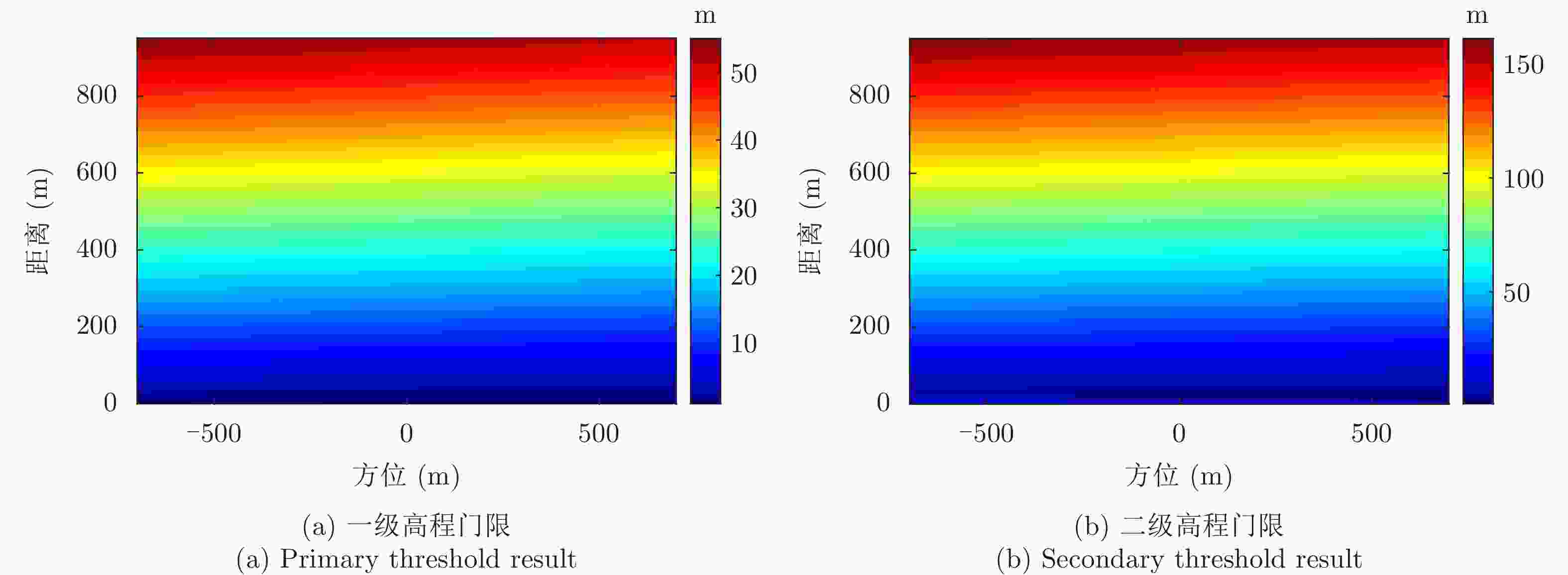
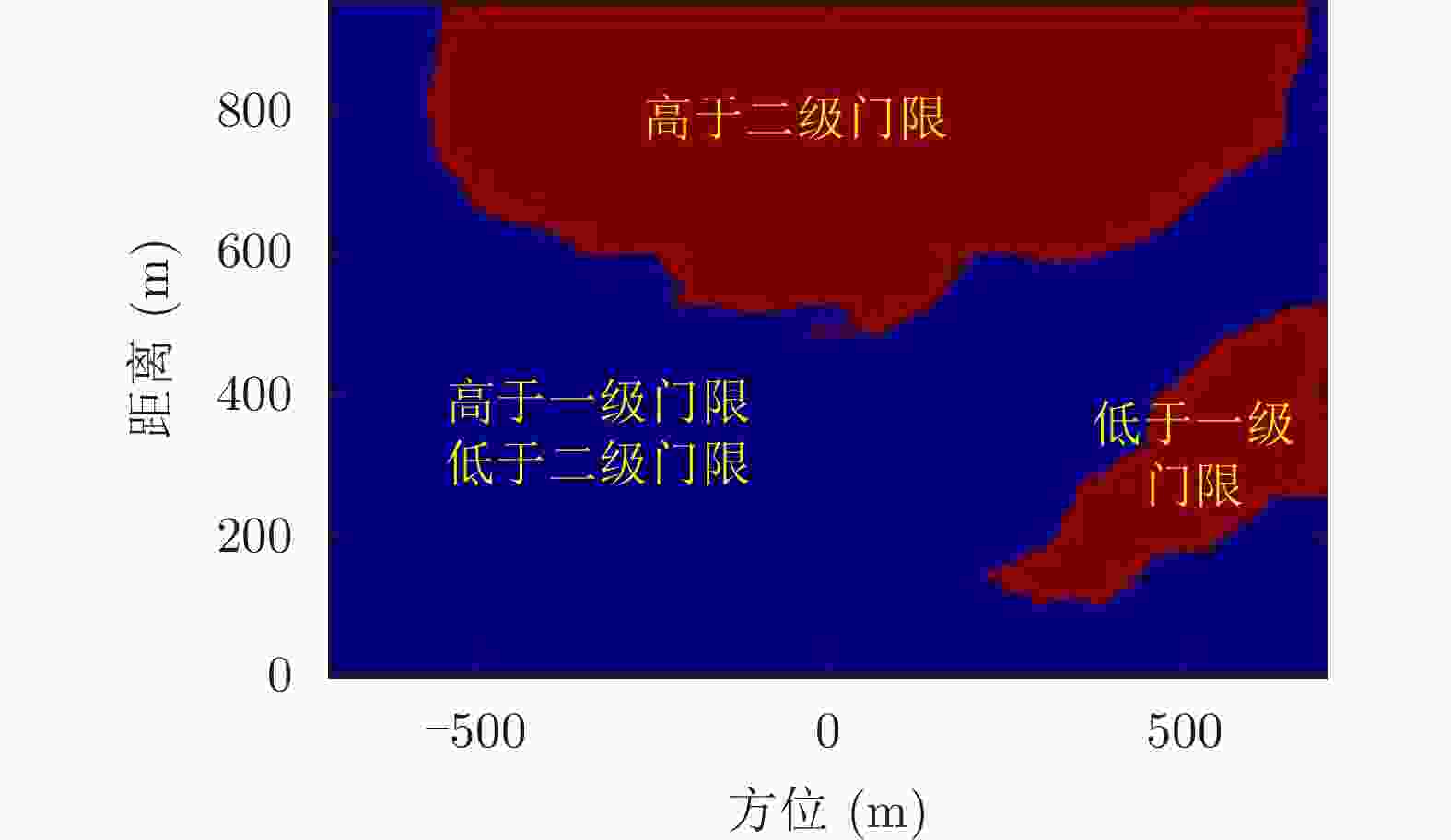
-
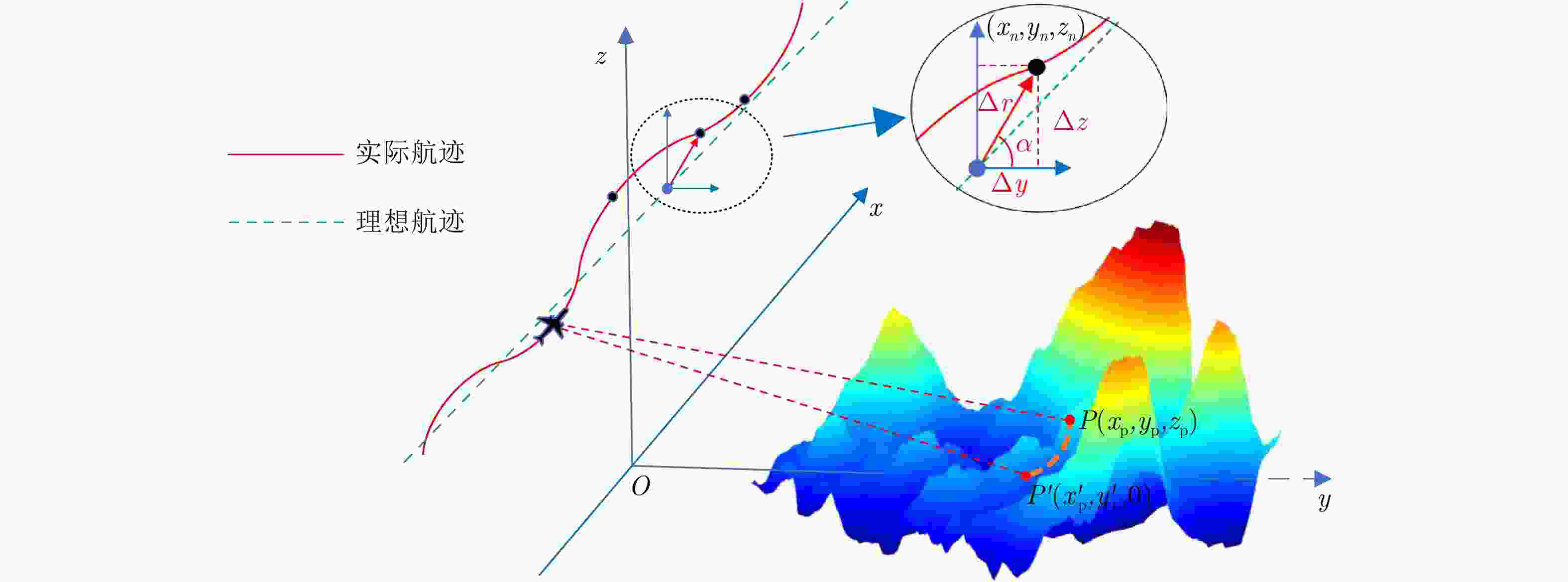
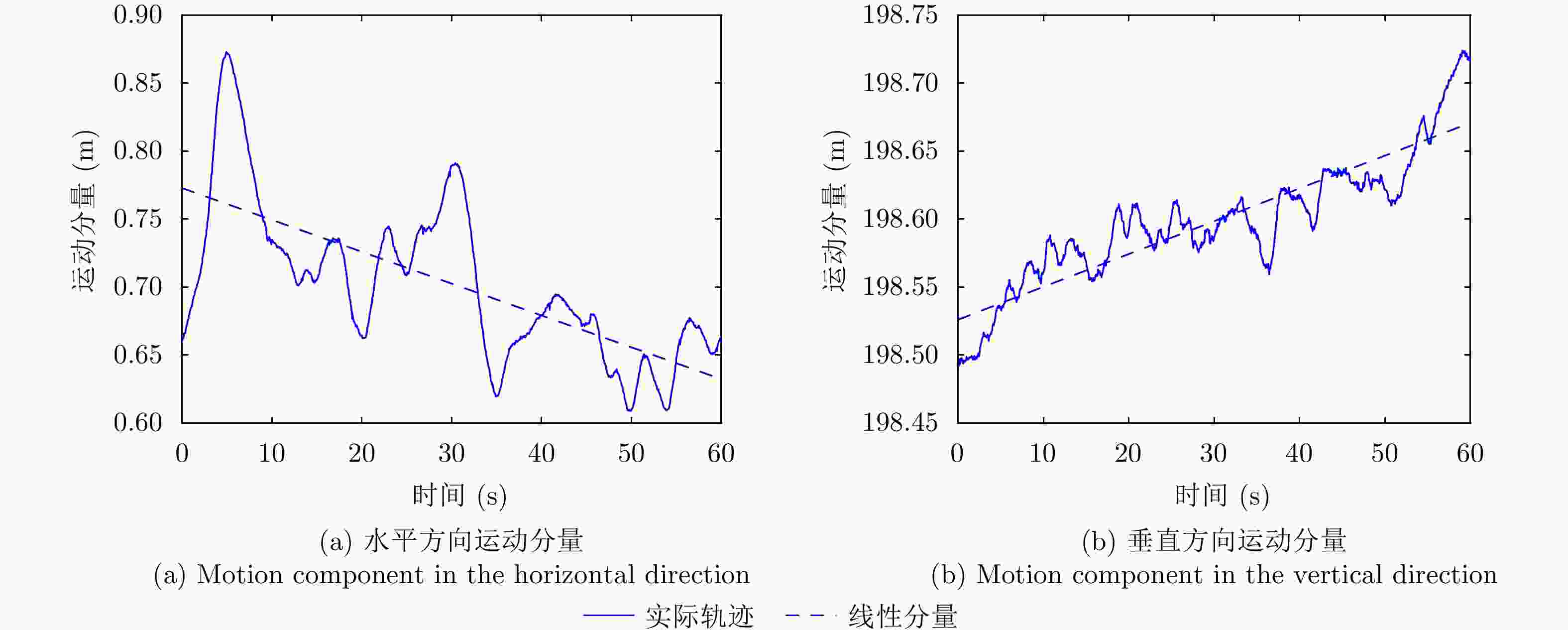
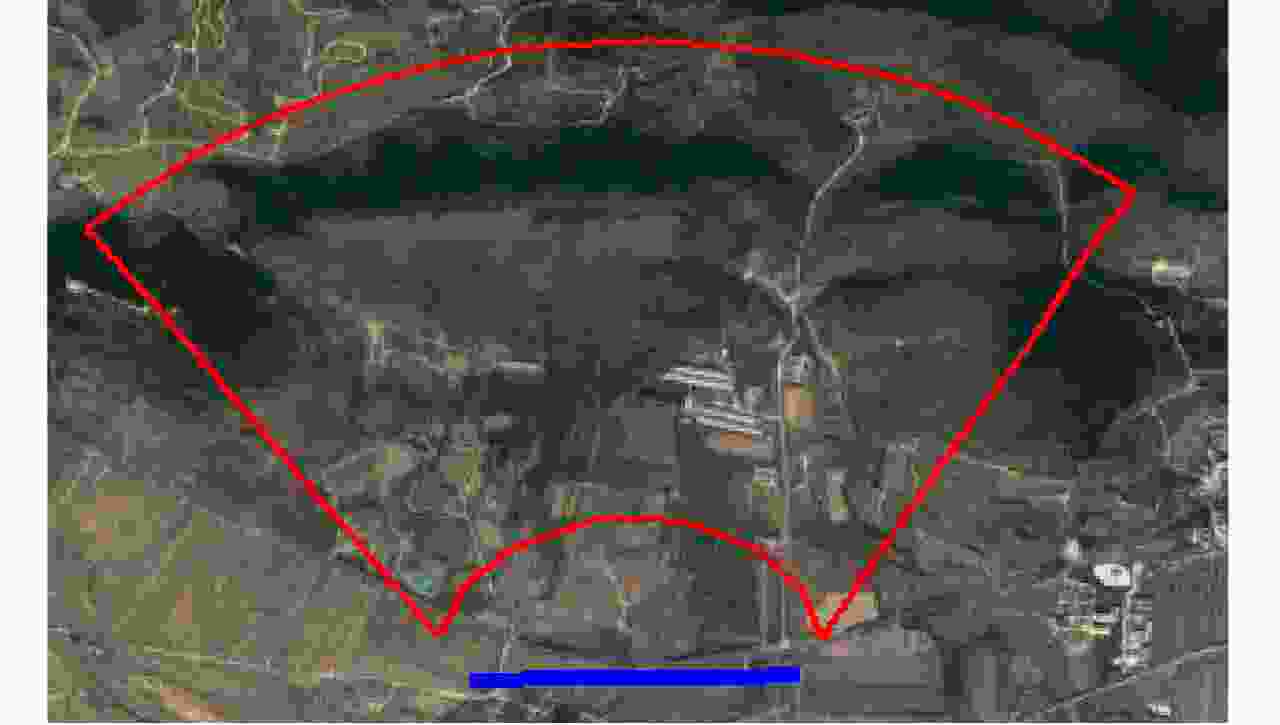
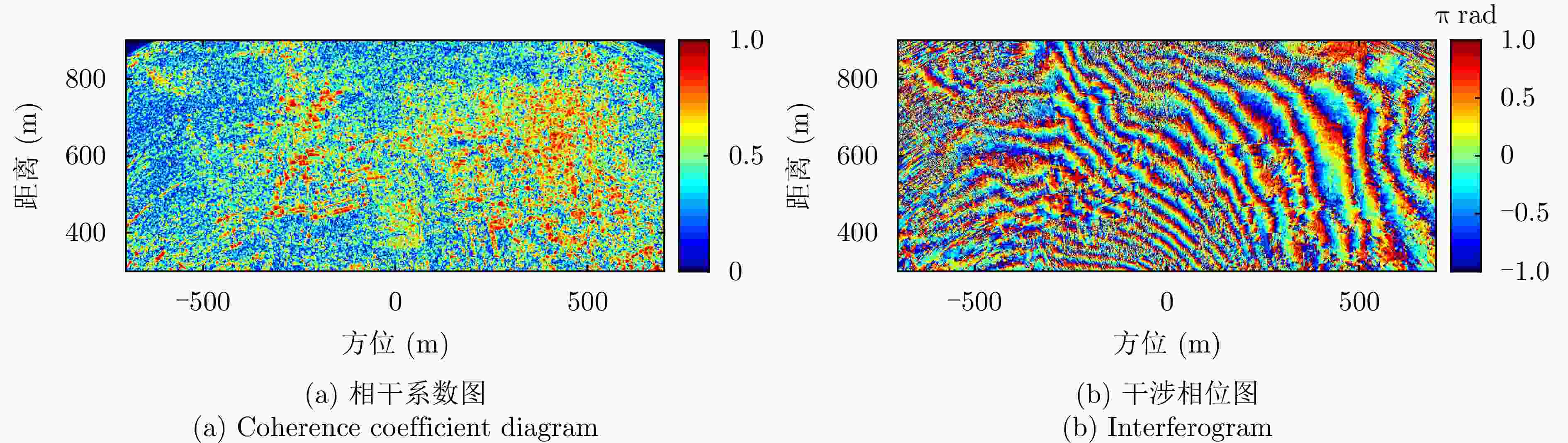
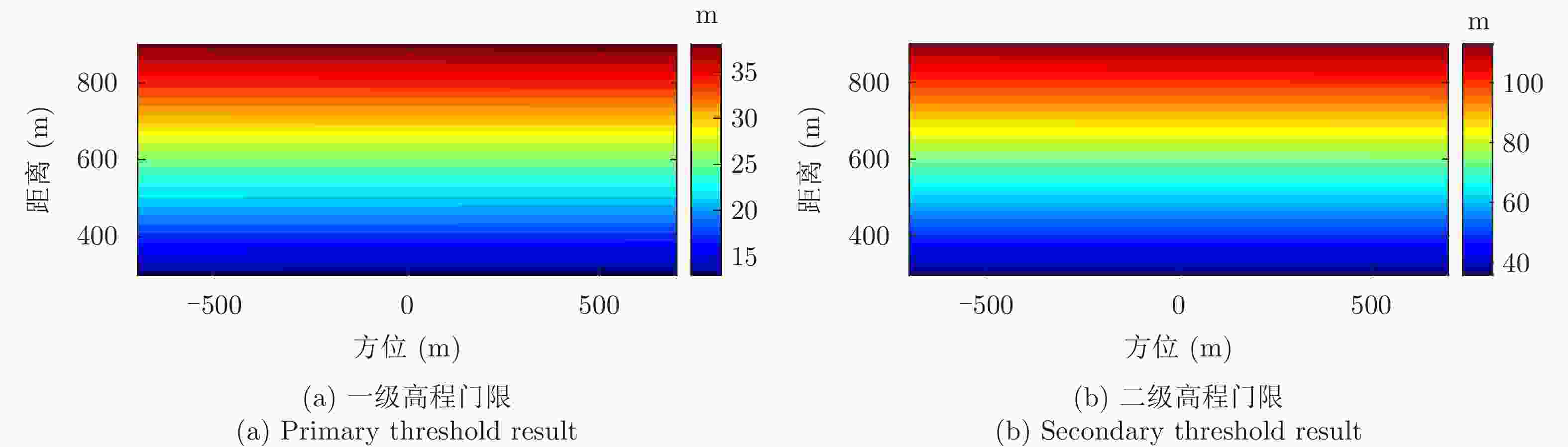
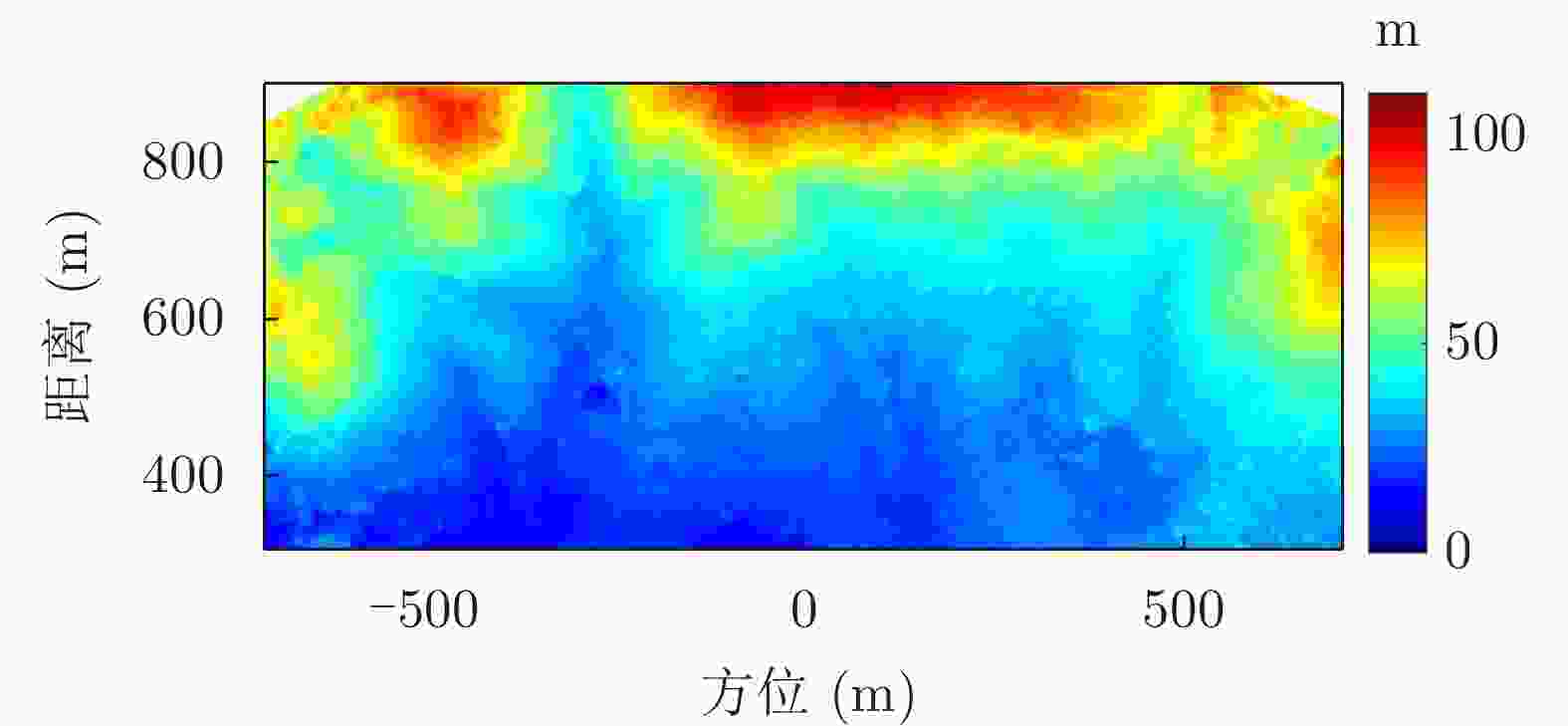
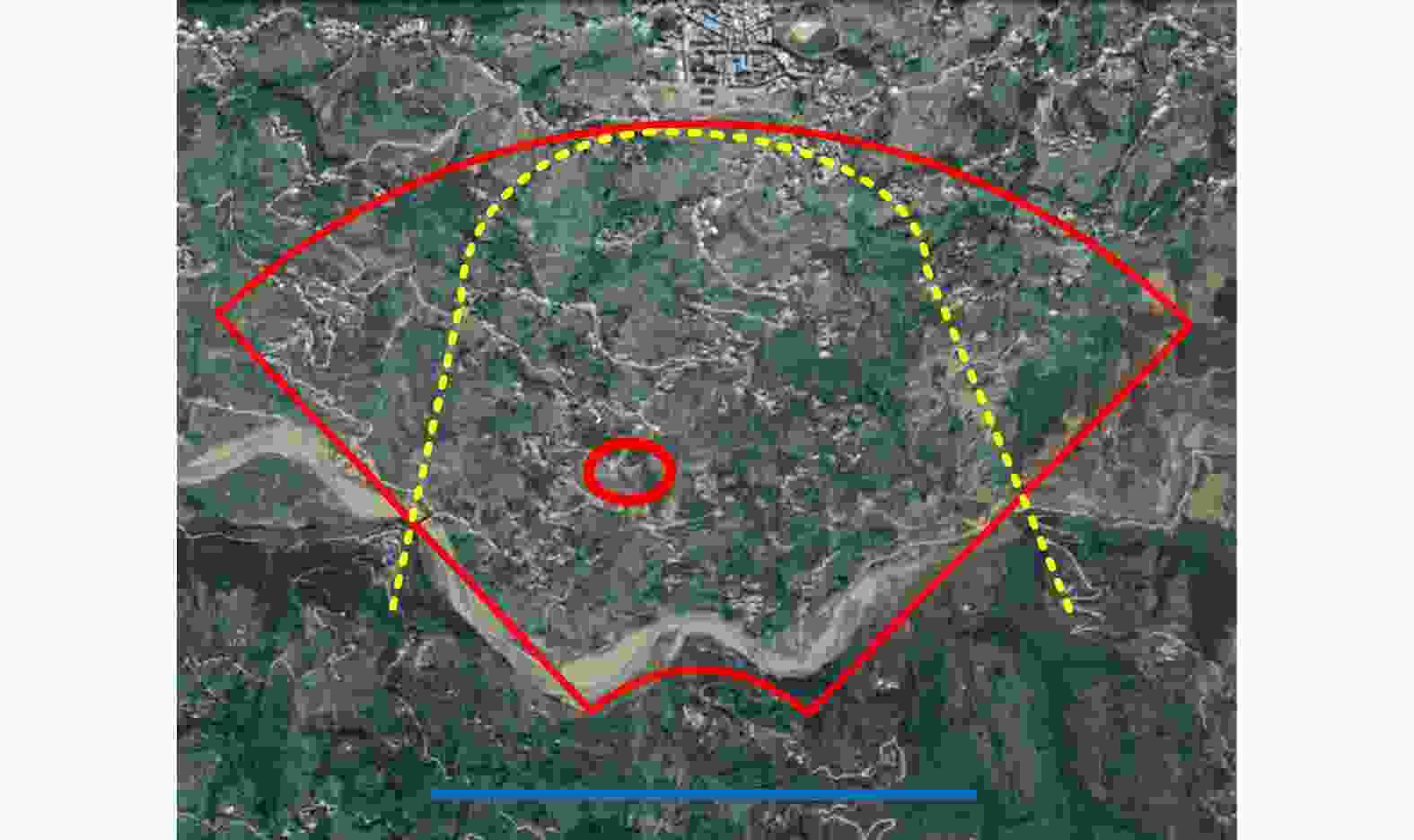
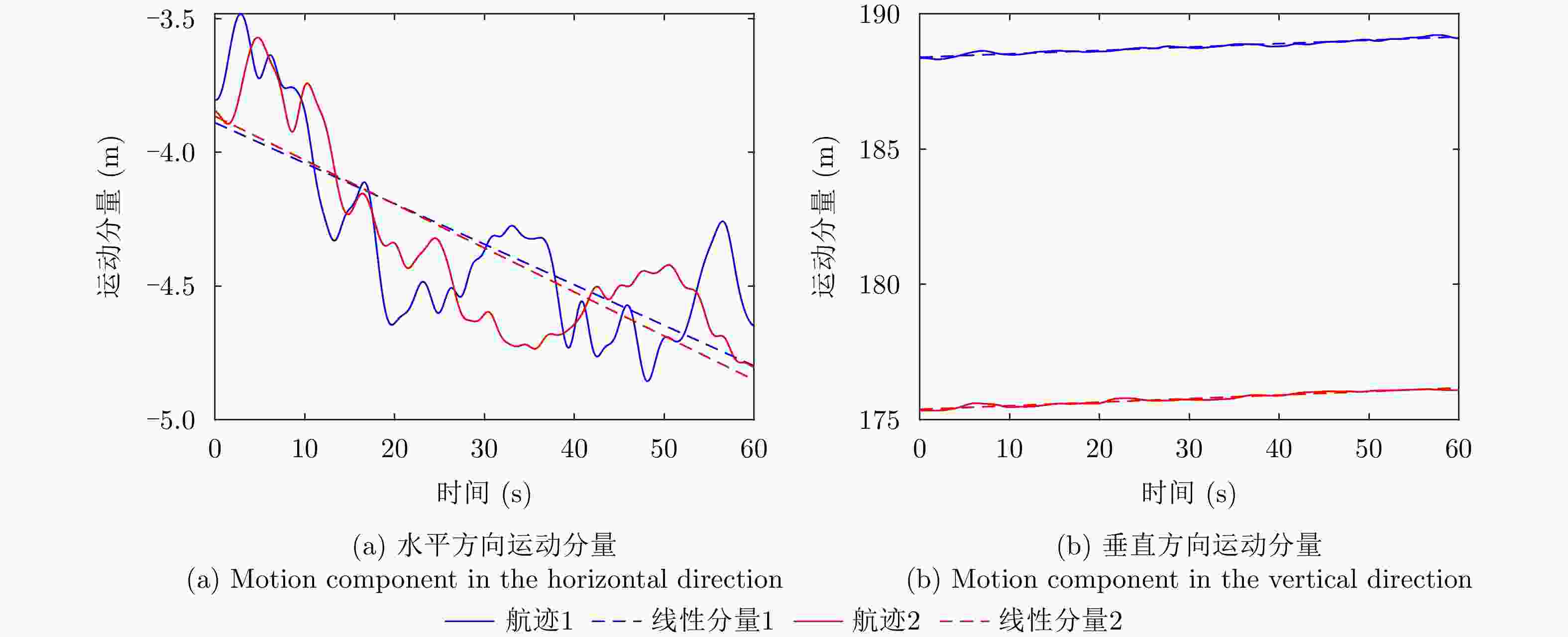
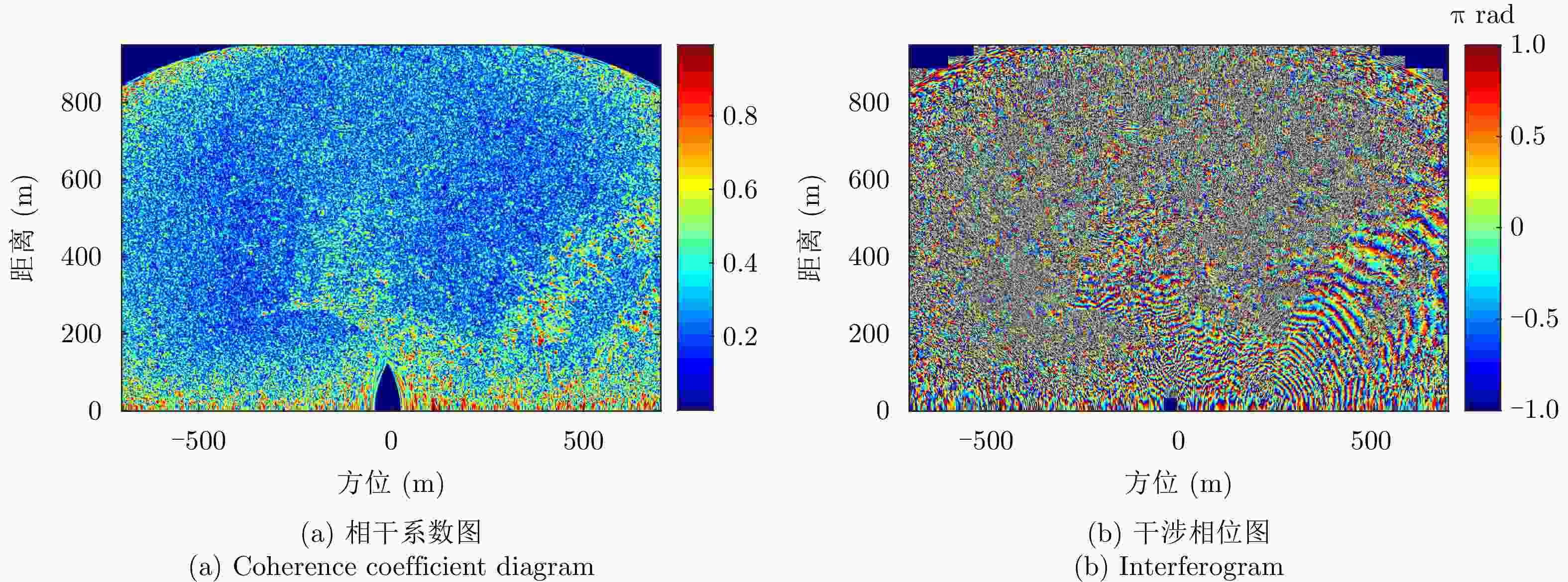
摘要: 小型化、轻量化的无人机(UAV)为合成孔径雷达(SAR)提供了更加灵活、机动的观测平台,无人机载干涉SAR (InSAR)逐步应用于干涉测量领域。无人机小而轻,易受气流扰动的影响,采用多航过模式进行干涉测量时,飞行航迹非线性且不平行。非线性、不平行的飞行轨迹导致两幅图像之间存在几何畸变。在复杂地形条件下,无人机载InSAR的干涉图像对之间的偏移量大且具有明显的空变特性,给图像配准带来了很大的技术挑战,常规的基于多项式拟合的配准方法不再适用。该文提出了一种利用地形辅助分区的图像配准方法。首先基于航迹信息生成高程门限,利用外部地形对测量区域进行图像分区处理,然后对区域内的偏移量构建多项式变换模型,对各区域边界处的偏移量施加约束,并进行联合求解,最后获得连续的全局偏移量拟合面,通过对辅图像进行重采样实现精配准。基于P波段无人机载InSAR获取的实测数据,初步验证了该方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 无人机载干涉合成孔径雷达 /
- 图像配准 /
- 复杂地形 /
- 多项式模型 /
- 图像分区
Abstract: Miniaturized and lightweight Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) provide a flexible platform for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). The application of UAV Interferometric SAR (InSAR) is gradually increasing in interferometric measurement fields. UAVs are small and light, which are easily affected by airflow disturbances. Their trajectories are nonlinear and unparallel when adopting the multipass mode for interferometry. The nonlinear and unparallel trajectories result in geometric distortion between the interferometric image pairs. Under complex topography conditions, the interferometric image pairs of UAVs have large offsets that are obviously space-dependent, thereby resulting in substantial technical challenges during image registration. Conventional image registration methods based on polynomial fitting are no longer applicable. In this study, we proposed an image registration method based on image partition with topography assistance. First, an elevation threshold is generated based on the UAV trajectories, and the measurement area is partitioned using the assisted topography. Then, a polynomial fitting model is constructed for offsets within each partition with constraints applied at the partition boundaries for joint optimization. Finally, continuous global offset fitting surfaces are obtained, and precise image registration is achieved by resampling the slave image. The effectiveness of the proposed method is preliminarily validated using real measurement data obtained from UAV InSAR in the P-band. -
表 1 系统参数
Table 1. System parameters
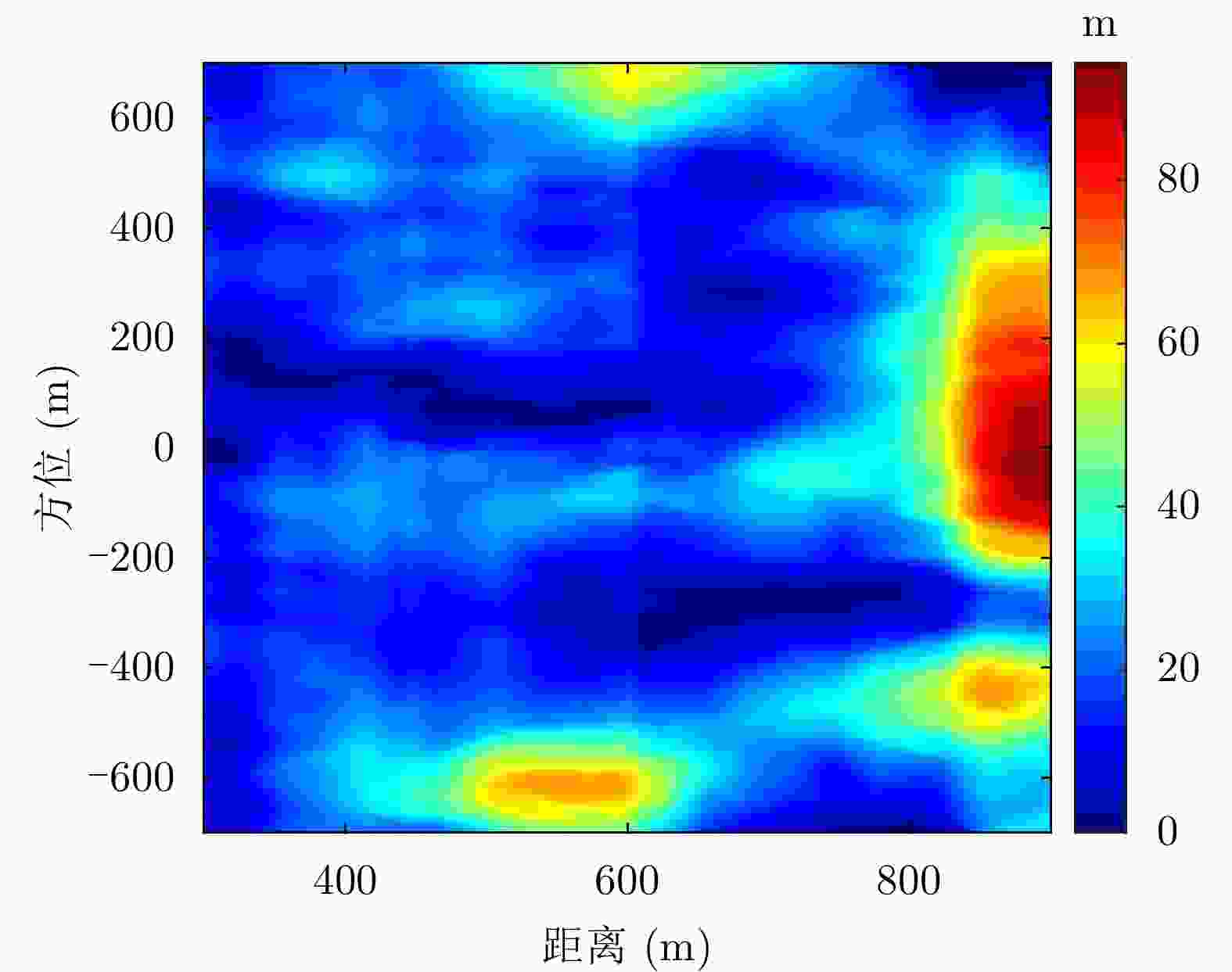
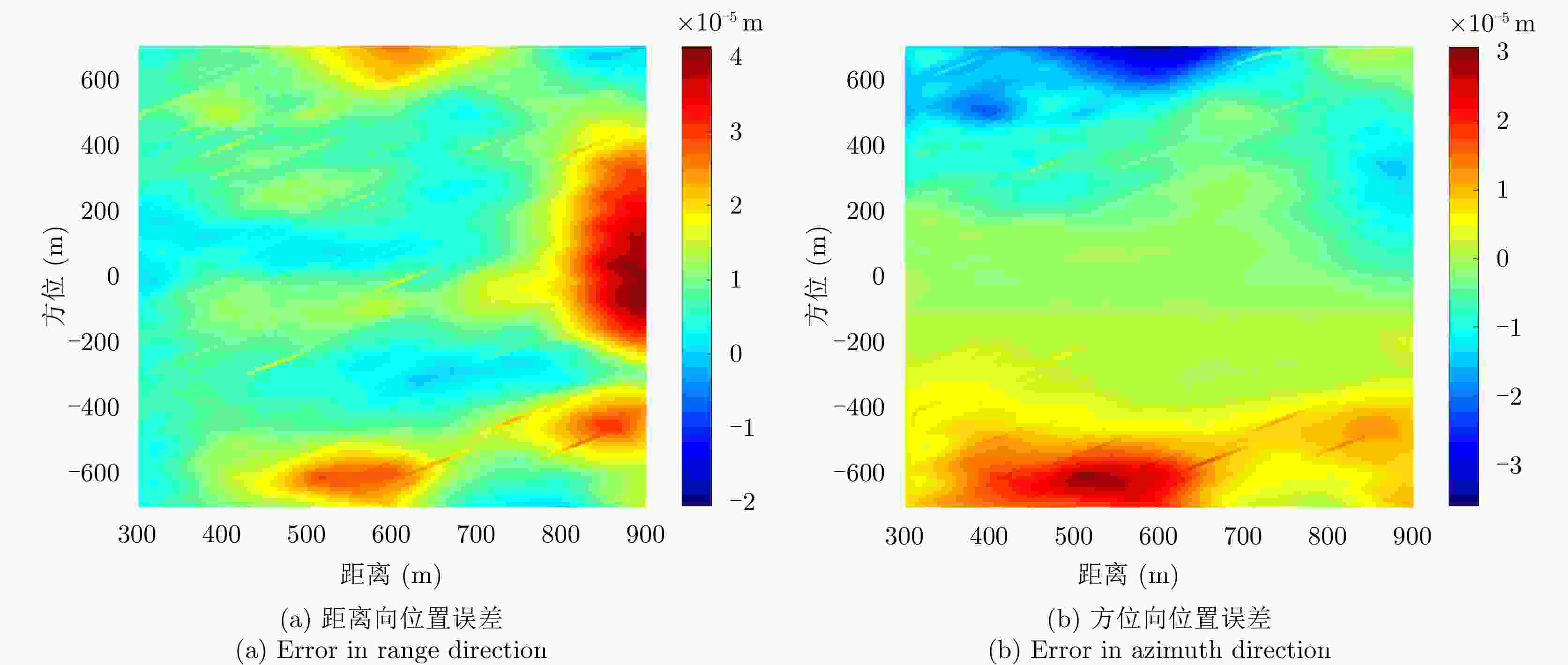
参数 数值 中心频率 400 MHz 信号带宽 60 MHz 脉冲宽度 2 μs 脉冲重复周期 200 μs 表 2 金海湖场景干涉图评价
Table 2. Evaluation of interferograms of Jinhai Lake
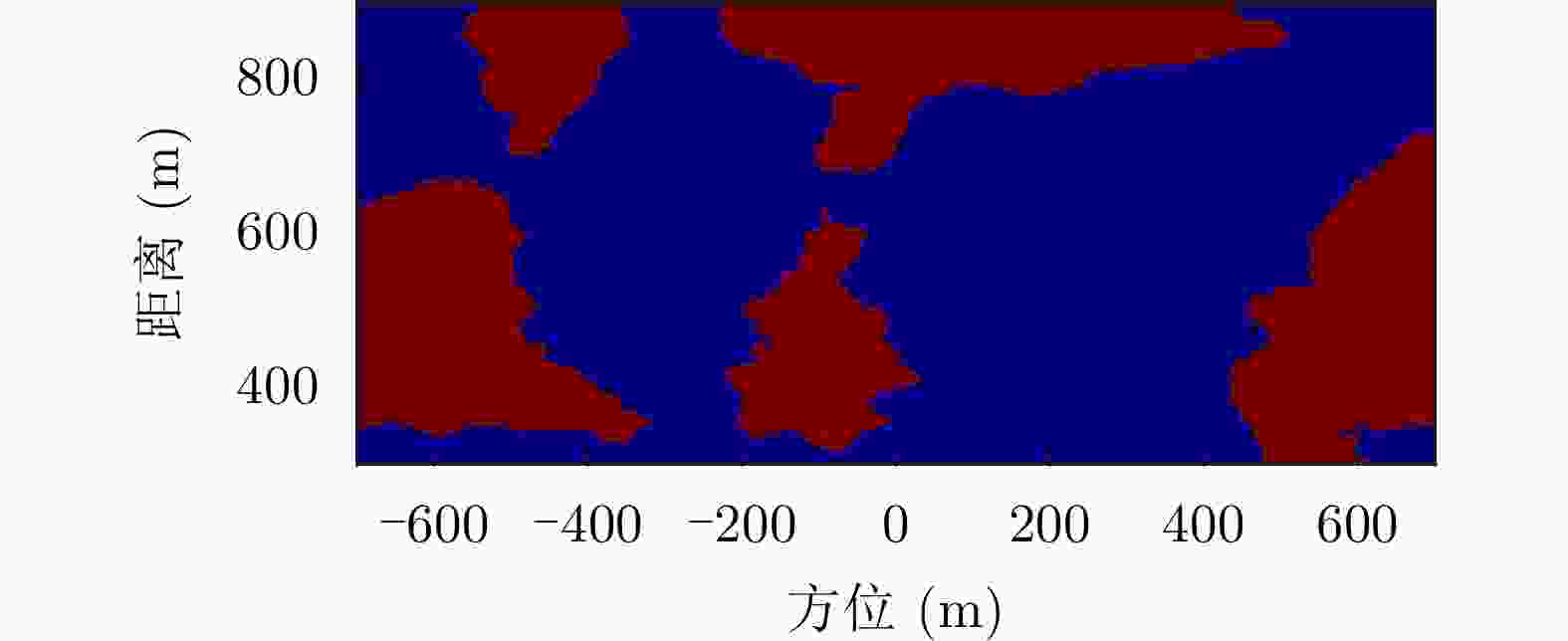
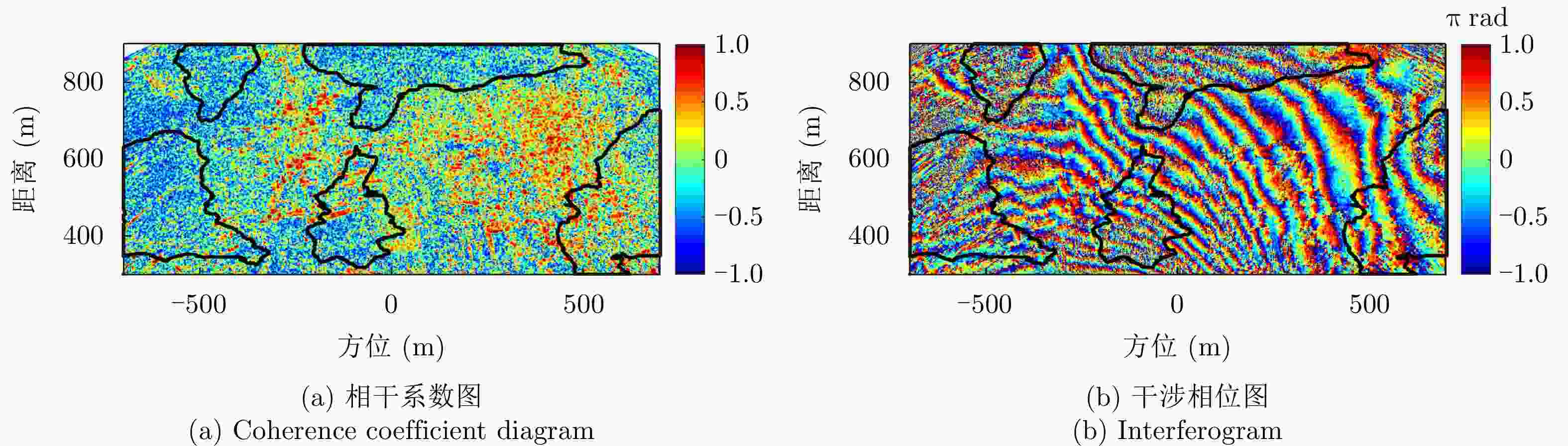
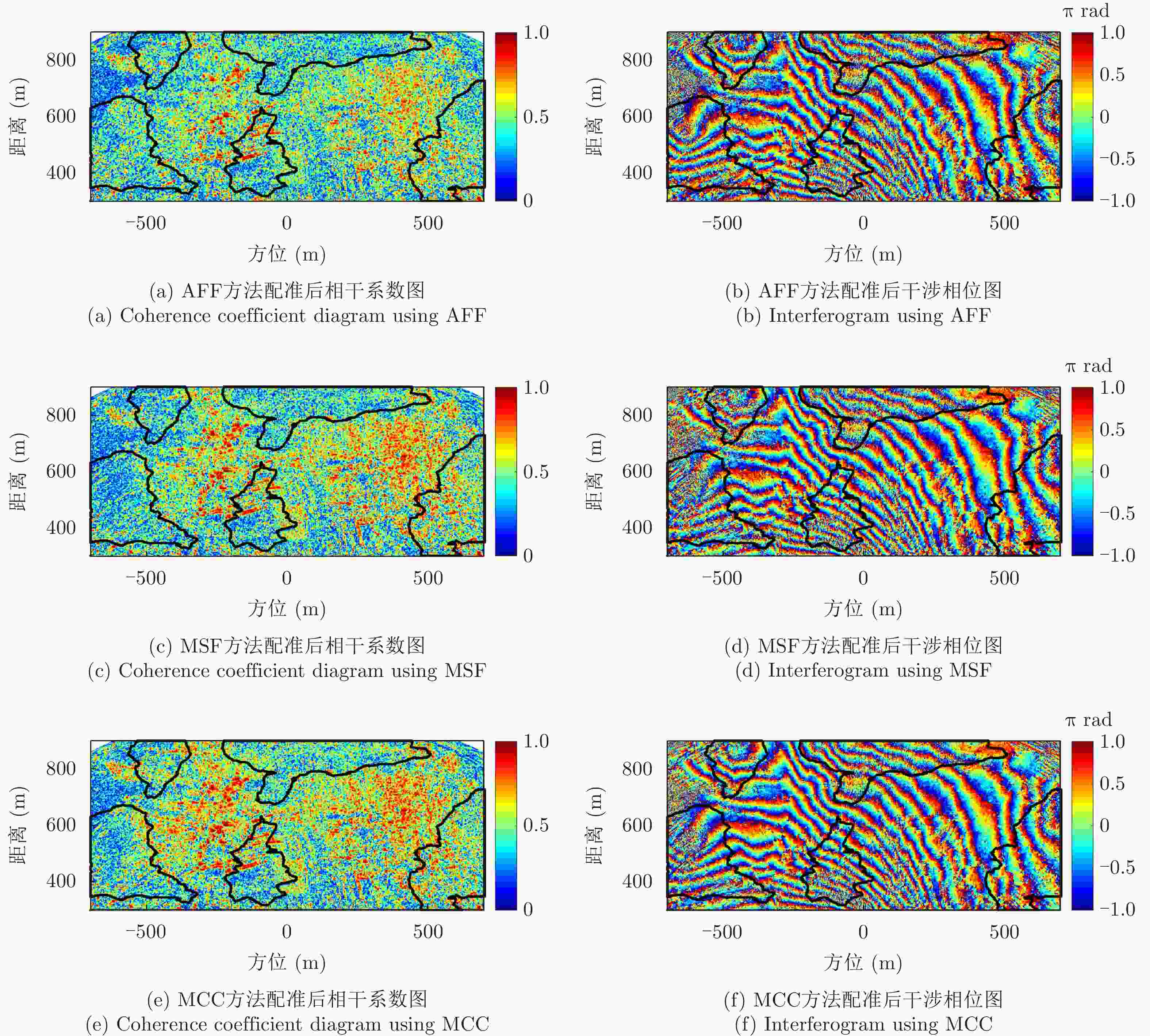
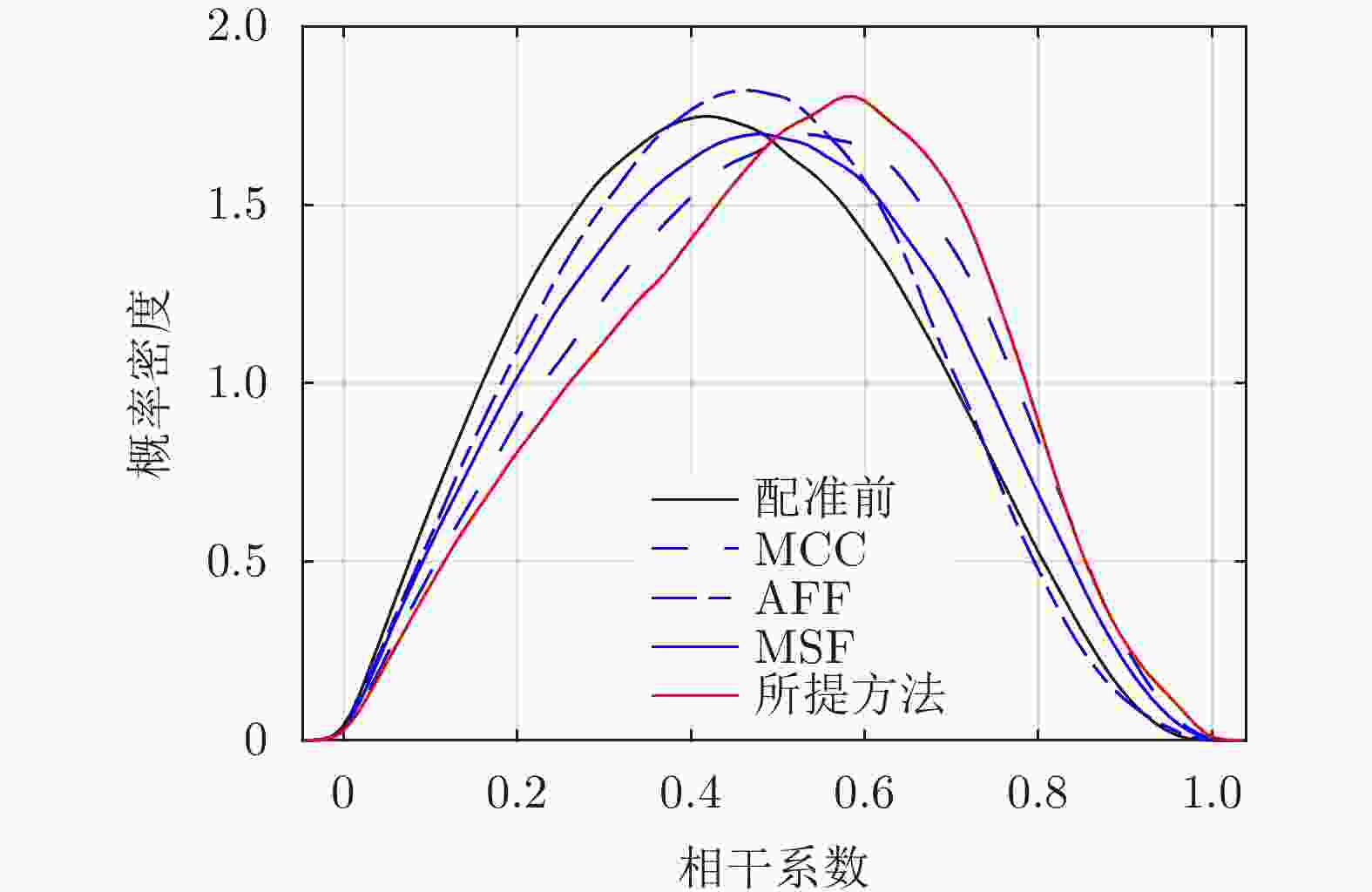
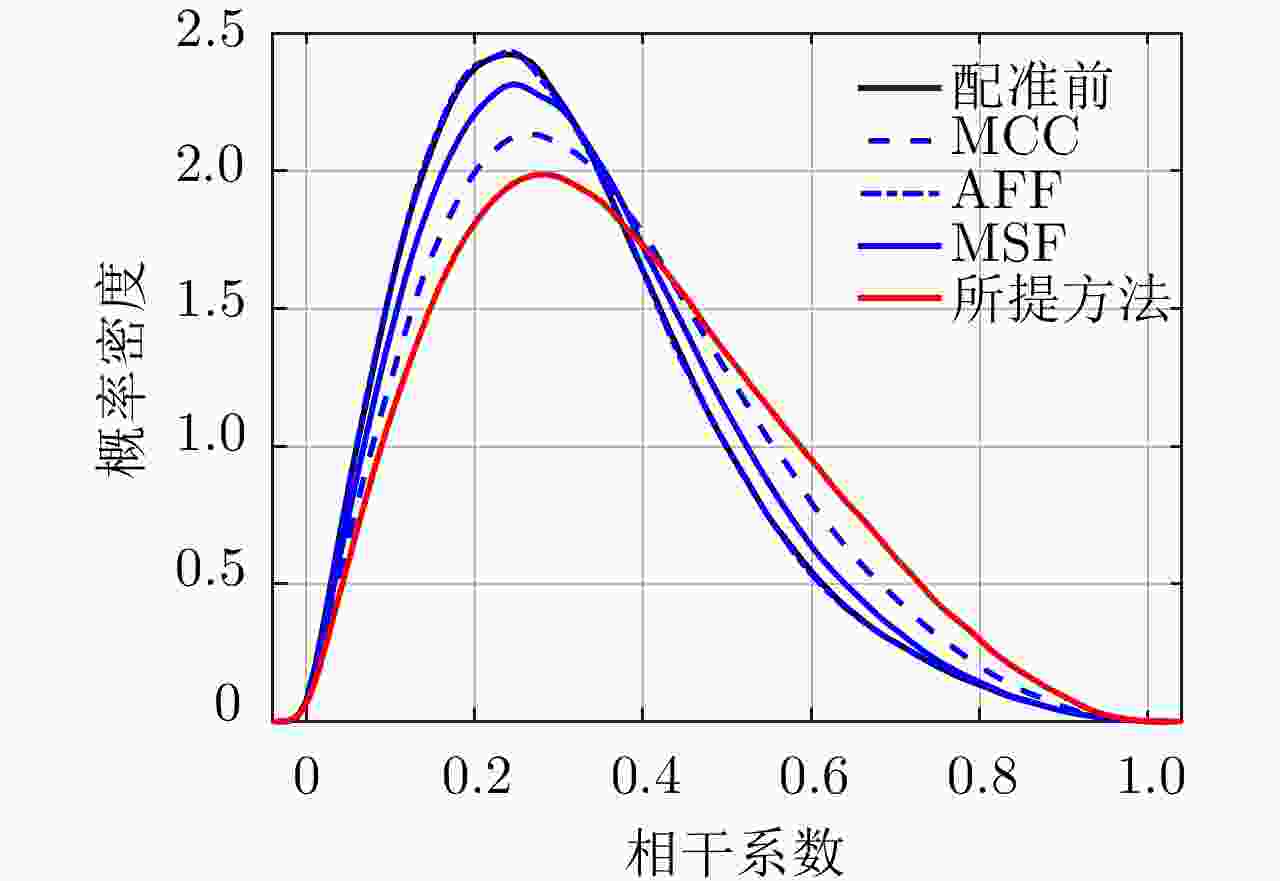
方法 平均相干系数 残差点占比(%) 配准前 0.44 23.60 AFF 0.48 19.88 MSF 0.47 20.35 MCC 0.52 19.66 所提方法 0.58 15.33 表 3 老林沟场景干涉图评价
Table 3. Evaluation of interferograms of Laolin Gou
方法 平均相干系数 残差点占比(%) 配准前 0.30 35 AFF 0.31 35 MSF 0.32 34 MCC 0.35 32 所提方法 0.38 28 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] 韦顺军, 唐欣欣, 张晓玲. 基于DFT模型的大场景InSAR图像配准[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(5): 859–870. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20197459WEI Shunjun, TANG Xinxin, and ZHANG Xiaoling. Image registration algorithm for InSAR large scenes via DFT model[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(5): 859–870. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20197459 [3] LIN Xue, FANGI D S, and LI Fangfang. Acqusition of high-precision digital terrain model using P-band airborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. [4] ZENG Tao, LIU Minkun, WANG Yan, et al. Tomographic SAR imaging with large elevation aperture: A P-band small UAV demonstration[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(3): 132303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3391-2 [5] SANSOSTI E, BERARDINO P, MANUNTA M, et al. Geometrical SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(10): 2861–2870. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.875787 [6] ZOU Weibao and CHEN Libin. Determination of optimum tie point interval for SAR image coregistration by decomposing autocorrelation coefficient[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7): 5067–5084. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2896383 [7] MA Zhangfeng, JIANG Mi, ZHAO Yi, et al. Minimum spanning tree co-registration approach for time-series sentinel-1 TOPS data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 3004–3013. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2920717 [8] YAGUE-MARTINEZ N, EINEDER M, CONG Xiaoying, et al. Ground displacement measurement by TerraSAR-X image correlation: The 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 539–543. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2196020 [9] SCHEIBER R and MOREIRA A. Coregistration of interferometric SAR images using spectral diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2179–2191. doi: 10.1109/36.868876 [10] ZOU Weibao, LI Yan, LI Zhilin, et al. Improvement of the accuracy of InSAR image co-registration based on tie points— a review[J]. Sensors, 2009, 9(2): 1259–1281. doi: 10.3390/s90201259 [11] ZITOVÁ B and FLUSSER J. Image registration methods: A survey[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2003, 21(11): 977–1000. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00137-9 [12] HE Ke, CHEN Yongguang, JIA Xin, et al. A method based on interpolation mapping function for InSAR image registration[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Harbin, China, 2016: 351–355. [13] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-Like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 [14] PAUL S and PATI U C. SAR image registration using an improved SAR-SIFT algorithm and Delaunay- Triangulation-based local matching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 2958–2966. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2918211 [15] WANG Linhui, XIANG Yuming, YOU Hongjia, et al. A robust multiscale edge detection method for accurate SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4006305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3279141 [16] LI Xin, WANG Taoyang, CUI Hao, et al. SARPointNet: An automated feature learning framework for spaceborne SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 6371–6381. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3196383 [17] YANG Zhuoqian, DAN Tingting, and YANG Yang. Multi-Temporal remote sensing image registration using deep convolutional features[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 38544–38555. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853100 [18] XIANG Yuming, PENG Lingxiao, WANG Feng, et al. Fast registration of multiview slant-range SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4007505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3045099 [19] YE Yuanxin, TANG Tengfeng, ZHU Bai, et al. A multiscale framework with unsupervised learning for remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5622215. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3167644 [20] BOVEIRI H R, KHAYAMI R, JAVIDAN R, et al. Medical image registration using Deep Neural Networks: A comprehensive review[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2020, 87: 106767. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106767 [21] FREY O, WERNER C L, and COSCIONE R. Car-borne and UAV-borne mobile mapping of surface displacements with a compact repeat-pass interferometric SAR system at L-band[C]. IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 274–277. [22] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, LI Linghao, et al. First demonstration of single-pass distributed SAR tomographic imaging with a P-band UAV SAR prototype[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–18. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3221859 [23] WANG Zhen, DING Zegang, SUN Tao, et al. UAV-based P-band SAR tomography with long baseline: A multimaster approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 1–21. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3272039 [24] 邓云开, 袁泉, 胡程, 等. 一种多部地基SAR联合观测时的图形配准方法[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(11): 1269–1276. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.001DENG Yunkai, YUAN Quan, HU CHENG, et al. An image registration method applied for joint measurements of multiple GB-SAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(11): 1269–1276. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.11.001 [25] NITTI D O, HANSSEN R F, REFICE A, et al. Impact of DEM-assisted coregistration on high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(3): 1127–1143. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2074204 [26] 黄晓涛, 陈乐平, 范崇祎, 等. 低频叶簇穿透雷达成像技术[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 469–485. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020041302HUANG Xiaotao, CHEN Leping, FAN Chongyi, et al. Low frequency foliage penetration radar imaging technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 469–485. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020041302 [27] HAN Congrong, TIAN Weiming, and MEI Hongyan. MIMO radar fast imaging algorithm based on sub-image combination[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–6. [28] LIN Jiahe, LV Xiaolei, and LI Rui. Automatic registered back-projection approach based on object orientation for airborne repeat-track interferometric SAR[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 1066–1076. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5053 [29] 田卫明, 刘富强, 谢鑫, 等. 基于GPU粗细粒度和混合精度的SAR后向投影算法的并行加速研究[J/OL]. 信号处理, 1–12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2406.tn.20230509.0955.002.html, 2023.TIAN Weiming, LIU Fuqiang, XIE Xin, et al. Research on parallel acceleration processing technology of SAR back projection algorithm based on two granularities and mixing precision of GPU[J/OL]. Journal of Signal Processing, 1–12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2406.tn.20230509.0955.002.html, 2023. [30] 冯丽源, 邓云开, 聂祥飞, 等. 一种基于Non-Local Means的地基差分干涉雷达相位滤波改进方法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(1): 100–108. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.012FENG Liyuan, DENG Yunkai, NIE Xiangfei, et al. An improved phase filtering method for Ground-based differential interferometer radar based on Non-Local means[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(1): 100–108. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.012 [31] FANG Dongsheng, LV Xiaolei, YUN Ye, et al. An InSAR fine registration algorithm using uniform tie points based on voronoi diagram[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1403–1407. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2715189 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
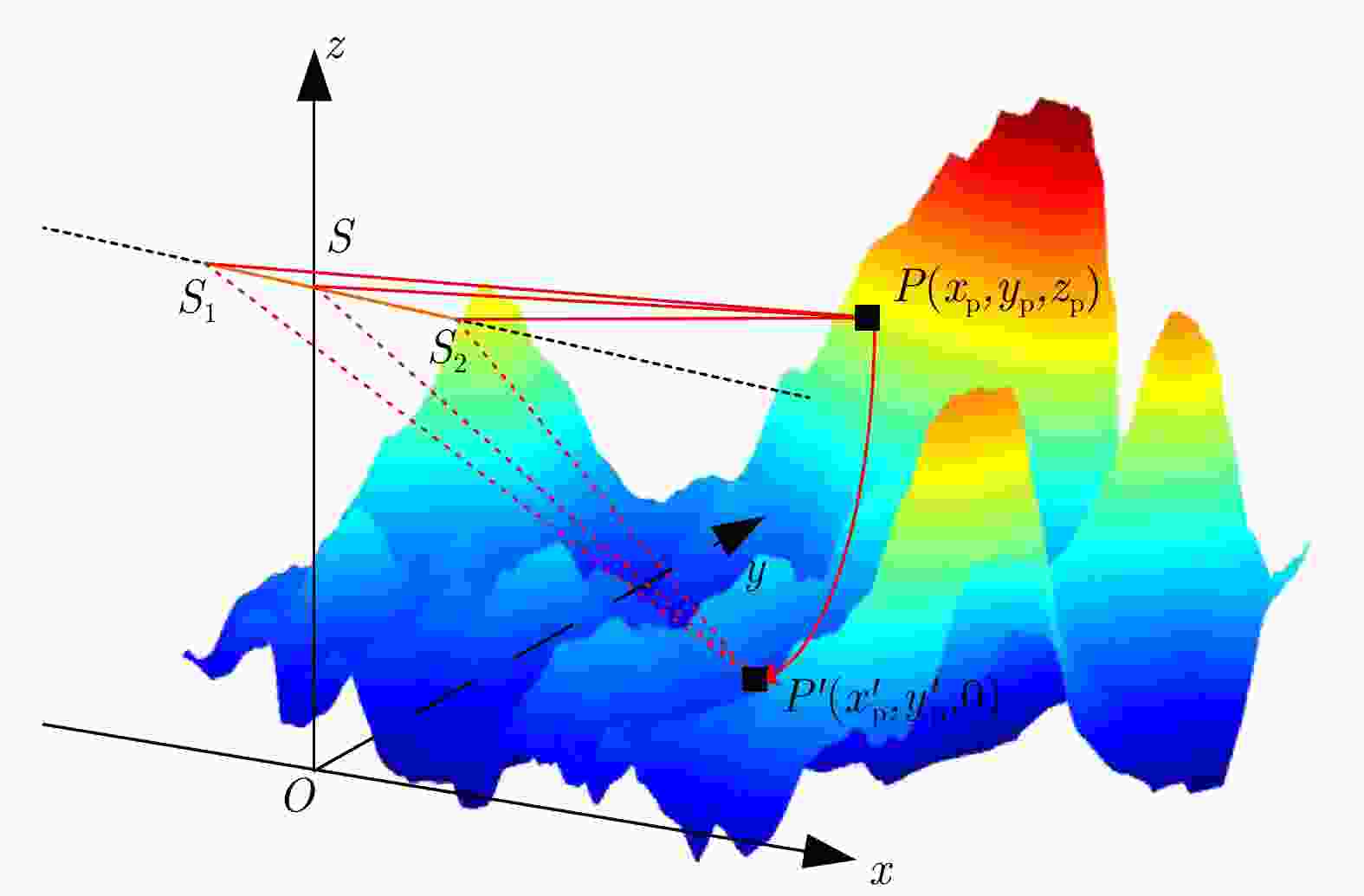
 下载:
下载: