-
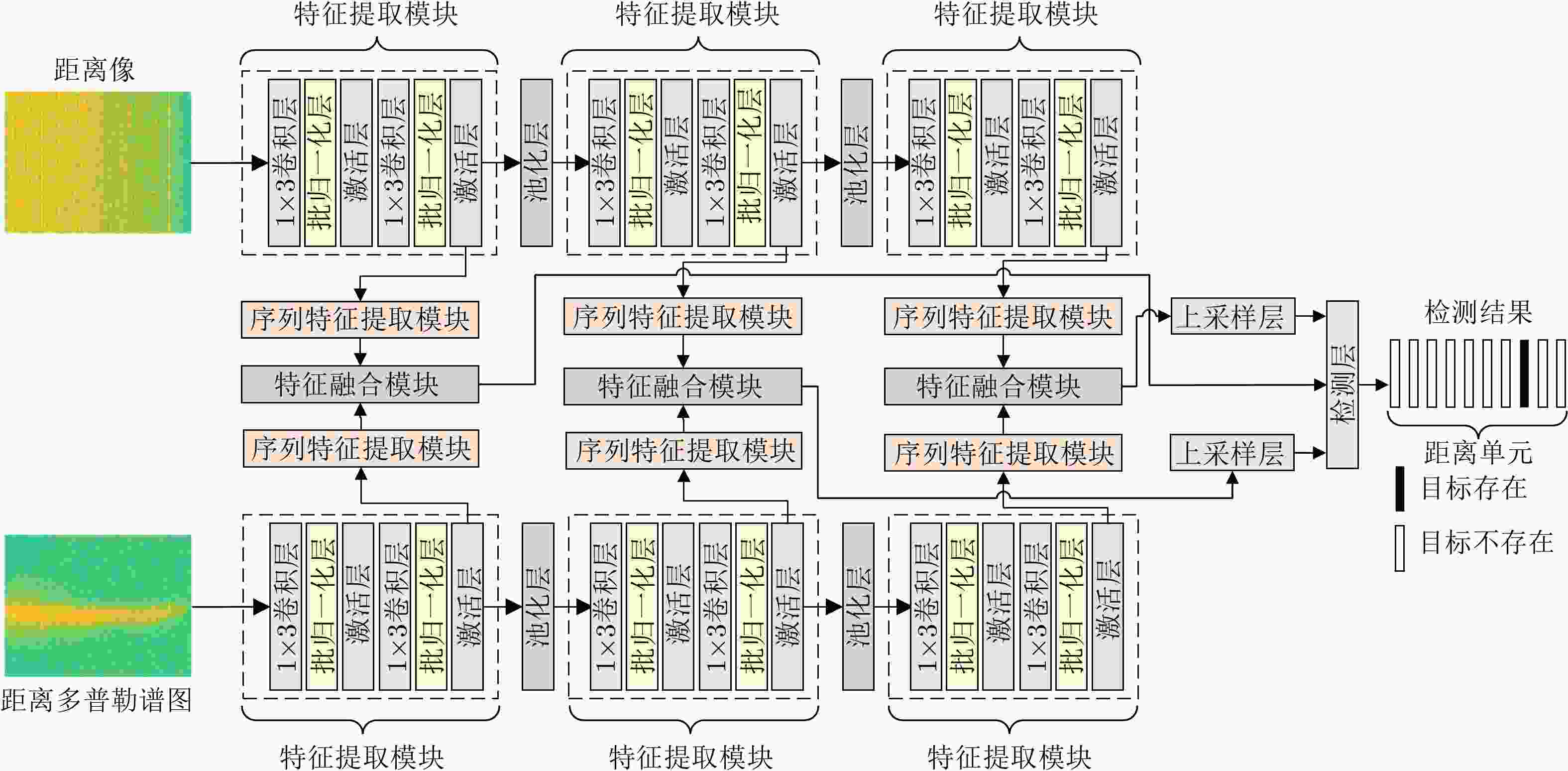
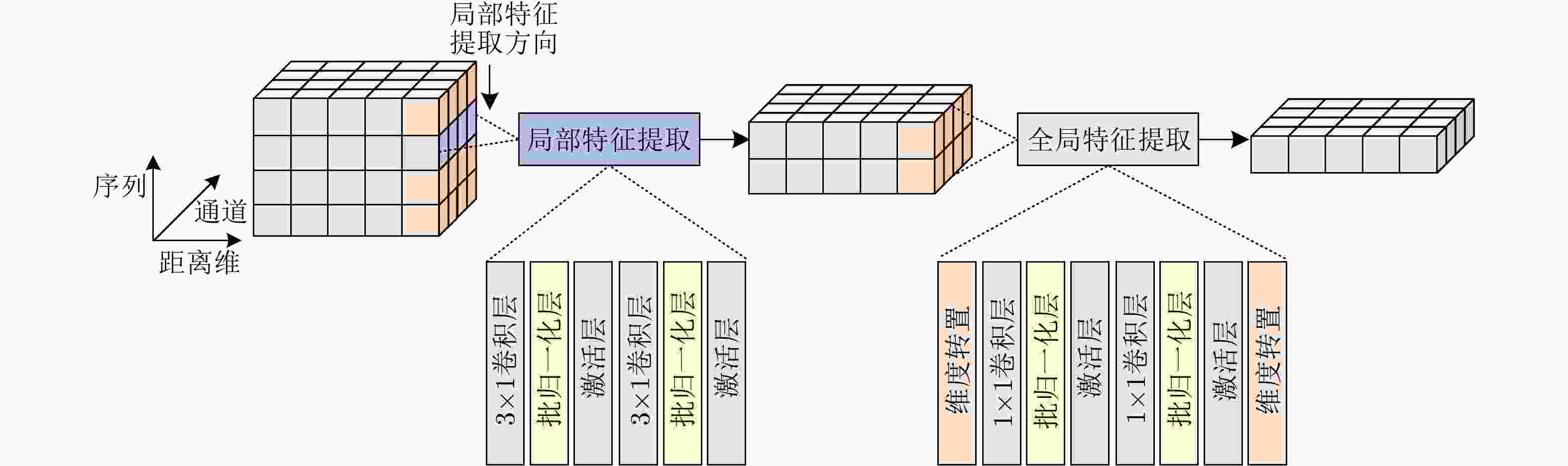
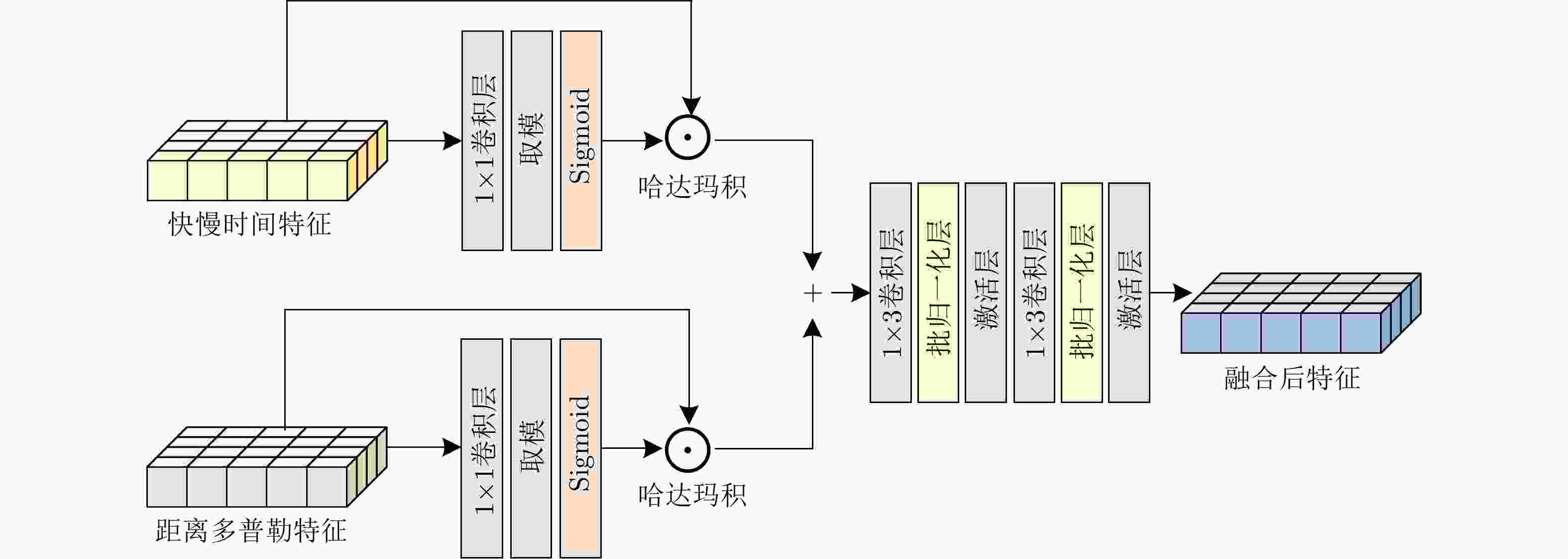
摘要: 该文考虑了海杂波环境下的雷达目标检测问题,提出了一种基于深度学习的海面目标检测器。该检测器通过融合从不同数据源中提取的多种互补性特征以增加目标和杂波的差异性,从而提升对海面目标的检测性能。具体来说,该检测器首先利用两个特征提取分支分别从距离像和距离多普勒谱图中提取多层次快时间特征和距离特征;然后,设计局部-全局特征提取结构从特征的慢时间维度或多普勒维度提取序列关联性;接着,提出基于自适应卷积权重学习的特征融合模块,实现快慢时间特征和距离多普勒特征的高效融合;最后,对多层次特征进行融合、上采样和非线性映射获得检测结果。基于两个公开雷达数据集上的实验验证了所提检测器的检测性能。Abstract: Considering the problem of radar target detection in the sea clutter environment, this paper proposes a deep learning-based marine target detector. The proposed detector increases the differences between the target and clutter by fusing multiple complementary features extracted from different data sources, thereby improving the detection performance for marine targets. Specifically, the detector uses two feature extraction branches to extract multiple levels of fast-time and range features from the range profiles and the range-Doppler (RD) spectrum, respectively. Subsequently, the local-global feature extraction structure is developed to extract the sequence relations from the slow time or Doppler dimension of the features. Furthermore, the feature fusion block is proposed based on adaptive convolution weight learning to efficiently fuse slow-fast time and RD features. Finally, the detection results are obtained through upsampling and nonlinear mapping to the fused multiple levels of features. Experiments on two public radar databases validated the detection performance of the proposed detector.
-
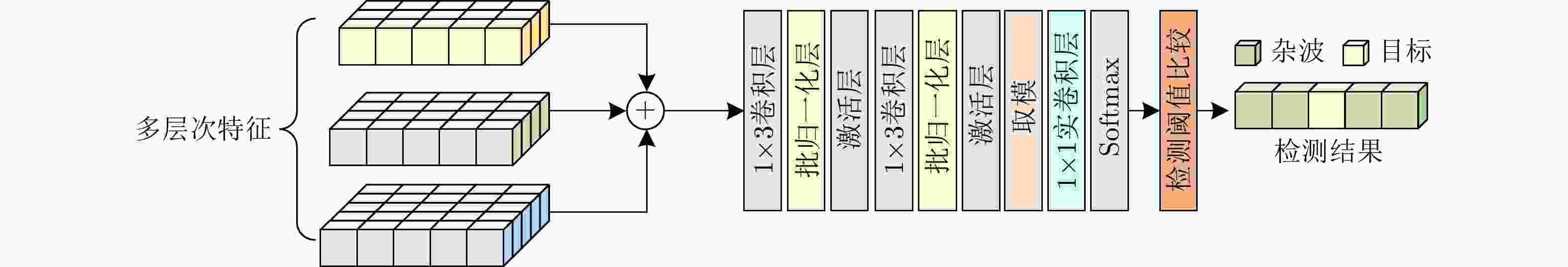
表 1 MFF检测器参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting of MFF detector
参数名称 特征提取模块 池化层 序列特征提取模块 特征融合模块 上采样层 检测层 核尺寸 (1,3), (1,3)
(1,3), (1,3)
(1,3), (1,3)(1,2) (3,1), (3,1)
(1,1), (1,1)(1,1), (1,1)
(1,3), (1,3)(1,4)
(1,2)(1,3), (1,3)
(1,1)步长 (1,1), (1,1)
(1,1), (1,1)
(1,1), (1,1)(1,1) (2,1), (2,1)
(1,1), (1,1)(1,1), (1,1)
(1,1), (1,1)(1,4)
(1,2)(1,1), (1,1)
(1,1)填充尺寸 (0,1), (0,1)
(0,1), (0,1)
(0,1), (0,1)(0,0) (1,0), (1,0)
(0,0), (0,0)(0,0), (0,0)
(0,1), (0,1)(0,0)
(0,0)(0,1), (0,1)
(0,0)通道维度 (1,16), (16,16)
(16,32), (32,32)
(32,64), (64,64)N/A (${C_1}$,$2{C_1}$),
($2{C_1}$,${C_1}$)
(16,8), (8,1)(${C_1}$,1), (${C_1}$,1)
(${C_1}$,${{{C_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{C_1}} 2}} \right. } 2}$),
(${{{C_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{C_1}} 2}} \right. } 2}$,${C_1}$)(64,64)
(32,32)(112,64), (64,64)
(64,2)注:对于3个序列特征提取模块和特征融合模块,${C_1}$依次设置为16, 32, 64。 表 2 雷达参数
Table 2. Radar parameters
数据集名称 带宽(MHz) 载频(GHz) 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 脉宽(μs) IPIX数据集 5 9.39 1000 0.2 雷达对海探测数据集 25 9.30~9.50 1600 3.0 表 3 IPIX数据集子数据集信息
Table 3. Information of sub-dataset in IPIX database
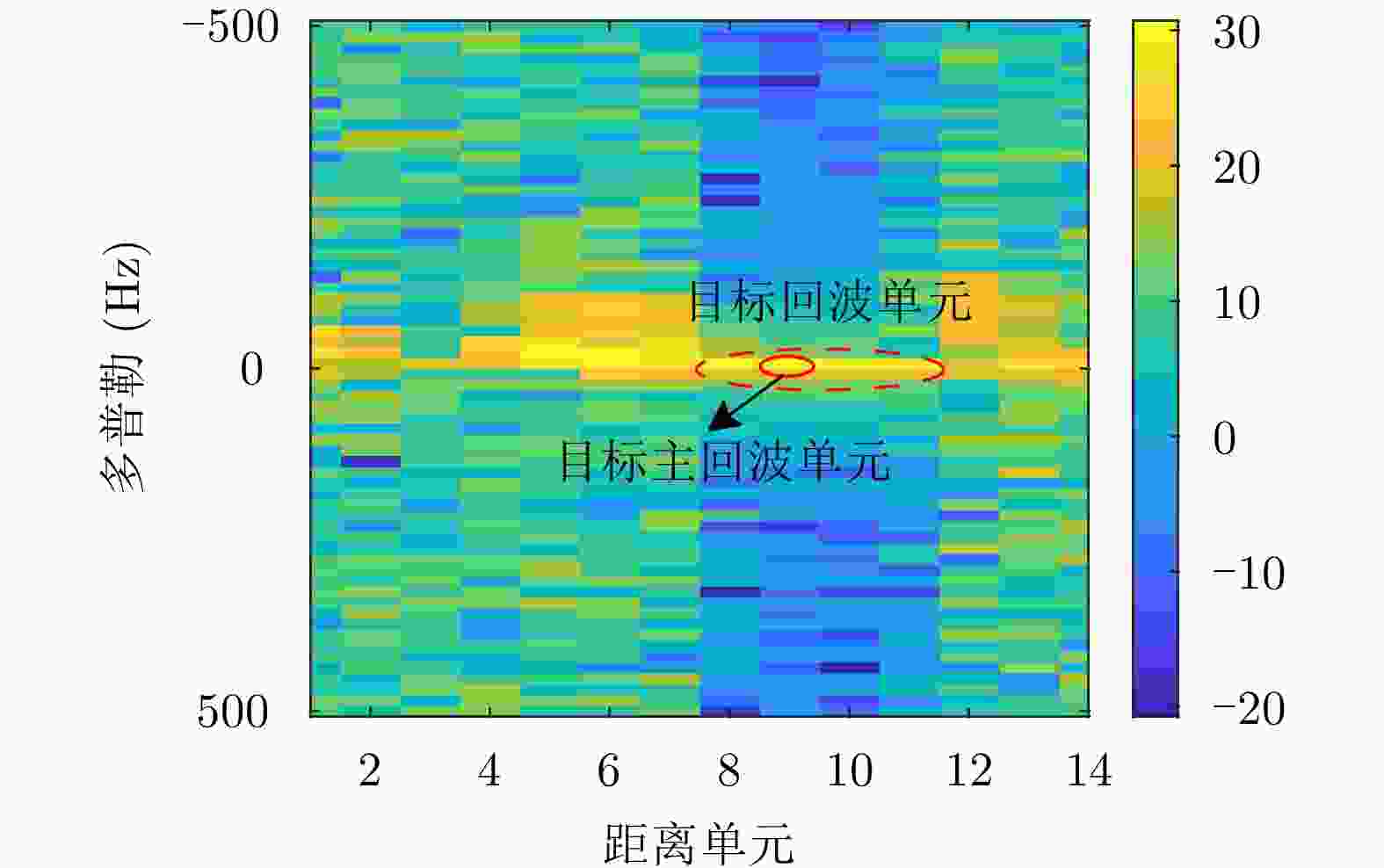
数据集
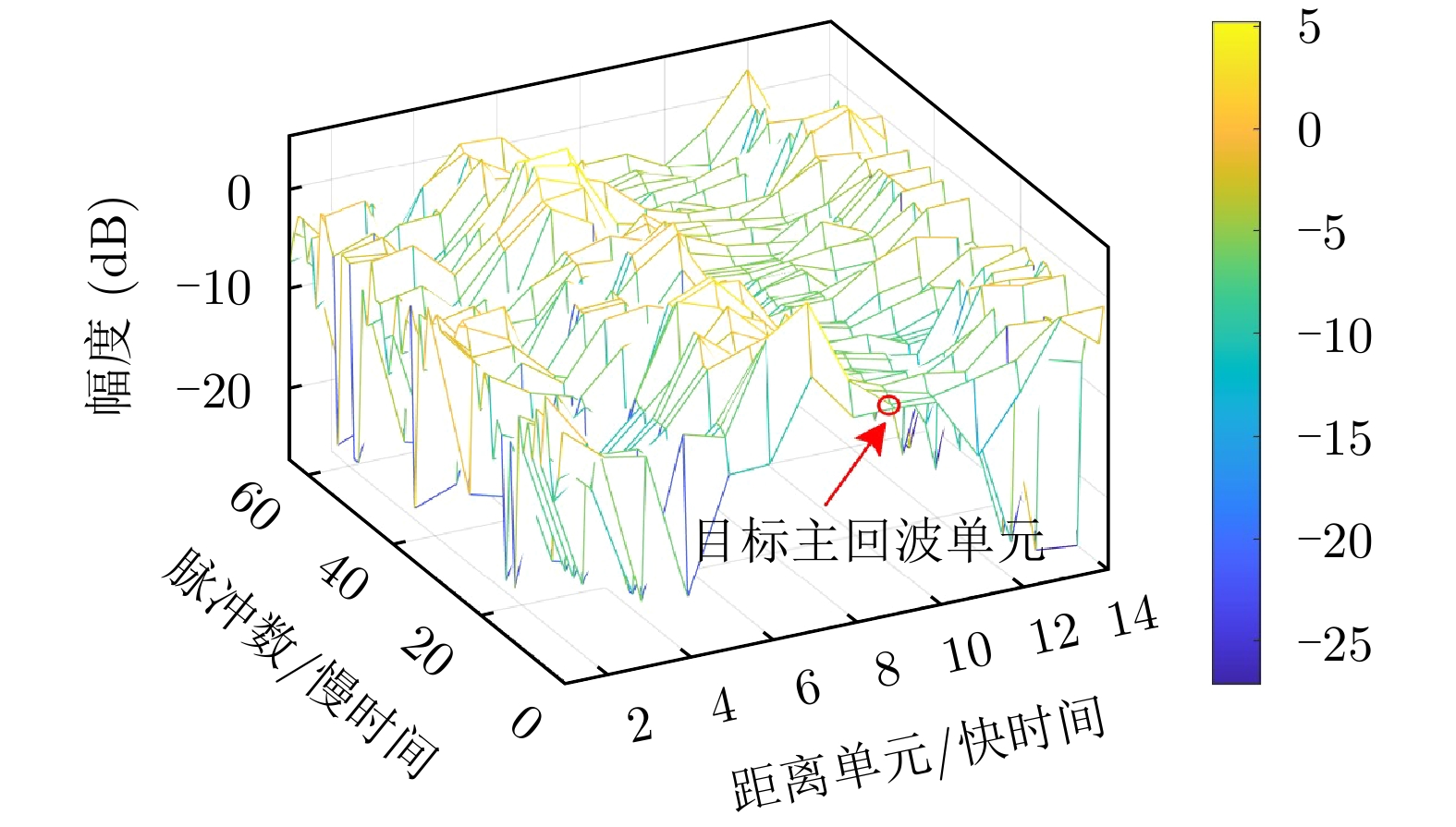
索引子数据集名称 目标主回
波单元目标次回
波单元#17 19931107_135603_starea 9 8, 10, 11 #18 19931107_141630_starea 9 8, 10, 11 #19 19931107_145028_starea 8 7, 9 #25 19931108_213827_starea 7 6, 8 #26 19931108_220902_starea 7 6, 8 #30 19931109_191449_starea 7 6, 8 #31 19931109_202217_starea 7 6, 8 #40 19931110_001635_starea 7 5, 6, 8 #54 19931111_163625_starea 8 7, 9, 10 #280 19931118_023604_stareC0000 8 7, 10 #283 19931118_035737_stareC0000 10 8, 9, 11, 12 #310 19931118_162155_stareC0000 7 6, 8, 9 #311 19931118_162658_stareC0000 7 6, 8, 9 #320 19931118_174259_stareC0000 7 6, 8, 9 表 4 训练样本数和测试样本数
Table 4. Sample number of training set and test set
数据集名称 训练集样本数 测试集样本数 IPIX数据集每个子数据集 7858 5237 雷达对海探测数据集 953 374 表 5 MFF检测器和其变体检测器检测性能
Table 5. Detection performance of the MFF detector and its variant detectors
检测器名称 平均实际虚警率 平均检测概率 MFF 0.0004 0.9870 变体1 0.0005 0.9478 变体2 0.0005 0.9814 表 6 不同特征融合方法检测性能
Table 6. Detection performance of different feature fusion approaches
融合方法 平均实际虚警率 平均检测概率 所提方法 0.0004 0.9870 特征串接 0.0003 0.9477 特征求和 0.0031 0.9619 表 7 不同检测器在IPIX数据集不同极化数据上的平均检测概率
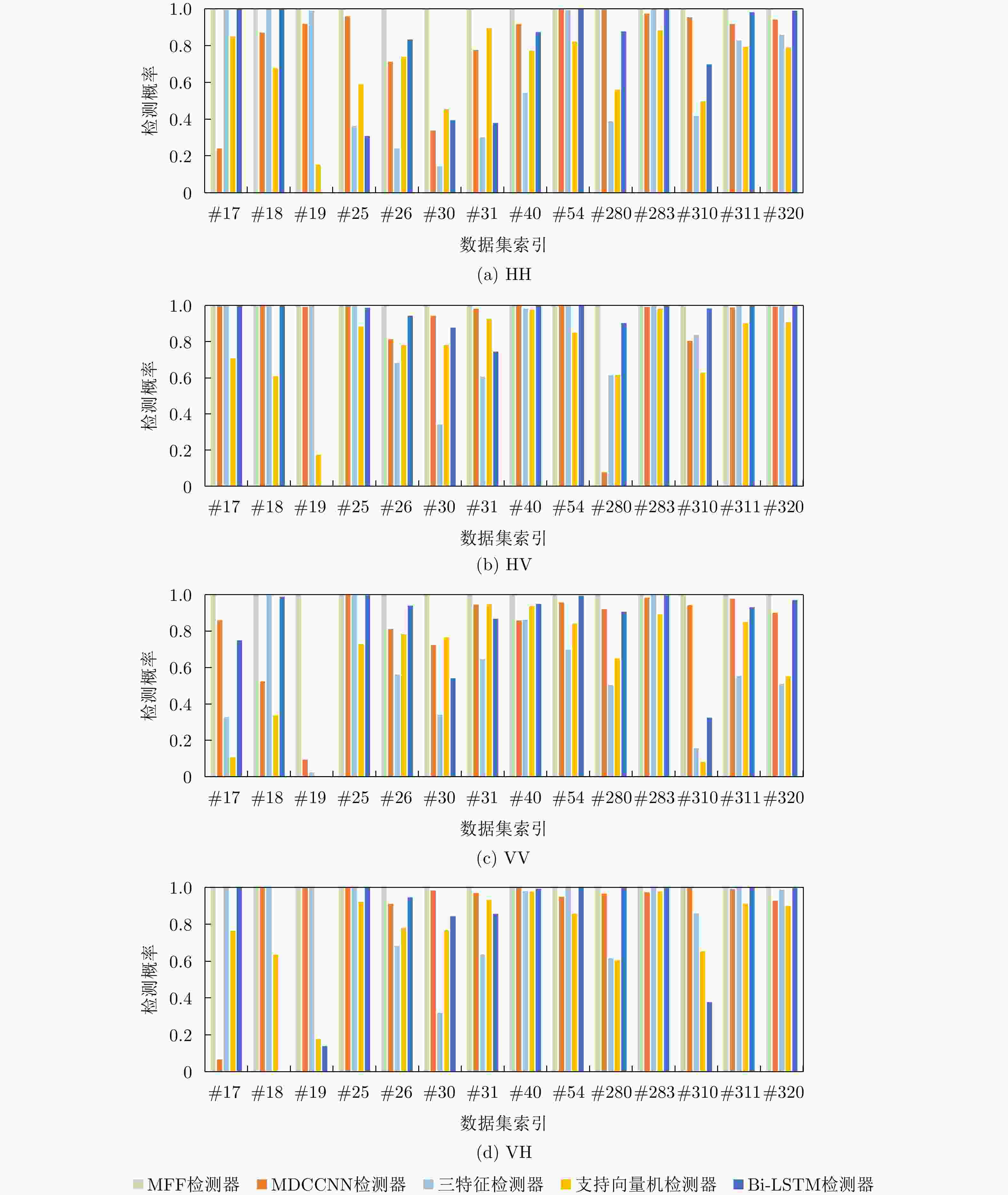
Table 7. Averagely detection probability of various detectors in IPIX database with different polarizations
检测器名称 HH HV VV VH MFF 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 三特征 0.6465 0.8620 0.5848 08630 支持向量机 0.6767 0.7673 0.6053 0.7761 MDCCNN 0.8224 0.8998 0.8217 0.9100 Bi-LSTM 0.7380 0.8889 0.7970 0.7963 表 8 不同检测器在IPIX数据集不同极化数据上的平均实际虚警率
Table 8. Averagely actual false alarm rate of various detectors in IPIX database with different polarizations
检测器名称 HH HV VV VH MFF 0.0014 0.0016 0.0016 0.0017 三特征 0.0037 0.0043 0.0038 0.0043 支持向量机 0.0033 0.0036 0.0042 0.0035 MDCCNN 0.0047 0.0020 0.0049 0.0020 Bi-LSTM 0.0042 0.0022 0.0057 0.0029 表 9 不同检测器在雷达对海探测数据集上的检测性能
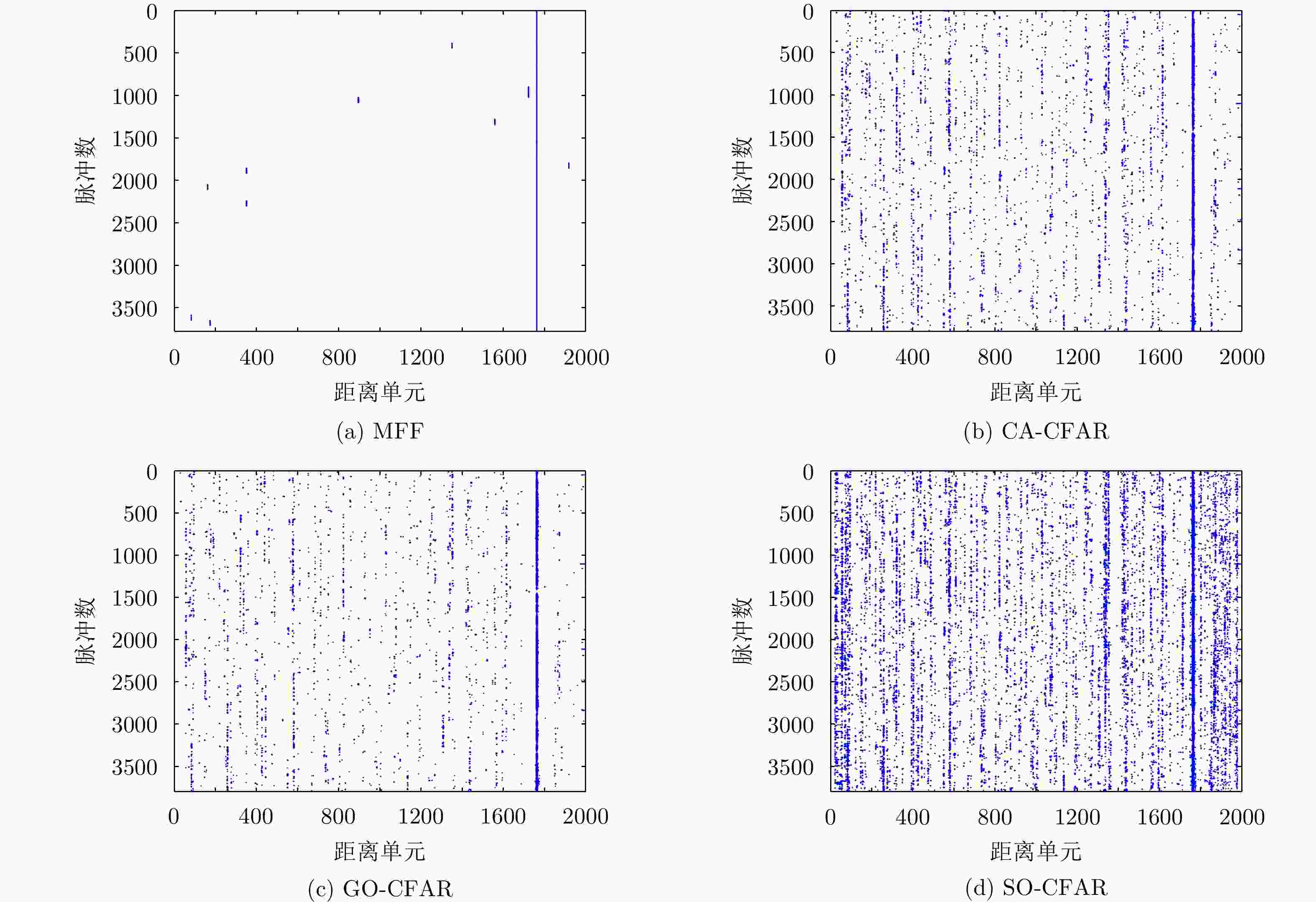
Table 9. Detection performance of various detectors in SDRDSP database
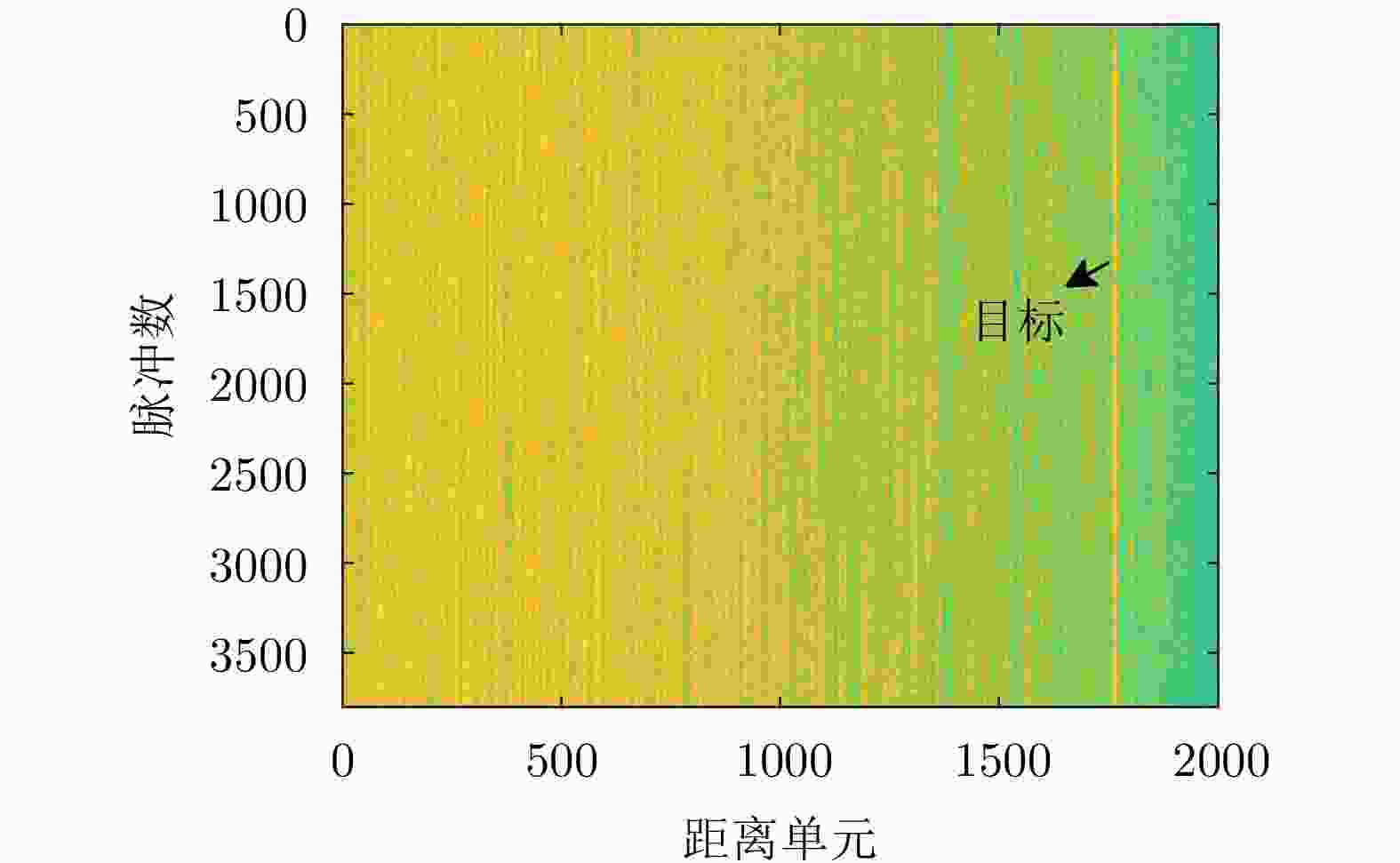
检测器名称 实际虚警率 检测概率 MFF 0.0004 0.9870 CA-CFAR 0.0083 0.9265 GO-CFAR 0.0052 0.8944 SO-CFAR 0.0225 0.9588 -
[1] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于深度学习的海上目标一维序列信号目标检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. One-dimensional sequence signal detection method for marine target based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004. [2] 赵文静, 刘畅, 刘文龙, 等. K分布海杂波背景下基于最大特征值的雷达信号检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092.ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Chang, LIU Wenlong, et al. Maximum eigenvalue based radar signal detection method for K distribution sea clutter environment[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092. [3] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友. 微多普勒理论在海面目标检测中的应用及展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20102.CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, and HE You. Applications and prospect of micro-motion theory in the detection of sea surface target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20102. [4] LO T, LEUNG H, LITVA J, et al. Fractal characterisation of sea-scattered signals and detection of sea-surface targets[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1993, 140(4): 243–250. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0034. [5] XU Xiaoke. Low observable targets detection by joint fractal properties of sea clutter: An experimental study of IPIX OHGR datasets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(4): 1425–1429. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2041144. [6] HU Jing, TUNG W W, and GAO Jianbo. Detection of low observable targets within sea clutter by structure function based multifractal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2006, 54(1): 136–143. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.861541. [7] 邵夫驰, 行鸿彦. 基于FRFT的多重分形海面小目标检测[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2020, 42(1): 69–74, 80.SHAO Fuchi and XING Hongyan. Small target detection based on multi-fractal characteristics of sea clutter FRFT spectrum[J]. Journal of Detection &Control, 2020, 42(1): 69–74, 80. [8] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657. [9] LI Yuzhou, XIE Pengcheng, TANG Zeshen, et al. SVM-based sea-surface small target detection: A false-alarm-rate-controllable approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1225–1229. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2894385. [10] 郭子薰, 水鹏朗, 白晓惠, 等. 海杂波中基于可控虚警K近邻的海面小目标检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 654–663. doi: 10.12000/JR20055.GUO Zixun, SHUI Penglang, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Sea-surface small target detection based on K-NN with controlled false alarm rate in sea clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 654–663. doi: 10.12000/JR20055. [11] YAN Kun, BAI Yu, WU H C, et al. Robust target detection within sea clutter based on graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7093–7103. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2911451. [12] 时艳玲, 姚婷婷, 郭亚星. 基于图连通密度的海面漂浮小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201028.SHI Yanling, YAO Tingting, and GUO Yaxing. Floating small target detection based on graph connected density in sea surface[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201028. [13] 许述文, 焦银萍, 白晓惠, 等. 基于频域多通道图特征感知的海面小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188.XU Shuwen, JIAO Yinping, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Small target detection based on frequency domain multichannel graph feature perception on sea surface[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188. [14] YAN Yujia, WU Guangxin, DONG Yang, et al. Floating small target detection in sea clutter using mean spectral radius[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4023405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3165163. [15] 左磊, 产秀秀, 禄晓飞, 等. 基于空域联合时频分解的海面微弱目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035.ZUO Lei, CHAN Xiuxiu, LU Xiaofei, et al. A weak target detection method in sea clutter based on joint space-time-frequency decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035. [16] 陈世超, 高鹤婷, 罗丰. 基于极化联合特征的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072.CHEN Shichao, GAO Heting, and LUO Feng. Target detection in sea clutter based on combined characteristics of polarization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072. [17] XU Shuwen, ZHENG Jibin, PU Jia, et al. Sea-surface floating small target detection based on polarization features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2852560. [18] 施赛楠, 杨静, 董泽远. 基于高维特征域随机森林的海面小目标检测[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(3): 63–69. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.03.011.SHI Sainan, YANG Jing, and DONG Zeyuan. Detection of small sea-surface target based on random forest in high-dimensional feature domain[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(3): 63–69. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.03.011. [19] CHEN Simin, FENG Chen, HUANG Yong, et al. Small target detection in X-band sea clutter using the visibility graph[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5115011. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3186283. [20] WANG Jin’gang and LI Songbin. Maritime radar target detection in sea clutter based on CNN with dual-perspective attention[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3500405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3230443. [21] WAN Hao, TIAN Xiaoqing, LIANG Jing, et al. Sequence-feature detection of small targets in sea clutter based on Bi-LSTM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4208811. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3198124. [22] WANG Yumiao, ZHAO Wenjing, WANG Xiang, et al. Nonhomogeneous sea clutter suppression using complex-valued U-Net model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4027705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3214633. [23] QU Qizhe, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A false alarm controllable detection method based on CNN for sea-surface small targets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4025705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3190865. [24] 李骁, 施赛楠, 董泽远, 等. 基于时频域深度网络的海面小目标特征检测[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2022, 20(2): 209–216, 230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.02.013.LI Xiao, SHI Sainan, DONG Zeyuan, et al. Feature detection of small sea-surface target via deep network in time-frequency domain[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2022, 20(2): 209–216, 230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.02.013. [25] CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. [26] IPIX Radar. The McMaster IPIX radar sea clutter database[EB/OL]. http://soma.ece.mcmaster.ca/ipix/, 2021. [27] TRABELSI C, BILANIUK O, ZHANG Ying, et al. Deep complex networks[C]. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1–19. [28] 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011.LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: