A Radar Anti-jamming Method under Multi-jamming Scenarios Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning in Complex Domains
-
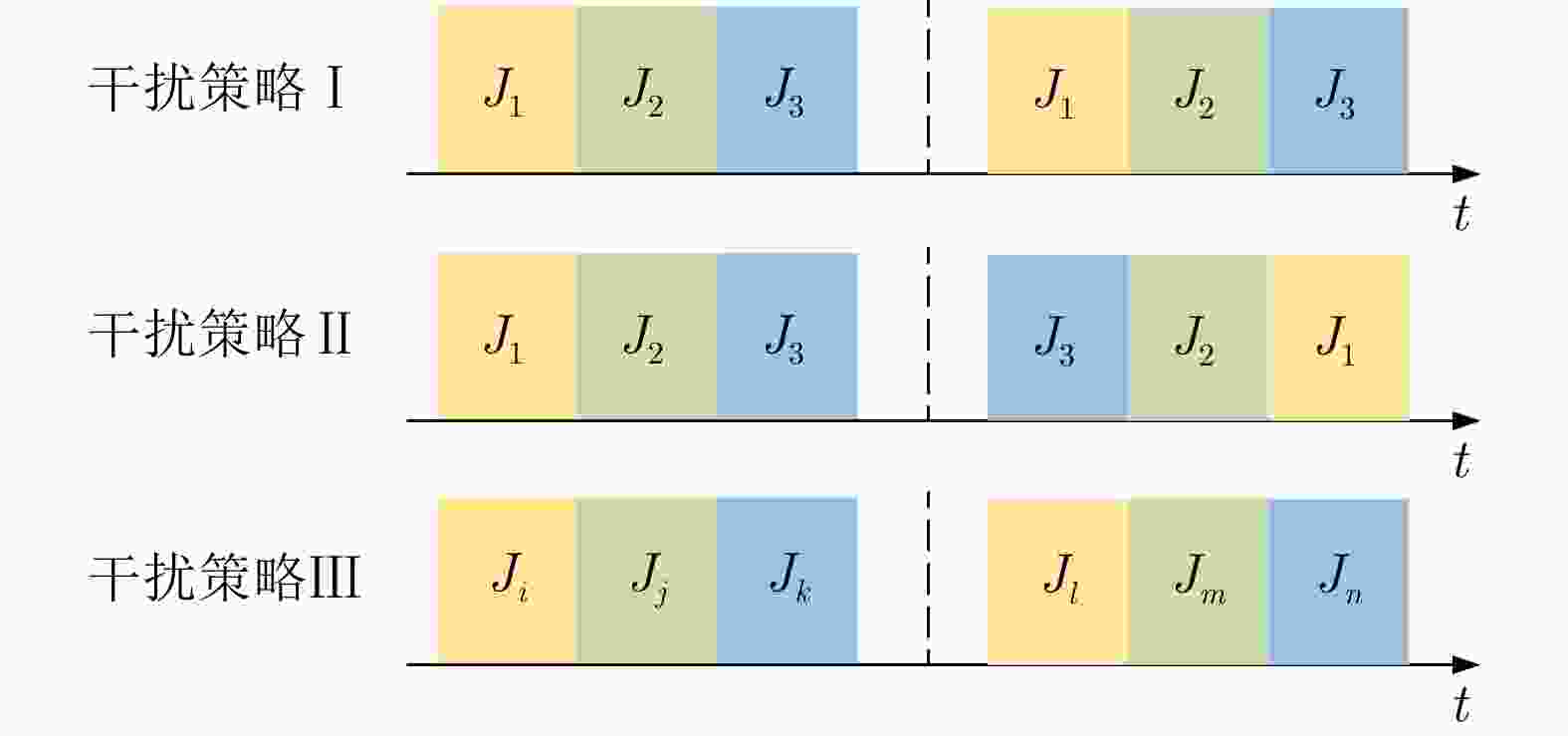
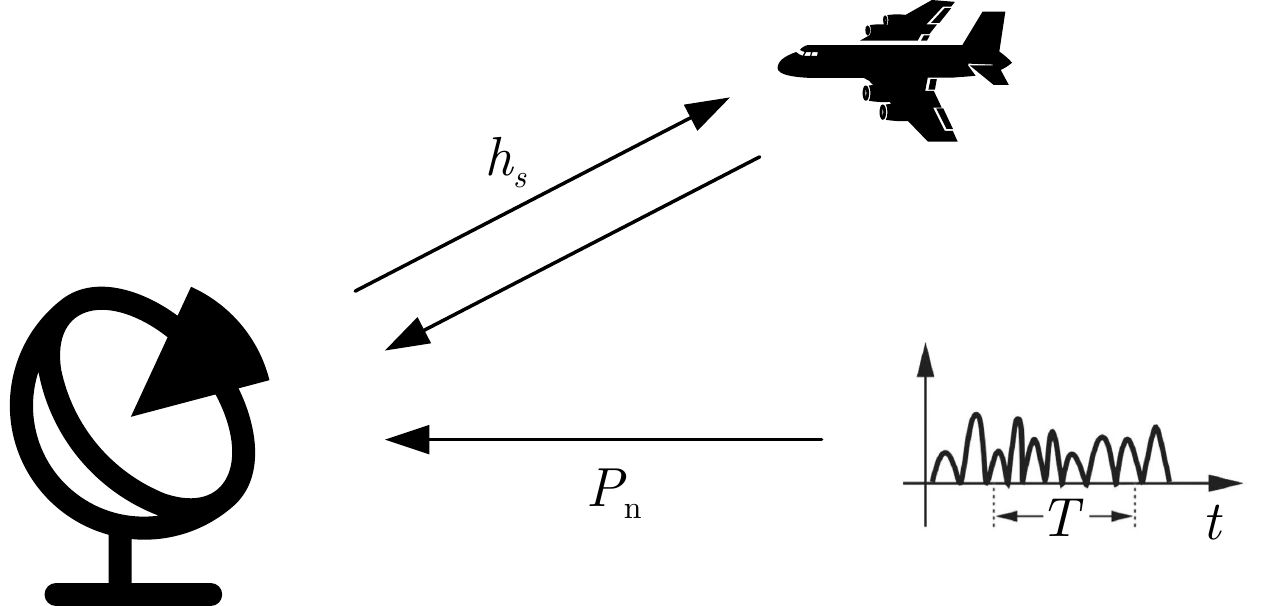
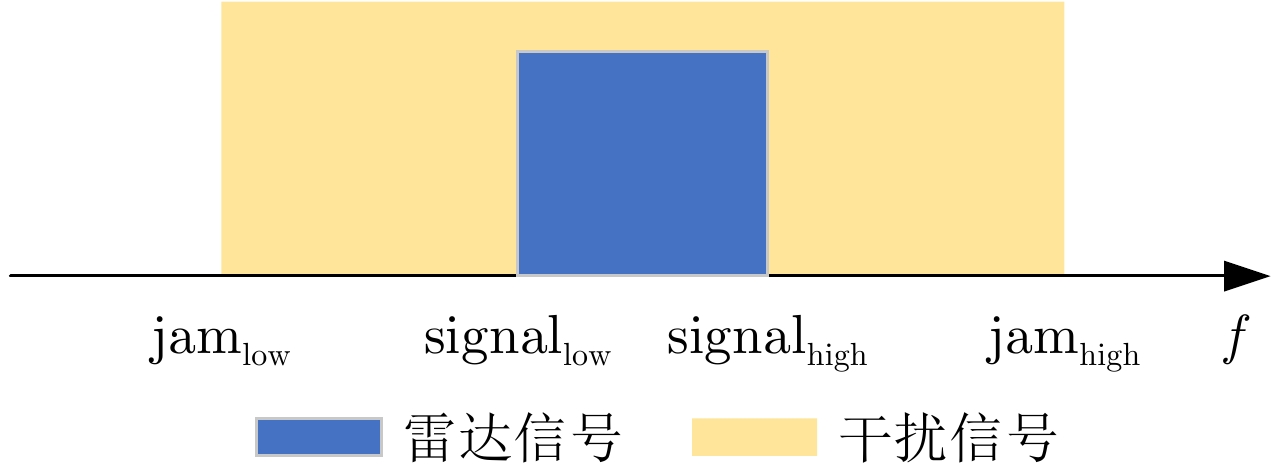
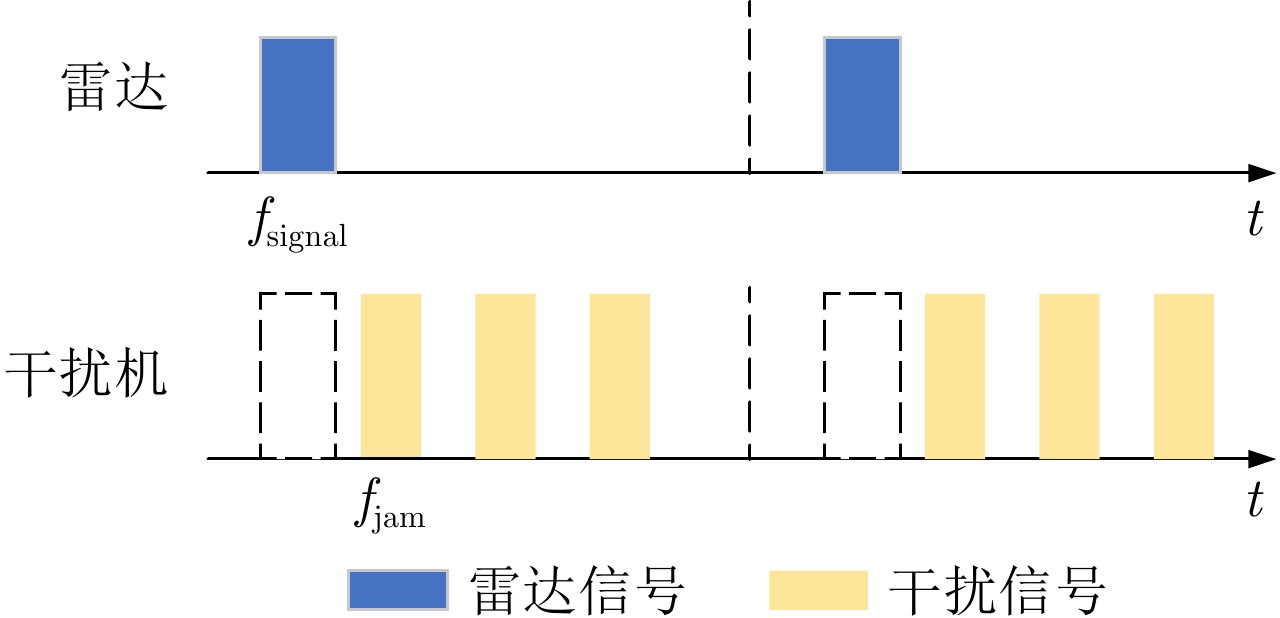
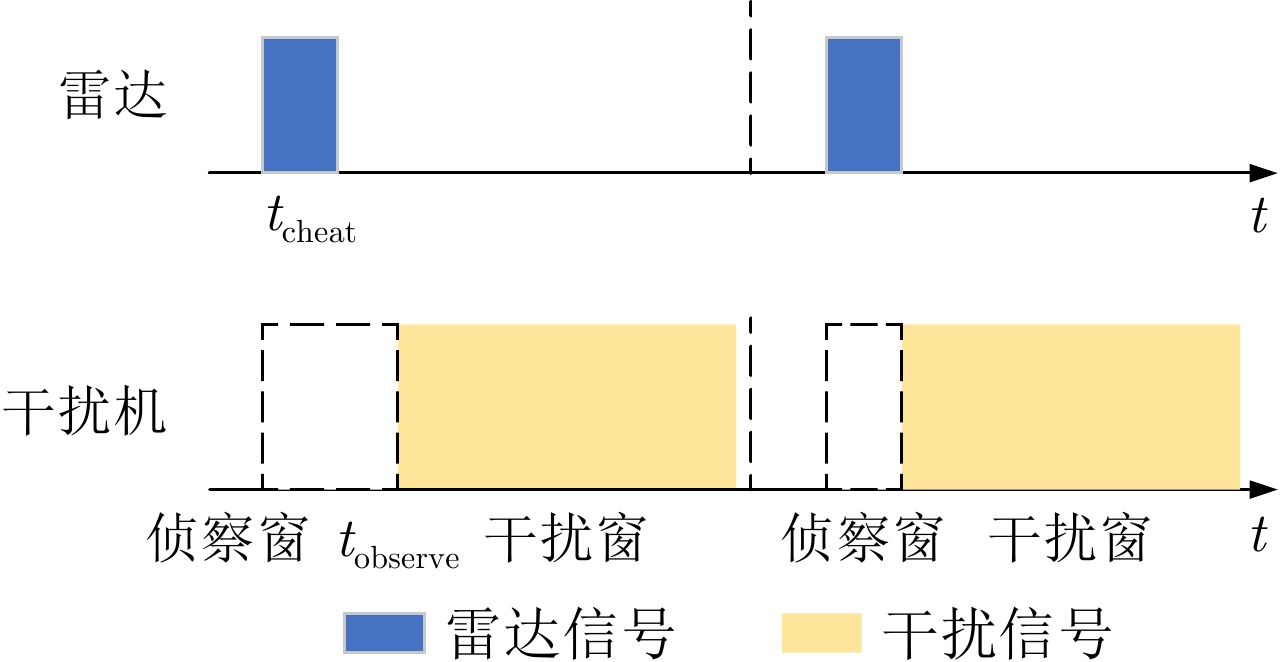
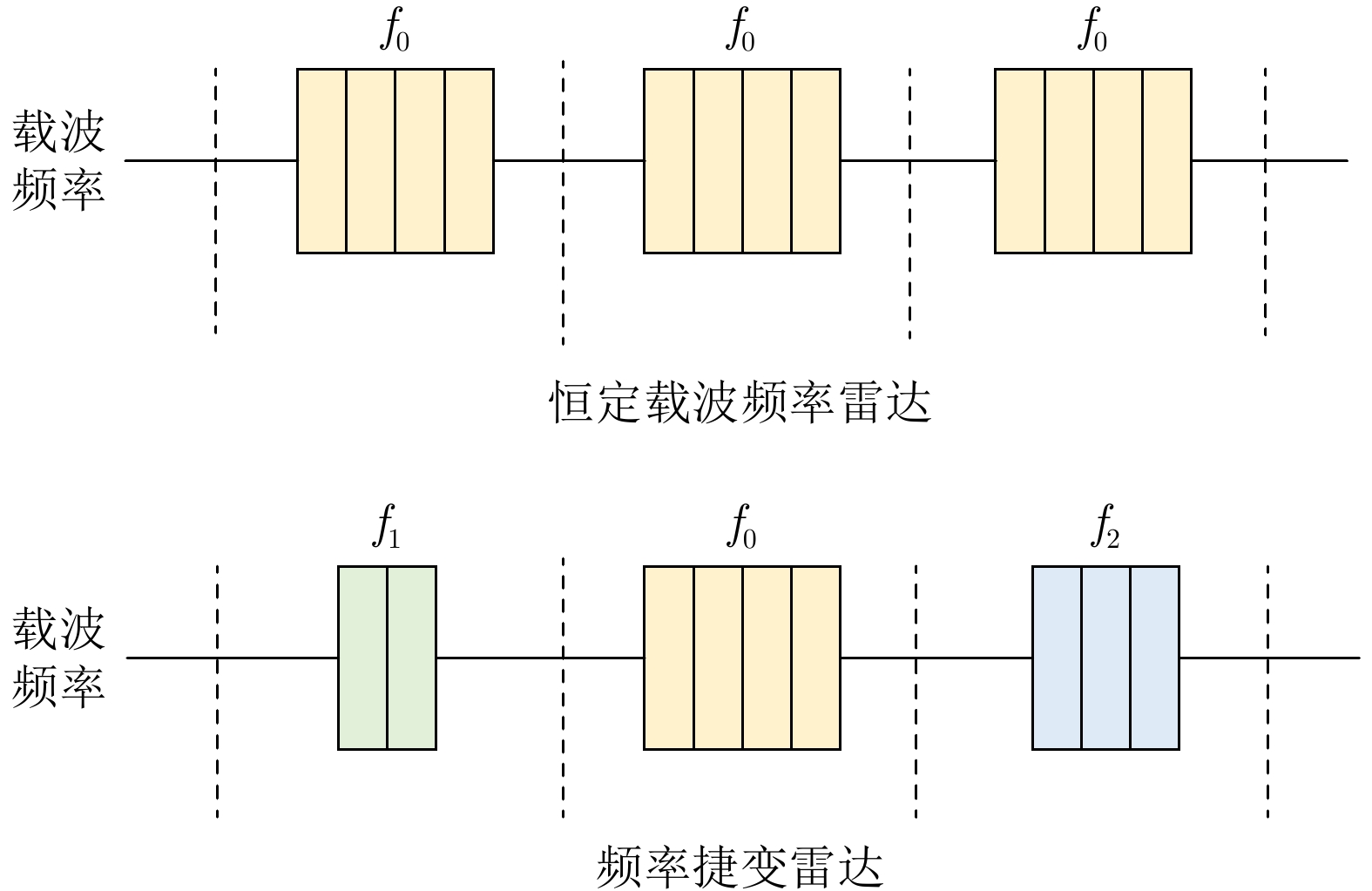
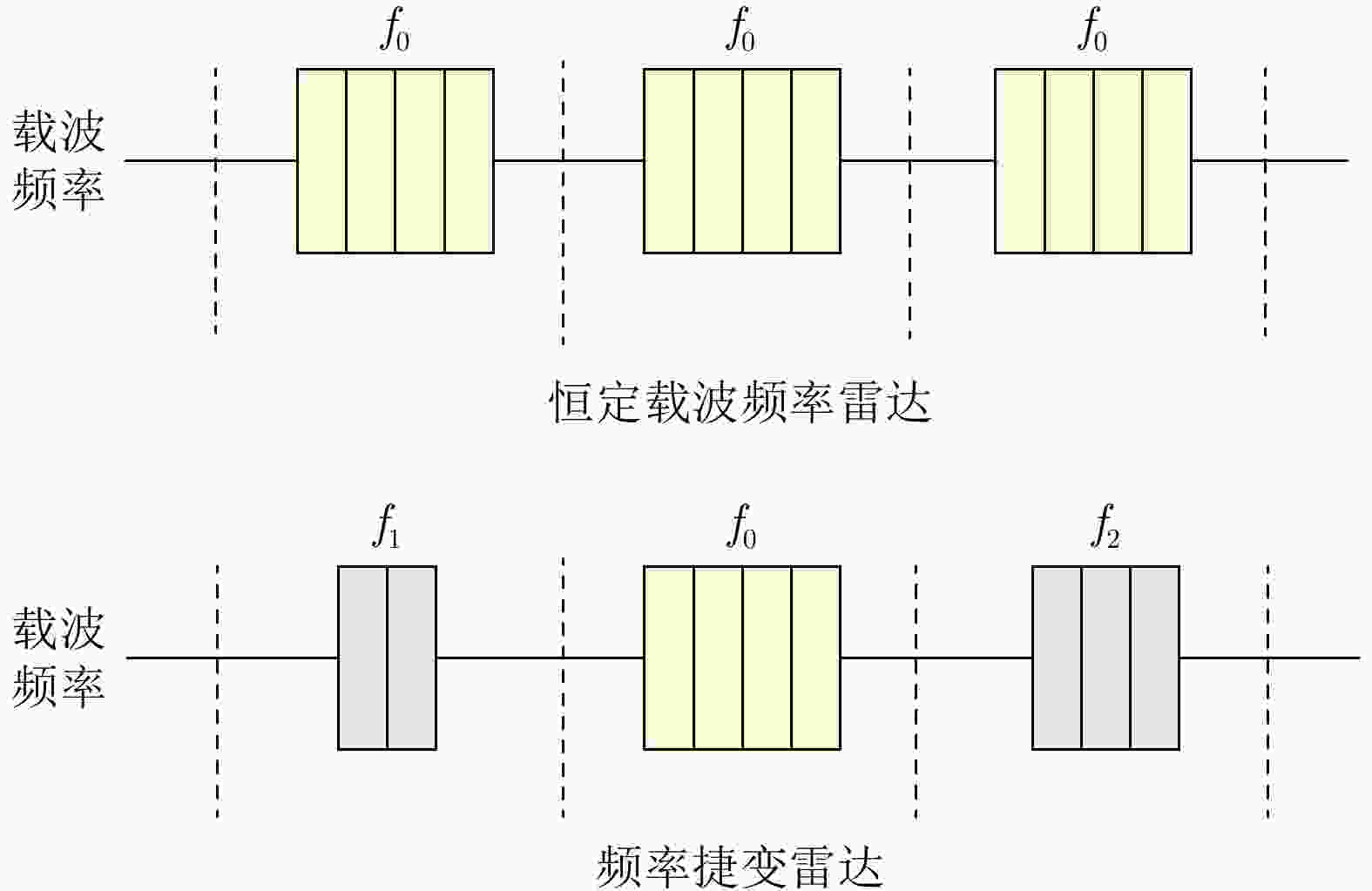
摘要: 在现代电子战中,雷达面临的干扰环境比以前更加复杂,机载干扰机会根据突袭任务与突袭阶段的不同而改变其干扰方式。近年来,基于强化学习的雷达抗干扰方法在单一干扰对抗场景下取得了一定进展,但在实际复杂多干扰场景下的研究仍有不足。为了解决该问题,本文提出了一种基于复数域深度强化学习的多干扰场景雷达抗干扰方法以优化频率捷变雷达的抗干扰策略。首先,针对突袭任务的阶段性特点建立了噪声瞄准干扰、距离假目标欺骗干扰与密集假目标转发干扰3种干扰模型,并设计了3种干扰顺序策略来模拟实际干扰场景。其次,针对多干扰场景模型,构建了一种融合信干噪比与目标航迹完整性的强化学习奖励函数,并针对干扰信号的复数域特征,提出了一种基于复数域深度强化学习的多干扰场景雷达抗干扰方法。最后,基于3种干扰顺序策略设计了雷达抗干扰仿真实验,结果表明,所提方法能够有效解决雷达面临的时序条件下复杂多干扰场景的主瓣干扰问题,与两种经典深度强化学习算法相比该方法抗干扰决策性能大幅提高,平均决策时间降低至405.3 ms。Abstract: In modern electronic warfare, the jamming environment of radar is more complex than ever. The airborne jammer adapts its jamming method based on diverse raid missions and stages. Recently, the reinforcement learning–based radar anti-jamming method has made some progress in the confrontation scenario of single jamming; however, the gap with respect to actual complex multi-jamming scenarios is large. To address this issue, this paper proposes a multi-jamming scenario radar anti-jamming method based on deep reinforcement learning in the complex domain to optimize the anti-jamming strategy of frequency agile radar. First, according to the stage characteristics of the raid mission, noise spot jamming, range deception jamming , and dense false target forwarding jamming models are established. The three jamming sequence strategies were designed to simulate actual jamming scenarios. Second, a reinforcement learning reward function that integrates the signal-to-noise ratio and target trajectory integrity is constructed for the multi-jamming scenario model. Thus, a multi-jamming scenario radar anti-jamming method based on deep reinforcement learning in a complex domain is proposed, which is based on the complex domain characteristics of the jamming signal. Finally, radar anti-jamming simulation experiments are performed based on the three jamming sequence strategies. The results show that the proposed method can effectively deal with the main-lobe jamming problem of complex multi-jamming scenarios under time-sequence conditions. Moreover, the average decision-making accuracy was improved, and the average decision-making time was reduced to 405.3 ms compared with the two classical reinforcement learning algorithms.
-
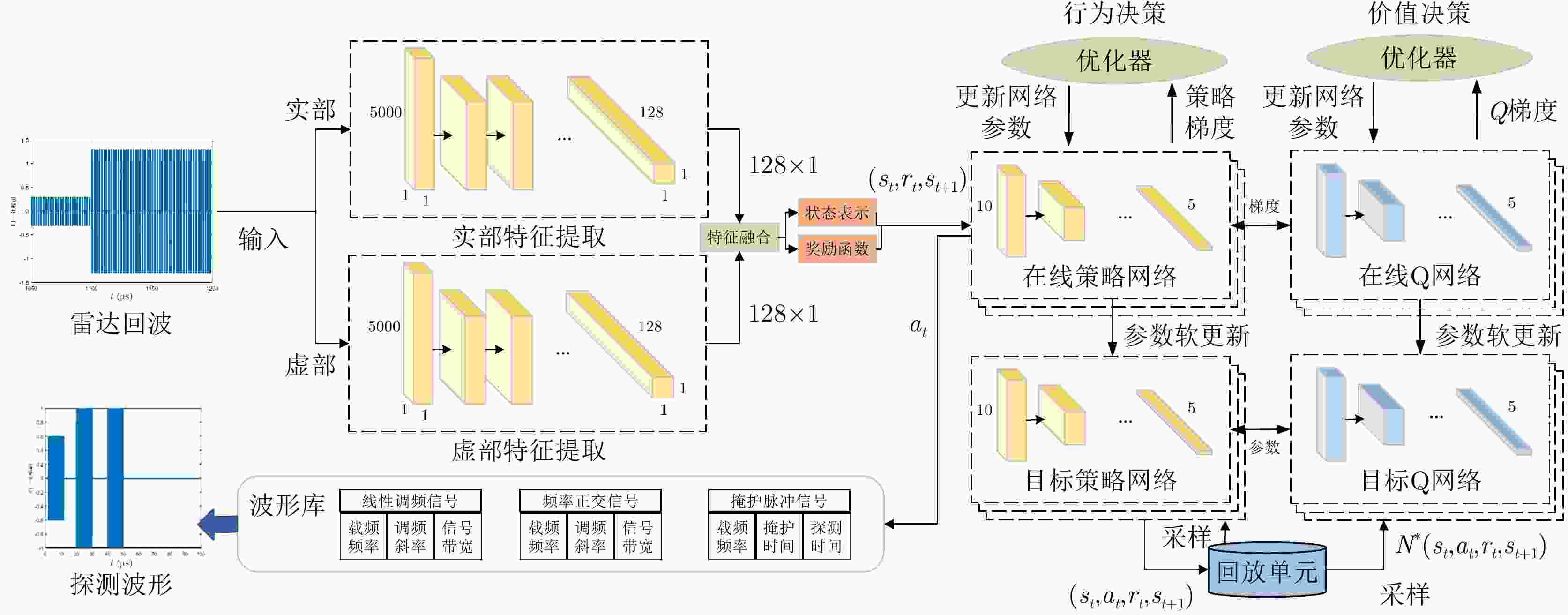
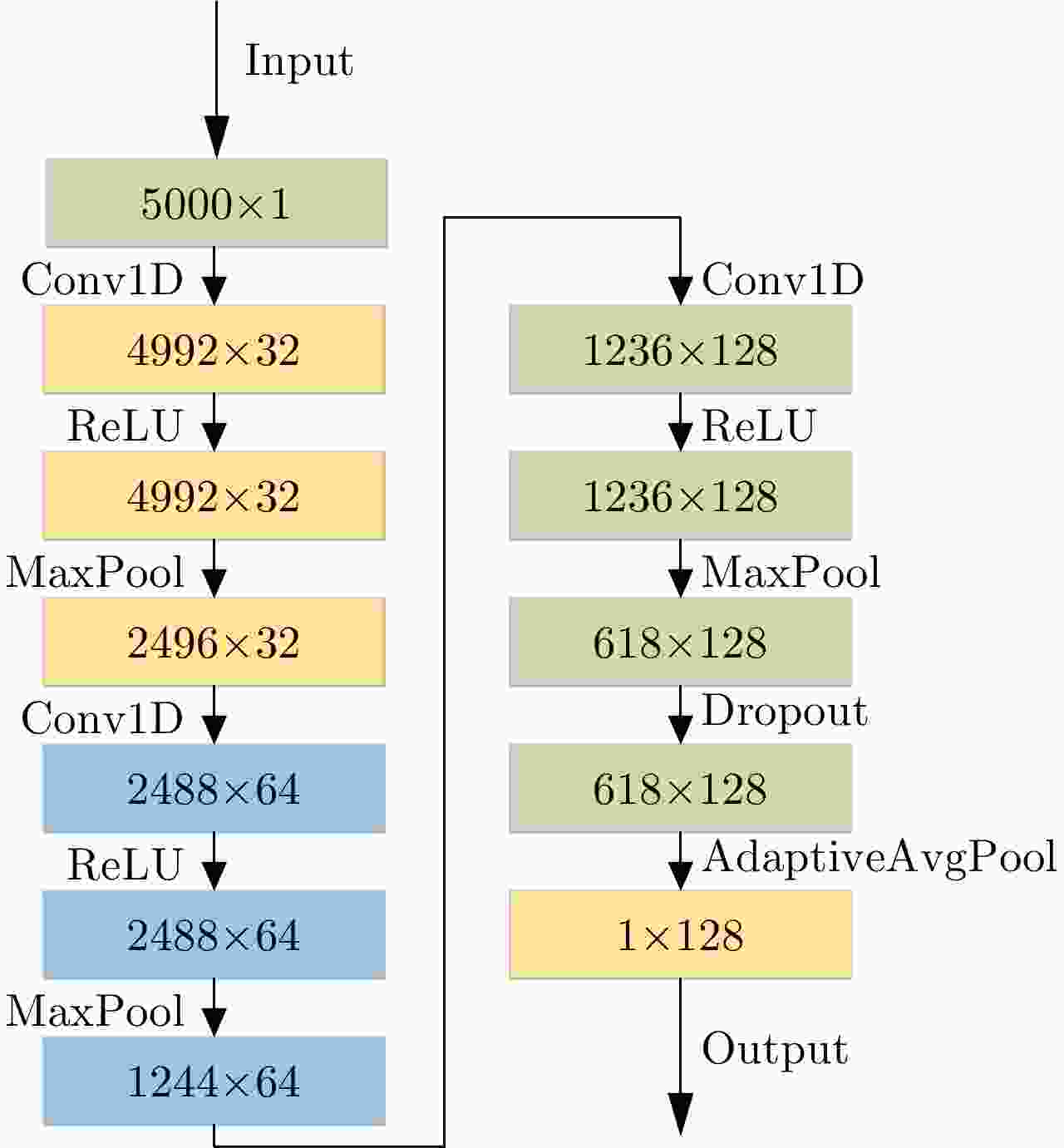
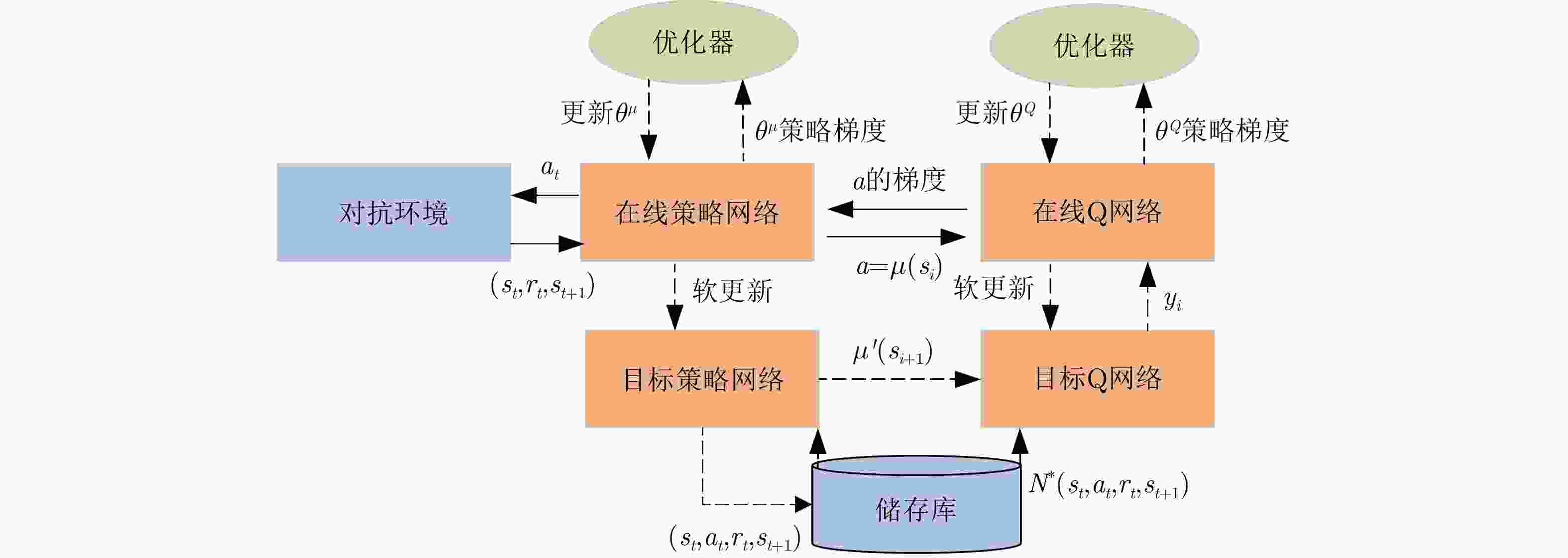
1 深度确定性策略梯度算法
1. Deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm
1. 使用权重 $ {\theta ^Q} $和 ${\theta ^\mu }$随机初始化Q网络参数 $Q\left( {s,a\mid {\theta ^Q}} \right)$和策略
网络参数 $\mu \left( {s\mid {\theta ^\mu }} \right)$2. 使用初始化目标网络 3. 使用权重 ${\theta ^{Q'}} \leftarrow {\theta ^Q}$, ${\theta ^{\mu '}} \leftarrow {\theta ^\mu }$初始化目标网络 $Q'$和 $\mu '$ 4. 初始化经验池R 5. for episode=1, 2, ···, ${{M}}$,执行: 6. 为行动探索初始化一个随机过程 ${{N}}$ 7. 获得一个初始化观察状态 ${s_1}$ 8. for ${{t}} = 1,2,\cdots,T$,执行: 9. 根据当前策略与探索噪声选择行动 ${a_t}$ 10. 执行动作 ${a_t}$,获得奖励 ${r_t}$与新的状态 ${s_{t + 1}}$ 11. 将样本 $\left( {{s_t},{a_t},{r_t},{s_{t + 1}}} \right)$存储至经验池R 12. 从R中随机采样出N个样本 $\left( {{s_i},{a_i},{r_i},{s_{i + 1}}} \right)$ 13. 设置 ${y_i} = {r_i} + \gamma Q'\left( {{s_{i + 1}},\mu '\left( {{s_{i + 1}}\mid {\theta ^{\mu '}}} \right)\mid {\theta ^{Q'}}} \right)$ 14. 使用损失函数L更新Q网络参数 15. 使用采样样本的策略梯度更新行为策略 16. 更新目标网络参数: $ {\theta }^{{Q}^{\prime }}\leftarrow \tau {\theta }^{Q}+\left(1-\tau \right){\theta }^{{Q}^{\prime }} $ ${\theta ^{\mu '}} \leftarrow \tau {\theta ^\mu } + \left( {1 - \tau } \right){\theta ^{\mu '}}$ 17. end for 18. end for 表 1 雷达发射信号仿真参数表
Table 1. Radar transmit signal simulation parameters
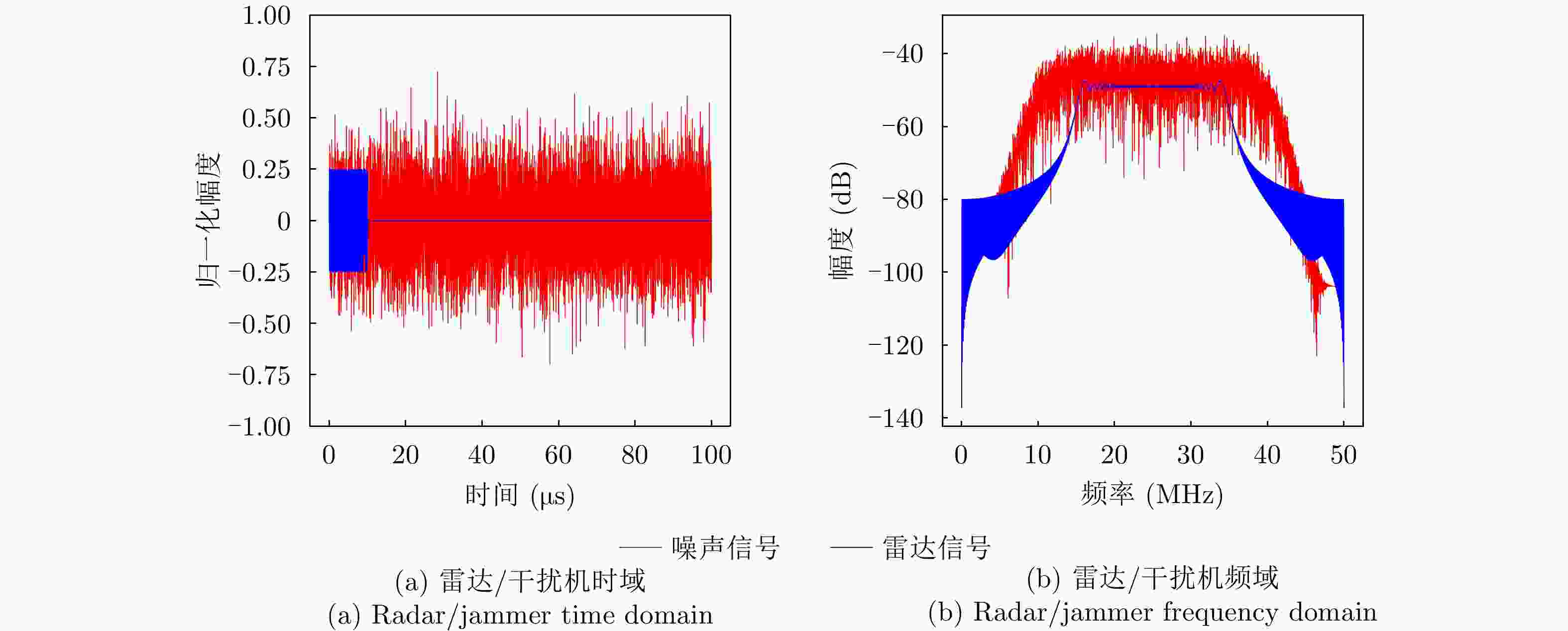
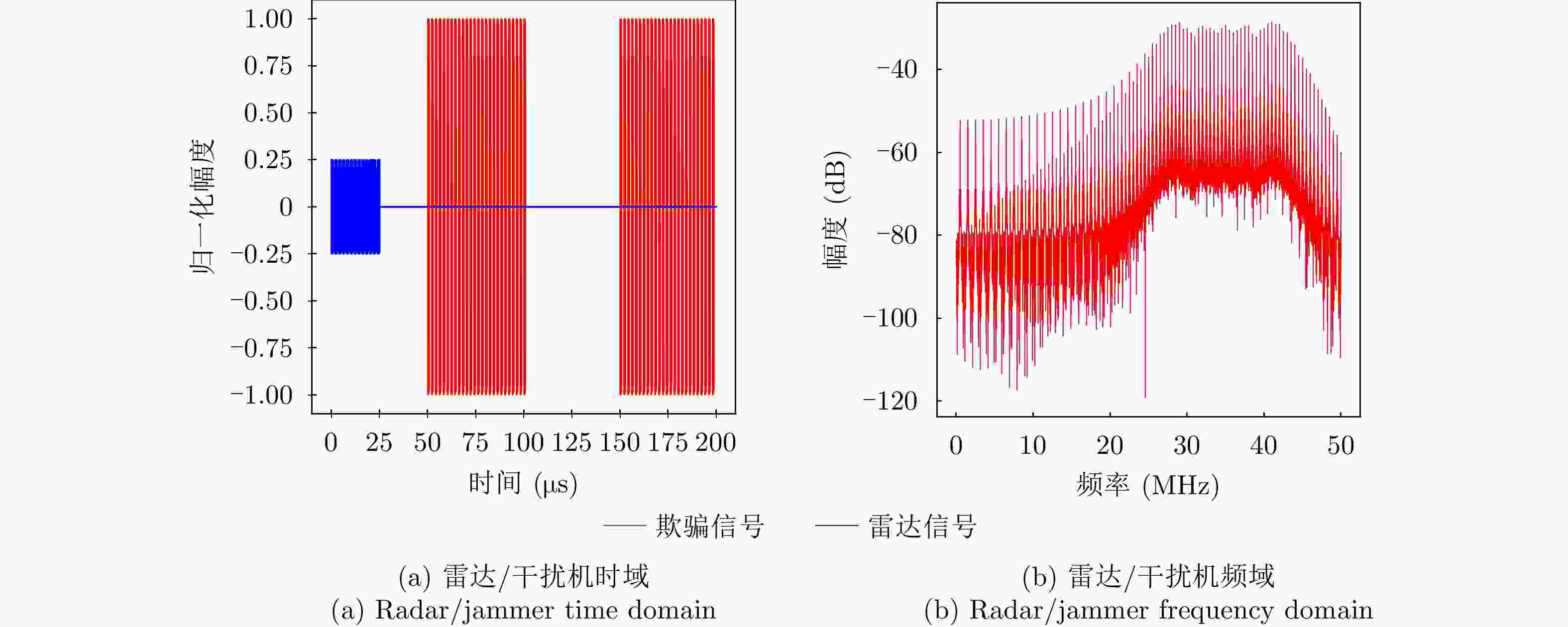
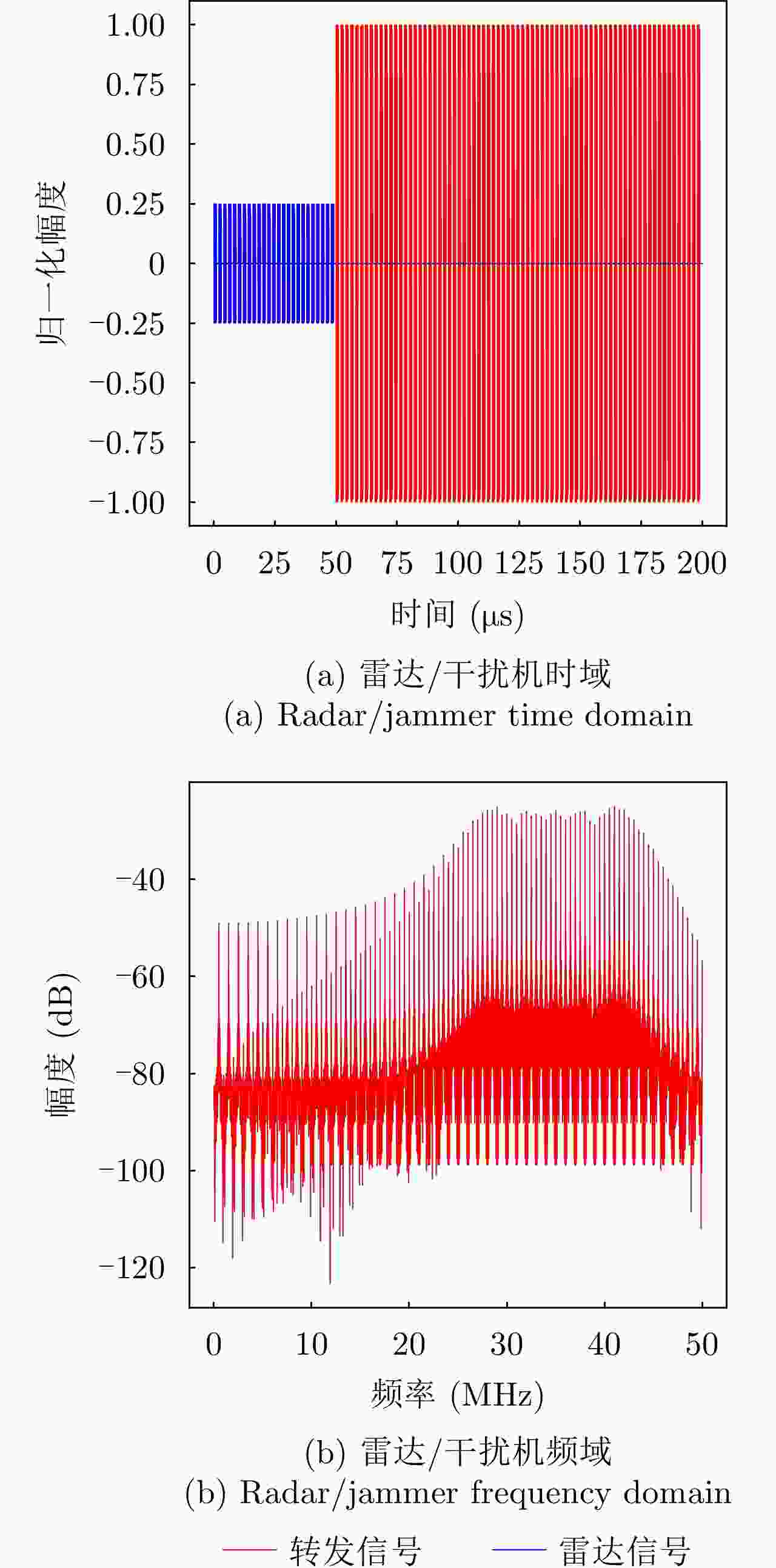
参数类型 数值 信号类型 LFM 采样频率 ${f_{\rm{s}}}$ (MHz) 100 脉冲宽度 ${T_{\rm{p}}}$ (μs) 10 脉冲重复周期 ${T_{\rm{r}}}$ (μs) 50 下变频后的中频频率 ${f_I}$ (MHz) 25 调频斜率k (Hz/s) 2×1012 带宽B (MHz) 20 表 2 3种干扰类型下的态势预测性能
Table 2. Posture prediction performance under 3 interference types
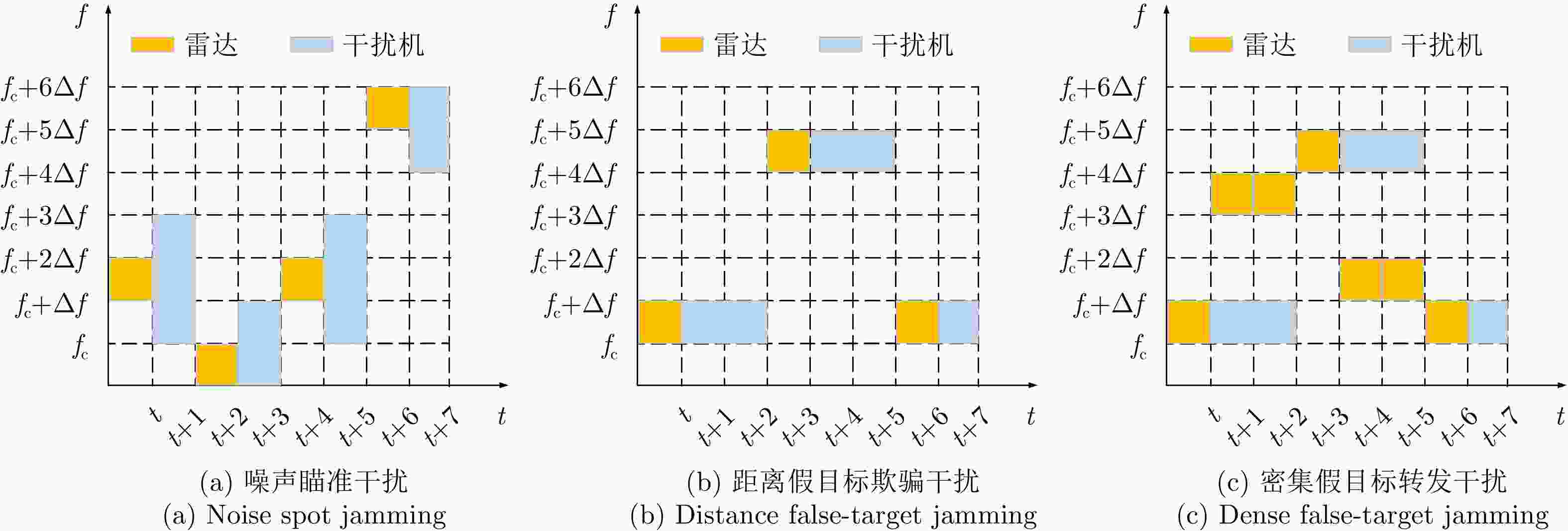
干扰类型 总体区间 步进 识别时间(ms) 识别精度(%) 噪声瞄准干扰 [3~4 GHz] 1 MHz 96 98.6 距离假目标欺骗干扰 [3~4 GHz] 1 MHz 132 97.4 密集假目标转发干扰 [1~1000 μs] 1 μs 144 94.4 表 3 算法参数设置
Table 3. Algorithm parameters setting
参数 PPO TD3 DRL-ANCD Q网络学习率 10–3 10–3 10–3 策略网络学习率 10–3 10–3 10–3 优化器 Adam Adam Adam 目标网络更新率 10–3 5×10–3 5×10–3 批输入 128 128 128 折扣系数 0.99 0.99 0.99 奖励缩放 1.0 1.0 1.0 PPO裁剪参数 0.2 None None 表 4 单一干扰类型下3种强化学习算法抗干扰性能
Table 4. Performance of 3 RL algorithms for a single jamming type
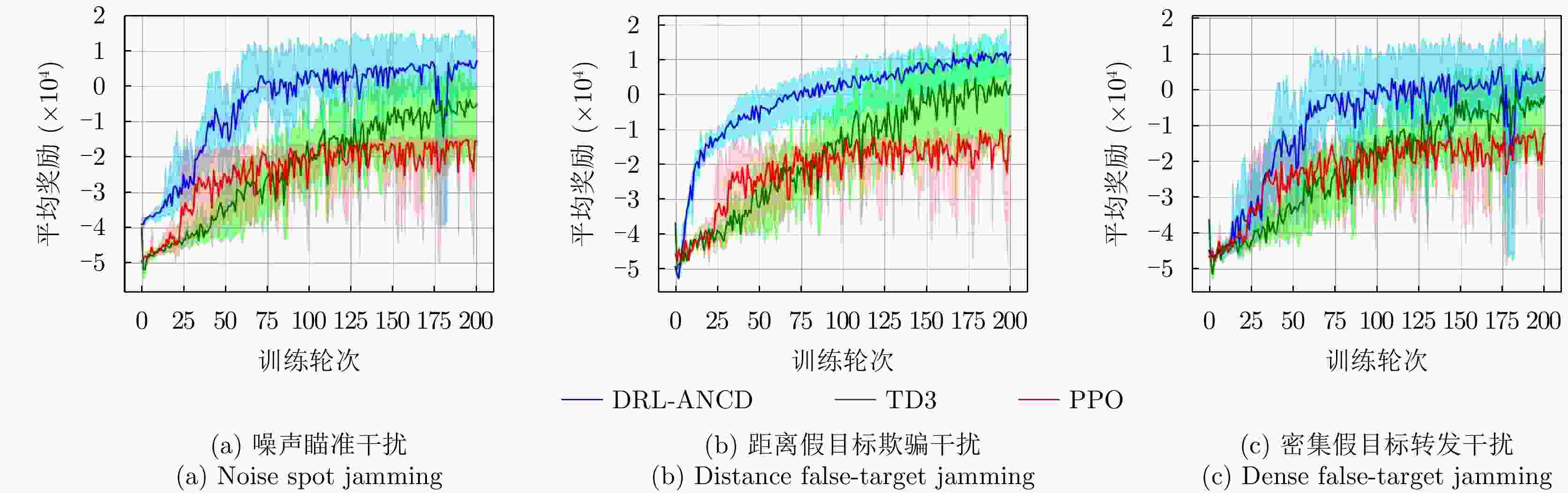
干扰类型 算法名称 平均奖励 决策时间(ms) 噪声瞄准干扰 PPO –215 188 TD3 –51 333 DRL-ANCD 53 244 距离假目标欺骗干扰 PPO –168 168 TD3 –25 225 DRL-ANCD 94 203 密集假目标转发干扰 PPO –156 269 TD3 –45 340 DRL-ANCD 24 289 表 5 在线网络参数
Table 5. Online net parameters
网络 网络层 输入 输出 激活 策略网络 MLP1 State 256 ReLU MLP2 256 256 ReLU MLP3 256 128 ReLU MLP4 128 1 None Q网络 MLP1 State+action 256 ReLU MLP2 Action+256 256 ReLU MLP3 256 128 ReLU MLP4 128 1 None 表 6 多干扰策略下3种强化学习算法抗干扰性能
Table 6. Performance of 3 RL algorithms for a multi-jamming strategies
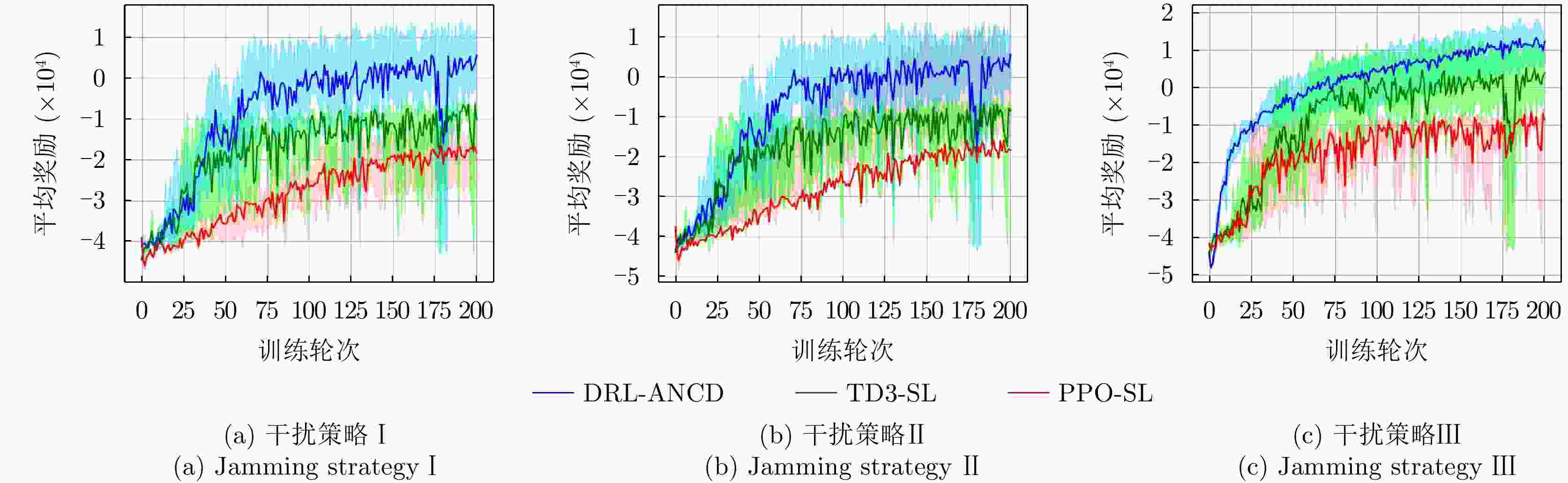
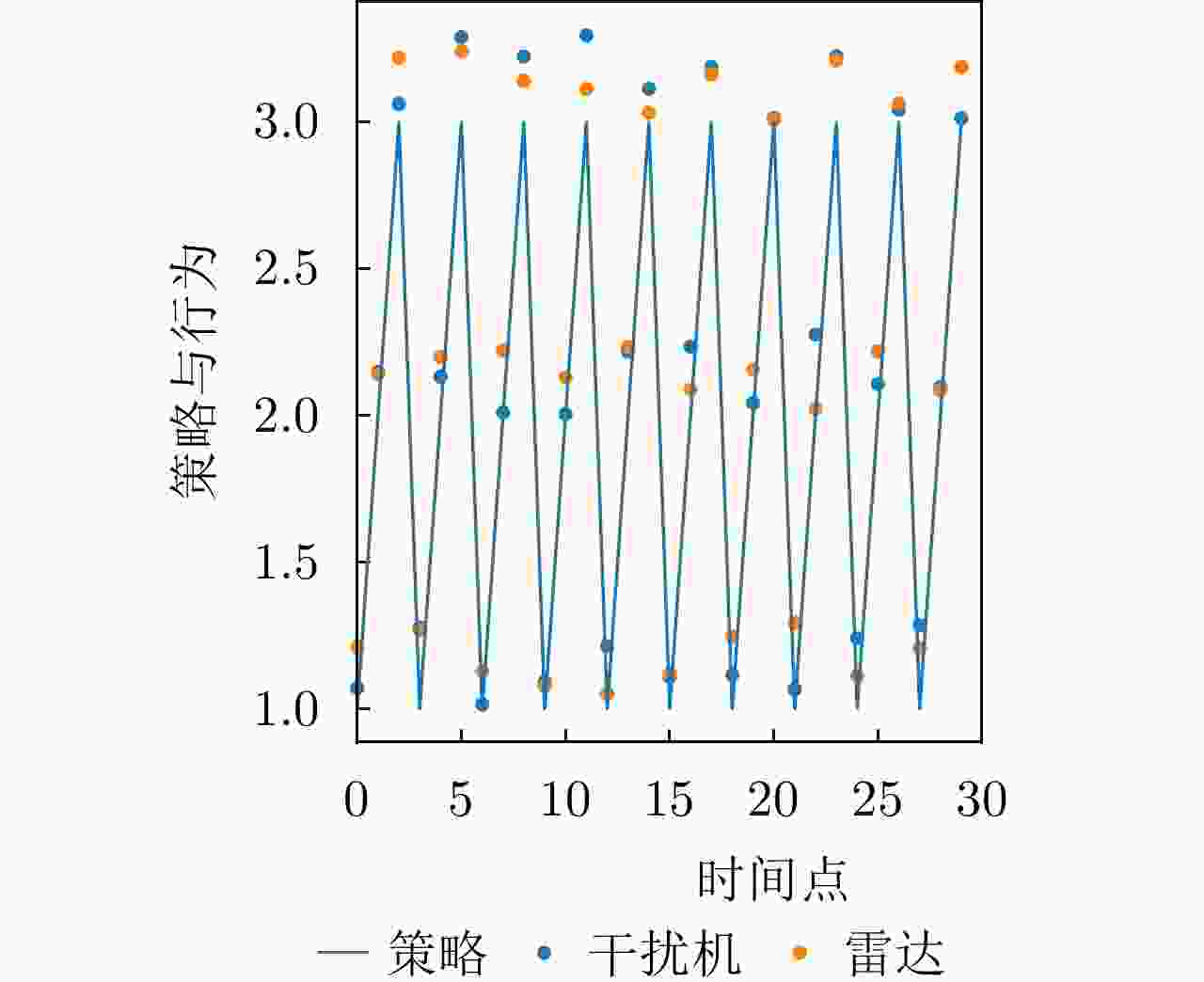
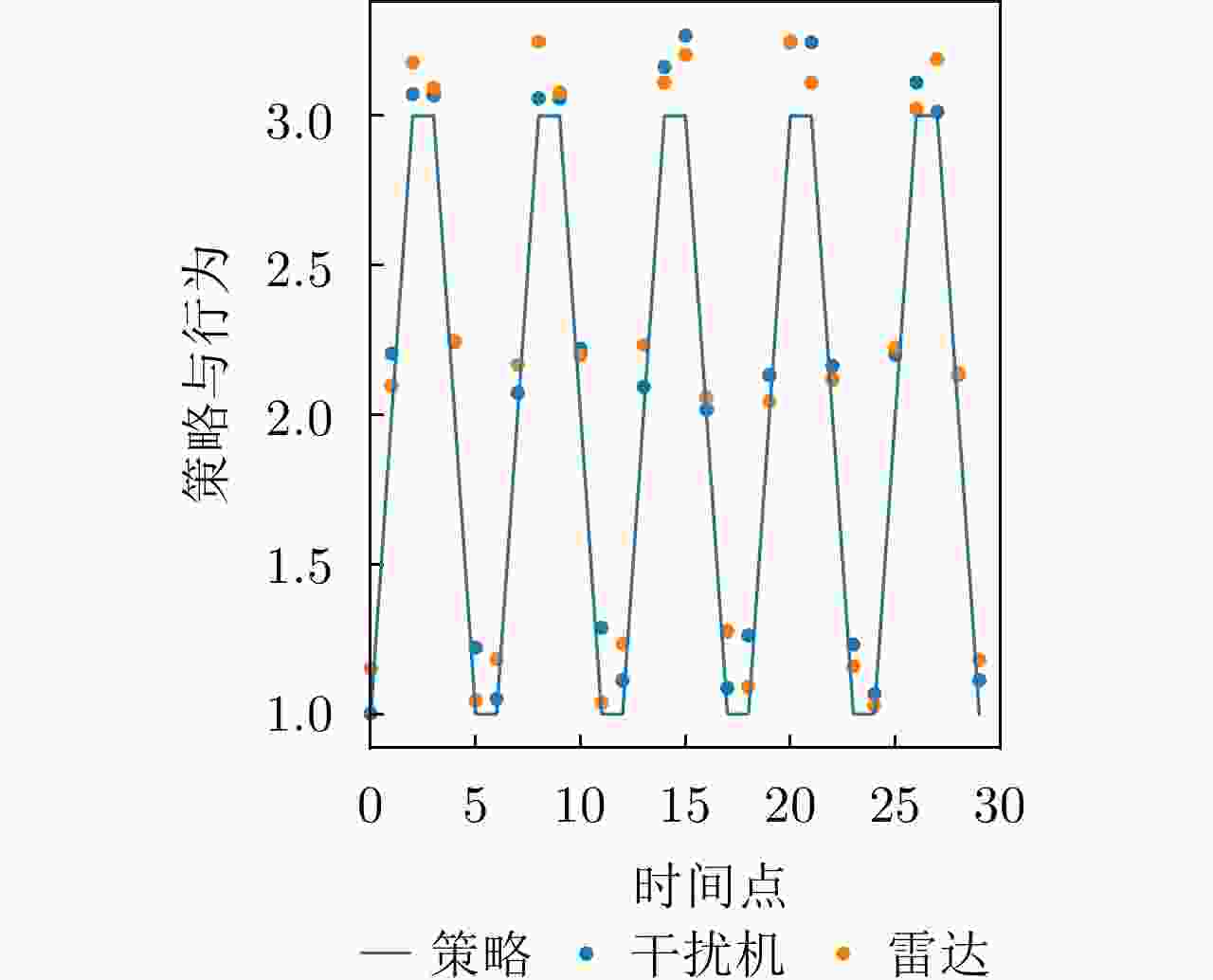
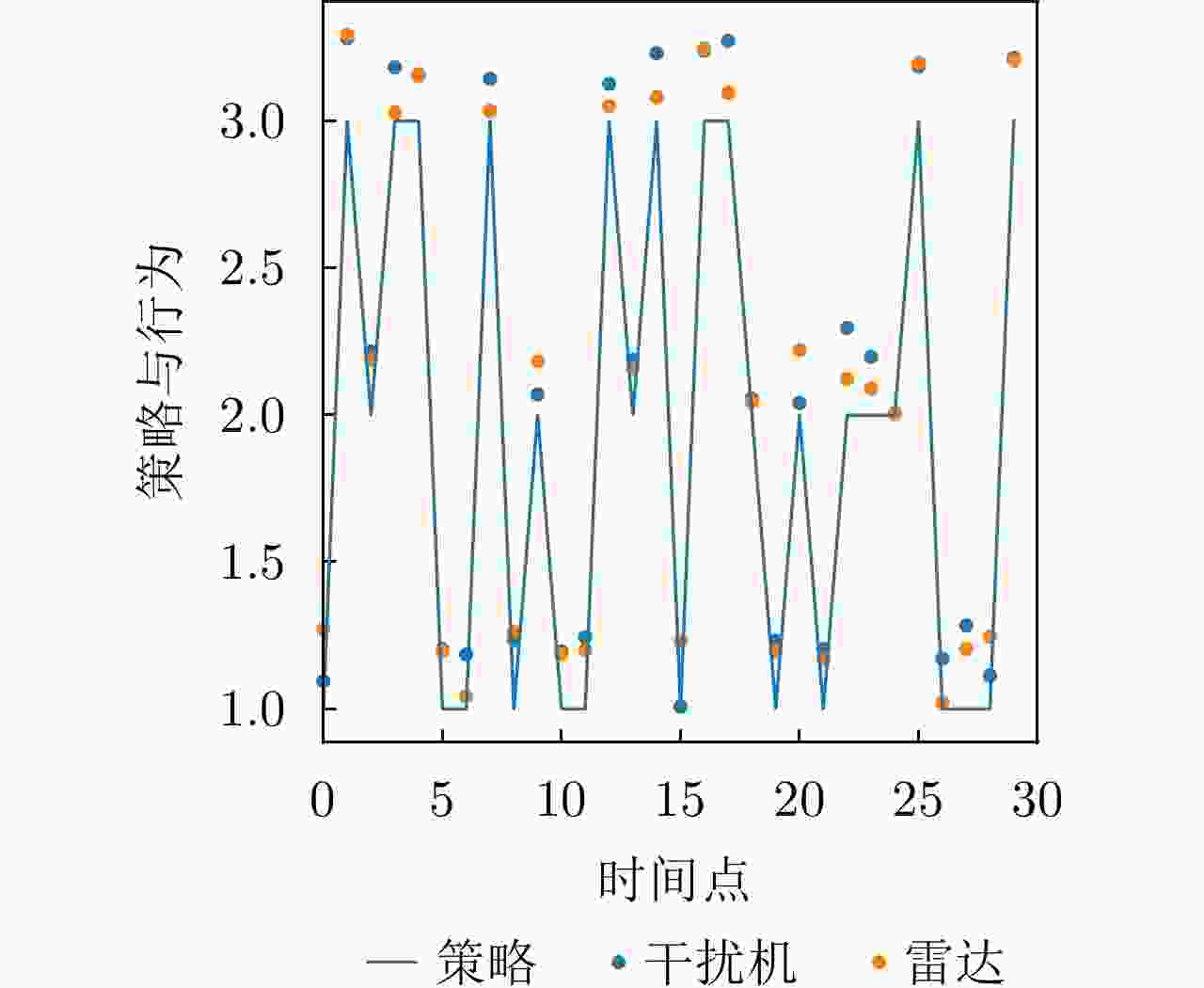
干扰策略 算法名称 对抗奖励 决策时间(ms) 干扰策略Ⅰ PPO-SL –202 356 TD3-SL –125 443 DRL-ANCD 3 402 干扰策略Ⅱ PPO-SL –221 375 TD3-SL –122 429 DRL-ANCD 14 392 干扰策略Ⅲ PPO-SL –124 386 TD3-SL 25 463 DRL-ANCD 107 422 -
[1] KOGON S M, HOLDER E J, and WILLIAMS D B. Mainbeam jammer suppression using multipath returns[C]. Conference Record of the Thirty-First Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1997: 279–283. [2] GRECO M, GINI F, and FARINA A. Radar detection and classification of jamming signals belonging to a cone class[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(5): 1984–1993. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.909326 [3] NERI F. Introduction to Electronic Defense Systems[M]. SciTech Publishing, Raleigh, NC, 2006. [4] 李宇环, 岳显昌, 张兰. 基于压缩感知的时域抗射频干扰方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(7): 2767–2772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.671-1815.2020.07.035LI Yuhuan, YUE Xianchang, and ZHANG Lan. Time-domain radio frequency interference suppression method based on compressed sensing[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(7): 2767–2772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.671-1815.2020.07.035 [5] 杜思予, 刘智星, 吴耀君, 等. 基于SVM的捷变频雷达密集转发干扰智能抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 173–185. doi: 10.12000/JR22065DU Siyu, LIU Zhixing, WU Yaojun, et al. Dense-repeated jamming suppression algorithm based on the support vector machine for frequency agility radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 173–185. doi: 10.12000/JR22065 [6] 董淑仙, 吴耀君, 方文, 等. 频率捷变雷达联合模糊C均值抗间歇采样干扰[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 289–300. doi: 10.12000/JR21205DONG Shuxian, WU Yaojun, FANG Wen, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming method based on frequency-agile radar joint fuzzy C-means[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 289–300. doi: 10.12000/JR21205 [7] 施龙飞, 任博, 马佳智, 等. 雷达极化抗干扰技术进展[J]. 现代雷达, 2016, 38(4): 1–7, 29.SHI Longfei, REN Bo, MA Jiazhi, et al. Recent developments of radar anti-interference techniques with polarimetry[J]. Modern Radar, 2016, 38(4): 1–7, 29. [8] 陈新竹. 多功能数字阵列雷达空域抗有源干扰方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 上海交通大学, 2022.CHEN Xinzhu. Research on spatial jamming cancellation in mutifunction digital array radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2022. [9] 刘智星, 杜思予, 吴耀君, 等. 脉间-脉内捷变频雷达抗间歇采样干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001LIU Zhixing, DU Siyu, WU Yaojun, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming method for interpulse and intrapulse frequency-agile radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001 [10] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [11] 李彦冬, 郝宗波, 雷航. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2016, 36(9): 2508–2515, 2565.LI Yandong, HAO Zongbo, and LEI Hang. Survey of convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 36(9): 2508–2515, 2565. [12] 刘全, 翟建伟, 章宗长, 等. 深度强化学习综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(1): 1–27. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.00001LIU Quan, ZHAI Jianwei, ZHANG Zongzhang, et al. A survey on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(1): 1–27. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.00001 [13] 刘朝阳, 穆朝絮, 孙长银. 深度强化学习算法与应用研究现状综述[J]. 智能科学与技术学报, 2020, 2(4): 312–326. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.202034LIU Zhaoyang, MU Chaoxu, and SUN Changyin. An overview on algorithms and applications of deep reinforcement learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2020, 2(4): 312–326. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.202034 [14] DAYAN P and DAW N D. Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain[J]. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience , 2008, 8(4): 429–453. doi: 10.3758/CABN.8.4.429 [15] CAROTENUTO V, DE MAIO A, ORLANDO D, et al. Adaptive radar detection using two sets of training data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(7): 1791–1801. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2778684 [16] 汪浩, 王峰. 强化学习算法在雷达智能抗干扰中的应用[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(3): 40–44, 48.WANG Hao and WANG Feng. Application of reinforcement learning algorithms in anti-jamming of intelligent radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(3): 40–44, 48. [17] XING Qiang, ZHU Weigang, and JIA Xin. Research on method of intelligent radar confrontation based on reinforcement learning[C]. 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Applications (ICCIA), Beijing, China, 2017: 471–475. [18] LI Kang, JIU Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Reinforcement learning based anti-jamming frequency hopping strategies design for cognitive radar[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Qingdao, China, 2018: 1–5. [19] LI Kang, JIU Bo, and LIU Hongwei. Deep Q-network based anti-jamming strategy design for frequency agile radar[C]. 2019 International Radar Conference (RADAR), Toulon, France, 2019: 1–5. [20] WANG Shanshan, LIU Zheng, XIE Rong, et al. Reinforcement learning for compressed-sensing based frequency agile radar in the presence of active interference[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 968. doi: 10.3390/rs14040968 [21] LI Xinzhi and DONG Shengbo. Research on efficient reinforcement learning for adaptive frequency-agility radar[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(23): 7931. doi: 10.3390/s21237931 [22] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191 [23] WATERS W M and LINDE G J. Frequency-agile radar signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1979, AES-15(3): 459–464. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1979.308841 [24] 李尔康. 基于干扰认知的雷达反干扰波形设计与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022.LI Erkang. Design and implementation of radar anti-jamming waveform based on jamming cognition[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. [25] 张昭建, 谢军伟, 杨春晓, 等. 掩护脉冲信号抗转发式欺骗干扰性能分析[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2016, 36(4): 149–152, 156.ZHANG Zhaojian, XIE Junwei, YANG Chunxiao, et al. Performance analysis of screening pulse signal confronts to deception jamming[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2016, 36(4): 149–152, 156. [26] 李研. 雷达抗干扰波形设计及仿真分析[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2022.LI Yan. Radar anti-jamming waveform design and simulation analysis[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2022. [27] 温鹏飞. 基于雷达数据的目标航迹识别和聚类研究[D]. [硕士论文], 合肥工业大学, 2020.WANG Pengfei. Research on track recognition and clustering based on radar data[D]. [Master dissertation], Hefei University of Technology, 2020. [28] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [29] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347, 2017. [30] FUJIMOTO S, HOOF H, and MEGER D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[C]. 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1587–1596. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: