-
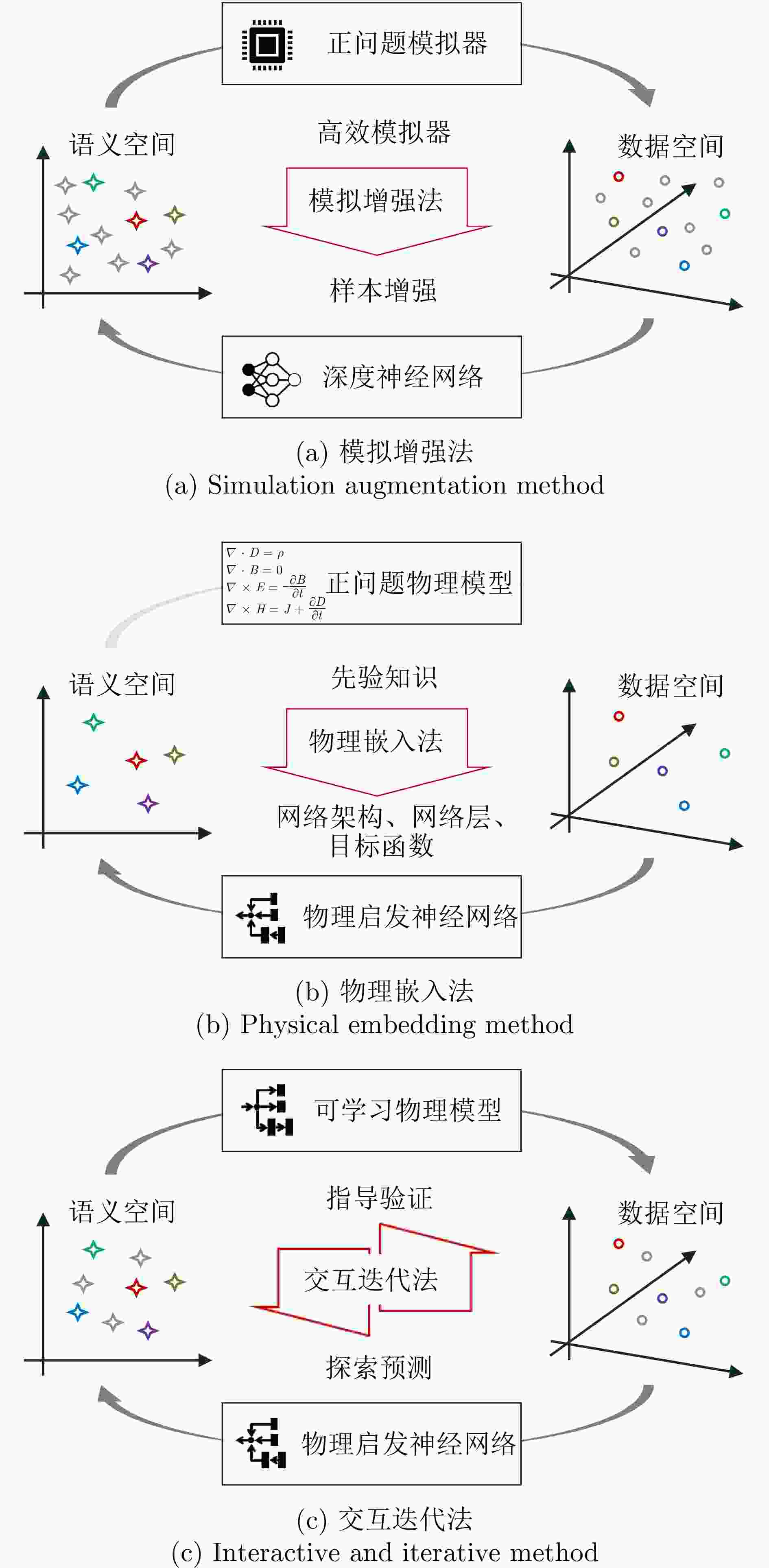
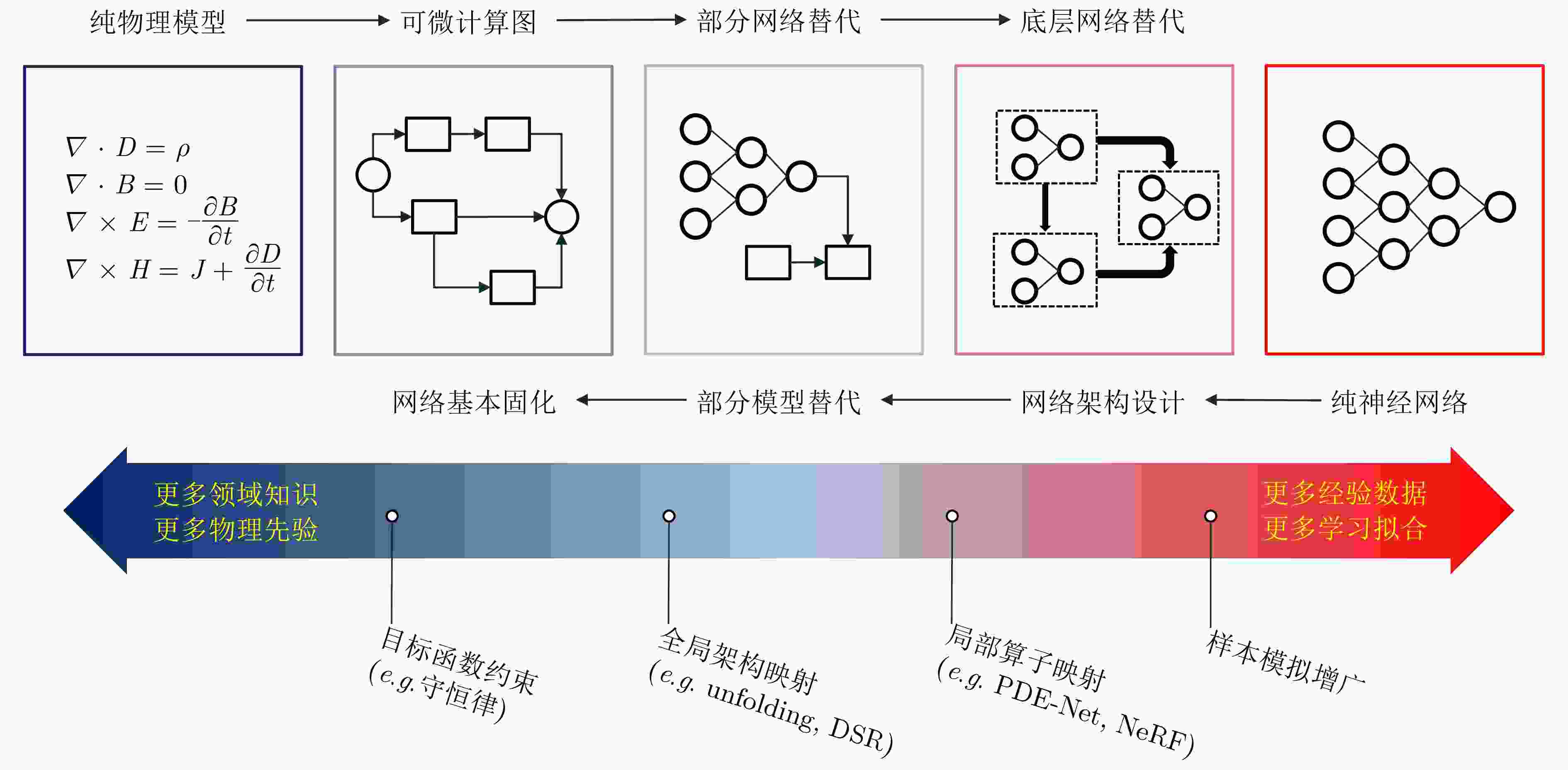
摘要: 高分辨率雷达成像技术和人工智能、大数据技术的快速发展,有力促进了雷达图像智能解译技术的进步。由于雷达传感器本身的特殊性和电磁散射成像物理的复杂性,雷达图像的解译缺乏光学图像的直观性,准确迅速识别分类的需求对雷达图像解译提出了迫切的挑战。在借鉴人脑光视觉感知机理和计算机视觉图像处理相关技术基础上,进一步融合电磁散射物理规律及其雷达成像机理,我们提出发展微波域雷达图像解译的“微波视觉”的新交叉领域研究。该文介绍微波视觉的概念与内涵,提出微波视觉认知模型,阐述其基础理论问题与技术路线,最后介绍了作者团队在相关问题上的初步研究进展。Abstract: With the rapid development of high-resolution radar imaging technology, artificial intelligence, and big data technology, remarkable advancements have been made in the intelligent interpretation of radar imagery. Despite growing demands, radar image intrpretation is now facing various technical challenges mainly because of the particularity of the radar sensor itself and the complexity of electromagnetic scattering physical phenomena. To address the problem of microwave radar imagery perception, this article proposes the development of the cross-disciplinary microwave vision research, which further integrates electromagnetic physics and radar imaging mechanism with human brain visual perception principles and computer vision technologies. This article discusses the concept and implication of microwave vision, proposes a microwave vision perception model, and explains its basic scientific problems and technical roadmaps. Finally, it introduces the preliminary research progress on related issues achieved by the authors’ group.
-
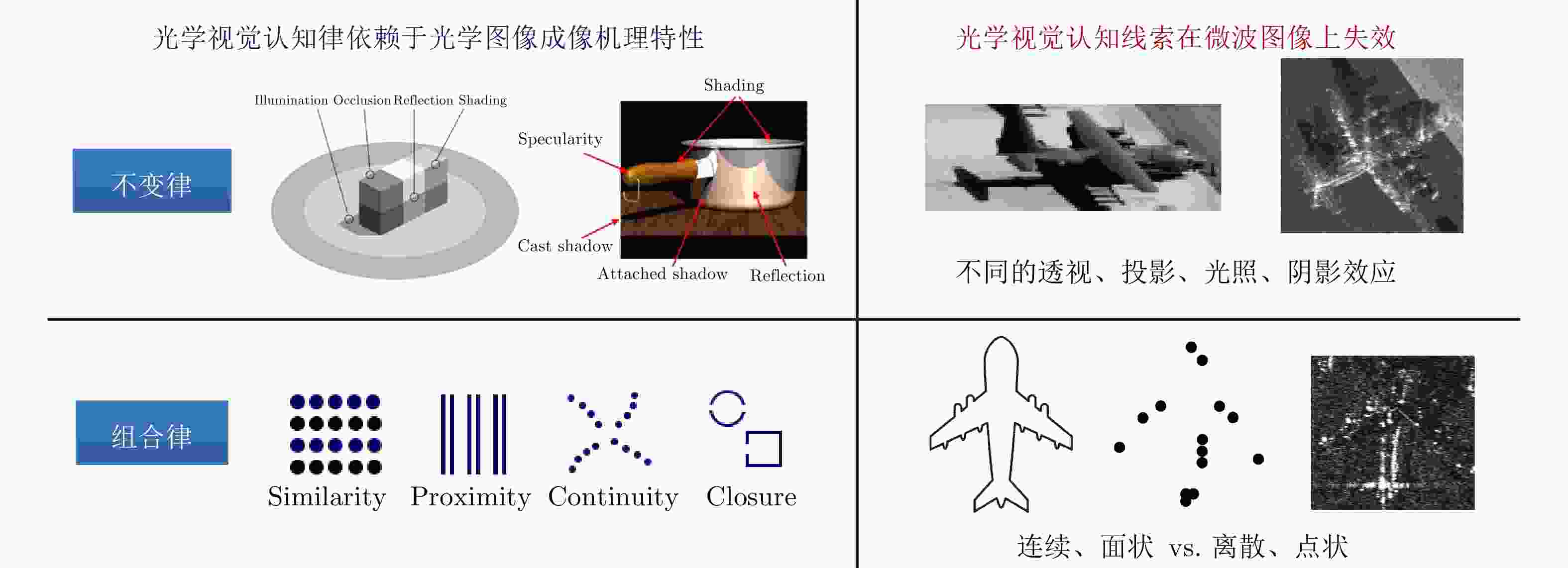
表 1 光学图像和SAR图像对比
Table 1. Comparison between optical and SAR images
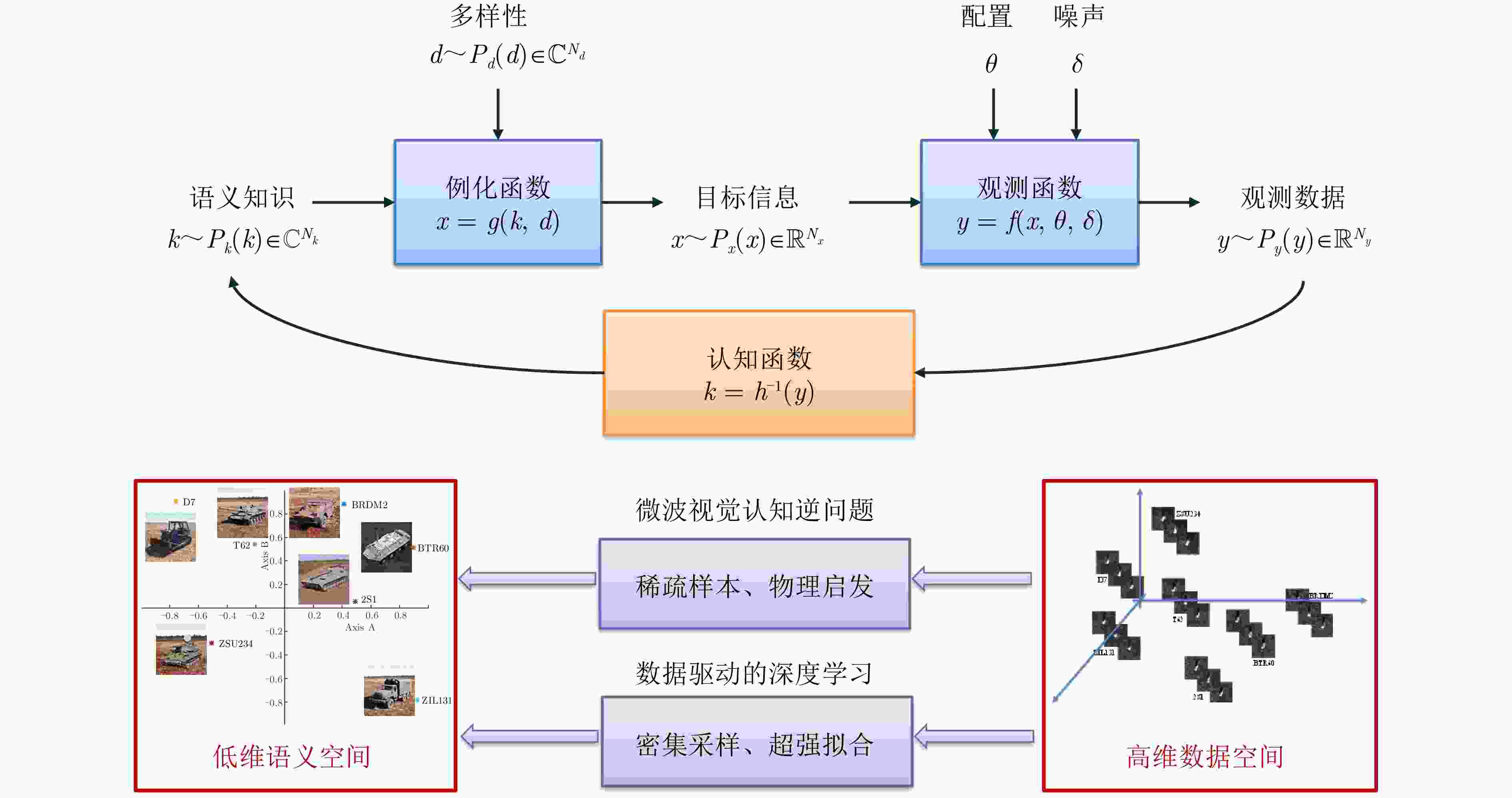
图像特性 光学图像 SAR图像 物理特性 波段 可见光波段 微波波段 探测方式 外界光源、被动接收 主动辐射、后向散射 反射/散射形态 连续、面状 离散、点状 成像机制 聚焦机制 真实孔径 相干合成孔径 随机噪声 加性噪声 乘性相干斑 投影方式 透视投影 斜距投影 投影方向 俯仰角-方位角 距离向-方位向 图像形态 图像畸变效应 透视效应,分辨率与距离成正比 收缩、叠掩、倒置,分辨率与距离无关 目标与场景呈现方式 自然图像:人眼视角、大目标小背景 遥感图像:鹰眼视角、大背景小目标 数据形式 颜色、强度 相位、幅度、极化 表 2 微波视觉认知模型中的基本概念
Table 2. Notations of the perception model of microwave vision
概念 定义 举例 目标语义知识 $ k{\text{~}}{P}_{k}\left(k\right)\in {\mathbb{C}}^{{N}_{k}} $ 目标型号:T72, BTR60 ··· 目标多样性 $ d{\text{~}}{P}_{d}\left(d\right)\in {\mathbb{C}}^{{N}_{d}} $ 细节变化、个体差异、背景环境··· 目标物理信息 $ x{\text{~}}{P}_{x}\left(x\right)\in {\mathbb{R}}^{{N}_{x}} $ 目标几何模型、表面材质··· 观测数据 $ y{\text{~}}{P}_{y}\left(y\right)\in {\mathbb{R}}^{{N}_{y}} $ SAR图像 观测配置 $ \theta $ 波段、入射角、分辨率··· 观测噪声 $ \delta $ 传感器噪声、测量误差、模型误差··· -
[1] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047.WU Yirong. Concept on multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047. [2] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130.XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. [3] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 合成孔径雷达图像智能解译[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 1–463.XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Intelligent Interpretation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 1–463. [4] 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104.DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. [5] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059.GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. [6] 黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165.HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. [7] 邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. [8] 李军, 孙显, 于瀚雯, 等. 遥感与人工智能的交叉创新专题简介[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(5): 1026. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0103.LI Jun, SUN Xian, YU Hanwen, et al. Special topic: Artificial intelligence innovation in remote sensing[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023, 53(5): 1026. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0103. [9] 高勋章, 张志伟, 刘梅, 等. 雷达像智能识别对抗研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098.GAO Xunzhang, ZHANG Zhiwei, LIU Mei, et al. Intelligent radar image recognition countermeasures: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098. [10] 罗汝, 赵凌君, 何奇山, 等. SAR图像飞机目标智能检测识别技术研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 307–330. doi: 10.12000/JR23056.LUO Ru, ZHAO Lingjun, HE Qishan, et al. Intelligent technology for aircraft detection and recognition through SAR imagery: Advancements and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 307–330. doi: 10.12000/JR23056. [11] 刘宏伟, 位寅生, 关键, 等. “雷达智能探测新技术专题”编者按[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 封二.LIU Hongwei, WEI Yinsheng, GUAN Jian, et al. Editorial comments of special issue on novel the intelligent radar detecting technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): Inside front cover. [12] 金亚秋, 徐丰. 加强智能科学交叉领域研究[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(17): 1.JIN Yaqiu and XU Feng. Enhance the research in interdisciplinary fields of intelligent science[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2018, 36(17): 1. [13] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 从物理智能到微波视觉[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004.XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004. [14] 金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083.JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. [15] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. [16] 丁赤飚, 徐丰, 董秋雷, 等. “合成孔径雷达微波视觉理论与技术专刊”编者按[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 封二.DING Chibiao, XU Feng, DONG Qiulei, et al. Editorial comments of theory and system of synthetic aperture radar microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): Inside front cover. [17] ROCK I and DIVITA J. A case of viewer-centered object perception[J]. Cognitive Psychology, 1987, 19(2): 280–293. doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(87)90013-2. [18] PIZLO Z. Perception viewed as an inverse problem[J]. Vision Research, 2001, 41(24): 3145–3161. doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(01)00173-0. [19] MARR D. Vision: A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2010: 31–38. [20] WAGEMANS J, ELDER J H, KUBOVY M, et al. A century of Gestalt psychology in visual perception: I. Perceptual grouping and figure-ground organization[J]. Psychological Bulletin, 2012, 138(6): 1172–1217. doi: 10.1037/a0029333. [21] MONGA V, LI Yuelong, and ELDAR Y C. Algorithm unrolling: Interpretable, efficient deep learning for signal and image processing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2021, 38(2): 18–44. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.3016905. [22] LIU Zhuoyang and XU Feng. Interpretable neural networks: Principles and applications[J]. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 6: 974295. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.974295. [23] XU Feng and ZHANG Xu. On the concept of semantic electromagnetics[C]. 2022 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES-China), Xuzhou, China, 2022: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ACES-China56081.2022.10065038. [24] FU Shilei and XU Feng. Differentiable SAR renderer and image-based target reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6679–6693. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3215069. [25] KARNIADAKIS G E, KEVREKIDIS I G, LU Lu, et al. Physics-informed machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(6): 422–440. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00314-5. [26] GUO Qian, XU Huilin, and XU Feng. Causal adversarial autoencoder for disentangled SAR image representation and few-shot target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5221114. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3330478. [27] LI Shangyang, LIU Zhuoyang, FU Shilei, et al. Intelligent beamforming via physics-inspired neural networks on programmable metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(6): 4589–4599. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3140891. [28] 刘彻, 杨恺乔, 鲍江涵, 等. 智能电磁计算的若干进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 657–683. doi: 10.12000/JR23133.LIU Che, YANG Kaiqiao, BAO Jianghan, et al. Recent progress in intelligent electromagnetic computing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 657–683. doi: 10.12000/JR23133. [29] SOHL-DICKSTEIN J, WEISS E A, MAHESWARANATHAN N, et al. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 2256–2265. [30] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, TANCIK M, et al. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2022, 65(1): 99–106. doi: 10.1145/3503250. [31] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [32] EDELMAN S. On What it Means To See, and What We Can Do About It[M]. DICKINSON S, LEONARDIS A, SCHIELE B, et al. Object Categorization: Computer and Human Vision Perspectives. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 69–86. [33] LECUN Y. A path towards autonomous machine intelligence version 0.9.2, 2022-06-27[EB/OL]. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=BZ5a1r-kVsf, 2022. [34] FRISTON K. Is the free-energy principle neurocentric?[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2010, 11(8): 605. doi: 10.1038/nrn2787-c2. [35] ZHANG Zhengquan and XU Feng. An overview of the free energy principle and related research[J]. Neural Computation, 2024. doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01642. [36] 尤瑞希, 钱昱彤, 徐丰. 格式塔感知规律在SAR图像中的有效性初探[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 345–359. doi: 10.12000/JR23187.YOU Ruixi, QIAN Yutong, and XU Feng. Preliminary research on the effectiveness of Gestalt perceptual principles in SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 13(2): 345–359. doi: 10.12000/JR23187. [37] LI Dong and ZHANG Yunhua. Epipolar geometry comparison of SAR and optical camera[C]. SPIE 9901, 2nd ISPRS International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing (CVRS 2015), Xiamen, China, 2015: 99010V. doi: 10.1117/12.2234943. [38] JIA Hecheng and XU Feng. Ship Detection in SAR Images with Human-in-the-Loop[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.08213, 2024. [39] ZHANG Xu, XU Feng, YANG Ying, et al. A primitive scatterer dictionary for semantic representation of radar target images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3321386. [40] ZHANG Xu, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. A unified bidirectional scattering distribution function for convex quadric surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 2003015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3294017. [41] ZHANG Xu and XU Feng. Coherent spatially varying bidirectional scattering distribution function of rough surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2004017. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3136572. [42] YUE Dongxiao, XU Feng, FRERY A C, et al. A generalized gaussian coherent scatterer model for correlated SAR texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2947–2964. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958125. [43] SONG Qian, CHEN Hui, XU Feng, et al. EM simulation-aided zero-shot learning for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(6): 1092–1096. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2936897. [44] LV Xiaoling, QIU Xiaolan, YU Wenming, et al. Simulation-aided SAR target classification via dual-branch reconstruction and subdomain alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5214414. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3305094. [45] SONG Qian, XU Feng, ZHU Xiaoxiang, et al. Learning to generate SAR images with adversarial autoencoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3086817. [46] GUO Qian, QIAN Yutong, WANG Haipeng, et al. Recognition rate versus substitution rate curve: An objective utility assessment criterion of simulated training data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5224415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3154932. [47] GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Scattering enhanced attention pyramid network for aircraft detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7570–7587. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027762. [48] XU Huilin and XU Feng. Multi-scale capsule network with coordinate attention for sar automatic target recognition[C]. 2021 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Bali, Indonesia, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/APSAR52370.2021.9688428. [49] SONG Qian, XU Feng, and ZHU Xiaoxiang. Physical-aware radar image synthesis with projective network[C]. 2021 XXXIVth General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS), Rome, Italy, 2021: 1–4. doi: 10.23919/URSIGASS51995.2021.9560559. [50] LEI Zhengxin, XU Feng, WEI Jiangtao, et al. SAR-NeRF: Neural radiance fields for synthetic aperture radar multi-view representation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.05087, 2023. [51] WEI Jiangtao, LUOMEI Yixiang, ZHANG Xu, et al. Learning surface scattering parameters from SAR images using differentiable ray tracing[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.01175, 2024. [52] FU Shilei, JIA Hecheng, PU Xinyang, et al. Extension of differentiable SAR renderer for ground target reconstruction from multi-view images and shadows[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5217013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3320515. [53] WANG Yanni, JIA Hecheng, FU Shilei, et al. Reinforcement learning for SAR view angle inversion with differentiable SAR renderer[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.01165, 2024. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: