Subband Information Geometry Detection Method Based on Orthogonal Projection for Weak Radar Targets
-
摘要: 基于信息几何理论的雷达目标检测是一种新兴的技术,它将目标检测问题转化为流形上目标与杂波的区分问题,在低信杂比检测中具有优势。对于复杂背景下的弱小目标检测,目标与杂波难以区分,限制着检测性能。因此,该文基于矩阵信息几何检测器,提出一种基于正交投影的子带信息几何目标检测方法。该文利用滤波器组对雷达回波信号进行子带分解,并在矩阵流形上稳健估计子带内强杂波信号子空间,提出基于流形的正交投影方法以抑制强杂波,增强目标与杂波的区分性。最后,采用仿真数据和实测海杂波数据验证所提方法的有效性。结果表明,所提方法能够有效抑制强杂波,具有较好的检测性能。Abstract: Herein, a novel and effective method for detecting radar targets with a low signal-to-clutter ratio is proposed based on the information geometry theory. In the proposed method, the target detection problem is converted to distinguishing the target from a clutter background on a manifold. However, this is challenging when dealing with small and weak targets embedded in a complex and strong clutter background, which limits the detection performance. Therefore, to address this issue, an orthogonal projection based subband information geometry detection method is proposed. In this method, the received radar signal undergoes subband decomposition by a designed filter bank, and the robust estimation of clutter signal subspace in each subband is implemented on the matrix manifold. Subsequently, the suppression of the strong clutter is achieved through orthogonal projection based on the manifold, thereby improving the discrimination between the target and the clutter. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated using simulated and real sea clutter data. The experimental results confirm that the proposed method effectively suppresses strong clutter and exhibits excellent detection performance.
-
1 基于正交投影的子带信息几何检测方法
1. Subband MIG detection method based on orthogonal projection
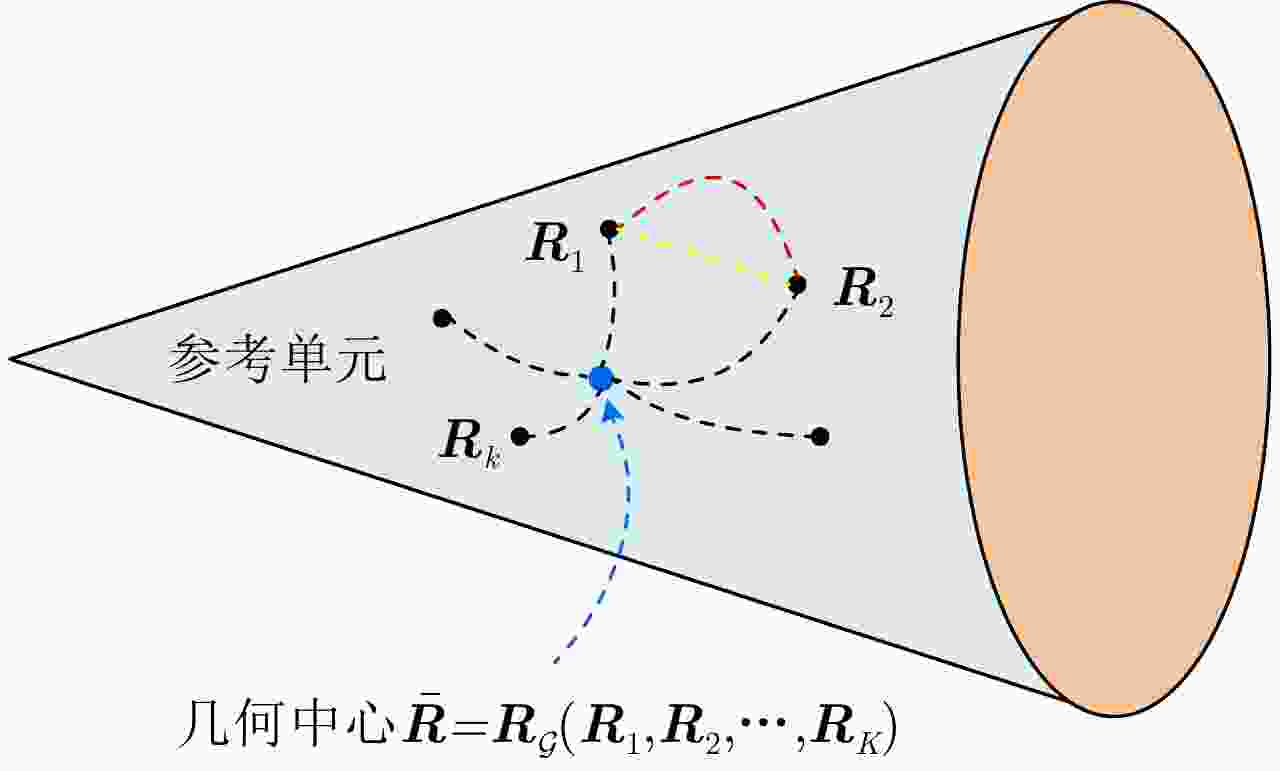
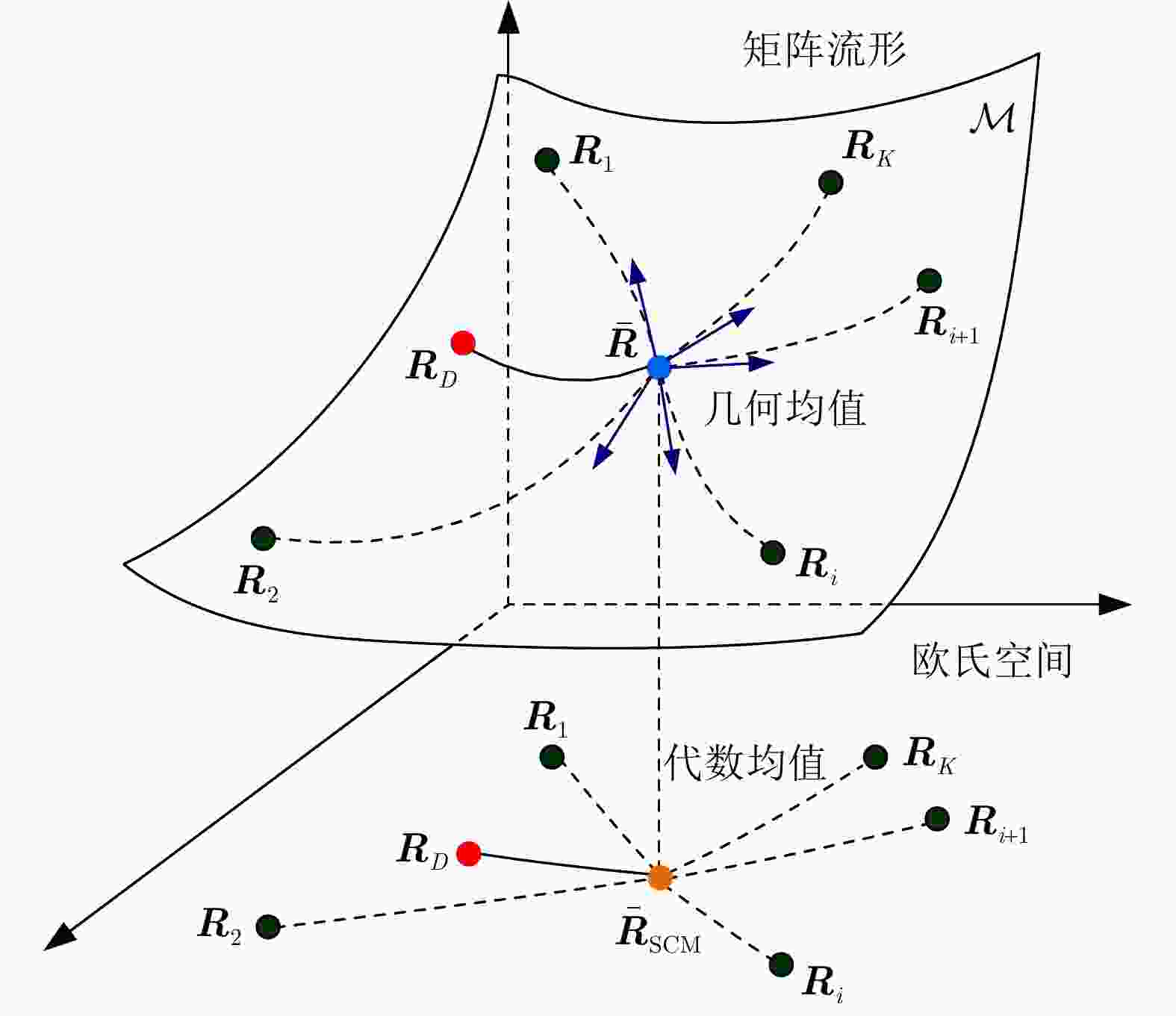
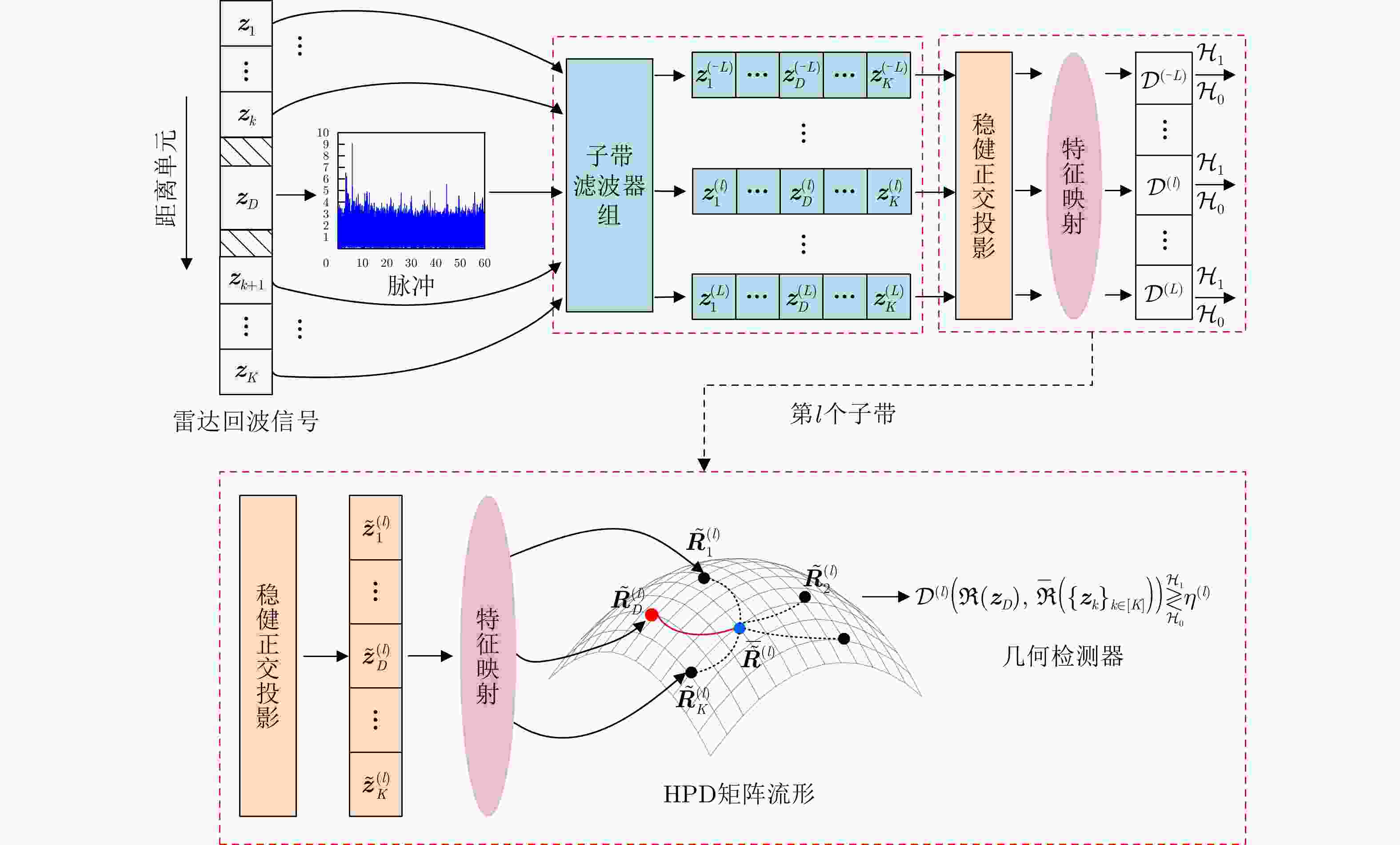
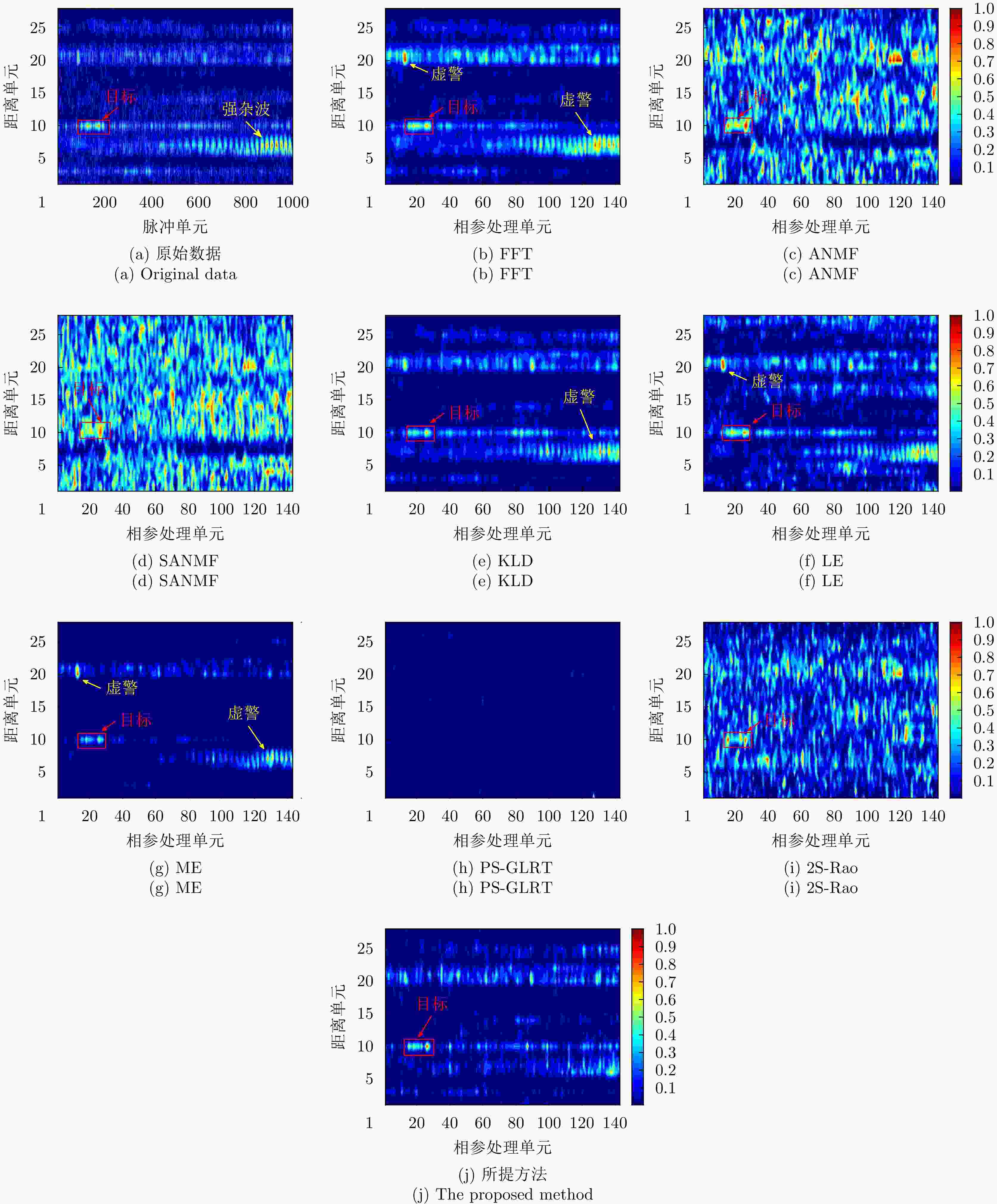
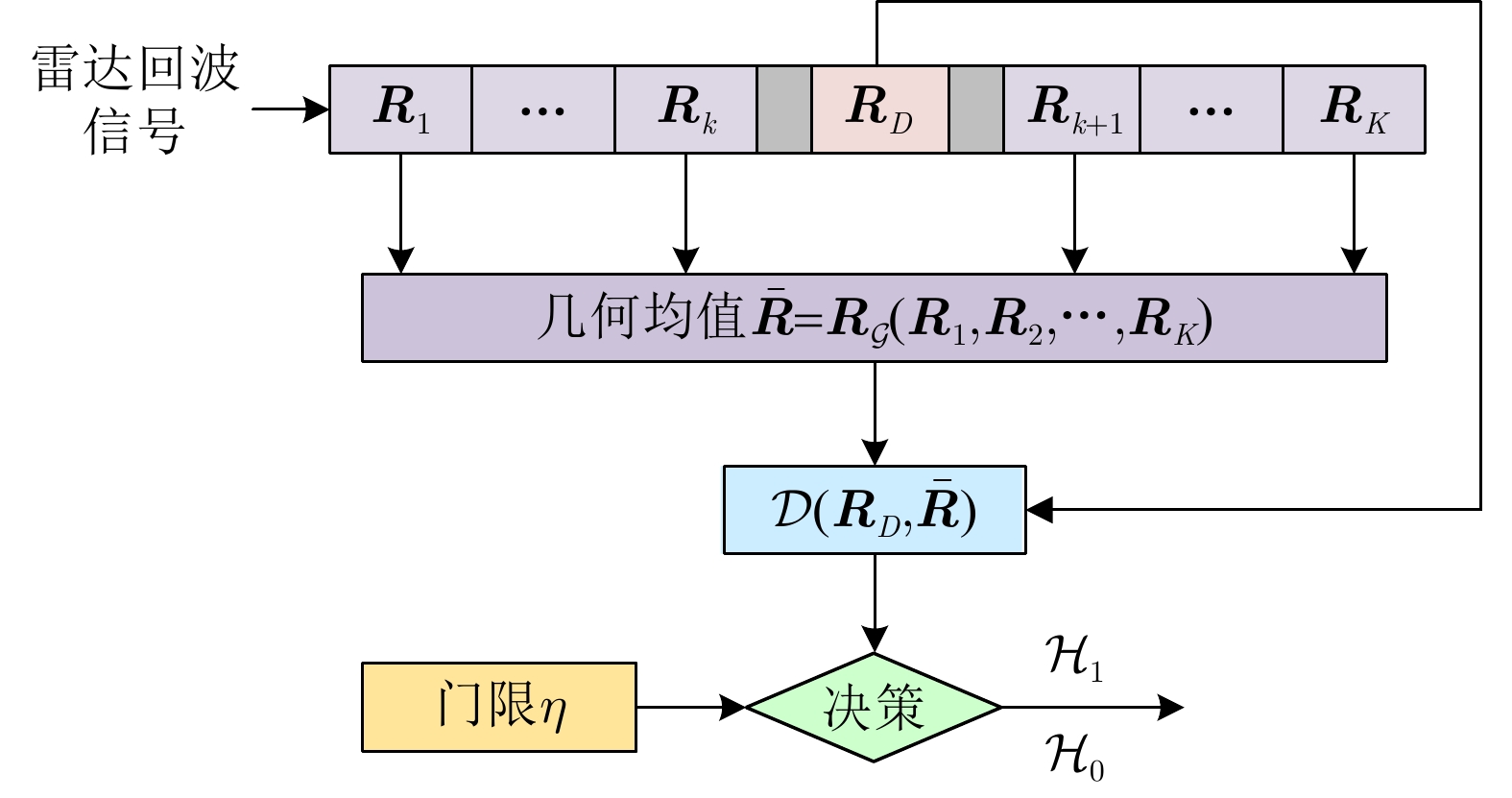
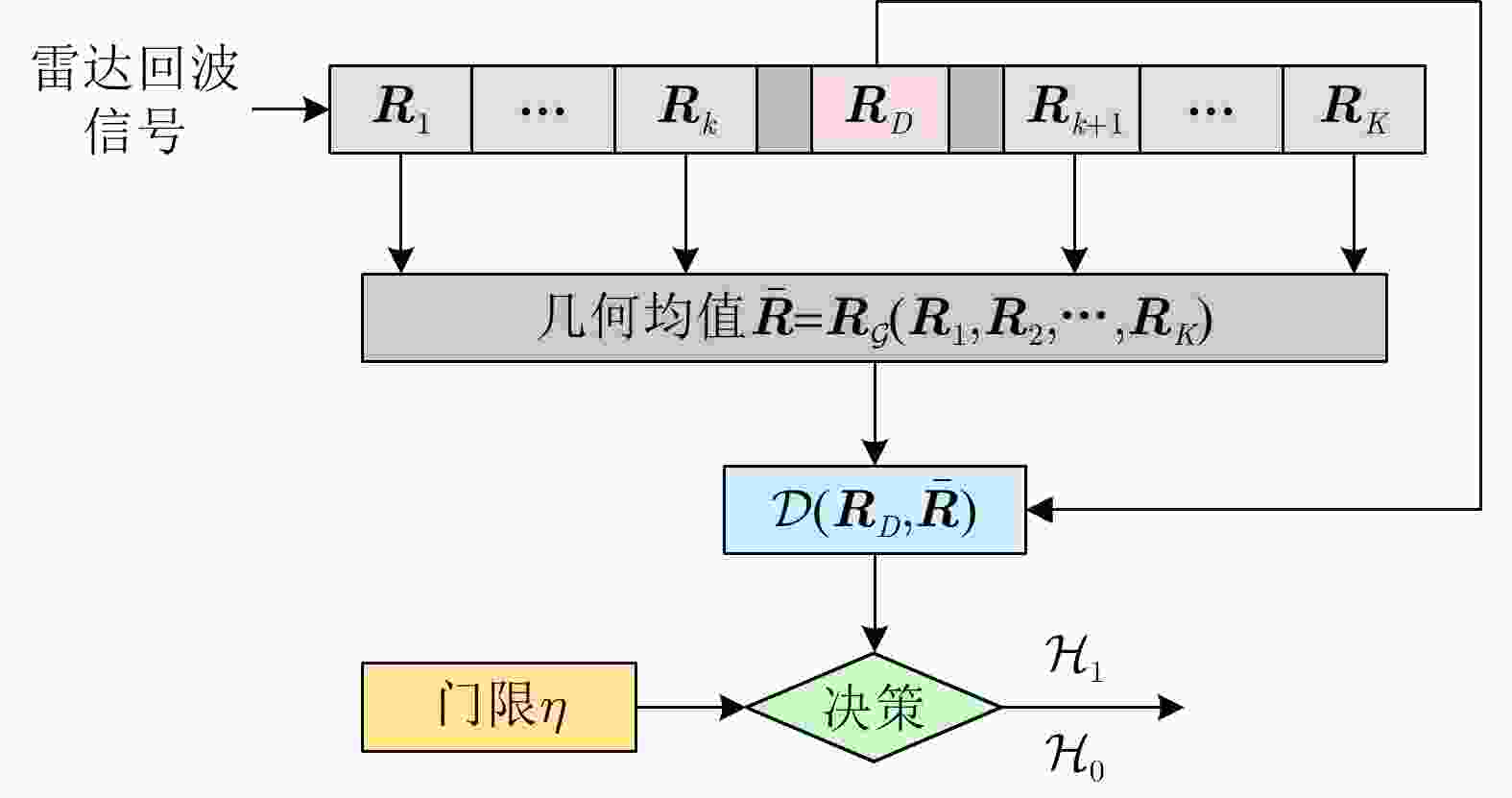
输入:雷达待检测单元回波信号$ {{\boldsymbol{z}}_D} $和杂波参考单元回波信号$ {\left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right\}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}} $。 输出:检测决策:${\mathcal{D}^{(l)} }\left( {\Re \left( { { {\boldsymbol{z} }_D} } \right),\bar \Re \left( { { {\left\{ { { {\boldsymbol{z} }_k} } \right\} }_{k \in \left[ K \right]} } } \right)} \right)\mathop \gtrless \limits_{ {\mathcal{H}_0} }^{ {\mathcal{H}_1} } {\eta ^{(l)} }, \;\;{l = - L,-(L-1), \cdots ,0, \cdots ,L}$。 For $l = - L,-(L-1), \cdots ,0, \cdots ,L$: 1:首先基于子带滤波器,对雷达回波信号进行子带滤波,获得子带滤波信号$ {\boldsymbol{z}}_D^{(l)} = \mathfrak{L}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_D}} \right) $和$ {\left\{ {{\boldsymbol{z}}_k^{(l)} = \mathfrak{L}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right)} \right\}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}} $; 2:基于流形估计子带内的杂波信号子空间,并进行稳健的正交投影,得到目标增强信号$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde z}}_D^{(l)} = \mathfrak{P}\left( {{\boldsymbol{z}}_D^{(l)}} \right) $和$ {\left\{ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde z}}_k^{(l)} = \mathfrak{P}\left( {{\boldsymbol{z}}_k^{(l)}} \right)} \right\}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}} $; 3:将基于流形正交投影后的信号表征为HPD矩阵,计算待检测单元HPD矩阵$ \Re \left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_D}} \right) $和杂波参考单元HPD矩阵$ {\left\{ {\Re \left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right)} \right\}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}} $,并计算
几何均值$ \bar \Re \left( {{{\left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right\}}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}}} \right) $;4:计算几何检测统计量$ {\mathcal{D}^{(l)}}\left( {\Re \left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_D}} \right),\bar \Re \left( {{{\left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right\}}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}}} \right)} \right) $,并与门限$ {\eta ^{(l)}} $进行比较,完成检测判决
$ {\mathcal{D}^{(l)}}\left( {\Re \left( {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_D}} \right),\bar \Re \left( {{{\left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{z}}_k}} \right\}}_{k \in \left[ K \right]}}} \right)} \right)\mathop \gtrless \limits_{{\mathcal{H}_0}}^{{\mathcal{H}_1}} {\eta ^{(l)}} $。End 表 1 不同方法的计算复杂度
Table 1. The computation complexity of different methods
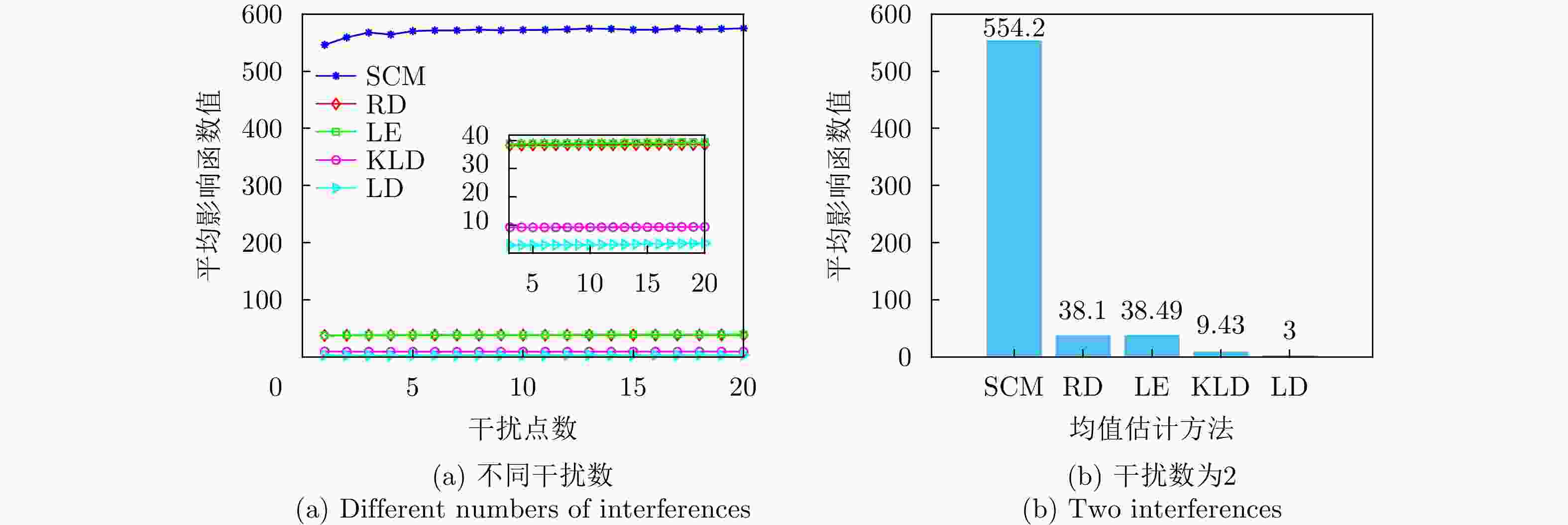
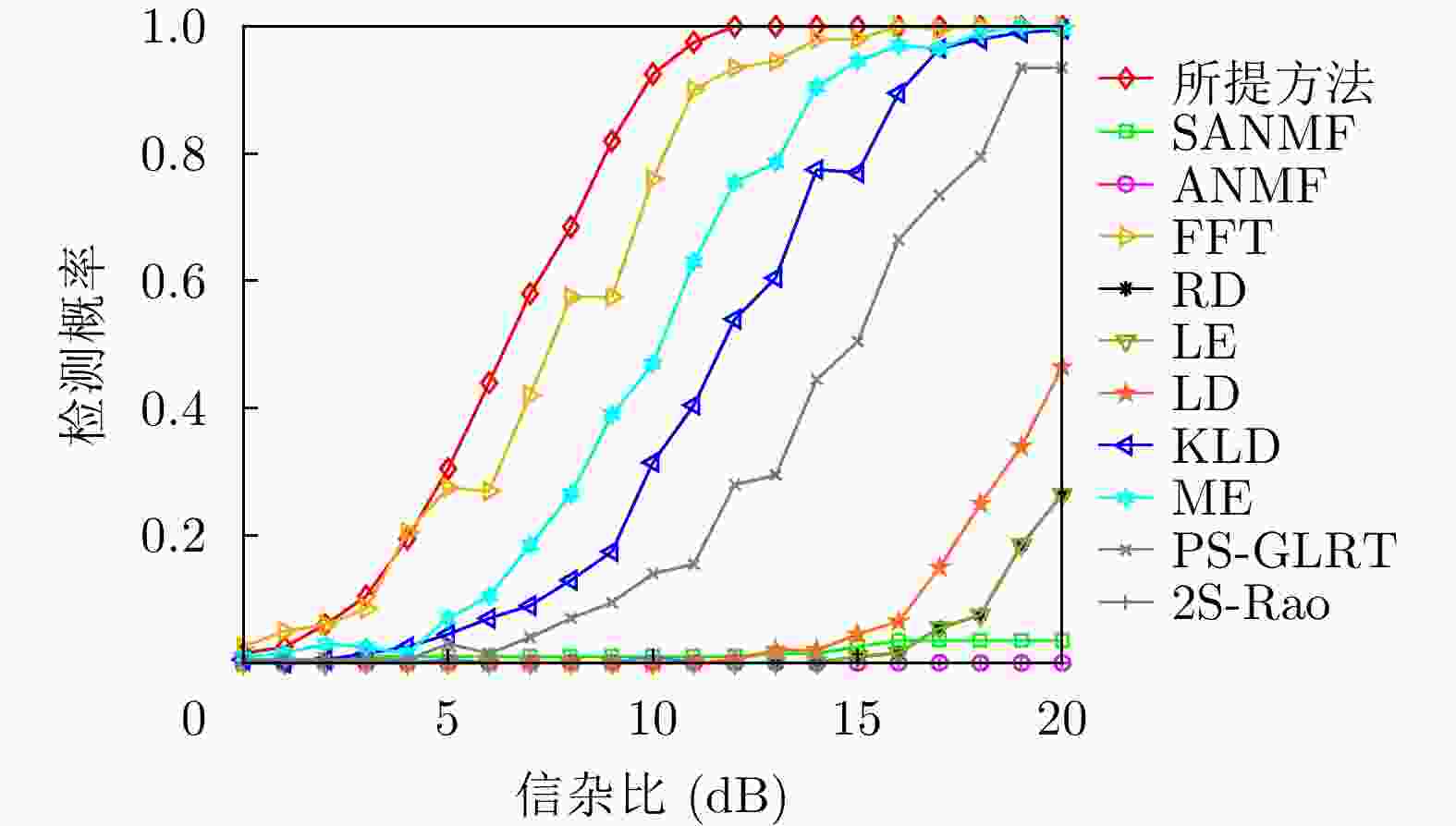
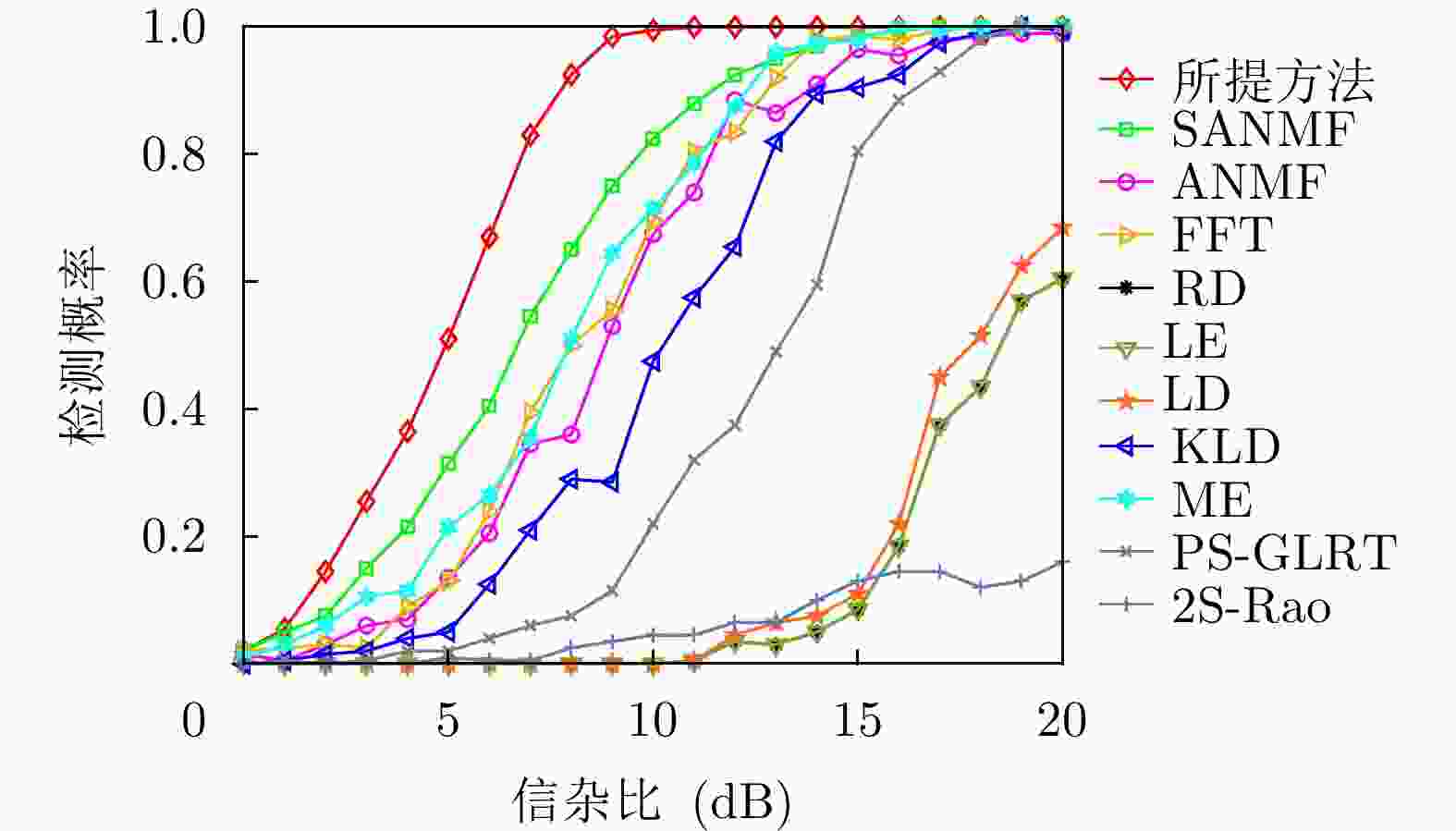
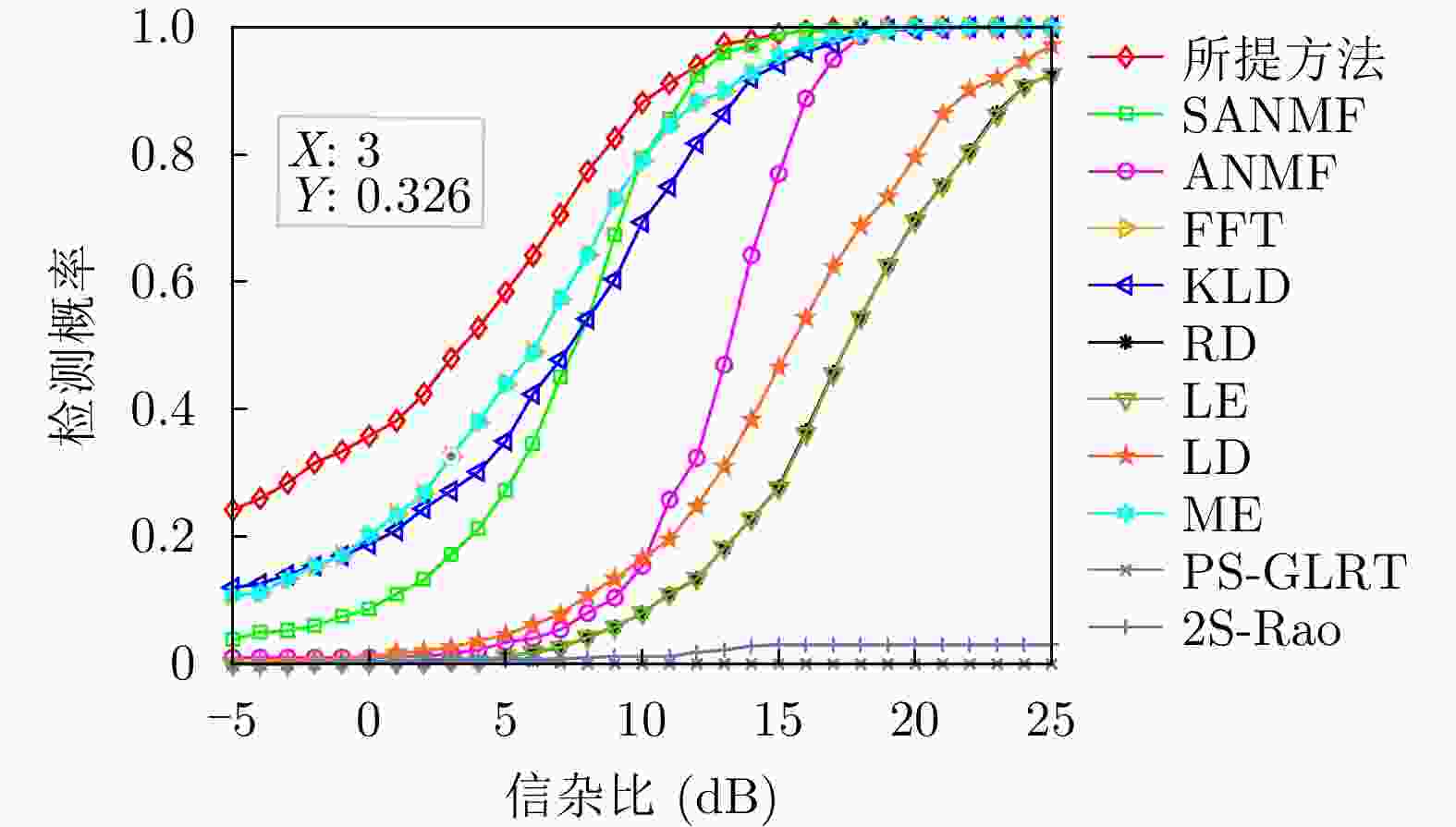
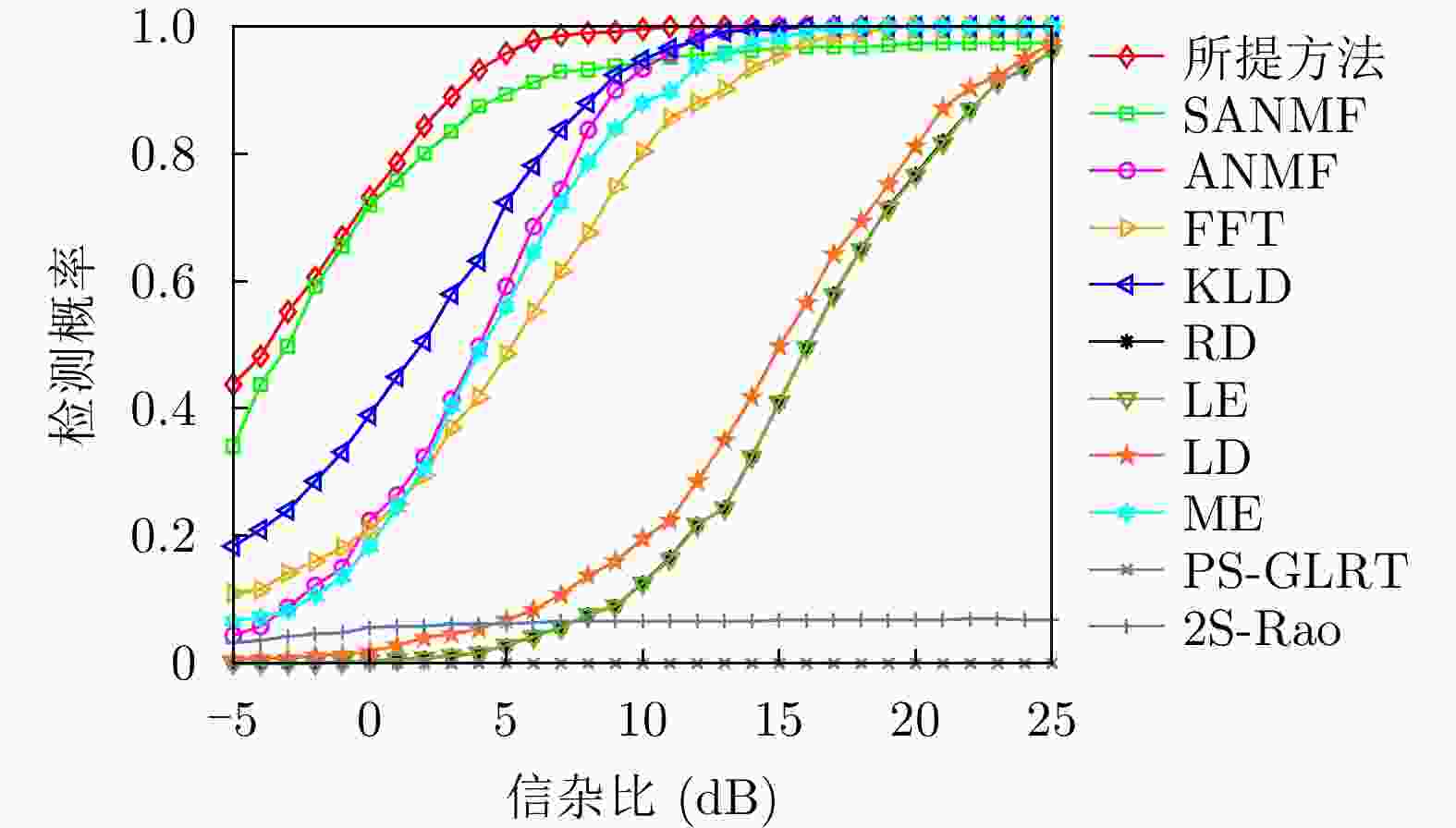
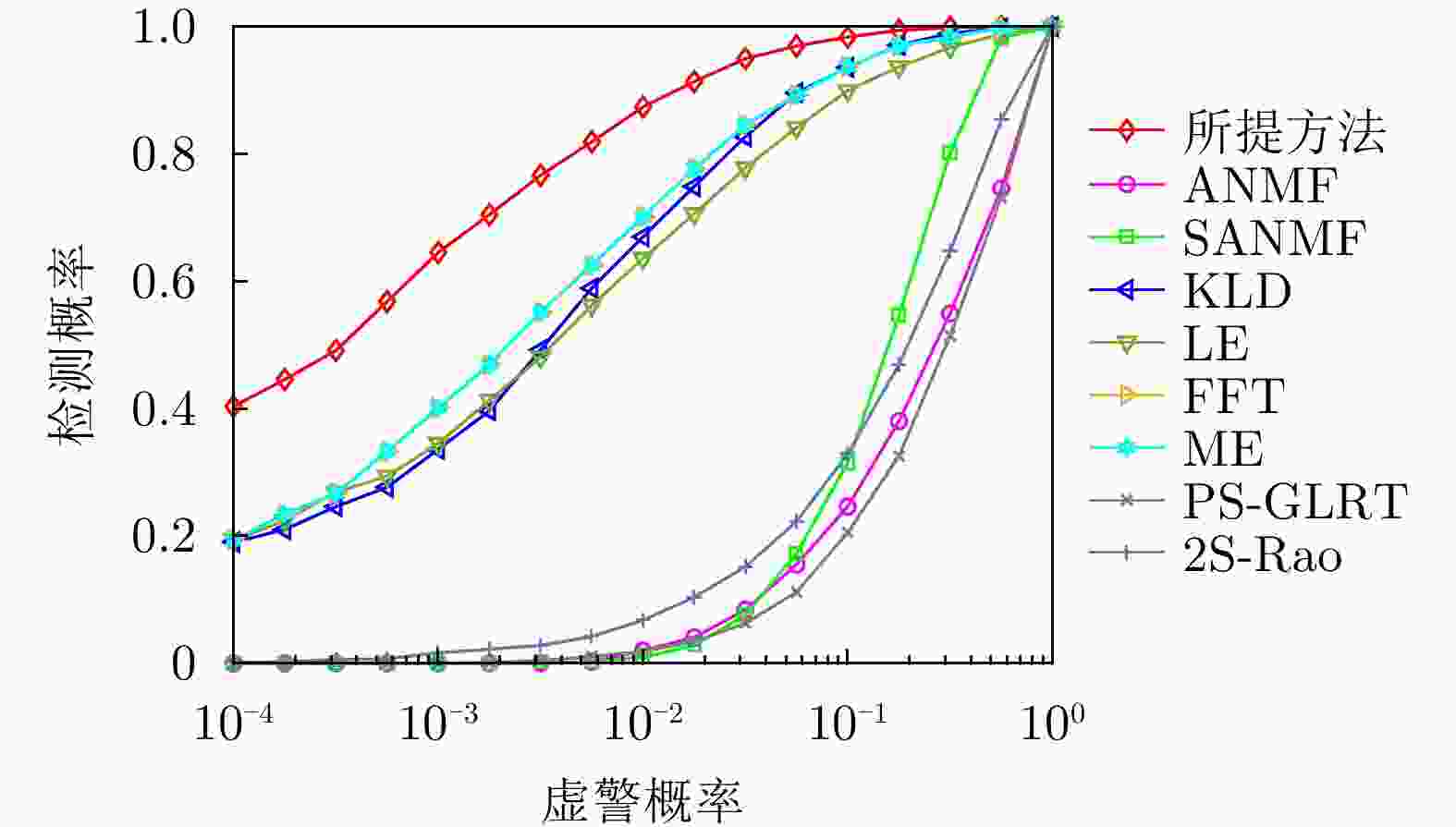
方法 计算复杂度 本文方法 $ \mathcal{O}\left( {M\left( {K{n^3} + {n^3} + \left( {n + Q} \right)\log \left( {n + Q} \right)} \right)} \right) $ RD $ \mathcal{O}\left( {\nu K{n^3}} \right) $ LE $ \mathcal{O}\left( {K{n^3}} \right) $ KLD $ \mathcal{O}\left( {K{n^3}} \right) $ LD $ \mathcal{O}\left( {\varepsilon K{n^3}} \right) $ FFT $ \mathcal{O}\left( {n\log n + Kn} \right) $ ANMF $ \mathcal{O}\left( {{n^3} + K{n^2}} \right) $ SANMF $ \mathcal{O}\left( {M\left( {{n^3} + K{n^2}} \right)} \right) $ ME $ \mathcal{O}\left( {K\left( {{n^3} + n} \right)} \right) $ PS-GLRT $ \mathcal{O}\left( {{n^3} + K{n^2}} \right) $ 2S-Rao $ \mathcal{O}\left( {{n^3} + K{n^2}} \right) $ 表 2 数据文件19980204_155537_ANTSTEP参数
Table 2. Parameters of data file 19980204_155537_ANTSTEP
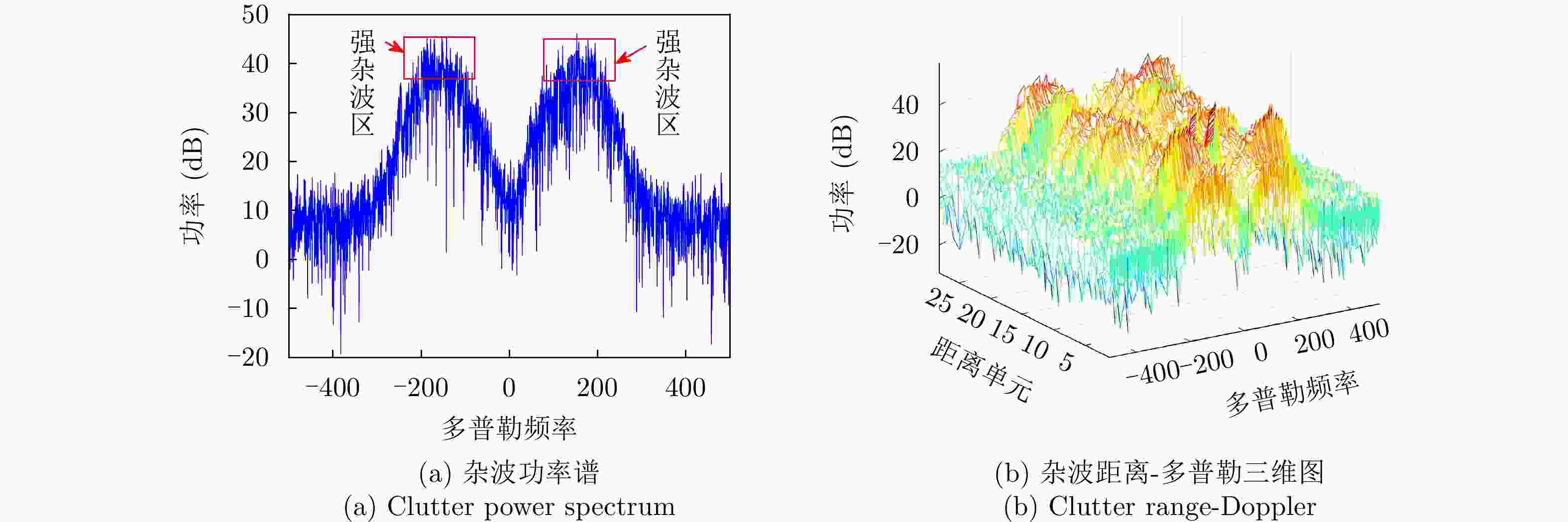
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 9.39 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1000 距离单元数 28 脉冲数 60000 距离分辨率(m) 30 表 3 数据文件20210106150614_02_staring参数
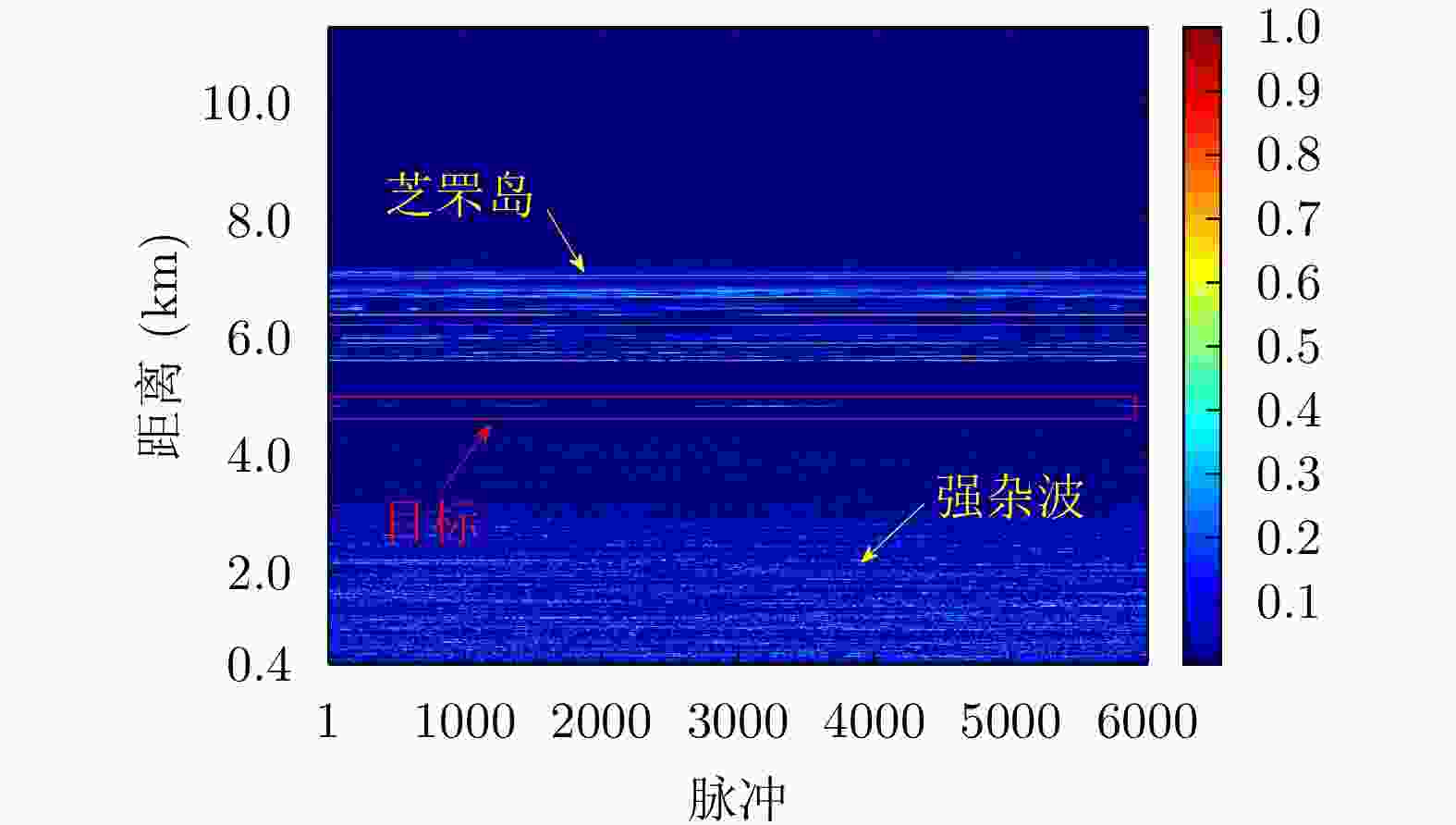
Table 3. Parameters of data file 20210106150614_02_staring
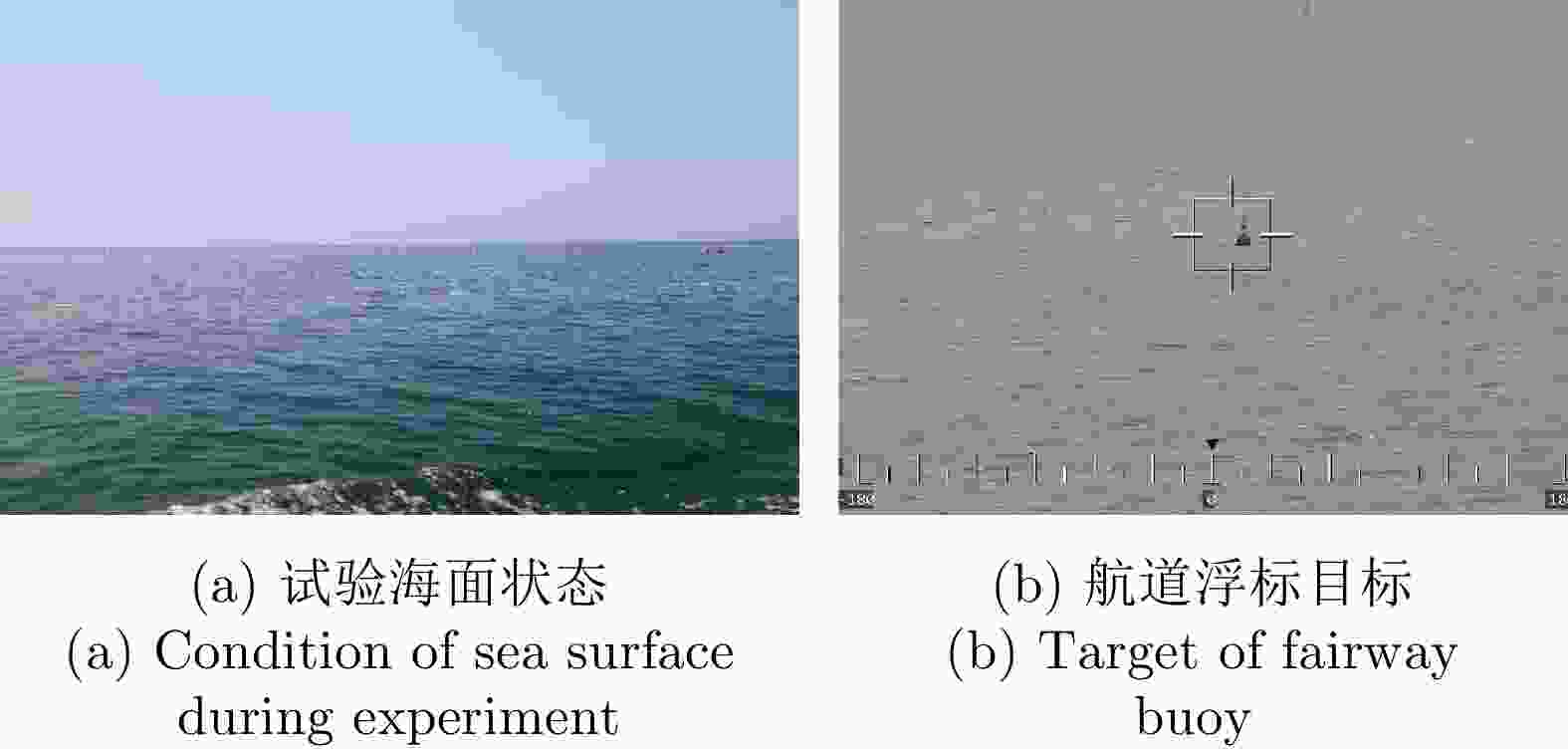
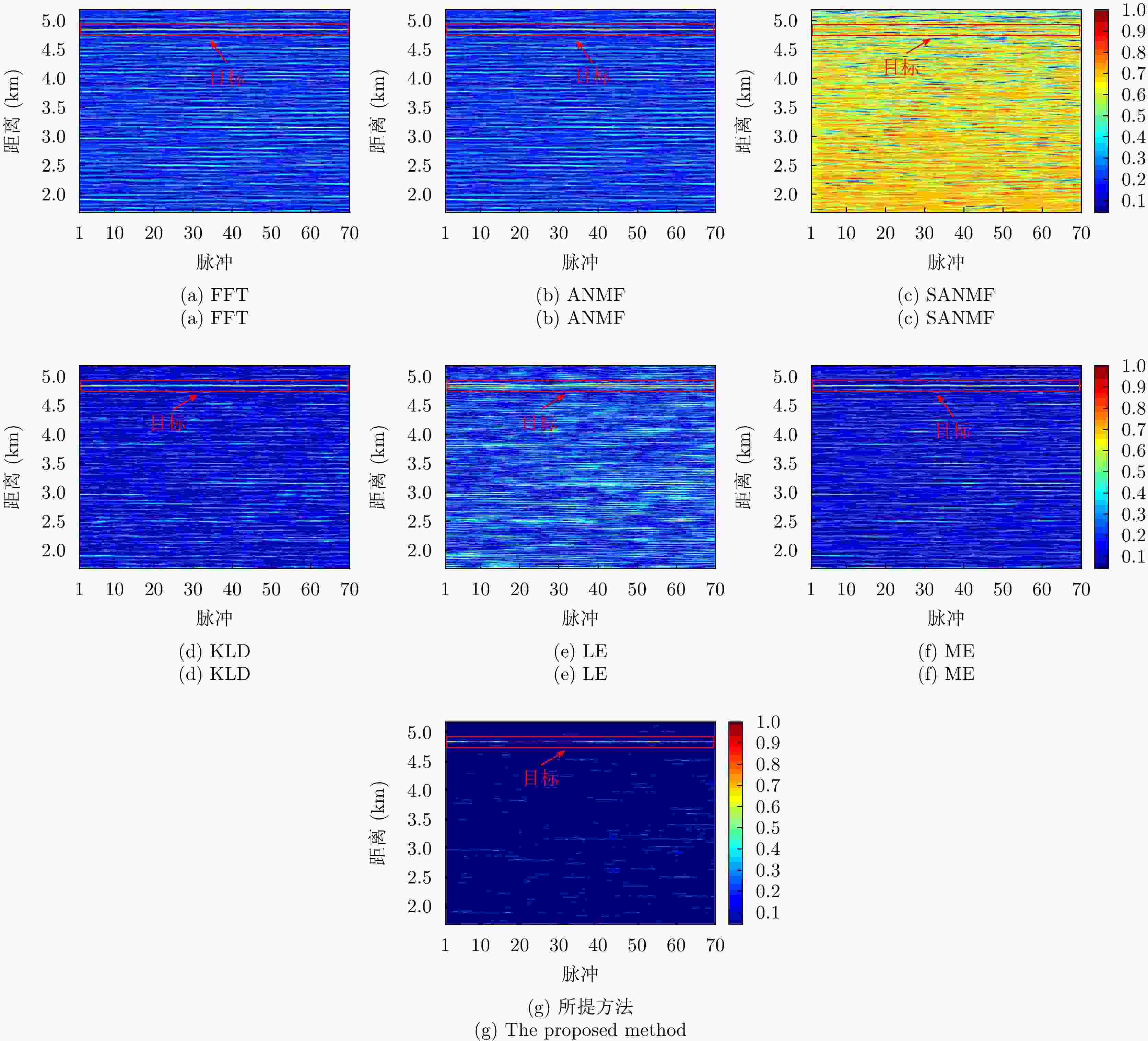
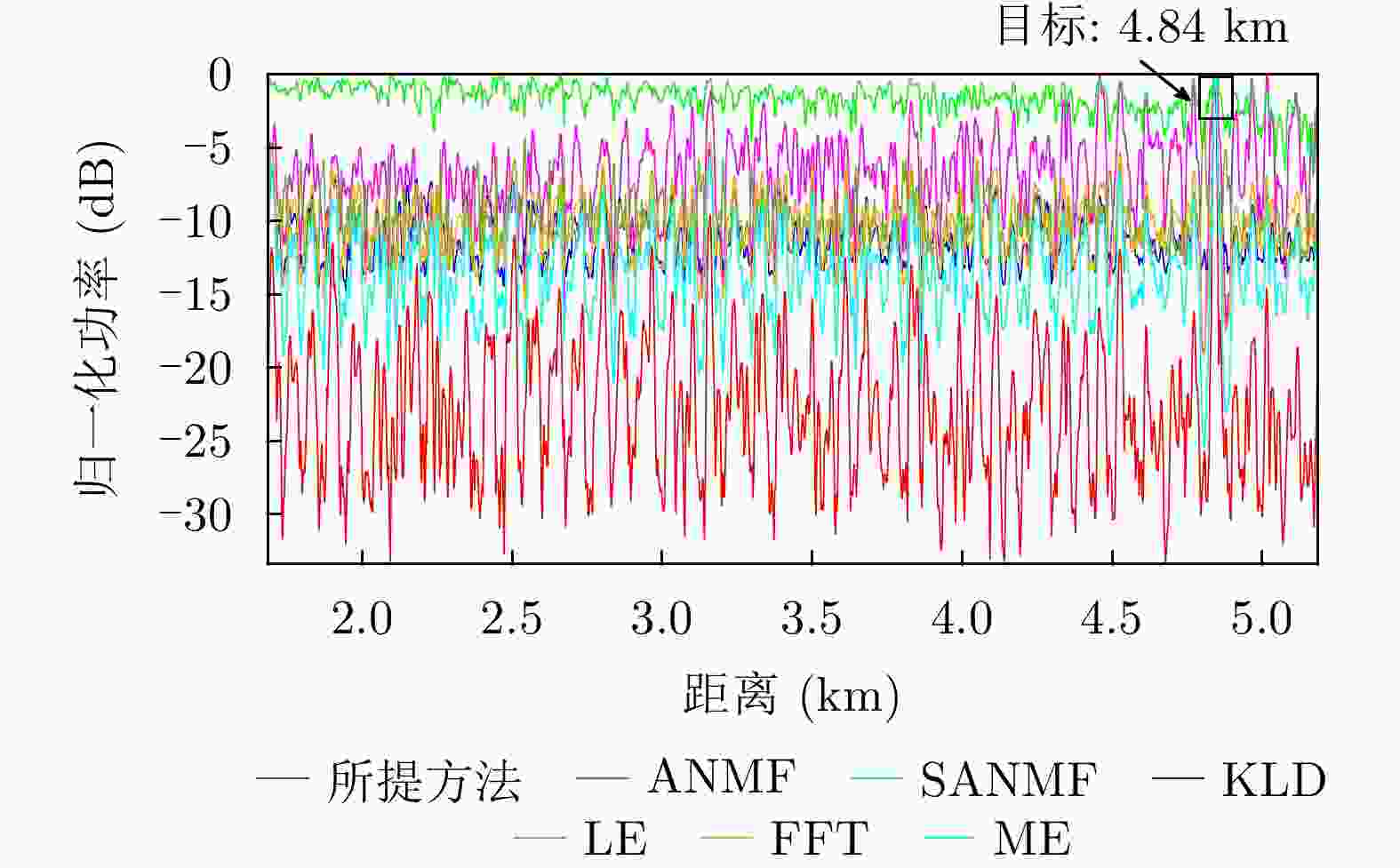
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 9.3~9.5 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1704 距离单元数 4346 脉冲数 6000 采样频率(MHz) 60 目标位置(km) 4.84 -
[1] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084 [2] 朱文涛. 海面慢速弱小目标雷达探测技术研究[J]. 科技视界, 2018(22): 64–67. doi: 10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2018.22.030ZHU Wentao. Research on radar detection technology for slow and weak targets on the sea[J]. Science &Technology Vision, 2018(22): 64–67. doi: 10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2018.22.030 [3] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测目标探测技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar low-observable target detection[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004 [4] 陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068 [5] WATTS S. Cell-averaging CFAR gain in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(5): 321–327. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960745 [6] ARMSTRONG B C and GRIFFITHS H D. CFAR detection of fluctuating targets in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1991, 138(2): 139–152. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0020 [7] CONTE E, DE MAIO A, and RICCI G. Covariance matrix estimation for adaptive CFAR detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(2): 415–426. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1008976 [8] SANGSTON K J and FARINA A. Coherent radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter: Clairvoyant detectors[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(11): 42–63. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150132 [9] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8 [10] RONG Yao, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Adaptive radar detection in low-rank heterogeneous clutter via invariance theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1492–1506. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3058447 [11] SHUI Penglang and SHI Yanling. Subband ANMF detection of moving targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3578–3593. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324742 [12] 时艳玲, 林毓峰, 梁丹丹. 非平稳海杂波背景下子带分段ANMF检测器[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(4): 782–789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.11SHI Yanling, LIN Yufeng, and LIANG Dandan. Subband segmented ANMF detector in non-stationary sea clutter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 782–789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.11 [13] 时艳玲, 王磊, 李君豪. 基于投影空间下奇异值分解的海面小目标CFAR检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(2): 512–519. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.20SHI Yanling, WANG Lei, and LI Junhao. CFAR detection for small targets on sea surface based on singular value decomposition in projection space[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 512–519. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.20 [14] YANG Yong, XIAO Shunping, and WANG Xuesong. Radar detection of small target in sea clutter using orthogonal projection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 382–386. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2875705 [15] 王炜鹏, 冯远, 单涛. 采用改进型时频滤波的海杂波抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(2): 208–216. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.02.006WANG Weipeng, FENG Yuan, and SHAN Tao. A sea clutter suppression method using improved time-frequency filtering method[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(2): 208–216. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.02.006 [16] CHENG Yongqiang, HUA Xiaoqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. The geometry of signal detection with applications to radar signal processing[J]. Entropy, 2016, 18(11): 381. doi: 10.3390/e18110381 [17] HUA Xiaoqiang, ONO Y, PENG Linyu, et al. Target detection within nonhomogeneous clutter via total Bregman divergence-based matrix information geometry detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4326–4340. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3095725 [18] HUA Xiaoqiang and PENG Linyu. MIG median detectors with manifold filter[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 188: 108176. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108176 [19] CHEN Xixi, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Heterogeneous clutter suppression via affine transformation on Riemannian manifold of HPD matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5109813. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3147494 [20] WU Hao, CHENG Yongqiang, CHEN Xixi, et al. Geodesic normal coordinate-based manifold filtering for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3183432 [21] ARNAUDON M, BARBARESCO F, and YANG Le. Riemannian medians and means with applications to radar signal processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(4): 595–604. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2261798 [22] BARBARESCO F. Innovative tools for radar signal processing based on Cartan’s geometry of SPD matrices & information geometry[C]. 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–6. [23] BARBARESCO F and MEIER U. Radar monitoring of a wake vortex: Electromagnetic reflection of wake turbulence in clear air[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2010, 11(1): 54–67. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2010.01.001 [24] HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Matrix CFAR detectors based on symmetrized Kullback-Leibler and total Kullback-Leibler divergences[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 69: 106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.06.019 [25] YANG Zheng, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Enhanced matrix CFAR detection with dimensionality reduction of Riemannian manifold[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 2084–2088. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3037489 [26] 杨政, 程永强, 吴昊, 等. 基于黎曼流形监督降维的矩阵CFAR增强检测[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(11): 2013–2021. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.11.001YANG Zheng, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Enhanced matrix CFAR detection based on supervised dimensionality reduction of Riemannian manifold[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(11): 2013–2021. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.11.001 [27] ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Wenlong, and JIN Minglu. Spectral norm based mean matrix estimation and its application to radar target CFAR detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(22): 5746–5760. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2945991 [28] WU Hao, CHENG Yongqiang, CHEN Xixi, et al. Adaptive matrix information geometry detector with local metric tensor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 3758–3773. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3189179 [29] 高永婵, 潘丽燕, 李亚超, 等. 空/时对称阵列雷达非高斯杂波背景下多秩距离扩展目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 765–777. doi: 10.12000/JR22013GAO Yongchan, PAN Liyan, LI Yachao, et al. Multi-rank range-spread target detection method for space/time symmetric array radar under non-Gaussian clutter background[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 765–777. doi: 10.12000/JR22013 [30] 丁昊, 薛永华, 黄勇, 等. 均匀和部分均匀杂波中子空间目标的斜对称自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(4): 418–430. doi: 10.12000/JR14133DING Hao, XUE Yonghua, HUANG Yong, et al. Persymmetric adaptive detectors of subspace signals in homogeneous and partially homogeneous clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(4): 418–430. doi: 10.12000/JR14133 [31] 邹鲲, 来磊, 骆艳卜, 等. 子空间干扰非高斯杂波的抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 715–722. doi: 10.12000/JR19050ZOU Kun, LAI Lei, LUO Yanbo, et al. Suppression of non-Gaussian clutter from subspace interference[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 715–722. doi: 10.12000/JR19050 [32] CABANES Y, BARBARESCO F, ARNAUDON M, et al. Unsupervised machine learning for pathological radar clutter clustering: The p-mean-shift algorithm[C]. C&ESAR 2019, Rennes, France, 2019: 1–21. [33] AMARI S I. Information Geometry and Its Applications[M]. Tokyo: Springer, 2016: 1–376. [34] MOAKHER M. A differential geometric approach to the geometric mean of symmetric positive-definite matrices[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2005, 26(3): 735–747. doi: 10.1137/S0895479803436937 [35] MOAKHER M. On the averaging of symmetric positive-definite tensors[J]. Journal of Elasticity, 2006, 82(3): 273–296. doi: 10.1007/s10659-005-9035-z [36] HIAI F and PETZ D. Riemannian metrics on positive definite matrices related to means[J]. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 2009, 430(11/12): 3105–3130. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2009.01.025 [37] ARSIGNY V, FILLARD P, PENNEC X, et al. Geometric means in a novel vector space structure on symmetric positive-definite matrices[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2007, 29(1): 328–347. doi: 10.1137/050637996 [38] MOAKHER M and BATCHELOR P G. Symmetric Positive-Definite Matrices: From Geometry to Applications and Visualization[M]. WEICKERT J and HAGEN H. Visualization and Processing of Tensor Fields. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 285–298. [39] CHERIAN A, SRA S, BANERJEE A, et al. Jensen-Bregman LogDet divergence with application to efficient similarity search for covariance matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(9): 2161–2174. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.259 [40] ZHANG Xianda. Matrix Analysis and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017: 1–723. [41] HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Robust covariance estimators based on information divergences and riemannian manifold[J]. Entropy, 2018, 20(4): 219. doi: 10.3390/e20040219 [42] ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Chang, LIU Wenlong, et al. Maximum eigenvalue-based target detection for the K-distributed clutter environment[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(11): 1294–1306. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5229 [43] MAO Linlin, GAO Yongchan, YAN Shefeng, et al. Persymmetric subspace detection in structured interference and non-homogeneous disturbance[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(6): 928–932. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2913332 [44] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, and HUANG Lei. Rao tests for distributed target detection in interference and noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 117: 333–342. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.06.012 [45] IPIX Radar File. IPIX radar dataset files in Grimsby on the shores of Lake Ontario[OL]. http://soma.mcmaster.ca/ipix. 1998. [46] 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089 [47] 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: