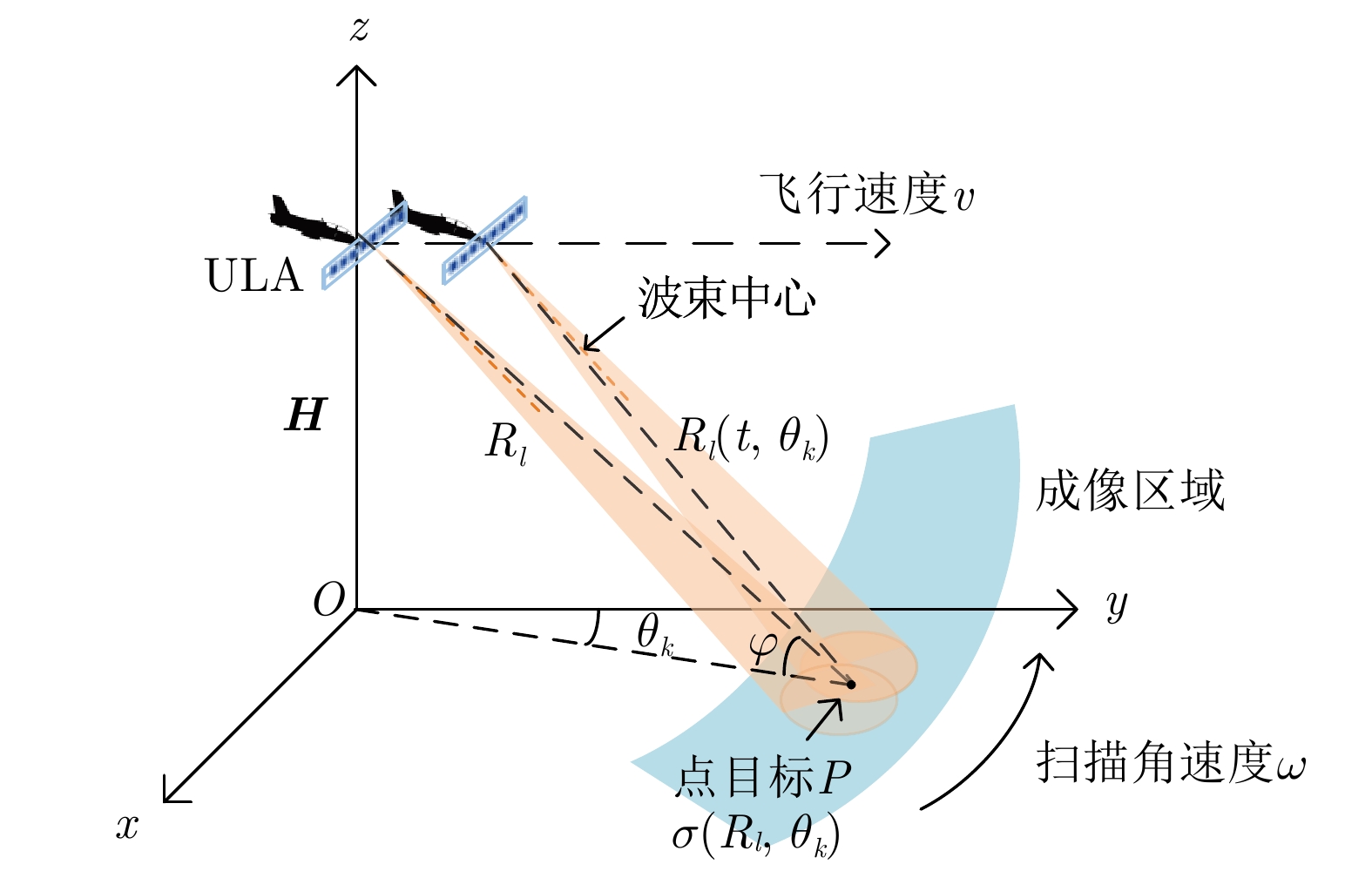
Forward-looking Imaging via Iterative Super-resolution Estimation in Airborne Multi-channel Radar
-
摘要: 波达角估计算法用于机载多通道雷达前视成像时可以突破瑞利极限,实现同一波束主瓣宽度内的多目标分辨,改善成像的方位向分辨率,然而天线波束覆盖有限且其快速扫描使得可用于协方差矩阵估计的数据样本缺乏,导致对目标位置和幅度估计出现误差。该文提出了一种基于单快拍迭代超分辨处理的多通道雷达前视成像算法,通过对单个空域快拍的迭代谱估计可获得目标的准确位置和幅度信息,再通过多个脉冲的非相干累积得到前视方位高分辨成像。仿真和实测数据处理结果表明,所提算法具有分辨多目标的能力,相较于传统前视成像算法显著提高了前视图像的方位分辨率,同时保证了点目标的精确重构和面目标的轮廓重构。Abstract: The direction of arrival estimation algorithm can overcome the Rayleigh limit, effectively separate multiple targets within the main lobe, and improve the azimuth resolution when applied to forward-looking imaging in airborne multi-channel radar. However, the limited antenna beam coverage and rapid scanning result in a scarcity of data samples available for covariance matrix estimation, leading to direction and amplitude estimation errors. Herein, we propose a forward-looking imaging algorithm based on single-snapshot iterative super-resolution estimation. The algorithm performs single-snapshot iterative spectral estimation to accurately determine the azimuth and amplitude of the target. Subsequently, a high-resolution image is achieved through non-coherent accumulation. Simulation and experimental data processing results show that the proposed algorithm can resolve multiple targets, significantly improving the azimuth resolution of the forward-looking image compared with traditional forward-looking imaging algorithms. Moreover, it ensures the accurate reconstruction of point targets and contour reconstruction of area targets.
-
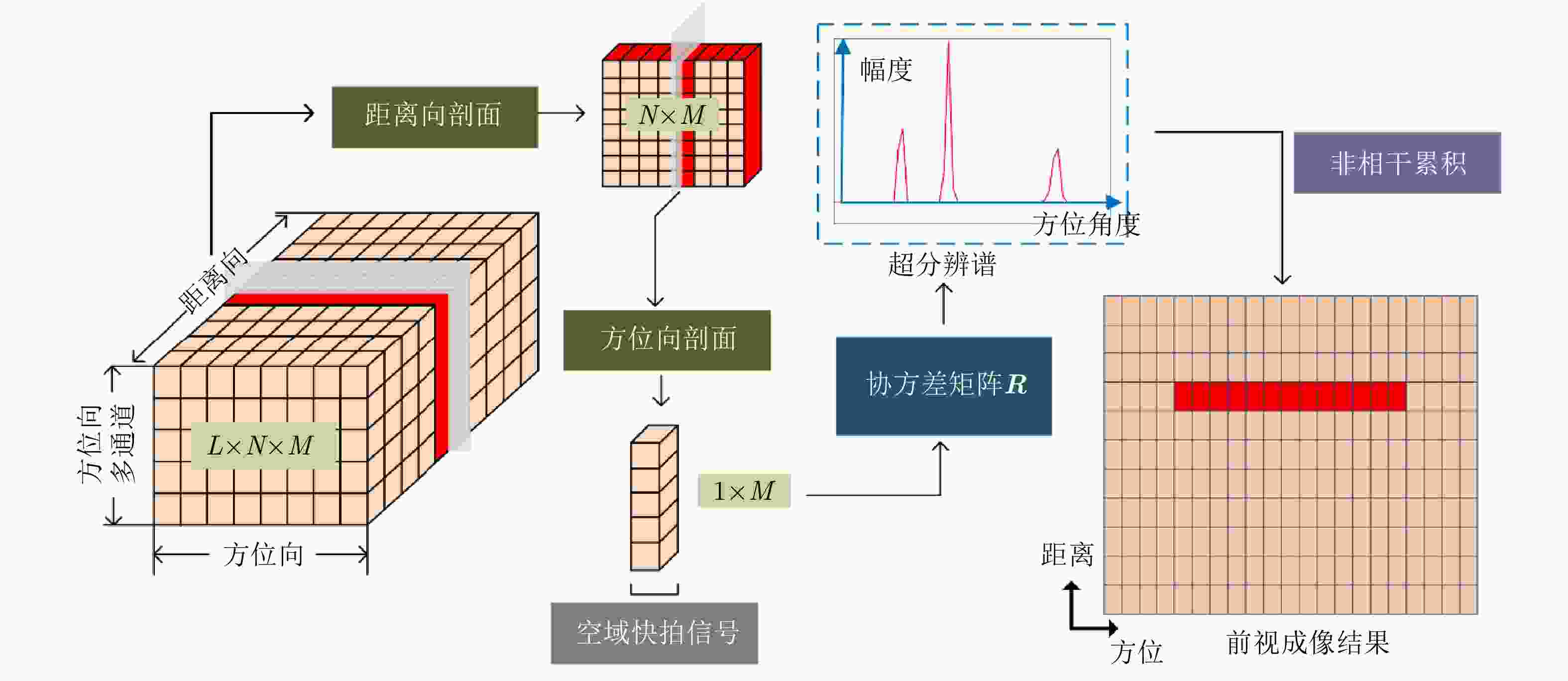
1 迭代超分辨算法流程
1. Flow chart of iterative super-resolution algorithm
根据当前波束中心 $ \bar \theta $,由式(12)计算得空域不混叠范围;在此范
围上构建空域导引矢量矩阵A初始化: ${\hat {\boldsymbol{x}}_1} = {{\boldsymbol{A}}^{\text{H} } }{\boldsymbol{s}}$,基于此计算信号的空间功率分布矩阵 ${{\boldsymbol{P}}_1}$ 重复以下操作: ${{\boldsymbol{w}}_{t + 1} } = {\left( {{\boldsymbol{A}}{{\boldsymbol{P}}_t}{{\boldsymbol{A}}^{\text{H} } } + {{\boldsymbol{R}}_{\rm{N}}} } \right)^{ - 1} }{\boldsymbol{A}}{{\boldsymbol{P}}_t}$ ${\hat {\boldsymbol{x} }_{t + 1} } = {\boldsymbol{w} }_{t + 1} ^{\text{H} }{\boldsymbol{s} }$ ${\hat {\boldsymbol{P}}_{t + 1} } = [{\hat {\boldsymbol{x}}_t}\hat {\boldsymbol{x}}_t^{\text{H} }] \odot {{\boldsymbol{I}}_{K \times K} }$ 直到收敛 表 1 点目标仿真实验系统参数
Table 1. Point target simulation parameters
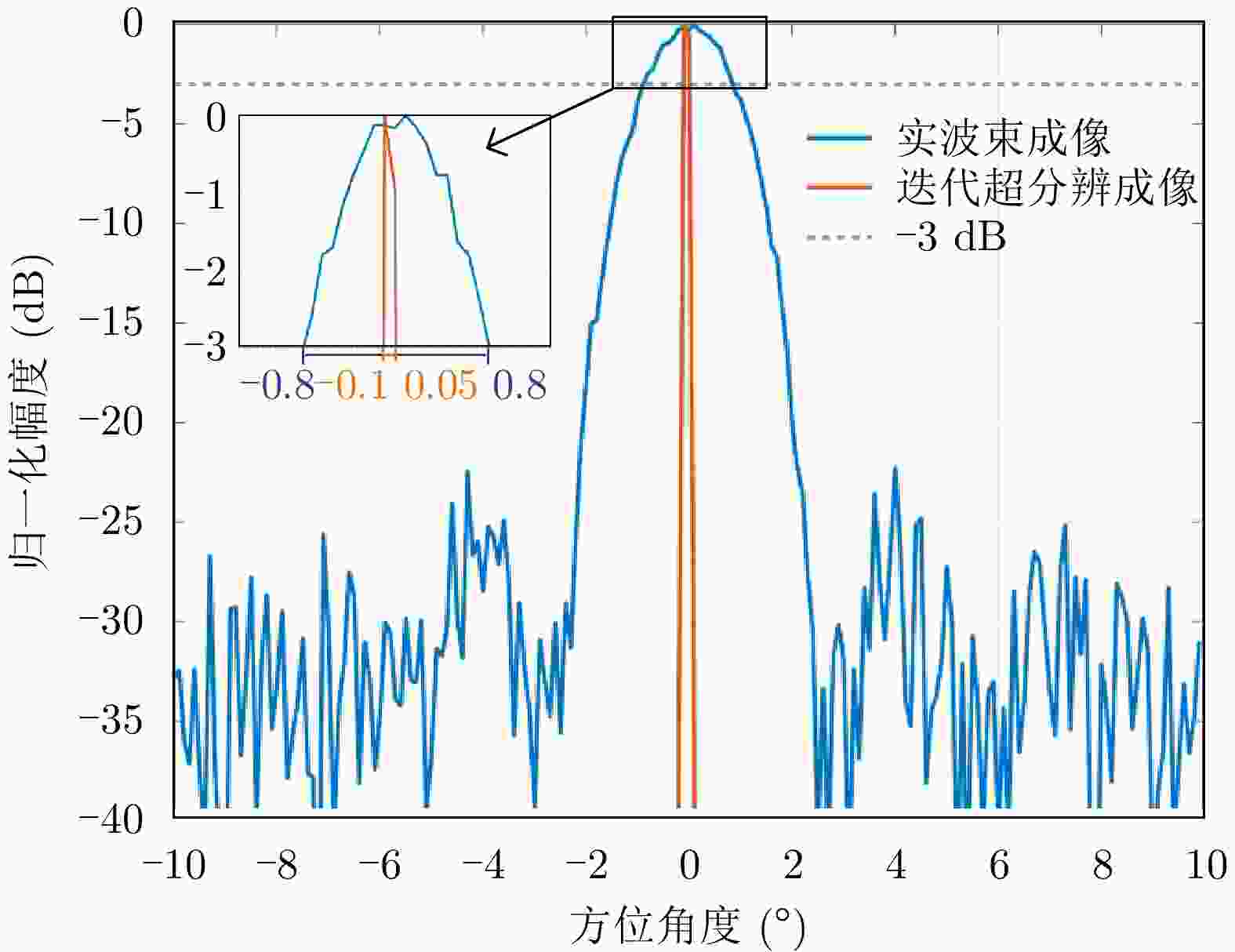
参数名称 参数值 雷达波长(m) 0.03 系统带宽(MHz) 20 采样频率(MHz) 30 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1000 通道数 8 通道间隔(m) 0.09 波束方位向主瓣宽度(°) 2.11 机载平台运动速度(m/s) 100 波束扫描速度(°/s) 100 前视扫描范围(°) –10~10 目标点距离(m) 1000, 1250, 1250, 1250, 1500 目标点方位角(°) 0, –3, –2, 3, 0 目标点SNR (dB)
20, 25, 25, 20, 20 表 2 场景仿真实验系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of simulation for simulated scenario
参数名称 参数值
(场景1)参数值
(场景2)雷达波长(m) 0.03 0.03 系统带宽(MHz) 40 40 采样频率(MHz) 50 50 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1000 1000 通道数 8 8 通道间隔(m) 0.045 0.120 波束方位向主瓣宽度(°) 4.23 1.59 波束扫描范围(°) –20~20 –8~8 机载平台运动速度(m/s) 100 80 表 3 实测数据系统参数
Table 3. Parameters of measured data
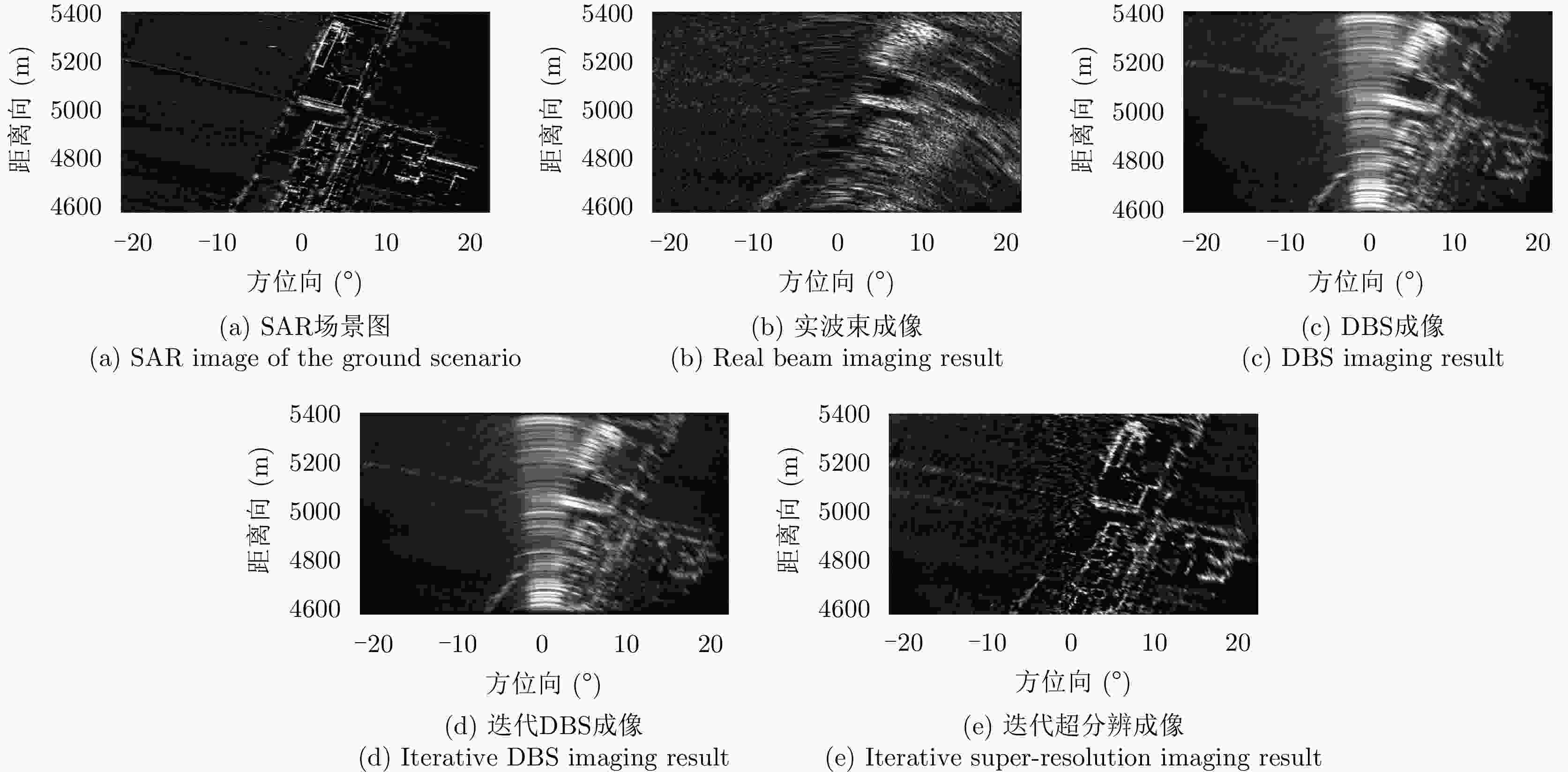
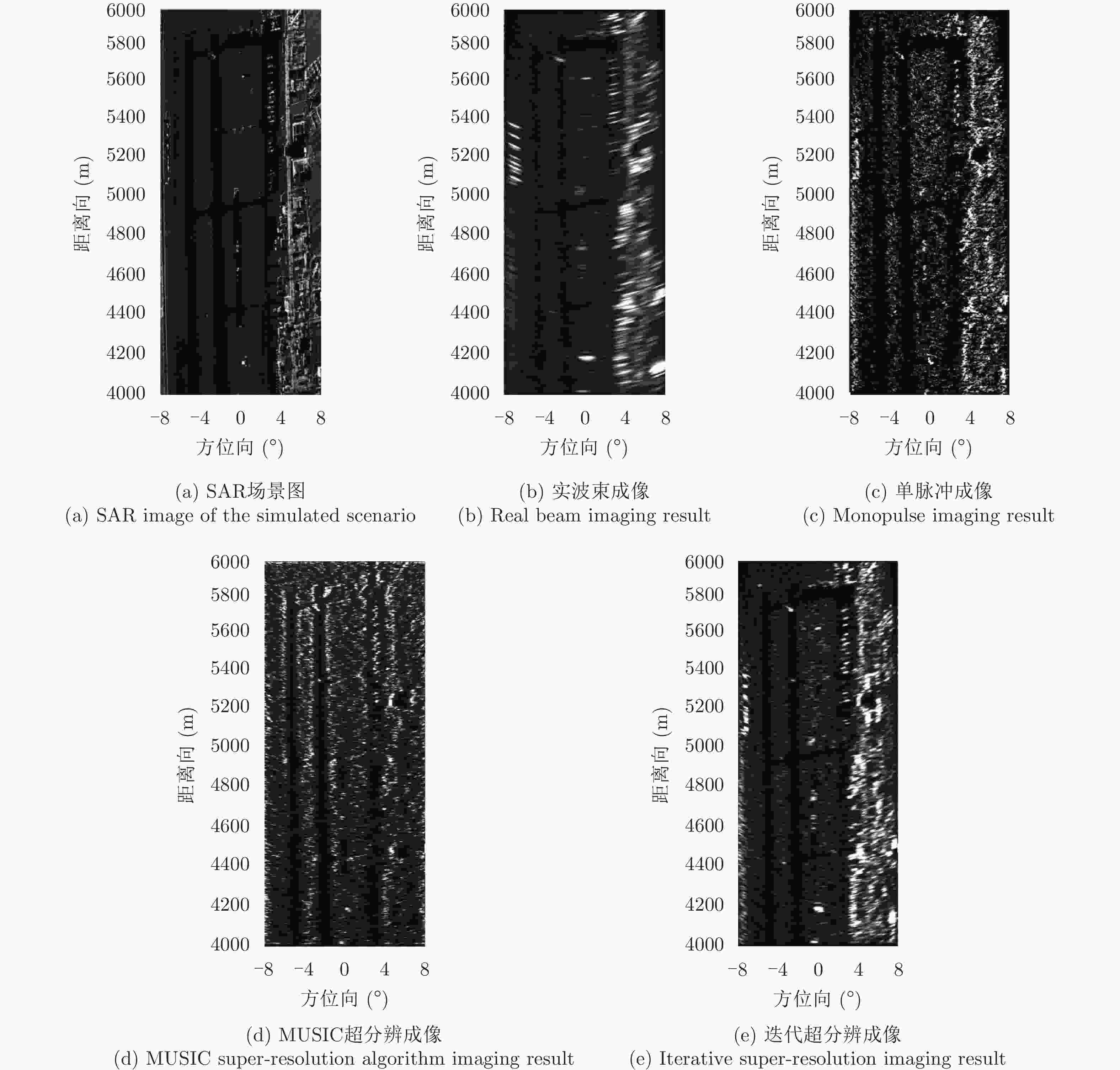
参数名称 第1组实测数据 第2组实测数据 雷达波段 X Ku 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 417 3125 通道数 4 4 通道间隔(m) 0.150 0.037 波束主瓣宽度(°) 2.42 6.31 波束扫描范围(°) –14~14 –20~20 扫描速度(°/s) 80 70 机载平台速度(m/s) 145 68 表 4 地面实测数据成像结果图像熵和对比度对比
Table 4. Entropy and contrast of the measured data results
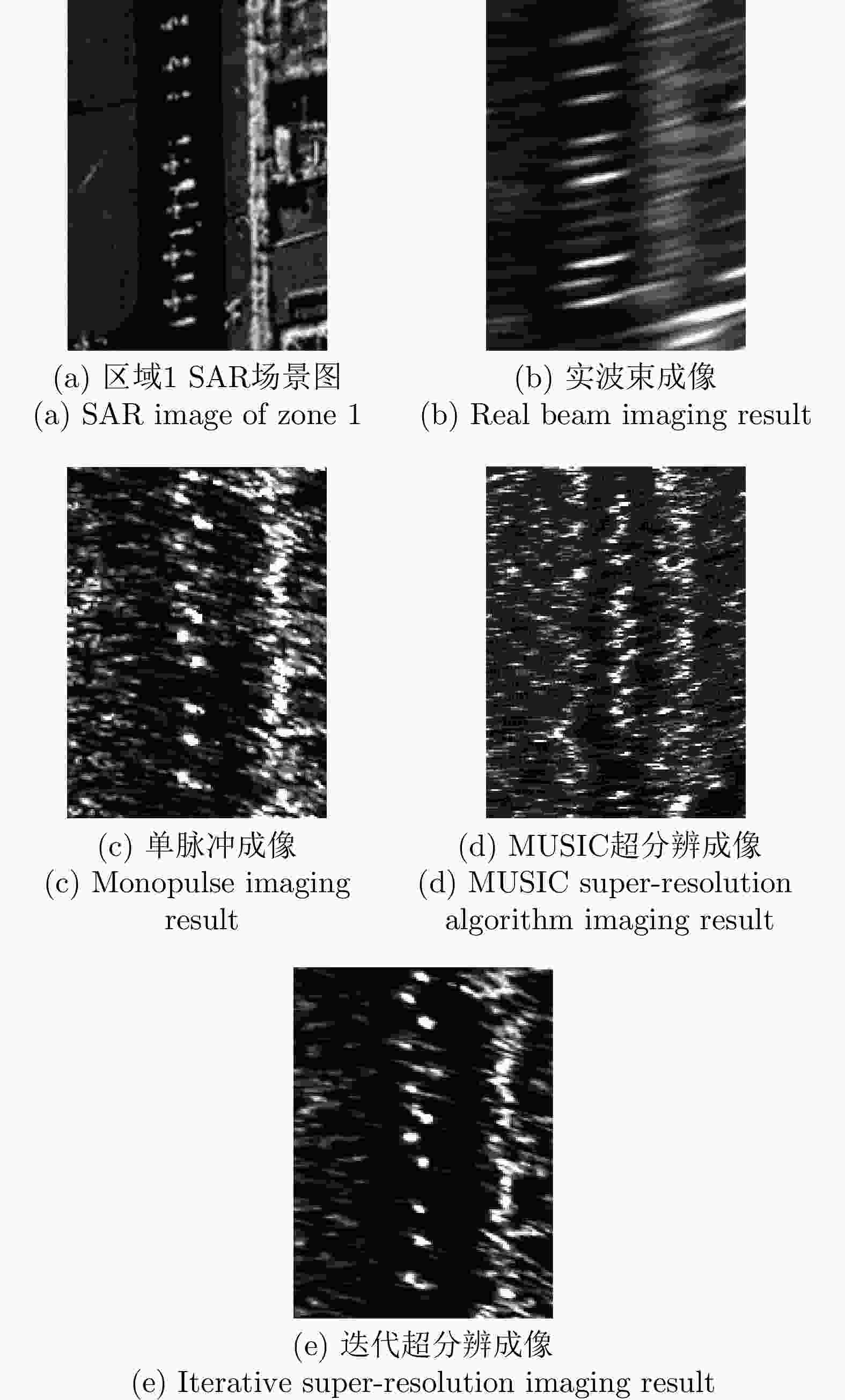
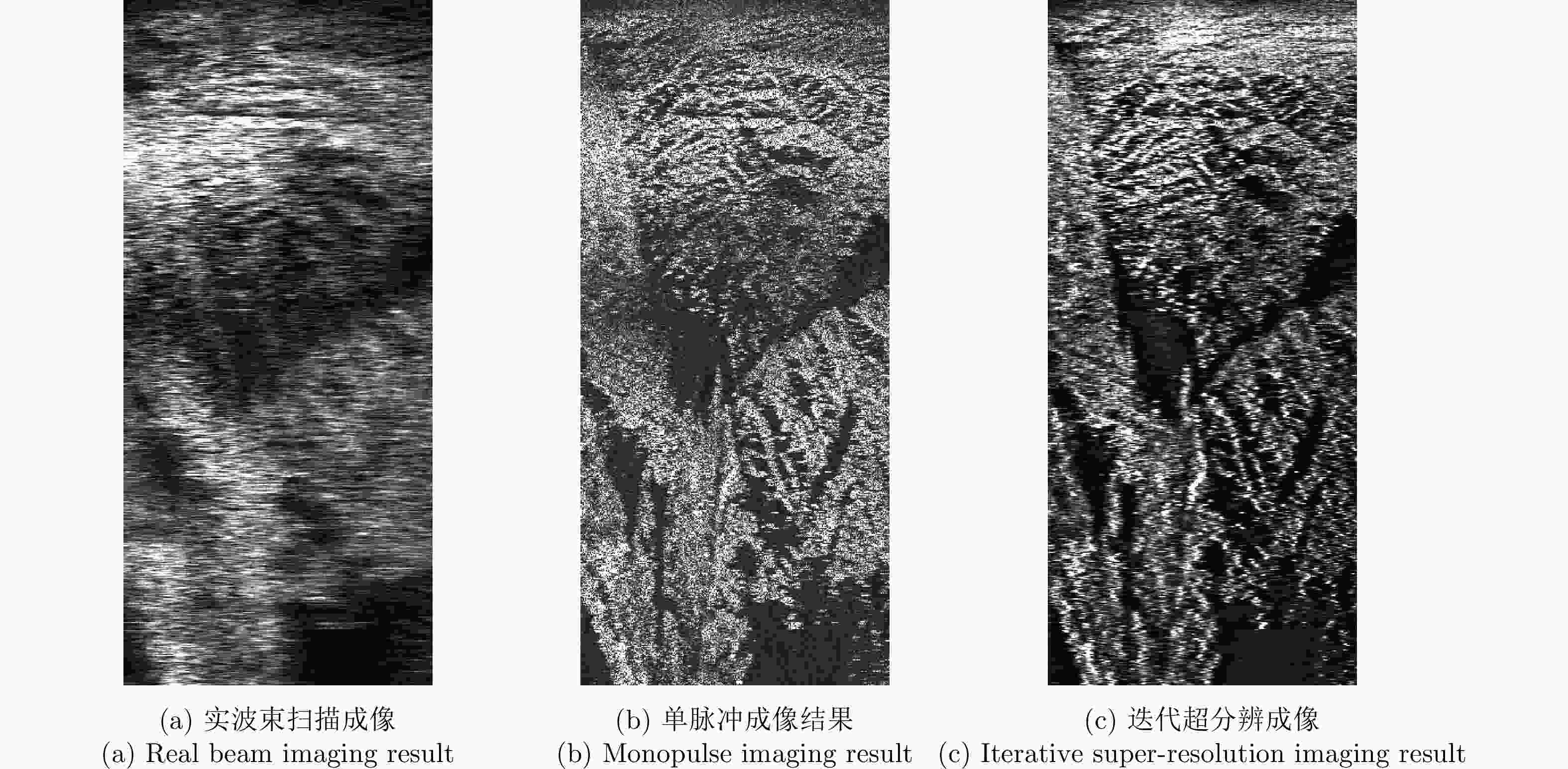
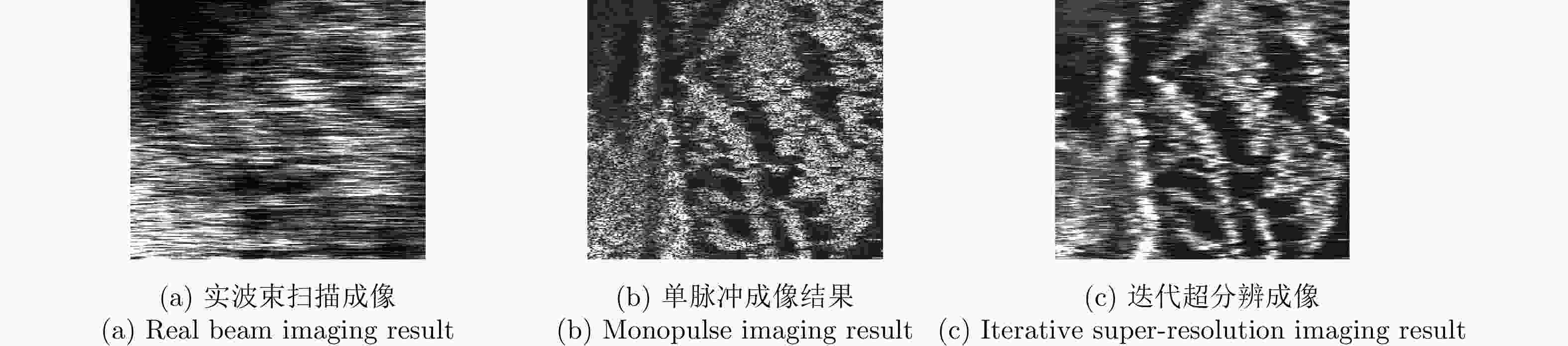
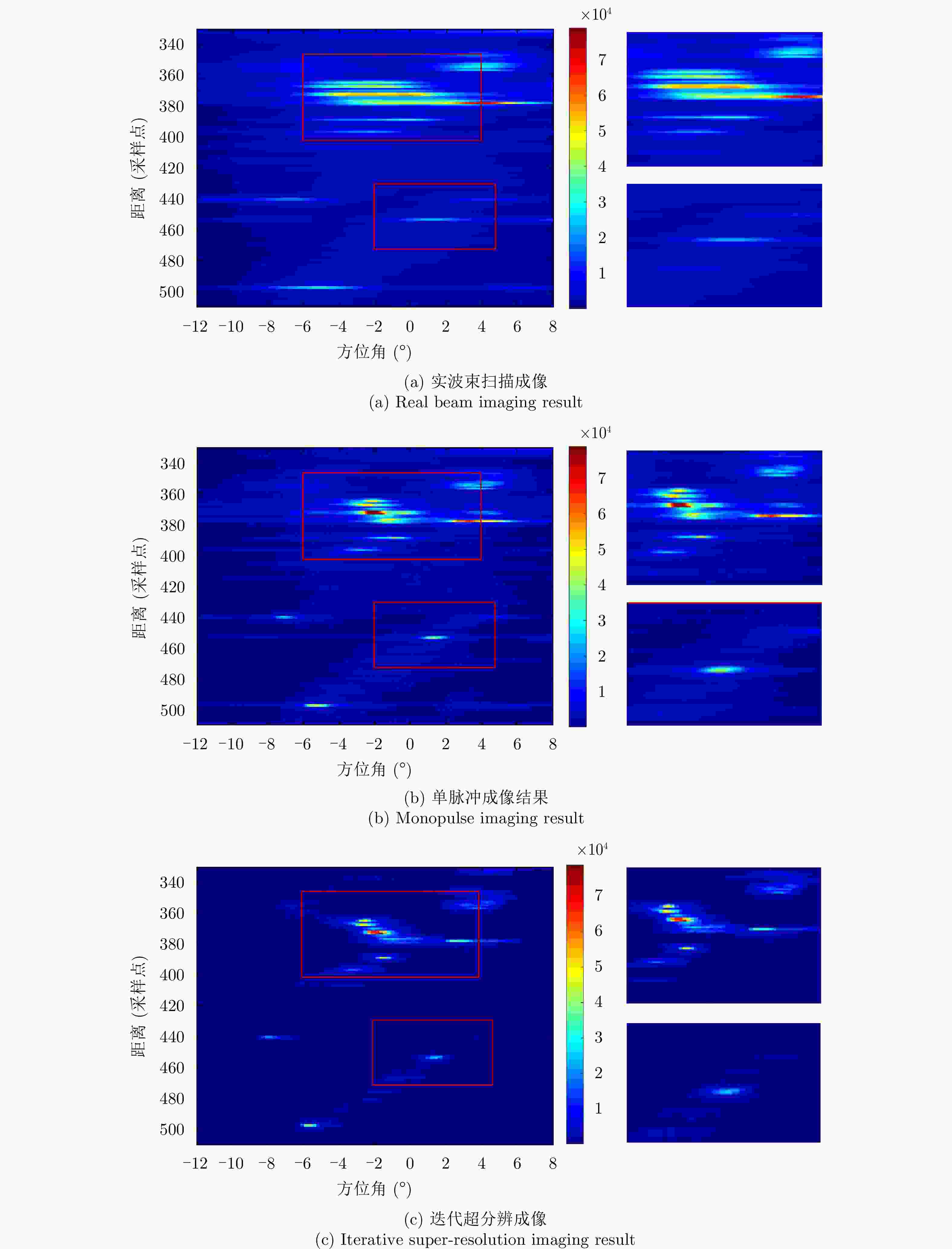
成像方法 图像熵 对比度 实波束成像 3.8625 4.42 单脉冲成像结果 1.6530 8.12 迭代超分辨成像 1.2543 9.59 -
[1] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [2] 樊晨阳, 贺思三, 郭乾. 雷达前视成像技术的研究现状[J]. 电光与控制, 2021, 28(9): 59–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2021.09.013FAN Chenyang, HE Sisan, and GUO Qian. Research status of radar forward-looking imaging technology[J]. Electronics Optics&Control, 2021, 28(9): 59–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2021.09.013 [3] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [4] 陈洪猛. 机载广域监视雷达高分辨成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.CHEN Hongmeng. Study of high resolution imaging for airborne wide area surveillance radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2016. [5] ONAT E and ÖZKAZANÇ Y. An analysis of Doppler beam sharpening technique used in fighter aircraft[C]. The 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, Izmir, Turkey, 2018: 1–4. [6] MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. Doppler beam sharpening using estimated Doppler centroid based on edge detection and fitting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 123604–123615. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937992 [7] 杨志伟, 贺顺, 廖桂生. 机载单通道雷达实波束扫描的前视探测[J]. 航空学报, 2012, 33(12): 2240–2245.YANG Zhiwei, HE Shun, and LIAO Guisheng. Forward-looking detection for airborne single-channel radar with beam scanning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2012, 33(12): 2240–2245. [8] 温晓杨, 匡纲要, 胡杰民, 等. 基于实波束扫描的相控阵雷达前视成像[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(7): 1977–1991. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0545WEN Xiaoyang, KUANG Gangyao, HU Jiemin, et al. Forward-looking imaging based on real beam scanning phased array radars[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(7): 1977–1991. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0545 [9] SUTOR T, WITTE F, and MOREIRA A. New sector imaging radar for enhanced vision: SIREV[C]. SPIE 3691, Enhanced and Synthetic Vision, Orlando, USA, 1999. [10] 吴迪, 朱岱寅, 田斌, 等. 单脉冲成像算法性能分析[J]. 航空学报, 2012, 33(10): 1905–1914.WU Di, ZHU Daiyin, TIAN Bin, et al. Performance evaluation for monopulse imaging algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2012, 33(10): 1905–1914. [11] 吴迪, 杨成杰, 朱岱寅, 等. 一种用于单脉冲成像的自聚焦算法[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(8): 1962–1968. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.08.027WU Di, YANG Chengjie, ZHU Daiyin, et al. An autofocusing algorithm for monopulse imaging[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(8): 1962–1968. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.08.027 [12] 李悦丽, 马萌恩, 赵崇辉, 等. 基于单脉冲雷达和差通道多普勒估计的前视成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 131–142. doi: 10.12000/JR20111LI Yueli, MA Meng’en, ZHAO Chonghui, et al. Forward-looking imaging via Doppler estimates of sum-difference measurements in scanning monopulse radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 131–142. doi: 10.12000/JR20111 [13] WALTERSCHEID I, ESPETER T, GIERULL C, et al. Results and analysis of hybrid bistatic SAR experiments with spaceborne, airborne and stationary sensors[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: II-238–II-241. [14] YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, YANG Haiguang, et al. A first experiment of airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR - Preliminary results[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 4202–4204. [15] LIU Zhutian, YE Hongda, LI Zhongyu, et al. Optimally matched space-time filtering technique for BFSAR nonstationary clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3090462 [16] 武俊杰, 孙稚超, 杨建宇, 等. 基于GF-3照射的星机双基SAR成像及试验验证[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(3): 241–247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.03.002WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, YANG Jianyu, et al. Spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR using GF-3 illumination—technology and experiment[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(3): 241–247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.03.002 [17] ZHANG Yongchao, MAO Deqing, ZHANG Qian, et al. Airborne forward-looking radar super-resolution imaging using iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(7): 2044–2054. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2920859 [18] ZHANG Qiping, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. TV-sparse super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6534–6549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977719 [19] TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. Fast sparse-TSVD super-resolution method of real aperture radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6609–6620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027053 [20] HUO Weibo, TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, et al. Balanced tikhonov and total variation deconvolution approach for radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3505805. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2021.3072389 [21] 毛德庆. 机载雷达扫描波束超分辨成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022.MAO Deqing. Research on scanning beam super-resolution imaging methods for airborne radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. [22] ZHANG Yin, SHEN Jiahao, TUO Xingyu, et al. Scanning radar forward-looking superresolution imaging based on the Weibull distribution for a sea-surface target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3194118 [23] GUPTA I J, BEALS M J, and MOGHADDAR A. Data extrapolation for high resolution radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1994, 42(11): 1540–1545. doi: 10.1109/8.362783 [24] CHO B L and SUN S G. Cross-range resolution improvement in forward-looking imaging radar using autoregressive model-based data extrapolation[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 933–941. doi: 10.1049/IET-RSN.2014.0495 [25] 张洁. 阵列雷达前视成像技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2018.ZHANG Jie. Study on array radar forward-looking imaging techniques[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. [26] ZHANG Jie, WU Di, ZHU Daiyin, et al. An airborne/missile-borne array radar forward-looking imaging algorithm based on super-resolution method[C]. The 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2017: 1–5. [27] BLUNT S D and GERLACH K. Adaptive pulse compression via MMSE estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(2): 572–584. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1642573 [28] BLUNT S D, CHAN T, and GERLACH K. Robust DOA estimation: The reiterative superresolution (RISR) algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 332–346. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705679 [29] YARDIBI T, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Source localization and sensing: A nonparametric iterative adaptive approach based on weighted least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(1): 425–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417172 [30] ROBERTS W, STOICA P, LI Jian, et al. Iterative adaptive approaches to MIMO radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(1): 5–20. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2038964 [31] 张小飞, 张胜男, 徐大专. 自适应对角线加载的波束形成算法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2007, 27(2): 66–71. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2007.02.011ZHANG Xiaofei, ZHANG Shengnan, and XU Dazhuan. Adaptive diagonal loading beamforming algorithm[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2007, 27(2): 66–71. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2007.02.011 [32] CARLSON B D. Covariance matrix estimation errors and diagonal loading in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1988, 24(4): 397–401. doi: 10.1109/7.7181 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: