Deep Network for SAR Target Recognition Based on Attribute Scattering Center Convolutional Kernel Modulation(in English)
-
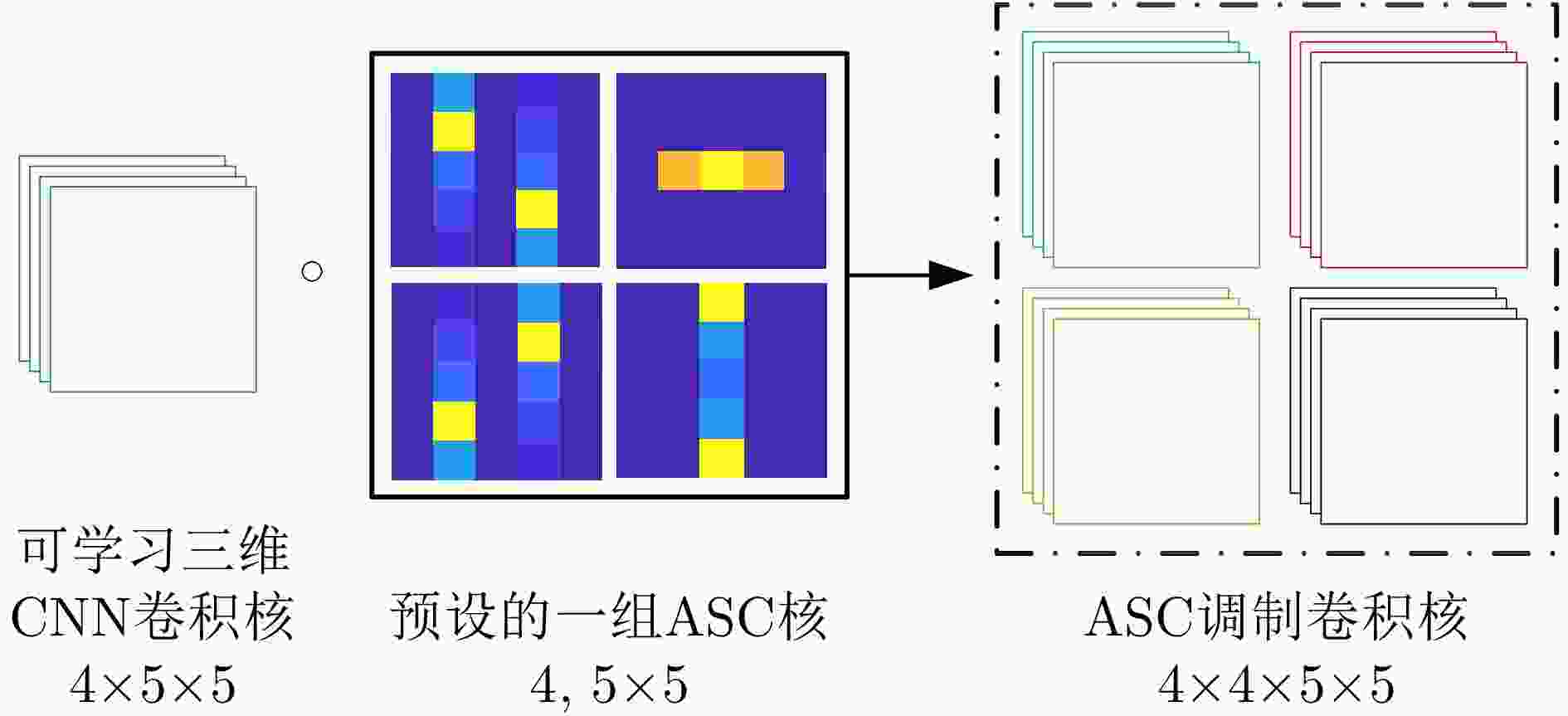
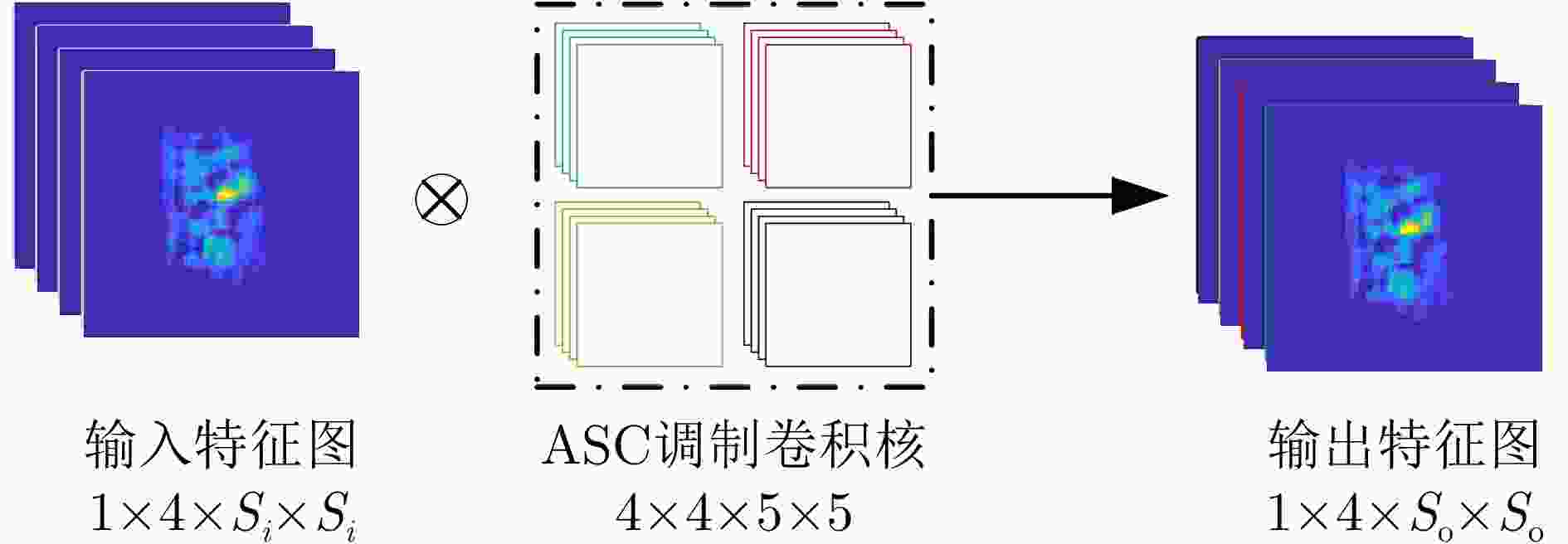
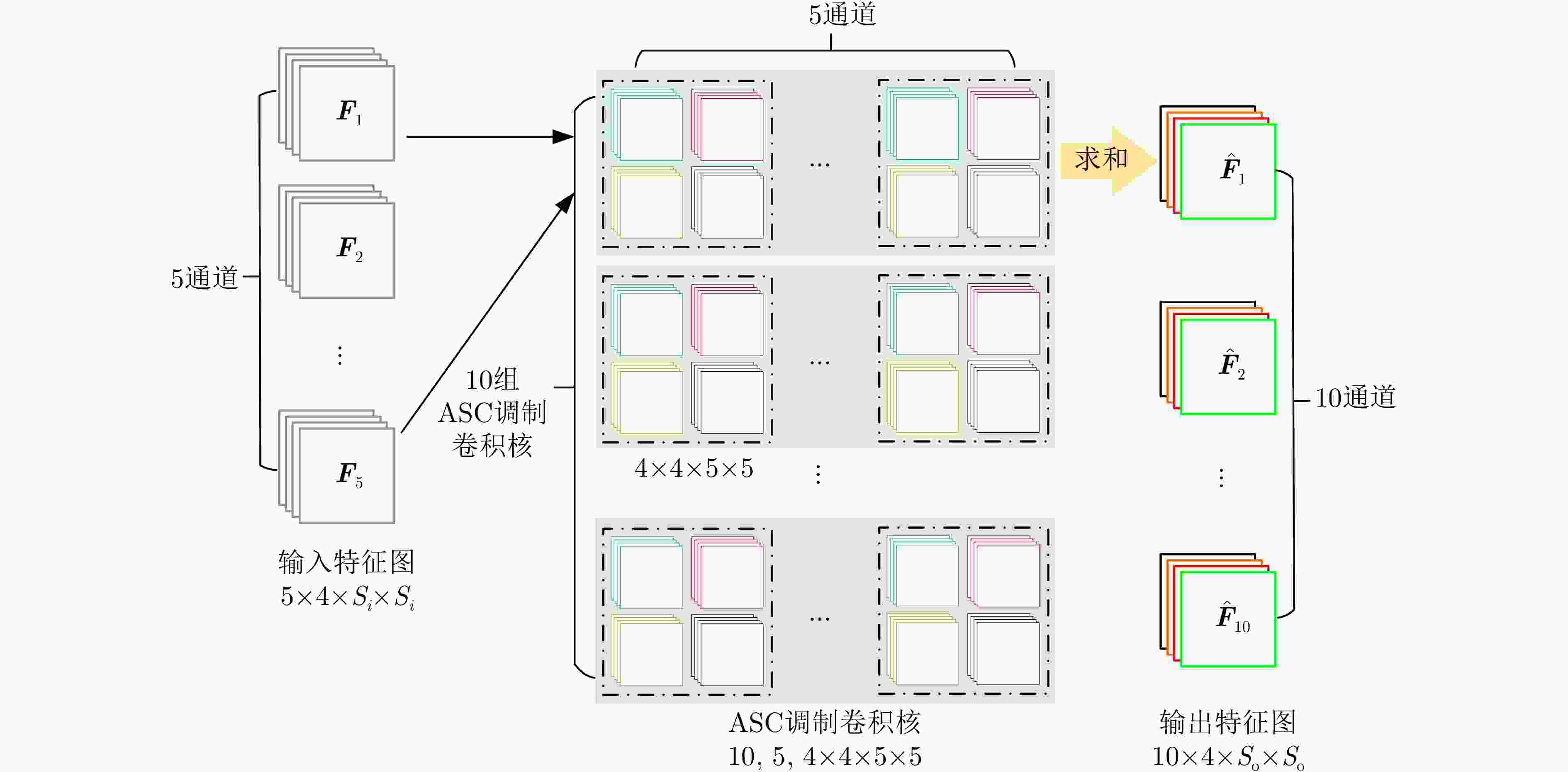
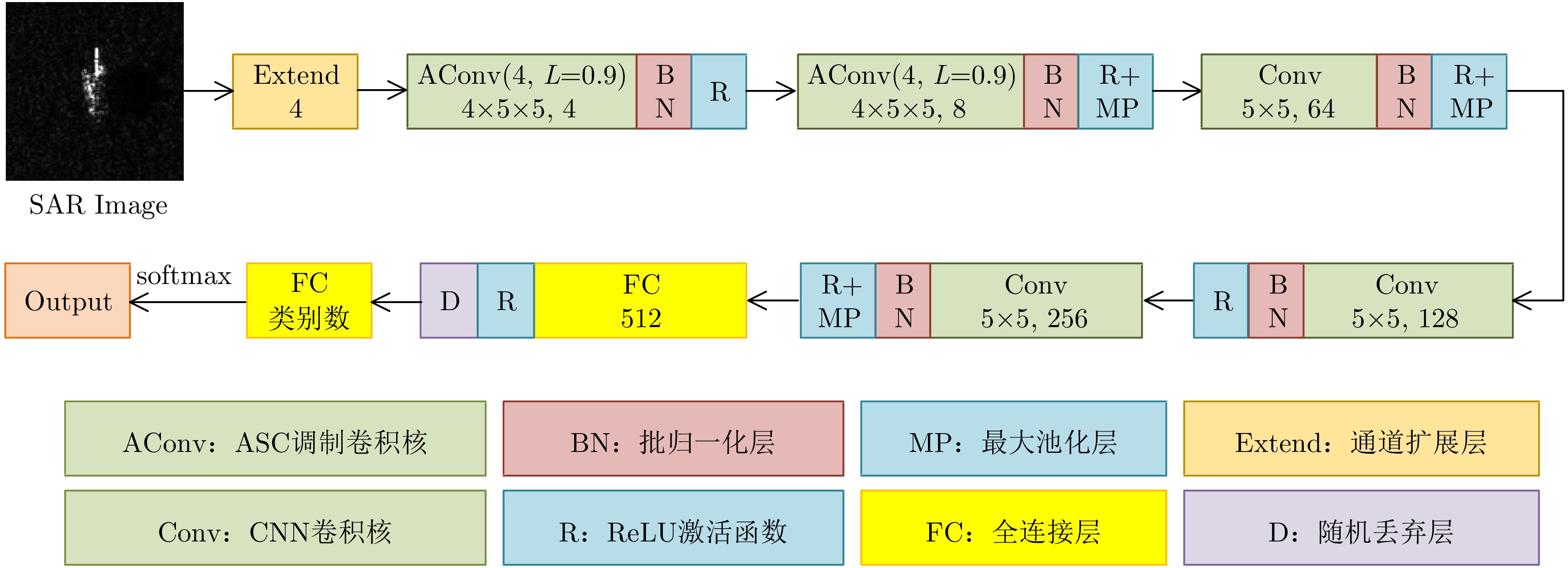
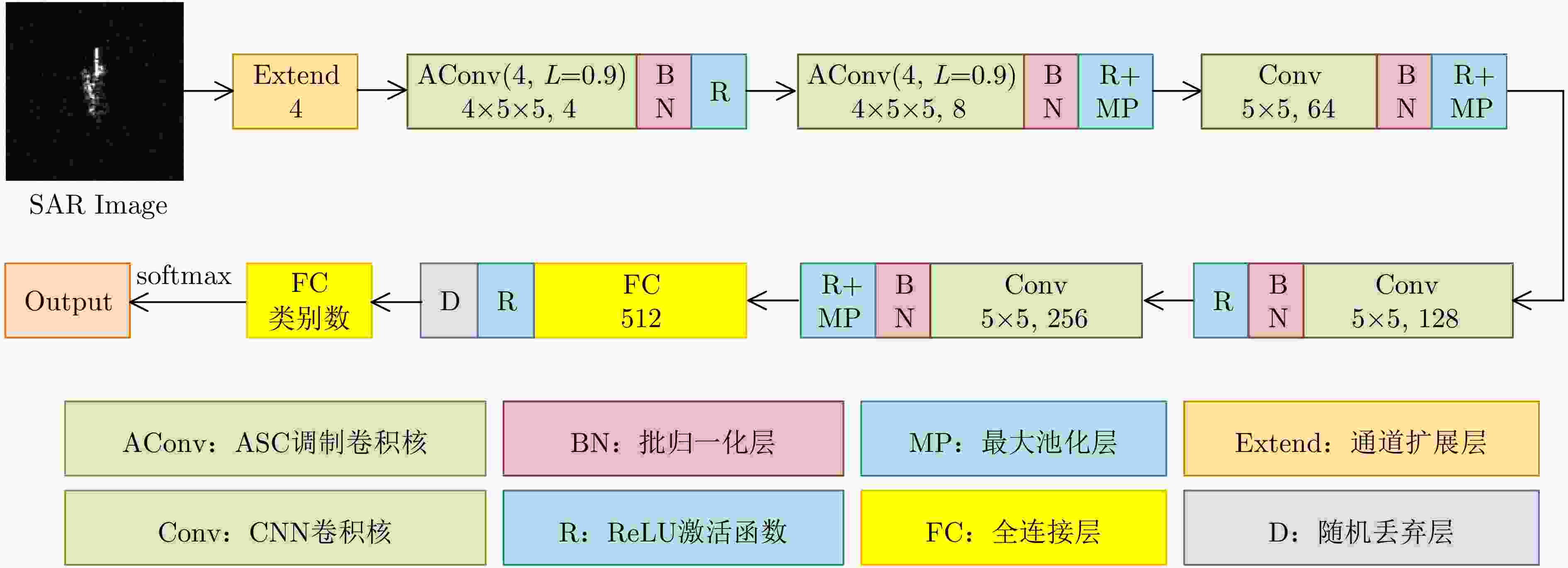
摘要: 卷积神经网络(CNN)的特征提取能力与其参数量有关,一般来说,参数量越多,CNN的特征提取能力越强。但要学好这些参数需要大量的训练数据,而在实际应用中,可用于模型训练的合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像往往是有限的。减少CNN的参数量可以降低对训练样本的需求,但同时也会降低CNN的特征表达能力,影响其目标识别性能。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于属性散射中心(ASC)卷积核调制的SAR目标识别深层网络。由于SAR图像具有电磁散射特性,为了提取更符合SAR目标特性的散射结构和边缘特征,所提网络使用预先设定的具有不同指向和长度的ASC核对少量CNN卷积核进行调制以生成更多卷积核,从而在降低网络参数量的同时保证其特征提取能力。此外,该网络在浅层使用ASC调制卷积核来提取更符合SAR图像特性的散射结构和边缘特征,而在高层使用CNN卷积核来提取SAR图像的语义特征。由于同时使用ASC调制卷积核和CNN卷积核,该网络能够兼顾SAR目标的电磁散射特性和CNN的特征提取优势。使用实测SAR图像进行的实验证明了所提网络可以在降低对训练样本需求的同时保证优秀的SAR目标识别性能。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 目标识别 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 属性散射中心(ASC) /
- 卷积核调制
Abstract: The feature extraction capability of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) is related to the number of their parameters. Generally, using a large number of parameters leads to improved feature extraction capability of CNNs. However, a considerable amount of training data is required to effectively learn these parameters. In practical applications, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images available for model training are often limited. Reducing the number of parameters in a CNN can decrease the demand for training samples, but the feature expression ability of the CNN is simultaneously diminished, which affects its target recognition performance. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a deep network for SAR target recognition based on Attribute Scattering Center (ASC) convolutional kernel modulation. Given the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of SAR images, the proposed network extracts scattering structures and edge features that are more consistent with the characteristics of SAR targets by modulating a small number of CNN convolutional kernels using predefined ASC kernels with different orientations and lengths. This approach generates additional convolutional kernels, which can reduce the network parameters while ensuring feature extraction capability. In addition, the designed network uses ASC-modulated convolutional kernels at shallow layers to extract scattering structures and edge features that are more consistent with the characteristics of SAR images while utilizing CNN convolutional kernels at deeper layers to extract semantic features of SAR images. The proposed network focuses on the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of SAR targets and shows the feature extraction advantages of CNNs due to the simultaneous use of ASC-modulated and CNN convolutional kernels. Experiments based on the studied SAR images demonstrate that the proposed network can ensure excellent SAR target recognition performance while reducing the demand for training samples. -
表 1 MSTAR的3类7型子数据集的具体信息
Table 1. The detailed information of three-target MSTAR data
类别 型号 训练样本数 测试样本数 BMP2 SNC21 233 196 SN9563 0 195 SN9566 0 196 BTR70 C71 233 196 T72 SNS7 0 191 SN132 232 196 SN812 0 195 表 2 MSTAR的10类14型子数据集的具体信息
Table 2. The detailed information of ten-target MSTAR data
类别 训练样本数 测试样本数 BTR60 255 195 2S1 299 274 BRDM2 298 274 D7 299 274 T62 299 273 ZIL131 299 274 ZSU23/4 299 274 BMP2 233 587 BTR70 233 196 T72 232 582 表 3 OpenSARShip的3类数据集具体信息
Table 3. The detailed information of three-target OpenSARShip data
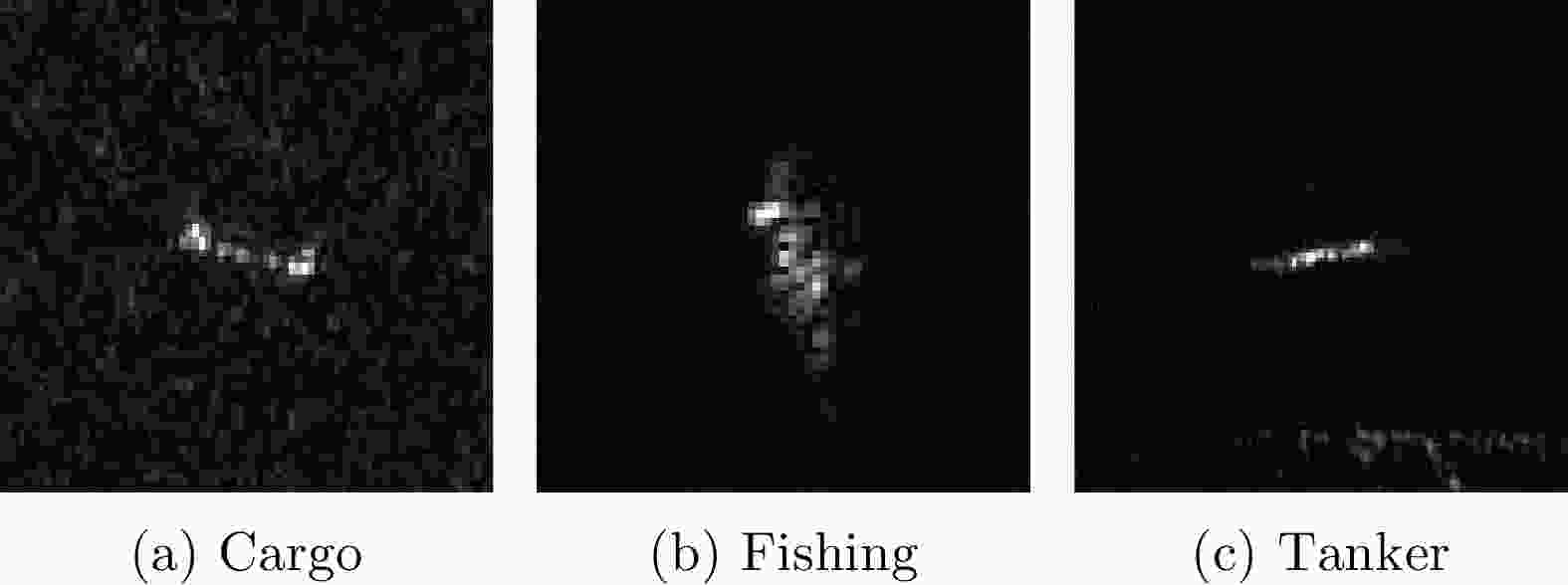
类别 训练样本数 测试样本数 Cargo 241 159 Fishing 92 23 Tanker 115 76 表 4 不同方法对3类7型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能以及各方法参数量
Table 4. Recognition performance of different methods on three-target MSTAR data and the number of parameters of each method
方法 参数量 PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.9319 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.9253 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.9385 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.9495 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ 0.9861 所提方法 $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.9875 表 5 不同方法对10类14型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能以及各方法参数量
Table 5. Recognition performance of different methods on ten-target MSTAR data and the number of parameters of each method
方法 参数量 PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.9166 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.9138 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.9219 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.9422 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ 0.9781 所提方法 $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.9844 表 6 不同方法对OpenSARShip的3类数据集的识别性能以及各方法参数量
Table 6. Recognition performance of different methods on three-target OpenSARShip data and the number of parameters of each method
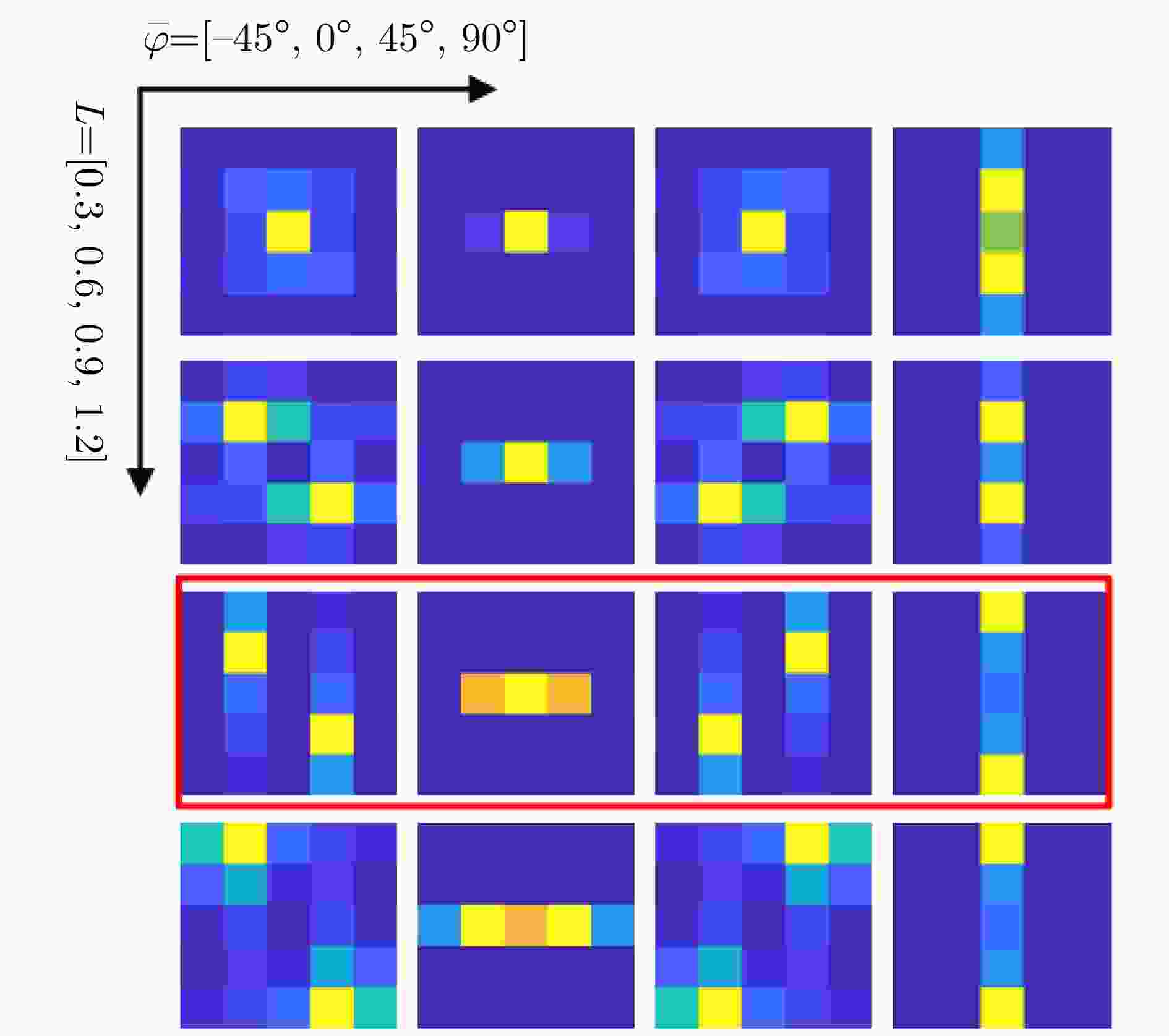
方法 参数量 PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.7713 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.7403 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.7791 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.8062 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ – 所提方法 $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.8101 表 7 预设的ASC核的方向数取不同的M值时对3类7型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能
Table 7. Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different values of M
方向数M PCC 2 0.9722 3 0.9817 4 0.9875 5 0.9810 6 0.9744 表 8 预设的ASC核的长度L取不同值时对3类7型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能
Table 8. Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different values of L
长度L PCC 0.3 0.9729 0.6 0.9788 0.9 0.9875 1.2 0.9810 表 9 不同层卷积层采用ASC调制卷积核时对3类7型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能
Table 9. Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different convolution layers using ASC modulated convolutional kernels
采用层 VGG16 ResNet18 所提方法 不采用 0.9319 0.9480 0.9495 第1层 0.9795 0.9663 0.9795 第1, 2层 0.9839 0.9769 0.9875 第1~3层 0.9773 0.9736 0.9810 第1~4层 0.9758 0.9729 0.9736 第2, 3层 0.9766 0.9641 0.9751 第3, 4层 0.9714 0.9582 0.9707 表 10 不同方法在不同训练样本数下对3类7型MSTAR子数据集的识别性能
Table 10. Recognition performance of different methods on three-target MSTAR data with different number of training samples
方法 训练样本比例 100% 50% 30% 25% 20% VGG16 0.9319 0.8886 0.8352 0.7883 0.7370 ResNet34 0.9253 0.8813 0.8278 0.7590 0.7267 A-ConvNet 0.9385 0.9062 0.8769 0.8337 0.7875 BaseNet 0.9495 0.8974 0.8674 0.8227 0.7758 CA-MCNN 0.9861 0.9641 0.9165 0.8938 0.8608 所提方法 0.9875 0.9670 0.9480 0.9187 0.8711 表 1 The detailed information of three-target MSTAR data
Category Type Number of
training samplesNumber of
testing samplesBMP2 SNC21 233 196 SN9563 0 195 SN9566 0 196 BTR70 C71 233 196 T72 SNS7 0 191 SN132 232 196 SN812 0 195 表 2 The detailed information of ten-target MSTAR data
Category Number of
training samplesNumber of
testing samplesBTR60 255 195 2S1 299 274 BRDM2 298 274 D7 299 274 T62 299 273 ZIL131 299 274 ZSU23/4 299 274 BMP2 233 587 BTR70 233 196 T72 232 582 表 3 The detailed information of three-target OpenSARShip data
Category Number of
training samplesNumber of
testing samplesCargo 241 159 Fishing 92 23 Tanker 115 76 表 4 Recognition performance of different methods on three-target MSTAR data and the number of parameters of each method
Methods Parameters PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.9319 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.9253 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.9385 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.9495 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ 0.9861 Proposed $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.9875 表 5 Recognition performance of different methods on ten-target MSTAR data and the number of parameters of each method
Methods Parameters PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.9166 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.9138 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.9219 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.9422 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ 0.9781 Proposed $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.9844 表 6 Recognition performance of different methods on three-target OpenSARShip data and the number of parameters of each method
Methods Parameters PCC VGG16 $6.51 \times {10^7}$ 0.7713 ResNet34 $2.13 \times {10^7}$ 0.7403 A-ConvNet $3.03 \times {10^5}$ 0.7791 BaseNet $2.27 \times {10^6}$ 0.8062 CA-MCNN $6.52 \times {10^6}$ – Proposed $2.26 \times {10^6}$ 0.8101 表 7 Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different values of M
M PCC 2 0.9722 3 0.9817 4 0.9875 5 0.9810 6 0.9744 表 8 Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different values of L
L PCC 0.3 0.9729 0.6 0.9788 0.9 0.9875 1.2 0.9810 表 9 Recognition performance on three-target MSTAR data under different convolution layers using ASC modulated convolutional kernels
Convolution layers used VGG16 ResNet18 Proposed Without ASC 0.9319 0.948 0.9495 First layer 0.9795 0.9663 0.9795 First & Second layers 0.9839 0.9769 0.9875 First to Third layers 0.9773 0.9736 0.9810 First to Fourth layers 0.9758 0.9729 0.9736 Second & Third layers 0.9766 0.9641 0.9751 Third & Fourth layers 0.9714 0.9582 0.9707 表 10 Recognition performance of different methods on three-target MSTAR data with different number of training samples
Methods Training sample ratio 100% 50% 30% 25% 20% VGG16 0.9319 0.8886 0.8352 0.7883 0.7370 ResNet34 0.9253 0.8813 0.8278 0.7590 0.7267 A-ConvNet 0.9385 0.9062 0.8769 0.8337 0.7875 BaseNet 0.9495 0.8974 0.8674 0.8227 0.7758 CA-MCNN 0.9861 0.9641 0.9165 0.8938 0.8608 Proposed 0.9875 0.9670 0.9480 0.9187 0.8711 -
[1] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1006–1114. [2] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–14. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556. [3] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [4] TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. [5] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986. [6] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021: 1−22. https://iclr.cc/virtual/2021/index.html. [7] CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. [8] 喻玲娟, 王亚东, 谢晓春, 等. 基于FCNN和ICAE的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066.YU Lingjuan, WANG Yadong, XIE Xiaochun, et al. SAR ATR based on FCNN and ICAE[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066. [9] 赵鹏菲, 黄丽佳. 一种基于EfficientNet与BiGRU的多角度SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133.ZHAO Pengfei and HUANG Lijia. Target recognition method for multi-aspect synthetic aperture radar images based on EfficientNet and BiGRU[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133. [10] HUANG Xiayuan, YANG Qiao, and QIAO Hong. Lightweight two-stream convolutional neural network for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 667–671. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983718. [11] LIU Jiaming, XING Mengdao, YU Hanwen, et al. EFTL: Complex convolutional networks with electromagnetic feature transfer learning for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5209811. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3083261. [12] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with HOG feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759. [13] QOSJA D, WAGNER S, and BRÜGGENWIRTH S. Benchmarking convolutional neural network backbones for target classification in SAR[C]. 2023 IEEE Radar Conference, San Antonio, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2351548.2023.10149802. [14] LIU Zhuang, MAO Hanzi, WU Chaoyuan, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11966–11976. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01167. [15] 张翼鹏, 卢东东, 仇晓兰, 等. 基于散射点拓扑和双分支卷积神经网络的SAR图像小样本舰船分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 411–427. doi: 10.12000/JR23172.ZHANG Yipeng, LU Dongdong, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Few-shot ship classification of SAR images via scattering point topology and dual-branch convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 411–427. doi: 10.12000/JR23172. [16] LUAN Shangzhen, CHEN Chen, ZHANG Baochang, et al. Gabor convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4357–4366. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2835143. [17] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 微波视觉与SAR图像智能解译[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 285–306. doi: 10.12000/JR23225.XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Microwave vision and intelligent perception of radar imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 285–306. doi: 10.12000/JR23225. [18] GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750. [19] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098. [20] 李飞. 雷达图像目标特征提取方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.LI Fei. Study on target feature extraction based on radar image[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2014. [21] ROSS T D, WORRELL S W, VELTEN V J, et al. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 566–573. doi: 10.1117/12.321859. [22] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672. [23] SUN Yongguang, DU Lan, WANG Yan, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on dictionary learning and joint dynamic sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1777–1781. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2608578. [24] DENG Sheng, DU Lan, LI Chen, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on Euclidean distance restricted autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(7): 3323–3333. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2670083. [25] NI Jiacheng and XU Yuelei. SAR automatic target recognition based on a visual cortical system[C]. 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2013: 778–782. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2013.6745270. [26] LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: