Sparse Reconstruction-based Direction of Arrival Estimation for MIMO Radar in the Presence of Unknown Mutual Coupling
-
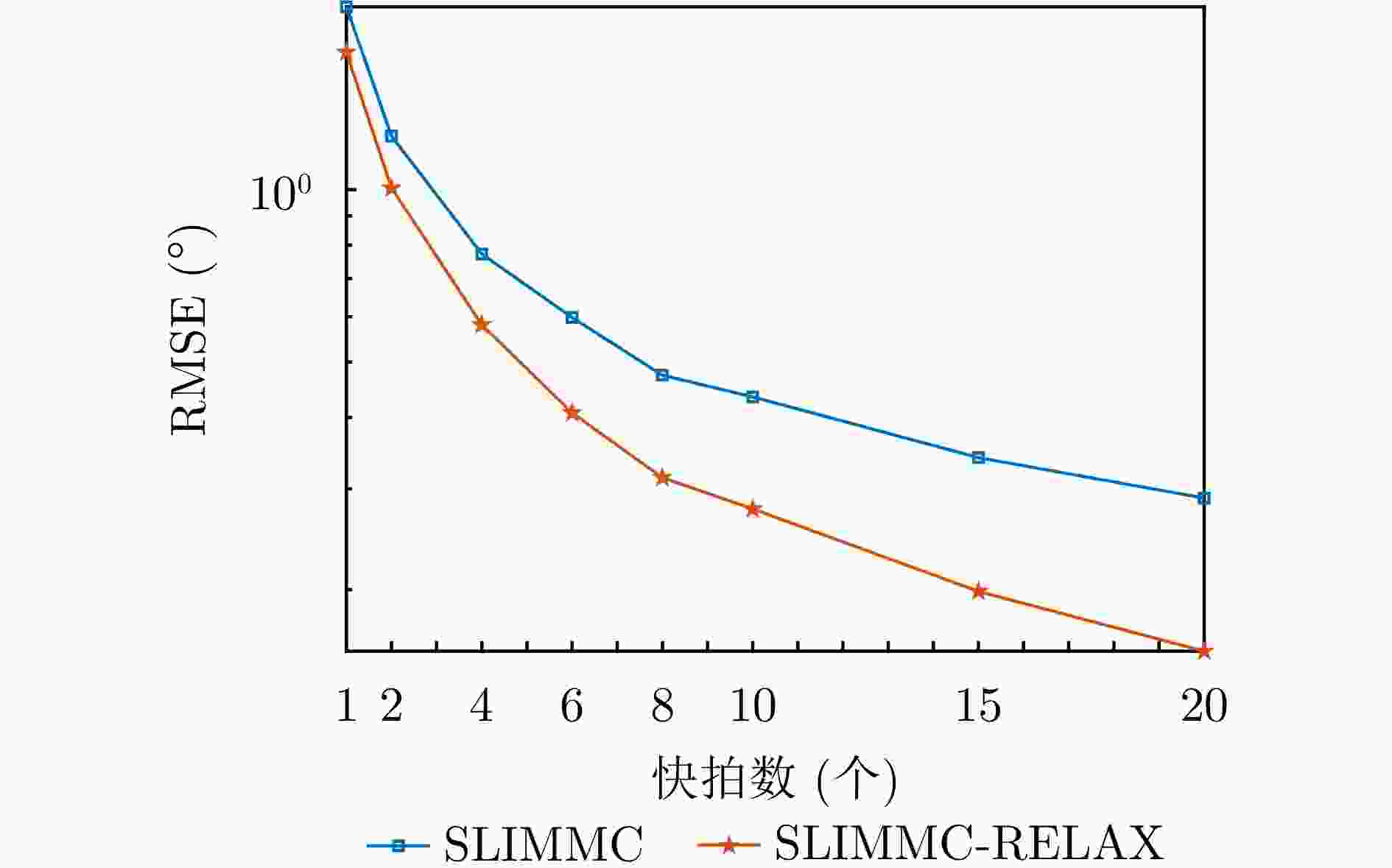
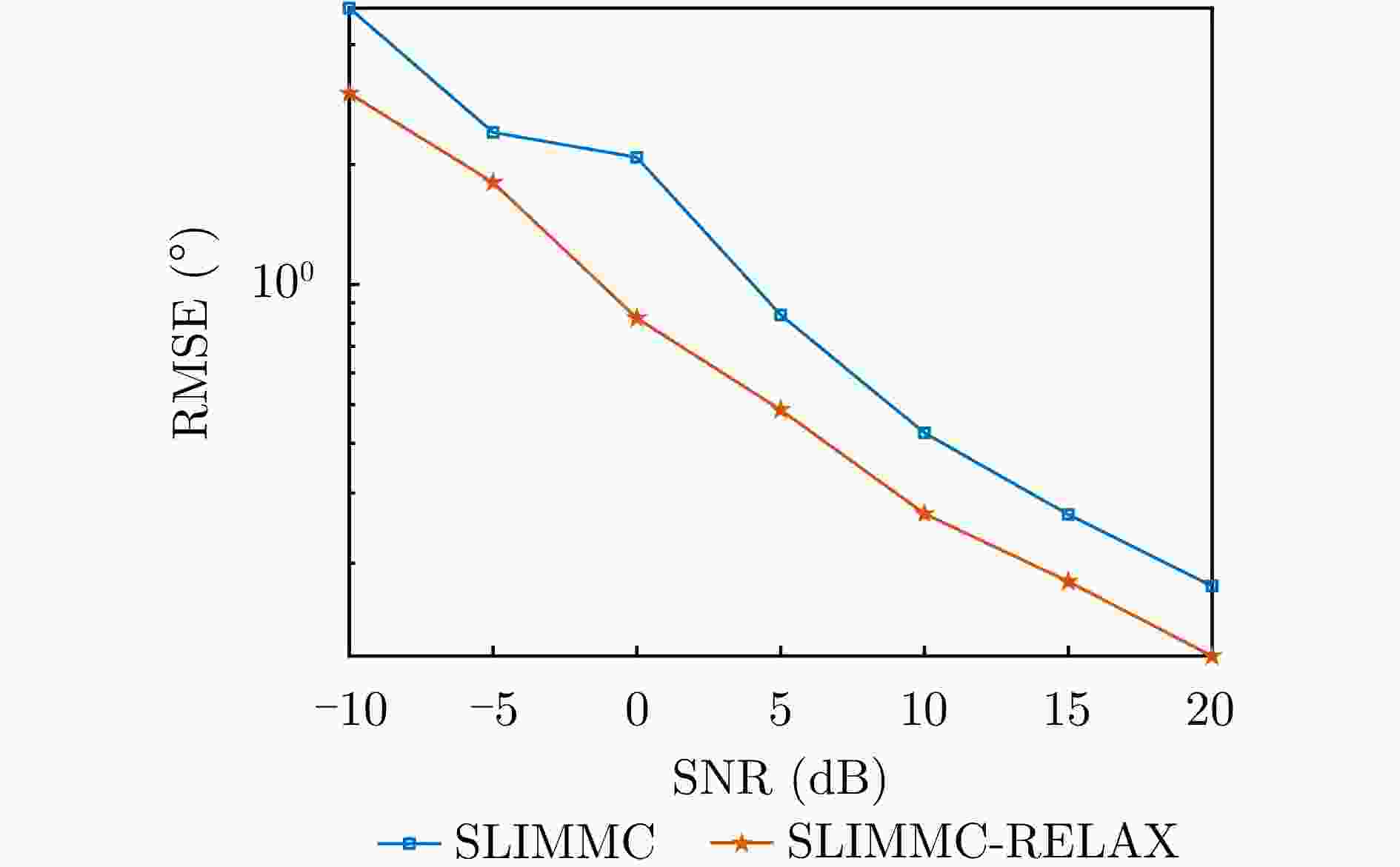
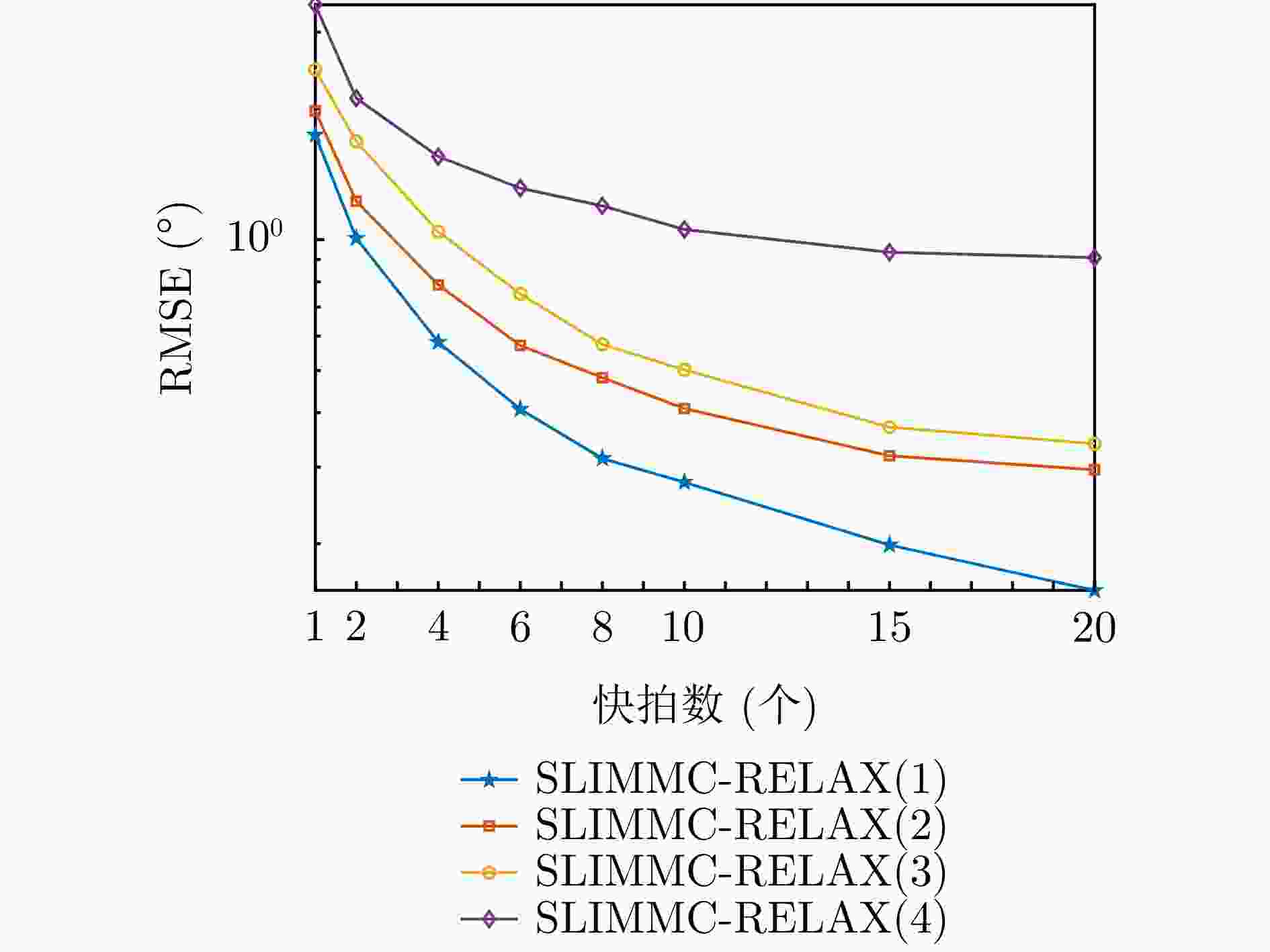
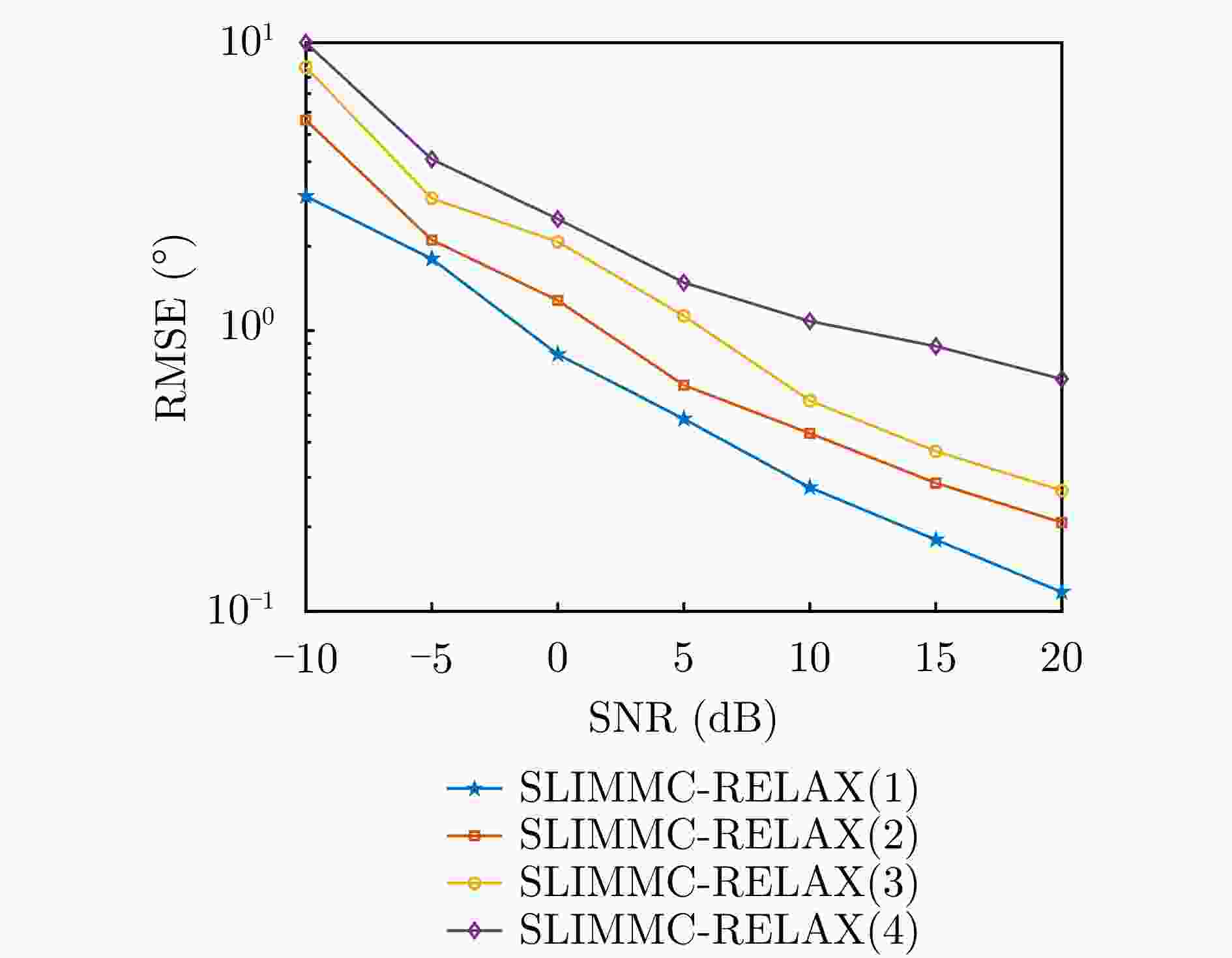
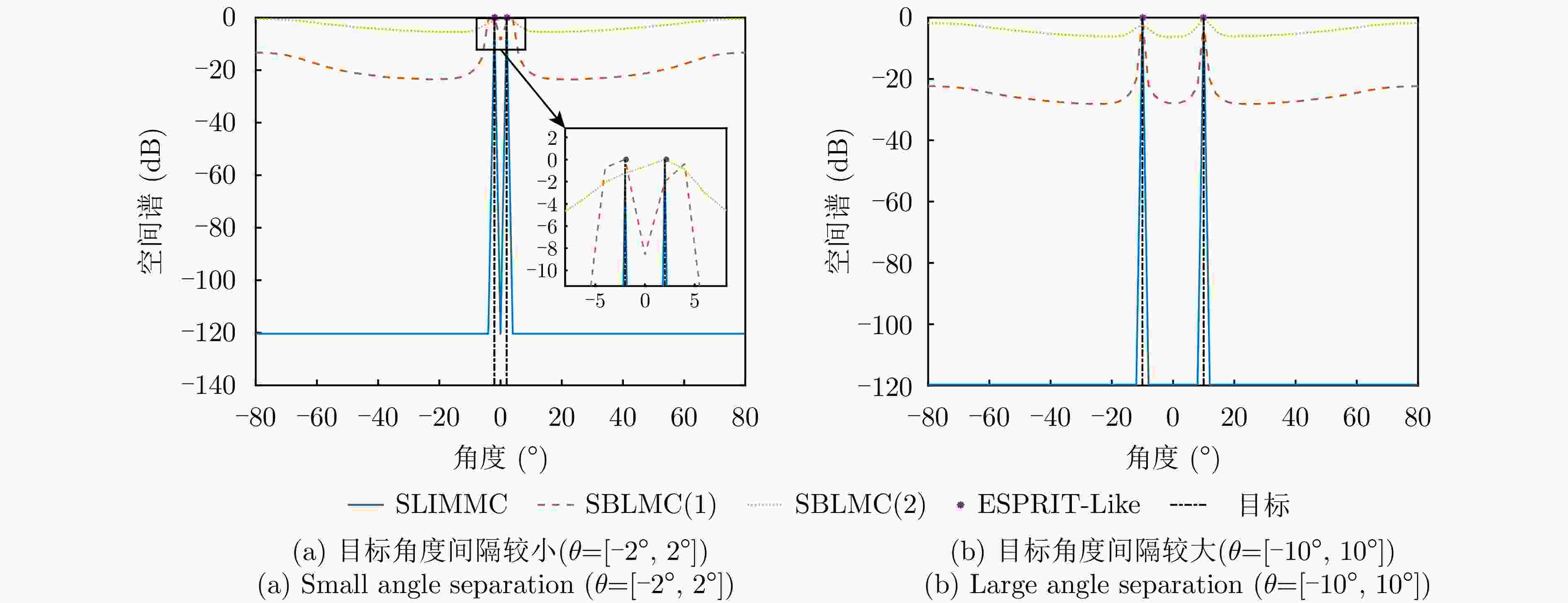
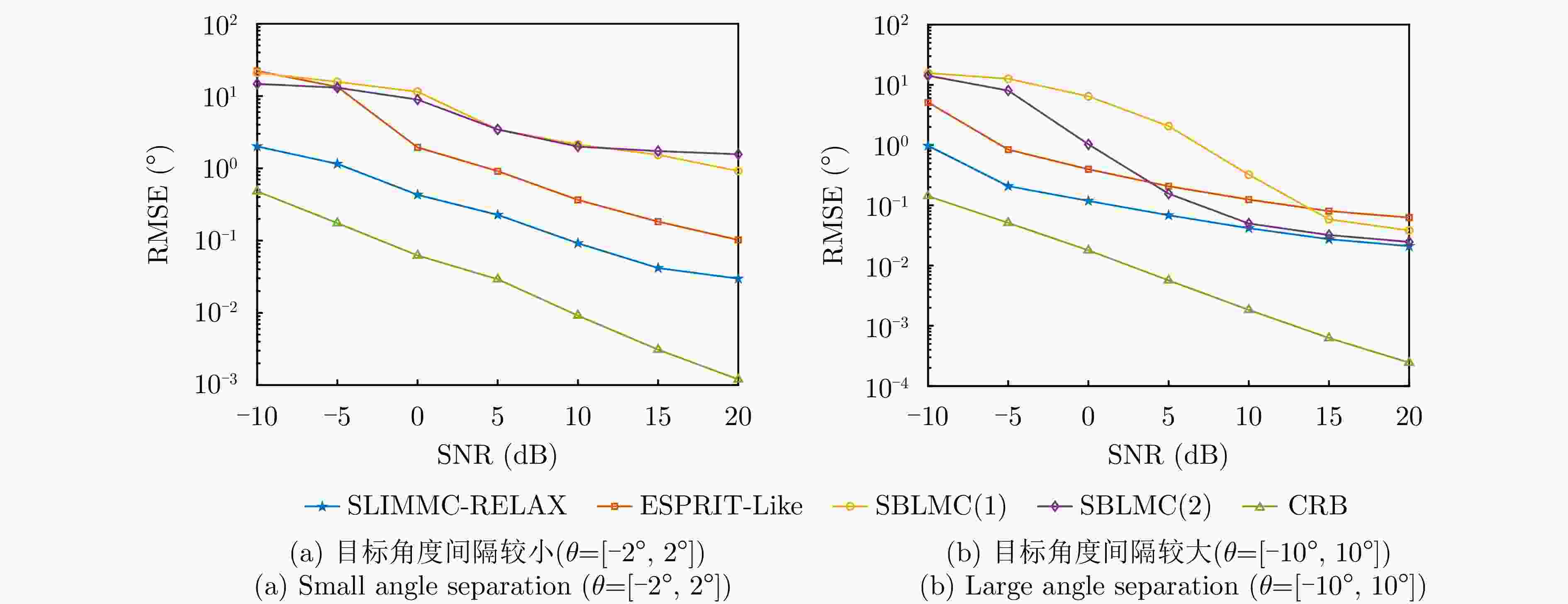
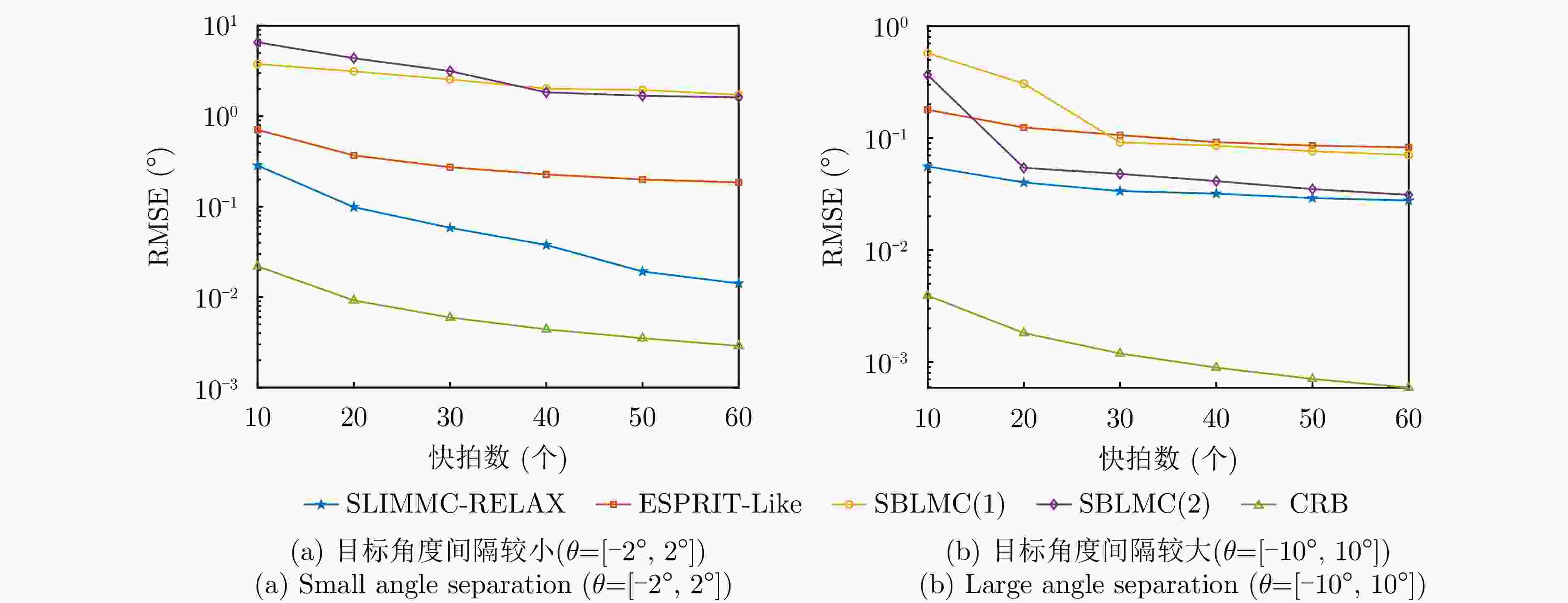
摘要: 为了降低阵列互耦对多输入多输出(MIMO)雷达波达角度(DOA)估计性能的影响,实现少量快拍条件下的目标角度估计,该文提出了基于迭代最小化稀疏学习(SLIM)算法的互耦校正和目标角度估计算法。所提算法利用目标回波信号的空域稀疏性,通过迭代优化算法估计了MIMO雷达发射和接收阵列的阵元互耦系数,以及目标稀疏空间谱。该算法无需设置超参数,且具有良好的收敛特性。仿真结果表明,当MIMO雷达发射和接收阵列存在互耦时,如果目标角度间隔较小,所提算法能够在较高信噪比条件下基于少量快拍高精度地估计目标角度;如果目标角度间隔较大,则在较低信噪比和少量快拍条件下仍有较高的角度估计精度。
-
关键词:
- MIMO雷达 /
- 波达角度估计 /
- 阵列互耦 /
- 迭代最小化稀疏学习算法 /
- 少量快拍
Abstract: To improve the accuracy of Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation in Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radar systems under unknown mutual coupling, we propose a mutual coupling calibration and DOA estimation algorithm based on Sparse Learning via Iterative Minimization (SLIM). The proposed algorithm utilizes the spatial sparsity of target signals and estimates the spatial pseudo-spectra and the mutual coupling matrices of MIMO arrays through cyclic optimization. Moreover, it is hyperparameter-free and guarantees convergence. Numerical examples demonstrate that for MIMO radar systems under unknown mutual coupling conditions, the proposed algorithm can accurately estimate the DOA of targets with small angle separations and relatively high Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNRs), even with a limited number of samples. In addition, low DOA estimation errors are achieved for targets with large angle separations and small sample sizes, even under low-SNR conditions. -
1 RELAX算法
1. RELAX algorithm
输入:$\hat K$, ${\text{\{}}{\hat \theta _k}{\text{\} }}_{k = 1}^{\hat K}$, ${\text{\{}}{\hat x_{k,l}}{\text{\} }}_{k = 1,l = 1}^{\hat K,L}$ 输出:${\text{\{}}{\hat \theta _k}{\text{\} }}$ $\hat K$:SLIMMC算法得到的目标个数 ${\text{\{}}{\hat \theta _k}{\text{\} }}_{k = 1}^{\hat K}$:SLIMMC算法得到的目标角度 ${\text{\{}}{\hat x_{k,l}}{\text{\} }}_{k = 1,l = 1}^{\hat K,L}$:SLIMMC算法得到的目标回波 重复: for k = 1, 2, ···, $\hat K$ $ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde y}}_{k,l}} = {{\boldsymbol{y}}_l} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1,i \ne k}^{\hat K} {{\boldsymbol{a}}{\text{(}}{{\hat \theta }_i}{\text{)}}} {\hat x_{i,l}}\;,\;\;\;\;l = 1,2, \cdots ,L $ $ {\hat \theta _k} = \mathop {{\text{argmax}}}\limits_{{\theta _k}} \displaystyle\sum\limits_{l = 1}^L {\bigr|{\boldsymbol{a}}_{}^{\text{H}}{\text{(}}{\theta _k}{\text{)}}{{{\boldsymbol{\tilde y}}}_{k,l}}{\bigr|^2}} $ $ {\hat x_{i,l}} = \dfrac{{{\boldsymbol{a}}_{}^{\text{H}}\left({{\hat \theta }_k}\right){{{\boldsymbol{\tilde y}}}_{k,l}}}}{{\left\|{\boldsymbol{a}}_{}^{\text{H}}\left({{\hat \theta }_k}\right) \right\|{^2}}}\;,\;\;\;\;l = 1,2, \cdots ,L $ end 直到收敛 表 1 非零互耦系数取值
Table 1. Nonzero mutual coupling coefficients setting
非零互耦系数
个数发射阵列非零
互耦系数接收阵列非零
互耦系数Kt=Kr=2 [1, –0.4+0.002j] [1, 0.4+0.1121j] Kt=Kr=3 [1, –0.4+0.002j, – 0.1046 –0.0566j][1, 0.4+0.1121j, 0.1383 +0.0708j]表 2 不同互耦效应下的非零互耦系数
Table 2. Different mutual coupling coefficients
参数组 发射阵列非零互耦系数 接收阵列非零互耦系数 1 [1, – 0.1346 –0.0566j][1, 0.1683 +0.0708j]2 [1, 0.1552 +0.2875j][1, – 0.2637 –0.1667j]3 [1, –0.45+0.002j] [1, 0.4+0.1121j] 4 [1, 0.3742 +0.5918j][1, – 0.6262 –0.3679j]表 3 SBLMC算法超参数
Table 3. Hyperparameters for the SBLMC algorithm
算法 超参数 SBLMC(1) a=b=c=d=e1=f1=e2=f2=10–2 SBLMC(2) a=b=c=d=e1=f1=e2=f2=1 表 4 算法计算复杂度和运行时间
Table 4. Computational complexity and running time for the three algorithms
算法 计算复杂度 运行时间(s) [–2°, 2°] [–10°, 10°] SLIMMC $ O{\text{(}}{J^3} + {N_{\text{t}}}{N_{\text{r}}}{J^2} + N_{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}N_{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}J + L{N_{\text{t}}}{N_{\text{r}}}J{\text{)}} $ 1.3744 1.2526 SBLMC(1) $ O{\text{(}}{J^3} + L{N_{\text{t}}}{N_{\text{r}}}{J^2} + N_{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}N_{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}J{\text{)}} $ 105.1702 123.9081 SBLMC(2) $ O{\text{(}}{J^3} + L{N_{\text{t}}}{N_{\text{r}}}{J^2} + N_{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}N_{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}J{\text{)}} $ 37.1674 37.4897 ESPRIT-Like $ \begin{gathered} O{\text{((}}N'_{\text{t}} N'_{\text{r}} + {N_{\text{t}}}{N_{\text{r}}}{\text{)}}N'_{\text{t}} N'_{\text{r}} L + {{\text{(}}N'_{\text{t}} N'_{\text{r}} {\text{)}}^3} \\ + 2{P^2}{\text{[(}}N'_{\text{t}} - 1{\text{)}}N'_{\text{r}} + {\text{(}}N'_{\text{r}}- 1{\text{)}}N'_{\text{t}} {\text{]}} + 12{P^3}{\text{)}} \\ \end{gathered} $ 0.0551 0.0629 -
[1] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO Radar Signal Processing[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2009. doi: 10.1002/9780470391488. [2] HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R, and CIMINI L. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448. [3] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812. [4] 何子述, 程子扬, 李军, 等. 集中式MIMO雷达研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128.HE Zishu, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. A survey of collocated MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128. [5] 张国鑫, 易伟, 孔令讲. 基于1比特量化的大规模MIMO雷达系统直接定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062.ZHANG Guoxin, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Direct position determination for massive MIMO system with one-bit quantization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062. [6] LI Da, TANG Bo, and XUE Lei. Multi-spectrally constrained low-PAPR waveform optimization for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 5097–5110. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3247976. [7] TANG Bo and STOICA P. MIMO multifunction RF systems: Detection performance and waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4381–4394. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3202315. [8] 吴文俊, 唐波, 汤俊, 等. 杂波环境中雷达通信一体化系统波形设计算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 570–580. doi: 10.12000/JR22105.WU Wenjun, TANG Bo, TANG Jun, et al. Waveform design for dual-function radar-communication systems in clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 570–580. doi: 10.12000/JR22105. [9] 杨婧, 余显祥, 沙明辉, 等. MIMO系统探通一体化信号矩阵设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 262–274. doi: 10.12000/JR22087.YANG Jing, YU Xianxiang, SHA Minghui, et al. Dual function radar and communication signal matrix design method for MIMO system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 262–274. doi: 10.12000/JR22087. [10] LIU Chunlin and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Super nested arrays: Linear sparse arrays with reduced mutual coupling—part I: Fundamentals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(15): 3997–4012. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2558159. [11] ZHENG Zhengzhi, WANG Wenqin, KONG Yangyang, et al. MISC array: A new sparse array design achieving increased degrees of freedom and reduced mutual coupling effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(7): 1728–1741. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2897954. [12] YAN Hangqi, WANG Yuexian, WANG Ling, et al. Design of nonredundant sparse planar arrays with reduced mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1272–1283. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3337216. [13] AMANI N, JANSEN F, FILIPPI A, et al. Sparse automotive MIMO radar for super-resolution single snapshot DOA estimation with mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 146822–146829. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3122967. [14] LIU Xiaoli and LIAO Guisheng. Direction finding and mutual coupling estimation for bistatic MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(2): 517–522. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.08.017. [15] ZHENG Zhidong, ZHANG Jin, and ZHANG Jianyun. Joint DOD and DOA estimation of bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of unknown mutual coupling[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(12): 3039–3048. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.06.013. [16] XU Yang and ZHENG Zhi. Joint DOD and DOA estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of unknown mutual coupling[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2023, 42(4): 2468–2479. doi: 10.1007/s00034-022-02201-5. [17] TIAN Ye, WANG Ran, CHEN Hua, et al. Real-valued DOA estimation utilizing enhanced covariance matrix with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(4): 912–916. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3148260. [18] 杨康, 文方青, 黄冬梅, 等. 基于实值三线性分解的互耦条件下双基地MIMO雷达角度估计算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 314–321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.12.YANG Kang, WEN Fangqing, HUANG Dongmei, et al. Real-value-based trilinear decomposition based direction estimation algorithm for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of mutual coupling[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 314–321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.12. [19] WANG Xianpeng, MENG Dandan, HUANG Mengxing, et al. Reweighted regularized sparse recovery for DOA estimation with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(2): 290–293. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2884457. [20] ROCCA P, HANNAN M A, SALUCCI M, et al. Single-snapshot DOA estimation in array antennas with mutual coupling through a multiscaling BCS strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(6): 3203–3213. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2684137. [21] HAWES M, MIHAYLOVA L, SEPTIER F, et al. Bayesian compressive sensing approaches for direction of arrival estimation with mutual coupling effects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(3): 1357–1368. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2655013. [22] CHEN Peng, CAO Zhenxin, CHEN Zhimin, et al. Off-grid DOA estimation using sparse Bayesian learning in MIMO radar with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(1): 208–220. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2881663. [23] FRIEDLANDER B and WEISS A J. Direction finding in the presence of mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1991, 39(3): 273–284. doi: 10.1109/8.76322. [24] ZHOU Jianxiong, ZHU Rongqiang, and LI Haorun. Mutual coupling compensation for compact MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(7): 6018–6023. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3161333. [25] ZHU Jingjing, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Adaptive detectors for FDA-MIMO radar with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 1437–1441. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3321555. [26] LIU Long, ZHANG Hu, LAN Lan, et al. Joint range and angle estimation by FDA-MIMO radar with unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 3669–3683. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3230383. [27] XU Luzhou, ZHAO Kexin, LI Jian, et al. Wideband source localization using sparse learning via iterative minimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(12): 3504–3514. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.04.005. [28] ZHANG Kun and SHUI Penglang. Estimation of complex high-resolution range profiles of ships by sparse recovery iterative minimization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3042–3056. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3068431. [29] WU Chaoyi, REN Jiaying, TAN F W, et al. Computationally efficient implementation of SLIM for parameter estimation in few-bit PMCW MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2023, 1: 339–352. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2023.3284297. [30] 张贤达. 矩阵分析与应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013.ZHANG Xianda. Matrix Analysis and Applications [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013. [31] WU Jinlong, WEN Fangqing, and SHI Junpeng. Direction finding in bistatic MIMO radar with direction-dependent mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(7): 2231–2234. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3072310. [32] LI Jian and STOICA P. Efficient mixed-spectrum estimation with applications to target feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(2): 281–295. doi: 10.1109/78.485924. [33] WU Chaoyi, ZHANG Tianyi, LI Jian, et al. Parameter estimation in PMCW MIMO radar systems with few-bit quantized observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 810–821. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3146790. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: