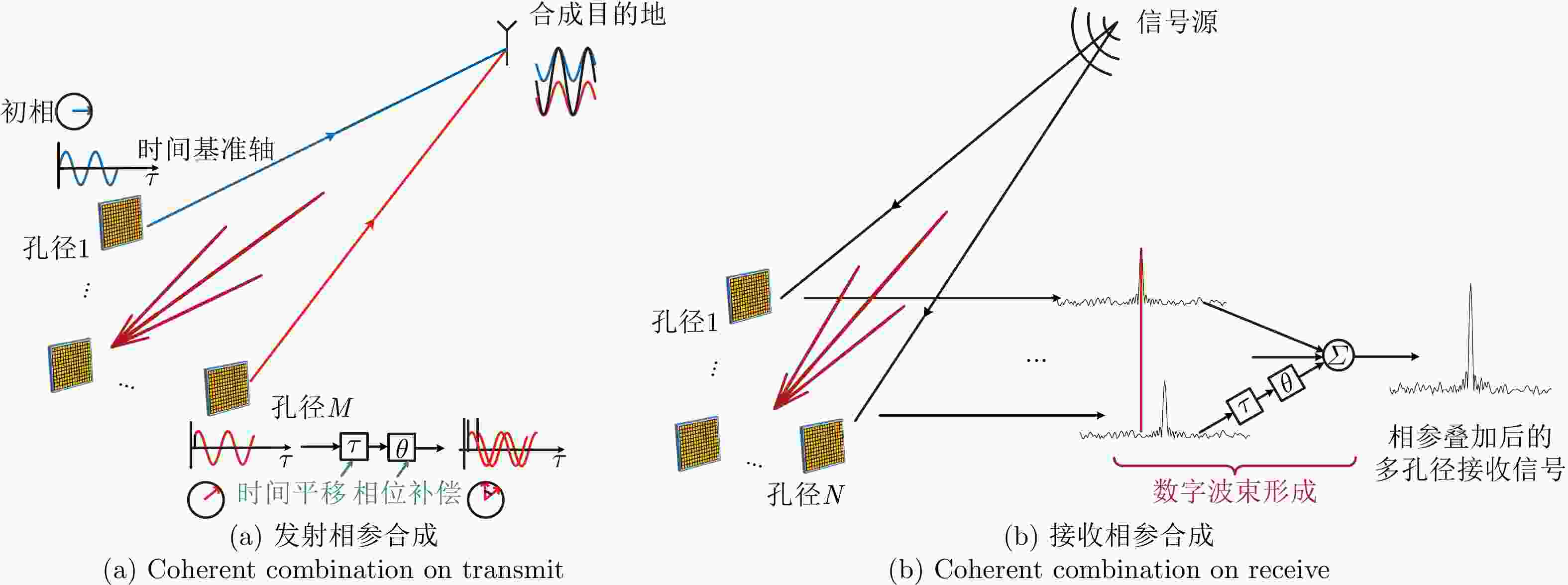
Review of Principles, Development and Technical Implementation of Coherently Combining Distributed Apertures(in English)
-
摘要: 分布式孔径相参合成通过对多个分散布置小孔径的收/发信号进行相参调整,使协同的分布式系统可以用相对低的成本获得比拟于大孔径的功率孔径积,是替代大孔径的可行技术选择。该文首先阐述了分布式孔径相参合成的概念和实现原理,根据是否需要合成目的地处的外部信号输入,将相参合成的实现架构分为闭环式和开环式两类;然后,较为全面地综述了分布式孔径相参合成在导弹防御、深空遥测遥控、超远距离雷达探测、射电天文多领域发展应用情况;进一步阐述相参合成必要且用于对准各孔径收发信号时间和相位的关键技术,包括高精度分布式时频传递和同步技术,以及相参合成参数估计、测量标定和预测技术;最后对分布式孔径相参合成研究进行了总结和展望。Abstract: Coherently combining distributed apertures adjusts the transmitted/received signals of multiple distributed small apertures, allowing coordinated distributed systems to obtain high power aperture products at much lower cost than large aperture. This is a promising and viable technology as an alternative to using large apertures. This study describes the concept and principles of coherently combining distributed apertures. Depending on whether external signal inputs at the combination destination are necessary, the implementation architecture of coherent combination is classified into two categories: closed- and open-loop. The development of coherently combining distributed apertures and their application in fields such as missile defense, deep space telemetry control, radar detection over ultralong range, and radio astronomy are then comprehensively presented. Furthermore, key techniques for aligning the time and phase of the transmitted/received signals for each aperture are elaborated, which are also necessary for coherently combining distributed apertures, including high-precision distributed time-frequency transfer and synchronization, and coherently combining parameters estimation, measurement and calibration, and prediction. Finally, summary is presented, and the scope of future works in this field is explored.
-
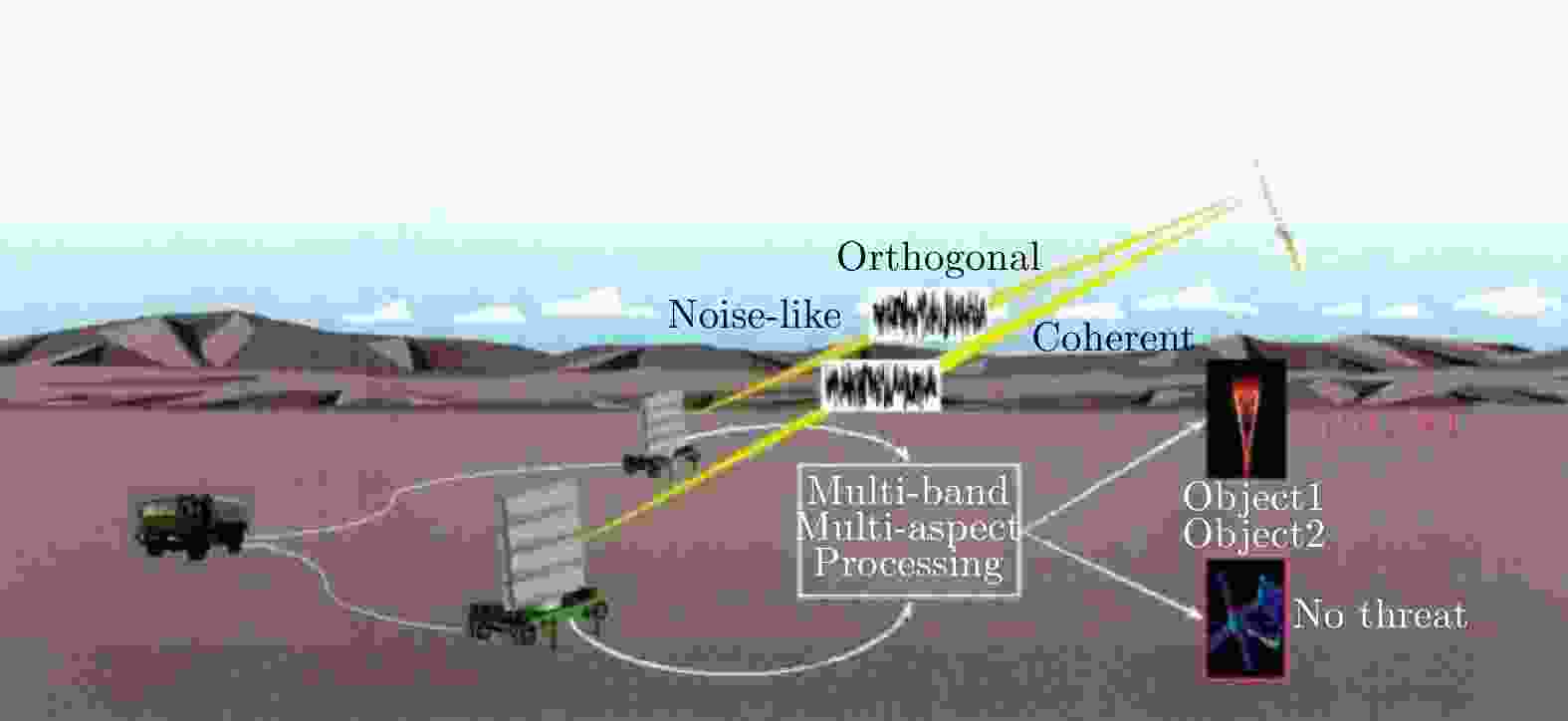
图 4 Conceptual architecture for coherently combining multiple radar apertures [ 5]
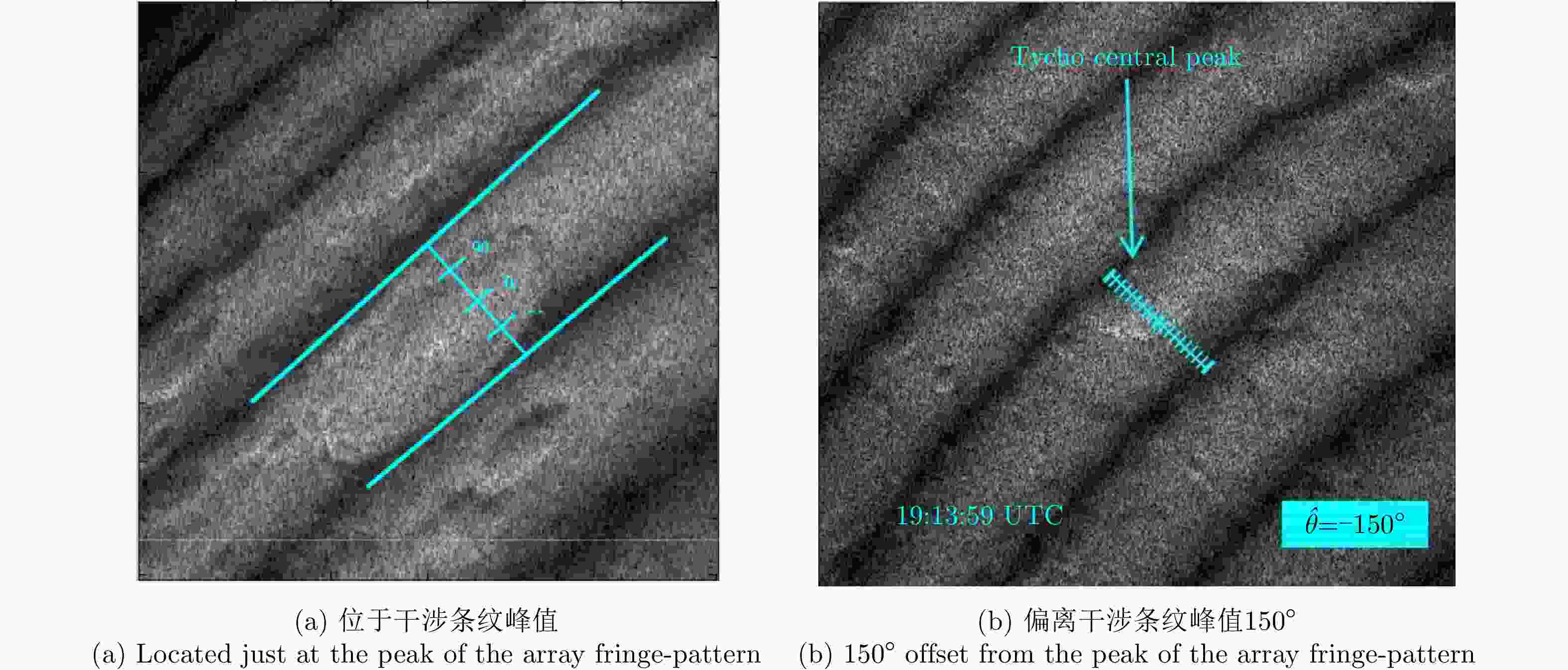
图 5 Doppler-delay images comparison where Tycho central peak appears to be located just at the peak of the array fringe-pattern and with 150° offset [ 38]
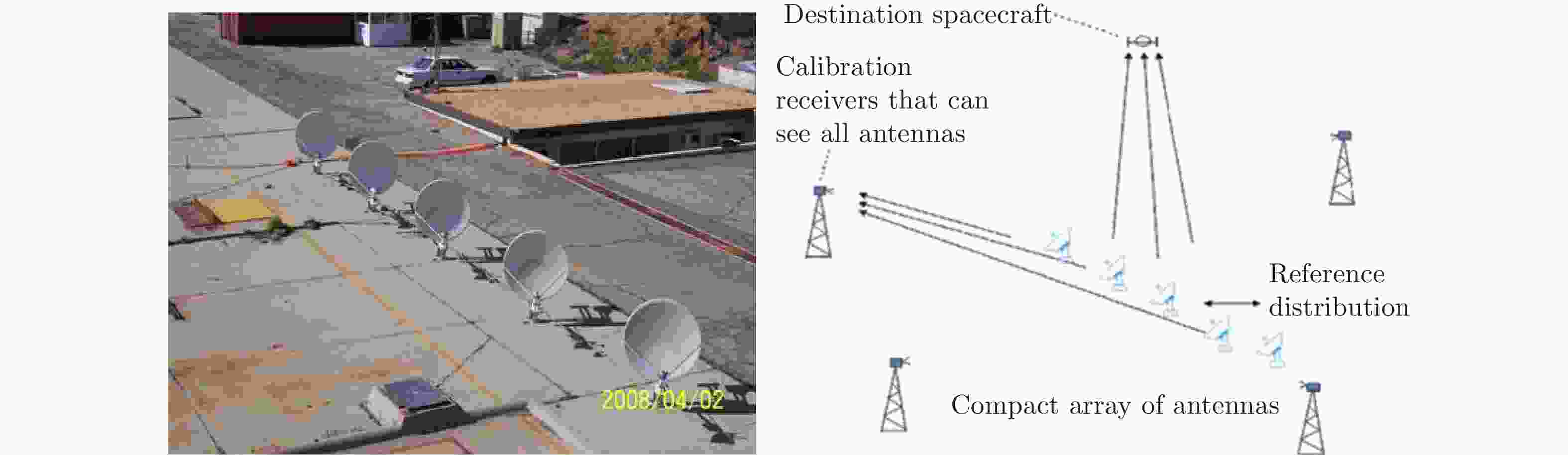
图 6 Five 1.2 m Ku-band antennas coherent uplink array and bias calibration scheme [ 39]
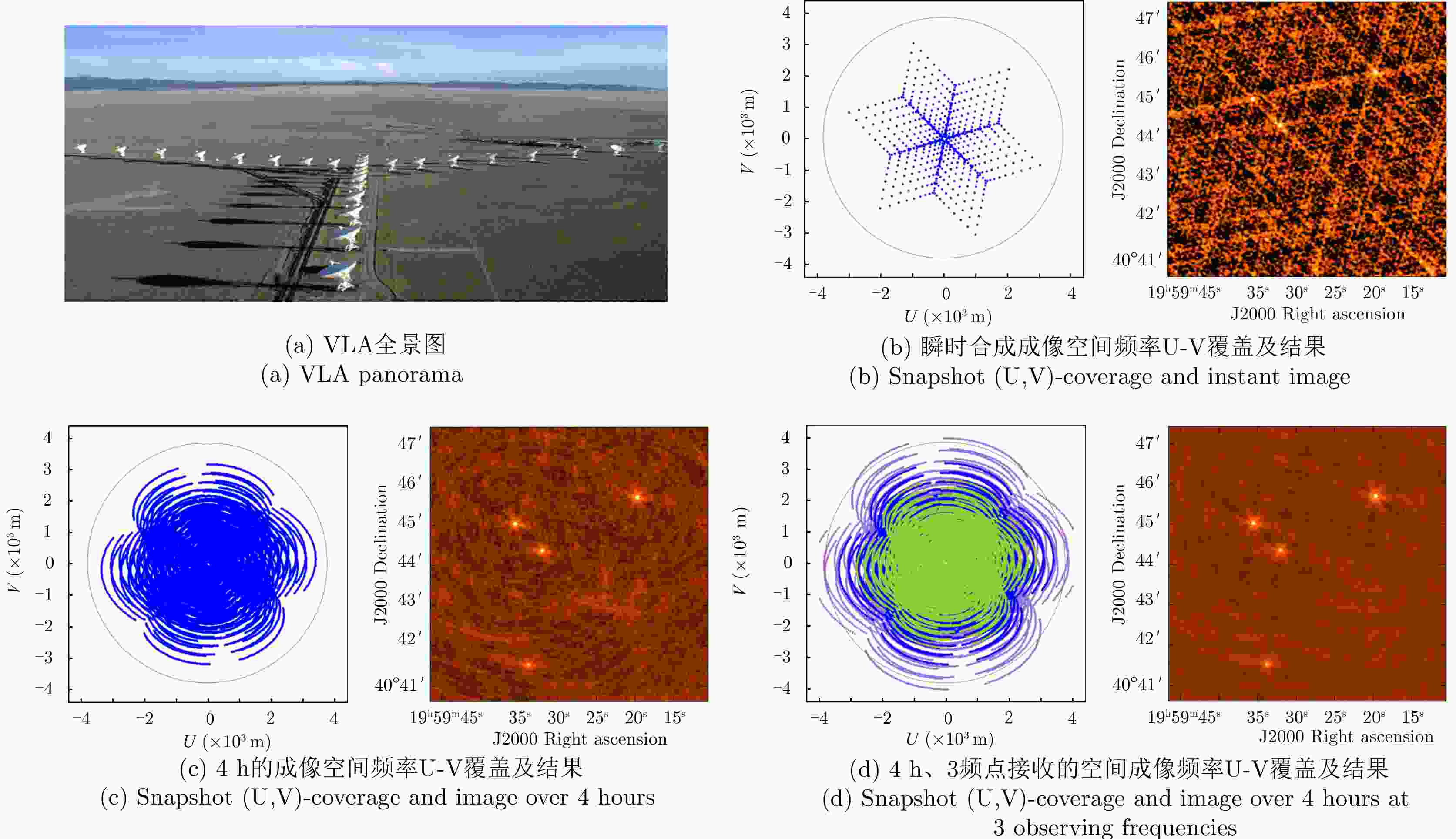
图 8 Small aperture in the Very Large Array (VLA) coherently combining on receive, and further accumulating in time and spectral dimensions [ 47]
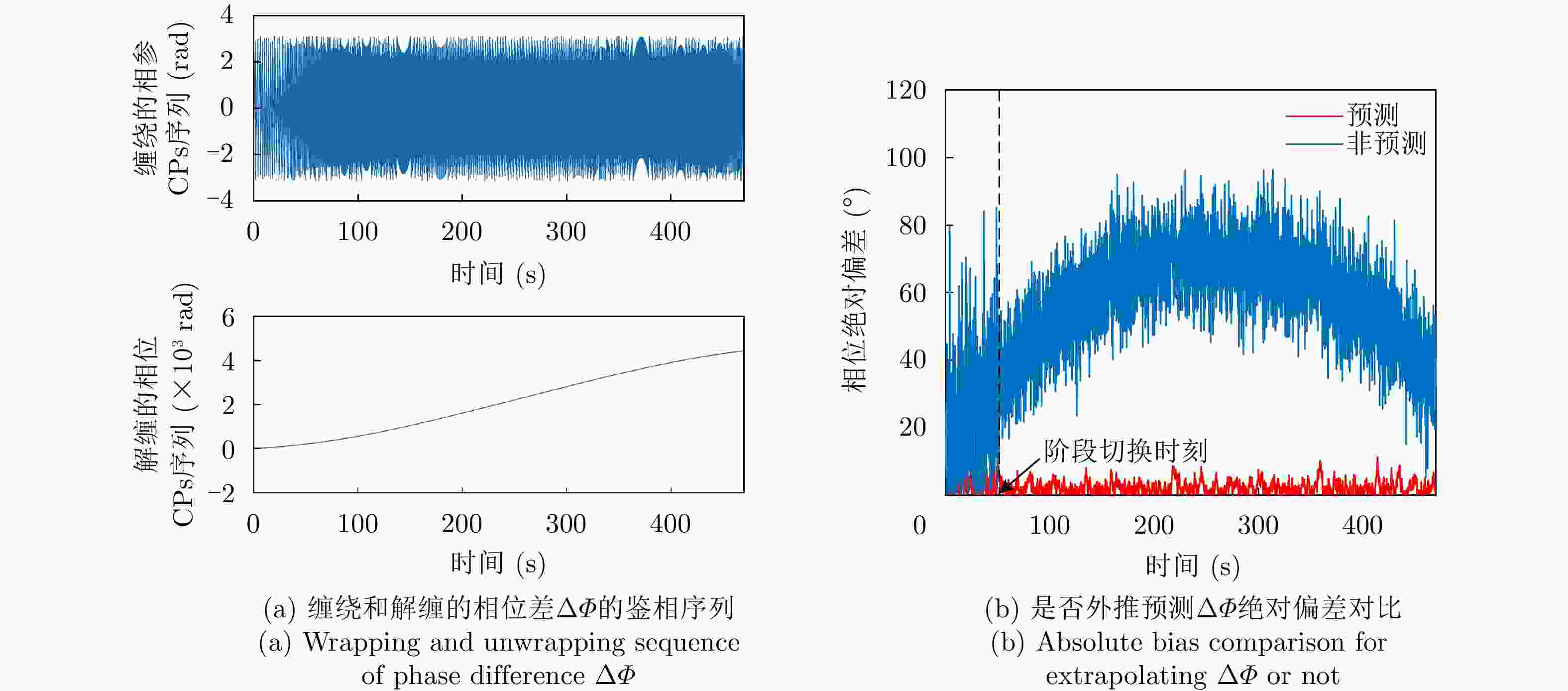
图 15 Time-varying phase bias
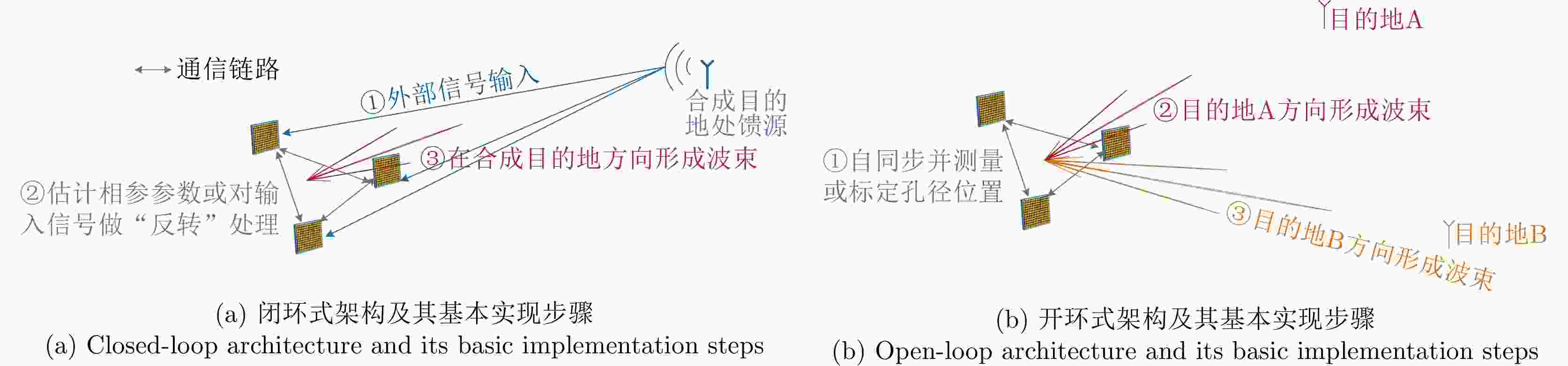
$ \Delta \varPhi $ due to combination destination motion, and extrapolation-based prediction for compensation [ 31]表 1 闭环式和开环式架构对比
Table 1. Closed-loop vs. open-loop architectures
实现架构 外部馈源输入 孔径精确位置 时频同步 相参性退化因素 波束形成位置 闭环式 必需,且一定源于合成目的地 非必需 非必需(信号“反转”合成类方法必需) 统一考虑 只能指向馈源方向 开环式 可能需要,输入不做限定且一般不源于
合成目的地4 必需 必需 拆分考虑 可自由切换 雷达 T/R组件数 T/R组件平均发射功率 天线孔径(m2) 相对功率孔径积 相对探测距离 电扫范围(°) TPY-2 25344 3.2 W 9.2 0.0012 0.19 ±60 “堆叠式”TPY-2 50688 3.2 W 18.4 0.0098 0.31 ±60 SBX 45264 2.0 W 249.0 1.0000 1.00 ±12 GBR-P 16896 1.2 W 105.0 0.0400 0.45 ±11 Have Stare 4 -- 70.0 kW (总) 573.0 4.1000 1.40 -- 时频传递方案 时间准确度 频率稳定度 特点 长波[67] ~1 μs 1×10–12@1 d 覆盖范围广,传递距离可达3000 km TWSTFT[67] ~ns 1×10–14@1 d 需要租用卫星使用时间及接收设备 White Rabbit[68] <ns 2×10–15@1 d 需要千兆同步以太网 光载射频[69] ~ps 1.6×10–18@1 d 长距离传输需要中继 自由空间光学频率梳传递[70] 100 fs 4×10−19@10000 s 需要瓦级功率的高稳定光学频率梳,以及纳瓦级高灵敏度的线性光学采样 无线稀疏双音[53] ~ps ~10–15@1 d 高精度测量基线长度并结合PLL电路实现小范围节点间的时频传递 表 1 Comparison of closed-loop and open-loop architectures
Architectures External signal inputs Precise aperture positions Time-frequency
synchronizationFactors causing coherence degradation Direction of the synthetic beam closed-loop Essential, and must originate from the combination destination Non-essential Non-essential (essential for signal “reverse processing” combination methods) Bundled consideration Restrict pointing to the feed source open-loop May be essential, inputs are unrestricted, and are typically not derived from the combination destination 3 Essential Essential Separated consideration Switch arbitrarily 表 2 Comparison of typical radars in X-band [ 22]
Radar Number of T/R module T/R module average power Antenna area (m 2) Relative power aperture product Relative range Elecrtonic scan (°) TPY-2 25344 3.2 W 9.2 0.0012 0.19 ±60 “Stacked” AN/TPY-2 50688 3.2 W 18.4 0.0098 0.31 ±60 SBX 45264 2.0 W 249.0 1.0000 1.00 ±12 GBR-P 16896 1.2 W 105.0 0.0400 0.45 ±11 Have Stare 4 -- 70 kW total 573.0 4.1000 1.40 -- Time-frequency transfer scheme Time accuracy Frequency stability Features Long wave time service [ 67] ~1 μs 1×10 –12@1 d Wide application scope (up to 3000 km) TWSTFT [ 67] ~ns 1×10 –14@1 d Requires satellite availability and receiving equipment White Rabbit [ 68] <ns 2×10 –15@1 d Require gigabit synchronous ethernet Optical carrier RF transfer [ 69] ~ps 1.6×10 –18@1 d Long-distance transfer necessitates relay stations Optical frequency comb-based
time-frequency transfer [ 70]100 fs 4×10 –19@10000 s Require Watt-level power high-stability Optical Frequency Combs (OFCs)
and nanoWatt-level high-sensitivity linear optical sampling systemsWireless sparse dual-tone [ 53] ~ps ~10 –15@1 d Require high-precision baseline length measurement, combined with
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) circuits transferring time-frequency between
nodes within a localized deployment area -
[1] LAZIO J, VIRKKI A K, PINILLA-ALONSO N, et al. The next-generation ground-based planetary radar[J]. Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, 2021, 53(4): 434. doi: 10.3847/25c2cfeb.9c808c46. [2] 鲁耀兵, 高红卫. 分布孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 216–217.LU Yaobing and GAO Hongwei. Distributed Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 216–217. [3] KORDIK A M, METCALF J G, CURTIS D D, et al. Graceful performance degradation and improved error tolerance via mixed-mode distributed coherent radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(5): 5251–5262. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3236487. [4] NANZER J A, MGHABGHAB S R, ELLISON S M, et al. Distributed phased arrays: Challenges and recent advances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4893–4907. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3092401. [5] CUOMO K M, COUTTS S D, MCHARG J C, et al. Wideband aperture coherence processing for next generation radar (NexGen)[R]. Bostan: Lincoln Laboratory, 2004. [6] 刘泉华, 张凯翔, 梁振楠, 等. 地基分布式相参雷达技术研究综述[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(12): 2443–2459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.12.001.LIU Quanhua, ZHANG Kaixiang, LIANG Zhennan, et al. Research overview of ground-based distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(12): 2443–2459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.12.001. [7] THOME G D, ENZMANN R P, and STEUDEL F. System and method for coherently combining a plurality of radars[P]. US, 7358892, 2008. [8] SHARP E and DIAB M. Van Atta reflector array[J]. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1960, 8(4): 436–438. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1960.1144877. [9] SKOLNIK M and KING D. Self-phasing array antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1964, 12(2): 142–149. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1964.1138179. [10] EBERLE J. An adaptively phased, four-element array of thirty-foot parabolic reflectors for passive (Echo) communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1964, 12(2): 169–176. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1964.1138190. [11] YOUNG D P, JACKLIN N, PUNNOOSE R J, et al. Time reversal signal processing for communication[R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, 2011. [12] 陈秋菊, 姜秋喜, 曾芳玲, 等. 基于时间反演电磁波的稀疏阵列单频信号空间功率合成[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(20): 204101. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.204101.CHEN Qiuju, JIANG Qiuxi, ZENG Fangling, et al. Single frequency spatial power combining using sparse array based on time reversal of electromagnetic wave[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(20): 204101. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.204101. [13] YAVUZ M E and TEIXEIRA F L. Ultrawideband microwave sensing and imaging using time-reversal techniques: A review[J]. Remote Sensing, 2009, 1(3): 466–495. doi: 10.3390/rs1030466. [14] TAN Long, PAN Jifei, JIANG Qiuxi, et al. Application of time-reversal in electromagnetic power synthesis under distributed motion platform[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(12): e11822. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11822. [15] HEIMILLER R C, BELYEA J E, and TOMLINSON P G. Distributed array radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(6): 831–839. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309395. [16] NANZER J A, SCHMID R L, COMBERIATE T M, et al. Open-loop coherent distributed arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1662–1672. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2637899. [17] ELLISON S M, MGHABGHAB S, DOROSHEWITZ J J, et al. Combined wireless ranging and frequency transfer for internode coordination in open-loop coherent distributed antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 68(1): 277–287. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2943292. [18] MGHABGHAB S R and NANZER J A. Open-loop distributed beamforming using wireless frequency synchronization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(1): 896–905. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3022385. [19] ELLISON S M, MGHABGHAB S R, and NANZER J A. Scalable high-accuracy ranging and wireless frequency synchronization for open-loop distributed phased arrays[C]. 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Springfield, USA, 2020: 41–44. doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS48704.2020.9184602. [20] FLETCHER A S and ROBEY F C. Performance bounds for adaptive coherence of sparse array radar[C]. 11th Conference Adaptive Sensors Array Processing, Lexington, USA, 2003. [21] COUTTS S, CUOMO K, MCHARG J, et al. Distributed coherent aperture measurements for next generation BMD radar[C]. Fourth IEEE Workshop on Sensor Array and Multichannel Processing, Waltham, USA, 2006: 390–393. doi: 10.1109/SAM.2006.1706161. [22] Committee on an Assessment of Concepts and Systems for U.S. Boost-Phase Missile Defense in Comparison to Other Alternatives, Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences, and National Research Council of the National Academies. Making Sense of Ballistic Missile Defense: An Assessment of Concepts and Systems for U.S. Boost-Phase Missile Defense in Comparison to Other Alternatives[M]. Washington: National Academies Press, 2012: (4)6–(4)10. [23] MISHORY J. DOD advises against ‘Stacked’ AN/TPY-2 radars to boost missile defense[J]. Inside the Army, 2013, 25(17): 115–116. [24] Acquisition,Technology & Logistics Agency (ATLA). Electronic systems research center[EB/OL]. https://www.mod.go.jp/atla/en/densouken.html. 2019. [25] 鲁耀兵, 张履谦, 周荫清, 等 分布式阵列相参合成雷达技术研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(8): 1657–1662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.08.12.LU Yaobing, ZHANG Lüqian, ZHOU Yinqing, et al. Study on distributed aperture coherence-synthetic radar technology[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(8): 1657–1662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.08.12. [26] 鲁耀兵, 高红卫, 周宝亮. 分布式孔径相参合成雷达技术[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 55–64. doi: 10.12000/JR17014.LU Yaobing, GAO Hongwei, and ZHOU Baoliang. Distributed aperture coherence-synthetic radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 55–64. doi: 10.12000/JR17014. [27] 周宝亮, 雷子健, 周东明, 等. 分布式孔径相参雷达预警探测技术[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(11): 1330–1338. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.008.ZHOU Baoliang, LEI Zijian, ZHOU Dongming, et al. Early-warning detection technology of distributed aperture coherent radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(11): 1330–1338. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.008. [28] 殷丕磊. 地基宽带分布式全相参雷达技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京理工大学, 2016.YIN Pilei. Research on ground-based wideband distributed coherent aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. [29] ZENG Tao, YIN Pilei, and LIU Quanhua. Wideband distributed coherent aperture radar based on stepped frequency signal: Theory and experimental results[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(4): 672–688. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0221. [30] YIN Pilei, YANG Xiaopeng, LIU Quanhua, et al. Wideband distributed coherent aperture radar[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 1114–1117. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875762. [31] LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, WANG Luoshengbin, et al. Dual-radar coherently combining: Generalised paradigm and verification example[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(5): 689–699. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5089. [32] LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, LIU Xiang, et al. A clean signal reconstruction approach for coherently combining multiple radars[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2018, 2018(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s13634-018-0569-1. [33] 刘兴华. 分布式多雷达认知协同探测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2019.LIU Xinghua. Research on cognitive collaboration technology of distributed radars[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2019. [34] LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, and XIAO Shunping. Performance gain bounds of coherently combining multiple radars in a target-based calibration manner[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30(2): 278–287. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.02.07. [35] VILNROTTER V, LEE D, CORNISH T, et al. Uplink arraying experiment with the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft[R]. California: Jet Propulsion Laboratory IPN Progress Report 42–166, 2006. [36] VILNROTTER V, LEE D, MUKAI R, et al. Three-antenna Doppler-delay imaging of the crater Tycho for uplink array calibration applications[R]. California: Jet Propulsion Laboratory IPN Progress Report 42–169, 2007. [37] DAVARIAN F. Uplink arraying next steps[R]. California: Jet Propulsion Laboratory IPN Progress Report 42–175, 2008. [38] VILNROTTER V, LEE D, TSAO P, et al. Uplink array calibration via lunar Doppler-delay imaging[C]. 2010 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2010: 1–12. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2010.5446969. [39] GELDZAHLER B J. Coherent uplink arraying techniques for next generation space communications and planetary radar systems[C]. SPIE 8040, Active and Passive Signatures II, Orlando, USA, 2011: 80400A. [40] GELDZAHLER B, MILLER M, BIRR R, et al. Field demonstration of coherent uplink from a phased array of widely separated antennas: Steps toward a verifiable real-time atmospheric phase fluctuation correction for a high resolution radar system[C]. Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies (AMOS), Maui, USA, 2014. [41] GELDZAHLER B, BERSHAD C, BROWN R, et al. A phased array of widely separated antennas for space communication and planetary radar[C]. Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance (AMOS) Technologies Conference, Wailea, Hawaii, 2017. [42] 王虎, 韩长喜, 薛慧. 美国深空先进雷达发展研究[J]. 飞航导弹, 2021(12): 122–126, 145. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20210252.WANG Hu, HAN Changxi, XUE Hui, United States deep space advanced radar development study[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2021(12): 122–126, 145. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20210252. [43] Johns HOPKINS. Johns Hopkins APL delivers new satellite tracking capability to U.S. space force[EB/OL]. https://www.jhuapl.edu/news/news-releases/220324-apl-delivers-satellite-tracking-capability-to-space-force, 2022. [44] SANCHEZ NET M, TAYLOR M, VILNROTTER V, et al. A ground-based planetary radar array[R]. California: Jet Propulsion Laboratory IPN Progress Report 42–229, 2022. [45] 龙腾. “中国复眼”: 深空雷达探测面临的挑战与机遇[J]. 高科技与产业化, 2023, 29(4): 14–17.LONG Teng. China’s compound eye: Challenges and opportunities for deep space radardetection[J]. High-Technology & Commercialization, 2023, 29(4): 14–17. [46] THOMPSON A R, MORAN J M, and SWENSON JR G W. Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy[M]. Cham: Springer, 2017: 44–56. [47] RAU U. Introduction to radio interferometry – algorithms and computing[EB/OL]. http://www.aoc.nrao.edu/~rurvashi/DataFiles/Talk_CHTCVisit_Intro_Radio_Interferometry_UR.pdf, 2019. [48] 彭勃, 金乘进, 杜彪, 等. 持续参与世界最大综合孔径望远镜SKA国际合作[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2012, 42(12): 1292–1307. doi: 10.1360/132012-662.PENG Bo, JIN Chengjin, DU Biao, et al. China’s participation in the SKA—the world’s largest synthesis radio telescope[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2012, 42(12): 1292–1307. doi: 10.1360/132012-662. [49] Focus on first Sgr A* results from the event horizon telescope[EB/OL]. https://iopscience.iop.org/journal/2041-8205/page/Focus_on_First_Sgr_A_Results, 2022. [50] 刘兴华, 徐振海, 肖顺平. 分布式相参雷达几何布置约束条件[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09.LIU Xinghua, XU Zhenhai, and XIAO Shunping. Geometric arrangement constraints of distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(8): 1723–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.08.09. [51] LEWANDOWSKI W, AZOUBIB J, and KLEPCZYNSKI W J. GPS: Primary tool for time transfer[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(1): 163–172. doi: 10.1109/5.736348. [52] LOMBARDI M A, NELSON L M, NOVICK A N, et al. Time and frequency measurements using the global positioning system[J]. Cal Lab: International Journal of Metrology, 2001, 8(3): 26–33. [53] MERLO J M, MGHABGHAB S R, and NANZER J A. Wireless picosecond time synchronization for distributed antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023, 71(4): 1720–1731. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3227878. [54] KIRCHNER D. Two-way Satellite Time and Frequency Transfer (TWSTFT): Principle, Implementation, and Current Performance[M]. STONE W R. Review of Radio Science 1996–1999. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999: 27–44. [55] FUJIEDA M, GOTOH T, NAKAGAWA F, et al. Carrier-phase-based two-way satellite time and frequency transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2012, 59(12): 2625–2630. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2012.2503. [56] FUJIEDA M, GOTOH T, and AMAGAI J. Advanced two-way satellite frequency transfer by carrier-phase and carrier-frequency measurements[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016, 723: 012036. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/723/1/012036. [57] IEEE.1588-2019 IEEE Standard for a precision clock synchronization protocol for networked measurement and control systems[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 1–499. [58] 李培基, 李卫, 朱祥维, 等. 网络时间同步协议综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(3): 30–38. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0008.LI Peiji, LI Wei, ZHU Xiangwei, et al. Overview of network time synchronization protocol[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(3): 30–38. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0008. [59] MGHABGHAB S, OUASSAL H, and NANZER J A. Wireless frequency synchronization for coherent distributed antenna arrays[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, Atlanta, USA, 2019: 1575–1576. doi: 10.1109/APUSNCURSINRSM.2019.8889331. [60] MGHABGHAB S R, SCHLEGEL A, and NANZER J A. Adaptive distributed transceiver synchronization over a 90 m microwave wireless link[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(5): 3688–3699. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2021.3138506. [61] RASHID M and NANZER J A. Frequency and phase synchronization in distributed antenna arrays based on consensus averaging and Kalman filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(4): 2789–2803. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3213788. [62] 杨文哲, 杨宏雷, 赵环, 等. 光纤时频传递技术进展[J]. 时间频率学报, 2019, 42(3): 214–223. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2019-03-0214-10.YANG Wenzhe, YANG Honglei, ZHAO Huan, et al. Technical progress of fiber-based time and frequency transfer[J]. Journal of Time and Frequency, 2019, 42(3): 214–223. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2019-03-0214-10. [63] 曾涛, 殷丕磊, 杨小鹏, 等. 分布式全相参雷达系统时间与相位同步方案研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 105–110. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20104.ZENG Tao, YIN Pilei, YANG Xiaopeng, et al. Time and phase synchronization for distributed aperture coherent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 105–110. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20104. [64] SEO M, RODWELL M, and MADHOW U. A feedback-based distributed phased array technique and its application to 60-GHz wireless sensor network[C]. 2008 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, USA, 2008: 683–686. doi: 10.1109/MWSYM.2008.4632924. [65] BIDIGARE P, OYARZYN M, RAEMAN D, et al. Implementation and demonstration of receiver-coordinated distributed transmit beamforming across an ad-hoc radio network[C]. 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2012: 222–226. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2012.6488994. [66] SUN Peilin, TANG Jun, HE Qian, et al. Cramer-Rao bound of parameters estimation and coherence performance for next generation radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2013, 7(5): 553–567. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0139. [67] 梁益丰, 许江宁, 吴苗, 等. 光纤时频同步技术的研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(5): 050004. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.050004.LIANG Yifeng, XU Jiangning, WU Miao, et al. Research progress on optical fiber time-frequency synchronization technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(5): 050004. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.050004. [68] KAUR N, FRANK F, PINTO J, et al. A 500-km cascaded white rabbit link for high-performance frequency dissemination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2022, 69(2): 892–901. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2021.3134163. [69] 全洪雷, 薛文祥, 赵文宇, 等. 国家授时中心高精度光纤微波频率传递研究进展[J]. 时间频率学报, 2021, 44(4): 255–265. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2021-04-0255-11.QUAN Honglei, XUE Wenxiang, ZHAO Wenyu, et al. Progress of high-resolution fiber-based microwave frequency dissemination in NTSC[J]. Journal of Time and Frequency, 2021, 44(4): 255–265. doi: 10.13875/j.issn.1674-0637.2021-04-0255-11. [70] DIDDAMS S A, VAHALA K, and UDEM T. Optical frequency combs: Coherently uniting the electromagnetic spectrum[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6501): eaay3676. doi: 10.1126/science.aay3676. [71] 袁一博. 光纤网络时间频率传输与同步技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 清华大学, 2017.YUAN Yibo. The research on fiber-based time and frequency dissemination and sychronization technique[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2017. [72] CLIVATI C, AIELLO R, BIANCO G, et al. Common-clock very long baseline interferometry using a coherent optical fiber link[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(8): 1031–1037. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.393356. [73] SHEN Qi, GUAN Jianyu, REN Jigang, et al. Free-space dissemination of time and frequency with 10−19 instability over 113 km[J]. Nature, 2022, 610(7933): 661–666. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05228-5. [74] 宋靖, 牛朝阳, 张剑云. 分布式全相参雷达正交频分LFM信号设计及性能分析[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2015, 45(8): 968–984. doi: 10.1360/N112014-00185.SONG Jing, NIU Zhaoyang, and ZHANG Jianyun. OFD-LFM signal design and performance analysis for distributed aperture fully coherent radar[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2015, 45(8): 968–984. doi: 10.1360/N112014-00185. [75] 宋靖, 周青松, 张剑云. 基于相关法的分布式全相参雷达相干参数估计及相参性能[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(7): 1710–1715. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141339.SONG Jing, ZHOU Qingsong, and ZHANG Jianyun. Coherent parameters estimation by cross-correlation for distributed aperture fully coherent radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(7): 1710–1715. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141339. [76] 陈金铭, 王彤, 吴建新, 等. 基于滤波器网格失配的分布式相参雷达目标参数估计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(11): 2460–2470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.09.CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, WU Jianxin, et al. Target parameter estimation method for distributed coherent aperture radar based on grid mismatch filtering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(11): 2460–2470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.09. [77] MGHABGHAB S and NANZER J A. Ranging requirements for open-loop coherent distributed arrays with wireless frequency synchronization[C]. 2020 IEEE USNC-CNC-URSI North American Radio Science Meeting, Montreal, Canada, 2020: 69–70. doi: 10.23919/USNC/URSI49741.2020.9321643. [78] ELLISON S M and NANZER J A. High-accuracy multinode ranging for coherent distributed antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(5): 4056–4066. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2985251. [79] HODKIN J E, ZILEVU K S, SHARP M D, et al. Microwave and millimeter-wave ranging for coherent distributed RF systems[C]. 2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2015: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2015.7118937. [80] ELLISON S M, MGHABGHAB S R, and NANZER J A. Multi-node open-loop distributed beamforming based on scalable, high-accuracy ranging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(2): 1629–1637. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3130793. [81] LIU Xiaoyu, WANG Tong, CHEN Jinming, et al. Efficient configuration calibration in airborne distributed radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 1799–1817. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3139431. [82] CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. Identifiability analysis of positioning and synchronization errors in airborne distributed coherence aperture radars[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5978–5993. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3144481. [83] 陈金铭, 王彤, 吴建新, 等. 基于特显点的机载分布式相参雷达同步误差校正方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 356–363. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190694.CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, WU Jianxin, et al. Airborne distributed coherent aperture radar synchronization error calibration method based on prominent points[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 356–363. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190694. [84] CHEN Jinming, WANG Tong, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. Time and phase synchronization using clutter observations in airborne distributed coherent aperture radars[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(3): 432–449. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.040. [85] ZHOU Dingsen, YANG Minglei, YANG Rong, et al. Distributed coherent aperture radar on moving platforms: Theoretical study and tests[C]. 2022 16th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2022: 518–523. doi: 10.1109/ICSP56322.2022.9965321. [86] OUASSAL H, YAN Ming, and NANZER J A. Decentralized frequency alignment for collaborative beamforming in distributed phased arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(10): 6269–6281. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3073120. [87] OUASSAL H, ROCCO T, YAN Ming, et al. Decentralized frequency synchronization in distributed antenna arrays with quantized frequency states and directed communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(7): 5280–5288. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2977751. [88] XIAO Xuedi, LI Shangyuan, XUE Xiaoxiao, et al. Photonics-assisted broadband distributed coherent aperture radar for high-precision imaging of dim-small targets[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2019, 11(5): 5502709. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2019.2934472. [89] 李尚远, 肖雪迪, 郑小平. 基于微波光子学的分布式相参孔径雷达[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 178–188. doi: 10.12000/JR19024.LI Shangyuan, XIAO Xuedi, and ZHENG Xiaoping. Distributed coherent aperture radar enabled by microwave photonics[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 178–188. doi: 10.12000/JR19024. [90] LEMBO L, MARESCA S, SERAFINO G, et al. In-field demonstration of a photonic coherent MIMO distributed radar network[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835849. [91] 吴剑旗, 戴晓霖, 杨利民, 等. 一种大基线分布雷达近场相参探测技术[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(6): 579–583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.06.001.WU Jianqi, DAI Xiaolin, YANG Limin, et al. Study on a near-field coherent detection technology for long-baseline distributed radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(6): 579–583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.06.001. [92] 臧会凯, 雷欢, 但晓东, 等. 分布式雷达相参发射原理与性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(8): 1801–1807. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141563.ZANG Huikai, LEI Huan, DAN Xiaodong, et al. Theory and performance analysis of coherent transmission for distributed radars[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(8): 1801–1807. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141563. [93] 王元昊, 王宏强, 刘兴华, 等. 分布式相参雷达相参效率及相参景深研究[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20221229.1852.012.html, 2023.WANG Yuanhao, WANG Hongqiang, LIU Xinghua, et al. Research on transmit coherent synthesis efficiency and coherent depth of field of distributed coherent aperture radar[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20221229.1852.012.html, 2023. [94] VILNROTTER V, JAO J, GIORGINI J, et al. Proving the uplink array for radar observations[R]. California: Jet Propulsion Laboratory IPN Progress Report 42–223, 2020. [95] VILNROTTER V, GIORGINI J, JAO J, et al. Development of an uplink array radar system for cis-lunar and planetary observations[C]. 2023 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2023: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/AERO55745.2023.10115810. [96] CUOMO K M, PIOU J E, and MAYHAN J T. Ultra-wideband coherent processing[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 203–222. [97] YANG Xiaopeng, YIN Pilei, ZENG Tao, et al. Applying auxiliary array to suppress mainlobe interference for ground-based radar[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2013, 12: 433–436. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2013.2254698. [98] ZHANG Honggang, LUO Jian, CHEN Xinliang, et al. Whitening filter for mainlobe interference suppression in distributed array radar[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059238. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公












 下载:
下载: