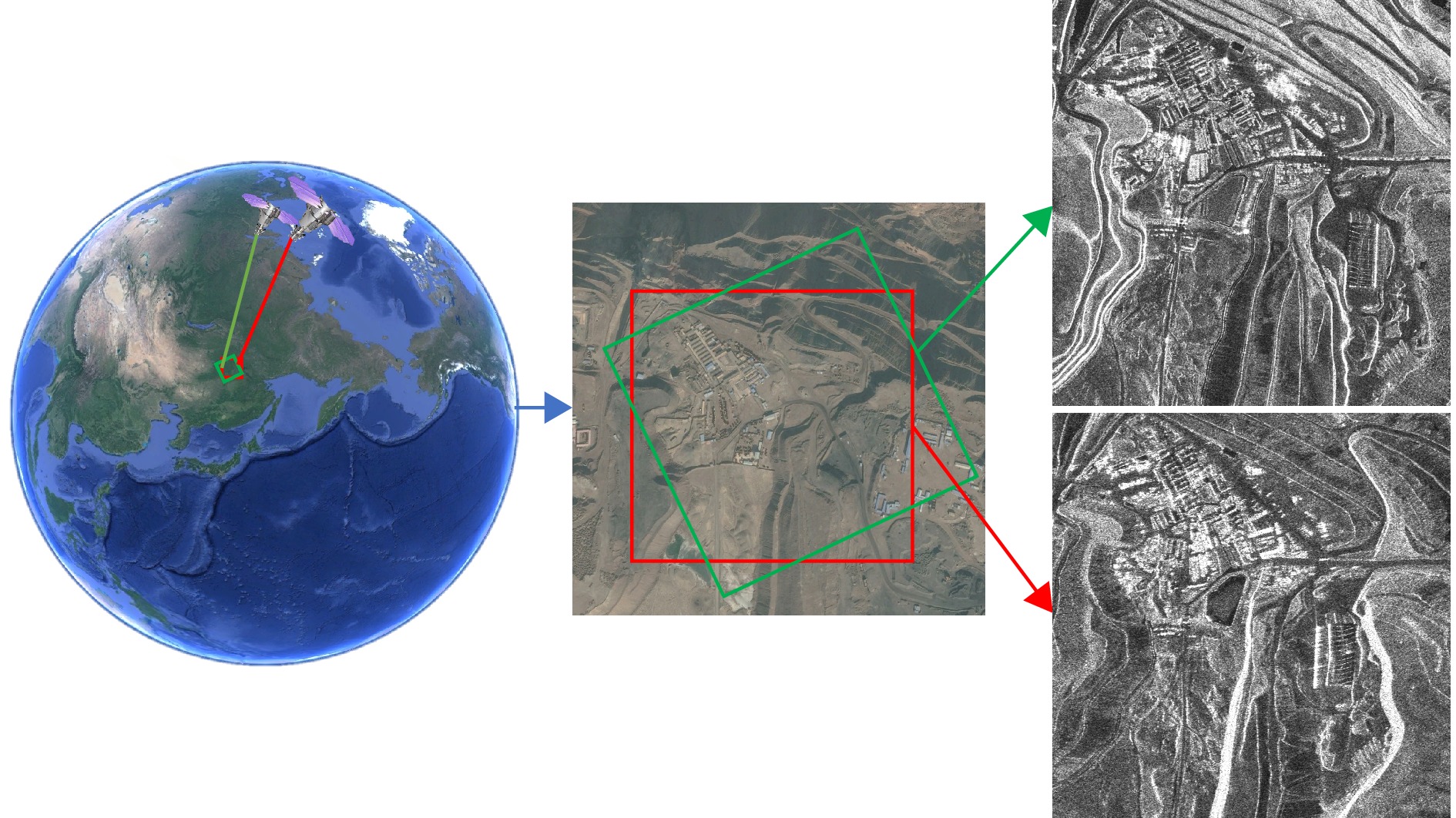
-
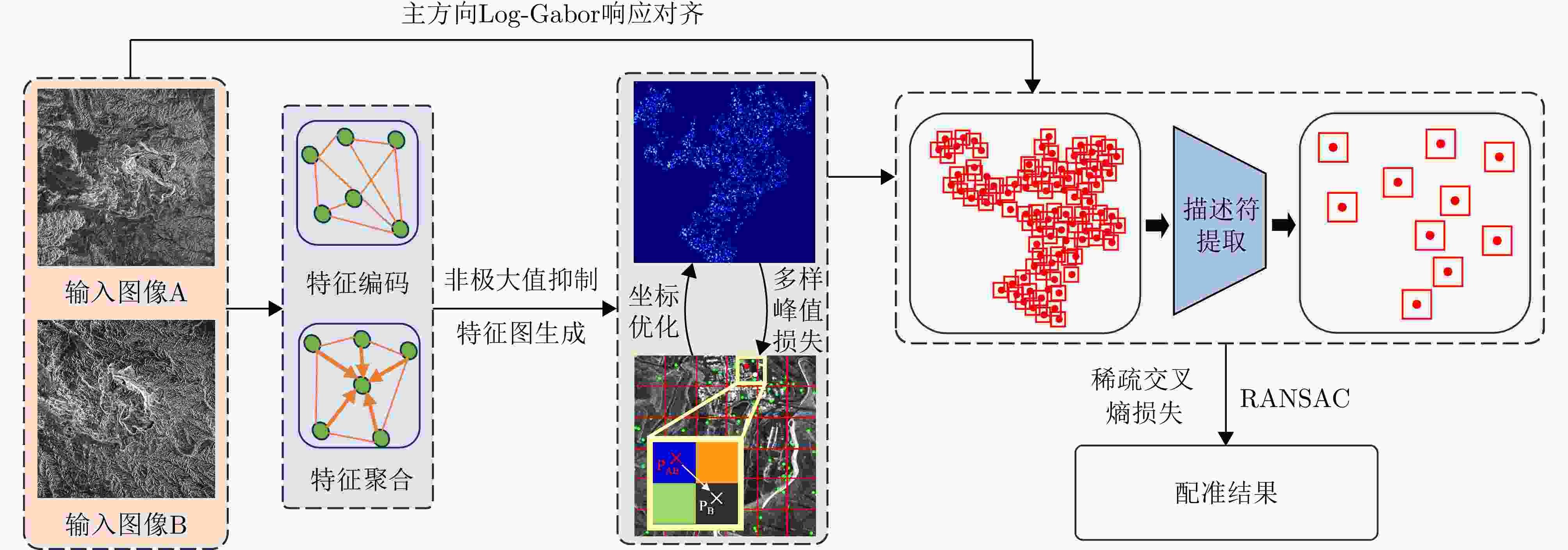
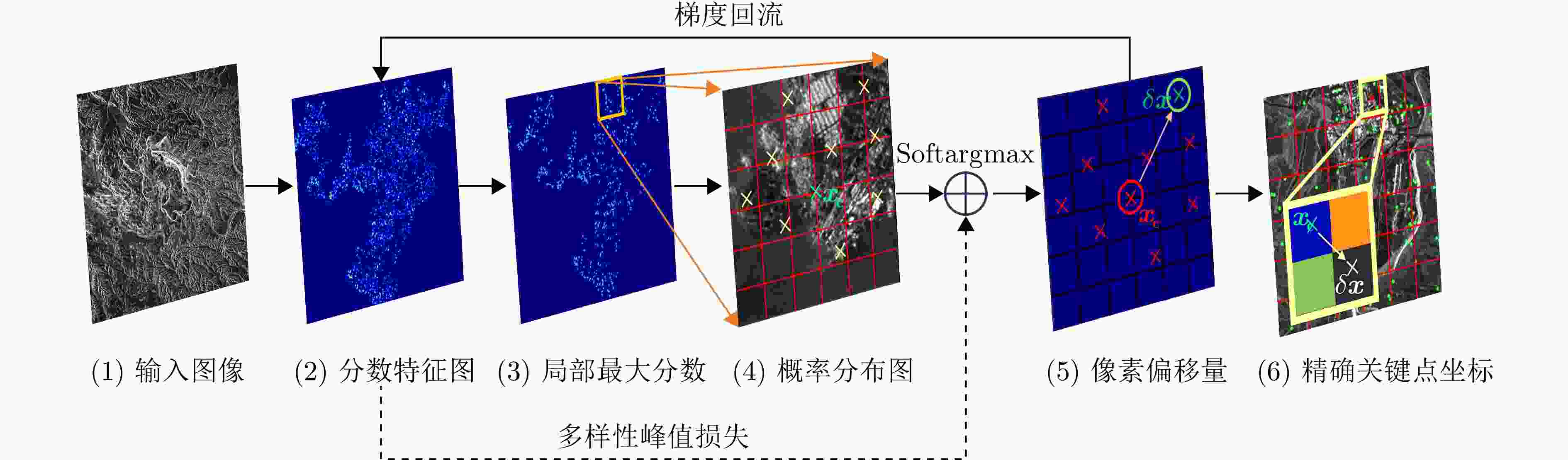
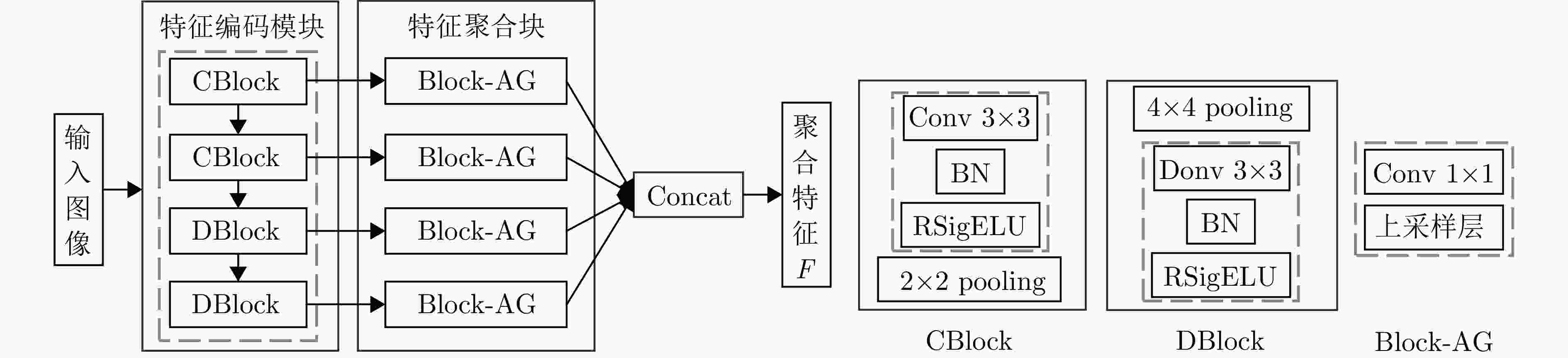
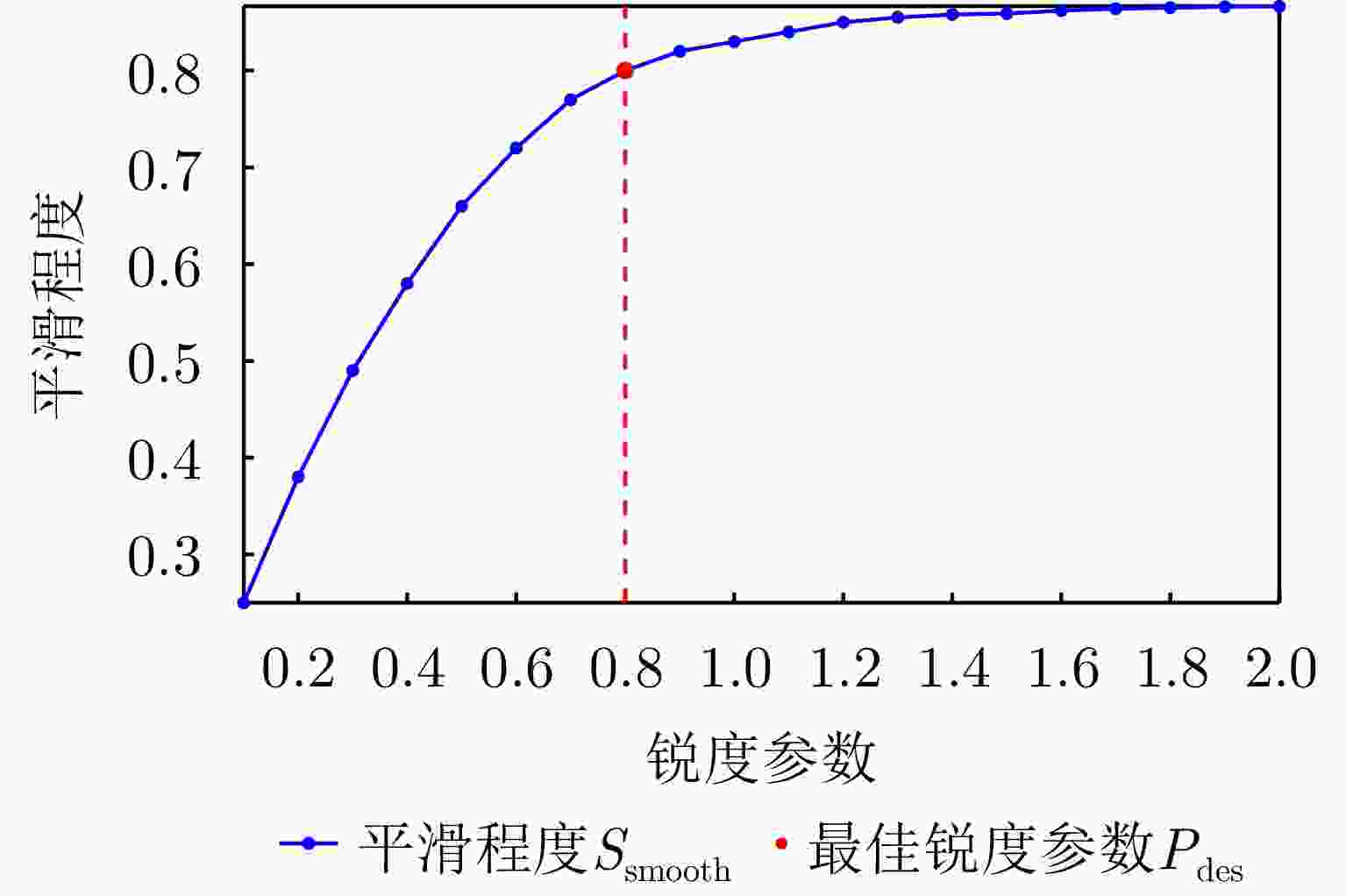
摘要: 由于侧视和相干成像机制,当高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像的成像视角变化较大时,图像间的特征差异会变大,使图像配准难度增加。针对高分辨率多视角SAR图像,传统的配准技术主要面临提取的关键点定位精度不足和匹配精度低的问题。基于上述难点,该文设计了一种端到端的高分辨率多视角SAR图像配准网络。文章主要贡献包括:提出基于局部像素偏移模型的高分辨率SAR图像特征提取方法,该方法提出多样性峰值损失监督训练关键点提取网络中响应权重分配部分,并通过检测像素偏移量来优化关键点坐标;提出基于自适应调整卷积核采样位置的描述符提取方法,利用稀疏交叉熵损失监督训练网络中描述符匹配。实验结果显示,相比于其他配准方法,该文提出的算法针对高分辨率多视角SAR图像配准效果显著,平均误差降低超过65%,正确匹配点对数提高了3~5倍,运行时间平均缩短50%以上。Abstract: Due to the side-looking and coherent imaging mechanisms, feature differences between high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images increase when the imaging viewpoint changes considerably, making image registration highly challenging. Traditional registration techniques for high-resolution multi-view SAR images mainly face issues, such as insufficient keypoint localization accuracy and low matching precision. This work designs an end-to-end high-resolution multi-view SAR image registration network to address the above challenges. The main contributions of this study include the following: A high-resolution SAR image feature extraction method based on a local pixel offset model is proposed. This method introduces a diversity peak loss to guide response weight allocation in the keypoint extraction network and optimizes keypoint coordinates by detecting pixel offsets. A descriptor extraction method is developed based on adaptive adjustment of convolution kernel sampling positions that utilizes sparse cross-entropy loss to supervise descriptor matching in the network. Experimental results show that compared with other registration methods, the proposed algorithm achieves substantial improvements in the high-resolution adjustment of convolution kernel sampling positions, which utilize sparse cross-entropy loss to supervise descriptor matching in the network. Experimental results illustrate that compared with other registration methods, the proposed algorithm achieves remarkable improvements in high-resolution multi-view SAR image registration, with an average error reduction of over 65%, 3~5-fold increases in the number of correctly matched point pairs, and an average reduction of over 50% in runtime.
-
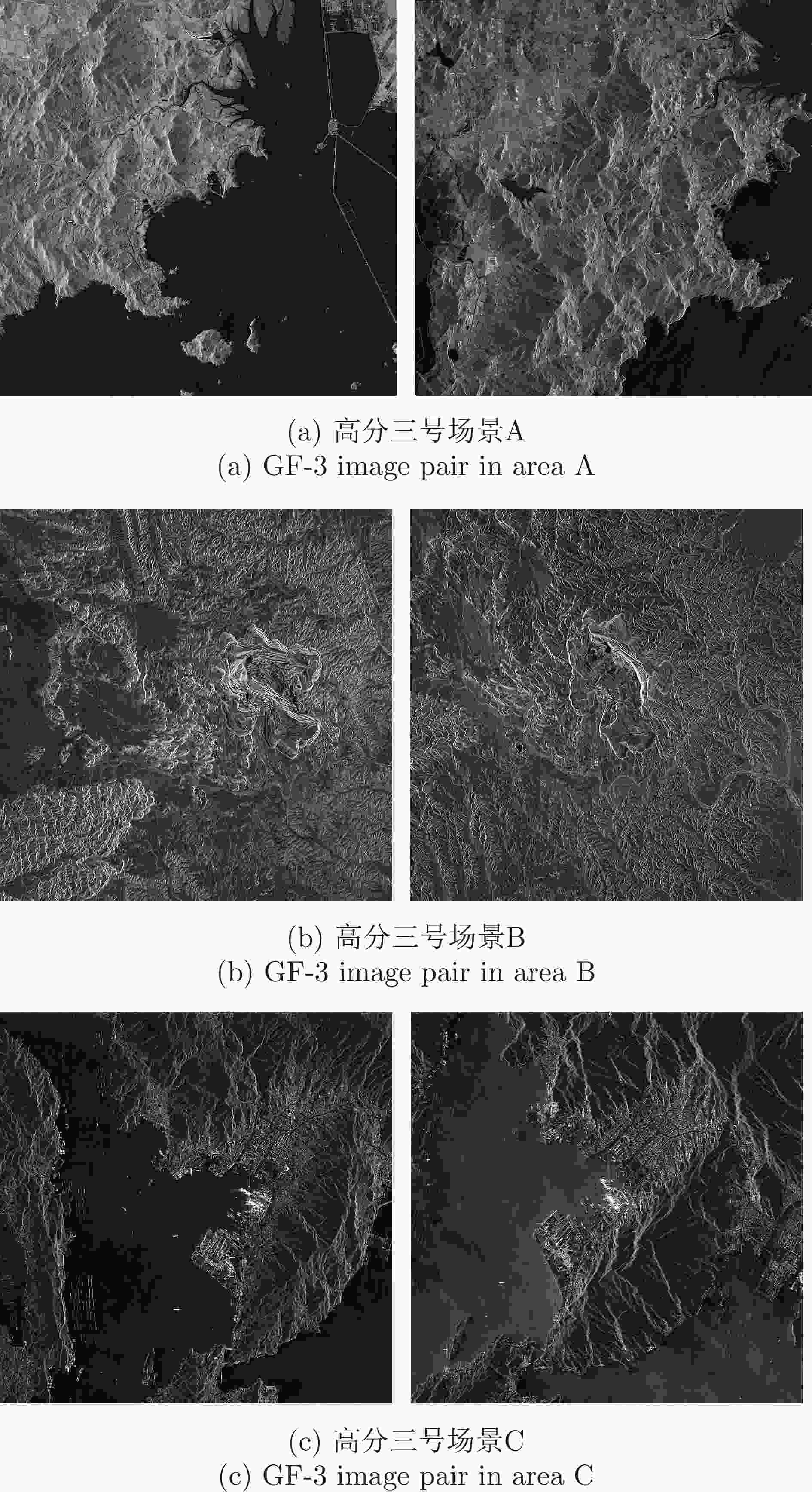
表 1 测试图像对详细信息
Table 1. Experiment image details
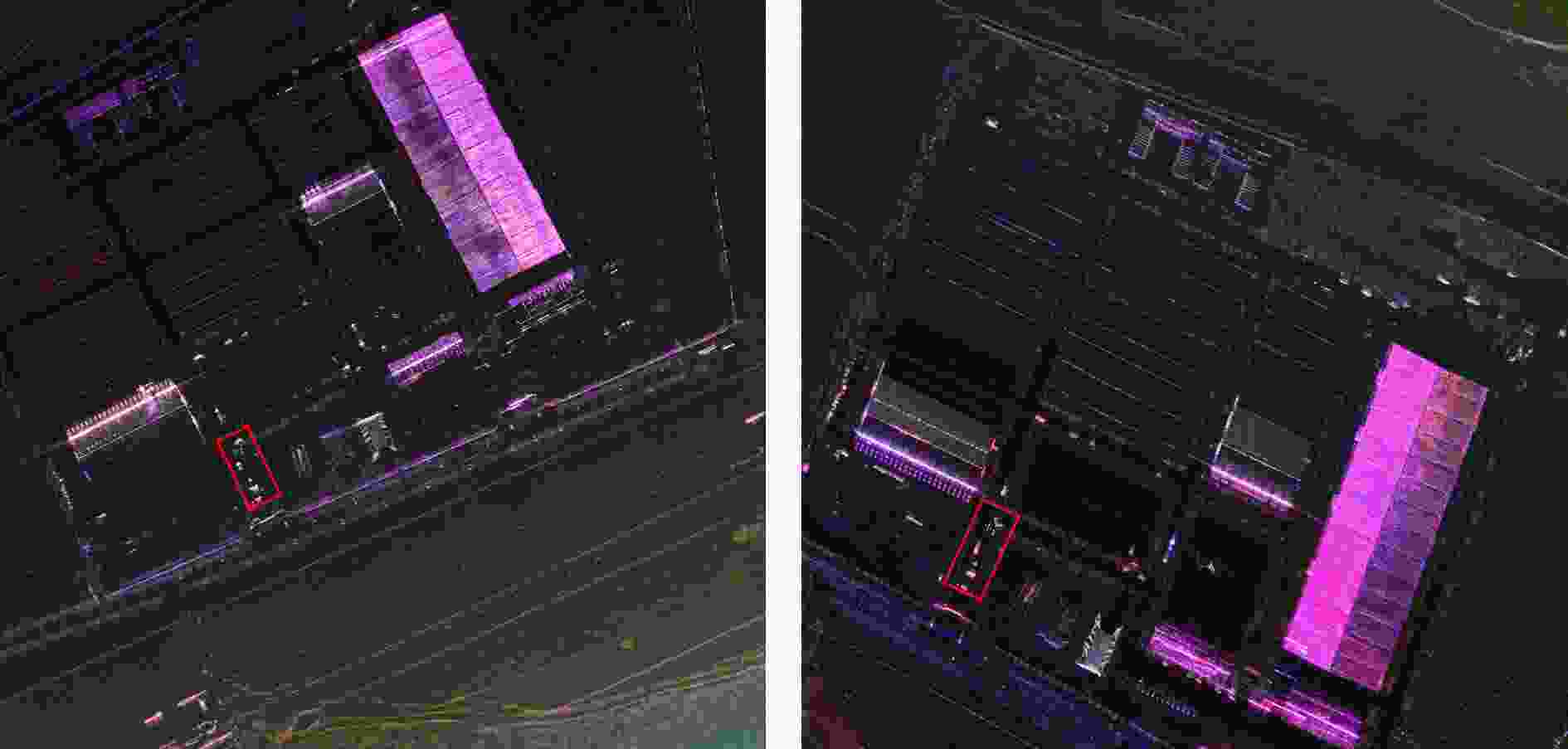
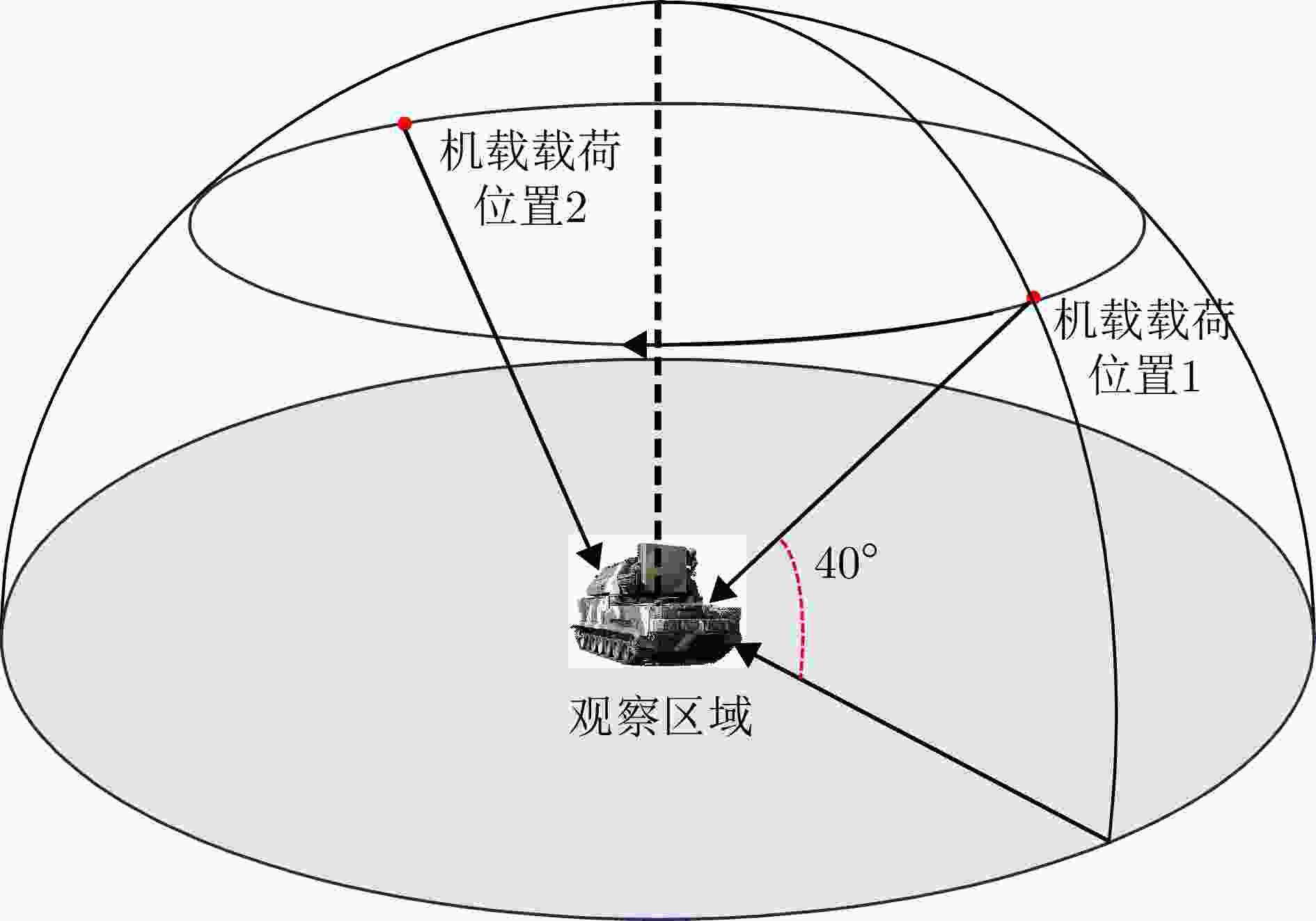
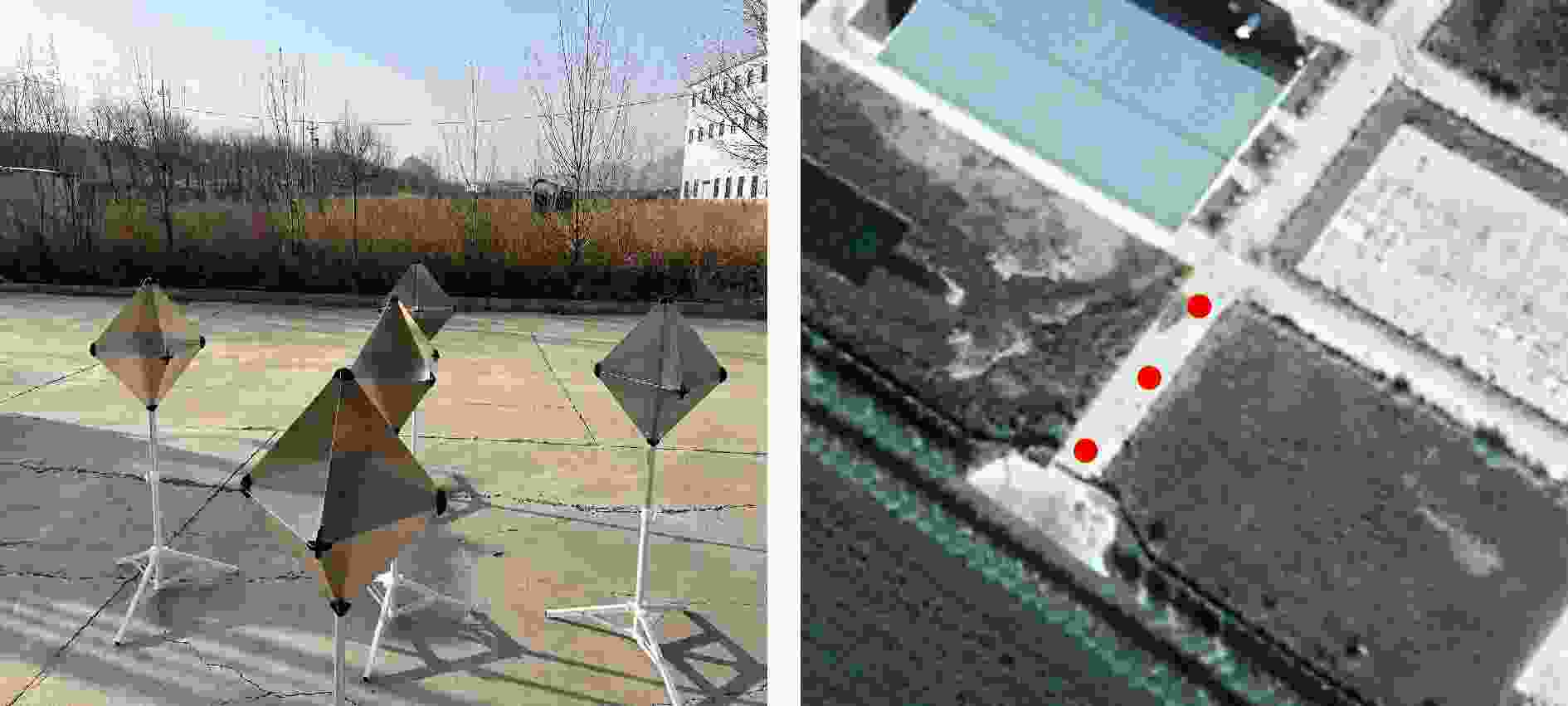
实验图像对 序号 分辨率(m) 轨道方向 入射角度(°) 场景 图像大小(像素) 侧视方向 高分三号场景A a $1 \times 1$ DEC 37.785728 海岸线 $13598 \times 12863$ 右侧视 b $1 \times 1$ ASC 23.309698 海岸线 $13536 \times 11813$ 右侧视 高分三号场景B a $1 \times 1$ DEC 36.342163 山地 $13354 \times 12391$ 右侧视 b $1 \times 1$ ASC 25.466631 山地 $14041 \times 12401$ 右侧视 高分三号场景C a $1 \times 1$ DEC 28.667541 港口 $13435 \times 13141$ 右侧视 b $1 \times 1$ ASC 37.788424 港口 $13728 \times 12705$ 右侧视 承德机载图像 a $0.15 \times 0.15$ 无 40 阵地 $6430 \times 6279$ 右侧视 b $0.15 \times 0.15$ 无 40 阵地 $6430 \times 6279$ 左侧视 表 2 训练数据集具体信息
Table 2. Training data set specific information
SAR载荷 数据量(对) 产品等级 分辨率(m) 波段 GF-3-Spotlight 740 L2 1 C ALOS-PALSAR 24 L2.2 12.5 L Sentinel-1 IW 16 L1-GRD 10 C Umbra 20 GEC 0.25 X 表 3 不同方法的量化指标结果
Table 3. Different methods of quantification quantitative index results
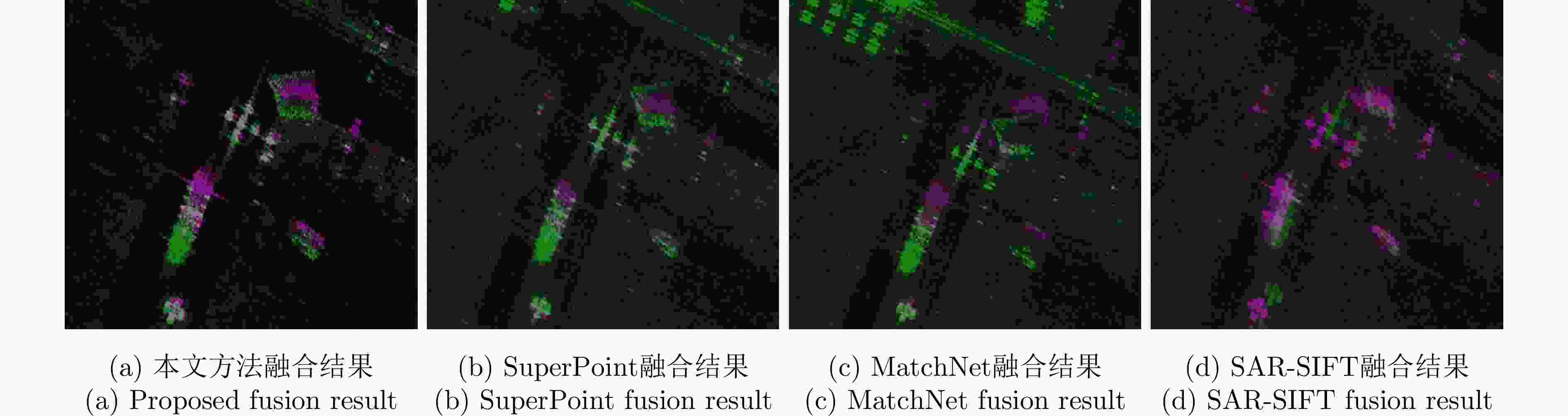
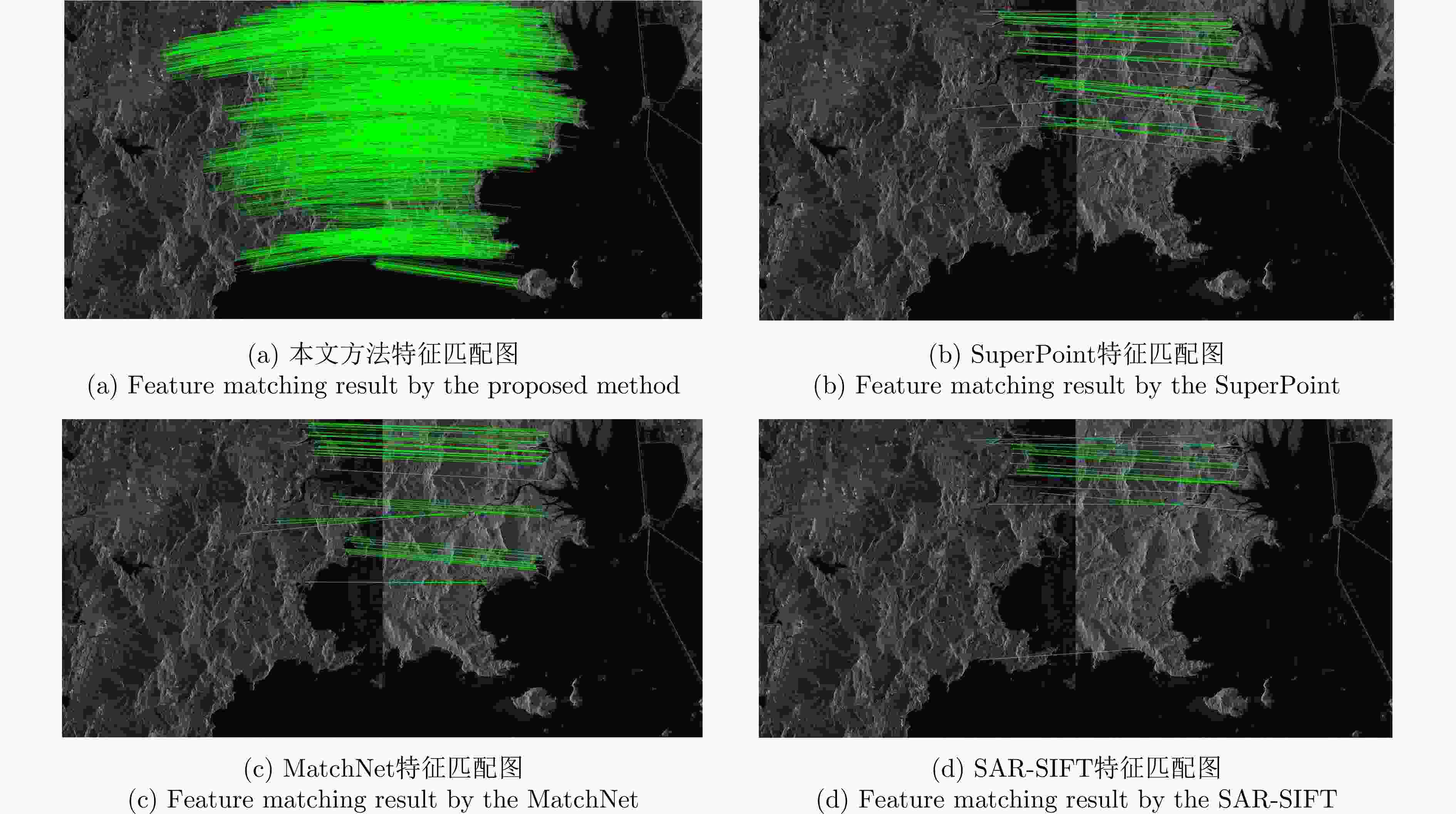
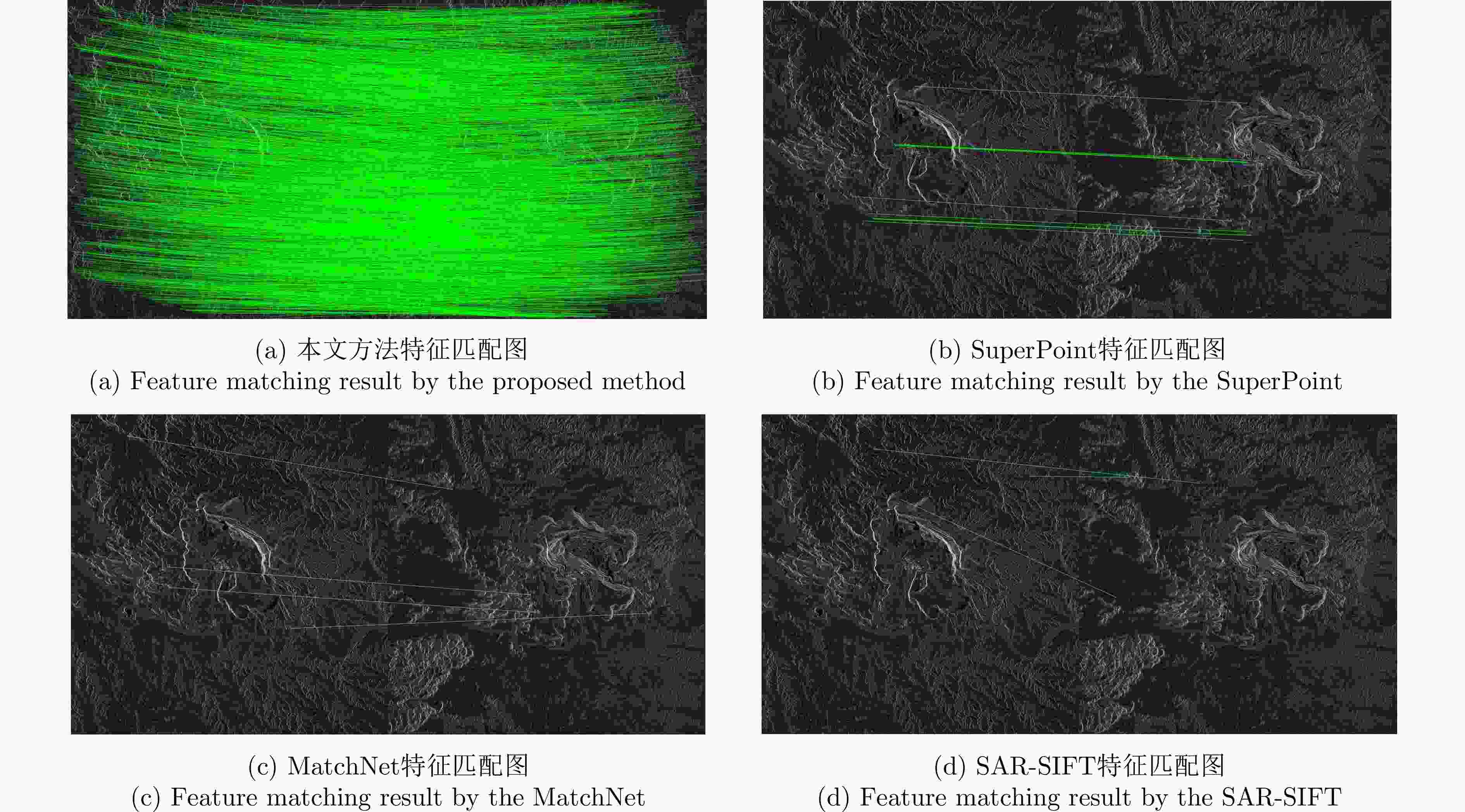
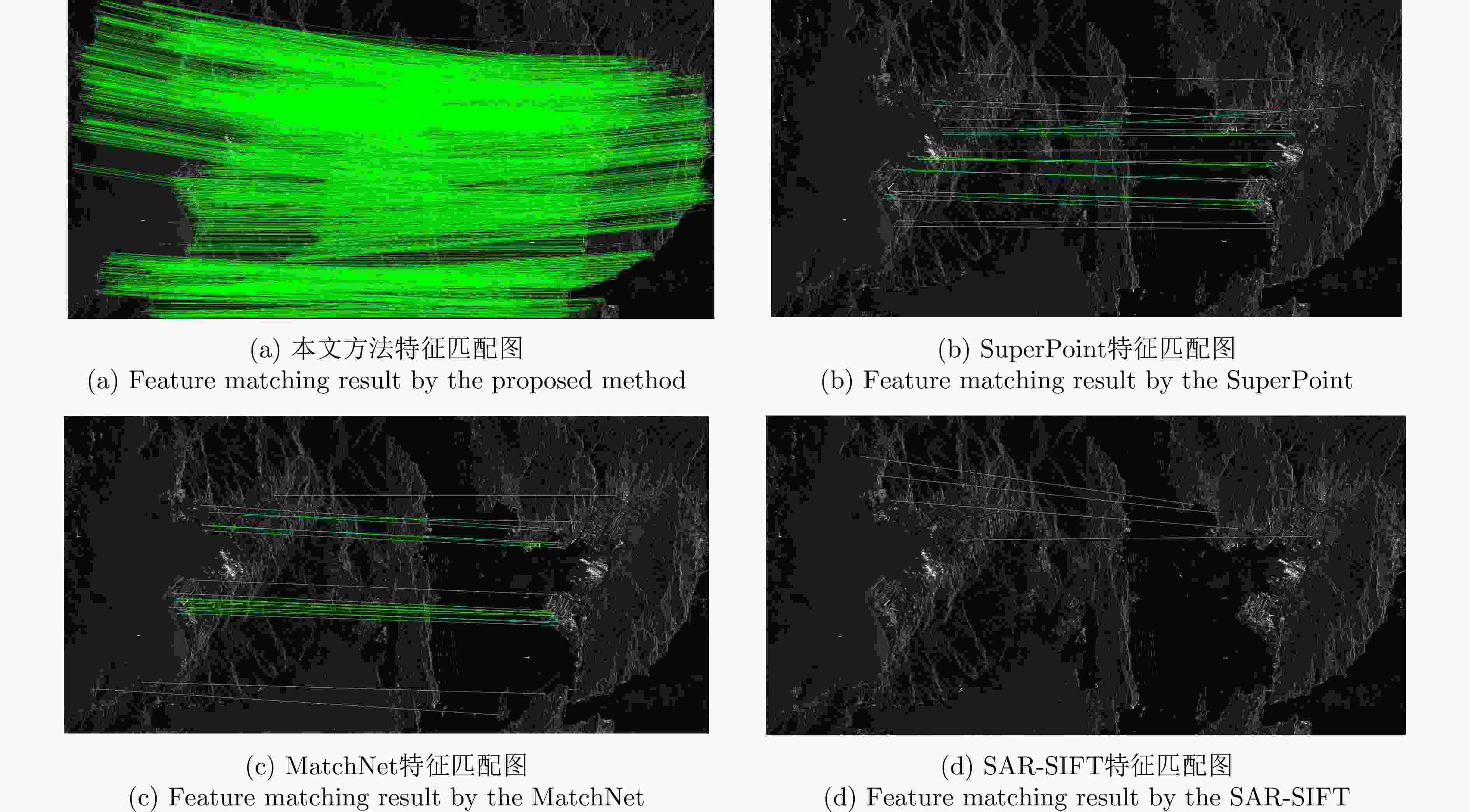
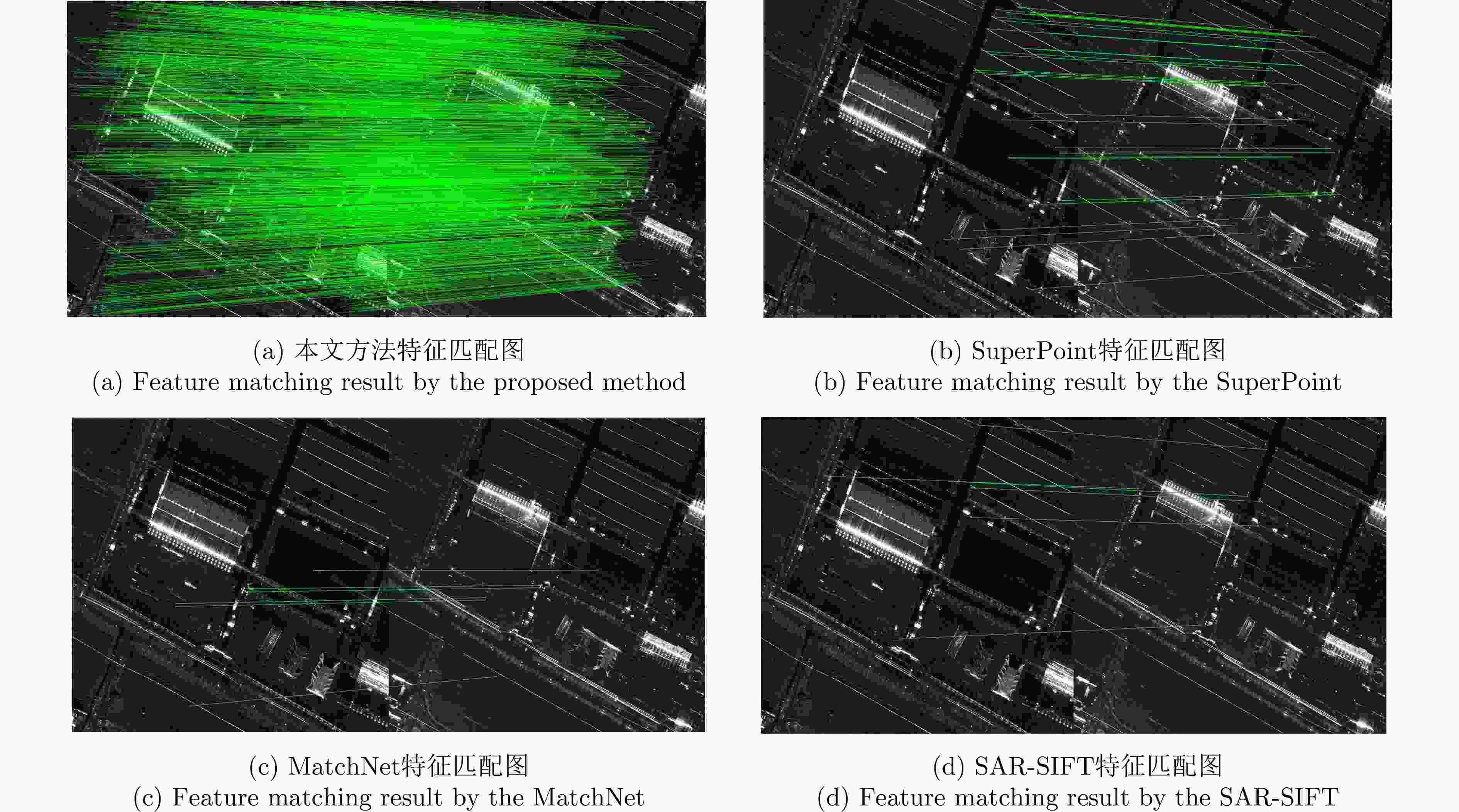
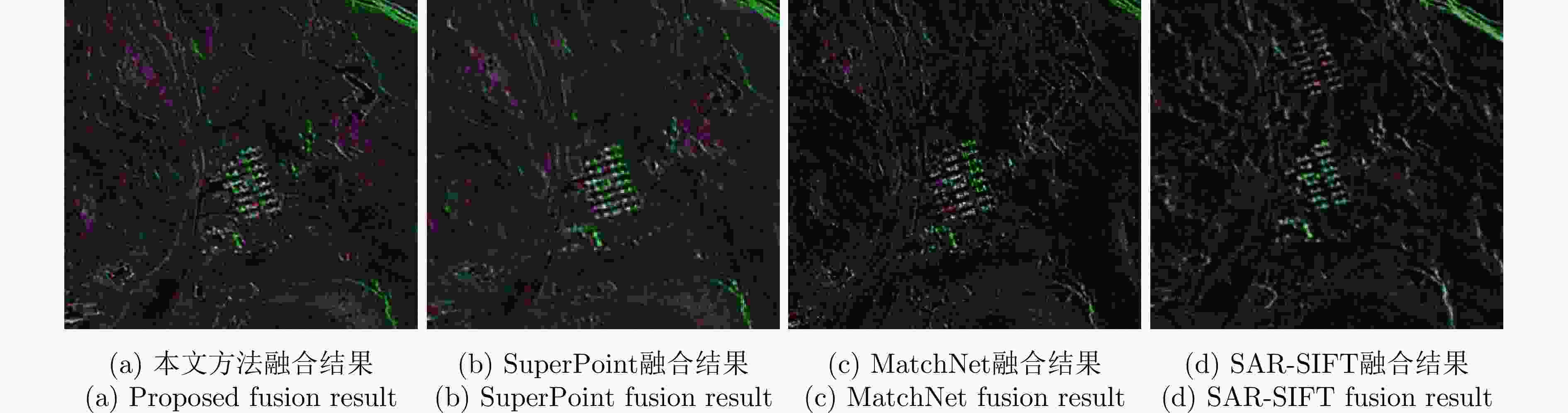
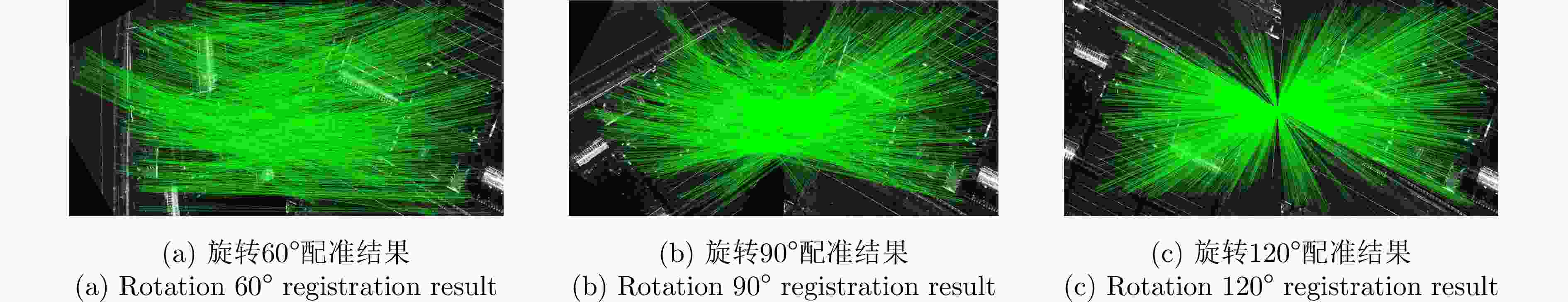
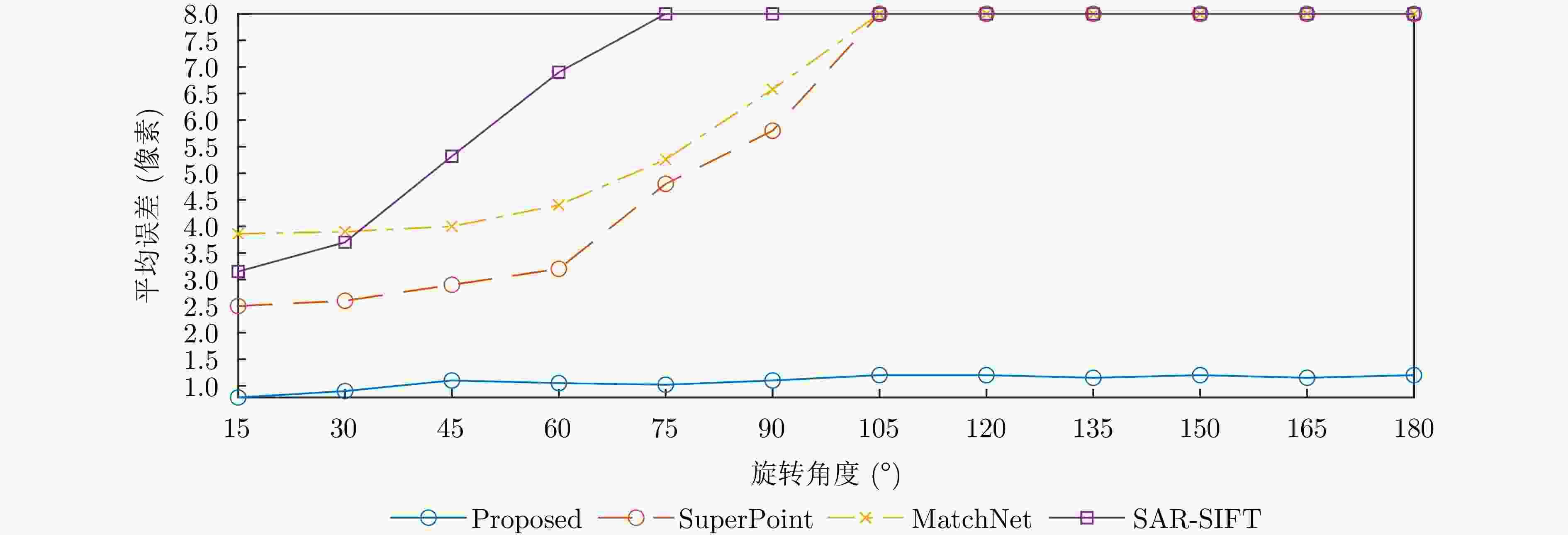
实验图像对 本文方法 SuperPoint MatchNet SAR-SIFT ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) 高分三号场景A 0.806 230 7.7 1.462 55 15.3 1.591 49 32 1.458 36 27.1 高分三号场景B 1.175 349 8.1 – 11 17.4 – 4 29.4 – 4 11.7 高分三号场景C 0.928 561 6.8 2.163 93 16.4 3.846 51 28.1 – 5 24.4 承德机载图像 0.962 206 8.5 4.030 42 15.8 6.503 7 32.5 – 3 19.4 表 4 不同方法的量化指标结果
Table 4. Different methods of quantification quantitative index results
高精度
图像对本文方法 SuperPoint MatchNet SAR-SIFT 本文方法
(密集描述符)ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) ME (像素) NCM Time (s) A, B 0.719 481 6.4 1.349 168 13.7 1.472 83 29.4 2.261 56 25.9 0.832 292 24.7 A, C 0.652 436 6.8 1.156 112 16.2 1.456 72 30.7 1.983 58 28.7 0.909 181 23.3 -
[1] 黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165.HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. [2] 徐真, 王宇, 李宁, 等. 一种基于CNN的SAR图像变化检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. doi: 10.12000/JR17075.XU Zhen, WANG Yu, LI Ning, et al. A novel approach to change detection in SAR images with CNN classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. doi: 10.12000/JR17075. [3] 王志豪, 李刚, 蒋骁. 基于光学和SAR遥感图像融合的洪灾区域检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR19095.WANG Zhihao, LI Gang, and JIANG Xiao. Flooded area detection method based on fusion of optical and SAR remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR19095. [4] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109.HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109. [5] 丁赤飚, 刘佳音, 雷斌, 等. 高分三号SAR卫星系统级几何定位精度初探[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024.DING Chibiao, LIU Jiayin, LEI Bin, et al. Preliminary exploration of systematic geolocation accuracy of GF-3 SAR satellite system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024. [6] XIANG Yuming, PENG Lingxiao, WANG Feng, et al. Fast registration of multiview slant-range SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19(3): 4007505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3045099. [7] WEI S and LAI Shanghong. Fast template matching based on normalized cross correlation with adaptive multilevel winner update[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(11): 2227–2235. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.2004615. [8] WANG Fei and VEMURI B C. Non-rigid multi-modal image registration using cross-cumulative residual entropy[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 74(2): 201–215. doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-0011-2. [9] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552. [10] 项德良, 徐益豪, 程建达, 等. 一种基于特征交汇关键点检测和Sim-CSPNet的SAR图像配准算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1081–1097. doi: 10.12000/JR22110.XIANG Deliang, XU Yihao, CHENG Jianda, et al. An algorithm based on a feature interaction-based keypoint detector and sim-CSPNet for SAR image registration[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1081–1097. doi: 10.12000/JR22110. [11] LIAO Furong, CHEN Yan, CHEN Yunping, et al. SAR image registration based on optimized ransac algorithm with mixed feature extraction[C]. 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 1153–1156. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323180. [12] DENG Yang and DENG Yunkai. Two-step matching approach to obtain more control points for SIFT-like very-high-resolution SAR image registration[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(7): 3739. doi: 10.3390/s23073739. [13] XIANG Deliang, XIE Yuzhen, CHENG Jianda, et al. Optical and SAR image registration based on feature decoupling network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235913. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3211858. [14] XIANG Yuming, JIAO Niangang, LIU Rui, et al. A geometry-aware registration algorithm for multiview high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5234818. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3205382. [15] GUO Qiangliang, XIAO Jin, HU Xiaoguang, et al. Local convolutional features and metric learning for SAR image registration[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22(2): 3103–3114. doi: 10.1007/s10586-018-1946-0. [16] FAN Jianwei, WU Yan, WANG Fan, et al. SAR image registration using phase congruency and nonlinear diffusion-based SIFT[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 562–566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351396. [17] FAN Yibo, WANG Feng, and WANG Haipeng. A transformer-based coarse-to-fine wide-swath SAR image registration method under weak texture conditions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1175. doi: 10.3390/rs14051175. [18] ELWAN M, AMEIN A S, MOUSA A, et al. SAR image matching based on local feature detection and description using convolutional neural network[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2022, 2022(1): 5669069. doi: 10.1155/2022/5669069. [19] MEN Peng, GUO Hao, AN Jubai, et al. An improved L2Net for repetitive texture image registration with intensity difference heterogeneous SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(11): 2527. doi: 10.3390/rs14112527. [20] ZHANG Yifan, LI Zhiwei, WANG Wen, et al. A robust registration method for multi-view SAR images based on best buddy similarity[C]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Changsha, China, 2024: 881–886. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLVIII-1-2024-881-2024. [21] LI Zeyi, ZHANG Haitao, and HUANG Yihang. A rotation-invariant optical and SAR image registration algorithm based on deep and Gaussian features[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(13): 2628. doi: 10.3390/rs13132628. [22] YU Wei, SUN Xiaohuai, YANG Kuiyuan, et al. Hierarchical semantic image matching using CNN feature pyramid[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 169: 40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2018.01.001. [23] SAUVALLE B and DE LA FORTELLE A. Unsupervised multi-object segmentation using attention and soft-argmax[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 3267–3276. doi: 10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00328. [24] NUNES C F G and PÁDUA F L C. A local feature descriptor based on Log-Gabor filters for keypoint matching in multispectral images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(10): 1850–1854. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2738632. [25] HOSANG J, BENENSON R, and SCHIELE B. Learning non-maximum suppression[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4507–4515. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.685. [26] CHUNG S W, CHUNG J S, and KANG H G. Perfect match: Self-supervised embeddings for cross-modal retrieval[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14(3): 568–576. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2020.2987720. [27] CHEN Feng, WU Fei, XU Jing, et al. Adaptive deformable convolutional network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 453: 853–864. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.128. [28] KILIÇARSLAN S and CELIK M. RSigELU: A nonlinear activation function for deep neural networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 174: 114805. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114805. [29] XU Jin, LI Zishan, DU Bowen, et al. Reluplex made more practical: Leaky ReLU[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Rennes, France, 2020: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ISCC50000.2020.9219587. [30] LI Jiayuan, HU Qingwu, and AI Mingyao. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3296–3310. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2959244. [31] GERMAIN H, BOURMAUD G, and LEPETIT V. S2DNet: Learning image features for accurate sparse-to-dense matching[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 626–643. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58580-8_37. [32] JAMIN A and HUMEAU-HEURTIER A. (Multiscale) cross-entropy methods: A review[J]. Entropy, 2019, 22(1): 45. doi: 10.3390/e22010045. [33] YAMADA M, SIGAL L, RAPTIS M, et al. Cross-domain matching with squared-loss mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1764–1776. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388235. [34] ZHU Li and ZHU Chunqiang. Application of Hausdorff distance in image matching[C]. 2014 IEEE Workshop on Electronics, Computer and Applications, Ottawa, Canada, 2014: 97–100. doi: 10.1109/IWECA.2014.6845566. [35] HE Yueping, WANG Xueqian, ZHANG Yiming, et al. A novel loss function for optical and SAR image matching: Balanced positive and negative samples[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4028805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3225965. [36] JIA Weikuan, SUN Meili, LIAN Jian, et al. Feature dimensionality reduction: A review[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2022, 8(3): 2663–2693. doi: 10.1007/s40747-021-00637-x. [37] DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, and RABINOVICH A. SuperPoint: Self-supervised interest point detection and description[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 224–236. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2018.00060. [38] HAN Xufeng, LEUNG T, JIA Yangqing, et al. MatchNet: Unifying feature and metric learning for patch-based matching[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3279–3286. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298948. [39] HASHIMOTO M, ENOMOTO M, and FUKUSHIMA Y. Coseismic deformation from the 2008 Wenchuan, China, earthquake derived from ALOS/PALSAR images[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 491(1/4): 59–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.034. [40] GEUDTNER D, TORRES R, SNOEIJ P, et al. Sentinel-1 system capabilities and applications[C]. 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1457–1460. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946711. [41] 李志远, 郭嘉逸, 张月婷, 等. 基于自适应动量估计优化器与空变最小熵准则的SAR图像船舶目标自聚焦算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 83–94. doi: 10.12000/JR21159.LI Zhiyuan, GUO Jiayi, ZHANG Yueting, et al. A novel autofocus algorithm of ship target in SAR image based on the adaptive momentum estimation optimizer and space-variant minimum entropy criteria[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 83–94. doi: 10.12000/JR21159. [42] 苏娟, 李彬, 王延钊. 一种基于封闭均匀区域的SAR图像配准方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141.SU Juan, LI Bin, and WANG Yanzhao. SAR image registration algorithm based on closed uniform regions[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: