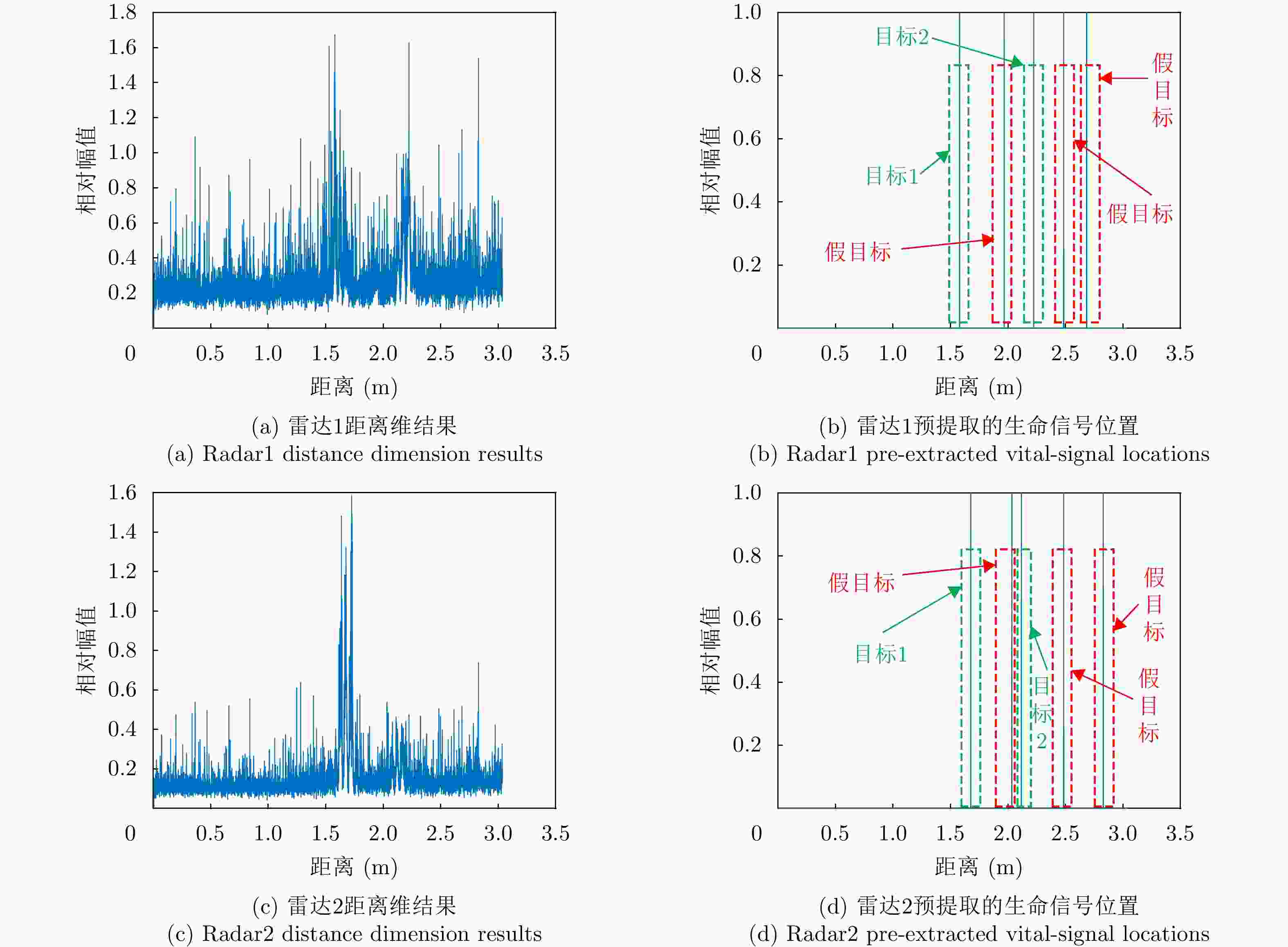
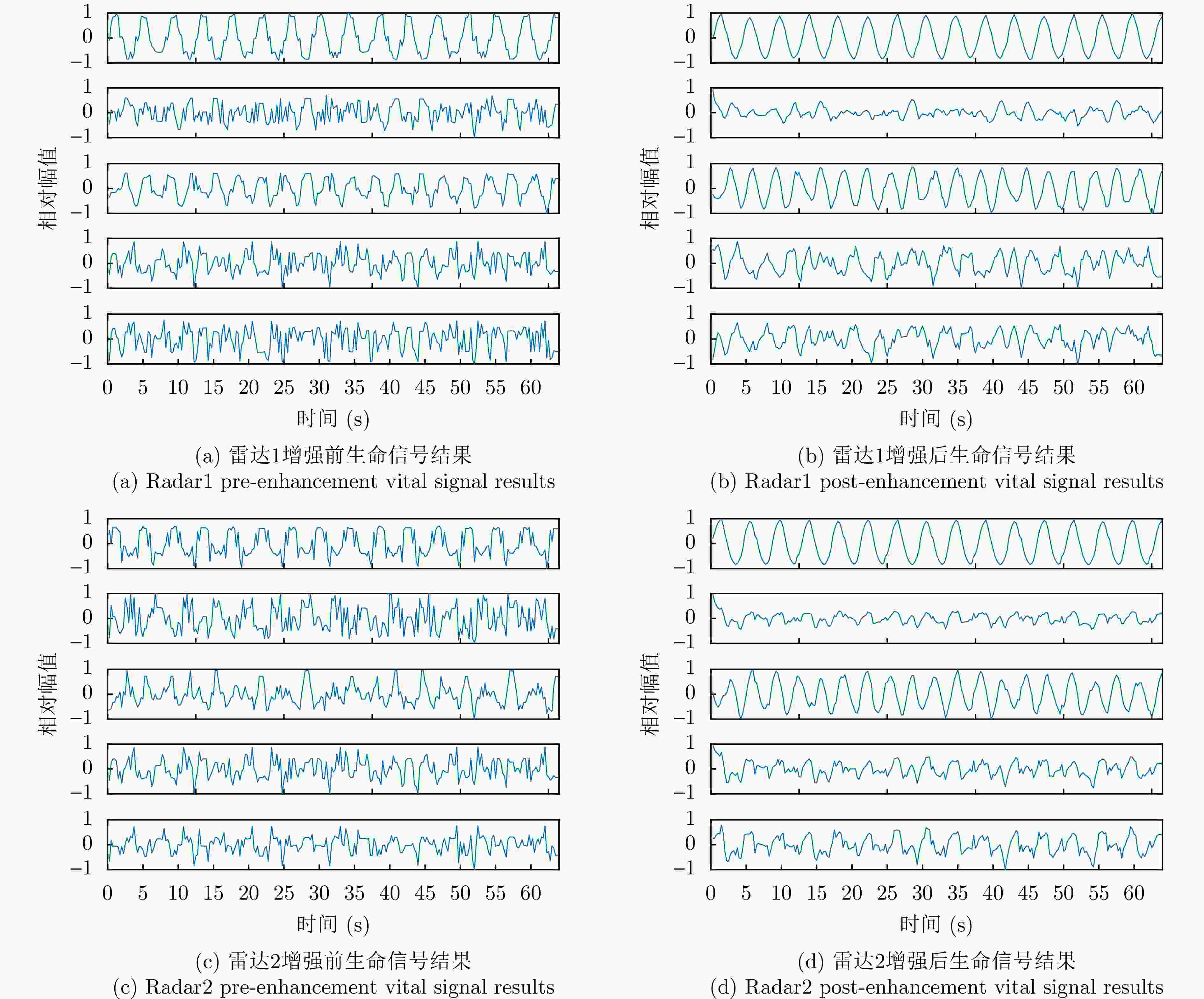
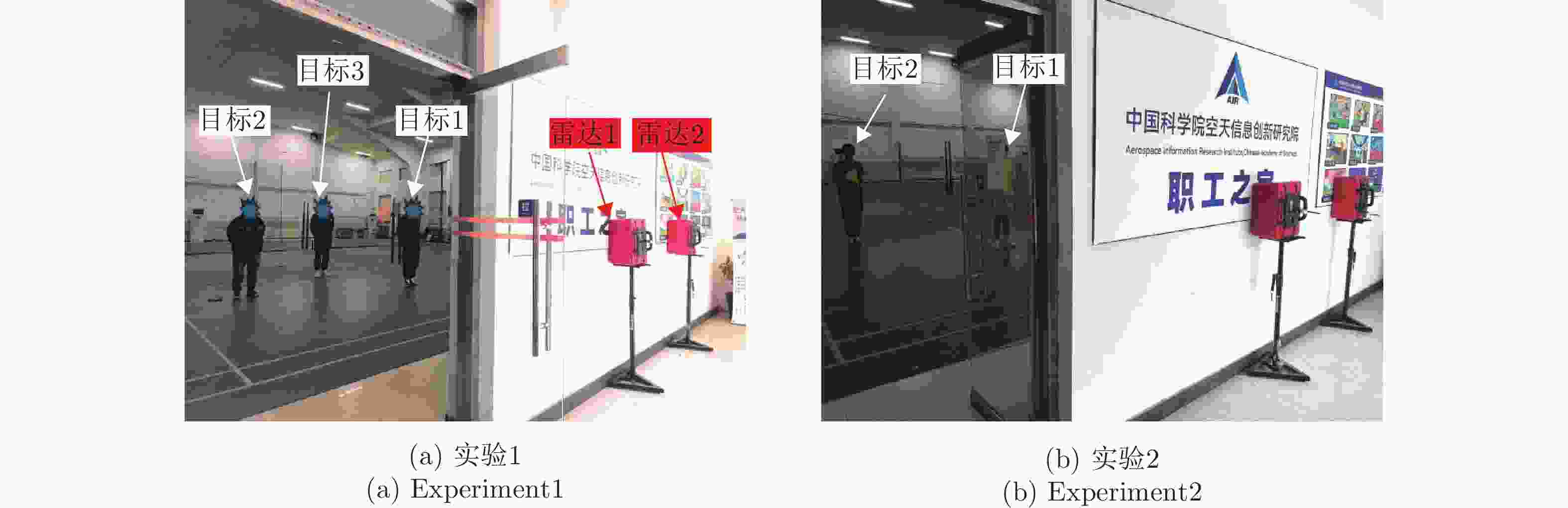
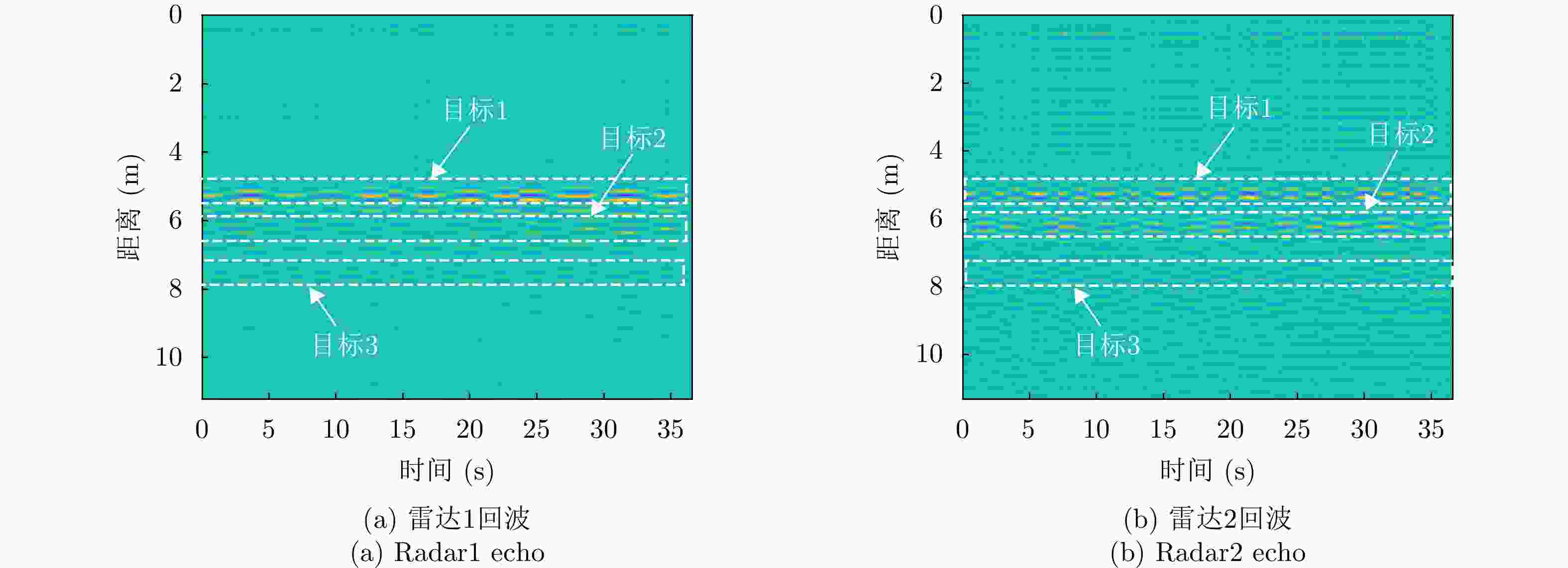
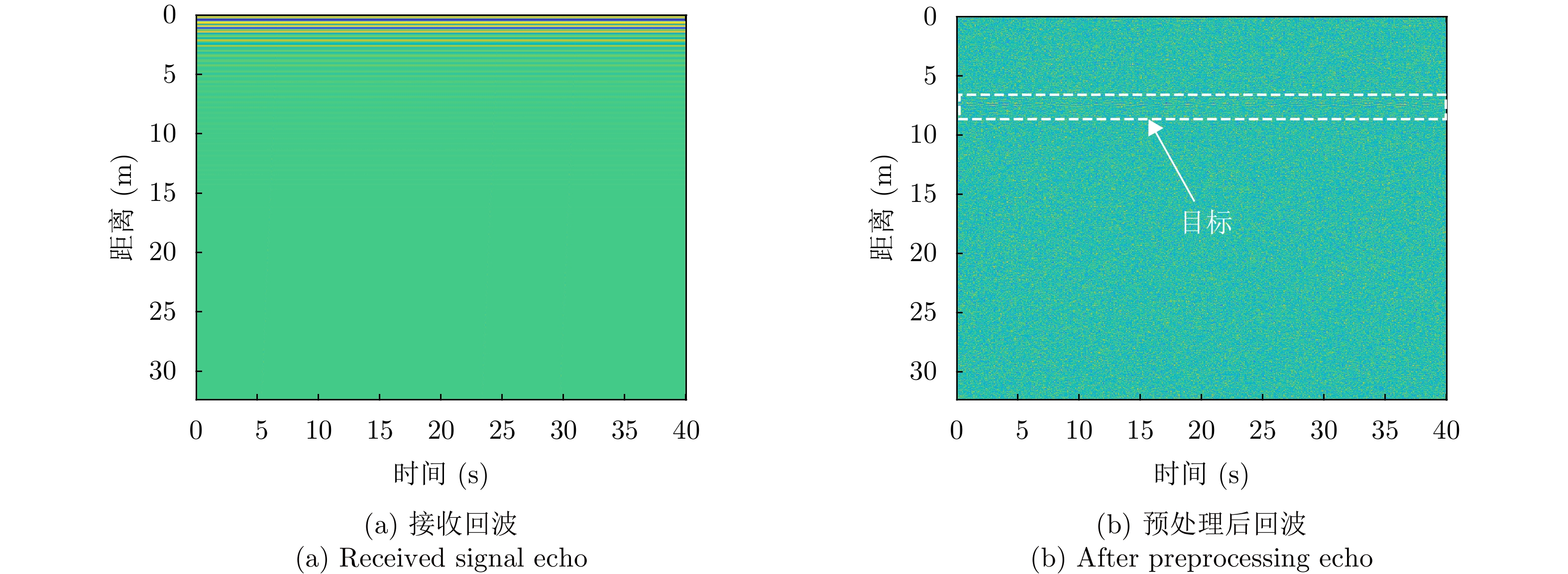
-
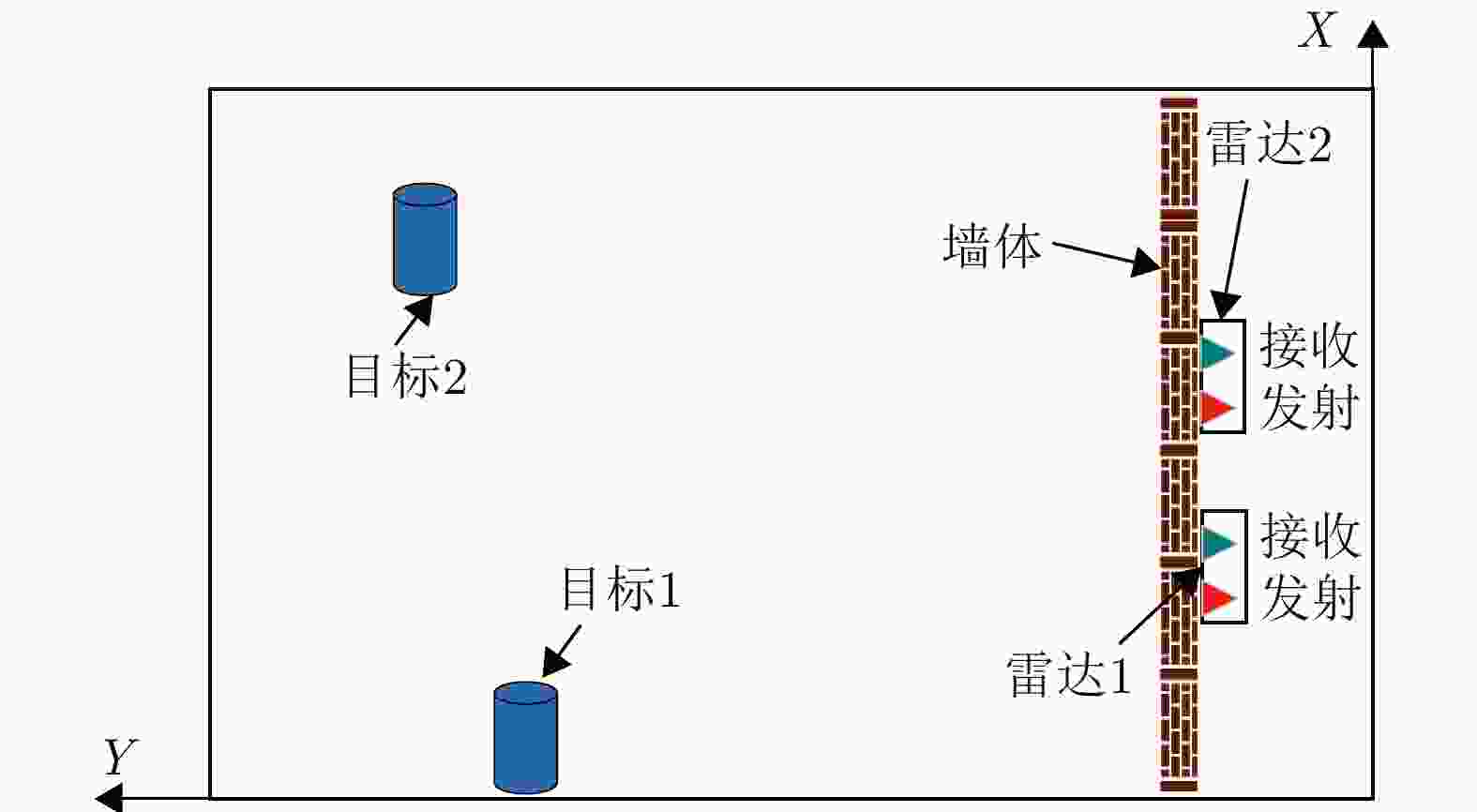
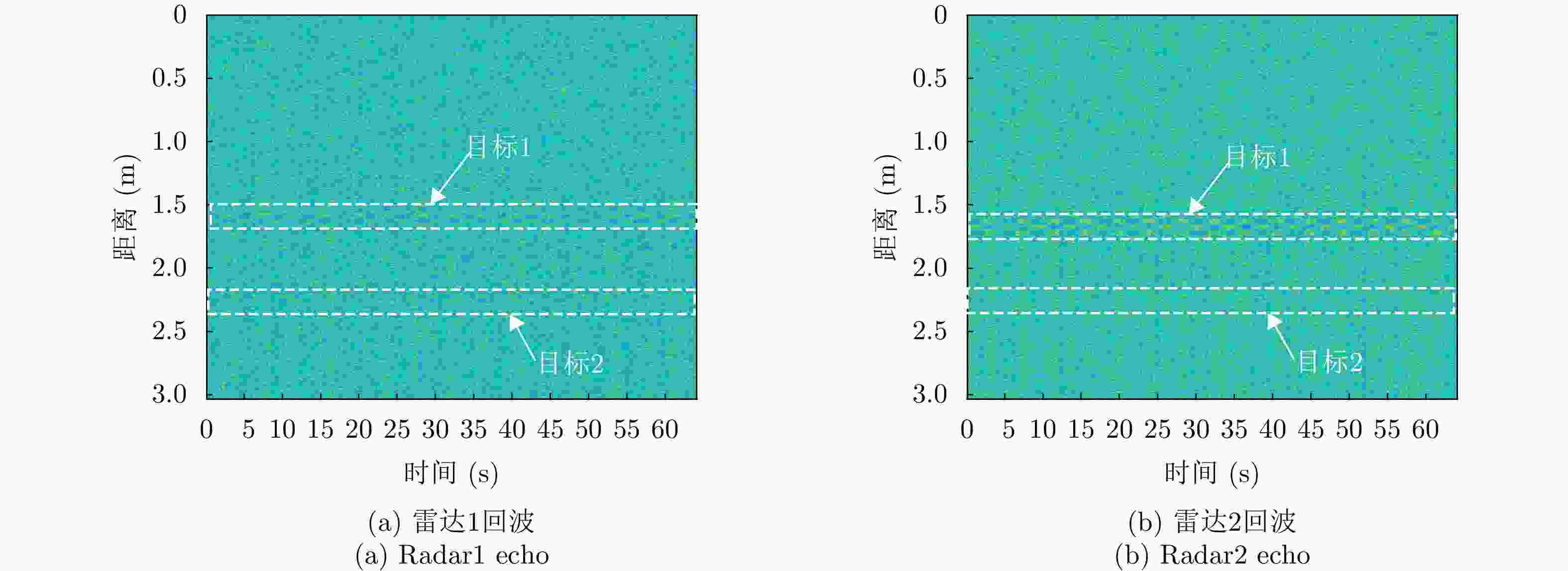
摘要: 超宽带雷达具有抗干扰能力强、穿透性强等特点,被广泛应用于穿墙人体目标探测。单发单收雷达具有体积小、重量轻的优势,但是无法实现目标的二维定位。MIMO阵列雷达能够实现对于目标的定位,但是存在着体积与分辨率之间的相互制约,同时运算时间较长。该文基于分布式穿墙雷达,提出了一种基于分布式雷达的多目标自动检测方法。首先,对回波信号进行时域预处理、时频转换等,基于恒虚警检测的目标距离测量方法获取目标候选距离单元,使用滤波矩阵进行候选信号增强;基于生命信息对增强后信号进行关联,实现目标匹配;最后使用定位模块来实现雷达位置自确定,进而实现生命目标位置的快速、自动检测。为了避免偶发误差对最终定位结果的影响,该文使用定位场景剖分的方法实现穿墙场景下的生命目标二维定位。实验结果表明,该文所提方法可以实现穿墙场景下多目标的检测定位,在实测数据中运算时间为0.95 s,优于其他对比方法4倍以上。Abstract: Ultra-WideBand (UWB) radar exhibits strong antijamming capabilities and high penetrability, making it widely used for through-wall human-target detection. Although single-transmitter, single-receiver radar offers the advantages of a compact size and lightweight design, it cannot achieve Two-Dimensional (2D) target localization. Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) array radar can localize targets but faces a trade-off between size and resolution and involves longer computation durations. This paper proposes an automatic multitarget detection method based on distributed through-wall radar. First, the echo signal is preprocessed in the time domain and then transformed into the time-frequency domain. Target candidate distance cells are identified using a constant false alarm rate detection method, and candidate signals are enhanced using a filtering matrix. The enhanced signals are then correlated based on vital information, such as breathing, to achieve target matching. Finally, a positioning module is employed to determine the radar’s location, enabling rapid and automatic detection of the target’s location. To mitigate the effect of occasional errors on the final positioning results, a scene segmentation method is used to achieve 2D localization of human targets in through-wall scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can successfully detect and localize multiple targets in through-wall scenarios, with a computation duration of 0.95 s based on the measured data. In particular, the method is over four times faster than other methods.
-
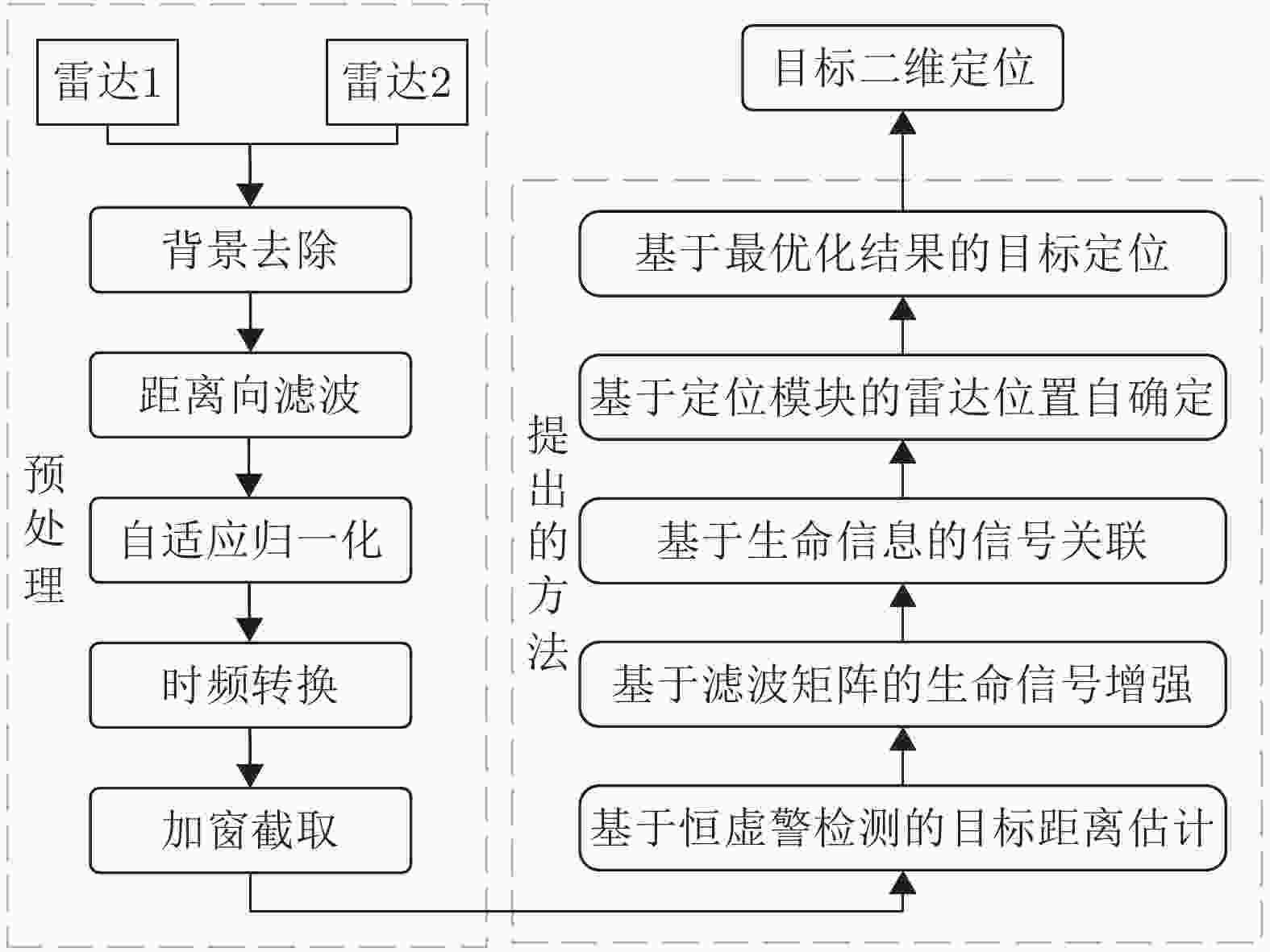
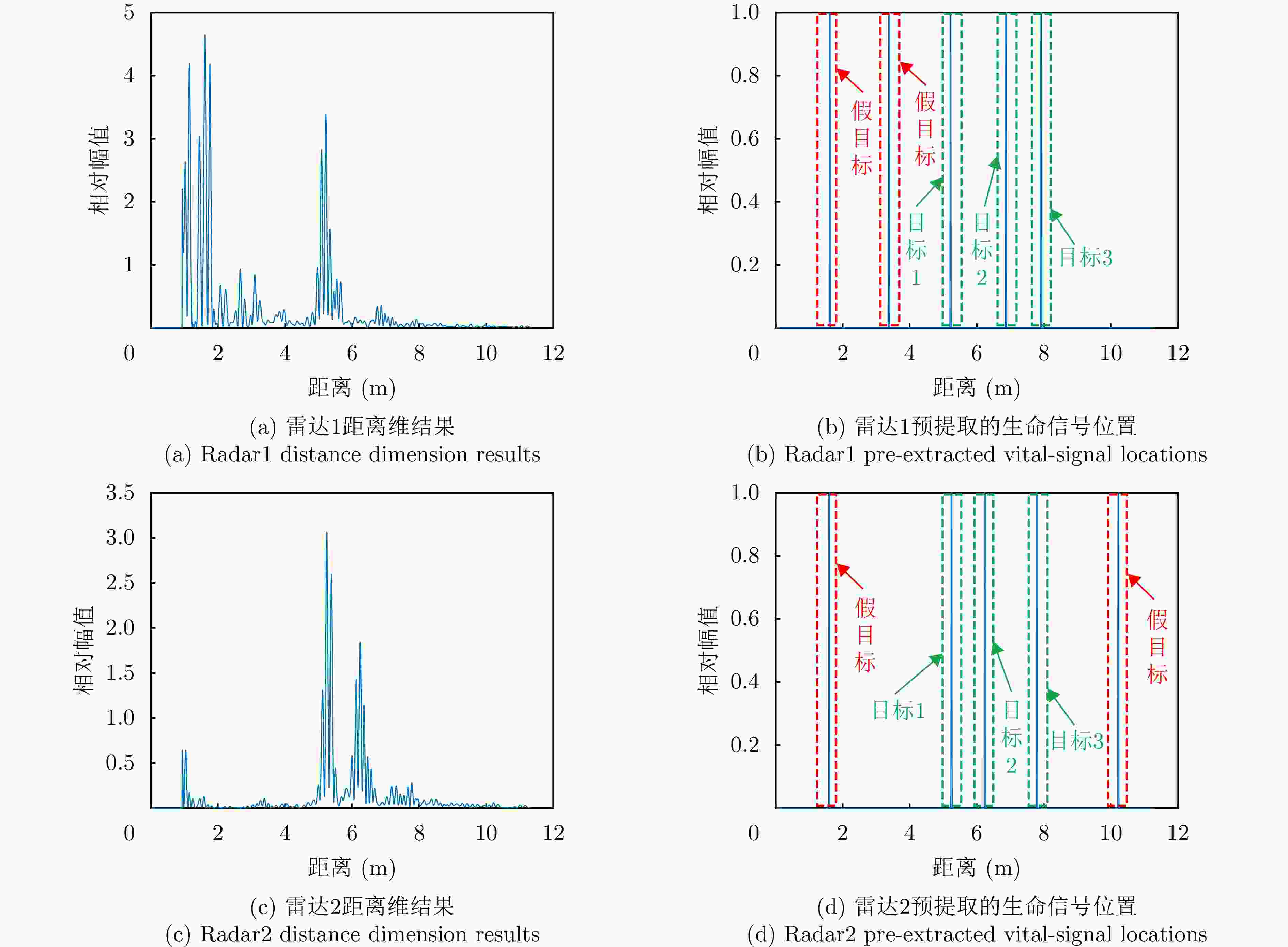
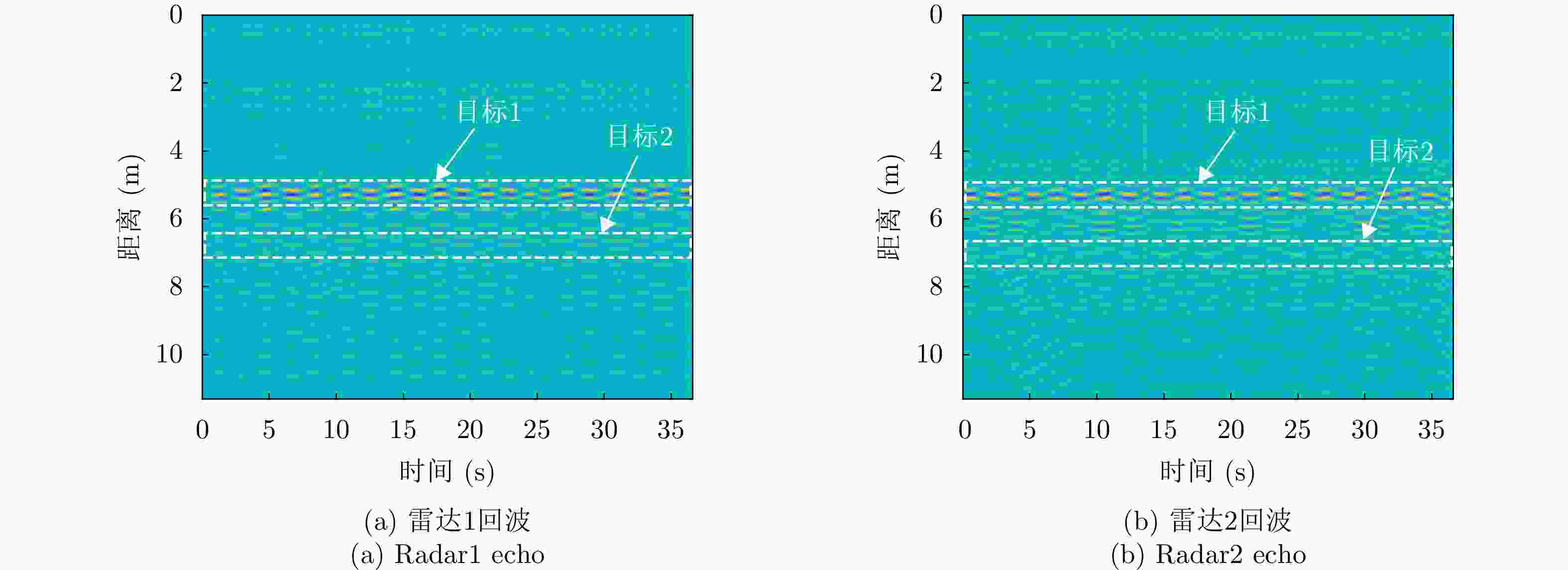
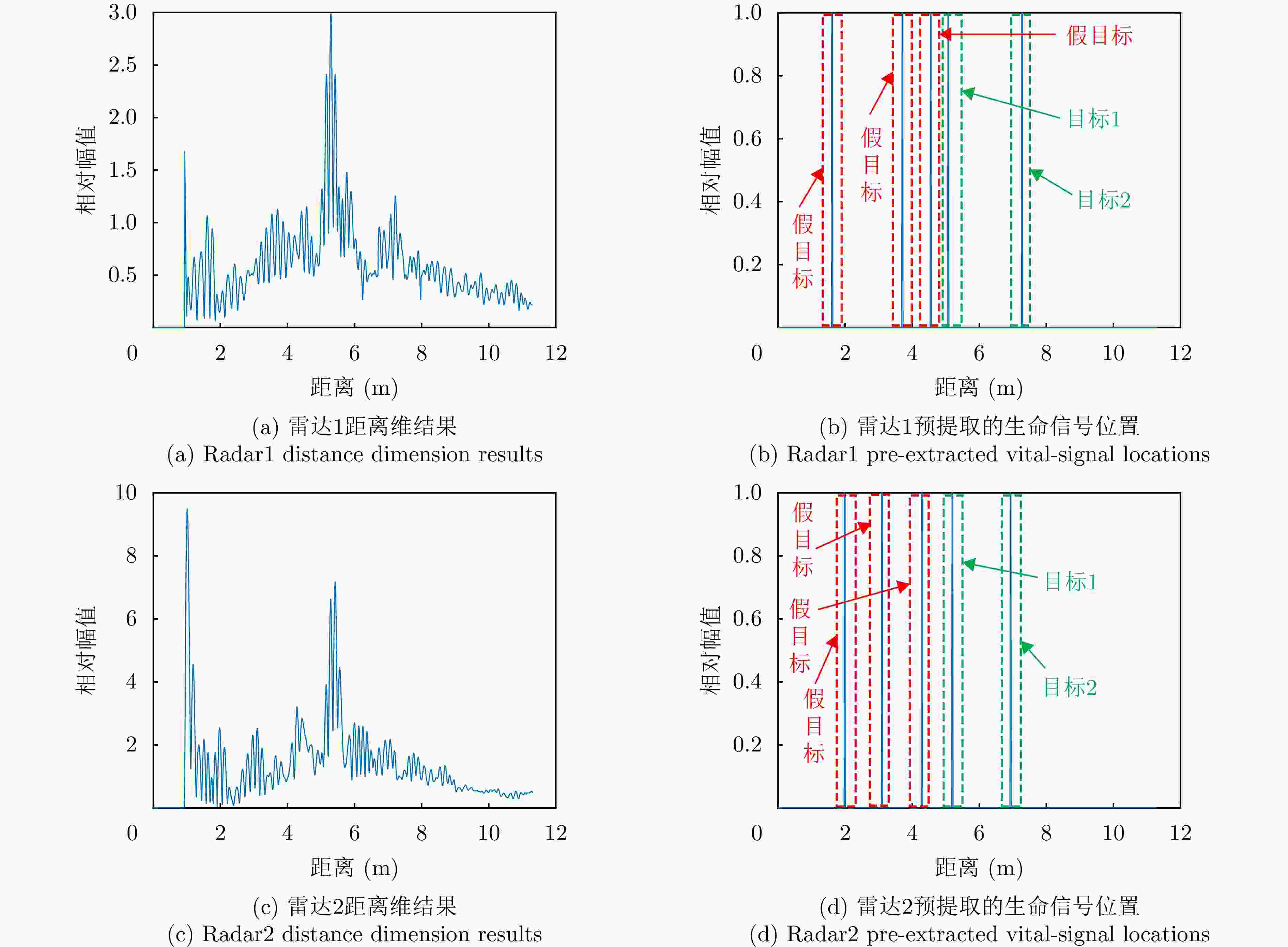
1 基于生命信息的信号关联处理流程
1. The signal correlations based on vital information
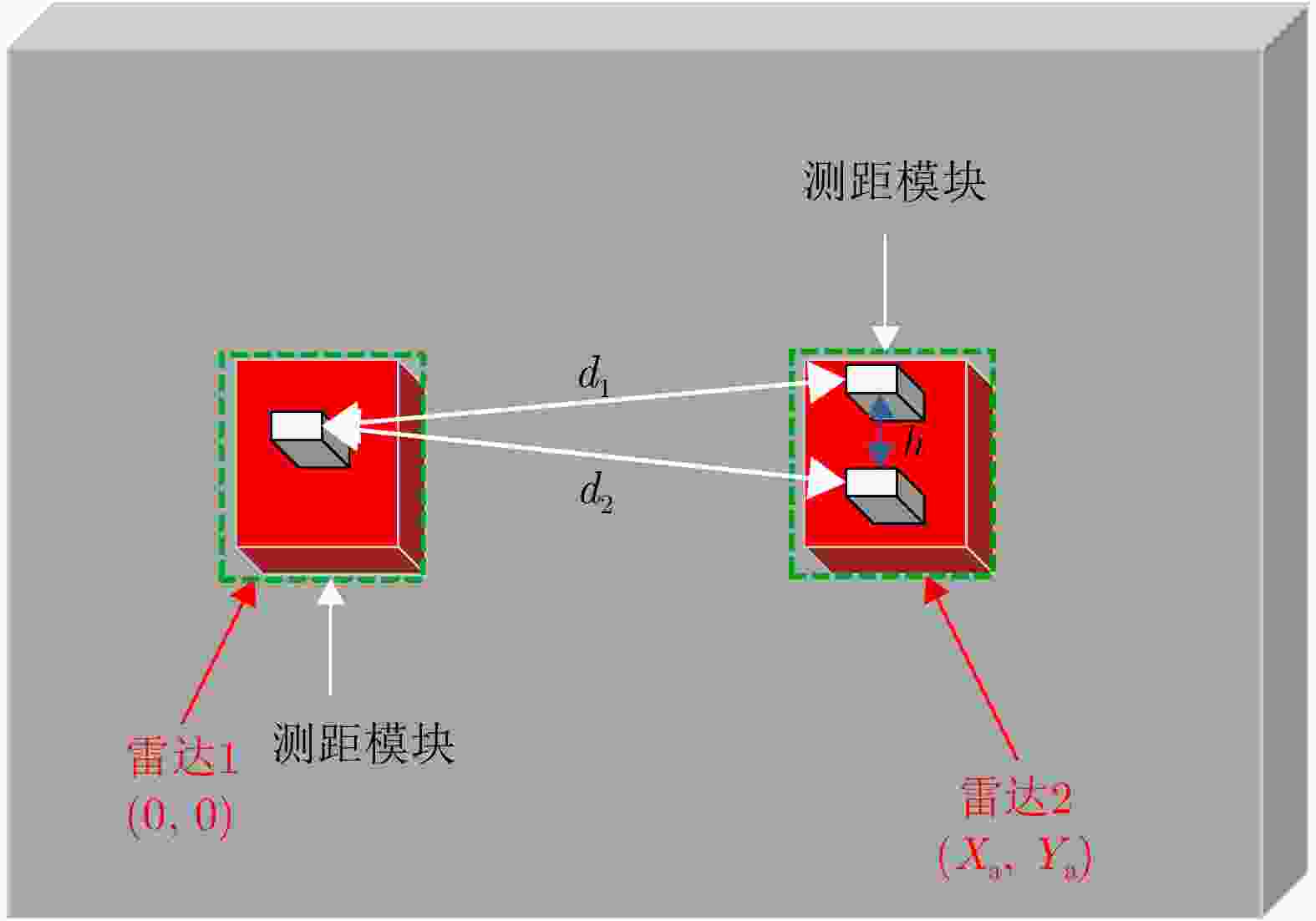
输入:两个雷达预处理后的回波信号矩阵信号矩阵${{\boldsymbol{X}}_1}$, ${{\boldsymbol{X}}_2}$,检测结果中P个目标对应的距离结果$k_1^1,k_2^1, \cdots ,k_P^1 \in J$和$ k_1^2,k_2^2, \cdots ,k_P^2 \in J $ 输出:步骤3中获取的$ i,j $结果,即为匹配结果。 1. 获取$ {\boldsymbol{R}}_{}^1(p,n) = {{\boldsymbol{X}}_1}\left( {k_p^1,k} \right) $, ${\boldsymbol{R}}_{}^2(p,n) = {{\boldsymbol{X}}_2}(k_p^2,k)$,将对应行标记为${\boldsymbol{r}}_p^1(n)$与$ {\boldsymbol{r}}_p^2(n) $ 2. 求解相关性 $ {{\mathrm{cov}}} \left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_i^1(m),{\boldsymbol{r}}_j^2(m)} \right) = \frac{{\left| {\displaystyle\sum \limits_{m = 1}^M {\boldsymbol{r}}_i^1(m){{\left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_j^2(m)} \right)^{\mathrm{T}}} }} \right|}}{{\sqrt {\displaystyle\sum \limits_{m = 1}^M {{\left( {\boldsymbol{{r}}_i^1(m)} \right)}^2}} \sqrt {\displaystyle \sum \limits_{m = 1}^M {{\left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_j^2(m)} \right)}^2}} }},\quad 1 \le i,j \le P $ $ {{\mathrm{cov}}} \left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_i^1(m),{\boldsymbol{r}}_j^2(m)} \right) $为$ {c_{ij}} $,得到相关矩阵C 3. 迭代进行目标的关联问题的求解,直至当前值不满足阈值$ \delta = 0.55 $ (1) 获取$ {c_{ij}} $,当$ {c_{ij}} > \delta $继续,否则输出i, j $ \begin{aligned} (i,j) =\;& \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_{i,j}\; {c_{ij}} \\ =\;& \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{i,j}\; ({\boldsymbol{C}}),{\text{ }}i,j \in 1,2, \cdots ,P \\ \end{aligned} $ (2) 去除C中i行j列数据,并进行记录,返回(1) 表 1 UWB测距模块测距定位结果(m)
Table 1. UWB ranging module ranging and positioning results (m)
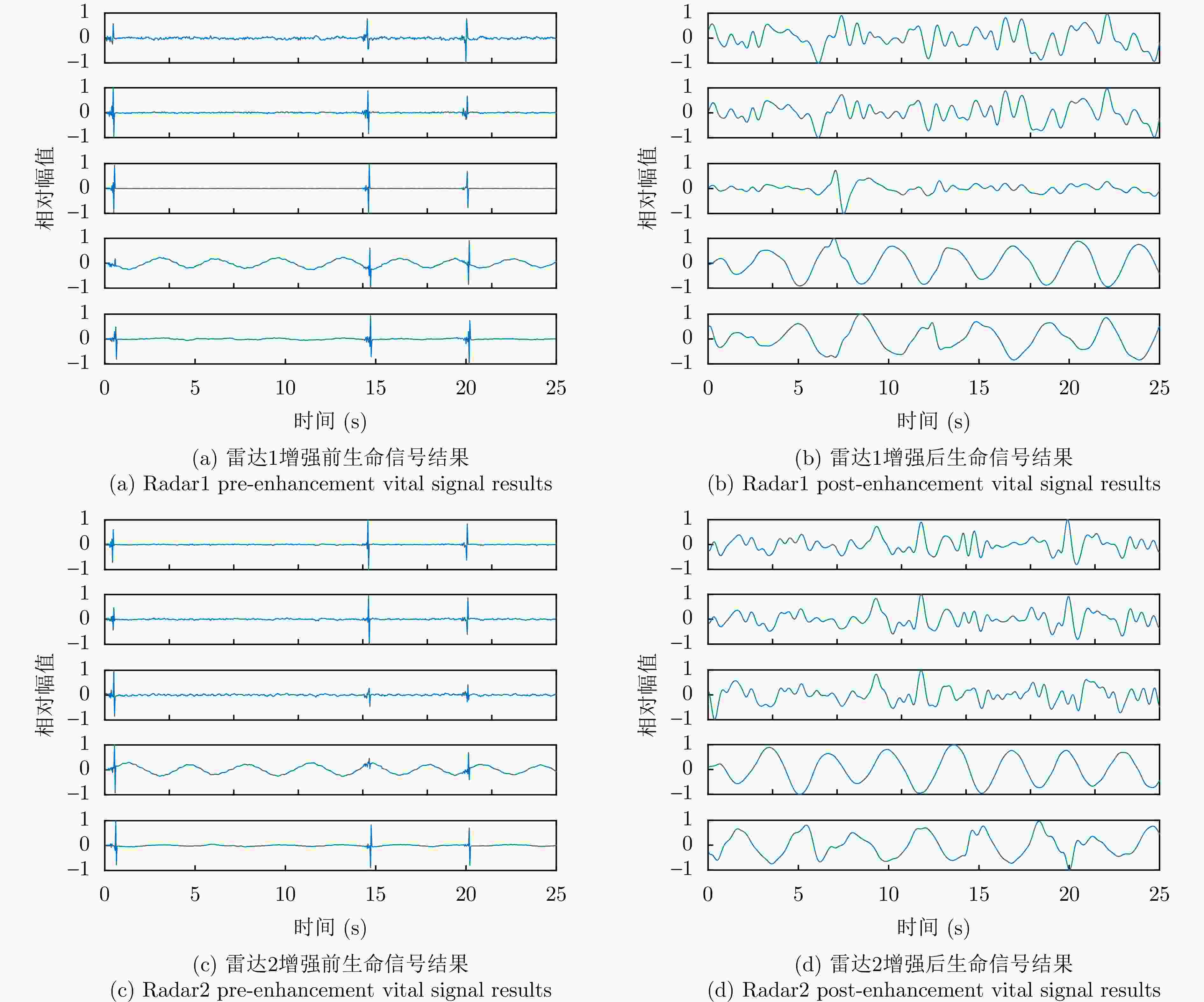
类别 真实距离 测量距离 误差值 标签1 1.56 1.55 0.01 标签2 1.56 1.56 0 坐标中Xa 1.50 1.55 –0.05 坐标中Ya 0 –0.05 0.05 表 2 仿真实验信号增强前后相同目标相关性对比
Table 2. Comparison of correlation between the same target before and after signal enhancement in simulation experiments
类别 增强前 增强后 增强百分比(%) 目标1 0.78 0.98 25.6 目标2 0.65 0.91 40.0 表 3 不同信噪比下的定位结果误差(m)
Table 3. The error of localization of results under different SNRs (m)
类别 –10 dB –8 dB –6 dB –4 dB –2 dB 0 dB 2 dB 4 dB 6 dB 8 dB 10 dB 12 dB 14 dB 目标1 0.08 0.08 0.05 0.09 0.05 0.07 0.09 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.09 0.10 0.07 目标2 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.10 0.08 0.14 0.15 0.10 0.14 0.10 0.12 0.10 0.10 表 4 实验1中两通道相同目标增强前后相关性
Table 4. In the experiment1 the correlation before and after enhancement of the same target in both channels
类别 增强前 增强后 增强百分比(%) 目标1 0.49 0.69 40.8 目标2 0.41 0.61 48.8 目标3 0.32 0.56 75.0 表 5 不同算法的运行时间、定位结果和平均定位精度对比
Table 5. Comparison of running time, localization results and average localization accuracy of different algorithms
表 6 实验2两通道中相同目标增强前后相关性
Table 6. Correlation before and after enhancement of the same target in both channels in experiment2
类别 增强前 增强后 增强百分比(%) 目标1 0.59 0.79 33.9 目标2 0.50 0.71 42.0 表 7 双目标定位结果示意表(m)
Table 7. The table of results of dual-targeting (m)
类别 真实坐标 定位坐标 定位误差 目标1 (–1.00, 7.00) (–1.08, 6.90) 0.13 目标2 (1.00, 5.00) (0.96, 5.06) 0.07 -
[1] 杨望笑, 窦银科, 稂时楠, 等. 基于改进剥层法的南极冰盖密度反演算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210410.YANG Wangxiao, DOU Yinke, LANG Shinan, et al. Antarctic ice sheet density inversion algorithm based on improved layer stripping method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210410. [2] 金添, 宋勇平. 穿墙雷达人体目标探测技术综述[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804.JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Review on human target detection using through-wall radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804. [3] 刘新, 阎焜, 杨光耀, 等. UWB-MIMO穿墙雷达三维成像与运动补偿算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356.LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Study on 3D imaging and motion compensation algorithm for UWB-MIMO through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. [4] YAN Kun, WU Shiyou, and FANG Guangyou. Detection of quasi-static trapped human being using mono-static UWB life-detection radar[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(7): 3129. doi: 10.3390/app11073129. [5] LIANG Xiao, PAN Jun, ZHENG Zhijie, et al. Enhancement of vital signals for UWB through-wall radar using nonconvex regularization[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 14(4): 392–401. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2023.2204197. [6] HARIKESH, CHAUHAN S S, BASU A, et al. Through the wall human subject localization and respiration rate detection using multichannel Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(2): 1510–1518. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3016755. [7] PAN Jun, YE Shengbo, NI Zhikang, et al. Enhancement of vital signals based on low-rank, sparse representation for UWB through-wall radar[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 13(1): 98–106. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2021.1995069. [8] ROHMAN B P A, ANDRA M B, and NISHIMOTO M. Through-the-wall human respiration detection using UWB impulse radar on hovering drone[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6572–6584. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3087668. [9] XU Yanyun, DAI Shun, WU Shiyou, et al. Vital sign detection method based on multiple higher order cumulant for Ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1254–1265. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164928. [10] 刘新, 朱海滨, 刘宗强, 等. 分布式无线组网超宽带穿墙雷达系统设计与联合定位[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 747–760. doi: 10.12000/JR23239.LIU Xin, ZHU Haibin, LIU Zongqiang, et al. The design and joint positioning method of an ultra-wideband through-wall radar system for distributed wireless networking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 747–760. doi: 10.12000/JR23239. [11] 史城, 叶盛波, 潘俊, 等. 一种基于分布式穿墙雷达的复杂条件下人体目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203.SHI Cheng, YE Shengbo, PAN Jun, et al. A human target detection method under complex conditions by distributed through-wall radar system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203. [12] ZHANG Yang, CHEN Fuming, XUE Huijun, et al. Detection and identification of multiple stationary human targets via bio-radar based on the cross-correlation method[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(11): 1793. doi: 10.3390/s16111793. [13] KOCUR D, ŠVECOVÁ M, and ROVŇÁKOVÁ J. Through-the-wall localization of a moving target by two independent ultra wideband (UWB) radar systems[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(9): 11969–11997. doi: 10.3390/s130911969. [14] JIA Yong, GUO Yong, YAN Chao, et al. Detection and localization for multiple stationary human targets based on cross-correlation of dual-station SFCW radars[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(12): 1428. doi: 10.3390/rs11121428. [15] NAHAR S, PHAN T, QUAIYUM F, et al. An electromagnetic model of human vital signs detection and its experimental validation[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2018, 8(2): 338–349. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2018.2811339. [16] ZETIK R, CRABBE S, KRAJNAK J, et al. Detection and localization of persons behind obstacles using M-sequence through-the-wall radar[C]. Conference on Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence, Orlando (Kissimmee), USA, 2006: 62010I. doi: 10.1117/12.667989. [17] XU Yanyun, WU Shiyou, CHEN Chao, et al. A novel method for automatic detection of trapped victims by ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3132–3142. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2178248. [18] 肖强, 曾庆宁, 王瑶, 等. 基于MGSC与改进维纳滤波的麦克风阵列语音增强[J]. 声学技术, 2017, 36(6): 567–573. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2017.06.012.XIAO Qiang, ZENG Qingning, WANG Yao, et al. Speech enhancement of microphone array based on MGSC and improved Wiener filter[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2017, 36(6): 567–573. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2017.06.012. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
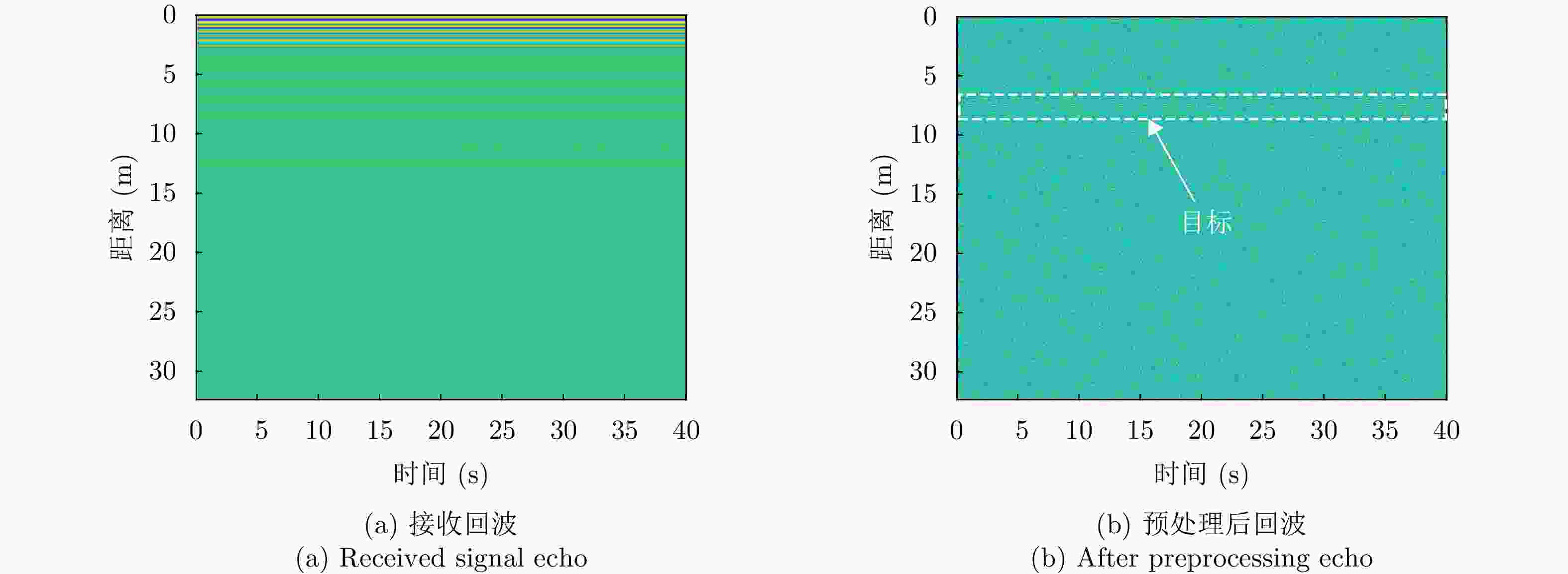
 下载:
下载: