Performance Analysis of SAR Active Deception Jamming Detection Based on Interferometric Phase
-
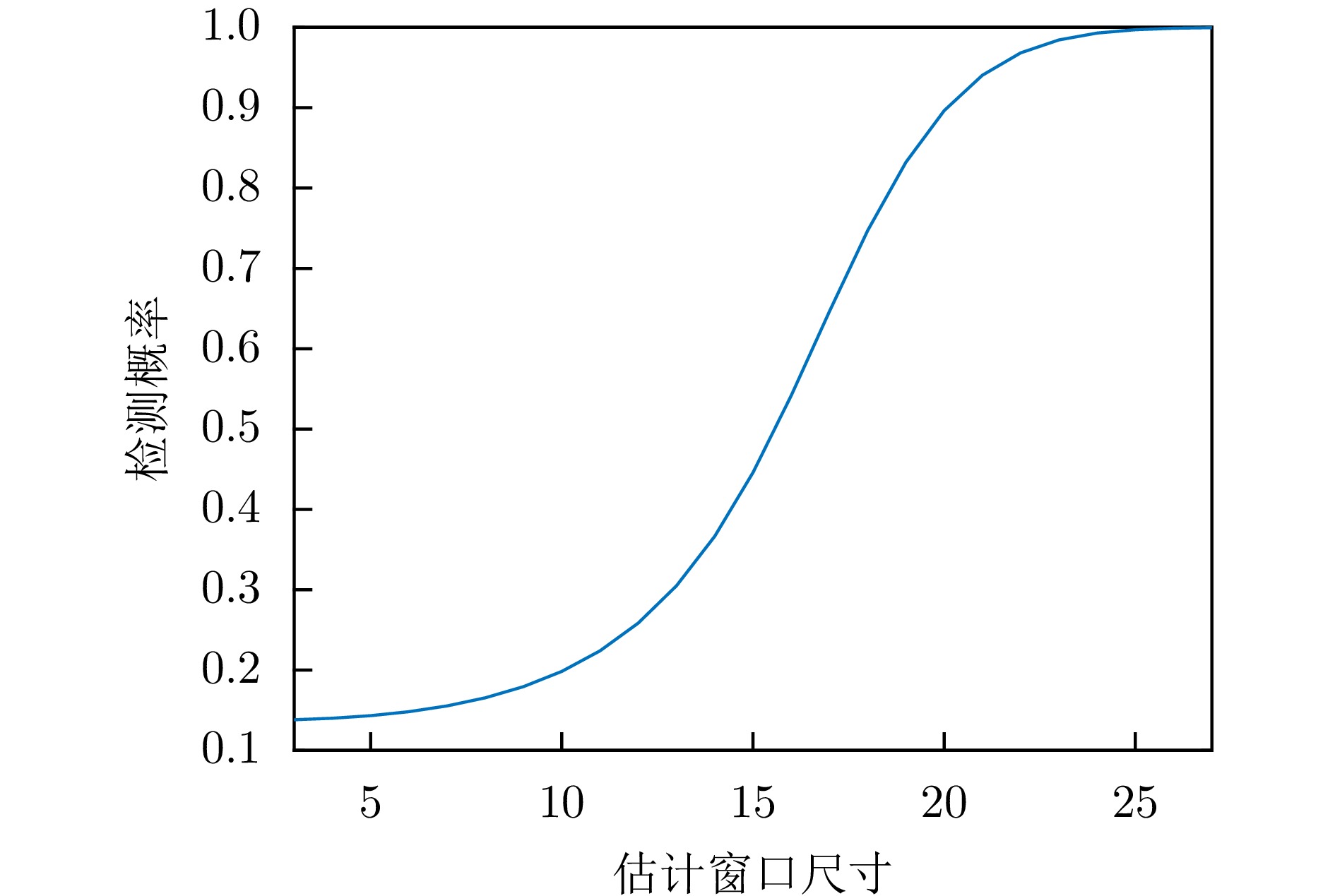
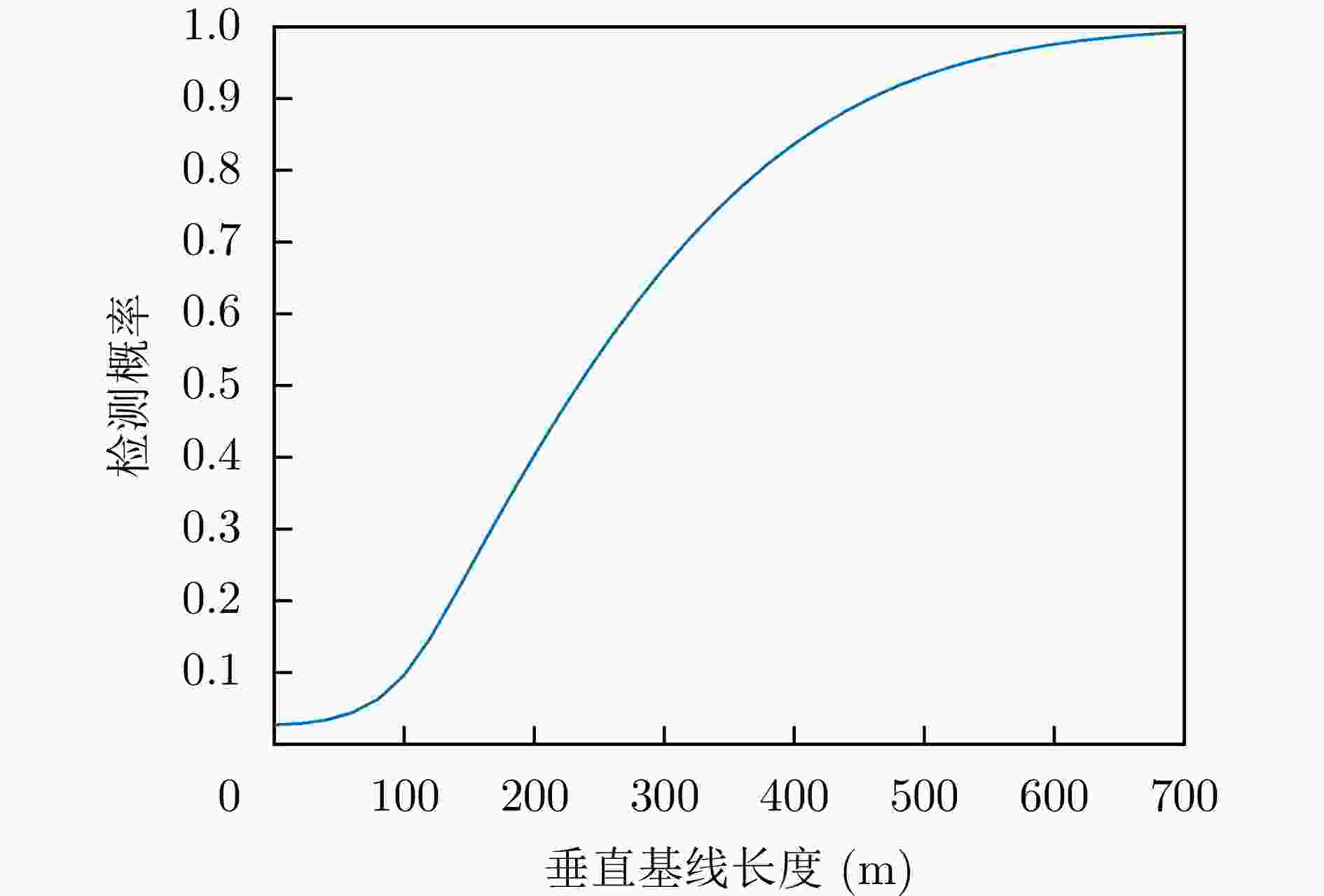
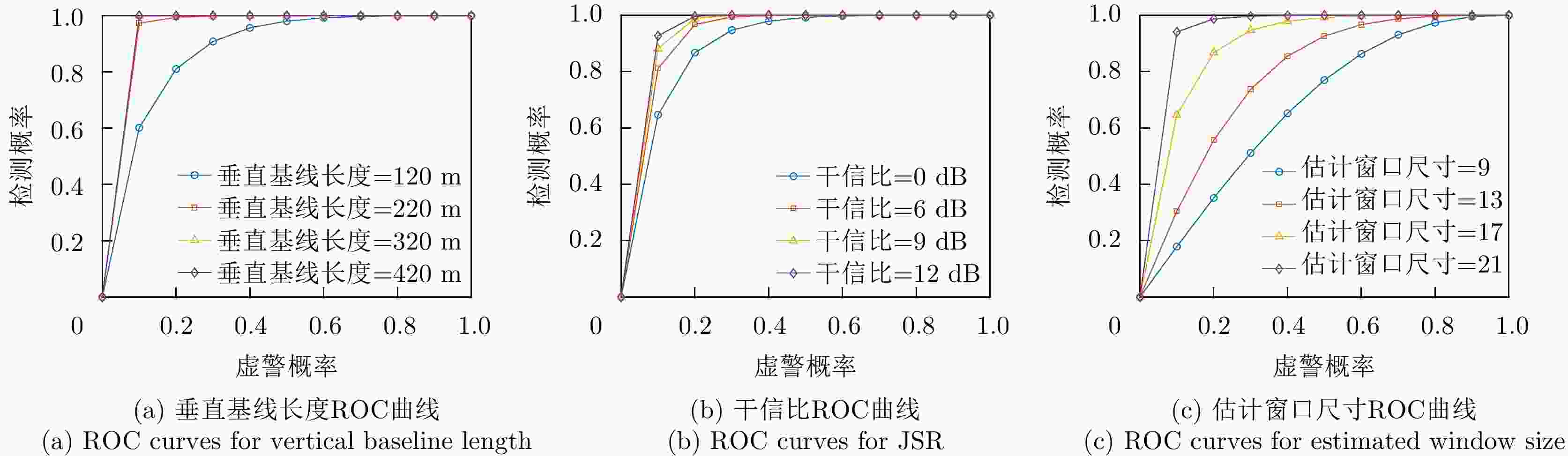
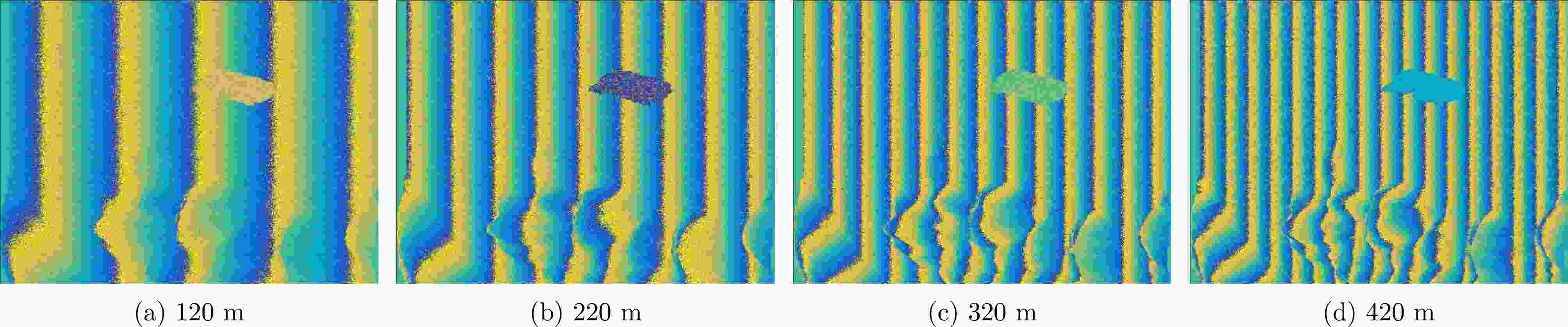
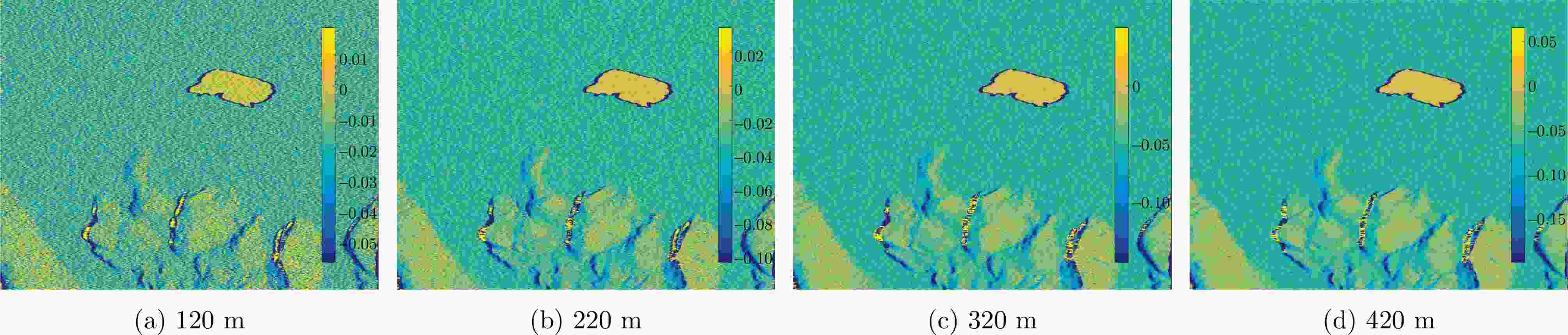
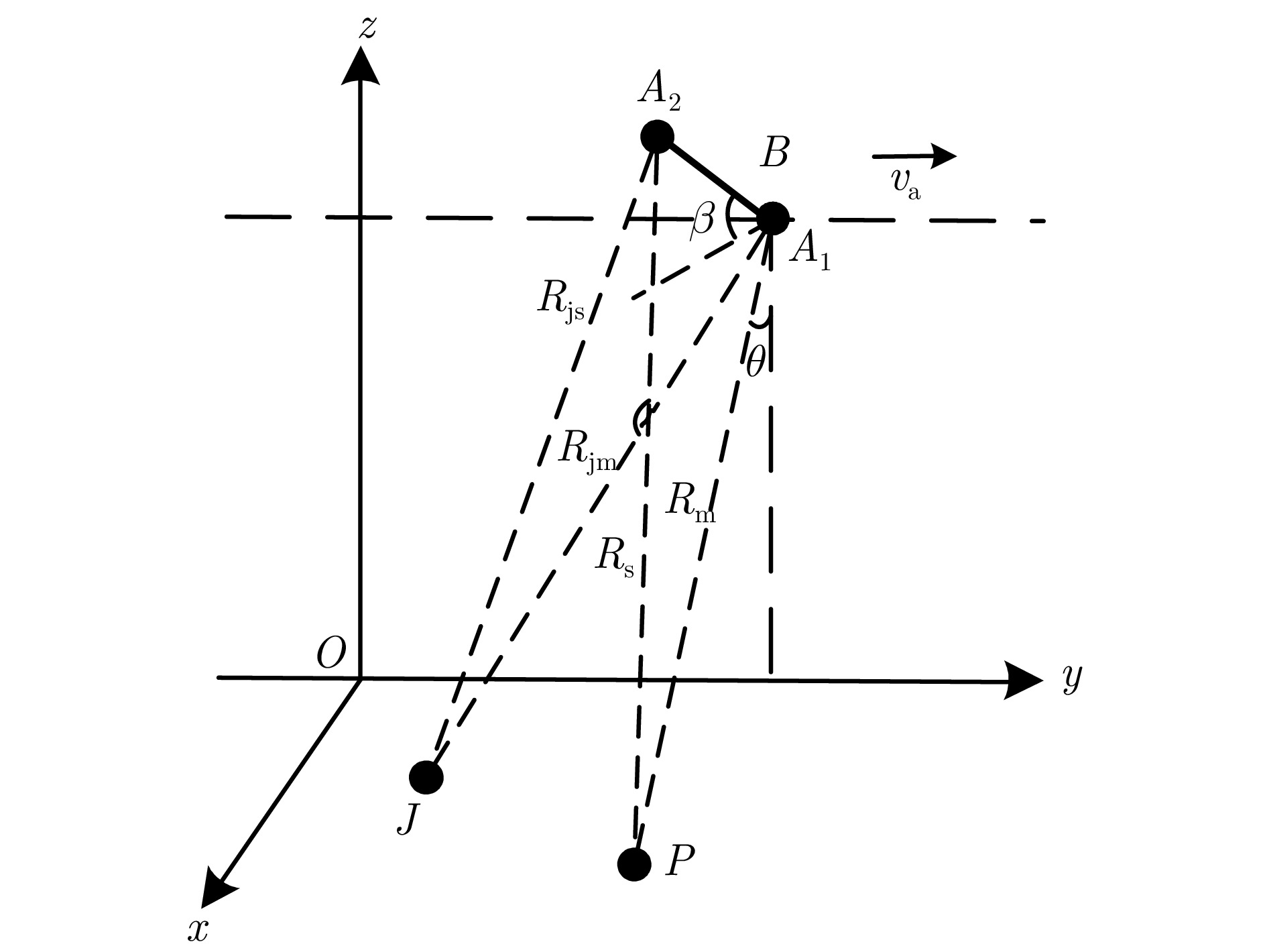
摘要: 对基于干涉相位的合成孔径雷达(SAR)有源欺骗干扰检测进行了性能分析。首先基于真实场景和虚假目标的斜距向局部条纹频率概率分布,推导了欺骗干扰检测概率的显式表达式。分别分析了垂直基线长度、干信比和局部条纹频率估计窗口尺寸3个因素对欺骗干扰检测概率(TPR)的影响。进而分析了在给定虚警概率(FPR)时,SAR系统能够达到检测概率要求时所需的垂直基线长度,为SAR系统的基线设计提供了理论依据。在现有低轨SAR参数条件下,要得到更大的干扰检测概率,所需垂直基线长度也越大,因此,在设计SAR系统的基线时,既要保证垂直基线足够大可满足检测概率的要求,还需要兼顾真实场景的相干系数,垂直基线不能太大,满足场景可进行干涉的条件。最后,对理论分析的结论进行了仿真验证。理论分析与实验结果表明:在虚警概率固定的情况下,一定范围内垂直基线长度越大/干信比越大/局部条纹频率估计窗口越大,则干扰检测概率越大。Abstract: The performance of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) active deception jamming detection based on the interferometric phase is analyzed. Based on the slant-range local fringe frequency probability distributions of a real scene and a false target, the influences of the vertical baseline length, jamming-to-signal ratio, and local fringe frequency estimation window size on the True Positive Rate (TPR) are analyzed. Furthermore, when the False Positive Rate (FPR) is known, the vertical baseline length required for the SAR system to meet the detection probability requirements is analyzed, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the baseline design of the SAR system. Finally, the result of theoretical analysis is verified by simulation. The theoretical analysis and experimental results show that, for a certain false alarm probability, as the vertical baseline length, jamming-to-signal ratio, or local fringe frequency estimation window value increases, the detection probability also increases.
-
表 1 固定参数表
Table 1. Fixed parameters table
参数 数值 中心斜距 1300 km下视角 50° 斜距向采样间隔 1.2 m 波长 0.0375 m真实场景信噪比 15 dB -
[1] 黄岩, 赵博, 陶明亮, 等. 合成孔径雷达抗干扰技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113.HUANG Yan, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. Review of synthetic aperture radar interference suppression[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113. [2] 韩朝赟, 岑熙, 崔嘉禾, 等. 纹理异常感知SAR自监督学习干扰抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168.HAN Zhaoyun, CEN Xi, CUI Jiahe, et al. Self-supervised learning method for SAR interference suppression based on abnormal texture perception[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 154–172. doi: 10.12000/JR22168. [3] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143.CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143. [4] CHEN Si, LIN Yang, YUAN Yue, et al. Airborne SAR suppression of blanket jamming based on second order blind identification and fractional order Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5212014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3294236. [5] LANG Wenhui, TANG Yaling, MEI Shengqun, et al. An anti-2D deceptive jamming method for multi-baseline interferometric SAR based on co-localization jammer[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 5388–5400. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3185254. [6] YANG Kaizhi, MA Fangfang, RAN Da, et al. Fast generation of deceptive jamming signal against spaceborne SAR based on spatial frequency domain interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4701015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3065312. [7] 曾铮, 张福博, 陈龙永, 等. 基于多输入多输出合成孔径雷达的二维混合基线抗欺骗干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 90–99. doi: 10.12000/JR18118.ZENG Zheng, ZHANG Fubao, CHEN Longyong, et al. A two-dimensional mixed baseline method based on MIMO-SAR for countering deceptive jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 90–99. doi: 10.12000/JR18118. [8] WANG Wenjing, WU Junjie, PEI Jifang, et al. An antideceptive jamming method for multistatic synthetic aperture radar based on collaborative localization and spatial suppression[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2757–2768. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997345. [9] LI Chen and ZHU Daiyin. The detection of deception jamming against SAR based on dual-aperture antenna cross-track interferometry[C]. 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICR.2006.343274. [10] JI Penghui and XING Shiqi. An anti-jamming method against SAR stationary deceptive targets based on DPCA processing[C]. 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Wuxi, China, 2019: 264–268. doi: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2019.8868613. [11] 姜予名, 李景文, 孙兵. 单站直达波欺骗干扰检测与抑制的DPCA方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(6): 1524–1532. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.09.JIANG Yuming, LI Jingwen, and SUN Bing. DPCA method for detection and suppression of monostatic direct-wave deceptive jamming[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(6): 1524–1532. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.09. [12] YANG Guang, LI Shaobin, and CAO Xinghui. SAR counter deception jamming based on radiometric calibration[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2009, Guilin, China, 2009: 60. doi: 10.1049/cp.2009.0114. [13] WANG Wenjing, WU Junjie, PEI Jifang, et al. Deception-jamming localization and suppression via configuration optimization for multistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5232016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3189409. [14] FENG Qingqing, XU Huaping, WU Zhefeng, et al. Deceptive jamming detection for SAR based on cross-track interferometry[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(7): 2265. doi: 10.3390/s18072265. [15] ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, JOUGHIN I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2002, 88(3): 333–382. doi: 10.1109/5.838084. [16] TREES H and BELL K L. Detection estimation and modulation theory, 2nd edition, part I[J]. A Papoulis Probability Random Variables & Stochastic Processes, 2001, 8(10): 293–303. doi: 10.1002/0471221104. [17] SPAGNOLINI U. 2-D phase unwrapping and instantaneous frequency estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(3): 579–589. doi: 10.1109/36.387574. [18] RIFE D and BOORSTYN R. Single tone parameter estimation from discrete-time observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1974, 20(5): 591–598. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1974.1055282. [19] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446. [20] GUARNIERI A M and TEBALDINI S. ML-based fringe-frequency estimation for InSAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(1): 136–140. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2028661. [21] KRIEGER G, FIEDLER H, ZINK M, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[C]. 2007 IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Edinburgh, UK, 2007: 1–5. [22] XU Huaping, WU Zhefeng, LIU Wei, et al. Analysis of the effect of interference on InSAR[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(10): 5659–5668. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2445931. [23] 徐华平, 单乐. 一种重复轨道星载自然场景SAR复图像数据快速仿真方法[P]. 中国, 105677942A, 2016.XU Huaping and SHAN Le. Rapid simulation method of repeat-pass spaceborne natural scene SAR complex image data[P]. CN, 105677942A, 2016. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: