Active Deception Jamming Recognition Method in Multimodal Radar Based on Small Samples
-
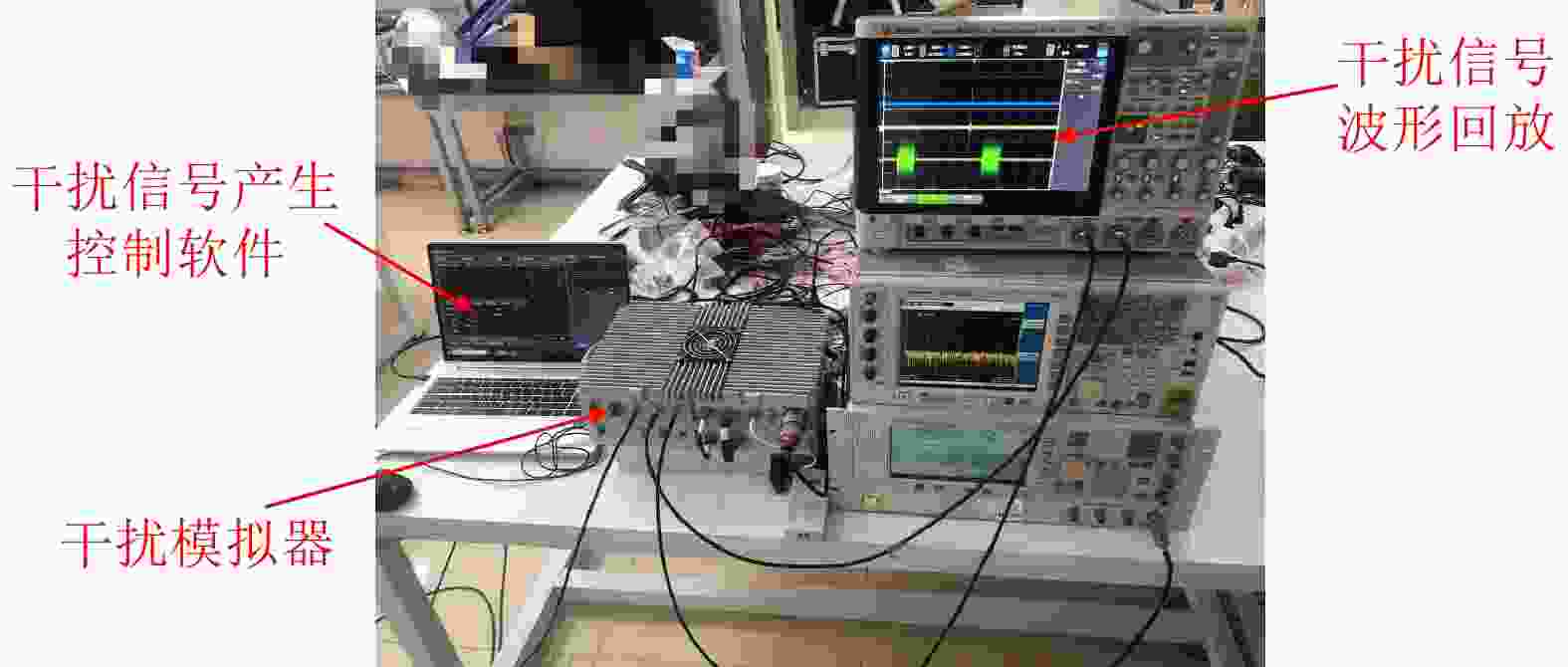
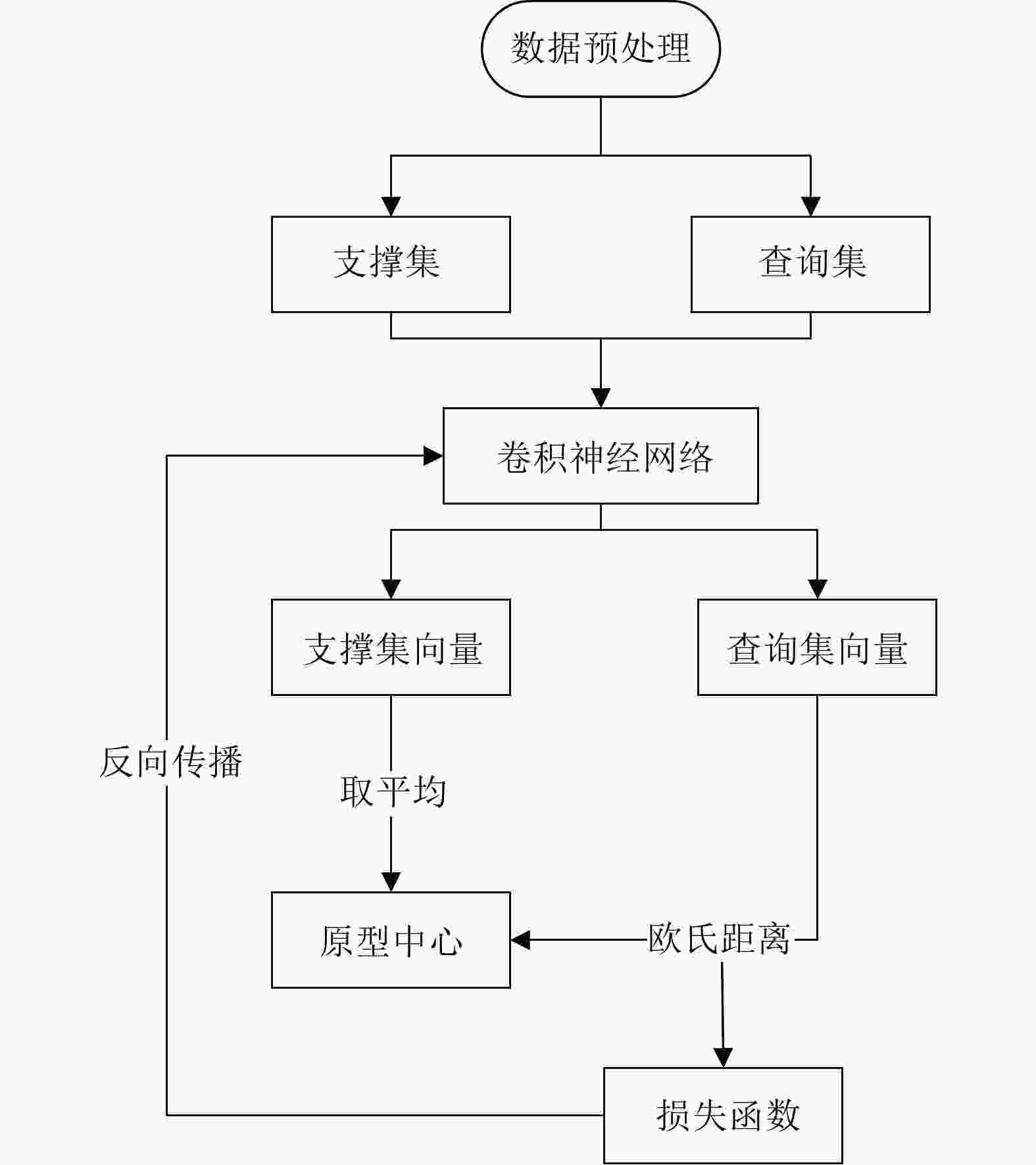
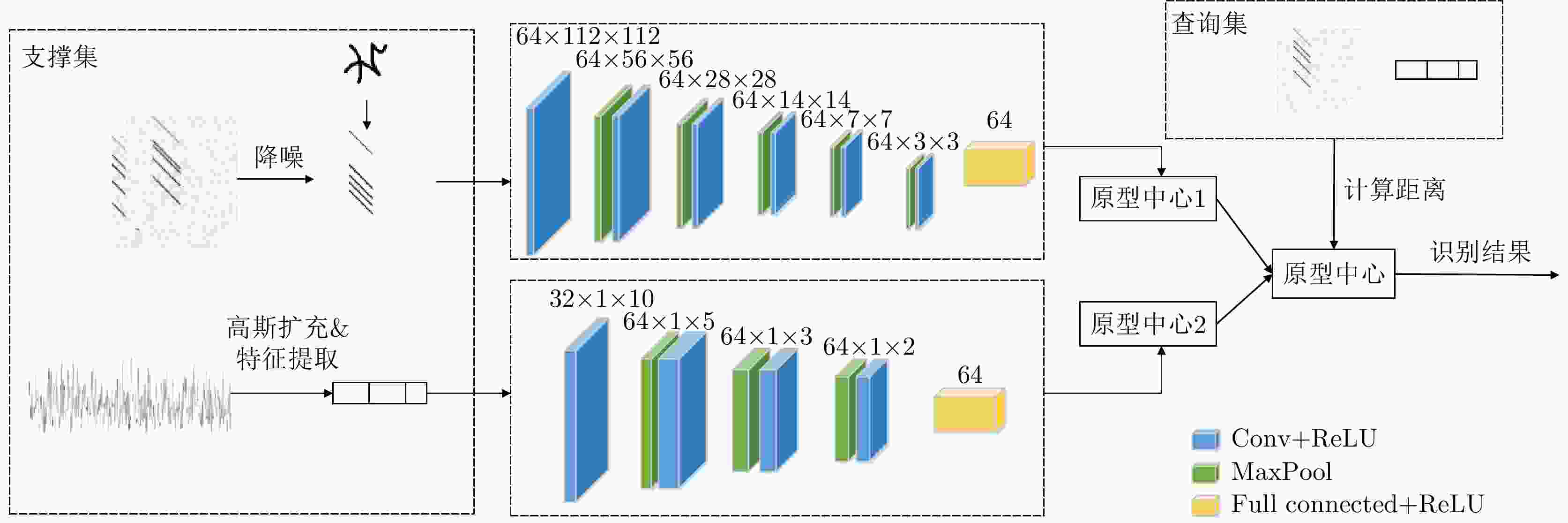
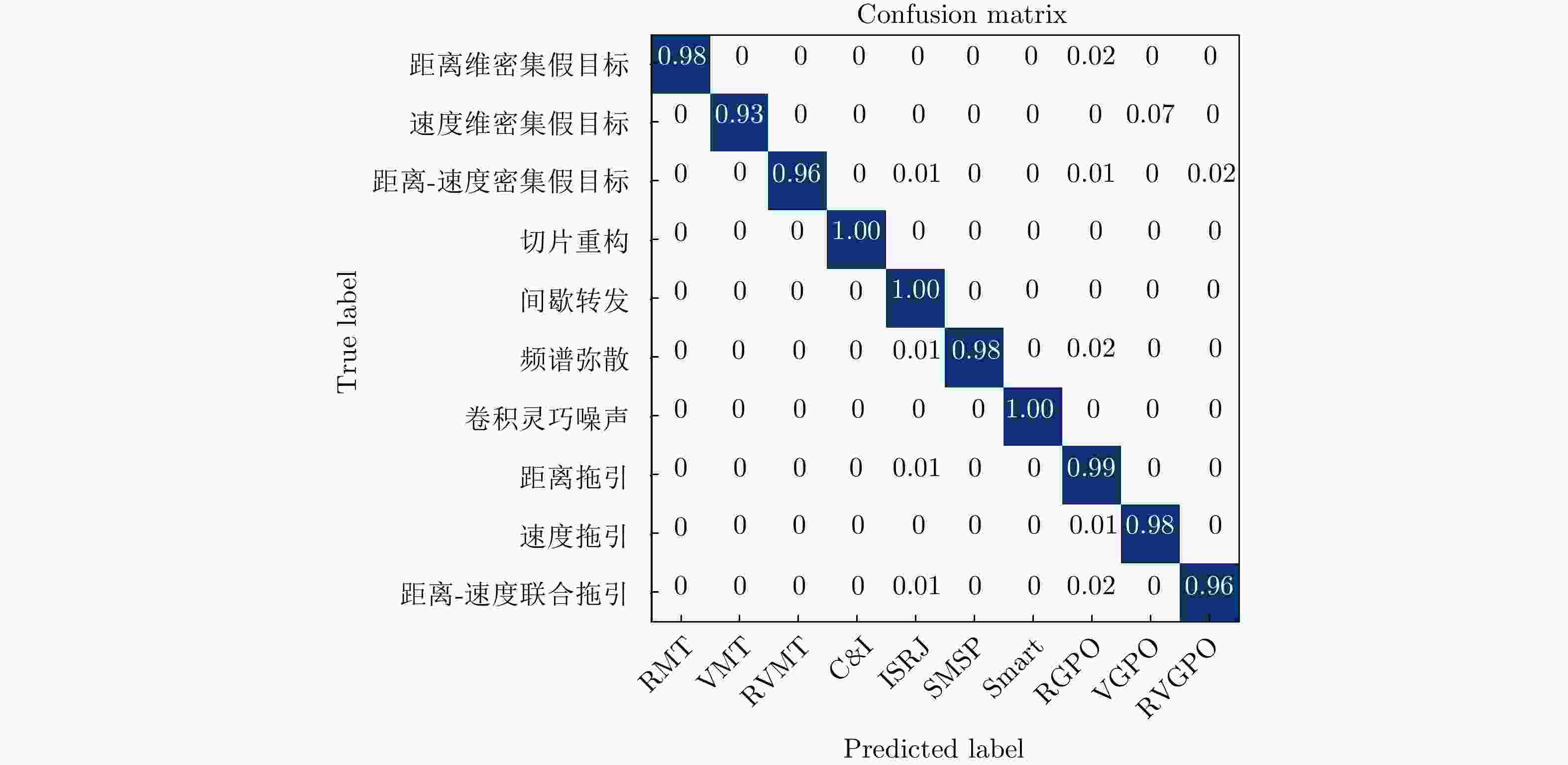
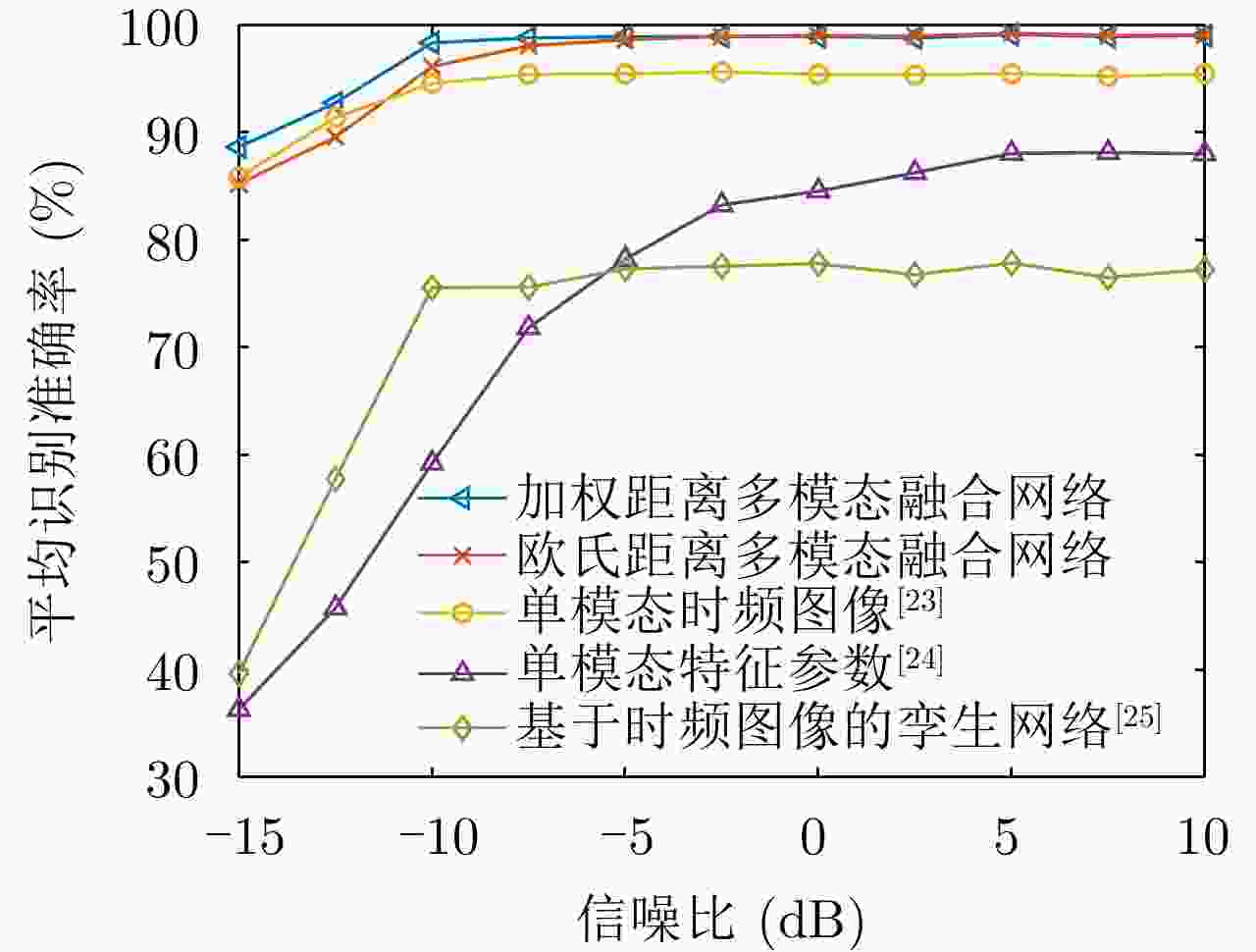
摘要: 干扰识别是雷达抗干扰的前提,但对于实际的雷达欺骗干扰识别,存在着样本数量不足的问题。针对此问题,该文提出一种面向小样本的多模态雷达有源欺骗干扰识别方法。该方法基于雷达信号提取的特征参数及时频图像两种模态信息,利用原型网络训练多模态特征,并借助图像降噪处理和加权欧氏距离提高低信噪比下的识别性能,实现小样本条件下的雷达欺骗干扰识别。仿真结果表明,该文所提方法在干信比为3 dB时,10种雷达欺骗干扰的平均识别准确率达到了97%以上。模拟器数据的测试结果表明所提方法具备良好的泛化能力。Abstract: Jamming recognition is a prerequisite for radar antijamming and actual radar deception jamming recognition; however, there is a problem of insufficient samples. To address this issue, we propose a multimodal radar active deception jamming recognition method based on small samples in this paper. This method is based on two modal information—feature parameters and time-frequency images extracted from radar signals—and utilizes prototype networks to train multimodal features. Furthermore, the model adopts the image denoising method and weighted Euclidean distance to improve the recognition performance at low signal-to-noise ratios. Thus, radar deception jamming recognition can be achieved under small sample conditions. Simulation results reveal that the proposed method achieves an average recognition accuracy of over 97% across 10 types of radar deception jamming when the jamming-to-signal ratio is 3 dB. Moreover, the test results from the simulator data verify the good generalization performance of the proposed method.
-
表 1 不同网络的复杂度参数表
Table 1. Table of complexity parameters for different networks
表 2 回波信号与欺骗干扰信号基本参数设置
Table 2. Basic parameter setting of echo signal and jamming signal
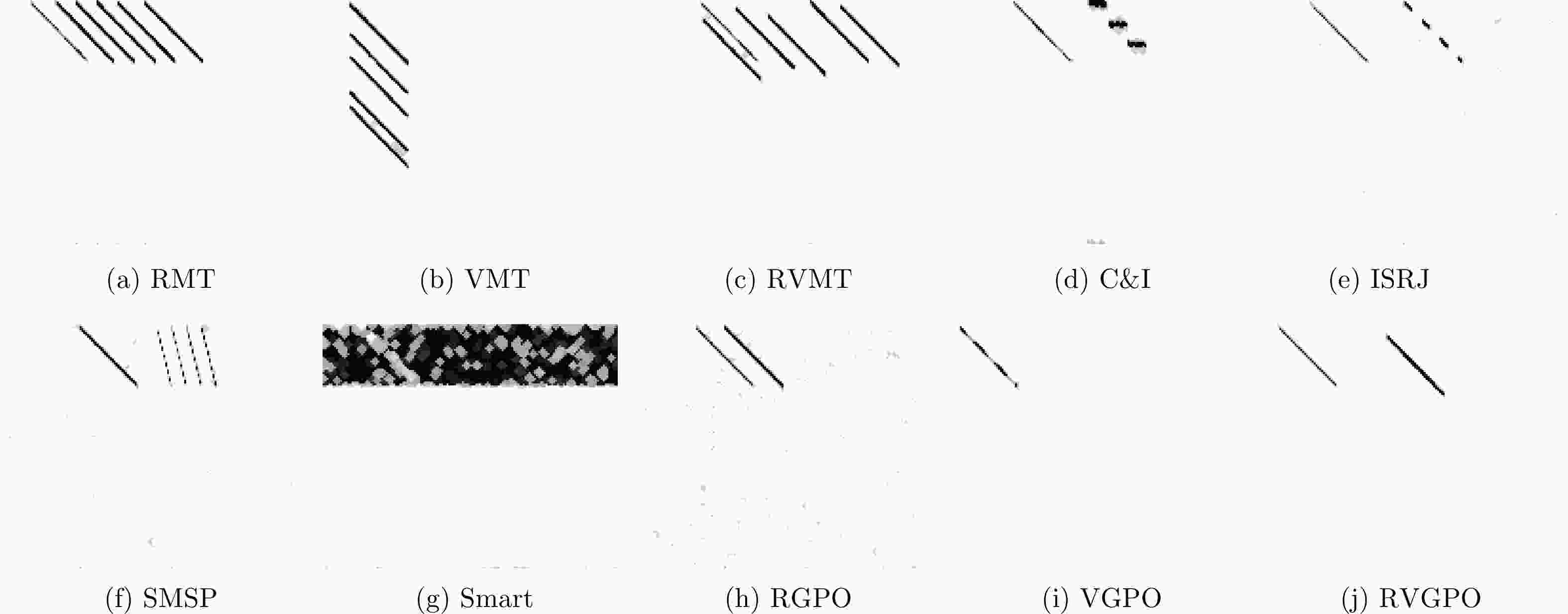
信号类型 参数 参数值 回波与干扰信号 载波 5.5 GHz 带宽 10 MHz 采样率 40 MHz 脉冲宽度 50 μs 脉冲重复频率 4000 Hz 信噪比 –10~10 dB 干信比 3 dB 密集假目标干扰 假目标数量 3~7 切片重构干扰 矩形脉冲串的个数 3~5 每一段填充的时隙数 3~5 间歇采样转发干扰 间歇采样脉冲宽度 7~9 μs 间歇采样周期 12~15 μs 频谱弥散干扰 采样倍数 3~5 卷积灵巧噪声干扰 噪声带宽倍数 0.3~0.7 距离拖引干扰 拖引速度 300~600 m/s 速度拖引干扰 拖引加速度 50~200 m/s2 距离速度联合拖引干扰 拖引速度 300~600 m/s 拖引加速度 50~200 m/s2 表 3 不同训练样本数下识别性能比较(%)
Table 3. Comparison of recognition performance under different numbers of training samples (%)
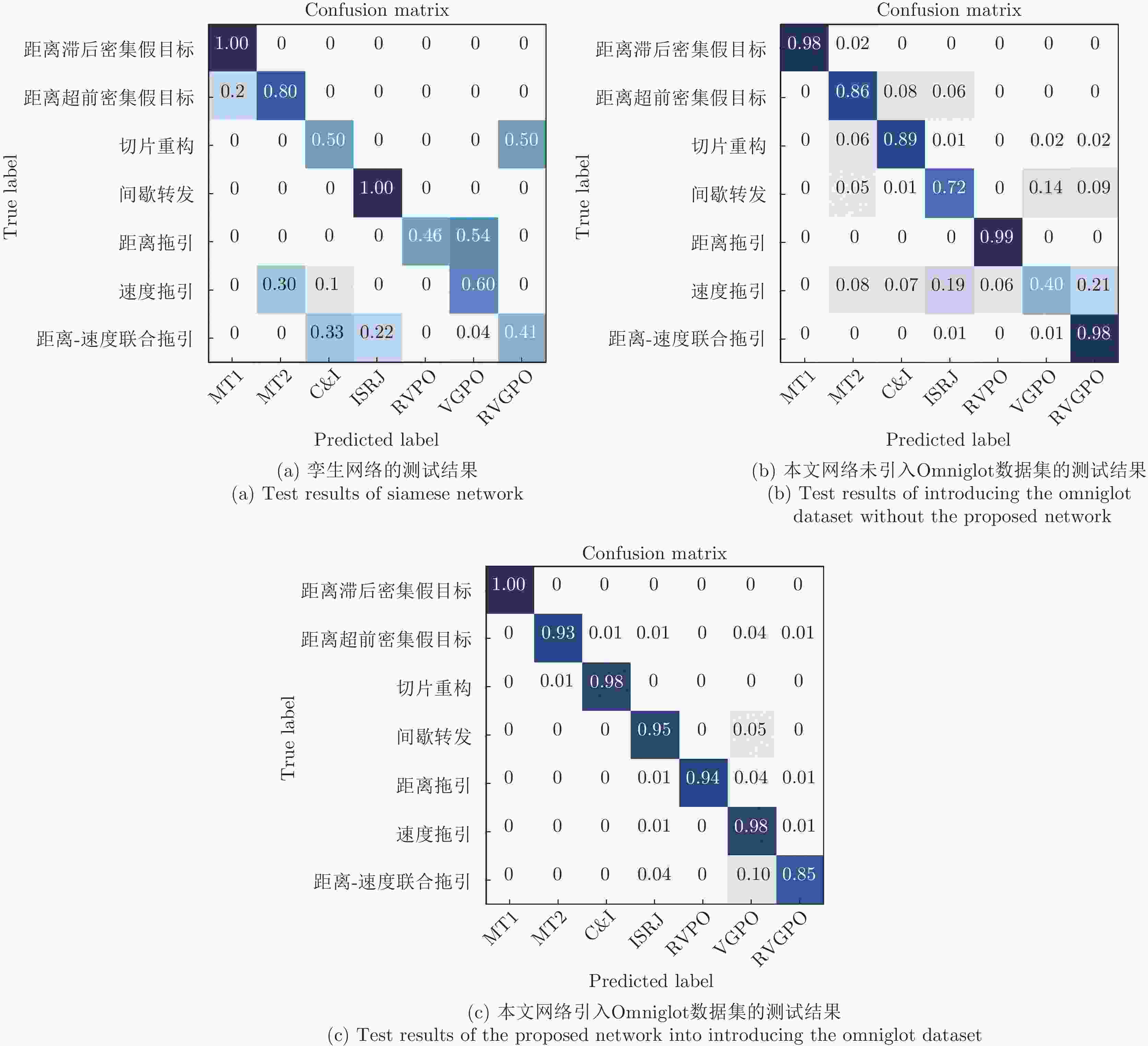
训练信噪比 2个训练样本 5个训练样本 10个训练样本 15个训练样本 20个训练样本 –10 dB 75.02 92.12 93.46 92.23 92.42 –5 dB 89.14 91.10 91.29 93.24 93.12 0 dB 86.11 92.18 92.29 94.89 93.27 5 dB 84.74 92.83 94.79 89.05 94.97 10 dB 83.17 87.73 87.85 88.41 90.67 随机信噪比 85.18 93.95 96.25 97.56 97.64 -
[1] KWAK C M. Application of DRFM in ECM for pulse type radar[C]. 2009 34th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, Busan, Korea (South), 2009: 1–2. [2] ZHANG Haoyu, YU Lei, CHEN Yushi, et al. Fast complex-valued CNN for radar jamming signal recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(15): 2867. doi: 10.3390/rs13152867 [3] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143 [4] MENDOZA A, SOTO A, and FLORES B C. Classification of radar jammer FM signals using a neural network[C]. SPIE 10188, Radar Sensor Technology XXI, Anaheim, USA, 2017: 101881G. [5] WU Zhilu, ZHAO Yanlong, YIN Zhengdong, et al. Jamming signals classification using convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Bilbao, Spain, 2017: 62–67. [6] ZHAO Qingyuan, LIU Yang, CAI Linjie, et al. Research on electronic jamming identification based on CNN[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–5. [7] LIU Qiang and ZHANG Wei. Deep learning and recognition of radar jamming based on CNN[C]. 2019 12th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 2019: 208–212. [8] HOWARD J and RUDER S. Universal language model fine-tuning for text classification[C]. The 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 2018: 328–339. [9] DING Kaize, WANG Jianling, LI Jundong, et al. Graph prototypical networks for few-shot learning on attributed networks[C]. The 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Online, 2020: 295–304. [10] CHOPRA S, HADSELL R, and LECUN Y. Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, USA, 2005: 539–546. [11] SHAO Guangqing, CHEN Yushi, and WEI Yinsheng. Convolutional neural network-based radar jamming signal classification with sufficient and limited samples[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 80588–80598. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990629 [12] 陈泽伟, 严远鹏. 基于改进DCGAN的毫米波雷达相互干扰时频图像生成研究——以生成样本对CNN干扰抑制模型性能影响为例[J]. 现代信息科技, 2022, 6(13): 55–61. doi: 10.19850/j.cnki.2096-4706.2022.013.014CHEN Zewei and YAN Yuanpeng. Research on generation of MMW radar mutual interference time-frequency image based on improved DCGAN—a case of performance effect of the generated samples on the CNN interference suppression model[J]. Modern Information Technology, 2022, 6(13): 55–61. doi: 10.19850/j.cnki.2096-4706.2022.013.014 [13] KOCH G, ZEMEL R, and SALAKHUTDINOV R. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 1–8. [14] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R S. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. [15] LU Yunlong and LI Siyu. CFAR detection of DRFM deception jamming based on singular spectrum analysis[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xiamen, China, 2017: 1–6. [16] 定少浒, 汤建龙. 基于SSA的DRFM速度欺骗干扰识别[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(1): 44–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.01.008DING Shaohu and TANG Jianlong. DRFM velocity deception jamming recognition based on singular spectrum analysis[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(1): 44–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.01.008 [17] LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, FENG Wei, et al. Radar deception jamming recognition based on weighted ensemble CNN with transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5107511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3129645 [18] JAMIL N, SEMBOK T M T, and BAKAR Z. A. Noise removal and enhancement of binary images using morphological operations[C]. 2008 International Symposium on Information Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2008: 1–6. [19] XI Bobo, LI Jiaojiao, LI Yunsong, et al. Deep prototypical networks with hybrid residual attention for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 3683–3700. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3004973 [20] 利强, 张伟, 金秋园, 等. 基于知识原型网络的小样本多功能雷达工作模式识别[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(6): 1344–1350. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210932LI Qiang, ZHANG Wei, JIN Qiuyuan, et al. Multi-function radar working mode recognition with few samples based on knowledge embedded prototype network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(6): 1344–1350. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210932 [21] GAO Meng, LI Hongtao, JIAO Bixuan, et al. Simulation research on classification and identification of typical active jamming against LFM radar[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 11384 Eleventh International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, Nanjing, China, 2019: 113840T. [22] LAKE B M, SALAKHUTDINOV R, and TENENBAUM J B. The Omniglot challenge: A 3-year progress report[J]. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 2019, 29: 97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2019.04.007 [23] WANG Jingyi, DONG Wenhao, and SONG Zhiyong. Radar active jamming recognition based on time-frequency image classification[C]. 2021 5th International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, Xiamen, China, 2021: 449–454. [24] TIAN Xinyi, CHEN Baixiao, and ZHANG Zhaoming. Multiresolution jamming recognition with few-shot learning[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar, Haikou, China, 2021: 2267–2271. [25] 梁先明. 一种优化孪生网络的小样本辐射源个体识别方法[J]. 电讯技术, 2022, 62(6): 695–701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.06.001LIANG Xianming. An emitter individual identification method for small samples based on optimized siamese networks[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2022, 62(6): 695–701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.06.001 [26] GU Jiuxiang, WANG Zhenhua, KUEN J, et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 77: 354–377. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.013 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: