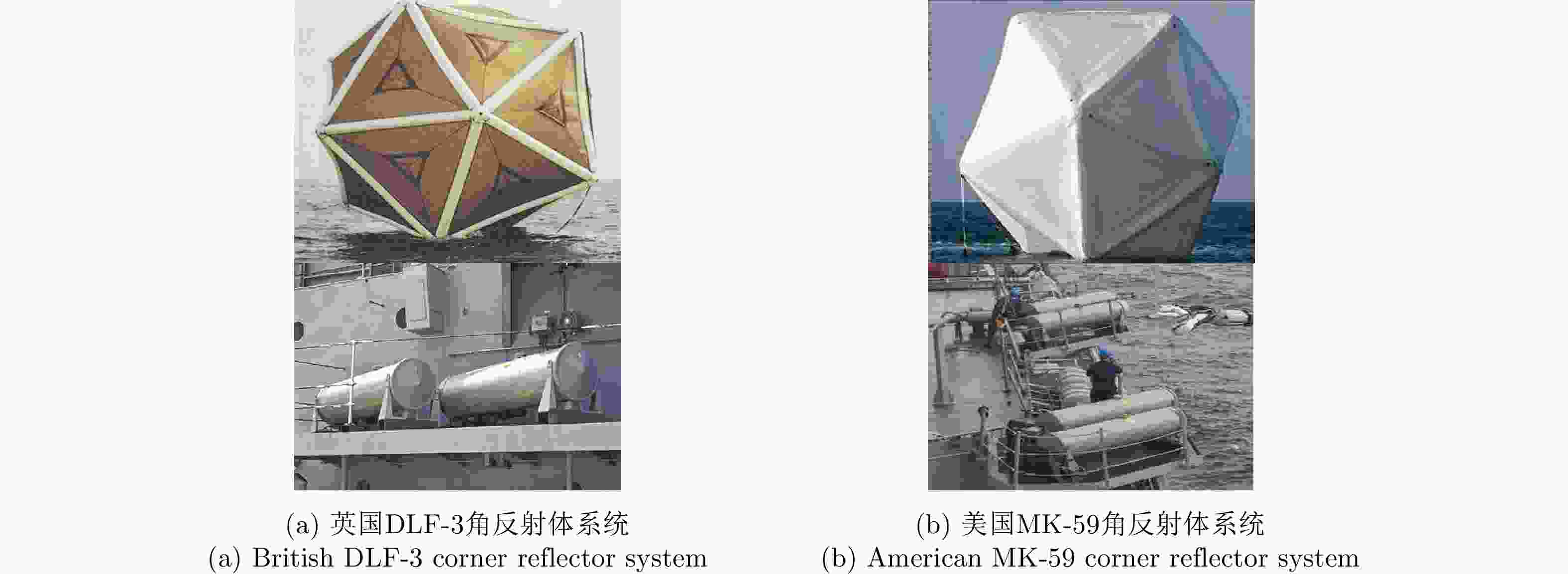
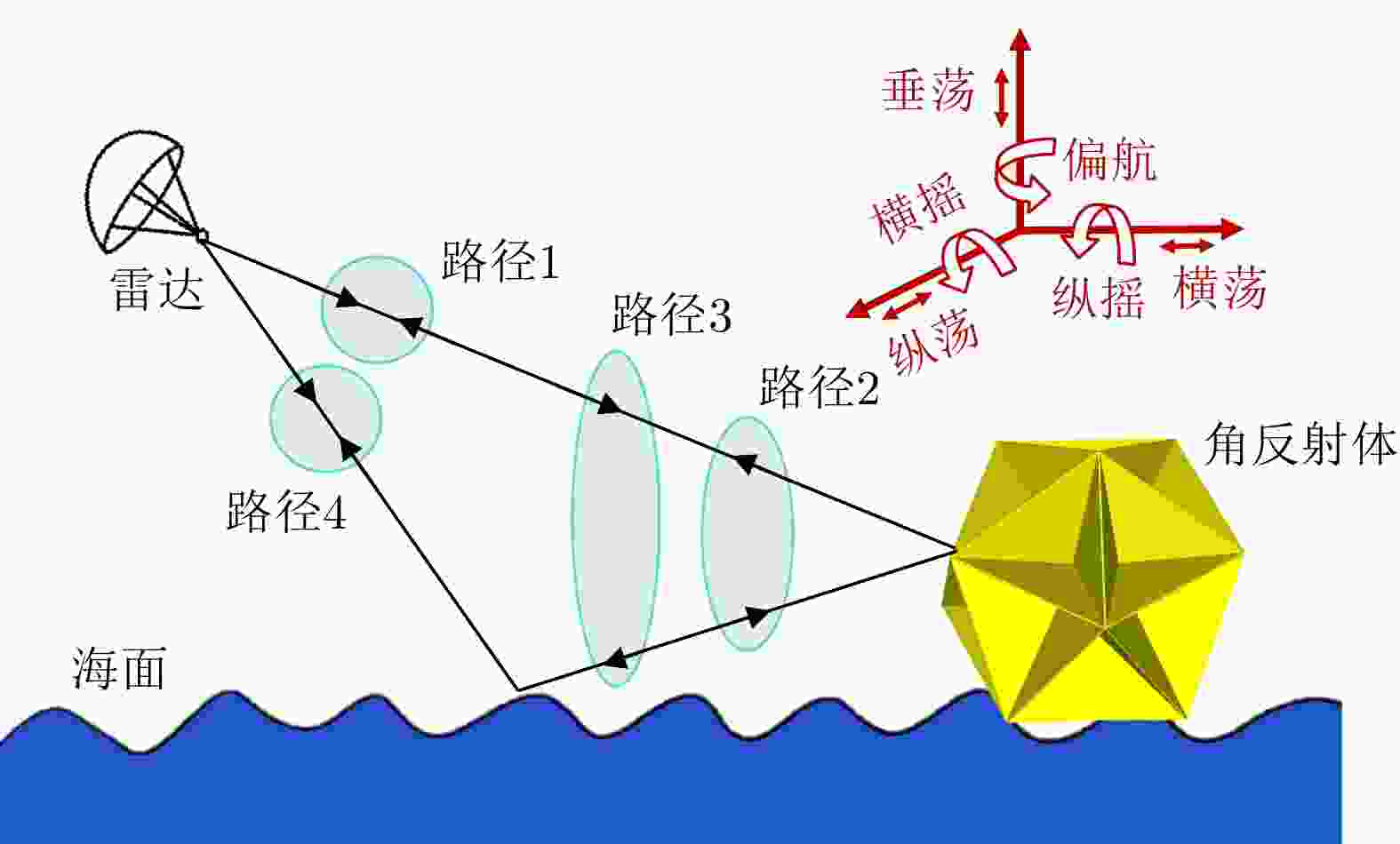
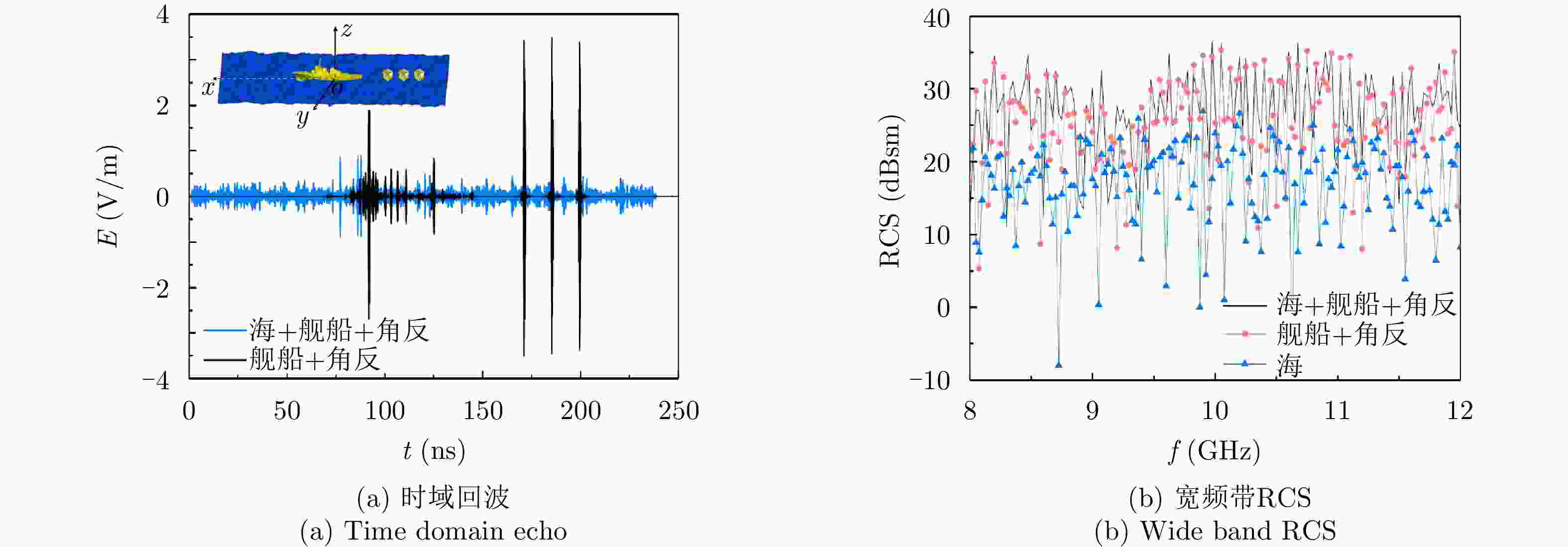
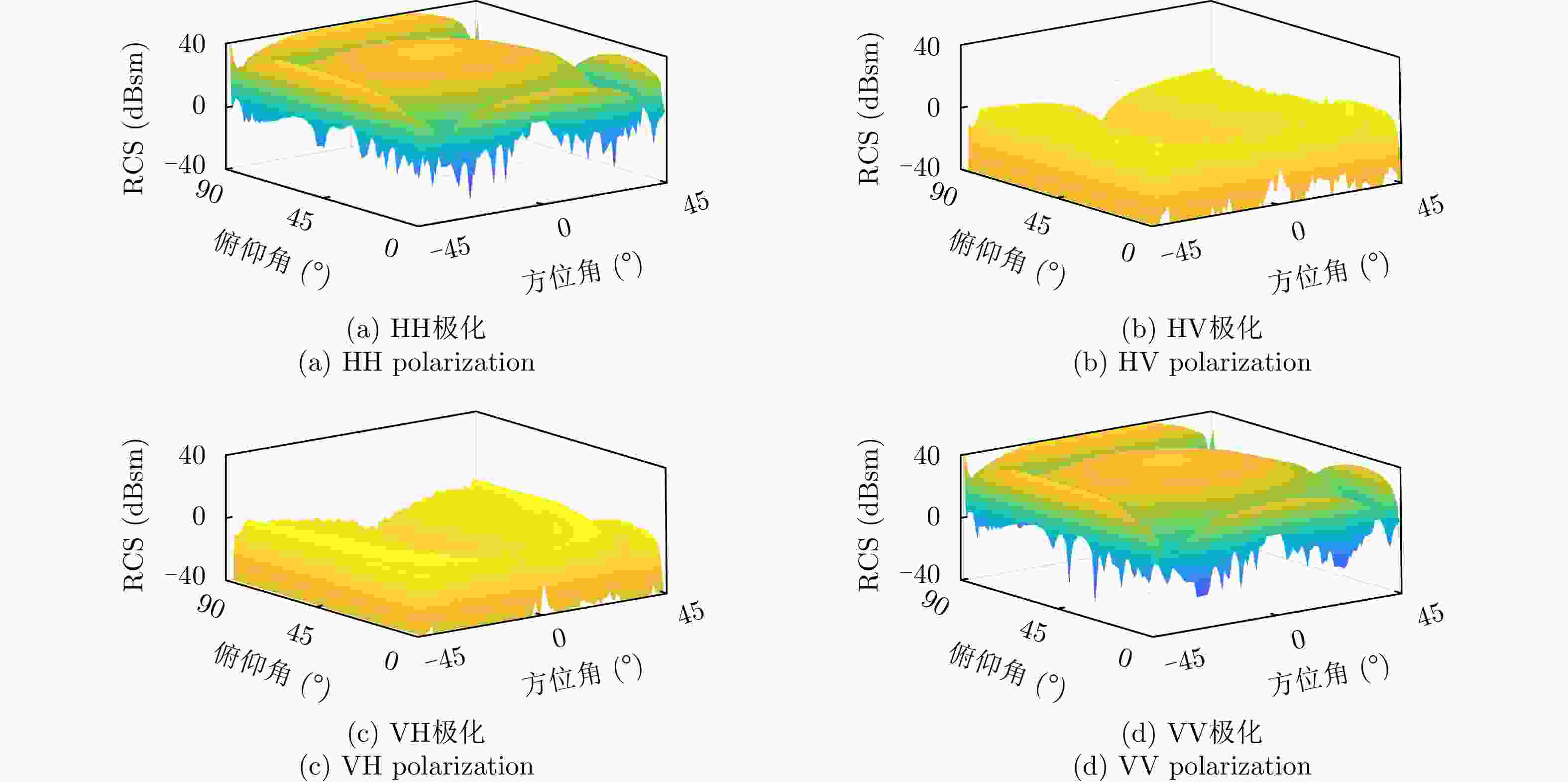
Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics and Radar Identification of Sea Corner Reflectors: Advances and Prospects
-
摘要: 雷达导引头是精确制导武器末制导的核心设备,具有作用距离远、不受天气影响等重要优点,在保证导弹打击精度方面发挥着重要作用。海面角反射体具有与舰船目标散射逼真度高、作战效费比高等优良特性,已成为雷达导引头的主要诱骗干扰手段之一,严重影响雷达目标探测性能。因此,如何准确高效地实现海面角反射体雷达鉴别是雷达导引头精确打击的难点和重点之一。角反射体电磁散射特性研究是提升角反射体雷达鉴别能力的基础。该文首先介绍了海面角反射体装备及战术运用;针对海面角反射体的电磁散射特性研究进展进行了总结;重点归纳梳理了海面角反射体雷达鉴别技术的两类主流方法,总结其特点及存在的问题;最后对海面角反射体雷达鉴别研究的未来发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: The radar seeker is the core equipment for the terminal guidance of precision-guided weapons. It has significant benefits, such as long range and weather resistance, and plays an important role in ensuring the accuracy of missile strikes. Sea corner reflectors have excellent characteristics, such as high scattering similarity of ship targets and combat effectiveness ratio, and they have emerged as one of the primary sources of interference for radar seekers with major consequences for radar detection performance. Therefore, a difficult and critical issue in ensuring the accuracy of radar seekers is accurately and efficiently identifying sea corner reflectors. Research on the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of corner reflectors is the foundation for improving radar identification capability. This paper first introduces sea corner reflector equipment and its tactical application. The research progress in elucidating the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of sea corner reflectors is then summarized. In addition, the research achievements in radar technology for identifying sea corner reflectors are summarized, and the characteristics of existing problems pertaining to various methods are presented. Simultaneously, their future development trends of the technology are discussed.
-
表 1 用于角反射体雷达鉴别的HRRP特征归纳表
Table 1. Summary of HRRP features for corner reflector radar identification
特征 特征公式 变量含义 径向尺寸 $ {\text{RL}} = \Delta d \cdot ({n_2} - {n_1}) $ $ \Delta d $为距离分辨率,$ {n_1} $和$ {n_2} $分别为目标第1个和
最后一个距离单元序号散射重心 ${\text{SM} } = \left(\left(\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_1} }^{ {n_2} } {n \cdot x(n)} \Bigr/ \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_1} }^{ {n_2} } {x(n)} \right) - {n_1}\right) \Bigr/ ({n_2} - {n_1})$ $ x(n) $为目标距离单元幅值 散射中心数目 $ {\text{NP}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{{n_1}}^{{n_2}} {u(n)} $ $ u(n) $为散射中心标记 最强散射中心间距离 $ {\text{DPK}} = \Delta d \cdot \left| {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right| $ $ {m_1} $和$ {m_2} $为最强的两个散射中心对应的序号 最强散射中心距目标
最前端的距离$ {\text{DEP}} = \Delta d \cdot ({m_1} - {n_1}) $ / 散射中心幅值分布熵 ${\text{EA} } = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{\rm{NP}}} { {p_{ {m_i} } } \cdot \ln {p_{ {m_i} } } }$ $ {p_{{m_i}}} $为序号$ {m_i} $的强散射中心幅值 散射中心位置分布熵 ${\text{EP} } = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{ {\rm{NP} } } { { m'_i} \cdot \ln { m'_i} }$ $ {m'_i} = {{\left( {{m_i} - {n_1}} \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\left( {{m_i} - {n_1}} \right)} {\left( {{n_2} - {n_1}} \right)}}} \right. } {\left( {{n_2} - {n_1}} \right)}} $ 散射对称性值 $ {{{\text{SYM}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_1}}^{{n_0}} {{{\left| {x(n)} \right|}^2}} } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{SYM}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_1}}^{{n_0}} {{{\left| {x(n)} \right|}^2}} } {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_0}}^{{n_2}} {{{\left| {x(n)} \right|}^2}} }}} \right. } {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = {n_0}}^{{n_2}} {{{\left| {x(n)} \right|}^2}} }} $ $ {n_0} = {{({n_1} + {n_2})} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{({n_1} + {n_2})} 2}} \right. } 2} $ 表 2 用于角反射体雷达鉴别的极化特征归纳表
Table 2. Summary of polarimetric features for corner reflector radar identification
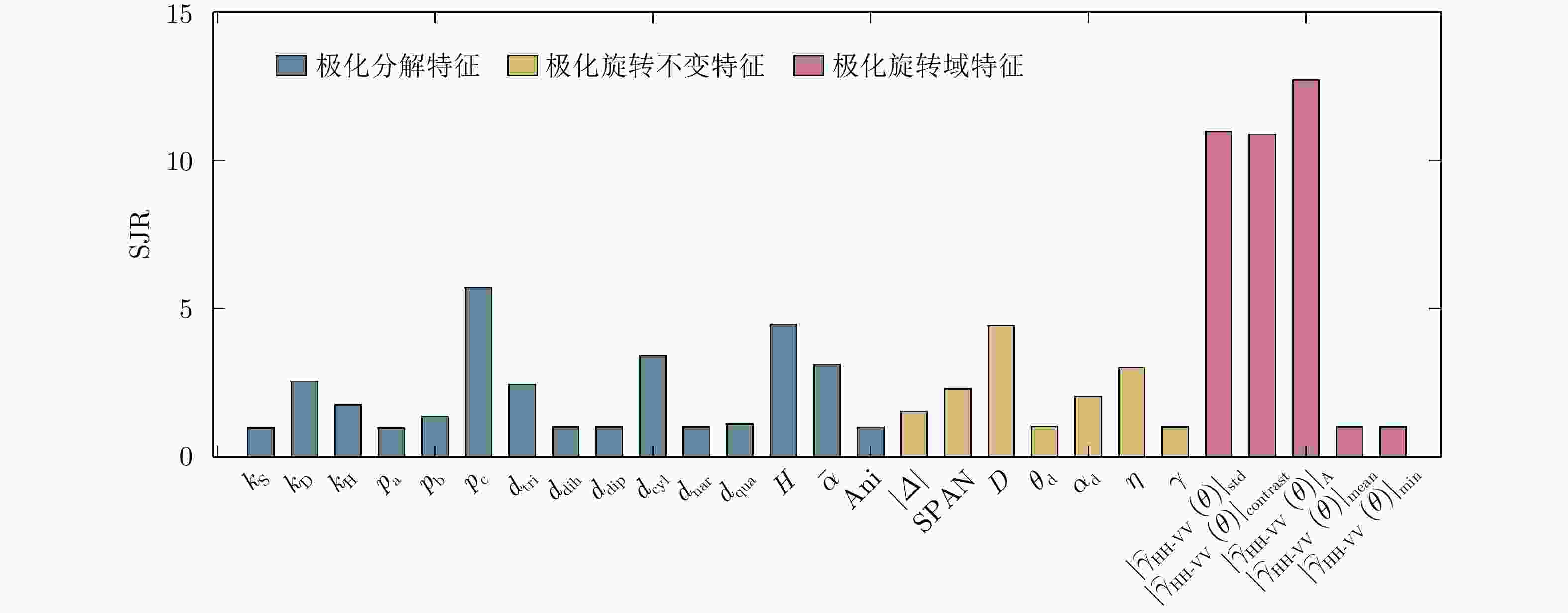
特征 特征公式 变量含义 Krogager分解特征 $k_{\text{S}}^{} = \left| {{S_{{\text{RL}}}}} \right|$, $ k_{\text{D}}^{} = \min \left( {\left| {{S_{{\text{LL}}}}} \right|,\left| {{S_{{\text{RR}}}}} \right|} \right) $, $ k_{\text{H}}^{} = \left| {\left| {{S_{{\text{RR}}}}} \right| - \left| {{S_{{\text{LL}}}}} \right|} \right| $ $ {S_{{\text{LL}}}} $, $ {S_{{\text{RR}}}} $和${S_{{\text{RL}}}}$为圆极化复散射系数 Pauli分解特征 $ {p_{\rm{a}}} = \dfrac{{{S_{{\text{HH}}}} + {S_{{\text{VV}}}}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} $, $ {p_{\rm{b}}} = \dfrac{{{S_{{\text{HH}}}} - {S_{{\text{VV}}}}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} $, $ {p_{\rm{c}}} = \dfrac{{{S_{{\text{HV}}}} + {S_{{\text{VH}}}}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} $ $ {S_{{\text{HH}}}} $, $ {S_{{\text{VV}}}} $, $ {S_{{\text{HV}}}} $和$ {S_{{\text{VH}}}} $为线极化复散射系数 Cameron分解特征 $d({z_1},{z_2}) = \arccos \left( {\dfrac{ {\max \left\{ {\left| {1 + {z_1}z_2^*} \right|,\left| { {z_1} + z_2^*} \right|} \right\} } }{ {\sqrt {1 + { {\left| { {z_1} } \right|}^2} } \cdot\sqrt {1 + { {\left| { {z_2} } \right|}^2} } } } } \right)$ $ {z_1} $和$ {z_2} $分别为待分类散射体和典型散射体的
散射类型参数,$* $表示共轭Cloude-Pottier分解
特征$ H = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^3 {{P_i}} {\log _3}{P_i} ,\; \bar \alpha = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^3 {{P_i}{\alpha _i}}, $ ${\rm{Ani} } = \dfrac { {\lambda _2} - {\lambda _3} } { { {\lambda _2} + {\lambda _3} } }$ $ {P_i} $为伪概率密度,$ {\alpha _i} $为特征矢量的系数因子,
$ {\lambda _i} $为特征值行列式模 $\left| \varDelta \right| = \left| { {S_{ {\text{HH} } } }{S_{ {\text{VV} } } } - {S_{ {\text{HV} } } }{S_{ {\text{VH} } } } } \right|$ / 极化总功率 ${\text{SPAN}} = {\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}}} \right|^2} + {\left| {{S_{{\text{HV}}}}} \right|^2} + {\left| {{S_{{\text{VH}}}}} \right|^2} + {\left| {{S_{{\text{VV}}}}} \right|^2}$ / 去极化因子 $ D = 1 - \dfrac{{{{\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}} + {S_{{\text{VV}}}}} \right|}^2}}}{{2\left( {{{\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{HV}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VV}}}}} \right|}^2}} \right)}} $ / 本征极化方位角 ${\theta _{\rm{d}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\arctan \dfrac{ {2{{\rm{Re}}} \left( {\tilde S_1^*{ {\tilde S}_{12} } } \right)} }{ { {{\rm{Re}}} \left( {\tilde S_1^*{ {\tilde S}_2} } \right)} }$ $ {\tilde S_1} = {S_{{\text{HH}}}} + {S_{{\text{VV}}}} $, $ {\tilde S_2} = {S_{{\text{HH}}}} - {S_{{\text{VV}}}} $, $ {\tilde S_{12}} = {S_{{\text{HV}}}} $ 本征极化椭圆度 ${\alpha _{\rm{d}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\arctan \dfrac{ {{\rm{j}}2\tilde S_{12}^\prime } }{ { {S_{ {\text{HH} } } } + {S_{ {\text{VV} } } } } }$ $\tilde S_{12}^\prime = {\tilde S_{12} }\cos \left( {2{\theta _{\rm{d}}} } \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}{\tilde S_2}\sin \left( {2{\theta _{\rm{d}}} } \right)$ 目标纵横比 $\eta = \dfrac{{{{\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{HV}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VV}}}}} \right|}^2}}}{{\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}}{S_{{\text{VV}}}} - {S_{{\text{HV}}}}{S_{{\text{VH}}}}} \right|}}$ / 目标极化形状因子 $ \gamma = \dfrac{{\left| {{S_{{\text{VV}}}}S_{{\text{HH}}}^* - {S_{{\text{VH}}}}S_{{\text{HV}}}^*} \right|}}{{{{\left| {{S_{{\text{HH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{HV}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VH}}}}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{S_{{\text{VV}}}}} \right|}^2}}} $ / 极化相关度 ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{mean} } } } = {\text{mean} }\left\{ {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|} \right\}$ $\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|$为极化相关方向图,$ {\text{mean}}\left\{ \cdot \right\} $为求均值 极化相关特征最小值 ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{min} } } } = {\text{min} }\left\{ {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|} \right\}$ $ {\text{min}}\left\{ \cdot \right\} $为求最小值 极化相关对比度 ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{contrast} } } } = {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{max} } } } - {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{min} } } }$ ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{max} } } }$为极化相关特征最大值 极化相关特征反熵 ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{\text{A} } } = \dfrac{ { { {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|}_{ {\text{max} } } } - { {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|}_{ {\text{min} } } } } }{ { { {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|}_{ {\text{max} } } } + { {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|}_{ {\text{min} } } } } }$ / 极化相关起伏度 ${\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\text{std} } } } = {\text{std} }\left\{ {\left| { { {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$} }{\gamma } }_{ {\text{HH} } {\text{-}} {\text{VV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|} \right\}$ $ {\text{std}}\left\{ \cdot \right\} $为求标准差 表 3 角反射体雷达鉴别方法适用场景和优缺点总结
Table 3. Applicable scenarios and pros & cons summary of corner reflector radar identification
关键
技术鉴别
分类具体鉴别方法 适用场景 优点 缺点 基于特征提取的角反射体鉴别方法 HRRP
特征连续统计跟踪算法 质心干扰[84] 简单易实现,计算效率高,具有实时性 对目标信息利用不充分 基于平移不变特征的
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[85] 融合空间邻域信息,提高目标鉴别能力 敏感于雷达观测角度且不适用于角反射体阵列 基于稀疏表达的
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[86] 模型简单,受噪声影响小 对目标姿态的适应性有待研究 运动
特征基于多普勒特征的
角反鉴别质心干扰[84]/
冲淡干扰[84,87]增强了对运动目标鉴别能力 不适用于拖曳式角反射体 基于微多普勒特征的
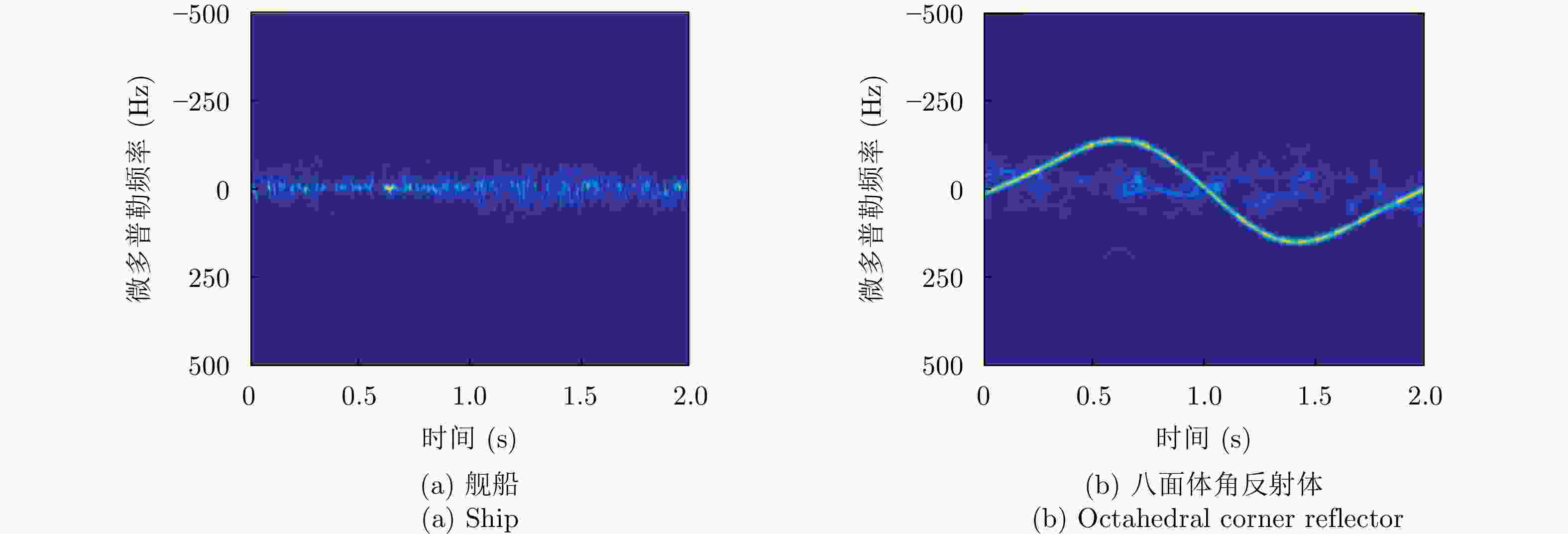
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[37,91] 海面目标和角反射体由于结构和尺寸不同,在微动特征上存在较大差异 对海面强杂波与目标运动变化敏感,对目标微多普勒的观测本身需要的条件苛刻 极化
特征基于极化目标分解的
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[99,100,132] 具有较强的物理可解释性 存在散射机理解译失真 基于极化旋转不变量
的角反鉴别冲淡干扰[105,106] 可以避免雷达观测角度的依赖性 部分极化不变量敏感于目标尺寸 基于极化旋转域的
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[14,82,119–121] 充分利用了雷达目标的散射多样性中蕴含的丰富的极化散射信息 对海况状态的适应性需要提高 基于极化域变焦的
角反鉴别质心干扰[123]/
冲淡干扰[122]有效提升雷达信息获取能力 理论分析和方法实现复杂 基于深度学习的角反射体鉴别方法 / / 冲淡干扰[10,85,106,127–132] 能够自动提取结构化特征,鉴别率高 需要大量标记样本且缺乏可解释性 其他
方法/ 基于波形选择的
角反鉴别冲淡干扰[133] 可以自适应优化不同场景下的鉴别性能 复杂结构和成本限制工程应用 基于复合制导的
角反鉴别质心干扰[136]/冲淡干扰[136] -
[1] 高烽. 雷达导引头概论[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2010.GAO Feng. Introduction to Radar Seeker[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2010. [2] 黄培康, 殷红成, 许小剑. 雷达目标特性[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.HUANG Peikang, YIN Hongcheng, and XU Xiaojian. Radar Target Characteristics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005. [3] 陈静. 雷达无源干扰原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009.CHEN Jing. Principles of Radar Passive Jamming[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2009. [4] 魏毅寅, 杨文华. 海战场典型干扰对抗场景及反舰导弹应对策略研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2020(5): 1–8. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2020.1.538WEI Yiyin and YANG Wenhua. Study on typical jamming scenes in naval battle field and countermeasures of anti-ship missile[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2020(5): 1–8. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2020.1.538 [5] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039WANG Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039 [6] 宫尚玉, 白梅, 王月悦. 美国海军软杀伤装备与技术发展研究[J]. 飞航导弹, 2021(10): 74–80. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20200341GONG Shangyu, BAI Mei, and WANG Yueyue. Research on the development of soft kill equipment and technology in US Navy[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2021(10): 74–80. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20200341 [7] 许海龙, 王隽, 张金华. 国外新型舰载诱饵发射系统发展研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2013, 36(2): 28–32. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2013.02.007XU Hailong, WANG Jun, and ZHANG Jinhua. Research into the development of foreign new shipborne decoy launching systems[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2013, 36(2): 28–32. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2013.02.007 [8] 刘丽, 武坦然, 崔静. 外军舰载软杀伤武器系统发展概述[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2018, 34(1): 60–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2018.01.014LIU Li, WU Tanran, and CUI Jing. A glimpse into the development of the ship-borne soft-killing weapon systems of foreign militaries[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2018, 34(1): 60–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2018.01.014 [9] 陈静. 雷达箔条干扰原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007.CHEN Jing. Principles of Radar Chaff Jamming[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2007. [10] 胡生亮, 范学满, 刘忠, 等. 基于集成学习的角反射体目标雷达识别理论与方法[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2019.HU Shengliang, FAN Xueman, LIU Zhong, et al. Radar Recognition Theory and Method of Corner Reflector Target Based on Ensemble Learning[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2019. [11] 张志远, 张介秋, 屈绍波, 等. 雷达角反射器的研究进展及展望[J]. 飞航导弹, 2014, 44(4): 64–70. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2014.04.021ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHANG Jieqiu, QU Shaobo, et al. Research progress and prospect of radar corner reflector[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2014, 44(4): 64–70. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2014.04.021 [12] 张林, 胡生亮, 胡海. 舰载充气式角反射体装备现状与战术运用研究现状[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2018, 39(6): 48–51. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.06.010ZHANG Lin, HU Shengliang, and HU Hai. Research on current equipment situation and tactical application of ship-born inflatable corner reflector[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2018, 39(6): 48–51. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.06.010 [13] 胡海, 张林, 张小东. 舰载充气式角反射体反导装备发展及运用[J]. 国防科技, 2018, 39(2): 74–77. doi: 10.13943/j.issn1671-4547.2018.02.12HU Hai, ZHANG Lin, and ZHANG Xiaodong. A study on equipment developments and operational using of ship born gas-filled anti-missile multi-corner reflector[J]. National Defense Science Technology, 2018, 39(2): 74–77. doi: 10.13943/j.issn1671-4547.2018.02.12 [14] 李郝亮. 极化旋转域雷达目标辨识与干扰鉴别[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2022.LI Haoliang. Radar target recognition and jamming identification in polarimetric rotation domain[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2022. [15] 梅益超. “橡皮鸭”——一种被动式反导弹充气诱饵[J]. 国外导弹与航天, 1986(4): 41–42.MEI Yichao. “Rubber Duck”—A passive anti-missile inflatable decoy[J]. Foreign Missiles and Aerospace, 1986(4): 41–42. [16] 汤广富, 李华, 甘荣兵, 等. 海战场环境下角反射器干扰分析[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2015, 30(5): 39–45, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2015.05.008TANG Guangfu, LI Hua, GAN Rongbing, et al. Analysis of corner reflector under naval battlefield[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2015, 30(5): 39–45, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2015.05.008 [17] 骆颖. 基于TDSBR的海上目标与角反射器复合时域电磁散射及干扰分析研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021.LUO Ying. TDSBR-based time-domain electromagnetic scattering and jamming analysis of marine targets and corner reflectors[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. [18] 赵宗顺, 胡生亮, 许江湖. 充气式雷达诱饵质心干扰样式研究[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2015(11): 144–146.ZHAO Zongshun, HU Shengliang, and XU Jianghu. Research on centroid jamming pattern of inflatable radar decoy[J]. Electronic Technology and Software Engineering, 2015(11): 144–146. [19] 王聘, 胡生亮, 张俊. 浮空式角反射体质心干扰使用时机研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2018, 46(5): 26–31, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2018.05.05WANG Pin, HU Shengliang, and ZHANG Jun. Using time of floating corner reflector centroid jamming[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2018, 46(5): 26–31, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2018.05.05 [20] 王涛, 胡生亮, 金嘉旺. 炮射雷达诱饵迷惑干扰使用研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2012, 35(4): 26–28. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2012.04.006WANG Tao, HU Shengliang, and JIN Jiawang. Research into confusion jamming usage of radar decoy shot by guns[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2012, 35(4): 26–28. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2012.04.006 [21] 赵宗顺, 胡生亮, 许江湖. 充气式雷达诱饵质心干扰能力分析[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2015(9): 38–40.ZHAO Zongshun, HU Shengliang, and XU Jianghu. Analysis of centroid jamming capability for inflatable radar decoy[J]. Electronic Technology &Software Engineering, 2015(9): 38–40. [22] WANG Liying, JIANG Ning, and SUN Yi. The mechanism analyzing and use of corner reflector against anti-ship missiles[C]. 5th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2017), 2017: 998–1002. [23] 卫鑫, 姜宁. 冲淡干扰在单舰反导作战中的作战运用[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2018, 38(2): 17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.02.005WEI Xin and JIANG Ning. Tactics usage of dilution jamming in single antimissile operation[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2018, 38(2): 17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.02.005 [24] 张俊, 胡生亮, 范学满, 等. 基于HRRP和PA的浮空式角反射体布放态势寻优[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2018(3): 105–109. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2018.7.167ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, FAN Xueman, et al. Optimization of the position situation of the air-floating corner reflector based on HRRP and PA[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2018(3): 105–109. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2018.7.167 [25] 王聘, 胡生亮, 姚强, 等. 浮空式角反射体阵列布放间隔寻优研究[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2018, 40(3): 32–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.03.008WANG Pin, HU Shengliang, YAO Qiang, et al. Optimal laying interval of the array of floating-type corner reflectors[J]. Command Control &Simulation, 2018, 40(3): 32–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.03.008 [26] 张俊, 胡生亮, 杨庆, 等. 基于RCS幅值特性相似度的浮空式角反射体布放态势寻优[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2019, 31(2): 32–36. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2019.02.006ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, YANG Qing, et al. Optimization of position situation of air-floating corner reflectors based on similarity of RCS amplitude characteristic[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2019, 31(2): 32–36. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2019.02.006 [27] ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, WU Lingang, et al. Air-floating corner reflectors dilution jamming placement position[C]. 2019 IEEE 8th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), Dali, China, 2019: 993–997. [28] 张俊, 胡生亮, 刘泰邑, 等. 基于探索性分析的浮空式角反射体质心干扰使用研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2019(4): 13–19, 75. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2019.9.021ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, LIU Taiyi, et al. Research on the use of centroid jamming of floating corner reflectors based on exploratory analysis[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2019(4): 13–19, 75. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2019.9.021 [29] 张俊, 胡生亮, 杨庆, 等. 异型角反射体阵列寻优研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2019, 31(6): 46–50. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2019.06.009ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, YANG Qing, et al. On optimization of heterotypic corner reflector arrays[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2019, 31(6): 46–50. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2019.06.009 [30] 柴刚, 陆益敏, 陈晓明. 角反射器在海军中的战术使用[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2006, 29(5): 11–14. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2006.05.003CHAI Gang, LU Yimin, and CHEN Xiaoming. Tactical usage of corner reflector in navy[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2006, 29(5): 11–14. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2006.05.003 [31] 谢伟, 徐波, 张亮. 对抗反舰导弹倾卸式复合干扰方法研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2022(1): 76–86. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220519XIE Wei, XU Bo, and ZHANG Liang. Research on anti-ship missile dumping compound jamming method[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2022(1): 76–86. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220519 [32] 王馨若. 基于反舰导弹的组合干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021.WANG Xinruo. Research of compound jamming on anti-ship missile[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. [33] 郭立新, 魏仪文. 复杂动态海面与目标电磁散射及回波仿真研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 76–109. doi: 10.12000/JR22202GUO Lixin and WEI Yiwen. Status and prospects of electromagnetic scattering echoes simulation from complex dynamic sea surfaces and targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 76–109. doi: 10.12000/JR22202 [34] 郭立新, 魏仪文, 柴水荣. 目标与复杂地海面复合电磁散射研究现状综述[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(1): 69–84. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019090204GUO Lixin, WEI Yiwen, and CHAI Shuirong. A review on the research of composite electromagnetic scattering from target and rough surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(1): 69–84. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019090204 [35] 殷红成, 郭琨毅. 目标电磁散射特性研究的若干热点和难点问题[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(1): 128–134. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019100401YIN Hongcheng and GUO Kunyi. Hot-topics and difficult problems in the research filed of electromagnetic scattering characteristics of targets[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(1): 128–134. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019100401 [36] 关键. 雷达海上目标特性综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114GUAN Jian. Summary of marine radar target characteristics[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114 [37] ZHU Hong, WANG Qingping, PAN Yujian, et al. A sea corner-reflector jamming identification method based on time-frequency feature[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Ningbo, China, 2015: 1–6. [38] TAO Zhiyu, GUO Yu, and FU Qiang. Discrimination method of ship and corner reflector based on SVM[C]. 2016 Sixth International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC), Harbin, China, 2016: 699–702. [39] ÜNAL İ, GULUM T O, and BAYRAMOĞLU E Ç. Investigations of electrical size effects on radar cross section for orthogonally distorted corner reflectors[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, USA, 2015: 1515–1519. [40] 来庆福. 反舰导弹雷达导引头抗舷外干扰技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.LAI Qingfu. Study on countering off-board interference for radar seeker of anti-ship missile[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011. [41] PALADINI R, MARTORELLA M, and BERIZZI F. Classification of man-made targets via invariant coherency-matrix eigenvector decomposition of polarimetric SAR/ISAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(8): 3022–3034. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2116121 [42] GENG N, RESSLER M A, and CARIN L. Wide-band VHF scattering from a trihedral reflector situated above a lossy dispersive halfspace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2609–2617. doi: 10.1109/36.789655 [43] 金建铭, 王建国译. 电磁场有限元方法[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 1998.JIN Jianming. WANG Jianguo. translation. Finite Element Method for Electromagnetic Field[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 1998. [44] 葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M]. 3版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2011.GE Debiao and YAN Yubo. Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves[M]. 3rd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2011. [45] ALGAFSH A, INGGS M, and MISHRA A K. The effect of perforating the corner reflector on maximum radar cross section[C]. 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2016: 1–4. [46] POLYCARPOU A C, BALANIS C A, and BIRTCHER C R. Radar cross section of trihedral corner reflectors using PO and MEC[J]. Annales Des Télécommunications, 1995, 50(5): 510–516. doi: 10.1007/BF02995750 [47] LI Chengfan, YIN Jingyuan, ZHAO Junjuan, et al. The selection of artificial corner reflectors based on RCS analysis[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2012, 60(1): 43–58. doi: 10.2478/s11600-011-0060-y [48] SHAN Xinjian, YIN Jingyuan, YU Danlin, et al. Analysis of artificial corner reflector’s radar cross section: A physical optics perspective[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 6(8): 2755–2765. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0582-x [49] 郭涛. 拖曳式无源假目标的RCS计算[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.GUO Tao. RCS computation of towed passive false target[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [50] POTTER L C, CHIANG D M, CARRIERE R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641 [51] GRIESSER T and BALANIS C. Backscatter analysis of dihedral corner reflectors using physical optics and the physical theory of diffraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(10): 1137–1147. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1143987 [52] BALDAUF J, LEE S W, LIN L, et al. High frequency scattering from trihedral corner reflectors and other benchmark targets: SBR versus experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1991, 39(9): 1345–1351. doi: 10.1109/8.99043 [53] ZHOU Xiao, ZHU Jiyue, YU Weming, et al. Time-domain shooting and bouncing rays method based on beam tracing technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(9): 4037–4048. doi: 10.1109/tap.2015.2448757 [54] ZAN Guocai, GUO Lixin, LIU Songhua, et al. Scattering characteristics of the multi-corner reflector based on SBR method[C]. 2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Hangzhou, China, 2018: 1–4. [55] GROOT J. Letter: Cross section computation of trihedral corner reflectors with the geometrical optics approximation[J]. European Transactions on Telecommunications, 1992, 3(6): 637–642. doi: 10.1002/ett.4460030618 [56] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 一种角反射体雷达散射截面积的高频预估算法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2016, 31(2): 331–335, 362. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2015061401FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. High-frequency method for the evaluation of the radar cross section of corner reflectors[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2016, 31(2): 331–335, 362. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2015061401 [57] 范学满, 胡生亮, 罗亚松, 等. 海上角反射体群的RCS快速混合预估算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(11): 2462–2467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.11.02FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, LUO Yasong, et al. Hybrid RCS evaluation method for maritime multi-corner reflectors[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(11): 2462–2467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.11.02 [58] 胡生亮, 范学满, 贺静波. 基于改进GO/AP法的三面角反射体RCS预估[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2017, 15(2): 185–190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.02.013HU Shengliang, FAN Xueman, and HE Jingbo. Evaluation of radar cross section of trihedral corner reflectors based on improved GO/AP method[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2017, 15(2): 185–190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.02.013 [59] 赵维江, 葛德彪. 三面角反射器的高频电磁散射分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 1998(3): 301–303. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.1998.03.016ZHAO Weijiang and GE Debiao. High-frequency electromagnetic scattering by a square trihedral corner reflector[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 1998(3): 301–303. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.1998.03.016 [60] 张俊, 胡生亮, 王聘, 等. 基于PO/AP的角反射体RCS模型构建及分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(7): 1478–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.07.10ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, WANG Pin, et al. RCS model construction and analysis for corner reflector based on PO/AP algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(7): 1478–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.07.10 [61] JIN Jianming, LING Feng, CAROLAN S T, et al. A hybrid SBR/MoM technique for analysis of scattering from small protrusions on a large conducting body[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1998, 46(9): 1349–1357. doi: 10.1109/8.719979 [62] SHAH M A, TOKGÖZ Ç, and SALAU B A. Radar cross section prediction using iterative physical optics with physical theory of diffraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(6): 4683–4690. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2021.3137202 [63] HE Yaomin, HE Huafeng, HU Changhua, et al. Polarization analysis of trihedral corner reflector with high-frequency approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(10): 9607–9620. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3177536 [64] 许小剑, 李晓飞, 刁桂杰, 等. 时变海面雷达目标散射现象学模型[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013.XU Xiaojian, LI Xiaofei, DIAO Guijie, et al. Radar Phenomenological Models for Ships on Time-evolving Sea Surface[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013. [65] JOHNSON J T. A numerical study of scattering from an object above a rough surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(10): 1361–1367. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2002.802152 [66] 吕方方. 海面目标动态回波仿真与特性分析[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.LV Fangfang. Dynamic echo simulation and characteristic analysis of sea surface targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [67] 昝国才. 基于SBR方法的角反射器与海面复合散射及多普勒特性研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.ZAN Guocai. SBR algorithm for study of composite scattering and doppler characteristics from the corner reflector and sea surface[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [68] LUO Ying, GUO Lixin, ZUO Yanchun, et al. Time-domain scattering characteristics and jamming effectiveness in corner reflectors[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 15696–15707. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053116 [69] 帅超, 廖贵超, 张阳新, 等. 充气式角反射器制作偏差对RCS特性影响的仿真研究[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2019, 43(2): 193–198. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2019.43.02.011SHUAI Chao, LIAO Guichao, ZHANG Yangxin, et al. Simulation on effect of manufacturing deviation of inflatable corner reflector on monostatic RCS[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019, 43(2): 193–198. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2019.43.02.011 [70] 葛尧, 王硕, 郭京. 基于FEKO计算的异型结构三面角反射器RCS特性分析[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2021(1): 121–125. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2021.1.509GE Yao, WANG Shuo, and GUO Jing. Analysis on RCS of the abnormal shape triangular trihedral corner reflector based on FEKO software[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2021(1): 121–125. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2021.1.509 [71] 赵俊娟, 尹京苑, 李成范. 基于FEKO平台的人工角反射器RCS模拟[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2013, 30(8): 79–81, 85. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2013.08.019ZHAO Junjuan, YIN Jingyuan, and LI Chengfan. RCS simulation of corner reflector based on FEKO[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2013, 30(8): 79–81, 85. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2013.08.019 [72] MIANROODI R Y, HEIDAR H, and ARMAKI H M. Expandable shipboard decoy including adequate RCS by using trihedral corner reflectors[J]. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2016, 10(5): 485–491. doi: 10.1049/iet-smt.2015.0228 [73] 刘良. 雷达宽角无源反射器的研究与设计[D]. [硕士论文], 南昌航空大学, 2014.LIU Liang. Research and design for RADAR passive reflector of wide-angle[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanchang Hangkong University, 2014. [74] 孟凯, 马武举. 海面漂浮二十面角反射器电磁散射特性研究[J]. 数字海洋与水下攻防, 2020, 3(5): 437–442. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2020.05.013MENG Kai and MA Wuju. Research on electromagnetic scattering characteristics of sea floating icosahedrons triangular trihedral corner reflectors[J]. Digital Ocean &Underwater Warfare, 2020, 3(5): 437–442. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2020.05.013 [75] LUO Ying, GUO Lixin, and ZUO Yanchun. Investigations of effects of geometric characteristics on RCS for corner reflectors[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics (ICCEM), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–2. [76] 胡生亮, 范学满, 张俊, 等. 顶角切除和角度公差对角反射体雷达散射截面积的影响分析[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2017(6): 89–93. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2017.06.15HU Shengliang, FAN Xueman, ZHANG Jun, et al. Effects analysis of removal of vertices and angle tolerance on RCS of TTCR[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2017(6): 89–93. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2017.06.15 [77] 张志远, 赵原源. 新型二十面体三角形角反射器的电磁散射特性分析[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2018, 40(4): 133–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.04.030ZHANG Zhiyuan and ZHAO Yuanyuan. Analysis of electromagnetic scattering characteristic for new type icosahedrons triangular trihedral corner reflectors[J]. Command Control &Simulation, 2018, 40(4): 133–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.04.030 [78] KUBICKE G, BOURLIER C, and SAILLARD J. High-frequency bistatic scattering by depolarizing, nearly omnidirectional reflectors: Higher order polyhedral reflectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(9): 3029–3035. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.928779 [79] 赵锋, 邱梦奇, 艾小锋, 等. 典型角反射器单/双基地RCS特性对比分析[J]. 现代防御技术, 2023, 51(1): 50–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086X.2023.01.007ZHAO Feng, QIU Mengqi, AI Xiaofeng, et al. Comparative analysis of monostatic and bistatic RCS characteristics for typical corner reflectors[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2023, 51(1): 50–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086X.2023.01.007 [80] QIU Mengqi, AI Xiaofeng, XU Zhiming, et al. Comparative analysis of monostatic and bistatic RCS scattering characteristics for corner reflector[C]. 2022 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES-China), Xuzhou, China, 2022: 1–3. [81] LUO Ying, ZUO Yanchun, GUO Lixin, et al. Bistatic RCS characteristics of corner reflector in time domain[C]. 2019 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Guangzhou, China, 2019: 1–3. [82] 李郝亮, 陈思伟, 王雪松. 海面角反射器的极化旋转域特性研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01LI Haoliang, CHEN Siwei, and WANG Xuesong. Study on characterization of sea corner reflectors in polarimetric rotation domain[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01 [83] 郭雷. 宽带雷达目标极化特征提取与核方法识别研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2009.GUO Lei. Wideband radar target polarimetric feature extraction and recognition method based on kernel method[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2009. [84] CUI Kaibo, WANG Wei, CHEN Xi, et al. A kind of method of anti-corner reflector interference for millimeter wave high resolution radar system[C]. 2016 Progress in Electromagnetic Research Symposium (PIERS), Shanghai, China, 2016: 1900–1906. [85] 范学满, 胡生亮, 陈鹏, 等. 基于分类器联合的反舰导弹HRRP目标识别与拒判研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2017, 29(4): 14–20. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2017.04.003FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, CHEN Peng, et al. HRRP recognition and rejection of anti-ship missile based on classifier combination[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2017, 29(4): 14–20. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2017.04.003 [86] 袁伟. 基于一维距离像稀疏表达的无源假目标识别[J]. 电讯技术, 2018, 58(7): 798–804. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2018.07.009YUAN Wei. Passive fake target recognition based on one-dimensional distance image sparse representation[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2018, 58(7): 798–804. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2018.07.009 [87] 潘哲. 一种反舰导弹抗无源假目标干扰算法[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2010, 25(3): 285–288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1522.2010.03.011PAN Zhe. An anti-jamming algorithm for passive false targets of anti-ship missile[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2010, 25(3): 285–288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1522.2010.03.011 [88] 张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049 [89] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友. 微多普勒理论在海面目标检测中的应用及展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, and HE You. Applications and prospect of micro-motion theory in the detection of sea surface target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102 [90] TAO Zhiyu and FU Qiang. Discrimination method of ship and corner reflector based on micro-doppler feature[C]. International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology (ICCIA 2016), Guilin, China, 2016: 324–329. [91] 黄孟俊, 陈建军, 赵宏钟, 等. 海面角反射器干扰微多普勒建模与仿真[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2012, 34(9): 1781–1787. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2012.09.06HUANG Mengjun, CHEN Jianjun, ZHAO Hongzhong, et al. Micro-doppler modeling and simulating of corner reflector in sea surface[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(9): 1781–1787. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2012.09.06 [92] 黄孟俊, 赵宏钟, 付强, 等. 一种基于微多普勒特征的海面角反射器干扰鉴别方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2012, 33(10): 1486–1491. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.10.018HUANG Mengjun, ZHAO Hongzhong, FU Qiang, et al. A sea corner-reflector jamming identification method based on micro-doppler feature[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(10): 1486–1491. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.10.018 [93] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [94] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. Target Scattering Mechanism in Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar: Interpretation and Application[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018. [95] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. [96] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 [97] KROGAGER E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. doi: 10.1049/el:19900979 [98] CAMERON W L, YOUSSEF N N, and LEUNG L K. Simulated polarimetric signatures of primitive geometrical shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(3): 793–803. doi: 10.1109/36.499784 [99] 涂建华, 汤广富, 肖怀铁, 等. 基于极化分解的抗角反射器干扰研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2009, 7(2): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.02.002TU Jianhua, TANG Guangfu, XIAO Huaitie, et al. A study of anti-corner reflector based on polarization decomposition[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2009, 7(2): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.02.002 [100] 朱珍珍, 汤广富, 程翥, 等. 基于极化分解的舰船和角反射器鉴别方法[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2010, 33(6): 15–21. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2010.06.022ZHU Zhenzhen, TANG Guangfu, CHENG Zhu, et al. Discrimination method of ship and corner reflector based on polarization decomposition[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2010, 33(6): 15–21. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2010.06.022 [101] FANG Maojin, ZHU Yongfeng, HUANG Mengjun, et al. Sea surface target polarization feature extraction based on modified odd-time and even-time scattering models[C]. 2013 2nd International Conference on Measurement, Information and Control, Harbin, China, 2013: 500–504. [102] 李伯达, 张志俊, 蒋洁, 等. 一种基于极化特性辅助的海面角反射器干扰对抗方法[P]. 中国, CN110865340A, 2020.LI Boda, ZHANG Zhijun, JIANG Jie, et al. An anti-sea corner reflector jamming method with polarization characteristics[P]. China, CN110865340A, 2020. [103] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 对海雷达目标识别中全极化HRRP的特征提取与选择[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. Feature extraction and selection of full polarization HRRP in target recognition process of maritime surveillance radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3261–3268. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160722 [104] HE Yaomin, YANG Huizhang, HE Huafeng, et al. A ship discrimination method based on high-frequency electromagnetic theory[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(16): 3893. doi: 10.3390/rs14163893 [105] WANG Miao, XIE Min, SU Qinning, et al. Identification of ship and corner reflector based on invariant features of the polarization[C]. IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 2019: 545–549. [106] LIANG Zhuorui, WANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaofeng, et al. Identification of ship and corner reflector in sea clutter environment[C]. 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 2020: 622–626. [107] WANG Wenqing, LI Shuangshuang, LI Mengyan, et al. A method of radar target recognition based on polarization invariant feature[C]. 4th Seminar on Novel Optoelectronic Detection Technology and Application, Nanjing, China, 2017: 106970P. [108] CHEN Siwei, WU Guoqing, DAI Dahai, et al. Roll-invariant features in radar polarimetry: A survey[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 5015–5018. [109] 陈伯孝, 郎思呈. 基于极化不变量和极化分解的海面角反射器干扰鉴别方法[P]. 中国, CN113759325A, 2021.CHEN Boxiao and LANG Sicheng. Sea corner reflector jamming identification method based on polarization invariants and polarization decomposition[P]. China, CN113759325A, 2021. [110] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Uniform polarimetric matrix rotation theory and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4756–4770. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2284359 [111] CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric coherence pattern: A visualization and characterization tool for PolSAR data investigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 286–297. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2746662 [112] CUI Xingchao, TAO Chensong, SU Yi, et al. PolSAR ship detection based on polarimetric correlation pattern[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(3): 471–475. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2976477 [113] LI Haoliang, CUI Xingchao, and CHEN Siwei. PolSAR ship detection with optimal polarimetric rotation domain features and SVM[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3932. doi: 10.3390/rs13193932 [114] CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 [115] CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, and WANG Xuesong. Crop discrimination based on polarimetric correlation coefficients optimization for PolSAR data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(16): 4233–4249. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1079345 [116] LI Haoliang, LI Mingdian, CUI Xingchao, et al. Man-made target structure recognition with polarimetric correlation pattern and roll-invariant feature coding[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3121100 [117] WU Guoqing, CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, et al. Null-pol response pattern in polarimetric rotation domain: Characterization and application[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3139889 [118] LI Haoliang, YANG Chengli, and CHEN Siwei. Characterization of complex corner reflectors in polarimetric rotation domain[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 590–593. [119] 陈思伟, 李永祯, 王雪松, 等. 一种对三面角角反射器干扰的极化鉴别方法[P]. 中国, ZL201518004597.2, 2017.CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, et al. A polarization identification method for trihedral corner reflector jamming[P]. China, ZL201518004597.2, 2017. [120] 李郝亮, 陈思伟. 基于极化旋转域特征的角反射器干扰鉴别方法[C]. 第十七届全国电波传播年会会议论文集, 延安, 2022: 207–210.LI Haoliang and CHEN Siwei. Corner reflector jamming identification with polarimetric rotation domain feature[C]. 17th Chinese National Symposium on Radio Propagation, Yan’an, China, 2022: 207–210. [121] 李郝亮, 王国玉, 张慧, 等. 简缩极化雷达导引头极化旋转域自适应角反射器鉴别方法[C]. 2022年度导弹突防技术学术年会, 北京: 2022: 477–486.LI Haoliang, WANG Guoyu, ZHANG Hui et al. Adaptive corner reflector identification method in polarimetric rotation domain for compact polarimetric radar seeker[C]. 2022 Missile Penetration Technology Symposium, Beijing, China, 2022: 477–486. [122] 吴国庆, 王罗胜斌, 庞晨, 等. 雷达极化域变焦角反组合体对抗方法: 抗冲淡式干扰[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(12): 2969–2983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220979WU Guoqing, WANG Luoshengbin, PANG Chen, et al. Radar polarization modulation countermeasures for combined corner reflector: Anti diluted jamming[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(12): 2969–2983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220979 [123] 王罗胜斌, 吴国庆, 徐振海, 等. 雷达极化域变焦角反组合体对抗方法: 抗质心式干扰[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(12): 2957–2968. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221139WANG Luoshengbin, WU Guoqing, XU Zhenhai, et al. Radar polarization modulation countermeasures for combined corner reflector: Anti centroid jamming[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(12): 2957–2968. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221139 [124] 刘涛, 杨子渊, 蒋燕妮, 等. 极化SAR图像舰船目标检测研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155LIU Tao, YANG Ziyuan, JIANG Yanni, et al. Review of ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155 [125] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143 [126] 黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165 [127] 张俊, 胡生亮, 杨庆, 等. 浮空式角反射体RCS统计特征及识别模型研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(4): 780–786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.04.12ZHANG Jun, HU Shengliang, YANG Qing, et al. RCS statistical features and recognition model of air-floating corner reflector[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(4): 780–786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.04.12 [128] YUAN Haodong, FU Xiongjun, ZHAO Congxia, et al. Ship and corner reflector identification based on extreme learning machine[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–5. [129] 胡生亮, 范学满, 贺静波. 基于元学习的反舰导弹目标识别研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2018, 30(1): 1–6. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2018.01.001HU Shengliang, FAN Xueman, and HE Jingbo. Target recognition of anti-ship missile based on meta-learning[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2018, 30(1): 1–6. doi: 10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2018.01.001 [130] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 基于集成间隔优化的对海雷达目标识别算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(12): 73–79. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.171212FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. Target recognition method for maritime surveillance radars based on ensemble margin optimization[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(12): 73–79. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.171212 [131] 范学满, 胡生亮, 贺静波. 基于聚类和随机参考分类器的对海雷达目标识别算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2017, 30(11): 983–994. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201711003FAN Xueman, HU Shengliang, and HE Jingbo. Target recognition algorithm for maritime surveillance radars based on clustering and random reference classifier[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 30(11): 983–994. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201711003 [132] 梁子尧. 反舰雷达导引头极化抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国运载火箭技术研究院, 2021.LIANG Ziyao. Research on polarization anti-jamming technology of anti-ship missile Seeker[D]. [Master dissertation], China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, 2021. [133] 张荣文, 李彦鹏, 教亚飞. 主动雷达导引头波形选择抗角反射器干扰方法研究[J]. 电光与控制, 2015, 22(9): 20–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2015.09.005ZHANG Rongwen, LI Yanpeng, and JIAO Yafei. Waveform selection of active radar seeker for anti-corner-reflector-interference[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2015, 22(9): 20–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2015.09.005 [134] 陈浩川, 张彬, 张振华. 精确制导多体制探测技术新进展[J]. 遥测遥控, 2017, 38(6): 23–29. doi: 10.13435/j.cnki.ttc.002896CHEN Haochuan, ZHANG Bin, and ZHANG Zhenhua. New development of multi-system and multi-band detection technology for precision guidance[J]. Journal of Telemetry,Tracking and Command, 2017, 38(6): 23–29. doi: 10.13435/j.cnki.ttc.002896 [135] 袁华, 严必虎. 外军反舰导弹装备使用现状及发展趋势研究[J]. 国防科技, 2014, 35(6): 46–50. doi: 10.13943/j.issn1671-4547.2014.06.10YUAN Hua and YAN Bihu. The use of anti-ship missiles and developing trend in foreign military[J]. National Defense Technology, 2014, 35(6): 46–50. doi: 10.13943/j.issn1671-4547.2014.06.10 [136] 王永. 雷达/红外成像复合制导面临的干扰及对抗[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2010, 30(4): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2010.04.004WANG Yong. Analysis on interference and anti-interference to radar/IR-imaging anti-ship missile[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2010, 30(4): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2010.04.004 [137] 张晓瑜, 欧阳中辉, 杨玉彬, 等. 被动雷达/红外复合制导抗干扰性能分析[J]. 兵工自动化, 2012, 31(4): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1576.2012.04.017ZHANG Xiaoyu, OUYANG Zhonghui, YANG Yubin, et al. Anti-jamming effectiveness analysis of passive radar/IR compound guidance[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2012, 31(4): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1576.2012.04.017 [138] 邢世其, 刘业民, 李永祯, 等. 箔条在现代海战场中的应用及现状[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2021, 37(2): 58–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2021.02.014XING Shiqi, LIU Yemin, LI Yongzhen, et al. Application and status of chaff in modern sea battlefield[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2021, 37(2): 58–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2021.02.014 [139] 李有才, 郑春弟, 黄强. 旋转式RCS可变角反射器的结构设计与可行性研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2011, 34(3): 106–109, 120. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2011.03.014LI Youcai, ZHENG Chundi, and HUANG Qiang. Structural design and feasibility study of rotary corner with variable RCS[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2011, 34(3): 106–109, 120. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2011.03.014 [140] 祝寄徐, 裴志斌, 屈绍波, 等. 一种旋转型的角反射器的设计[J]. 现代电子技术, 2013, 36(11): 1–4. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2013.11.026ZHU Jixu, PEI Zhibin, QU Shaobo, et al. Design of rotary-type corner reflector[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2013, 36(11): 1–4. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2013.11.026 [141] 郝炎祯, 诸德放, 陈朋, 等. GO/AP法角反射器可变RCS模拟技术[J]. 现代防御技术, 2017, 45(6): 138–144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2017.06.23HAO Yanzhen, ZHU Defang, CHEN Peng, et al. Variable RCS simulation technology for airborne corner reflector[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2017, 45(6): 138–144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2017.06.23 [142] 赵虎辰. 一种X波段全向雷达角反射器阵列设计[J]. 河北省科学院学报, 2019, 36(1): 26–29. doi: 10.16191/j.cnki.hbkx.2019.01.005ZHAO Huchen. Design of an X-band omnidirectional radar angular reflector array[J]. Journal of the Hebei Academy of Sciences, 2019, 36(1): 26–29. doi: 10.16191/j.cnki.hbkx.2019.01.005 [143] 冯德军, 谢前朋, 王俊杰, 等. 对雷达回波的无源电磁调控技术及其发展[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(6): 1236–1241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.06.10FENG Dejun, XIE Qianpeng, WANG Junjie, et al. Passive electromagnetic manipulation technology to radar echo and its development[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1236–1241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.06.10 [144] FERRER P J, LOPEZ-MARTINEZ C, AGUASCA A, et al. Transpolarizing trihedral corner reflector characterization using a GB-SAR system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 774–778. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2113313 [145] 祝寄徐, 裴志斌, 屈绍波, 等. 一种加载超材料吸波体的新型三面角反射器设计[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2013, 32(10): 52–54, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.10.014ZHU Jixu, PEI Zhibin, QU Shaobo, et al. Design of novel trihedral corner reflector loaded with meta-material absorbing body[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2013, 32(10): 52–54, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.10.014 [146] 张泽奎, 王东红, 雷忆三, 等. 基于超材料的RCS增强器设计[J]. 无线电工程, 2017, 47(5): 67–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2017.05.16ZHANG Zekui, WANG Donghong, LEI Yisan, et al. A novel RCS enhancing device based on metamaterial[J]. Radio Engineering, 2017, 47(5): 67–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2017.05.16 [147] 刘蕾. 电控可调无源散射体雷达特性研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2019.LIU Lei. Research on radar characteristics of electrically tunable passive scatterers[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2019. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
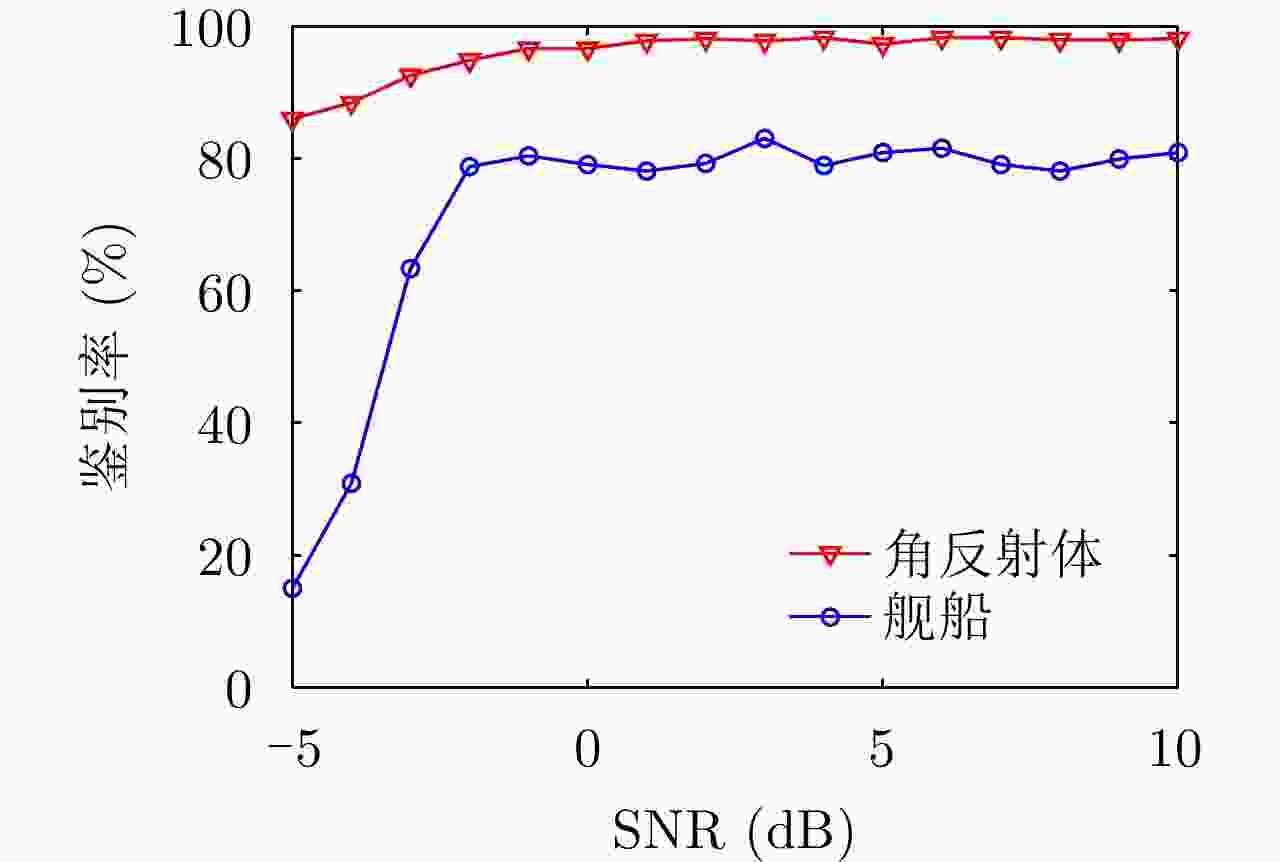
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: