-
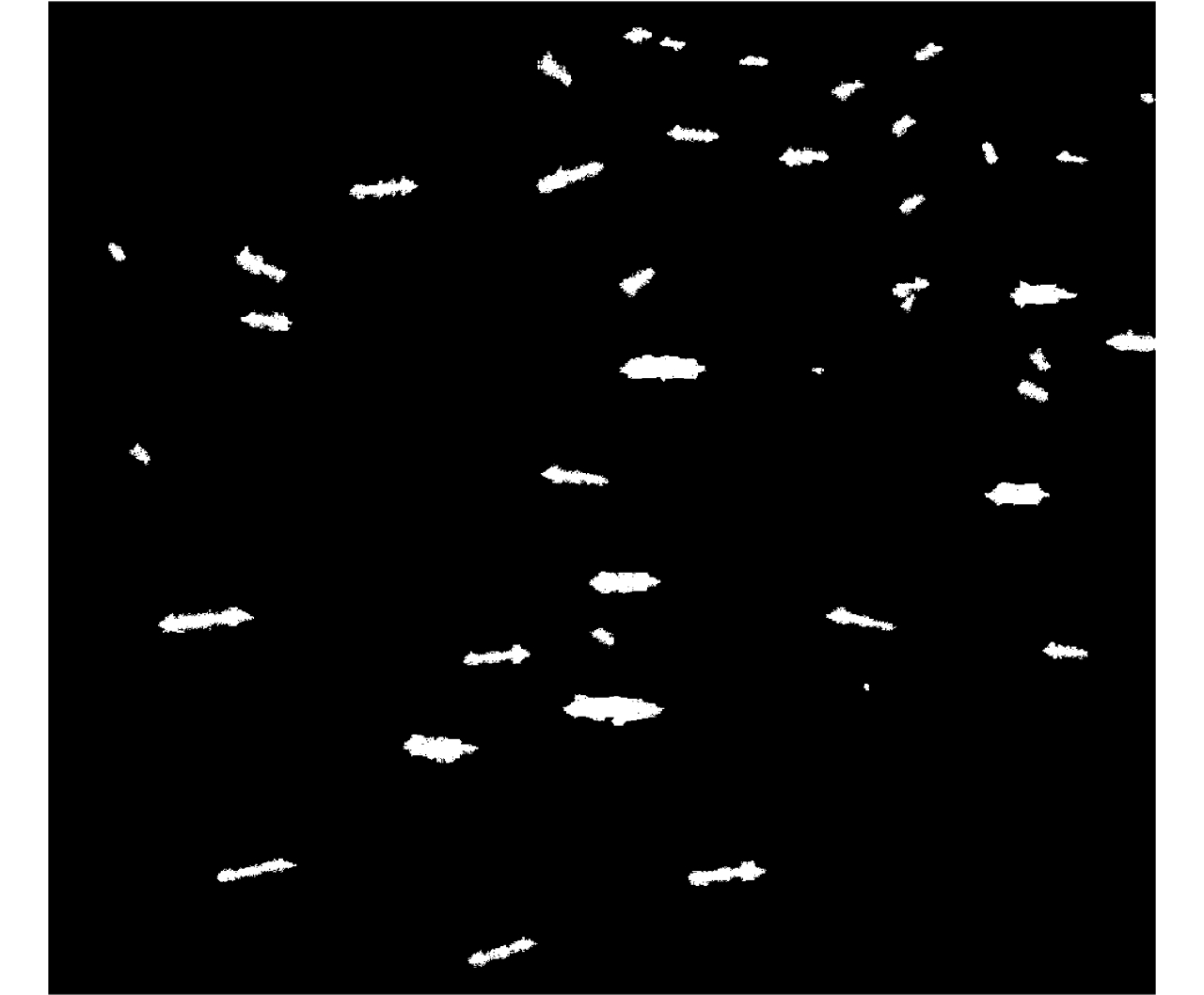
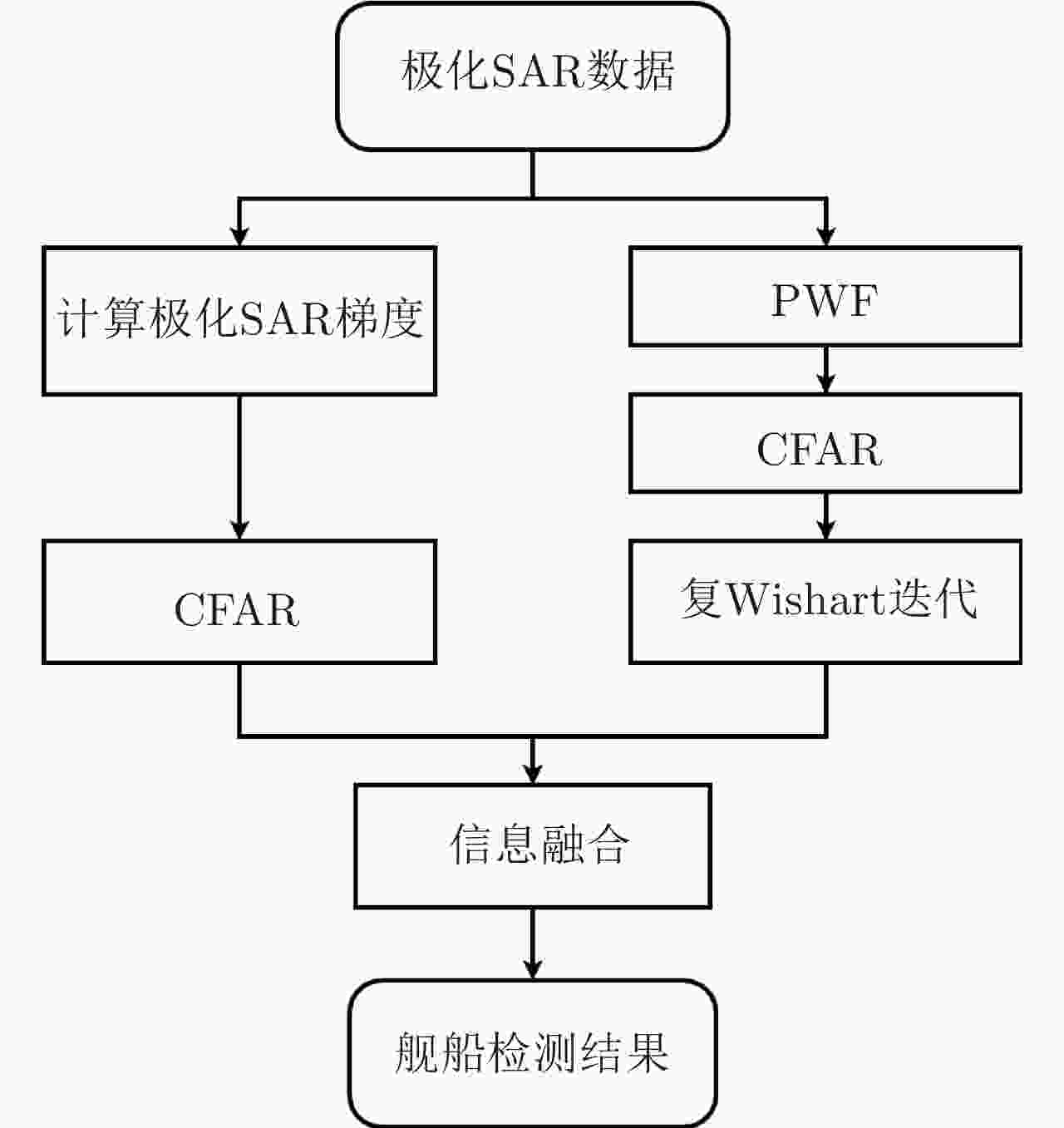
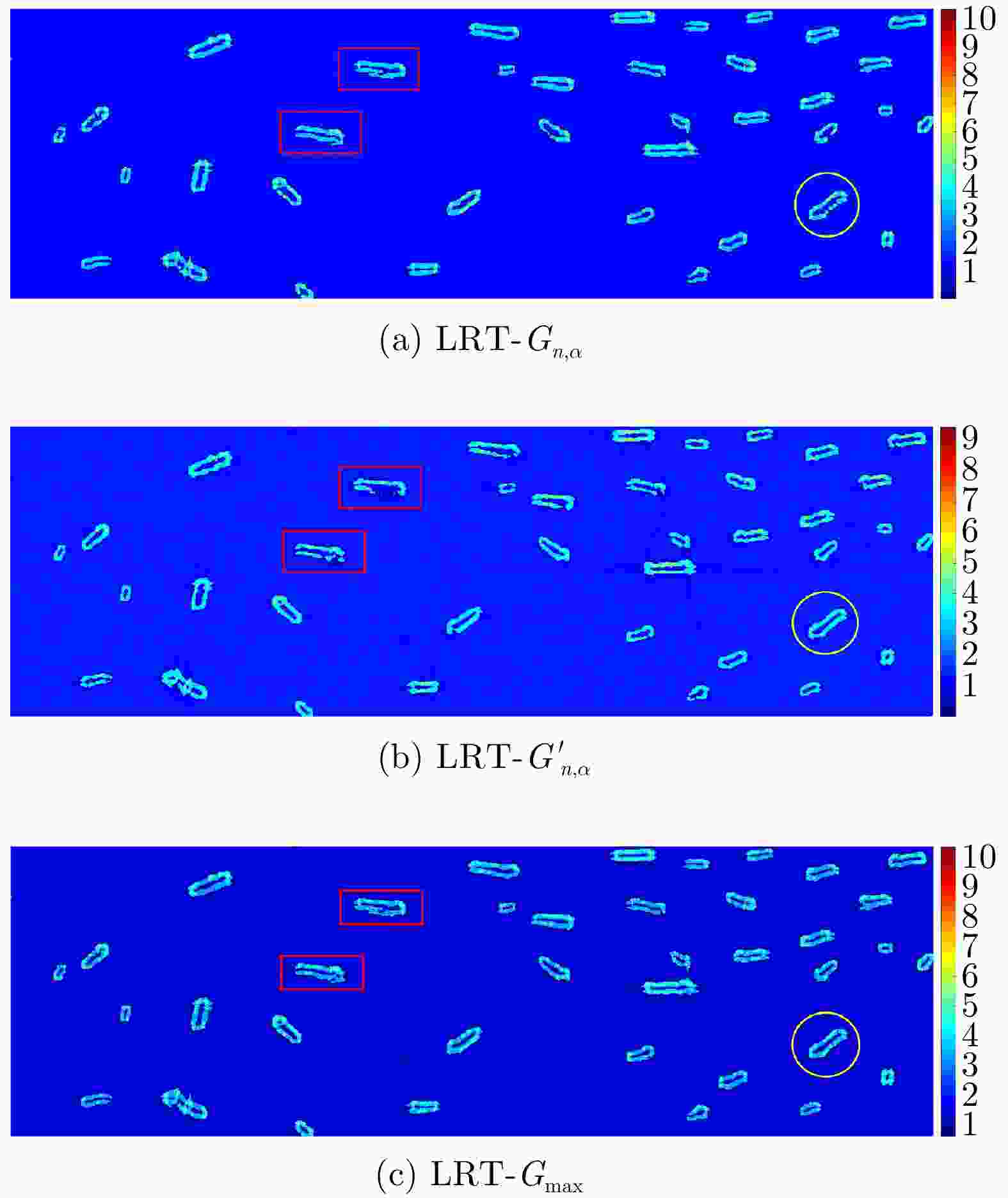
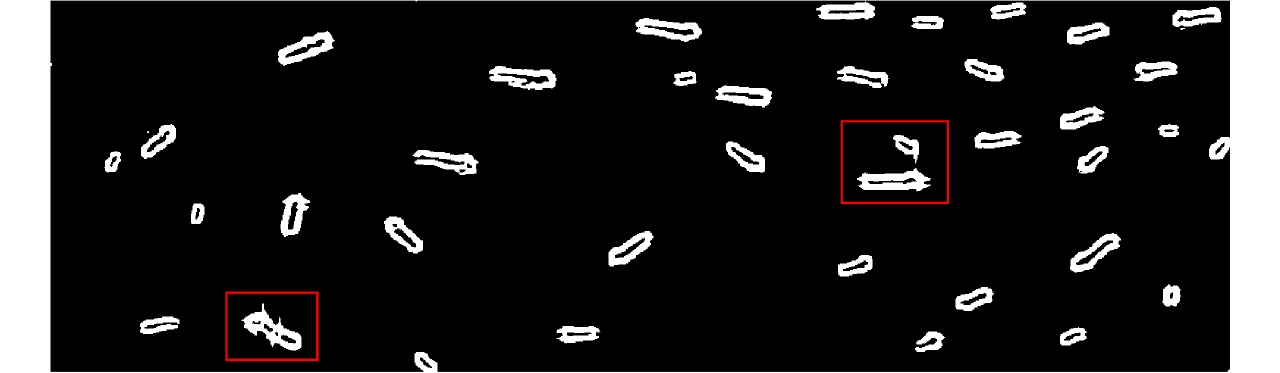
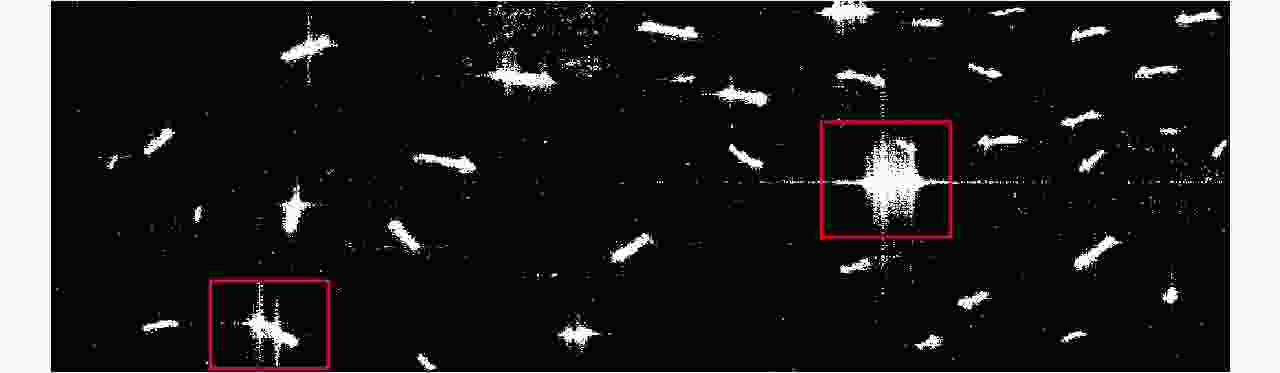
摘要: 舰船检测是极化SAR系统的重要应用之一。现有的舰船检测方法容易受到旁瓣泄露的干扰,使得舰船目标的形态难以提取,导致检测结果不符合真实情况。此外,在舰船过于密集、尺度不一致的情况下,相邻舰船由于旁瓣的影响有时会被认为是单个目标,从而造成漏检。针对这些问题,该文提出一种基于极化SAR梯度和复Wishart分类器的舰船检测方法。首先,将似然比检验(LRT)梯度引入对数比值梯度框架,使其适用于极化SAR数据;基于LRT梯度图进行恒虚警(CFAR)检测,提取舰船的边缘信息,消除伪影的同时抑制强旁瓣对舰船精细轮廓提取的影响。其次,利用复Wishart迭代分类器对舰船强散射部分进行检测,可排除大部分的杂波干扰且保持舰船形态细节。最后,将二者信息融合,从而可以保持舰船形态细节的同时克服旁瓣和伪信号的虚警。该文在3幅来自ALOS-2卫星的极化SAR图像上进行了对比实验,实验表明与其他方法相比,该文所提算法具有更少的虚警和漏检,且能够有效克服旁瓣泄露,保持舰船形态细节。
-
关键词:
- 舰船检测 /
- 极化合成孔径雷达 /
- 比值梯度 /
- 似然比检验 /
- 复Wishart分类器
Abstract: Ship detection is one of the most important applications of polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems. Current ship detection methods are susceptible to side flap interference, making it difficult to extract the target shape correctly. In addition, when ships are exceedingly dense and have different scales, adjacent ships may be considered as a single target because of the influence of strong sidelobes, causing missed detections. To address the issues of sidelobe interference and multi-scale dense ship detection, a ship detection method based on the polarimetric SAR gradient and the complex Wishart classifier is proposed. First, the Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) gradient is introduced into the log-ratio gradient framework to apply it to the polarimetric SAR data. Then, a Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) detector is applied to the gradient image to map the ship boundaries accurately. Second, the complex Wishart iterative classifier is used to detect the strong scattering part of the ship, which can eliminate most clutter interference and maintain the ship’s shape details. Finally, the LRT detection and complex Wishart classifier detection results are fused. Thus, not only the strong sidelobe interference can be greatly suppressed, but the dense targets with different scales are also distinguished and accurately located. This study performs comparative experiments on three polarimetric SAR images from the ALOS-2 satellite. Experimental results show that compared with the existing methods, the proposed algorithm has fewer false alarms and missed detections and can effectively overcome the problems of sidelobe interference while maintaining the shape details. -
表 3 实验场景1中对比方法的指标评价结果
Table 3. Results evaluation for experimental scenario 1
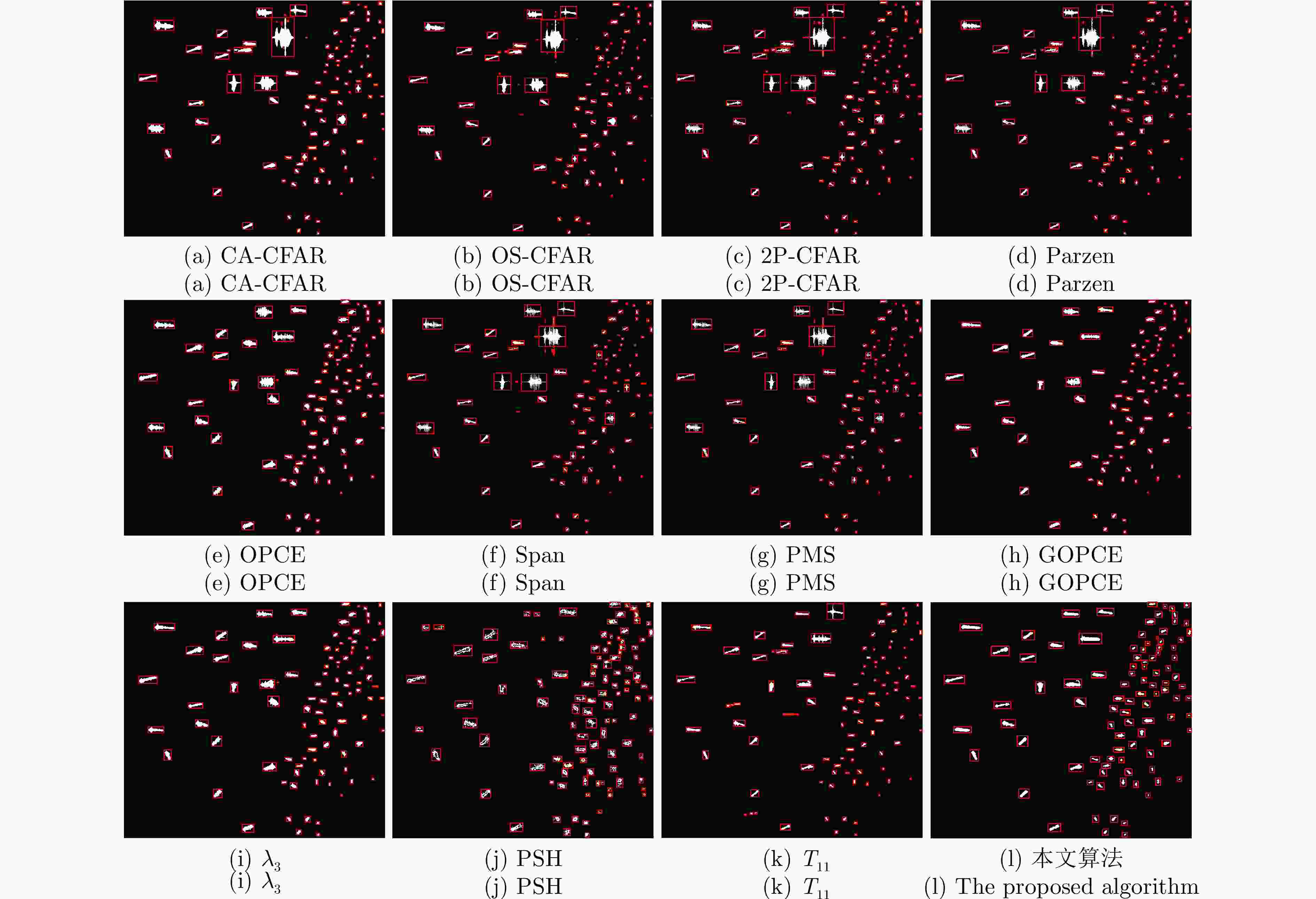
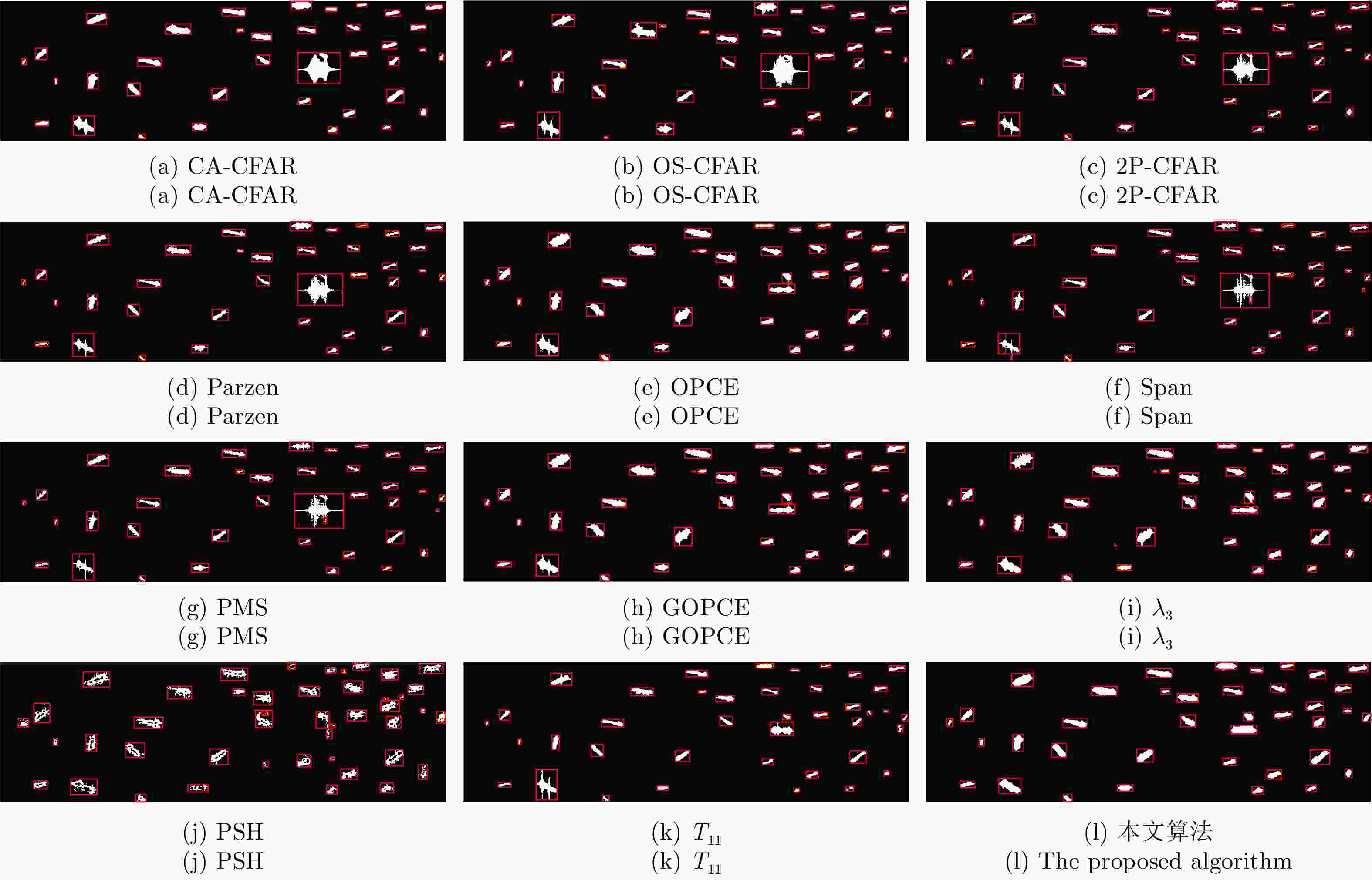
方法 召回率 准确率 F1 时间(s) OS-CFAR 0.4174 0.5386 0.4703 1.548 Span 0.4430 0.8715 0.5874 0.142 PMS 0.4517 0.8631 0.5931 0.152 2P-CFAR 0.4660 0.8494 0.6018 17.339 Parzen 0.4694 0.8477 0.6042 0.145 T11 0.4737 0.9302 0.6277 0.138 CA-CFAR 0.6793 0.8566 0.7577 4.325 λ3 0.7116 0.8981 0.7940 32.468 OPCE 0.7167 0.8917 0.7947 19.845 GOPCE 0.7167 0.8917 0.7947 29.904 本文方法 0.7471 0.9177 0.8237 92.673 表 2 实验场景3中对比方法的指标评价结果
Table 2. Results evaluation for experimental scenario 3
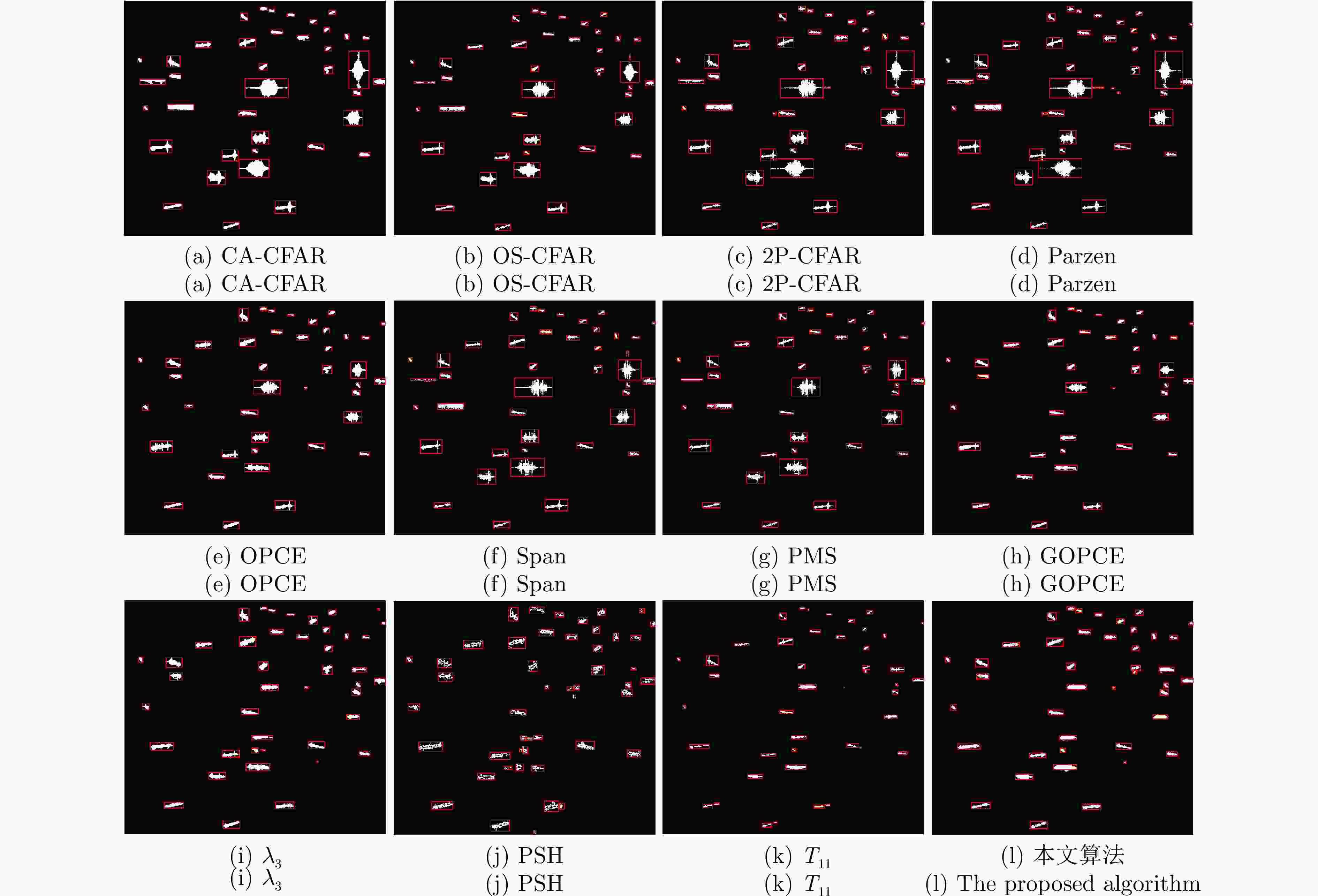
方法 虚警 漏检 召回率 准确率 F1 时间(s) OS-CFAR 20 3 0.969 0.823 0.890 5.765 2P-CFAR 14 0 1.000 0.876 0.934 61.898 Span 12 1 0.990 0.890 0.937 0.283 CA-CFAR 11 1 0.990 0.898 0.942 15.530 Parzen 11 1 0.990 0.898 0.942 0.261 T11 8 2 0.979 0.922 0.950 0.248 PSH 10 0 1.000 0.908 0.952 90.842 PMS 6 3 0.969 0.939 0.954 0.314 λ3 3 1 0.990 0.970 0.980 91.453 OPCE 1 1 0.990 0.990 0.990 67.250 GOPCE 1 1 0.990 0.990 0.990 88.925 本文方法 0 1 0.990 1.000 0.995 276.324 表 1 实验场景2中对比方法的指标评价结果
Table 1. Results evaluation for experimental scenario 2
方法 虚警 漏检 召回率 准确率 F1 时间(s) PSH 10 4 0.895 0.773 0.829 92.245 2P-CFAR 2 5 0.865 0.941 0.901 61.870 CA-CFAR 2 5 0.865 0.941 0.901 15.420 Span 4 3 0.923 0.900 0.911 0.283 Parzen 4 2 0.950 0.905 0.927 0.254 T11 5 1 0.976 0.889 0.930 0.252 OS-CFAR 2 3 0.923 0.947 0.935 5.981 PMS 3 2 0.950 0.927 0.938 0.322 OPCE 1 2 0.950 0.974 0.962 69.524 λ3 2 1 0.976 0.952 0.964 91.350 GOPCE 0 2 0.950 1.000 0.974 89.484 本文方法 0 0 1.000 1.000 1.000 298.198 -
[1] 杨汝良, 戴博伟, 李海英. 极化合成孔径雷达极化层次和系统工作方式[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 132–142. doi: 10.12000/JR16013.YANG Ruliang, DAI Bowei, and LI Haiying. Polarization hierarchy and system operating architecture for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 132–142. doi: 10.12000/JR16013. [2] WEISS M. Analysis of some modified cell-averaging CFAR processors in multiple-target situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1982, AES-18(1): 102–114. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1982.309210. [3] NOVAK L M, BURL M C, and IRVING W W. Optimal polarimetric processing for enhanced target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(1): 234–244. doi: 10.1109/7.249129. [4] AI Jiaqiu, YANG Xuezhi, DONG Zhangyu, et al. A new two parameter CFAR ship detector in Log-Normal clutter[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 195–199. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944196. [5] RITCEY J A and DU H. Order statistic CFAR detectors for speckled area targets in SAR[C]. Conference Record of the Twenty-Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1991: 1082–1086. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.1991.186613. [6] GOLDSTEIN G B. False-alarm regulation in log-normal and Weibull clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(1): 84–92. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309705. [7] LEVANON N and SHOR M. Order statistcs CFAR for Weibull background[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1990, 137(3): 157–162. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1990.0023. [8] ANASTASSOPOULOS V and LAMPROPOULOS G A. Optimal CFAR detection in Weibull clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(1): 52–64. doi: 10.1109/7.366292. [9] GUAN Jian, HE You, and PENG Yingning. CFAR detection in K-distributed clutter[C]. Fourth International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 1998: 1513–1516. doi: 10.1109/ICOSP.1998.770911. [10] NOVAK L M and BURL M C. Optimal speckle reduction in polarimetric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1990, 26(2): 293–305. doi: 10.1109/7.53442. [11] 杨汝良, 戴博伟, 谈璐璐, 等. 极化微波成像[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016.YANG Ruliang, DAI Bowei, TAN Lulu, et al. Polarimetric Microwave Imaging[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2016. [12] CHANEY R D, BUD M C, and NOVAK L M. On the performance of polarimetric target detection algorithms[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1990, 5(11): 10–15. doi: 10.1109/62.63157. [13] BOERNER W M, KOSTINSKI A B, and JAMES B D. On the concept of the polarimetric matched filter in high resolution radar imaging: An alternative for speckle reduction[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, ‘Remote Sensing: Moving Toward the 21st Century’, Edinburgh, UK, 1988: 69–72. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1988.570053. [14] KOSTINSKI A and BOERNER W. On the polarimetric contrast optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(8): 988–991. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1144209. [15] YANG Jian, DONG Guiwei, PENG Yingning, et al. Generalized optimization of polarimetric contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(3): 171–174. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.830127. [16] 殷君君, 安文韬, 杨健. 基于极化散射参数与Fisher-OPCE的监督目标分类[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 51(12): 1782–1786. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2011.12.007.YIN Junjun, AN Wentao, and YANG Jian. Supervised target classification using polarimetric scattering parameters and Fisher-OPCE[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University : Science and Technolog y, 2011, 51(12): 1782–1786. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2011.12.007. [17] XI Yuyang, ZHANG Xi, LAI Quan, et al. A new PolSAR ship detection metric fused by polarimetric similarity and the third eigenvalue of the coherency matrix[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 112–115. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7729019. [18] ZHANG Tao, YANG Zhen, and XIONG Huilin. PolSAR ship detection based on the polarimetric covariance difference matrix[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(7): 3348–3359. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2671904. [19] SHI Hao, ZHANG Qingjun, BIAN Mingming, et al. A novel ship detection method based on gradient and integral feature for single-polarization synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 563. doi: 10.3390/s18020 563. [20] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552. [21] SONG Shengli, XU Bin, and YANG Jian. SAR target recognition via supervised discriminative dictionary learning and sparse representation of the SAR-HOG feature[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(8): 683. doi: 10.3390/rs8080683. [22] LIN Huiping, SONG Shengli, and YANG Jian. Ship classification based on MSHOG feature and task-driven dictionary learning with structured incoherent constraints in SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 190. doi: 10.3390/rs10020190. [23] GAO Gui. A parzen-window-kernel-based CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 557–561. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2090492. [24] 张晓玲, 张天文, 师君, 等. 基于深度分离卷积神经网络的高速高精度SAR舰船检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111.ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, SHI Jun, et al. High-speed and high-accurate SAR ship detection based on a depthwise separable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111. [25] FAN Weiwei, ZHOU Feng, BAI Xueru, et al. Ship detection using deep convolutional neural networks for PolSAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(23): 2862. doi: 10.3390/rs11232862. [26] AN Quanzhi, PAN Zongxu, and YOU Hongjian. Ship detection in Gaofen-3 SAR images based on sea clutter distribution analysis and deep convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 334. doi: 10.3390/s18020334. [27] ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222. [28] RIGNOT E J M and VAN ZYL J J. Change detection techniques for ERS-1 SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1993, 31(4): 896–906. doi: 10.1109/36.239913. [29] MA Xiaoshuang, SHEN Huanfeng, ZHANG Liangpei, et al. Adaptive anisotropic diffusion method for polarimetric SAR speckle filtering[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(3): 1041–1050. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2328332. [30] NIELSEN A A, CONRADSEN K, and SKRIVER H. Change detection in full and dual polarization, single-and multifrequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 4041–4048. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2416434. [31] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, AINSWORTH T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621. [32] 张嘉峰, 朱博, 张鹏, 等. Wishart分布情形下极化SAR图像目标CFAR检测解析方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(2): 433–439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.02.024.ZHANG Jiafeng, ZHU Bo, ZHANG Peng, et al. Polarimetric SAR imagery target CFAR detection analytical algorithm with Wishart distribution[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(2): 433–439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.02.024. [33] WANG Hongmiao, ZENG Liang, ZHANG Tao, et al. A PolSAR despeckling method based on Wishart gradient and anisotropic diffusion[J]. Electronics Letters, 2021, 57(3): 126–128. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12086. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: