Transmit Waveform Design for Symbol-level Precoding-based One-bit Dual-functional Radar-communication
-
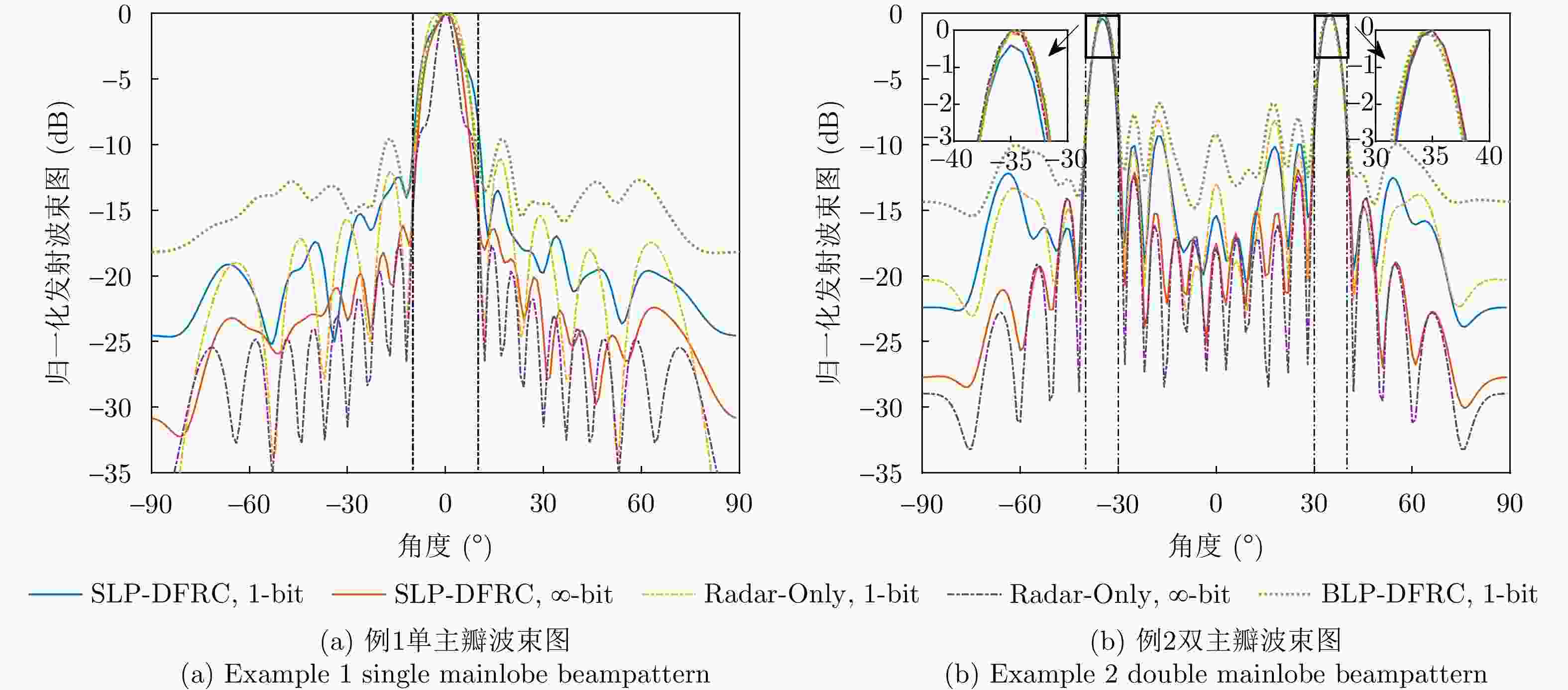
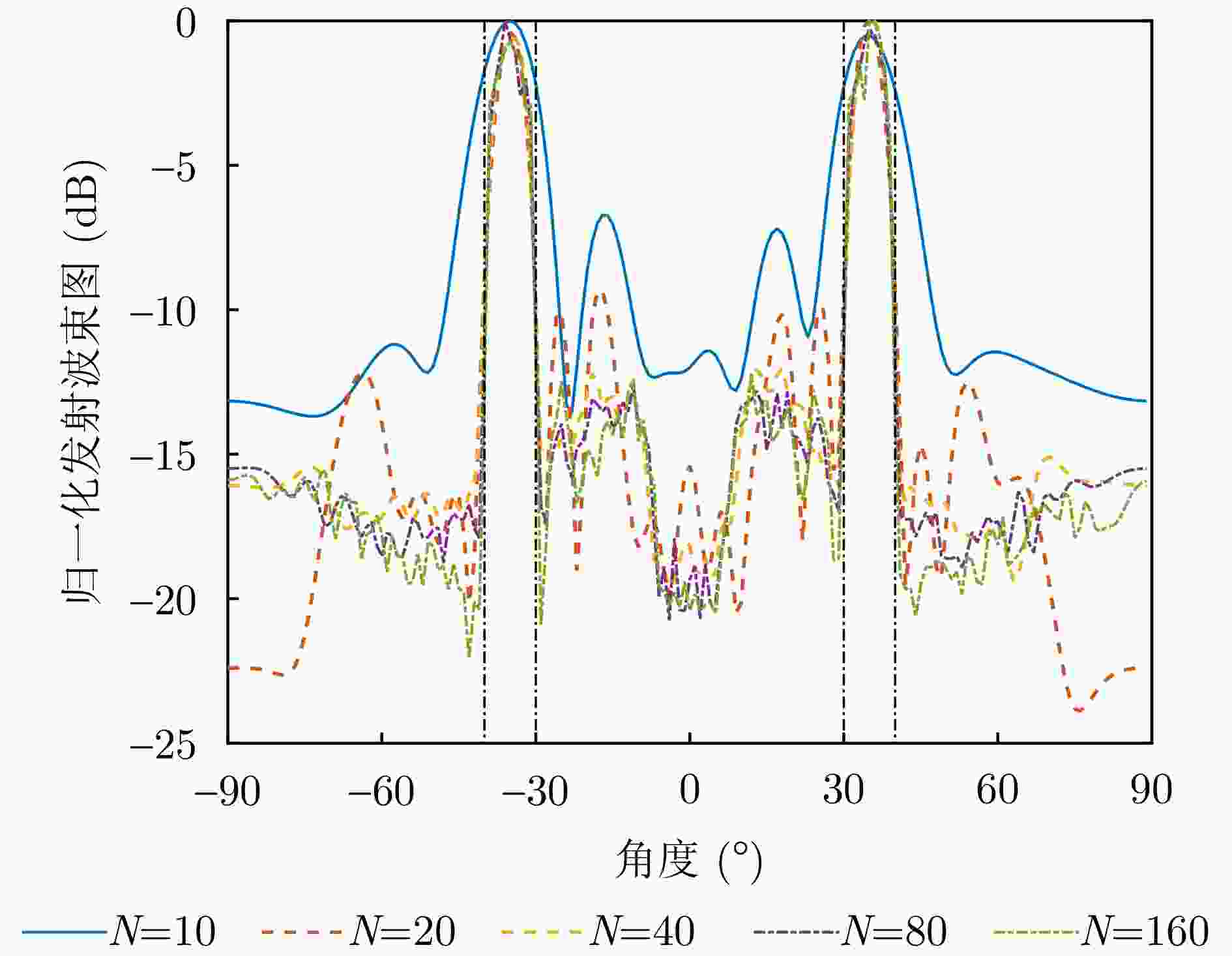
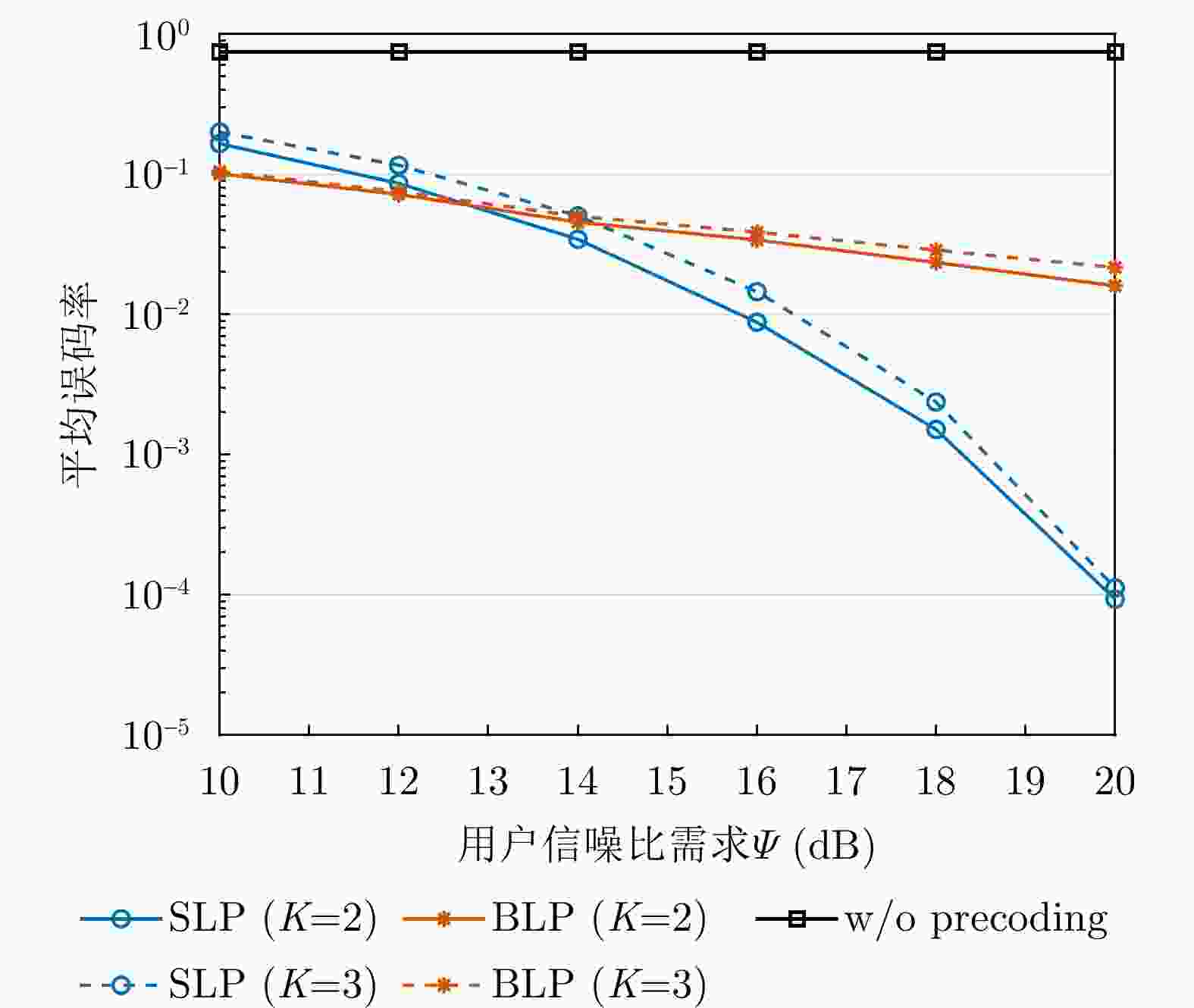
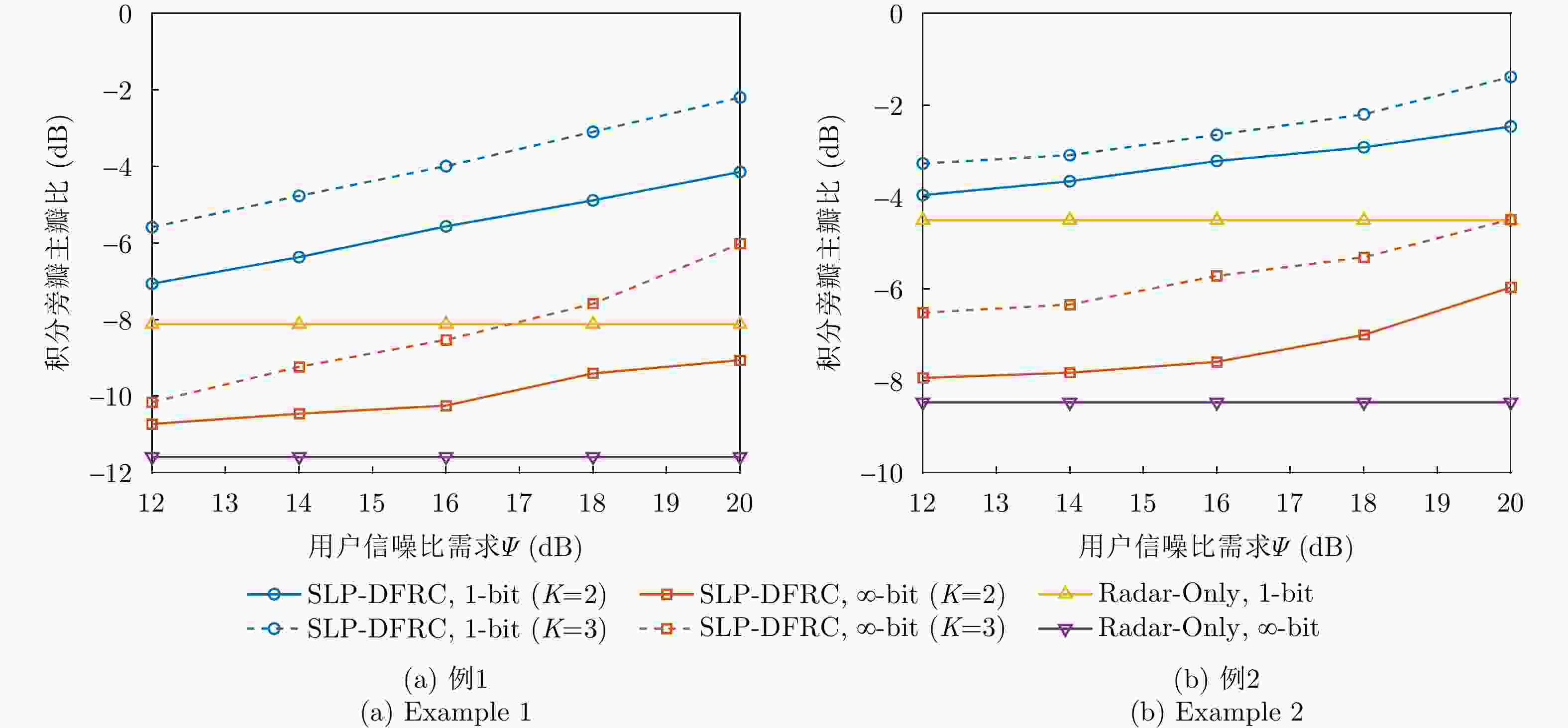
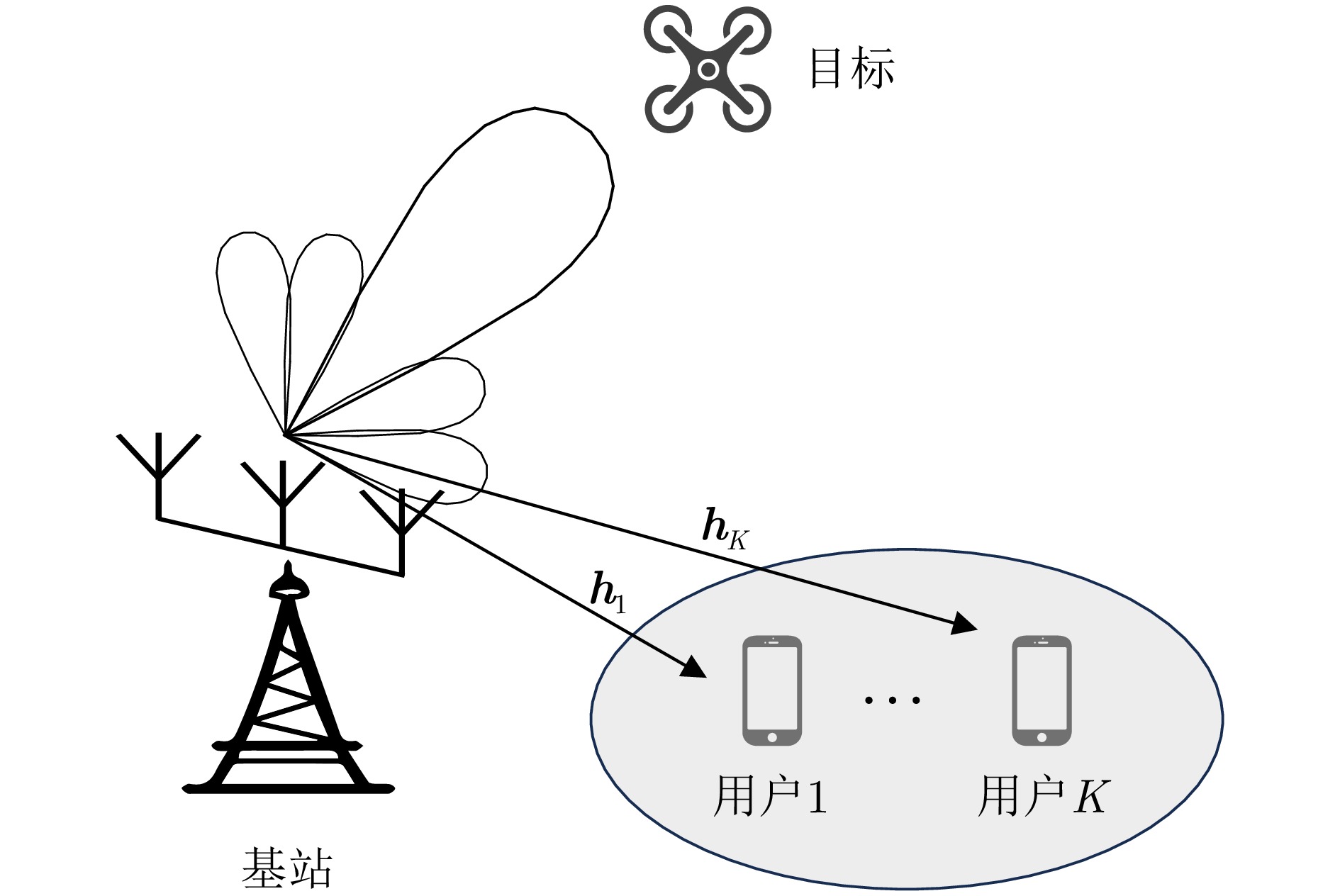
摘要: 在大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)通信和雷达系统中,采用单比特数模转换器(DAC)是一种降低发射系统硬件成本和功耗的有效方法。该文研究单比特量化下雷达通信一体化系统的发射波形设计,在给定通信服务质量约束下最小化雷达发射波束图的积分旁瓣主瓣比,通过提升发射波束的功率集中程度以获得良好的发射波束赋形性能。针对单比特量化导致发射波形仅具有低自由度可行域的问题,该文采用符号级预编码技术,基于有益干扰(CI)原理充分利用空域和时域自由度来辅助波形设计。由于所提出的波形设计问题具有非凸分式二次目标函数和大量的非凸离散约束,该文提出了一种基于丁克尔巴赫(Dinkelbach)变换和交替方向乘子法(ADMM)的算法来有效求解该NP-难问题。仿真结果表明,所设计的波形能够显著降低对DAC分辨率的需求,并在满足下行用户通信质量需求的条件下具有良好的雷达发射波束图性能。Abstract: This study explores the use of one-bit Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC) to mitigate the challenges of high hardware costs and excessive power consumption in large-scale Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) communication and radar systems. The present study focuses on the design of one-bit transmit waveforms for dual-functional radar and communication systems. Under preset communication Quality of Service (QoS) constraints, the objective was to minimize the integral sidelobe-to-mainlobe ratio of the radar transmit beampattern. This should help enhance the power concentration of the transmitted beampattern and improve the performance of the beampattern synthesis. To address the limited Degrees of Freedom (DoF) caused by one-bit quantization, this study employs symbol-level precoding technology and then fully utilizes the DoFs in spatial and temporal domains to assist waveform design based on the principle of Constructive Interference (CI). To address the nonconvex fractional quadratic objective function and the multiple nonconvex discrete constraints inherent in the proposed waveform design problem, this study introduces an algorithm that combines the Dinkelbach transform with the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM). This approach effectively tackles the NP-hard problem. The numerical results demonstrate that the designed waveform significantly reduces the required DAC resolution and achieves excellent radar beampattern performance while satisfying the QoS requirements of downlink multiuser communications.
-
1 梯度投影算法
1. Gradient projection algorithm
输入:$ \xi ,{\boldsymbol{e}},{{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{{\text{s}},{\text{R}}}},{{\boldsymbol{{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} }}_{{\text{m}},{\text{R}}}},{\boldsymbol{w}},{\boldsymbol{H}},\alpha ,\rho ,{\kappa _1},{\kappa _2},{\tau _0},{\delta _1},{\delta _2} $。 输出:$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}} $。 初始化:$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(0)} \in \mathcal{I} $,设置$ r = 0 $; 第1步:根据式(24)计算梯度$ \nabla f({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)}) $,令$ r = r + 1 $,$ \tau = {\tau _0} $; 第2步:计算$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} = {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)} - \tau \nabla f\left({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)}\right) $; 第3步:若$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} \in \mathcal{I} $,则令$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} = {\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} $,跳至第6步,否则令$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(0)}} = {\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} $, $ i = 0 $; 第4步:令$ i = i + 1 $,根据式(25)计算$ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde v}}^{(i)}} = {\mathcal{P}_\mathcal{B}}({{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(i - 1)}}) $,根据式(26)计算$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(i)}} = {\mathcal{P}_\mathcal{H}}\left({{\boldsymbol{\tilde v}}^{(i)}}\right) $; 第5步:若$ \left\| {{{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(i)}} - {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(i - 1)}}} \right\| < {\delta _2} $,令$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} = {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(i)}} $,进行下一步,否则返回第4步; 第6步:若$ f\left({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)}\right) < f\left({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)}\right) + {\kappa _1}\nabla f{\left({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)}\right)^{\rm T}}\left({\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} - {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)}\right) $,进行下一步,否则令$ \tau = {\kappa _2}\tau $,返回第2步; 第7步:若$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r)} - {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(r - 1)} < {\delta _1} $,输出$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}} $,否则返回第1步。 2 Dinkelbach-ADMM算法
2. Dinkelbach-ADMM algorithm
输入:$ {\varTheta _{\text{s}}},{\varTheta _{\text{m}}},{{\boldsymbol{h}}_k},{\varPsi _k},{s_k}[l],\varPhi ,{P_{{\text{tot}}}},\rho ,\nu ,{\varepsilon _1},{\varepsilon _2} $。 输出:x。 初始化:$ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{e}}^{(0)}},{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(0)},{{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(0)}}\right\} $,设置$ t = 0 $; 第1步:根据式(28)构造$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(0)}} $,根据式(12)更新$ {\xi ^{(0)}} $; 第2步:令$ t = t + 1 $, $ k = 0 $; 第3步:令$ k = k + 1 $,根据式(21)更新$ {{\boldsymbol{e}}^{(k)}} $,根据算法1更新$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(k)} $,根据式(17)更新$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}^{(k)}} $; 第4步:若$ {\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{e}}^{(k)}} - {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(k)}} \right\|_2} < {\varepsilon _1} $或$ \rho {\left\| {{\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(k)} - {\boldsymbol{x}}_{\text{R}}^{(k - 1)}} \right\|_2} < {\varepsilon _2} $,根据式(27)和式(28)更新$ {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(t)}} $,根据式(12)更新$ {\xi ^{\left( t \right)}} $,进行下一步,否则返
回第3步;第5步:若$ \left| {{\xi ^{(t)}} - {\xi ^{(t - 1)}}} \right| < \nu $,输出x,否则返回第2步。 -
[1] SAAD W, BENNIS M, and CHEN Mingzhe. A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(3): 134–142. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900287. [2] FANG Xinran, FENG Wei, CHEN Yunfei, et al. Joint communication and sensing toward 6G: Models and potential of using MIMO[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(5): 4093–4116. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3227215. [3] WEI Zhiqing, QU Hanyang, WANG Yuan, et al. Integrated sensing and communication signals toward 5G-A and 6G: A survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(13): 11068–11092. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3235618. [4] LU Shihang, LIU Fan, LI Yunxin, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Recent advances and ten open challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(11): 19094–19120. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3361173. [5] ELBIR A M, MISHRA K V, and CHATZINOTAS S. Terahertz-band joint ultra-massive MIMO radar-communications: Model-based and model-free hybrid beamforming[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1468–1483. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3117410. [6] HUA Haocheng, XU Jie, and HAN T X. Optimal transmit beamforming for integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(8): 10588–10603. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3262513. [7] ZHANG Ruoyu, CHENG Lei, WANG Shuai, et al. Integrated sensing and communication with massive MIMO: A unified tensor approach for channel and target parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(8): 8571–8587. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3351856. [8] SAXENA A K, FIJALKOW I, and SWINDLEHURST A L. Analysis of one-bit quantized precoding for the multiuser massive MIMO downlink[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4624–4634. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2715006. [9] CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Transmit signal design for large-scale MIMO system with 1-bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(9): 4466–4478. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2925343. [10] WEI Tong, CHENG Ziyang, and LIAO Bin. Transmit beampattern synthesis for MIMO radar with one-bit digital-to-analog converters[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 188: 108228. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108228. [11] WEI Tong, CHU Ping, CHENG Ziyang, et al. Transmit beampattern design for MIMO radar with one-bit DACs via block-sparse SDR[C]. 2020 IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SAM48682.2020.9104317. [12] DENG Minglong, CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, et al. Joint design of one-bit transmit waveform and receive filter for MIMO radar in signal dependent interference[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764158. [13] SAXENA A K, FIJALKOW I, and SWINDLEHURST A L. On one-bit quantized ZF precoding for the multiuser massive MIMO downlink[C]. 2016 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SAM.2016.7569670. [14] JACOBSSON S, DURISI G, COLDREY M, et al. Linear precoding with low-resolution DACs for massive MU-MIMO-OFDM downlink[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1595–1609. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2894120. [15] LI Ang, LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, et al. Interference exploitation 1-bit massive MIMO precoding: A partial branch-and-bound solution with near-optimal performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3474–3489. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2973987. [16] WU Zheyu, JIANG Bo, LIU Yafeng, et al. A novel negative ℓ1 penalty approach for multiuser one-bit massive MIMO downlink with PSK signaling[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 5323–5327. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747030. [17] WANG Yiran and LI Ang. ADMM based interference exploitation multi-user one-bit massive MIMO precoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(7): 9561–9566. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3244404. [18] LI Ang, MASOUROS C, SWINDLEHURST A L, et al. 1-bit massive MIMO transmission: Embracing interference with symbol-level precoding[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(5): 121–127. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000601. [19] CHENG Ziyang, SHI Shengnan, HE Zishu, et al. Transmit sequence design for dual-function radar-communication system with one-bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5846–5860. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3070586. [20] YU Xiaoyou, YANG Qi, XIAO Zhu, et al. A precoding approach for dual-functional radar-communication system with one-bit DACs[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1965–1977. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155532. [21] LIN Qi, SHEN Hong, LI Zhicheng, et al. One-bit transceiver optimization for mmWave integrated sensing and communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2025, 73(2): 800–816. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3440830. [22] MASOUROS C and ZHENG Gan. Exploiting known interference as green signal power for downlink beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(14): 3628–3640. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2430839. [23] LIU Rang, LI Ming, LIU Qian, et al. Dual-functional radar-communication waveform design: A symbol-level precoding approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1316–1331. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3111438. [24] WANG Chao, WANG Chengcai, LI Zan, et al. STAR-RIS-enabled secure dual-functional radar-communications: Joint waveform and reflective beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 4577–4592. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3297452. [25] CHENG Ziyang, HAN Chunlin, LIAO Bin, et al. Communication-aware waveform design for MIMO radar with good transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5549–5562. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2868042. [26] LIU Rang, LI Hongyu, LI Ming, et al. Secure symbol-level precoding design for QAM signals in MU-MISO wiretap systems[C]. ICC 2020--2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9149044. [27] SOLTANALIAN M, TANG Bo, LI Jian, et al. Joint design of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(5): 423–426. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2250279. [28] TANG Bo and TANG Jun. Joint design of transmit waveforms and receive filters for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(18): 4707–4722. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2569431. [29] WU Wenjun, TANG Bo, and WANG Xuyang. Constant-modulus waveform design for dual-function radar-communication systems in the presence of clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4005–4017. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3234927. [30] CHEN Shengyao, FENG Qi, RAN Longyao, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-enabled array radar for interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 7437–7452. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3417955. [31] 陈胜垚, 何煦, 冯起, 等. 智能超表面辅助的雷达通信一体化系统恒模发射波形与无源波束形成联合设计[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(12): 2841–2857. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0034.CHEN Shengyao, HE Xu, FENG Qi, et al. Joint design of constant modular transmit waveform and passive beamforming for RIS-aided dual-functional radar and communication[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2024, 54(12): 2841–2857. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0034. [32] JIANG Xue, CHEN Jiayi, LIU Xingzhao, et al. Phase-only robust minimum dispersion beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5664–5679. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3026177. [33] GHADIMI E, TEIXEIRA A, SHAMES I, et al. Optimal parameter selection for the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM): Quadratic problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(3): 644–658. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2354892. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: