Space-time Two-dimensional Clutter Suppression Method Based on Subarray Beam Pattern Design
-
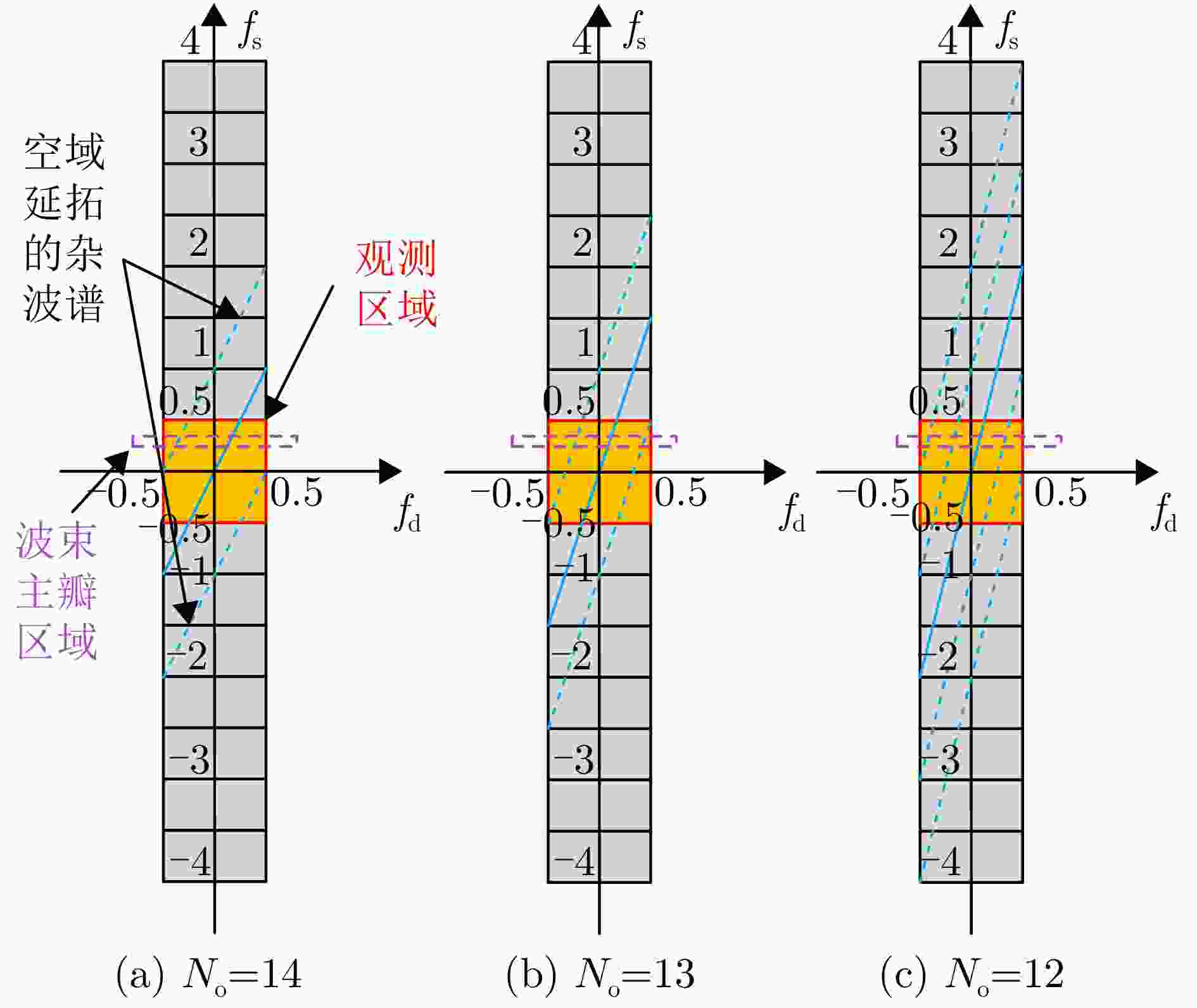
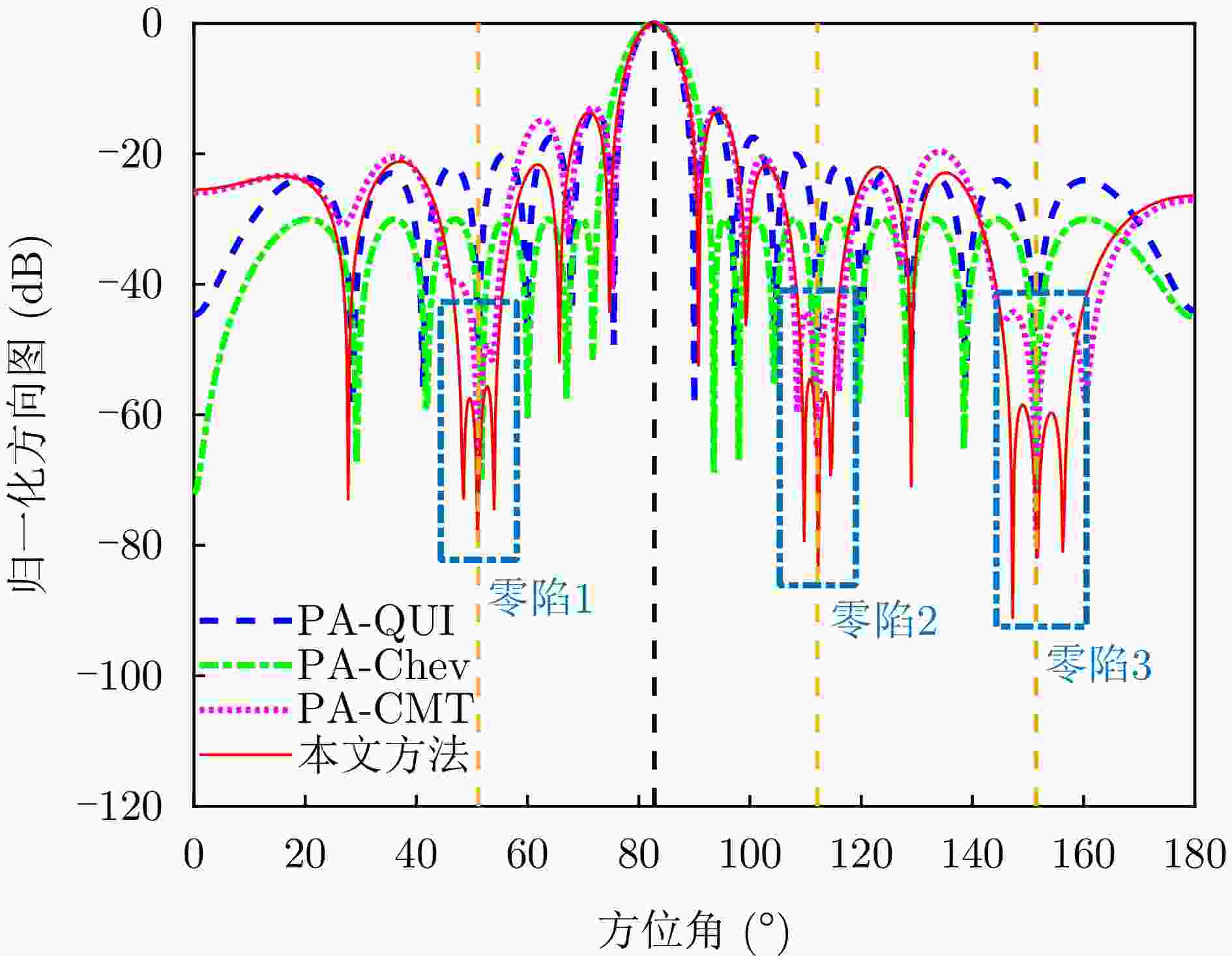
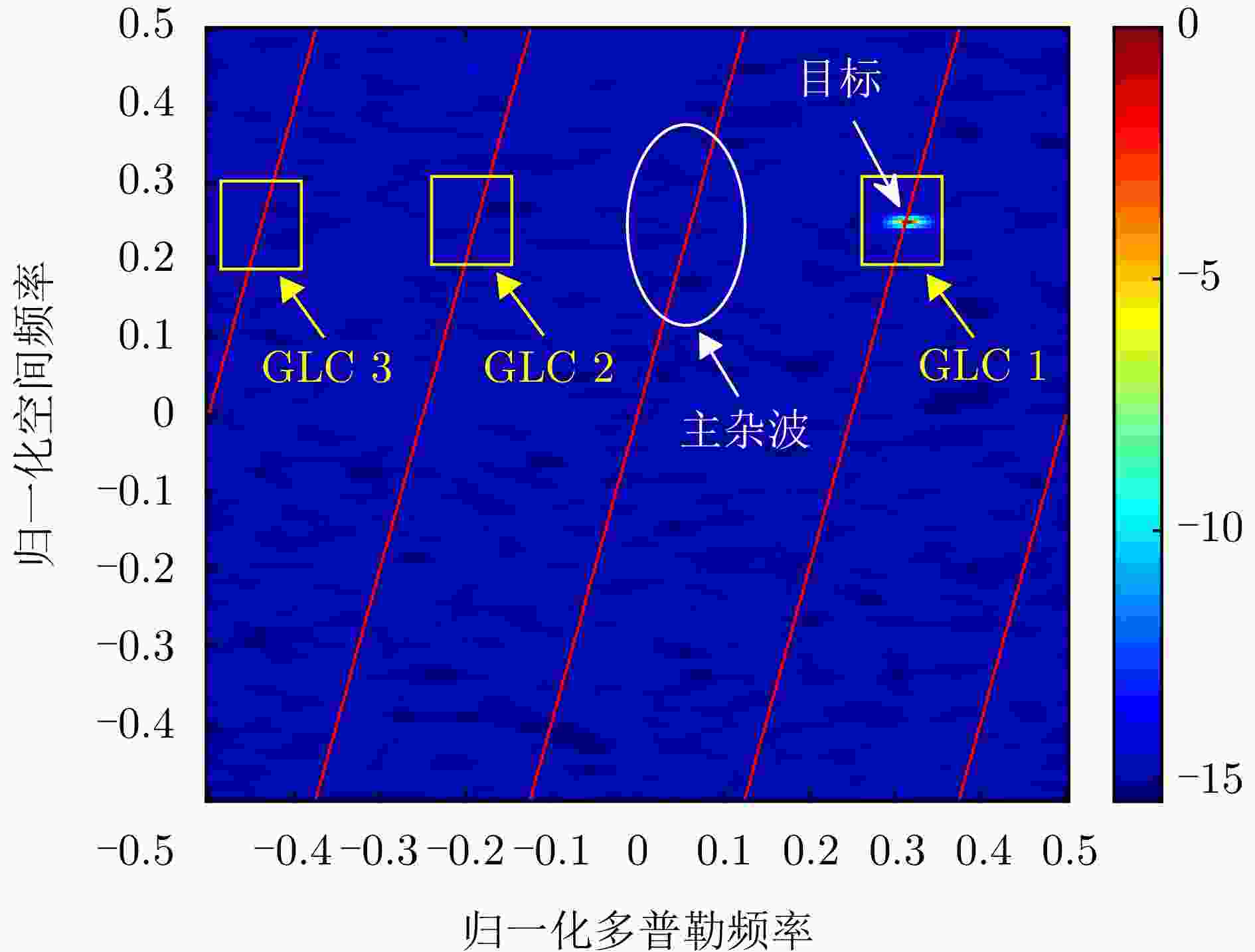
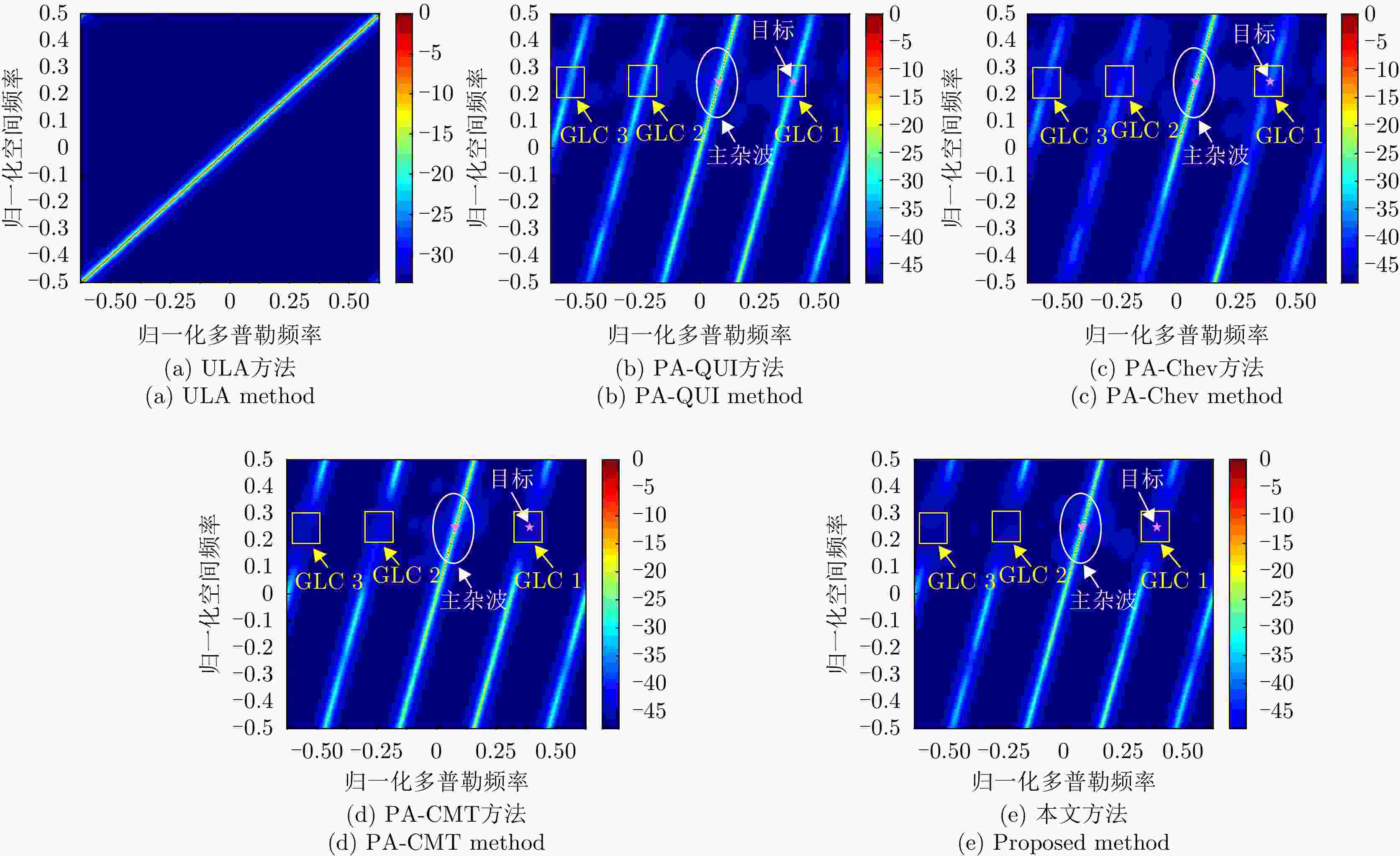
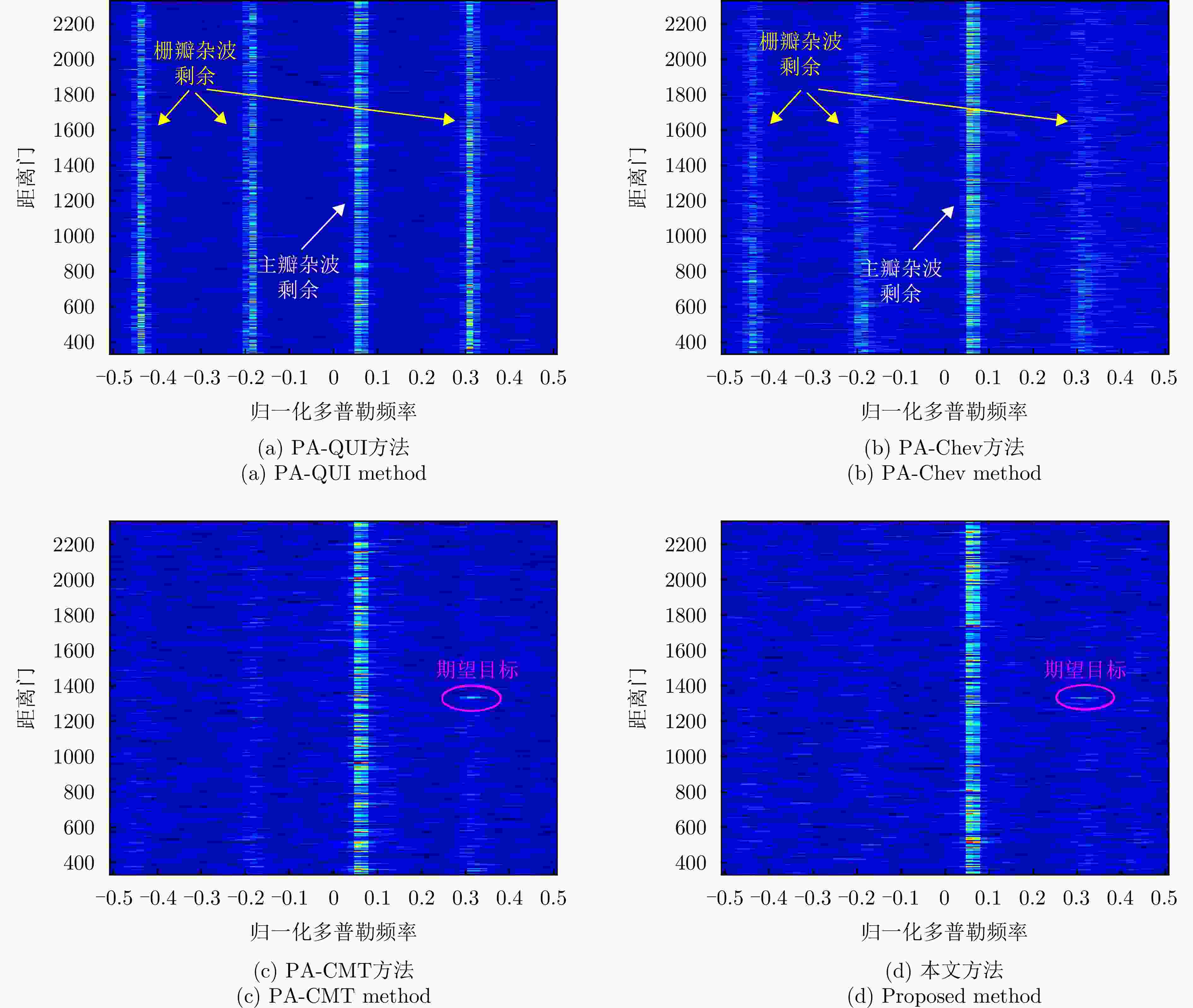
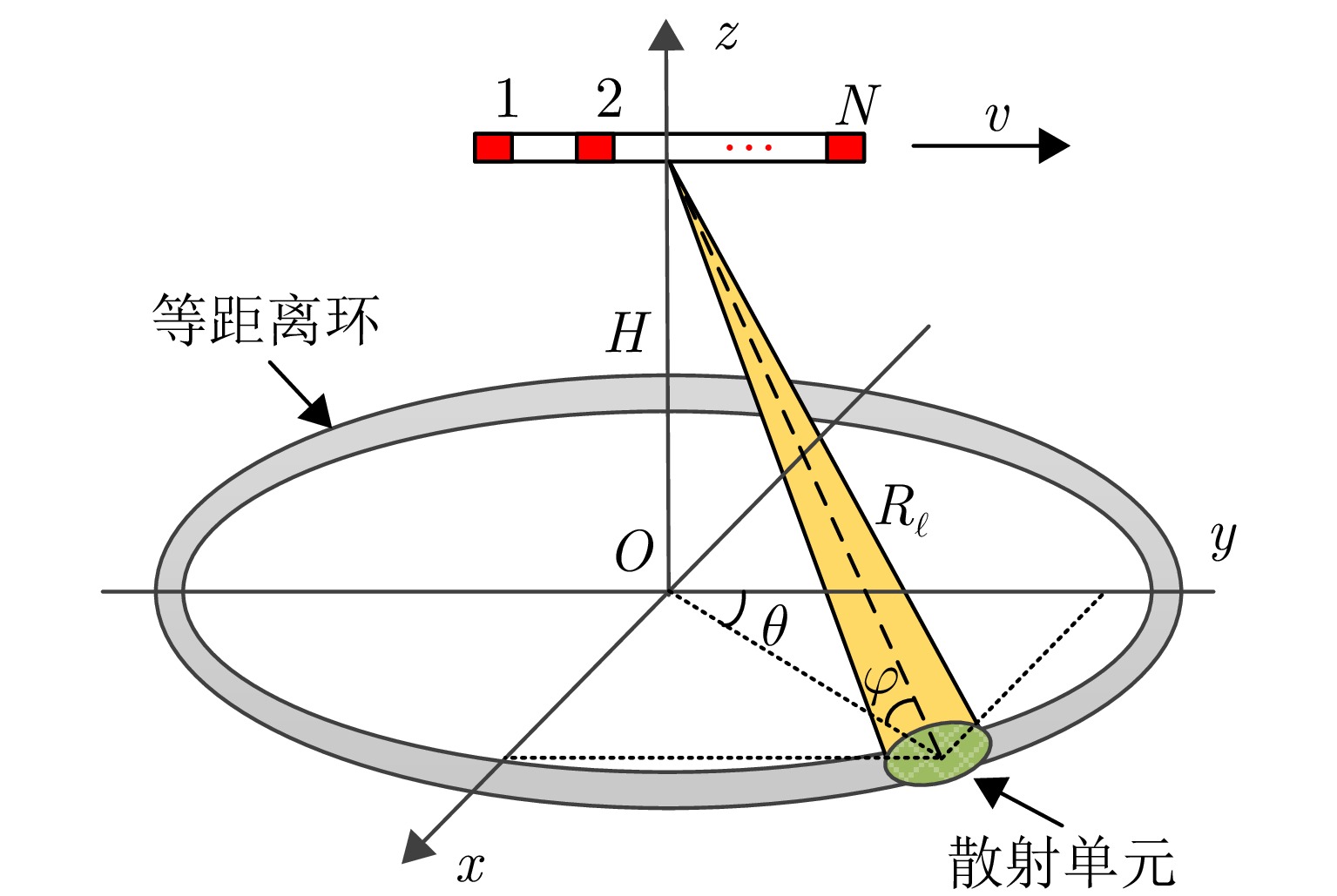
摘要: 机载雷达接收端采用子阵处理时面临栅瓣杂波导致的复杂空时耦合分布,使主瓣波束方向存在多个由栅瓣杂波导致的检测性能凹口,目标检测性能恶化严重。针对此问题,该文首先分析了子阵处理中栅瓣杂波空时谱分布特性,并在此基础上提出了基于接收子阵波束设计的空时二维杂波抑制方法。该方法采用重叠子阵构型方案,通过子阵方向图设计形成在子阵间栅瓣区域处的宽凹口,实现对子阵间栅瓣区域杂波的预滤波。进一步构建子阵级空时处理器,由于栅瓣杂波已经在子阵内完成预滤波,避免了栅瓣杂波在空时二维平面上的耦合扩散,从而提高了杂波抑制和动目标检测性能。仿真结果表明,所提方法显著改善了栅瓣杂波区的输出信杂噪比损失性能。Abstract: Airborne radar receivers that utilize subarray processing face challenges owing to the complex space-time coupling distribution caused by grating-lobe clutter. This results in multiple performance notches in the main beam, which severely affects target detection performance. To address this issue, we analyze the characteristics of grating-lobe clutter distribution in subarray processing and propose an approach for space-time clutter suppression based on the design of a receiving subarray beam pattern. Our approach leverages an overlapping subarray scheme to form wide nulls in the regions between subarrays where grating-lobe clutter is prevalent through beam pattern design. This design facilitates grating-lobe clutter pre-filtering between subarrays. Furthermore, we develop a subarray-level space-time processor that avoids the grating-lobe clutter coupling diffusion in the space-time two-dimensional plane by performing clutter pre-filtering within each subarray. This strategy enhances clutter suppression and moving-target-detection capabilities. Simulation results verify that the proposed method can remarkably improve the output signal to clutter plus noise ratio loss performance in grating-lobe clutter regions.
-
表 1 雷达系统仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of radar system
参数 数值 参数 数值 阵元总数 52 子阵数 10 子阵内阵元数 16 重叠阵元数 12 脉冲数 16 工作载频 1.2 GHz 波长 0.25 m 脉冲重频 2 kHz 信号带宽 5 MHz 平台高度 10 km 平台速度 125 m/s 目标方位角 82.79° 目标俯仰角 4.99° 目标斜距 115 km 空间频率展宽 0.1 多普勒滤波器带宽 0.06 幅度误差 0.03 相位误差 3° 信噪比 –5 dB 杂噪比 50 dB -
[1] BRENNAN L, MALLETT J, and REED I. Adaptive arrays in airborne MTI radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1976, 24(5): 607–615. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1976.1141412. [2] 谢文冲, 王永良, 熊元燚. 机载雷达空时自适应处理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2024: 86–95.XIE Wenchong, WANG Yongliang, and XIONG Yuanyi. Space Time Adaptive Processing Technique for Airborne Radar[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2024: 86–95. [3] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, and SO H C. Space-time adaptive processing with vertical frequency diverse array for range-ambiguous clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5352–5364. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2561308. [4] WEN Cai, HUANG Yan, PENG Jinye, et al. Slow-time FDA-MIMO technique with application to STAP radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 74–95. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098100. [5] SONG Di, FENG Qi, CHEN Shengyao, et al. Space-time adaptive processing using deep neural network-based shrinkage algorithm under small training samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9697–9703. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3255840. [6] 阚庆云, 许京伟, 廖桂生. 和差天线空时自适应测角方法及性能分析[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(1): 42–49. doi: 10.12263/DZXB. 20211458.KAN Qingyun, XU Jingwei, and LIAO Guisheng. Angle estimation approach and performance analysis for STAP with sum-difference antenna[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(1): 42–49. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211458. [7] XIE Lei, HE Zishu, TONG Jun, et al. A recursive angle-Doppler channel selection method for reduced-dimension space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(5): 3985–4000. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2983533. [8] HUANG Penghui, ZOU Zihao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A novel dimension-reduced space-time adaptive processing algorithm for spaceborne multichannel surveillance radar systems based on spatial-temporal 2-D sliding window[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5109721. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3144668. [9] GOLDSTEIN J S and REED I S. Reduced-rank adaptive filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(2): 492–496. doi: 10.1109/78.554317. [10] HERD J S and CONWAY M D. The evolution to modern phased array architectures[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(3): 519–529. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2494879. [11] HE Xiongpeng, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Range ambiguous clutter suppression approach with elevation time diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 359–373. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3101786. [12] ZHANG Tianfu, WANG Zhihao, XING Mengdao, et al. Research on multi-domain dimensionality reduction joint adaptive processing method for range ambiguous clutter of FDA-Phase-MIMO space-based early warning radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(21): 5536. doi: 10.3390/rs14215536. [13] LI Yuanshuai, CHANG Shaoqiang, LIU Zihao, et al. Range ambiguity suppression under high-resolution estimation using the MUSIC-AP algorithm for pulse-Doppler radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2024, 214: 109237. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109237. [14] WU Yong, TANG Jun, and PENG Yingning. On the essence of knowledge-aided clutter covariance estimate and its convergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 569–585. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705692. [15] WANG Degen, WANG Tong, CUI Wenchen, et al. A clutter suppression algorithm via enhanced sparse Bayesian learning for airborne radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(10): 10900–10911. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3263919. [16] VARADARAJAN V and KROLIK J L. Joint space-time interpolation for distorted linear and bistatic array geometries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 848–860. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862941. [17] WANG Yongliang, DUAN Keqing, and XIE Wenchong. Cross beam STAP for nonstationary clutter suppression in airborne radar[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 2013: 276310. doi: 10.1155/2013/276310. [18] MAILLOUX R J, SANTARELLI S G, ROBERTS T M, et al. Irregular polyomino-shaped subarrays for space-based active arrays[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 2009: 956524. doi: 10.1155/2009/956524. [19] 黄飞, 盛卫星, 马晓峰. 随机错位子阵阵列天线及其优化设计[J]. 电波科学学报, 2008, 23(5): 917–921. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.05.023.HUANG Fei, SHENG Weixing, and MA Xiaofeng. Plane antenna arrays with randomly staggered subarrays and its optimal design[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2008, 23(5): 917–921. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.05.023. [20] XIONG Ziyuan, XU Zhenhai, CHEN Siwei, et al. Subarray partition in array antenna based on the algorithm X[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2013, 12: 906–909. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2013.2272793. [21] KARADEMIR S, PROKOPYEV O A, and MAILLOUX R J. Irregular polyomino tiling via integer programming with application in phased array antenna design[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 2016, 65(2): 137–173. doi: 10.1007/s10898-015-0354-8. [22] DONG Wei, XU Zhenhai, LIU Xinghua, et al. Irregular subarray tiling via heuristic iterative convex relaxation programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(4): 2842–2852. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2955070. [23] ROCCA P, ANSELMI N, POLO A, et al. An irregular two-sizes square tiling method for the design of isophoric phased arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(6): 4437–4449. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2970088. [24] ZHOU Jian, WANG Yiqing, WANG Zhangling, et al. Irregular subarray tiling via rotational symmetry[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2023, 22(4): 903–907. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3228108. [25] MA Yankai, YANG Shiwen, CHEN Yikai, et al. High-directivity optimization technique for irregular arrays combined with maximum entropy model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(7): 3913–3923. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3044653. [26] YANG Feng, MA Yankai, LONG Weijun, et al. Synthesis of irregular phased arrays subject to constraint on directivity via convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(7): 4235–4240. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3044632. [27] JIANG Hailing, GONG Yu, ZHANG Junyi, et al. Irregular modular subarrayed phased array tiling by algorithm X and differential evolution algorithm[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2023, 22(7): 1532–1536. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2023.3250260. [28] TOYAMA N. Optimization of aperiodic array patterns using GA and SDA[C]. 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, USA, 2005: 69–72. doi: 10.1109/APS.2005.1551737. [29] WANG Hao, FANG Dagang, and CHOW Y L. Grating lobe reduction in a phased array of limited scanning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(6): 1581–1586. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.923354. [30] 程乃平, 潘点飞. 大型阵列天线子阵划分及栅瓣抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2014, 30(5): 535–543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2014.05.007.CHENG Naiping and PAN Dianfei. Subarray partition method and grating lobe suppression for large array antenna[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2014, 30(5): 535–543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2014.05.007. [31] KRIVOSHEEV Y V, SHISHLOV A V, and DENISENKO V V. Grating lobe suppression in aperiodic phased array antennas composed of periodic subarrays with large element spacing[J]. IEEE Antennas and propagation Magazine, 2015, 57(1): 76–85. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2015.2397155. [32] XU Xiaomin, LIAO Cheng, ZHOU Liang, et al. Grating lobe suppression of non-uniform arrays based on position gradient and sigmoid function[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 106407–106416. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932123. [33] YANG Gongqing, ZENG Hui, and XU Zhenhai. Adaptive gradient search algorithm for displaced subarrays with large element spacing[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(7): 1155–1159. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3074253. [34] ELAYAPERUMAL S and RAJAGOPAL S. Design of antenna array architecture with large inter element spacing and low grating lobes[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies, Bangalore, India, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CONECCT52877.2021.9622535. [35] LIU Zhixin, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Range-ambiguous clutter suppression for STAP-based radar with vertical coherent frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5106517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3291738. [36] GUERCI J R. Theory and application of covariance matrix tapers for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1999, 47(4): 977–985. doi: 10.1109/78.752596. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: