releases white paper titled “China’s space progrom: A 2021 perspective”[EB/OL]. https://www.cnsa.gov.cn/n6758823/n6758844/n6760320/index.html, 2021. [99] CRISTALLINI D, CARUSO M, FALCONE P, et al. Space-based passive radar enabled by the new generation of geostationary broadcast satellites[C]. 2010 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2010: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2010.5446694. [100] 谢卓成. 铱星STL信号体制及性能研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华中科技大学, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002799.XIE Zhuocheng. STL signal system and performance research of iridium satellite[D]. [Master dissertation], Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002799. [101] 刘悦. “下一代铱星”系统首批10颗卫星成功发射[J]. 国际太空, 2017(4): 52–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2017.04.010.LIU Yue. The first 10 satellites of Iridium NEXT launched successfully[J]. Space International, 2017(4): 52–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2017.04.010. [102] 秦红磊, 谭滋中, 丛丽, 等. 基于铱星机会信号的定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(9): 1691–1699. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0717.QIN Honglei, TAN Zizhong, CONG Li, et al. Positioning technology based on IRIDIUM signals of opportunity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(9): 1691–1699. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0717. [103] NEINAVAIE M and KASSAS Z M. Unveiling Starlink LEO satellite OFDM-Like signal structure enabling precise positioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 2486–2489. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3265951. [104] HUMPHREYS T E, IANNUCCI P A, KOMODROMOS Z M, et al. Signal structure of the Starlink Ku-band downlink[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 6016–6030. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3268610. [105] NEINAVAIE M and KASSAS Z M. Signal mode transition detection in Starlink LEO satellite downlink signals[C]. 2023 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, US, 2023: 360–364. doi: 10.1109/PLANS53410.2023.10139993. [106] KOZHAYA S, KANJ H, and KASSAS Z M. Multi-constellation blind beacon estimation, Doppler tracking, and opportunistic positioning with OneWeb, Starlink, Iridium NEXT, and Orbcomm LEO satellites[C]. 2023 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, USA, 2023: 1184–1195. doi: 10.1109/PLANS53410.2023.10139969. [107] 极客网. T-Mobile美国测试卫星直连手机发送紧急警报, 覆盖通信盲区[EB/OL]. https://finance.sina.com.cn/stock/relnews/us/2024-09-14/doc-incpatau1803357.shtml, 2024.Geeknet. T-Mobile in the United States tests direct satellite connection with mobile phones for sending emergency alerts, covering communication blind spots [EB/OL]. https://finance.sina.com.cn/stock/relnews/us/2024-09-14/doc-incpatau1803357.shtml, 2024. [108] 杨进佩, 刘中, 朱晓华. 用于无源雷达的GPS卫星信号性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(5): 1083–1086. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01981.YANG Jinpei, LIU Zhong, and ZHU Xiaohua. The performances analysis of GPS signals for passive radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2007, 29(5): 1083–1086. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01981. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: