MCJ-UNet: A Dual/Multi-channel-joint Phase Unwrapping Network for Interferometric SAR
-
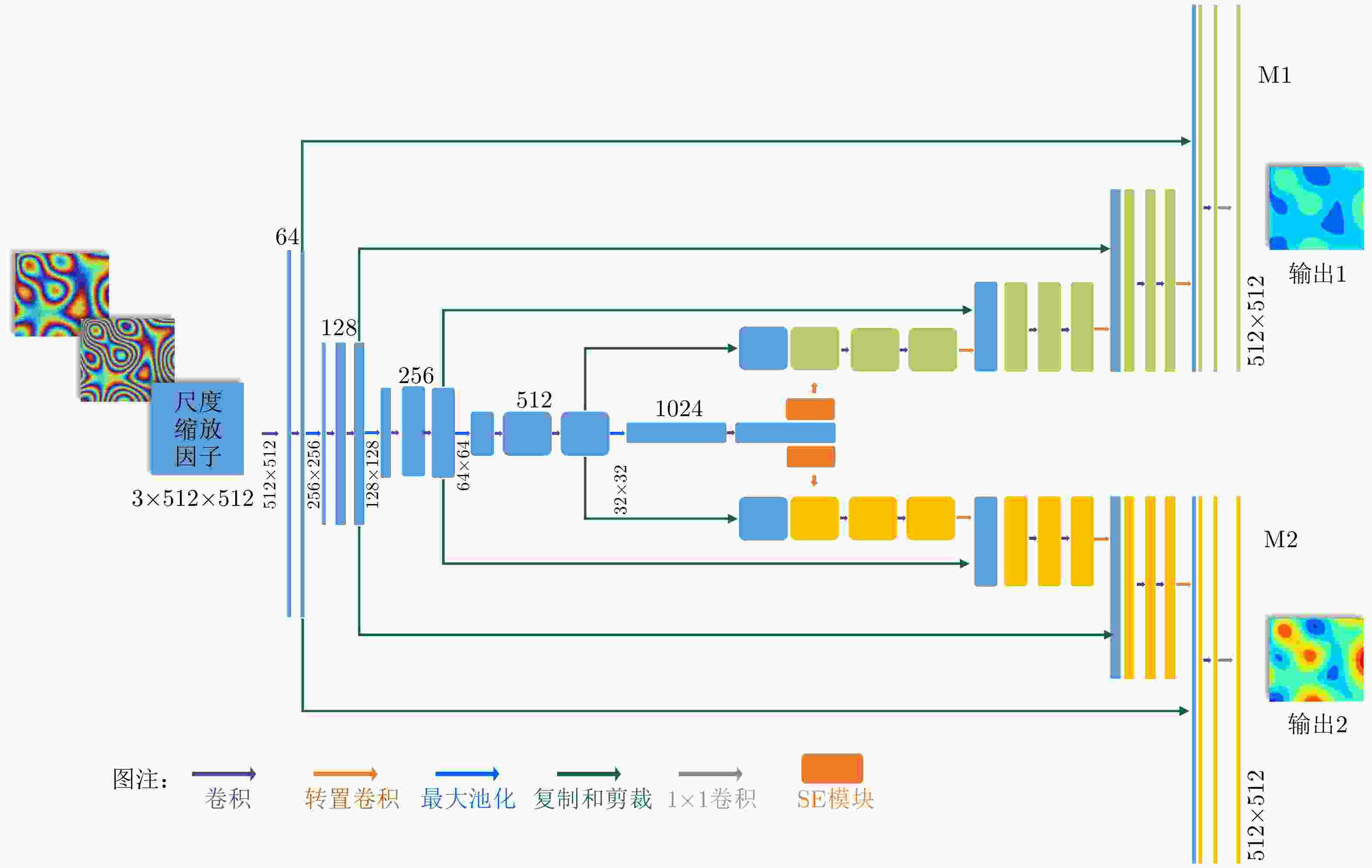
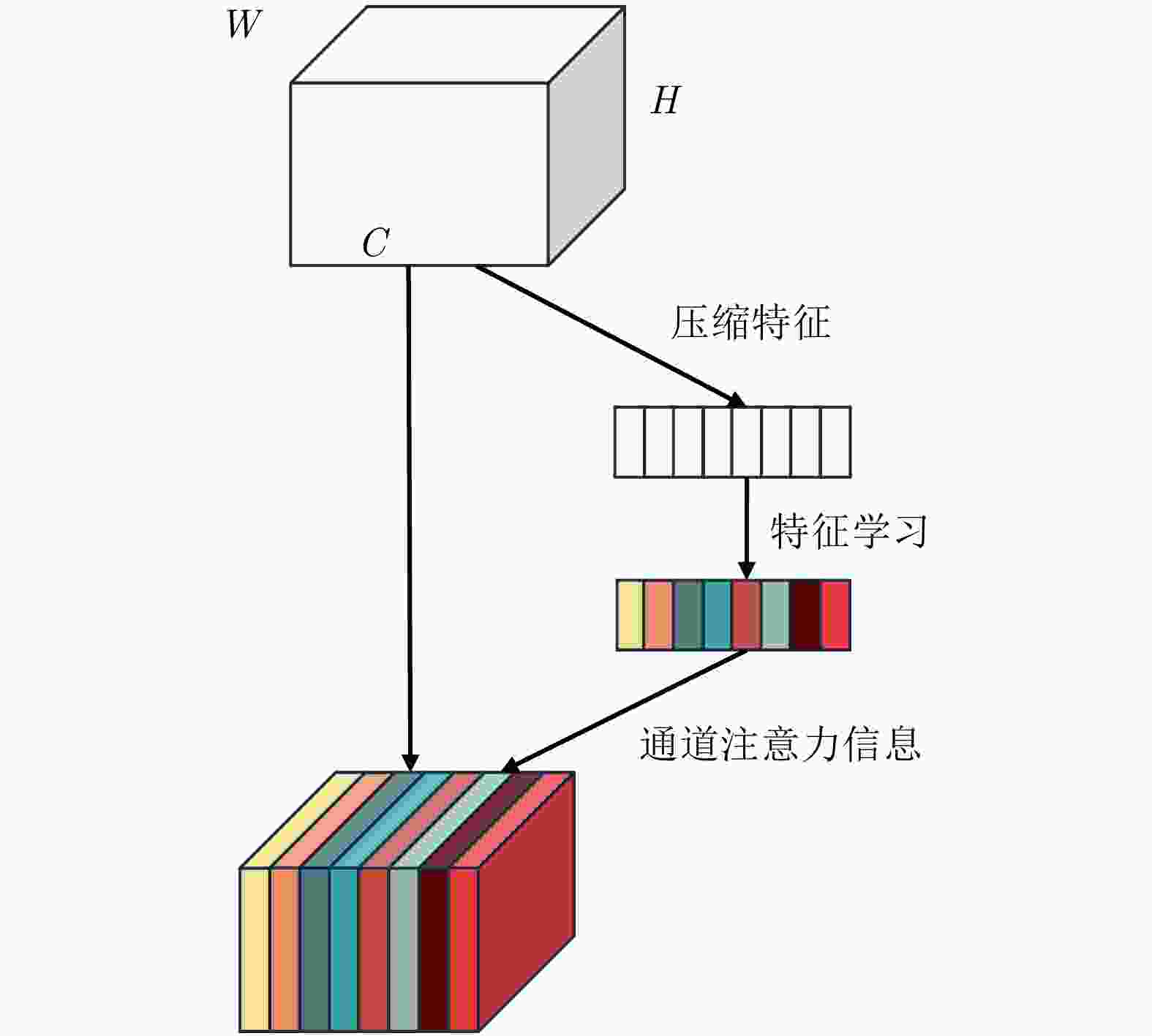
摘要: 干涉合成孔径雷达(InSAR)可实现地表高程的高效获取,在地形测绘中应用广泛。双/多通道InSAR技术可借助不同通道(基线、频点)的高程模糊度差异,解决相位欠采样问题,完成高程陡变区域的干涉相位解缠,实现InSAR技术在测绘困难区域的有效应用。该文即面向高效高精度相位解缠需求,利用深度学习这一有力工具,结合不同通道的相位特征及相互约束关系,提出了一种双/多通道联合干涉相位解缠网络:Multi-Channel-Joint-UNet (MCJ-UNet)。该网络的构建以双通道(双频、双基线) InSAR为基本观测构型,并可实现向多通道构型的扩展,其构建的核心思路主要包括3点:首先,将干涉相位解缠中的模糊数估计问题转化为语义分割问题,并采用UNet网络完成分割处理;其次,引入挤压激励模块(SE)动态调整信息权重,以增强网络不同通道对其所需信息的感知能力;最后,利用多通道联合约束下的相位残差优化损失函数,实现网络调谐。此外,为避免语义分割结果的边缘细节误差对解缠效果的影响,该文还提出了一种基于多通道联合约束的解缠误差自修正方法,以保证解缠质量。模拟地形仿真数据、真实地形仿真数据以及TerraSAR-X实测数据验证了所提方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 干涉合成孔径雷达(InSAR) /
- 多通道 /
- 相位解缠 /
- 深度学习 /
- UNet网络
Abstract: Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) enables the efficient retrieval of surface elevation and has extensive applications in terrain mapping. Dual/multi-channel InSAR techniques utilize the differences in the elevation ambiguity of different InSAR channels (i.e., baselines and frequencies) to perform Phase Unwrapping (PU). This enables the effective application of InSAR in regions with abrupt terrain changes. In response to the growing demand for efficient and precise PU, this study leverages deep learning and proposes a dual/multi-channel joint PU network, i.e., Multi-Channel-Joint-UNet (MCJ-UNet), which effectively combines multi-channel phase characteristics and their mutual constraint relationships. The proposed network is constructed based on the dual-channel (i.e., dual-frequency and dual-baseline) InSAR observation configuration. It can also be extended to multi-channel InSAR. The core concept of the proposed method can be summarized as follows. First, the method transforms the elevation ambiguity estimation problem in PU into semantic segmentation, and the UNet network is employed to accomplish the segmentation processing. Second, the squeeze-and-excitation module is introduced to dynamically adjust the information weights, enhancing the network’s perception of the required information across different channels. Third, a phase residual optimization loss function is employed in the context of multi-channel joint constraints to achieve network tuning. In addition, to mitigate the effect of edge detail errors in semantic segmentation results on PU performance, a self-correcting approach for PU errors based on multi-channel joint constraints is proposed. The proposed MCJ-UNet is verified by computer simulations based on simulated and real terrains and experiments based on real TerraSAR-X data. -
表 1 模拟地形仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of simulated terrain
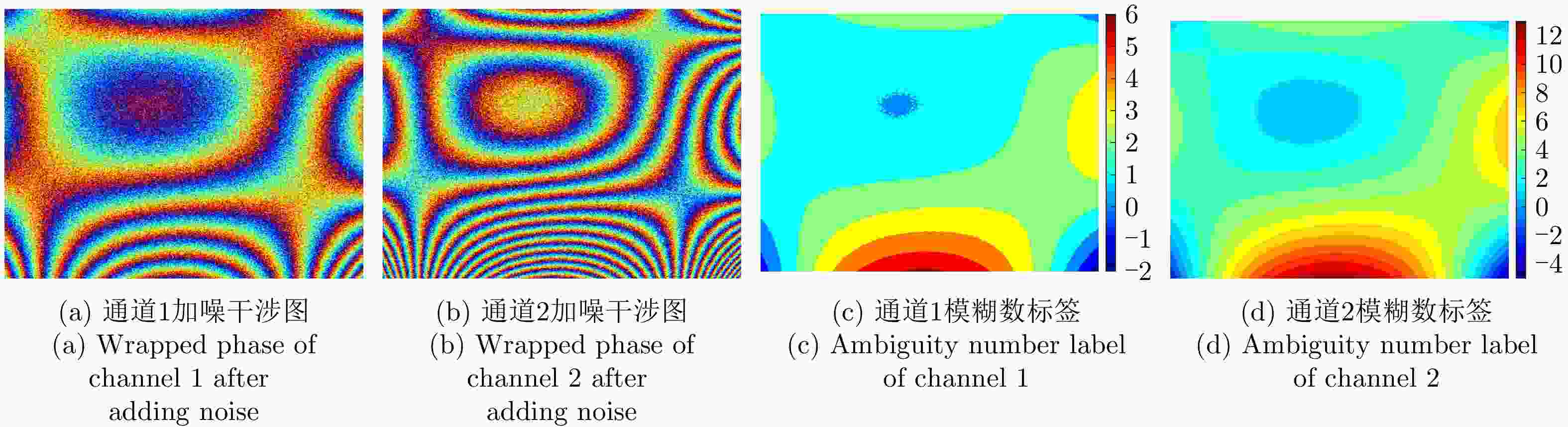
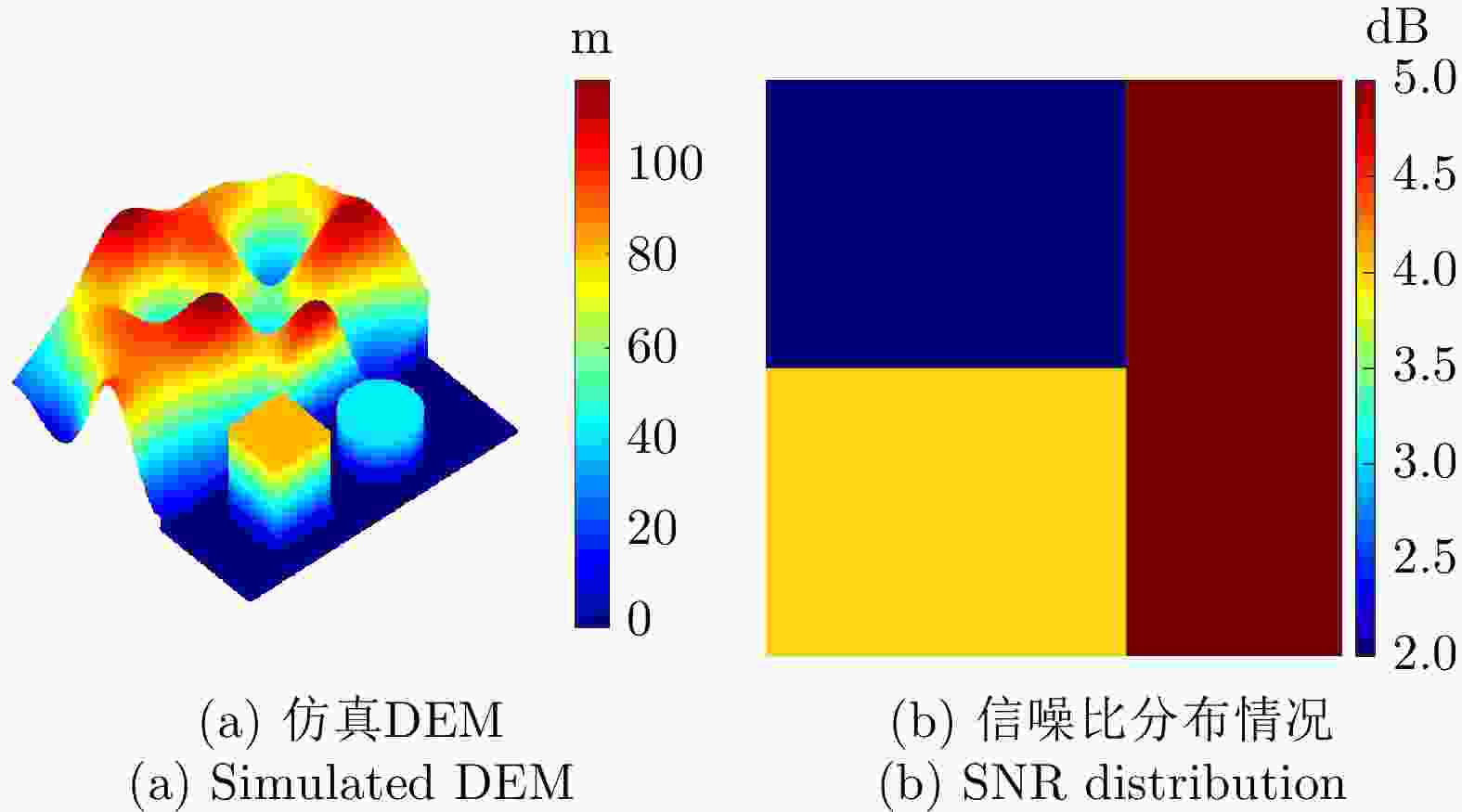
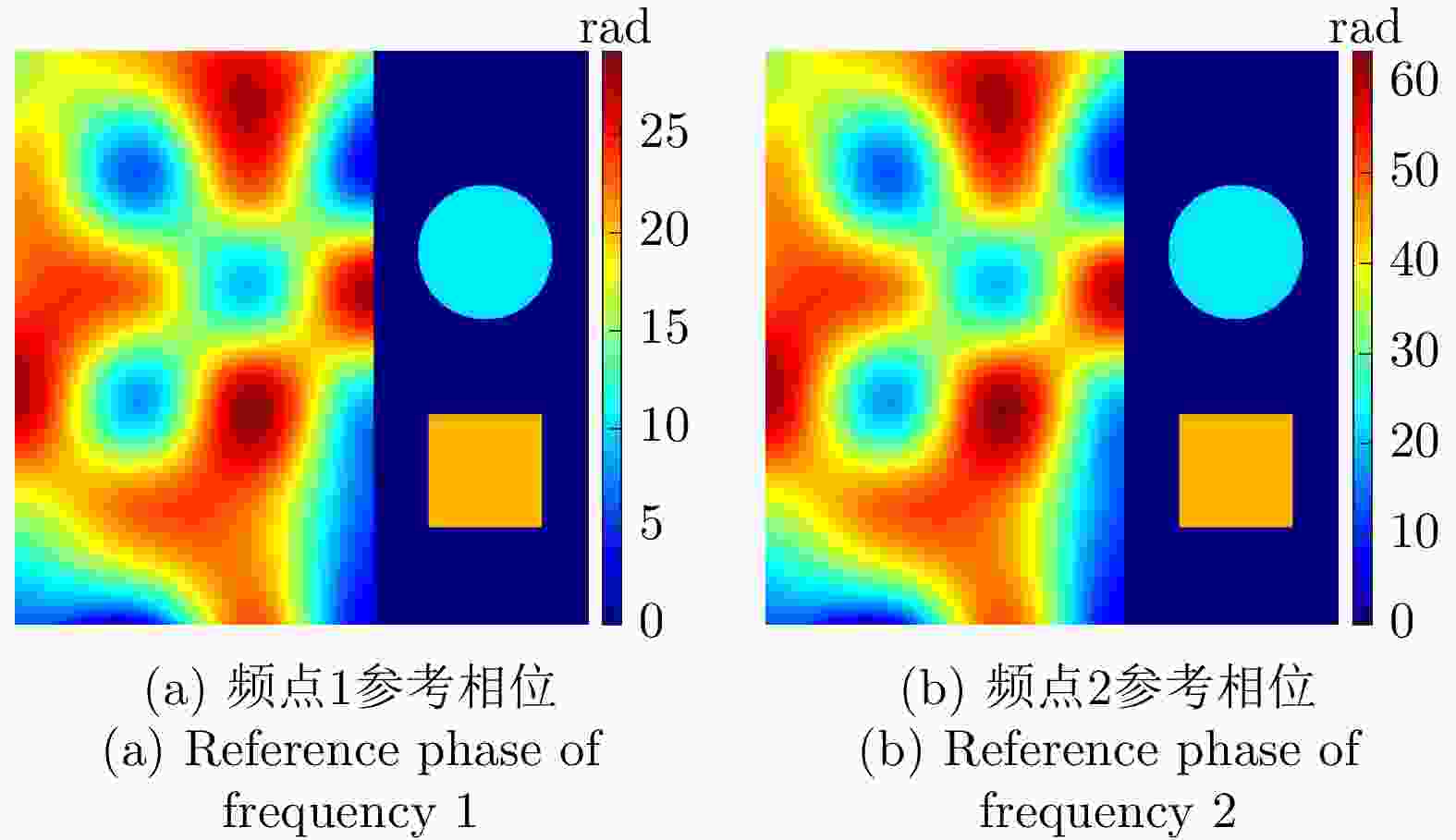
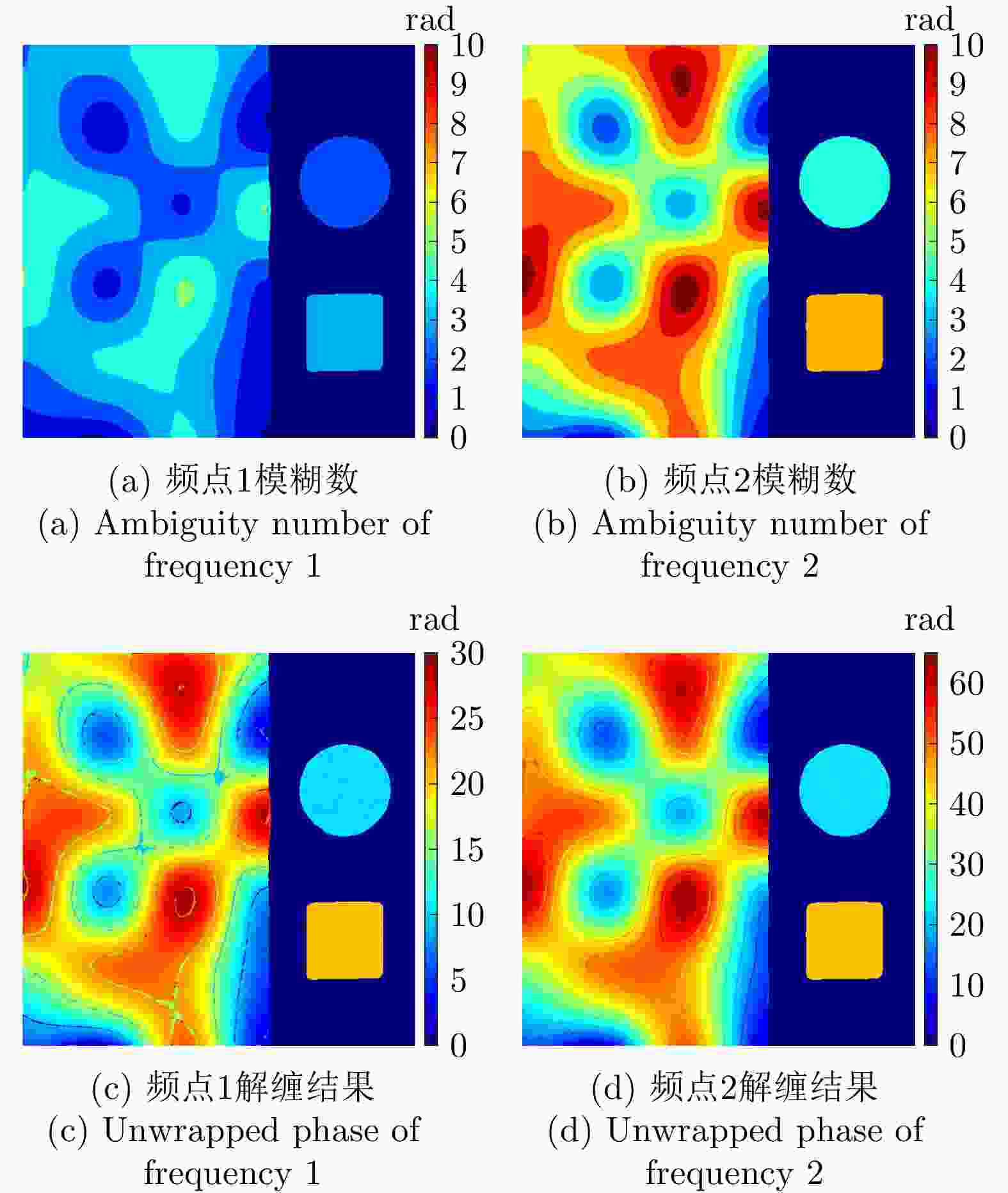
参数 数值 下视角 30° 频点1 5.25 GHz 频点2 11.50 GHz 图像尺寸 512×512 信噪比 2~5 dB 表 2 各方法所获取的仿真地形解缠相位评估结果
Table 2. Evaluation results of the unwrapped phase of simulated terrain obtained by different methods
处理方法 RMSE
(rad)网络运行
时间(s)后处理时间(s) MLE 2.49 – 28.4 TSPA 4.41 – 95.9 CANet 1.27 1.9 34.7 MCJ-UNet 1.38 2.1 2.1 表 3 真实地形仿真参数
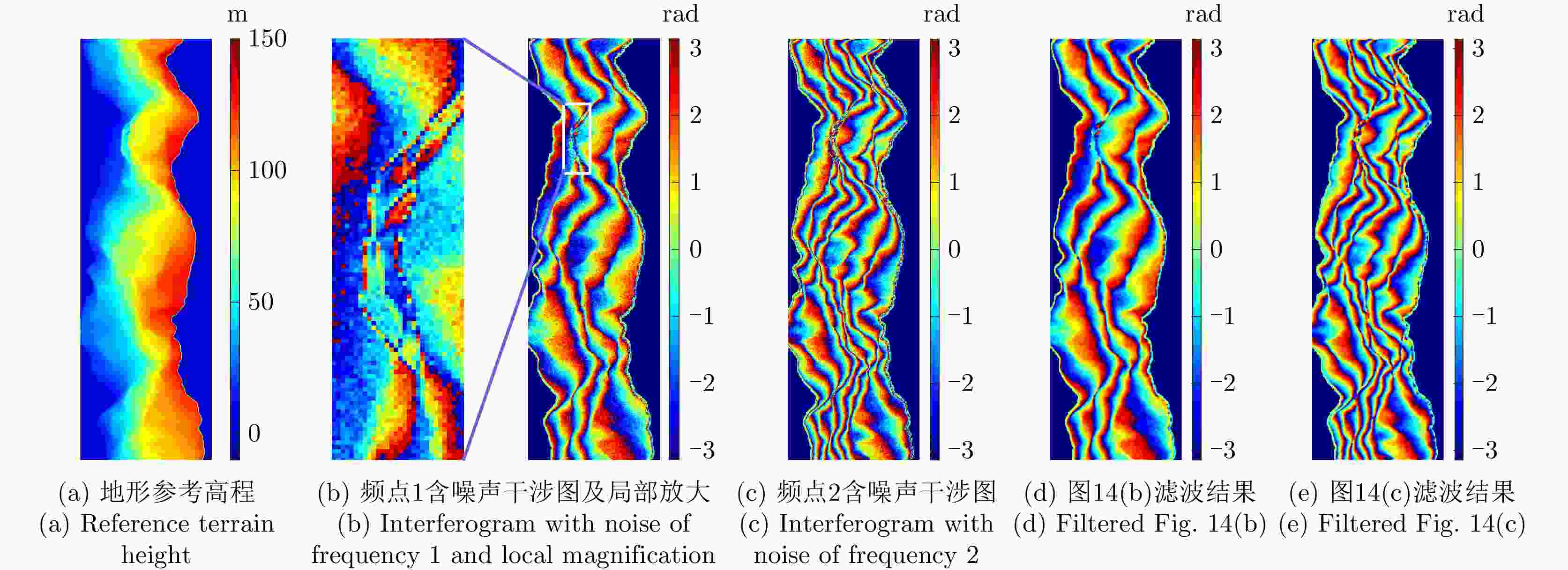
Table 3. Simulation parameters of real terrain
参数 数值 下视角 30° 频点1 6.20 GHz 频点2 11.50 GHz 卫星轨道高度 500 km 基线长度 205 m 图像尺寸 512×160 信噪比 7.5 dB 表 4 各方法所获取真实地形仿真相位解缠评估结果
Table 4. Evaluation results of real terrain simulation phase unwrapping obtained by different methods
处理方法 RMSE (rad) 网络运行时间(s) 后处理时间(s) MLE 5.50 – 9.1 TSPA 3.52 – 24.3 CANet 2.78 1.4 8.6 MCJ-UNet通道1 2.92 1.9 – MCJ-UNet通道2 2.85 1.9 – MCJ-UNet 2.55 1.9 0.6 表 5 多基线InSAR实测数据主要参数
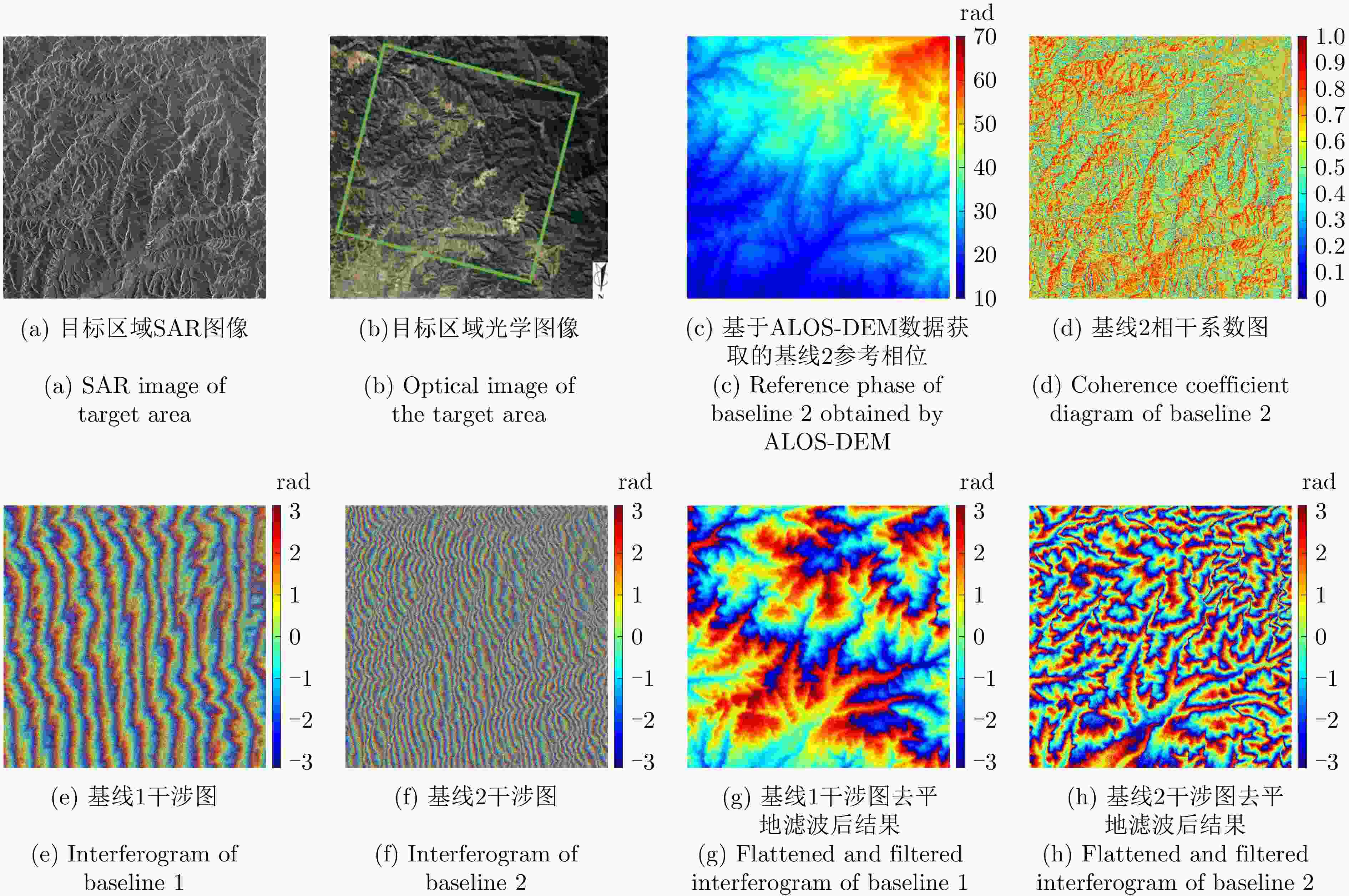
Table 5. Main parameters of multi-baseline InSAR real data
参数 数值 成像模式 条带 载频 9.65 GHz 入射角 33.14° 距离向分辨率 2.1 m 方位向分辨率 3.3 m 基线1长度 25.92 m 基线2长度 67.63 m 图像尺寸 4096×4096 表 6 各方法所获取实测数据解缠相位评估结果
Table 6. Evaluation results of unwrapped phase of real data obtained by different methods
处理方法 RMSE (rad) 网络运行
时间(s)后处理时间(s) MLE 4.91 – 1817.3 TSPA 1.82 – 15368.6 CANet 1.58 20.4 2884.2 MCJ-UNet通道1 1.97 22.6 – MCJ-UNet通道2 1.86 22.6 – MCJ-UNet 1.61 22.6 138.2 表 7 各对比方法的分类准确率及训练时间
Table 7. Classification accuracy and training time of each comparison method
方法 指标 方法
编号网络结构
是否加入
SE模块损失函数
是否加入
残差优化项通道1分类
准确率(%)通道2分类
准确率(%)训练时间(s) 1 否 否 92.50 91.14 11374.64 2 否 是 93.41 93.09 14727.56 3 是 否 96.83 95.98 12054.28 4 是 是 97.22 97.03 15236.20 -
[1] BAMLER R and HARTL P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Inverse Problems, 1998, 14(4): R1–R54. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/14/4/001 [2] BÜRGMANN R, ROSEN P A, and FIELDING E J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure earth’s surface topography and its deformation[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 169–209. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.169 [3] ITOH K. Analysis of the phase unwrapping algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(14): 2470. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.002470 [4] EINEDER M and KRIEGER G. Interferometric digital elevation model reconstruction-experiences from SRTM and multi channel approaches for future missions[C]. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea (South), 2005: 2664–2667. [5] JORDAN R L, HUNEYCUTT B L, and WERNER M. The SIR-C/X-SAR synthetic aperture radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 829–839. [6] 林圣, 王震, 丁泽刚, 等. 多频干涉SAR局部条纹频率估计方法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(3): 314–318. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.03.009LIN Sheng, WANG Zhen, DING Zegang, et al. Local fringe frequencies estimation method based on multi-frequency InSAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(3): 314–318. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.03.009 [7] GINI F and LOMBARDINI F. Multibaseline cross-track SAR interferometry: A signal processing perspective[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2005, 20(8): 71–93. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2005.1499278 [8] ZHU Xiaoxiang, WANG Yuanyuan, MONTAZERI S, et al. A review of ten-year advances of multi-baseline SAR interferometry using TerraSAR-X data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1374. doi: 10.3390/rs10091374 [9] DING Zegang, WANG Zhen, WANG Yan, et al. Refined multifrequency interferometric SAR phase unwrapping for extremely steep terrain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5221320. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3142996 [10] DING Zegang, WANG Zhen, LIN Sheng, et al. Local fringe frequency estimation based on multifrequency InSAR for phase-noise reduction in highly sloped terrain[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1527–1531. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2720695 [11] PASCAZIO V and SCHIRINZI G. Multifrequency InSAR height reconstruction through maximum likelihood estimation of local planes parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(12): 1478–1489. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2002.804274 [12] FERRAIOLI G, SHABOU A, TUPIN F, et al. Multichannel phase unwrapping with graph cuts[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 562–566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2021165 [13] XU Wei, CHANG E C, KWOH L K, et al. Phase-unwrapping of SAR interferogram with multi-frequency or multi-baseline[C]. 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2007: 730–732. [14] YU Hanwen, LI Zhenfang, and BAO Zheng. A cluster-analysis-based efficient multibaseline phase-unwrapping algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 478–487. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2055569 [15] FORNARO G, PAUCIULLO A, and SANSOSTI E. Phase difference-based multichannel phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(7): 960–972. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.849302 [16] ZENG Tao, LIU Tiandong, DING Zegang, et al. Phase unwrapping method based on multi-frequency InSAR in highly sloped terrain[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(12): 1058–1059. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.3795 [17] 葛仕奇, 陈亮, 丁泽刚, 等. 利用梯度重建的稳健多频InSAR相位解缠方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2013, 42(3): 367–373, 396.GE Shiqi, CHEN Liang, DING Zegang, et al. A robust multi-frequency phase unwrapping[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographiea Siniea, 2013, 42(3): 367–373, 396. [18] YU Hanwen and LAN Yang. Robust two-dimensional phase unwrapping for multibaseline SAR interferograms: A two-stage programming approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5217–5225. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2558541 [19] ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, LAN Yang, et al. Deep learning-based branch-cut method for InSAR two-dimensional phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5209615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099997 [20] ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, and LAN Yang. Deep convolutional neural network-based robust phase gradient estimation for two-dimensional phase unwrapping using SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4653–4665. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2965918 [21] WANG Kaiqiang, LI Ying, KEMAO Q, et al. One-step robust deep learning phase unwrapping[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(10): 15100–15115. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.015100 [22] ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, LAN Yang, et al. CANet: An unsupervised deep convolutional neural network for efficient cluster-analysis-based multibaseline InSAR phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5212315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3110518 [23] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [24] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [25] 黄国满. 机载多波段多极化干涉SAR测图系统—CASMSAR[J]. 测绘科学, 2014, 39(8): 111–115. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2014.08.011HUANG Guoman. An airborne interferometric SAR mapping system with multi-band and multi-polarization—CASMSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2014, 39(8): 111–115. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2014.08.011 [26] 周良将, 汪丙南, 王亚超, 等. 机载多维度SAR航空观测系统实验初步进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1243–1253. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220250ZHOU Liangjiang, WANG Bingnan, WANG Yachao, et al. Preliminary process of airborne multidimensional space joint-observation SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1243–1253. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220250 [27] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [28] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027 [29] WANG Wenjie and XIA Xianggen. A closed-form robust Chinese remainder theorem and its performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(11): 5655–5666. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2066974 [30] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [31] 杨真真, 孙雪, 邵静, 等. 基于多尺度偶数卷积注意力U-Net的医学图像分割[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(9): 1912–1921. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.09.014YANG Zhenzhen, SUN Xue, SHAO Jing, et al. Medical image segmentation based on multiscale even convolution attention U-Net[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(9): 1912–1921. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.09.014 [32] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [33] 梁峰, 谢先明, 徐有邈, 等. 一种改进的U-Net相位解缠方法[J]. 遥感信息, 2021, 36(5): 134–141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2021.05.018LIANG Feng, XIE Xianming, XU Youmiao, et al. An improved U-Net phase unwrapping method[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2021, 36(5): 134–141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2021.05.018 [34] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. [35] LOSHCHILOV I and HUTTER F. SGDR: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1608.03983. [36] GOLDSTEIN R M and WERNER C L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(21): 4035–4038. doi: 10.1029/1998GL900033 [37] ASF data search vertex[EB/OL]. https://search.asf.alaska.edu/, 2023. [38] GESCH D B, OIMOEN M J, and EVANS G A. Accuracy assessment of the U.S. Geological Survey national elevation dataset, and comparison with other large-area elevation datasets: SRTM and ASTER[R]. Open-File Report 2014-1008, 2014. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: