A Review of UWB Radar Detection of Respiration and Heartbeat Signals in Different Scenarios
-
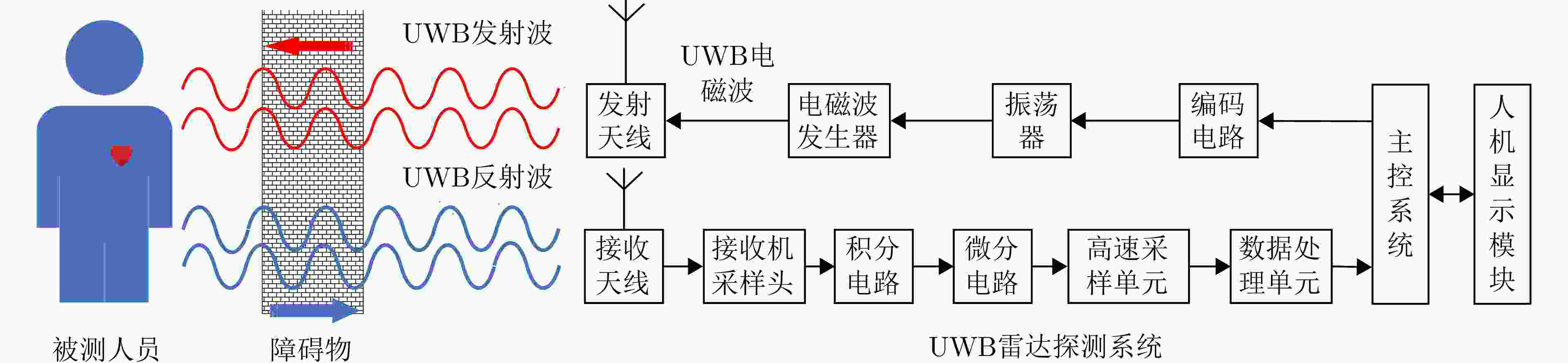
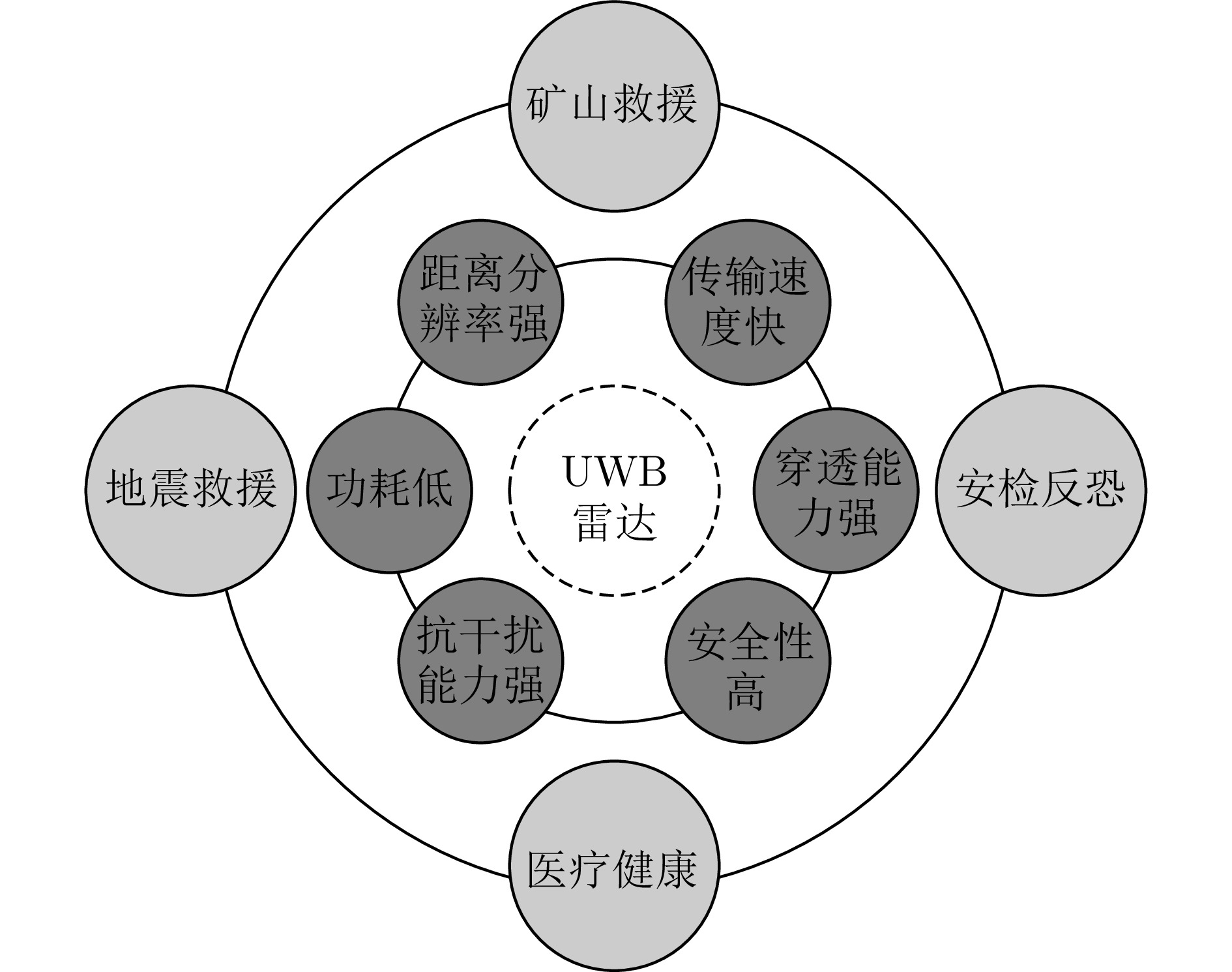
摘要: 超宽带(UWB)雷达由于具有结构简单、发射功率低、穿透能力强、分辨能力高、传输速度快等诸多优势,逐渐成为多探测场景广泛应用的生命信息探测技术及装备。要完成生命信息的有效探测,关键是利用雷达回波信息处理技术从UWB雷达回波中提取被测人员的呼吸心跳信号,这对不同场景实现生命信息的判定、位置信息的获取、疾病的监测和预防以及保障人员安全具有至关重要的意义。为此,该文介绍了UWB雷达及分类、电磁散射机理和探测原理;分析了呼吸心跳信号的雷达回波模型构建现状;从时域、频域、时频域分析方法等角度梳理了现有呼吸心跳信号的提取方法;并从矿山救援、地震救援、医疗健康、穿墙探测等场景归纳了呼吸心跳信号提取的研究进展。总结了当前研究中存在的主要问题,展望了未来研究工作应重点关注的领域。
-
关键词:
- 超宽带(UWB)雷达回波 /
- 生命信息探测 /
- 呼吸心跳信号 /
- 雷达回波模型 /
- 信号提取
Abstract: Due to their many advantages, such as simple structure, low transmission power, strong penetration capability, high resolution, and high transmission speed, UWB (Ultra-WideBand) radars have been widely used for detecting life information in various scenarios. To effectively detect life information, the key is to use radar echo information-processing technology to extract the breathing and heartbeat signals of the involved person from UWB radar echoes. This technology is crucial for determining life information in different scenarios, such as obtaining location information, monitoring and preventing diseases, and ensuring personnel safety. Therefore, this paper introduces a UWB radar and its classification, electromagnetic scattering mechanisms, and detection principles. It also analyzes the current state of radar echo model construction for breathing and heartbeat signals. The paper then reviews existing methods for extracting breathing and heartbeat signals, including time domain, frequency domain, and time-frequency domain analysis methods. Finally, it summarizes research progress in breathing and heartbeat signal extraction in various scenarios, such as mine rescue, earthquake rescue, medical health, and through-wall detection, as well as the main problems in current research and focus areas for future research. -
表 1 UWB雷达分类对比
Table 1. Comparison of UWB radars classifications
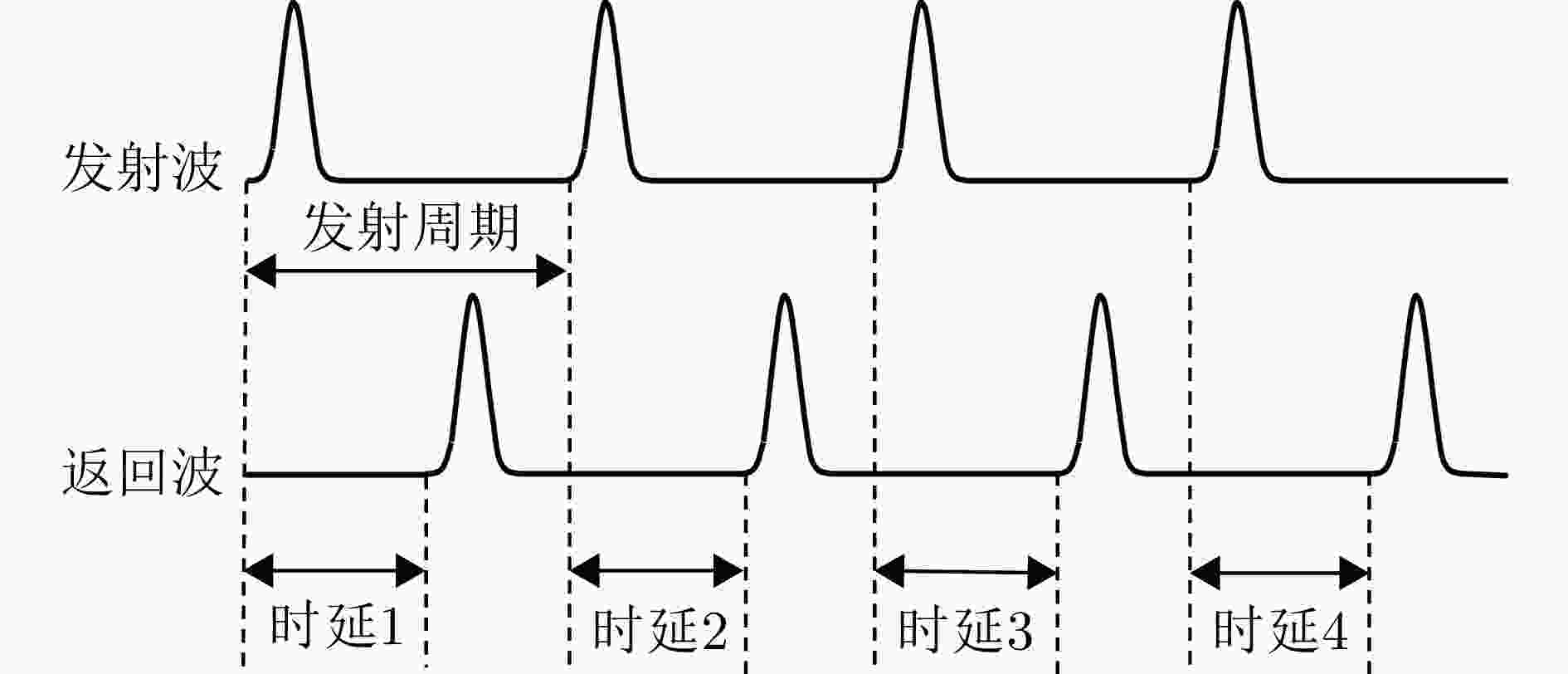
特性 连续波 脉冲波 调频连续波 步进频率连续波 高斯脉冲波 探测原理 多普勒效应、干涉相位 回波时延、干涉相位、多普勒效应 表达方程 $S(t) = A{\text{cos}}({\text{2\pi }}{f_0}t + {\pi }K{t^2})$
其中,A为振幅,$ {f_0} $为初始频率,K为调频斜率$S(t) = A{\text{cos}}({{2\pi }}({f_0}t + n\Delta f)t)$
其中,A为振幅,$ {f_0} $为初始频率,$\Delta f$为频率步进间隔,n为当前步进的索引$S(t) = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_n {Ap} (t - nT)$
其中,A为振幅,$ p(t) $为脉冲形状函数,
T为脉冲间隔波形图像 


优点 高距离分辨率、高速度分辨率 高距离分辨率、高图像分辨率 高时间、频率分辨率,脉冲持续时间极短(纳秒级),利于探测微弱信号 缺点 存在非线性问题、不适用于远距离探测 制造难度大、信号处理复杂、不适用于远距离探测 距离分辨率受到脉冲宽度限制、需要高采样率、模数转换器要求高 应用领域 医疗健康(跌倒检测)、汽车雷达、无人机避障雷达 医疗健康、交通监控 矿山救援与地震救援等需穿透障碍物的复杂灾害环境 表 2 干涉相位在连续波、脉冲波UWB雷达系统的优缺点对比
Table 2. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of interferometric phase in continuous wave and pulsed wave UWB radar systems
雷达系统 优点 缺点 连续波UWB雷达 实时动态监测能力强 时域分辨率低、信号处理复杂 脉冲波UWB雷达 时域分辨率高、多径分析能力强 脉冲信号的不连续性造成相位跳变,增加信号处理难度 表 3 呼吸心跳运动参数
Table 3. Respiratory heartbeat exercise parameters
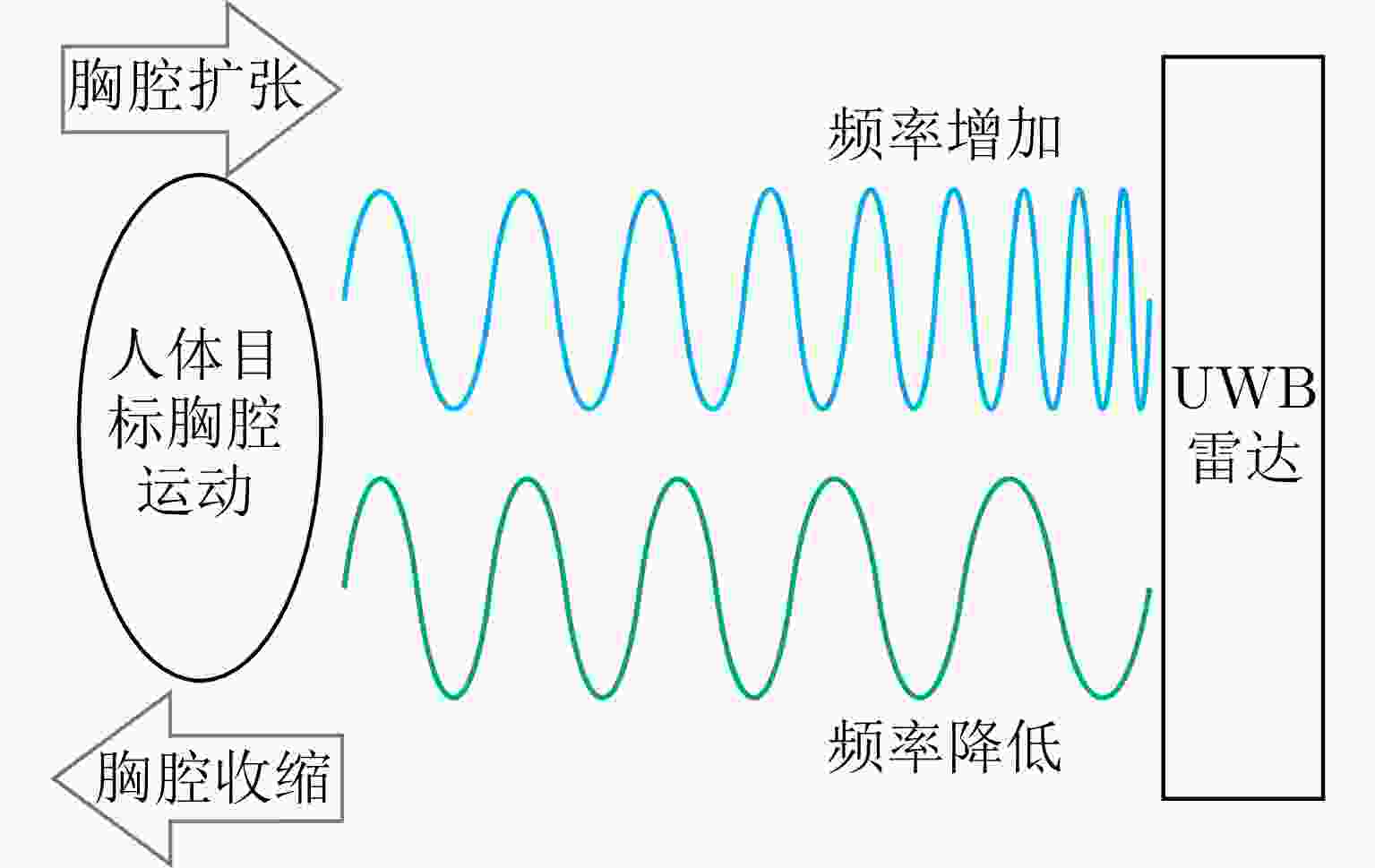
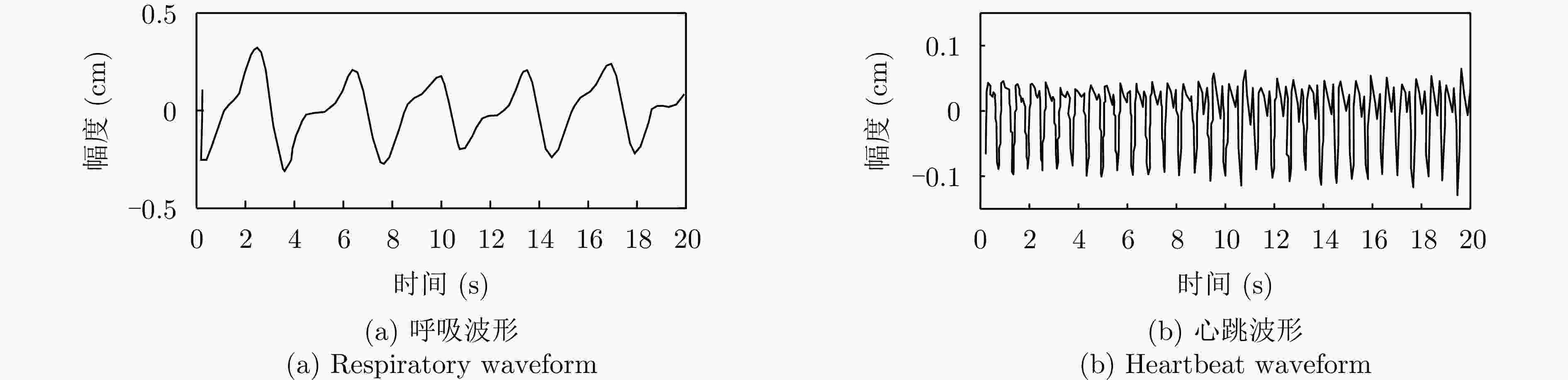
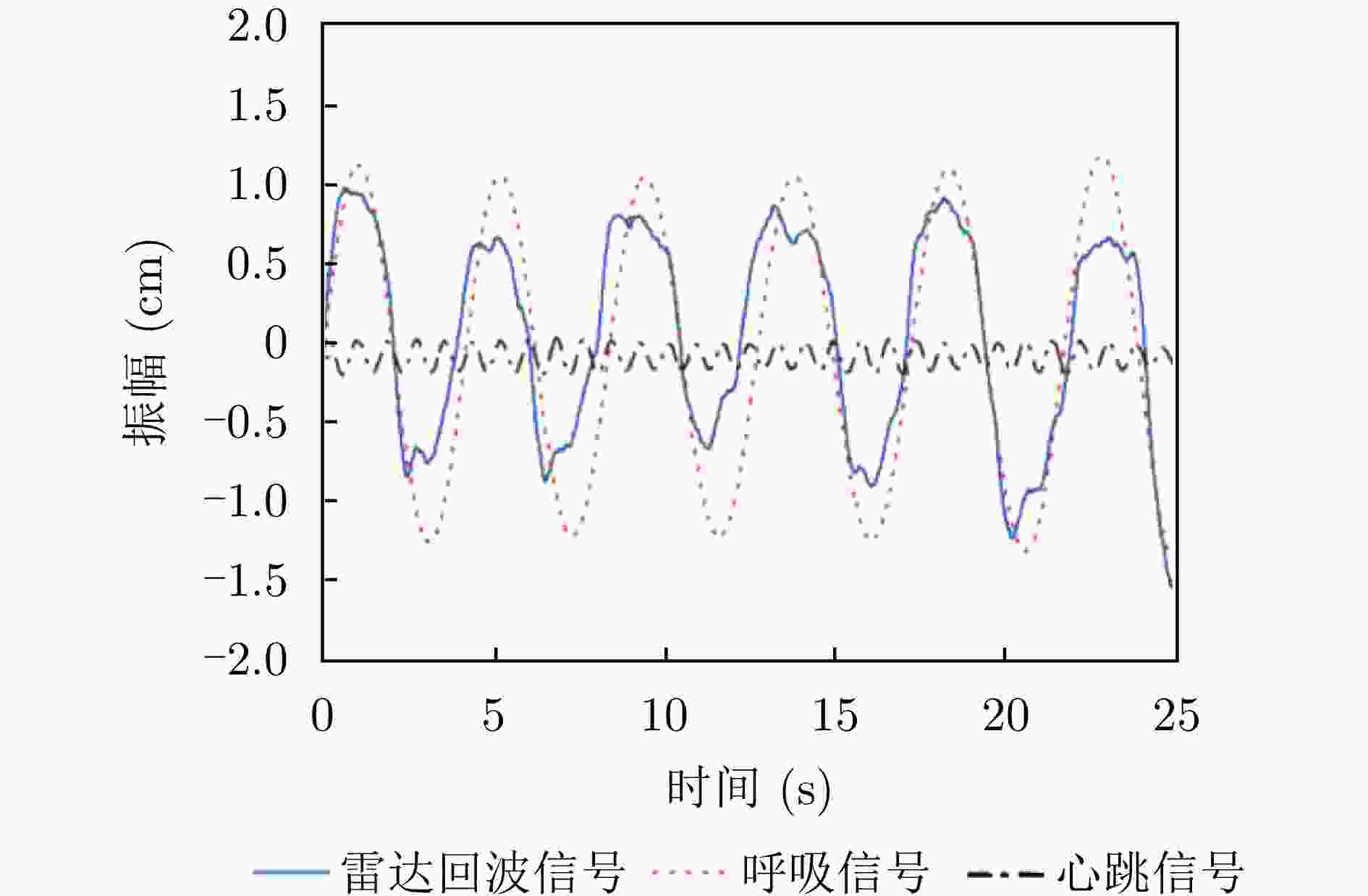
生命体征 频率(Hz) 胸腔振幅(mm) 胸腔振动面积(cm3) 呼吸 0.1~0.5 4~12 50 心跳 0.8~2.0 0.2~0.5 10 表 4 时域、频域和时频域分析方法对比
Table 4. Comparison of time-domain, frequency-domain and time-frequency-domain analysis methods
方法 优点 缺点 适用场景 典型方法 时域分析
方法易实现、适应性强、计算量小
且效率快、便于直接观察低信噪比环境处理能力不强、
易丢失信息、抗干扰性差用于睡眠、临床、健康检测
的呼吸心跳信号提取时域相关法、脉冲压缩法、
时域差分法频域分析
方法频谱精度高、计算量小,对幅度
变化较大的信号处理能力强存在边缘效应与信号失真、
不能反映信号的时变特性用于滤波去噪,在医疗健康
场景中提取呼吸心跳信号傅里叶变换、快速傅里叶变换、
频谱减法时频分析
方法利于非线性、不平稳及瞬时信号
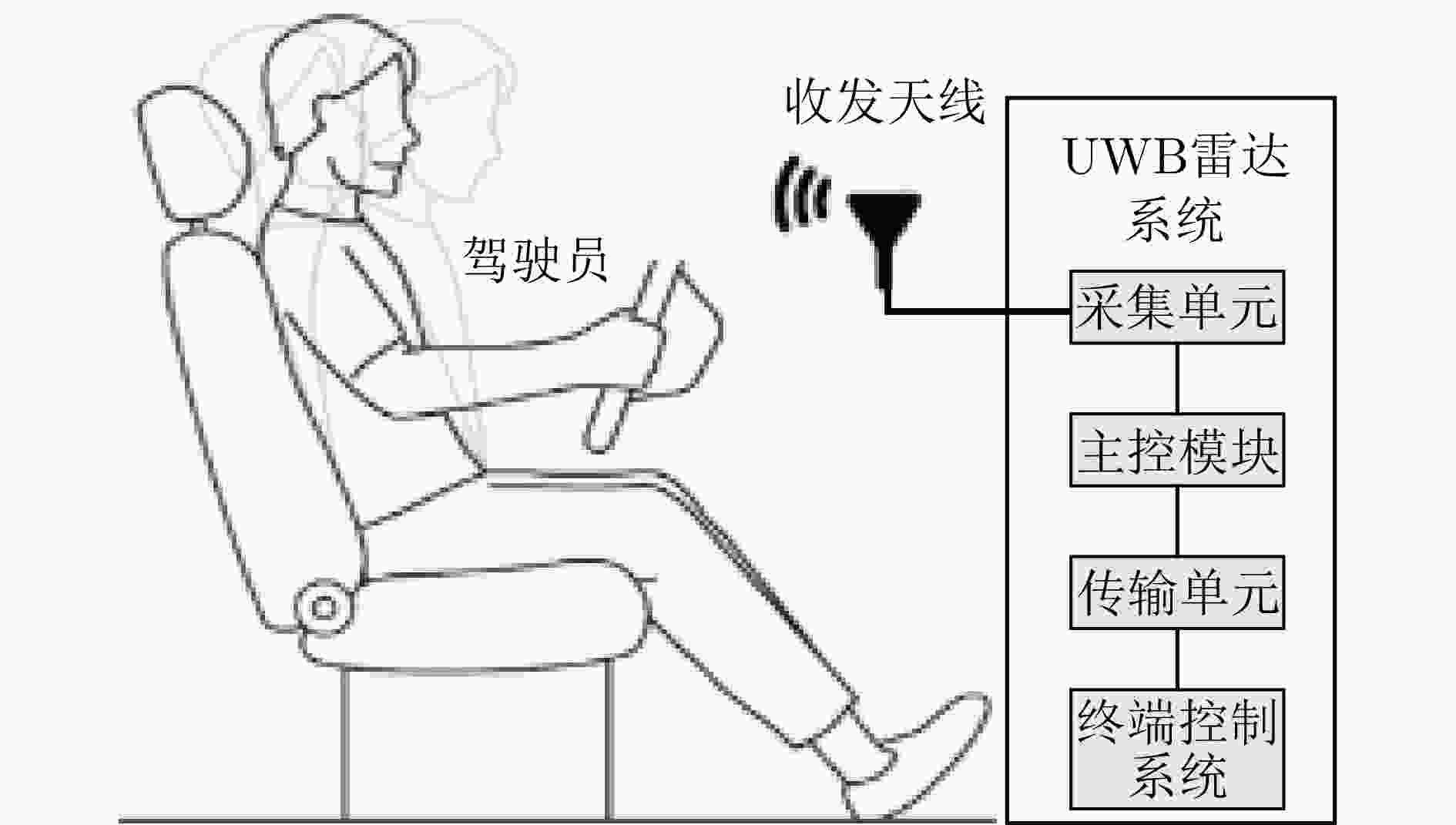
的处理、多分辨率强、准确性高运算复杂、性能依赖参数
选择、存在边缘效应用于灾害救援、医疗健康检测
等场景的多种信号处理任务短时傅里叶变换、小波变换、希尔
伯特-黄变换、模态分解系列算法表 5 EMD算法重构信号的频谱峰值
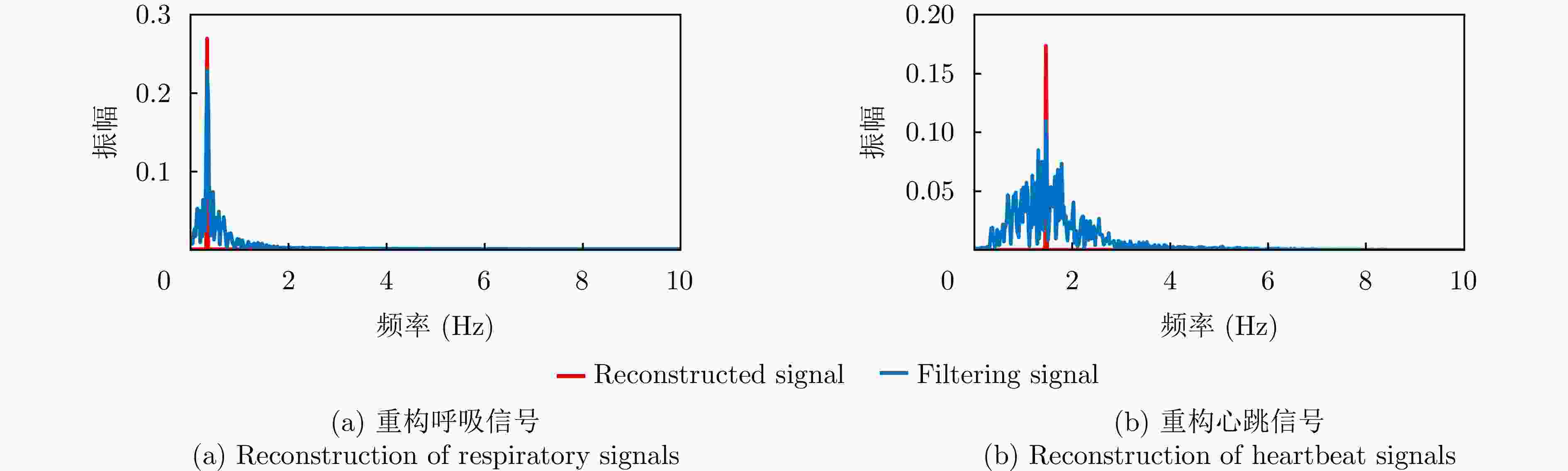
Table 5. Spectral peaks of signal reconstructed by EMD algorithm
重构信号 频谱峰值 重构呼吸信号 0.1~0.5 Hz 重构心跳信号 0.8~2.0 Hz 噪声干扰 其他频率 表 6 部分模态分解算法的优缺点对比
Table 6. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of some modal decomposition algorithms
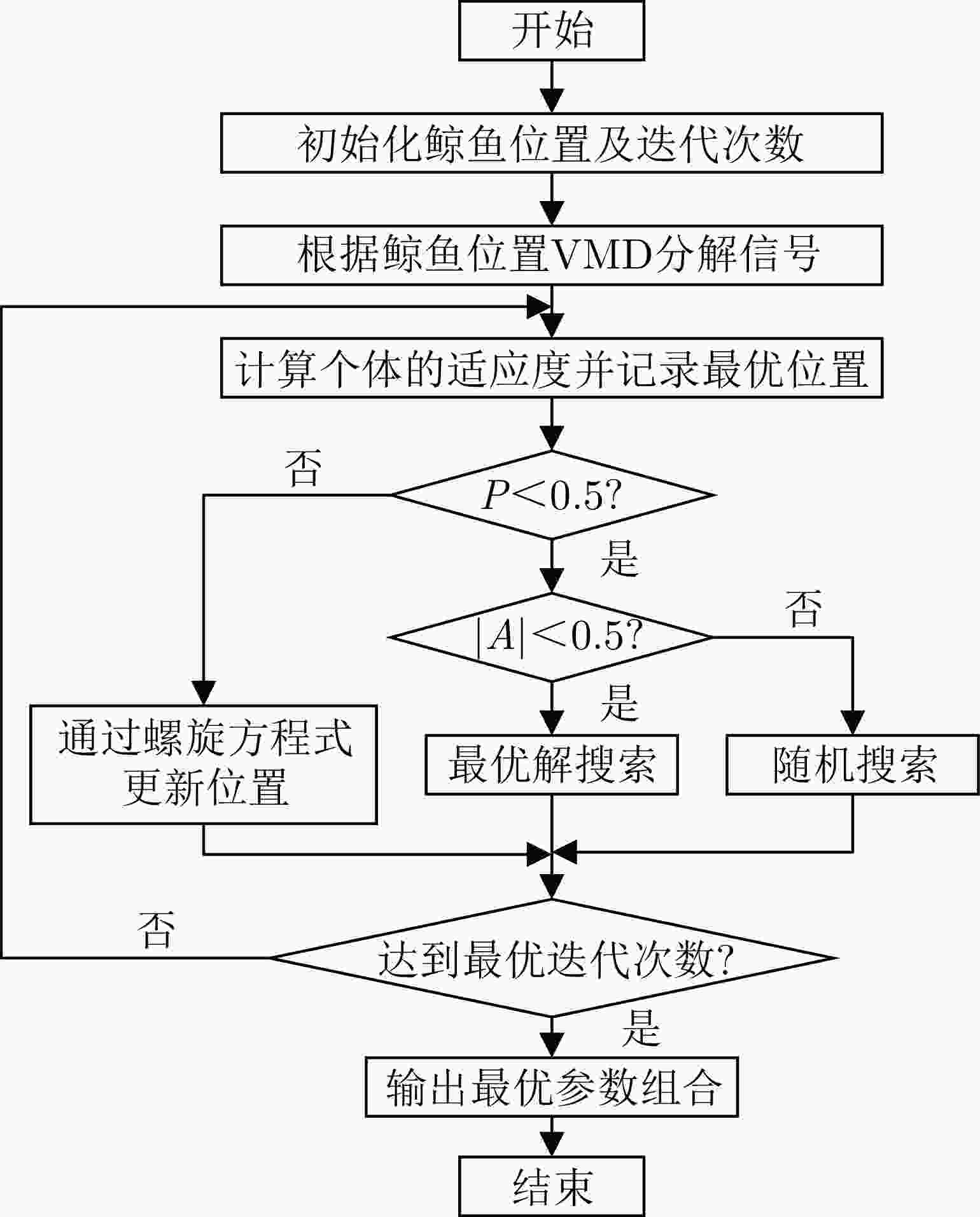
方法 优点 缺点 EMD 适应性较强、探测效果较好、速度快 存在模态混叠和虚假分量、IMF物理意义模糊 EEMD 无模态混叠现象、IMF物理意义明确 计算量大、工作效率低、模块响应时间长 CEEMD 计算量小、响应速度快、可消除重构信号的噪声 依据经验选择参数、不适用于低信噪比环境 VMD 可有效避免模态混叠和端点效应,探测性能强 计算时间长、参数选择效率低、实时性差 表 7 各神经网络方法的性能及优缺点对比
Table 7. Comparison of performance and advantages and disadvantages of each neural network method
方法 性能 优点 缺点 卷积神经
网络可有效处理复杂信号且捕捉信号中的
时空相关性高效的数据处理能力,精度高、
鲁棒性强、适应性强需预定义不同大小的卷积核,数据库要求
高,且存在退化现象、难以提高精度残差神经
网络可训练非常深的网络且可提取微弱信号 深度加深而计算量不增加、无退化现象
和梯度消失问题、训练效率高计算量大、数据需求量大、
设计和调试难度大前馈人工神经
网络可实现小数据集输入信号到输出结果的
非线性映射结构简单、计算效率高 难以捕捉信号的时空相关性,对输入信号的
设计和选择要求较高循环神经
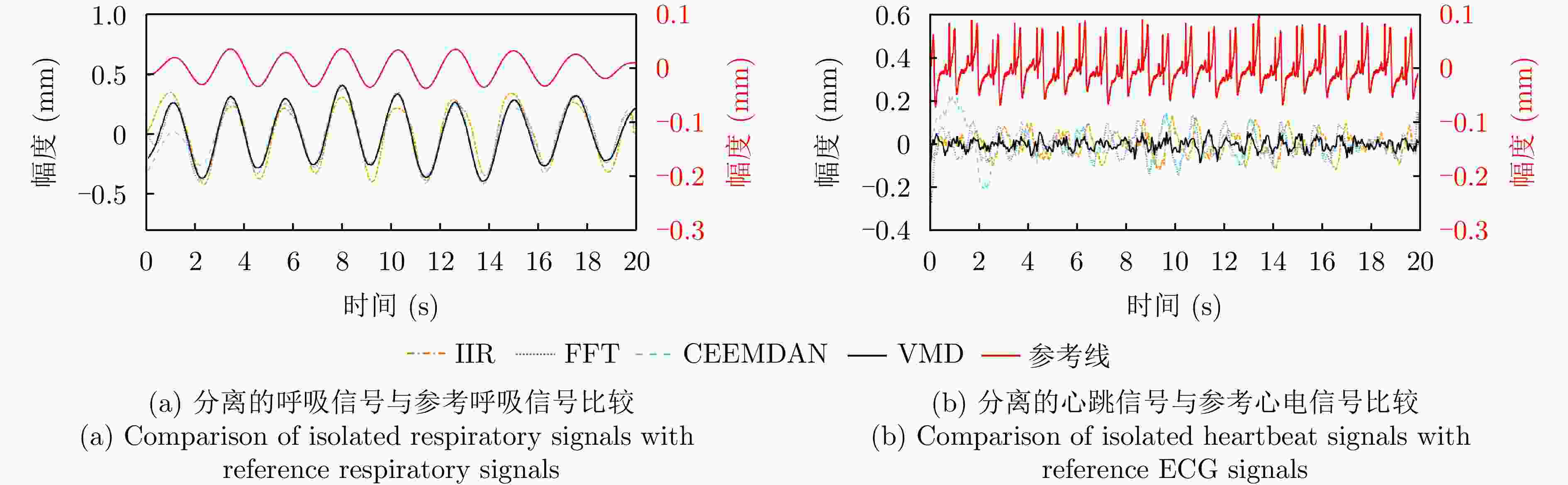
网络可提取序列化数据的动态信息并进行分类,
可学习特征在时间上的周期关系非独立的点序列组信号处理能力及
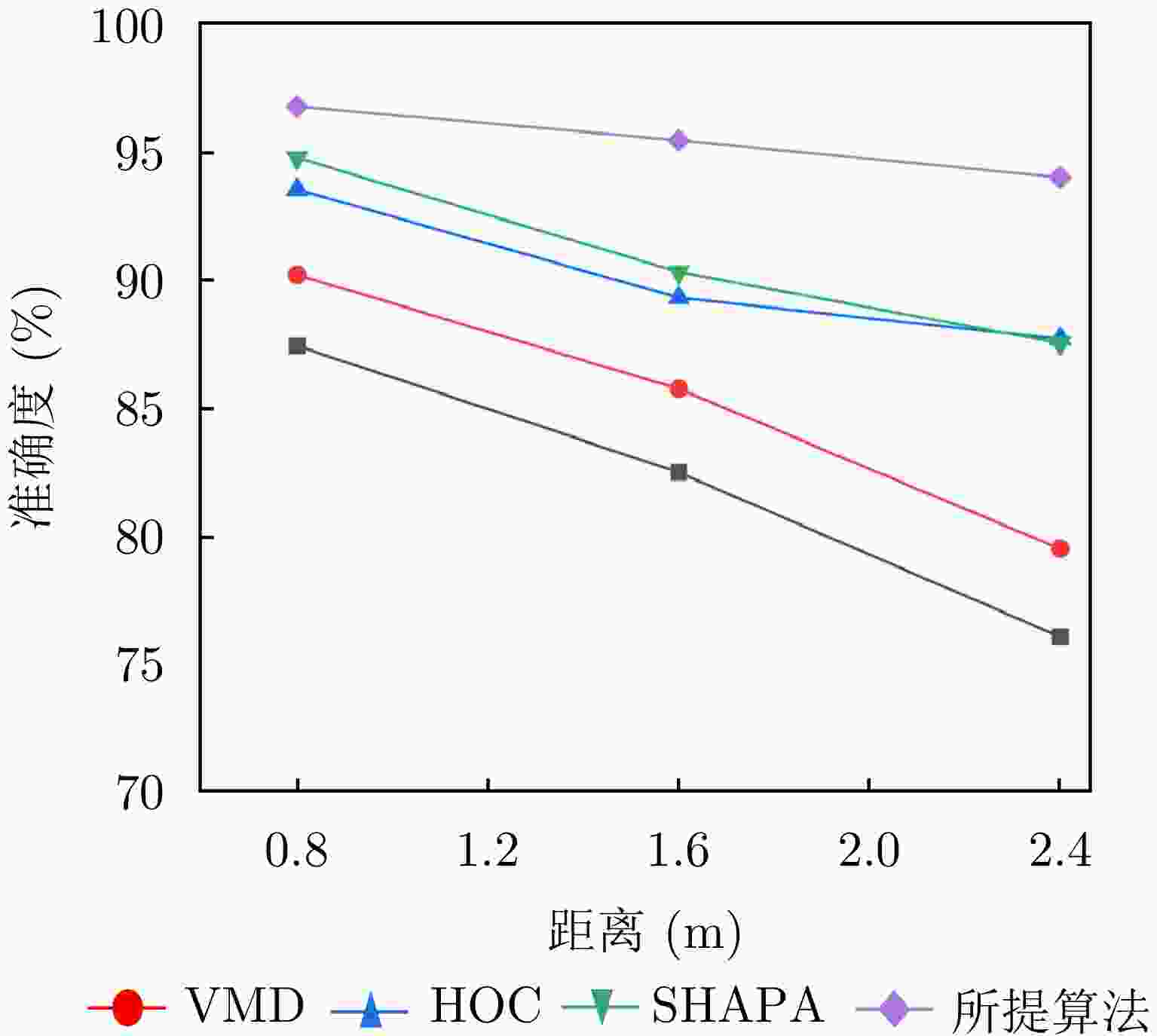
适应性强、记忆前序信息计算成本高、输入信息易损失,反向传播长
时依赖下存在梯度爆炸和梯度消失长短期记忆
网络可有效捕捉信号中时序依赖关系且记忆
长期的依赖关系可有效处理长时间依赖性,序列数据
适应性强,缓解梯度消失问题计算量大、参数多且调节难度大 表 8 各场景信号提取面临的问题与难点
Table 8. Problems and difficulties faced in signal extraction for each scene
场景 问题、难点 矿山救援场景 穿透能力与分辨率相互制约 地震救援场景 背景杂波和电磁干扰严重 医疗健康场景 实时性和准确性要求更高 穿墙探测场景 三维数据显示精度要求高 汽车驾驶场景 躯体、车辆抖动干扰严重 -
[1] 刘新, 阎焜, 杨光耀, 等. UWB-MIMO穿墙雷达三维成像与运动补偿算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356.LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Study on 3D imaging and motion compensation algorithm for UWB-MIMO through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. [2] 罗朋, 胡振峰, 田世伟, 等. UWB雷达芯片的研究现状与发展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1176–1192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211082.LUO Peng, HU Zhenfeng, TIAN Shiwei, et al. The status and trends of UWB radar integrated circuit[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1176–1192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211082. [3] 郑学召, 丁文, 蔡国斌, 等. 面向钻孔救援的UWB雷达回波信息处理关键问题研究进展[J]. 煤矿安全, 2023, 54(10): 219–225. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2023.10.030.ZHENG Xuezhao, DING Wen, CAI Guobin, et al. Research progress on key issues of UWB radar echo information processing for borehole rescue[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(10): 219–225. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2023.10.030. [4] 肖明国, 张彪, 康玉国, 等. 面向钻孔救援的UWB雷达探测技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭技术, 2024, 43(6): 174–177. doi: 10.13301/j.cnki.ct.2024.06.036.XIAO Mingguo, ZHANG Biao, KANG Yuguo, et al. Research progress of UWB radar detection technology for drilling rescue[J]. Coal Technology, 2024, 43(6): 174–177. doi: 10.13301/j.cnki.ct.2024.06.036. [5] 文虎, 刘盛铠, 郑学召, 等. 基于钻孔救援的UWB雷达波传输衰减研究及展望[J]. 工矿自动化, 2023, 49(4): 42–49. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.18053.WEN Hu, LIU Shengkai, ZHENG Xuezhao, et al. Research and prospect of UWB radar wave transmission attenuation based on borehole rescue[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2023, 49(4): 42–49. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.18053. [6] 敬芳菲. 基于超宽带雷达的生命体征提取技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.002229.JING Fangfei. Vital signs extraction technology based on UWB radar[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.002229. [7] QU Xiaodong, GAO Weicheng, MENG Haoyu, et al. Indoor human behavior recognition method based on wavelet scattering network and conditional random field model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5104815. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2023.3276023. [8] 屈乐乐, 刘淑杰, 杨天虹, 等. 基于多通道的调频连续波雷达生命信号提取[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1318–1326. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211073.QU Lele, LIU Shujie, YANG Tianhong, et al. Life signal extraction based on multi-channel frequency modulated continuous wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1318–1326. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211073. [9] 马铖. 面向低信噪杂比环境的随机信号雷达生命探测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 太原理工大学, 2022. doi: 10.27352/d.cnki.gylgu.2022.000168.MA Cheng. Research on life detection method of random signal radar in low signal to noise and clutter ratio environment[D]. [Master dissertation], Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022. doi: 10.27352/d.cnki.gylgu.2022.000168. [10] CHUNG S W, SHIH C C, and HUANG C C. Freehand three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of carotid artery using motion tracking technology[J]. Ultrasonics, 2017, 74: 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.09.020. [11] TSANG T K K and EL-GAMAL M N. Ultra-wideband (UWB) communications systems: An overview[C]. The 3rd International IEEE-NEWCAS Conference, Quebec, Canada, 2005: 381–386. doi: 10.1109/NEWCAS.2005.1496688. [12] 赵尤信, 姚海飞, 李佳慧, 等. 超宽带雷达生命探测技术研究[J]. 工矿自动化, 2023, 49(9): 178–186. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.18111.ZHAO Youxin, YAO Haifei, LI Jiahui, et al. Research on ultra wideband radar life detection technology[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2023, 49(9): 178–186. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.18111. [13] CHEN Xiaomin and KIAEI S. Monocycle shapes for ultra wideband system[C]. 2002 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Phoenix-Scottsdale, USA, 2002: 1. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2002.1009911. [14] LOPES A, OSÓRIO D F N, SILVA H, et al. Equivalent pipeline processing for IR-UWB and FMCW radar comparison in vital signs monitoring applications[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(12): 12028–12035. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3173218. [15] 邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. [16] HUANG Peng, HAI Yu, LI Zhongyu, et al. UWB-radar target scattering characteristic estimation method using joint Low-Rank and sparse characteristic[C]. IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 6037–6040. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282414. [17] RICHARDS M A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Chicago: McGraw-Hill Education, 2014: 71–75. [18] GAO Xiaomeng, JIANG Xiaonan, BI Songjie, et al. Measurement of the complex human Atrial-Ventricular motions using Contact-Based Doppler radar[C]. 2019 IEEE 20th Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference (WAMICON), Cocoa Beach, USA, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/WAMICON.2019.8765441. [19] 丁鹭飞, 耿富录. 雷达原理[M]. 3版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2019: 235–239.DING Lufei and GENG Fulu. Principle of Radar[M]. 3rd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2019: 235–239. [20] 漆晶, 汪正东, 谢广智. 基于胸腔信号样本的FMCW雷达身份验证[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2023, 21(5): 539–546, 554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.05.010.QI Jing, WANG Zhengdong, and XIE Guangzhi. FMCW radar authentication based on chest cavity signal samples[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2023, 21(5): 539–546, 554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.05.010. [21] LI Zhi, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. Through-wall multi-subject localization and vital signs monitoring using UWB MIMO imaging radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(15): 2905. doi: 10.3390/rs13152905. [22] LIU Fan, ZHANG Tingting, and CAO Pan. Asynchronous integration of communication and localization systems using IR-UWB signals[C]. 2021 IEEE Military Communications Conference, San Diego, USA, 2021: 521–527. doi: 10.1109/MILCOM52596.2021.9652951. [23] 张崇超, 张长春, 张群英. EEMD在超宽带雷达生命信号提取中的应用[J]. 电子测量技术, 2012, 35(4): 76–80, 101. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2012.04.019.ZHANG Chongchao, ZHANG Changchun, and ZHANG Qunying. Applications of EEMD in vital signal detection for UWB radar[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2012, 35(4): 76–80, 101. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2012.04.019. [24] WANG Jun, ZHU He, LEI Peng, et al. CNN based classification of rigid targets in space using radar micro-Doppler signatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2019, 28(4): 856–862. doi: 10.1049/cje.2018.08.003. [25] 刘翼群. 生命探测雷达信号处理算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.LIU Yiqun. Research on signal processing algorithm of life detection radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [26] PATERNIANI G, SGRECCIA D, DAVOLI A, et al. Radar-based monitoring of vital signs: A tutorial overview[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(3): 277–317. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2023.3244362. [27] LI Zongwei, PEI Yanbin, WANG Yuqi, et al. An enhanced respiratory mechanics model based on double-exponential and fractional calculus[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2023, 14: 1273645. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1273645. [28] 高晓阳. 生命探测雷达目标辨识算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021.GAO Xiaoyang. Research on target recognition algorithm of life detection radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. [29] LAZARO A, GIRBAU D, and VILLARINO R. Analysis of vital signs monitoring using an IR-UWB radar[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2010, 100: 265–284. doi: 10.2528/pier09120302. [30] SHYU K K, CHIU L J, LEE P L, et al. Detection of breathing and heart rates in UWB radar sensor data using FVPIEF-based two-layer EEMD[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(2): 774–784. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2018.2878607. [31] 吴佳茜, 梁步阁, 杨德贵, 等. 引入时距信息的IR-UWB雷达多域特征融合呼吸模式识别方法[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(2): 236–249. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.02.002.WU Jiaxi, LIANG Buge, YANG Degui, et al. IR-UWB radar multi-domain feature fusion respiratory pattern recognition method with time-distance information[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(2): 236–249. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.02.002. [32] 郭继坤, 王保生, 郝维来, 等. 基于超宽带信号的矿井塌方体下生命特征的检测方法[J]. 黑龙江科技大学学报, 2017, 27(1): 73–76, 96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2017.01.016.GUO Jikun, WANG Baosheng, HAO Weilai, et al. Research on detection method of life under mine based on ultra-wideband signal[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang University of Science & Technology, 2017, 27(1): 73–76, 96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2017.01.016. [33] HUO Ze, ZHANG Zhaoxia, YIN Yonggen, et al. Research on multitarget vital sign detection using IR-UWB radar in occlusion scenarios[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(9): 15327–15336. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2024.3380831. [34] HUANG Ling, WANG Zhao, TIAN Ming, et al. Influence of Parameters on Radar Localization of Human Target under Complex Shielding Environment[M]. KIM K J and KIM H Y. Information Science and Applications. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 3–9. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1465-4_1. [35] YANG Degui, ZHU Zhengliang, ZHANG Junchao, et al. The overview of human localization and vital sign signal measurement using handheld IR-UWB through-wall radar[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(2): 402. doi: 10.3390/s21020402. [36] SHYU K K, CHIU L J, LEE P L, et al. UWB simultaneous breathing and heart rate detections in driving scenario using multi-feature alignment two-layer EEMD method[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(17): 10251–10266. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2020.2992687. [37] 杨国成, 余慧敏. 基于N次峰值捕捉的超宽带雷达生命体征检测[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2020, 34(11): 204–210. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003126.YANG Guocheng and YU Huimin. Vital sign detection of ultra-wideband radar based on N peaks capture[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 34(11): 204–210. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003126. [38] JING Fangfei, LIANG Jing, WANG Yizhu, et al. Harmonics and intermodulation products-based fuzzy logic (HIPBFL) algorithm for vital sign frequency estimation using a UWB radar[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 228: 120294. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120294. [39] YAN Meihui, LUO Zhongtao, HE Zishu, et al. The five-domain-six-map method for signal analysis in over-the-horizon radar[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2147009.2021.9455249. [40] PAN Tianze, GUO Yuanyue, GUO Weiwei, et al. Detection of vital sign based on UWB radar by a time domain coherent accumulation method[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(15): 17054–17063. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2023.3283552. [41] ZHAO Dawei, WANG Jun, CHEN Gang, et al. Clutter cancellation based on frequency domain analysis in passive bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 43956–43964. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.2977961. [42] 薛帅康, 王小月, 许致火, 等. 面向人体呼吸心跳同时监测的雷达信号处理方法综述[J]. 电讯技术, 2023, 63(12): 1995–2002. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.220904002.XUE Shuaikang, WANG Xiaoyue, XU Zhihuo, et al. A review of radar signal processing for simultaneous monitoring of human vital signs[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2023, 63(12): 1995–2002. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.220904002. [43] TURLEY M. Impulsive noise rejection in HF radar using a linear prediction technique[C]. The International Conference on Radar (IEEE Cat. No.03EX695), Adelaide, Australia, 2003: 358–362. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2003.1278767. [44] LU Lian, REN Weixin, and WANG Shidong. Fractional Fourier transform: Time-frequency representation and structural instantaneous frequency identification[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 178: 109305. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.109305. [45] LI Tingpeng, WANG Zelong, and LIU Jiying. Evaluating effect of blanket jamming on radar via robust time-frequency analysis and peak to average power ratio[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 214504–214519. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3040514. [46] SUN Kewen, JIN Tian, and YANG Dongkai. An improved time-frequency analysis method in interference detection for GNSS receivers[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(4): 9404–9426. doi: 10.3390/s150409404. [47] LAO Guochao, YIN Canbin, YE Wei, et al. A frequency domain extraction based adaptive joint time frequency decomposition method of the maneuvering target radar echo[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 266. doi: 10.3390/rs10020266. [48] LIU Meiru, XIA Hong, SUN Lin, et al. Vibration signal analysis of main coolant pump flywheel based on Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2015, 47(2): 219–225. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2014.12.010. [49] 朱少民, 夏虹, 尹文哲, 等. 基于变分模态分解和希尔伯特变换的转子非平稳信号故障特征识别[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(5): 825–832. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202205050.ZHU Shaomin, XIA Hong, YIN Wenzhe, et al. Fault feature identification for rotor non-stationary signals based on VMD-HT[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(5): 825–832. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202205050. [50] TOMA R N, KIM C H, and KIM J M. Bearing fault classification using ensemble empirical mode decomposition and convolutional neural network[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(11): 1248. doi: 10.3390/electronics10111248. [51] CHENG Yao, WANG Zhiwei, CHEN Bingyan, et al. An improved complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and its application to rolling element bearing fault diagnosis[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 91: 218–234. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.01.038. [52] PENG Kecheng, CAO Xiaoqun, LIU Bainian, et al. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise with convolution based gated recurrent neural network: A new deep learning model for South Asian high intensity forecasting[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13(6): 931. doi: 10.3390/sym13060931. [53] CHUI K T, GUPTA B B, LIU R W, et al. Handling data heterogeneity in electricity load disaggregation via optimized complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition and wavelet packet transform[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(9): 3133. doi: 10.3390/s21093133. [54] WU Shiyou, TAN Kai, XIA Zhenghuan, et al. Improved human respiration detection method via ultra-wideband radar in through-wall or other similar conditions[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(3): 468–476. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0159. [55] LIANG Xiaolin, ZHANG Hao, YE Shengbo, et al. Improved denoising method for through-wall vital sign detection using UWB impulse radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 74: 72–93. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.12.004. [56] 高磊. 非接触人体体征信号提取及分离方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京理工大学, 2017.GAO Lei. Research on non-contact human body signal extraction and separation methods[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of science and Technology, 2017. [57] SUN Li, HUANG Shuaiming, LI Yusheng, et al. Remote measurement of human vital signs based on joint-range adaptive EEMD[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 68514–68524. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.2985286. [58] 弭晴, 马永涛, 黄祉同. 基于多序列WOA-VMD算法的超宽带雷达心率检测[J]. 传感技术学报, 2024, 37(7): 1144–1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2024.07.006.MI Qing, MA Yongtao, and HUANG Zhitong. Heart rate detection based on multi-sequence WOA-VMD algorithm using UWB radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2024, 37(7): 1144–1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2024.07.006. [59] NAISHADHAM K, PIOU J E, REN Lingyun, et al. Estimation of cardiopulmonary parameters from ultra wideband radar measurements using the state space method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2016, 10(6): 1037–1046. doi: 10.1109/tbcas.2015.2510652. [60] REN Lingyun, WANG Haofei, NAISHADHAM K, et al. Phase-based methods for heart rate detection using UWB impulse Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(10): 3319–3331. doi: 10.1109/tmtt.2016.2597824. [61] LI Meiyu and LIN J. Wavelet-transform-based data-length-variation technique for fast heart rate detection using 5.8-GHz CW Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2018, 66(1): 568–576. doi: 10.1109/tmtt.2017.2730182. [62] YANG Guocheng and YU Huimin. Vital signs detection based on UWB radar using trajectory capture and peak capture[C]. 2020 3rd International Conference on Electron Device and Mechanical Engineering (ICEDME), Suzhou, China, 2020: 657–661. doi: 10.1109/ICEDME50972.2020.00155. [63] WANG Yong, WANG Wen, ZHOU Mu, et al. Remote monitoring of human vital signs based on 77-GHz mm-wave FMCW radar[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(10): 2999. doi: 10.3390/s20102999. [64] QIAO Lihong, LI Xin, XIAO Bin, et al. Learning-refined integral null space pursuit algorithm for noncontact multisubjects vital signs measurements using SFCW-UWB and IR-UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 8506013. doi: 10.1109/tim.2022.3218031. [65] 何密, 平钦文, 戴然. 深度学习融合超宽带雷达图谱的跌倒检测研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169.HE Mi, PING Qinwen, and DAI Ran. Fall detection based on deep learning fusing ultrawideband radar spectrograms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169. [66] MALEŠEVIĆ N, PETROVIĆ V, BELIĆ M, et al. Contactless real-time heartbeat detection via 24 GHz continuous-wave Doppler radar using artificial neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 2351. doi: 10.3390/s20082351. [67] 周金海, 吴耿俊, 雷雯, 等. 基于呼吸样本空间的超宽带雷达身份识别[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2022, 36(1): 118–125. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2104217.ZHOU Jinhai, WU Gengjun, LEI Wen, et al. UWB radar identification based on breathing sample space[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2022, 36(1): 118–125. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2104217. [68] HE Mi, NIAN Yongjian, XU Luping, et al. Adaptive separation of respiratory and heartbeat signals among multiple people based on empirical wavelet transform using UWB radar[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4913. doi: 10.3390/s20174913. [69] ZHAO Heng, HONG Hong, MIAO Dongyu, et al. A noncontact breathing disorder recognition system using 2.4-GHz digital-IF Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(1): 208–217. doi: 10.1109/jbhi.2018.2817258. [70] 侯敏. 基于深度学习的人体微动特性分析与步态识别[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001623.HOU Min. Analysis of human micro-motion characteristics and gait recognition based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001623. [71] 郑学召, 孙梓峪, 郭军, 等. 矿山钻孔救援多源信息探测技术研究与应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(11): 94–102. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.05.0421.ZHENG Xuezhao, SUN Zhiyu, GUO Jun, et al. Research and application of multi-source information detection technology for drilling rescue of mine[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(11): 94–102. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.05.0421. [72] 王保生. 超宽带信号穿透塌方体衰减特性及生命特征检测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 黑龙江科技大学, 2017.WANG Baosheng. Study on attenuation characteristics and life characteristics detection method of ultra wide band signal through landslide[D]. [Master dissertation], Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, 2017. [73] 李欣欣. 遮蔽环境下基于超宽带雷达的生命探测技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 兰州理工大学, 2023. doi: 10.27206/d.cnki.ggsgu.2023.000714.LI Xinxin. Research on life detection technology based on Ultra-Wide-Band radar in sheltered environment[D]. [Master dissertation], Lanzhou University of Technology, 2023. doi: 10.27206/d.cnki.ggsgu.2023.000714. [74] 潘俊, 叶盛波, 史城, 等. 基于先验信噪比估计的超宽带穿墙雷达呼吸信号检测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1241–1248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211042.PAN Jun, YE Shengbo, SHI Cheng, et al. Study on respiration signal detection algorithm of Ultra-WideBand through-wall radar based on a priori signal-to-noise ratio estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1241–1248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211042. [75] LI Jing, LIU Lanbo, ZENG Zhaofa, et al. Advanced signal processing for vital sign extraction with applications in UWB radar detection of trapped victims in complex environments[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(3): 783–791. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2013.2259801. [76] MAO Kai, ZHU Qiuming, YE Xijuan, et al. UWB channel modeling and simulation with continuous frequency response[J]. China Communications, 2022, 19(11): 88–98. doi: 10.23919/jcc.2022.11.007. [77] CAI Jiajia, ZHOU Hao, HUANG Weimin, et al. Ship detection and direction finding based on time-frequency analysis for compact HF radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(1): 72–76. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2020.2967387. [78] 瑞泽, 熊明耀, 梁步阁. 穿墙雷达呼吸信号提取算法研究[J]. 电子技术, 2021, 50(7): 106–108.RUI Ze, XIONG Mingyao, and LIANG Buge. Study on algorithm of breathing signal extraction for through wall radar[J]. Electronic Technology, 2021, 50(7): 106–108. [79] WANG Kun, ZENG Zhaofa, and SUN Jiguang. Through-wall detection of the moving paths and vital signs of human beings[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(5): 717–721. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2018.2881311. [80] NEZIROVIC A, YAROVOY A G, and LIGTHART L P. Signal processing for improved detection of trapped victims using UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2005–2014. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2009.2036840. [81] ALAM M J, O’SHAUGHNESSY D D, and SELOUANI S A. Speech enhancement based on novel two-step a priori SNR estimators[C]. 9th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Brisbane, Australia, 2008: 565–568. [82] ZHANG Jingwen, QI Qingjie, CHENG Huifeng, et al. A multi-target localization and vital sign detection method using ultra-wide band radar[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(13): 5779. doi: 10.3390/s23135779. [83] 樊哲宁, 朱嘉健, 王立新, 等. 基于超宽带雷达及支持向量机的灾后人体呼吸信号识别方法与试验研究[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2021, 16(3): 597–604. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210320.FAN Zhening, ZHU Jiajian, WANG Lixin, et al. An approach and experiments for human respiratory signal recognition based on UWB radar and support vector machine[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2021, 16(3): 597–604. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210320. [84] PAN Jun, YE Shengbo, NI Zhikang, et al. Enhancement of vital signals based on low-rank, sparse representation for UWB through-wall radar[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 13(1): 98–106. doi: 10.1080/2150704x.2021.1995069. [85] LIANG Xiao, PAN Jun, ZHENG Zhijie, et al. Enhancement of vital signals for UWB through-wall radar using nonconvex regularization[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 14(4): 392–401. doi: 10.1080/2150704x.2023.2204197. [86] LIANG Xiao, YE Shengbo, SONG Chenyang, et al. Enhancement of vital signals for UWB through-wall radar using low-rank and block-sparse matrix decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(4): 620. doi: 10.3390/rs16040620. [87] ISLAM S M M, BORIĆ-LUBECKE O, and LUBECKE V M. Identity authentication in two-subject environments using microwave Doppler radar and machine learning classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2022, 70(11): 5063–5076. doi: 10.1109/tmtt.2022.3197413. [88] PURNOMO A T, LIN Dingbing, ADIPRABOWO T, et al. Non-contact monitoring and classification of breathing pattern for the supervision of people infected by COVID-19[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(9): 3172. doi: 10.3390/s21093172. [89] 胡锡坤, 金添. 基于自适应小波尺度选择的生物雷达呼吸与心跳分离方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 462–469. doi: 10.12000/JR16103.HU Xikun and JIN Tian. Adaptive wavelet scale selection-based method for separating respiration and heartbeat in bio-radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 462–469. doi: 10.12000/JR16103. [90] YE Chen, GUI Guan, and OHTSUKI T. Deep clustering with LSTM for vital signs separation in contact-free heart rate estimation[C]. ICC 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9149328. [91] QIAO Lihong, WANG Zehua, XIAO Bin, et al. Spectral unmixing successive variational mode decomposition for robust vital signs detection using UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 8502813. doi: 10.1109/tim.2023.3274171. [92] KANG Sun, KIM D K, LEE Y, et al. Non-contact diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea using impulse-radio ultra-wideband radar[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 5261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62061-4. [93] ZHENG Tianyue, CHEN Zhe, ZHANG Shujie, et al. MoRe-Fi: Motion-robust and fine-grained respiration monitoring via deep-learning UWB radar[C]. The 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Coimbra, Portugal, 2021: 111–124. doi: 10.1145/3485730.3485932. [94] 徐向阳. 基于UWB生物雷达的心跳呼吸提取技术实现[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.XU Xiangyang. Realization on extracting technology of heartbeat and respiration based on UWB bioradar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [95] 陶启明. 基于超宽带雷达的生命特征信息提取技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003124.TAO Qiming. Vital sign monitoring using ultra wide band radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2022. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003124. [96] YUAN Zhonghang, LU Shuaibing, HE Yi, et al. Nmr-VSM: Non-touch motion-robust vital sign monitoring via UWB radar based on deep learning[J]. Micromachines, 2023, 14(7): 1479. doi: 10.3390/mi14071479. [97] AHMED S, LEE Y, LIM Y H, et al. Noncontact assessment for fatigue based on heart rate variability using IR-UWB radar[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 14211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18498-w. [98] 乔嘉豪. 基于生物雷达的心跳分离与特征提取方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安工业大学, 2023. doi: 10.27391/d.cnki.gxagu.2023.000594.QIAO Jiahao. Research on the method of heartbeat separation and feature extraction based on bio-radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xi’an Technological University, 2023. doi: 10.27391/d.cnki.gxagu.2023.000594. [99] LIANG Xiaolin and JIANG Yongling. Detection of breathing rates in through-wall UWB radar utilizing JTFA[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems (TIIS), 2019, 13(11): 5527–5545. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2019.11.014. [100] JIN Yanghao, CHEN Jianlai, LIANG Buge, et al. First demonstration of using signal processing approach to suppress signal ringing in impulse UWB through-wall radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3505505. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2021.3070407. [101] ZHENG Tianyue, CHEN Zhe, CAI Chao, et al. V2iFi: In-vehicle vital sign monitoring via compact RF sensing[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(2): 70. doi: 10.1145/3397321. [102] SCHIRES E, GEORGIOU P, and LANDE T S. Vital sign monitoring through the back using an UWB impulse radar with body coupled antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2018, 12(2): 292–302. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2018.2799322. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
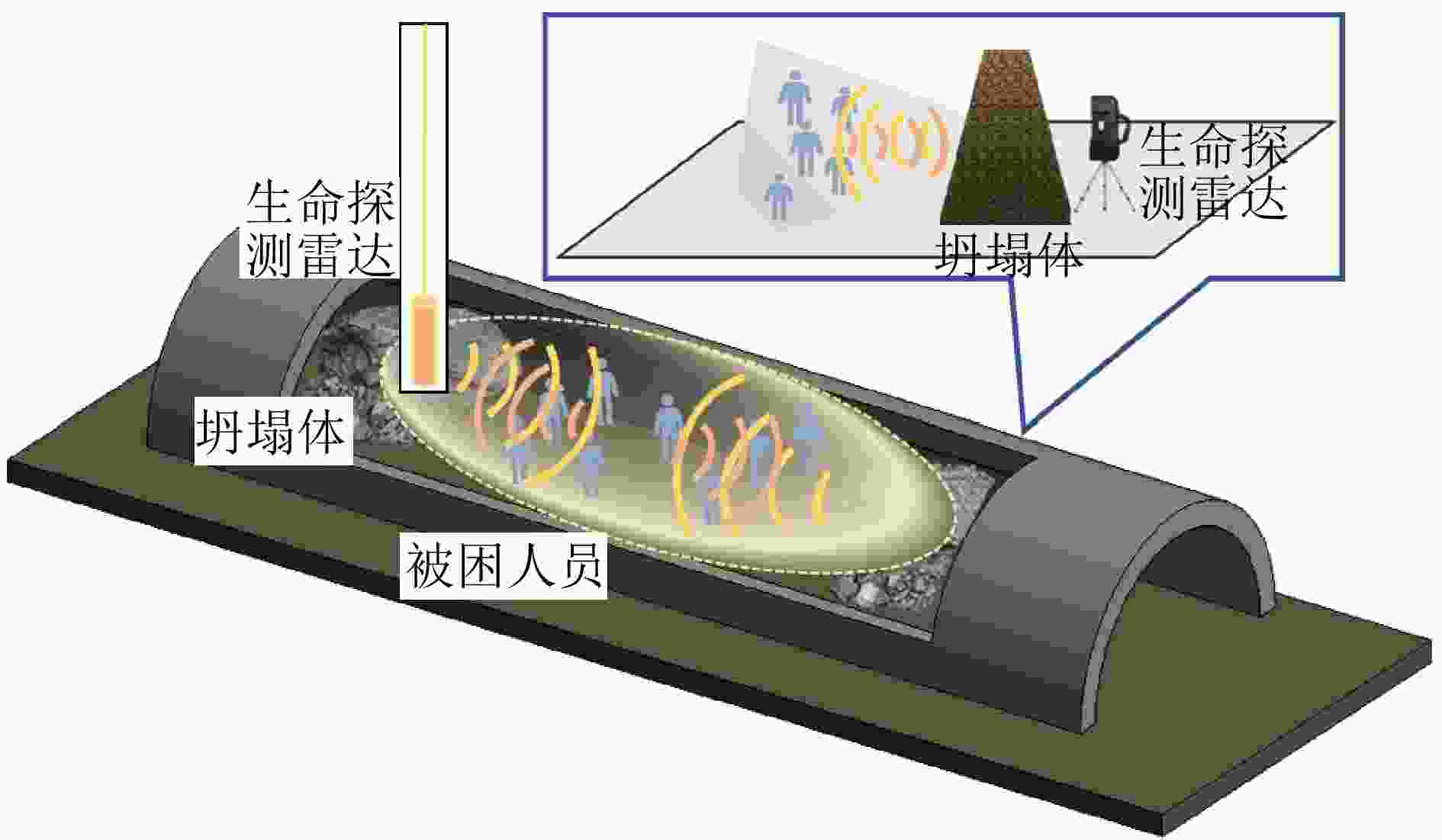
 下载:
下载: