Analysis and Experimental Validation of Key Technologies for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-borne Bistatic Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar
-
摘要: 双站干涉合成孔径雷达(SAR)技术可突破单站双天线干涉SAR的基线限制,获得更加灵活的基线构型,有利于提升干涉测量精度。无人机载双站干涉SAR机动性好、飞行成本低,具有很高的应用价值,也能为无人机载分布式干涉、三维成像等提供关键支撑,具有重要的研究意义。中国科学院空天信息创新研究院牵头设计研制了国内首套无人机载双站干涉SAR系统,并在内蒙古百灵机场开展了飞行实验。该文简要介绍了该系统方案设计、基本构成和主要性能,并重点介绍了该系统的空间、时间及相位同步和数据处理关键技术,然后介绍了首次飞行实验的方案和实施研究情况,最后给出了实验数据处理结果,验证了关键技术和该无人机载双站干涉SAR系统0.5 m高程测量精度等主要指标,为后续多无人机平台协同开展分布式干涉数据获取及处理研究提供了基础。Abstract: Bistatic interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) overcomes the baseline length limit of the configuration of single-station interferometric SAR with two antennas and has become the primary method of terrain mapping using spaceborne interferometric SAR. To reduce the cost of surveying and mapping while promoting the development and application of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-borne bistatic interferometric SAR, the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences took the lead in designing and developing a UAV-borne bistatic interferometric SAR processing system and performed flight experiments at Bailing Airport in Inner Mongolia. Herein, the system design, composition, and performance are introduced, and the scheme and implementation of the first flight experiment, along with the preliminary data processing results, are presented. In addition, the key performance metrics of the system, such as 0.5 m-elevation measurement accuracy, are verified in this study. The system serves as a foundation for future research topics, such as distributed InSAR using a multiaviation platform and tomography data acquisition and processing.
-
表 1 无人机载双站InSAR系统误差分配
Table 1. Systematic error distribution of UAV-borne bistatic InSAR
参数名称 参数值 飞行高度(相对于地面) 2 km 入射角 45° 基线角 0° 有效基线长度 30 m 水平基线长度 42.43 m 航迹控制精度(分配值) 1 m 时间同步引入的包络对齐误差 0.1个采样单元 运补残余误差导致的干涉相位误差 1° 同步链的干涉相位误差(分配值) 5° 去相干引入的相位误差 2.54° 基线测量误差(分配值) 4 mm 基线角误差(分配值) 0.003° 高程误差(理论分析值) 0.46 m 表 2 无人机载双站InSAR系统总体构成
Table 2. Overall composition of the UAV-borne bistatic InSAR system
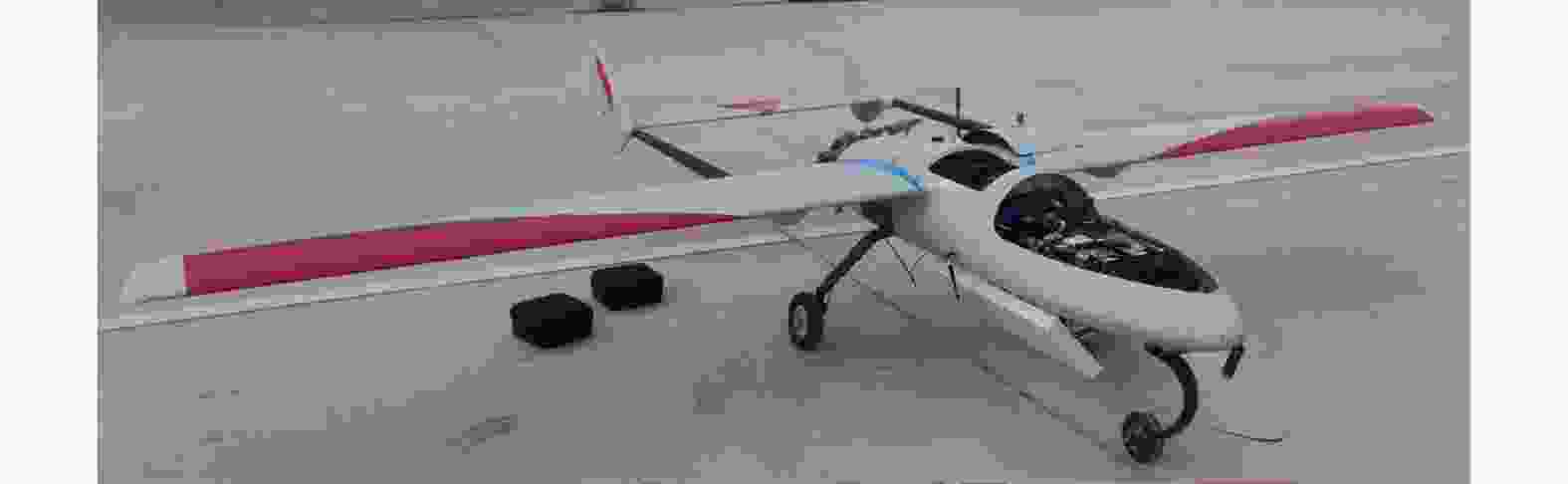
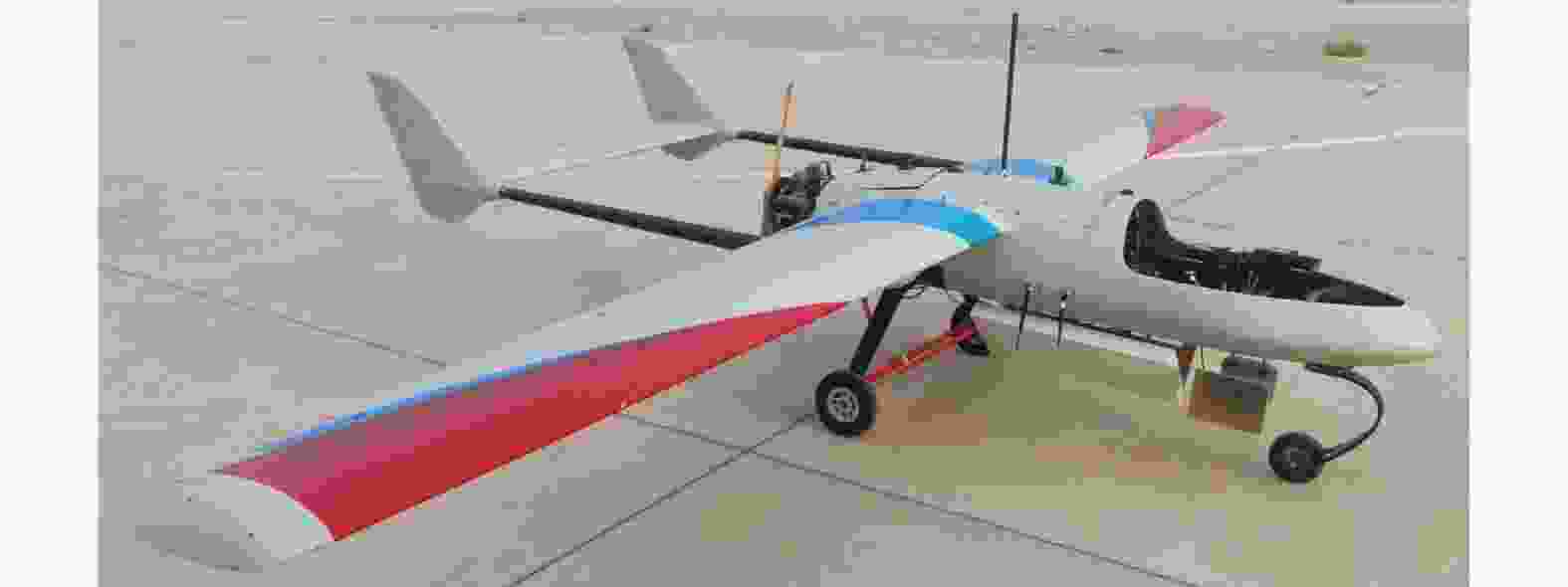
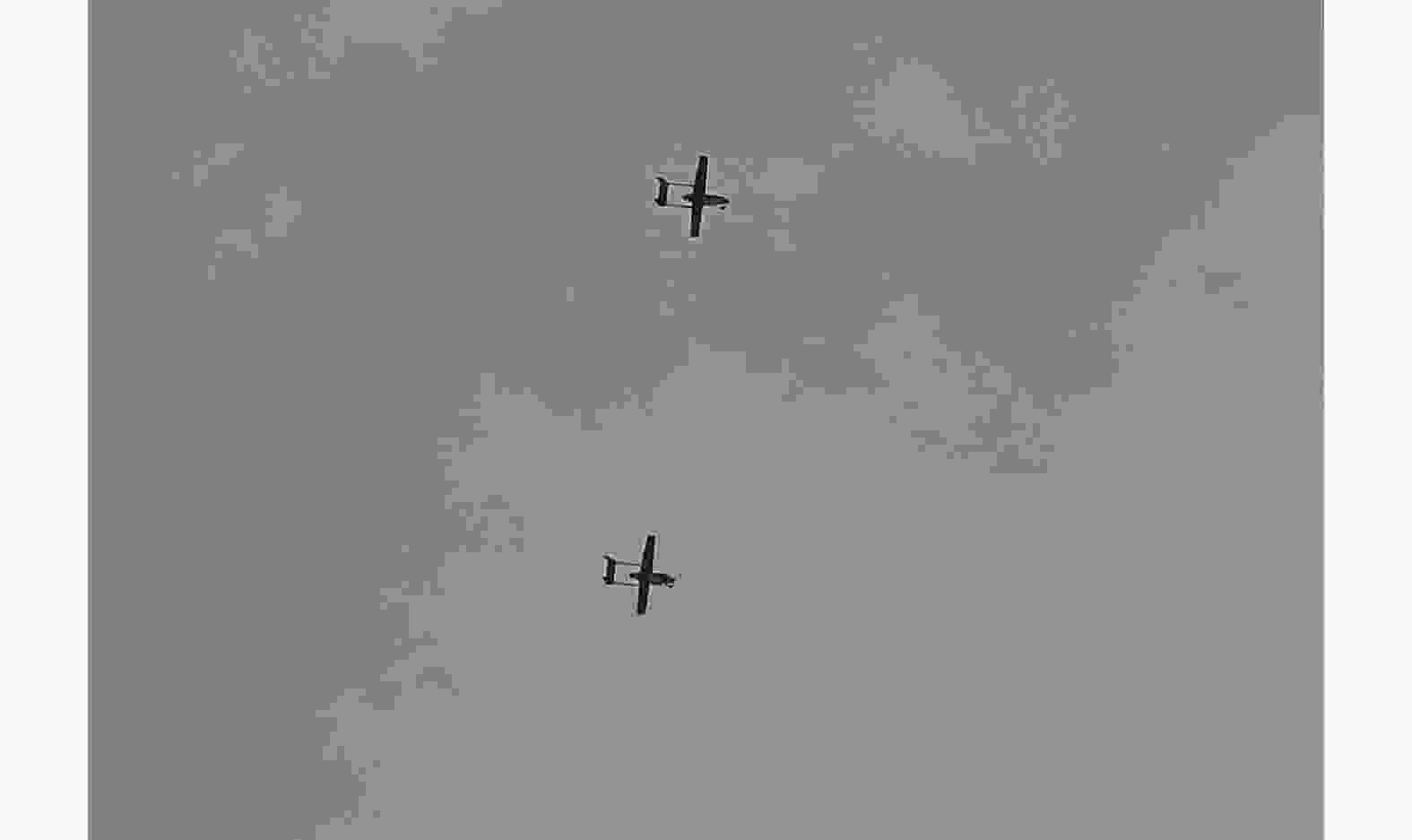
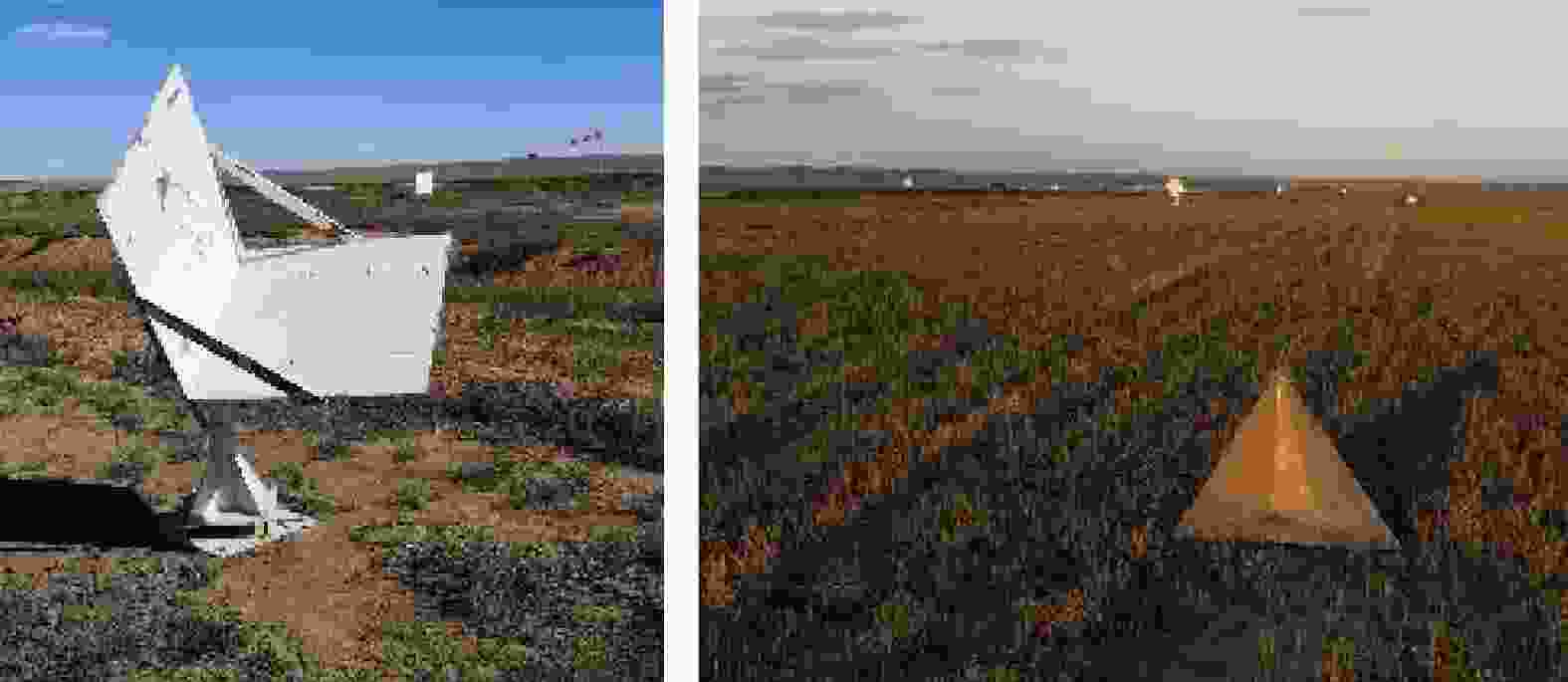
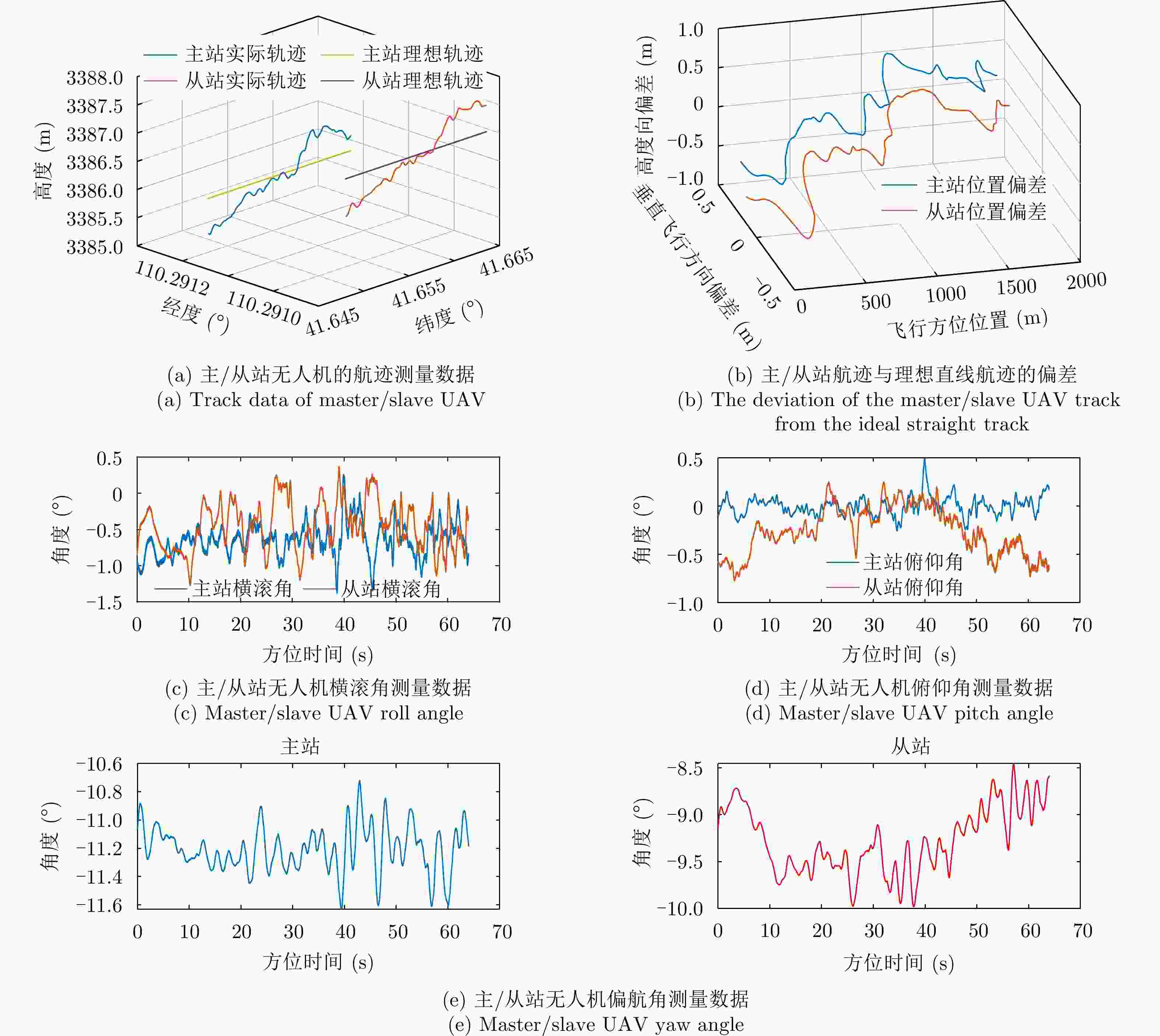
名称 说明 L-SAR(主站) 由L波段全极化SAR和双向同步链组成,其中,L波段全极化SAR由信号产生与发射通道、功放、双极化接收通道、天线及天线支架、开关组合、数据采集存储模块等组成 L-接收系统(从站) 由L波段双极化接收系统和双向同步链组成,其中L波段双极化接收系统由双极化接收通道、天线及天线支架、数据采集存储模块等组成 无人机双机编队 由两架固定翼HC-140无人机和两套协同控制器组成,其中,单架无人机最大作业载荷30 kg、最大翼展尺寸5.4 m,最大飞行速度45 m/s 位姿测量系统 由差分GPS模块和微型惯性测量组成;测量数据更新频率为200 Hz,地面后处理后,航迹测量精度0.05 m,偏航角测量精度0.02°,横滚和俯仰角测量精度0.015° 表 3 L-SAR载荷参数
Table 3. L-SAR load parameters
名称 参数名称 参数值 系统 波段 L波段 系统同步误差 ≤5° 噪声等效后向散射系数(NEσ0) ≤40 dB 主站 分辨率 ≤0.5 m 最大信号带宽 400 MHz 最大作用距离 ≥6 km 最大测绘带宽 ≥3 km 主站/从站 极化方式 全极化 极化隔离度 ≥25 dBc 极化通道相位不平衡度 ≤8° 幅度不平衡度 ≤0.3 dB 表 4 双站InSAR构型参数
Table 4. Configuration parameters of bistatic InSAR
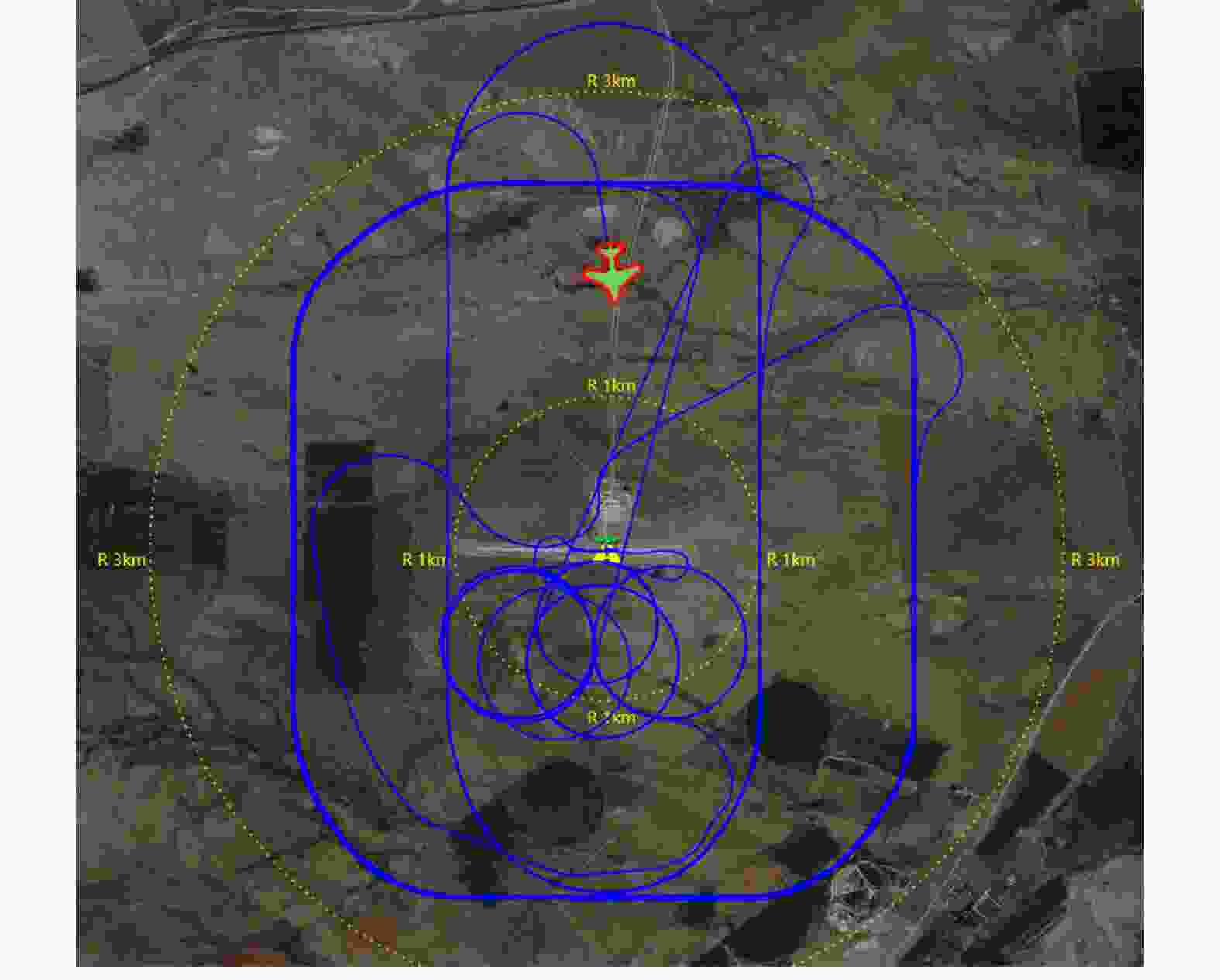
模式 飞行高度(m) 基线(m) 说明 模式1 1000 30 双站角0.87o,基线长度探底双机协同飞行安全距离的下限 模式2 2000 50 双站角0.72o,各项参数均比较合适 表 5 分辨率测试结果
Table 5. Results of resolution test
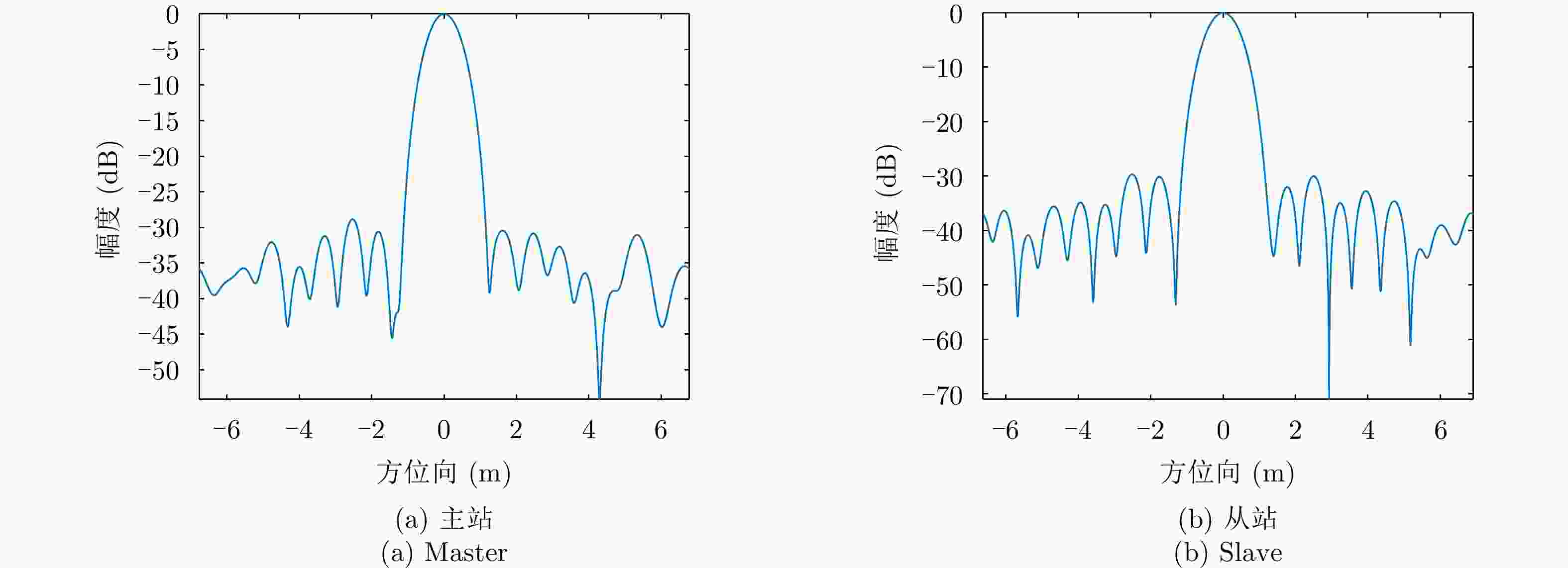
分辨率 距离向(m) 方位向(m) 主站 0.3747 0.4534 从站 0.3747 0.4860 表 6 主站数据极化定标前后的三面角极化质量评价
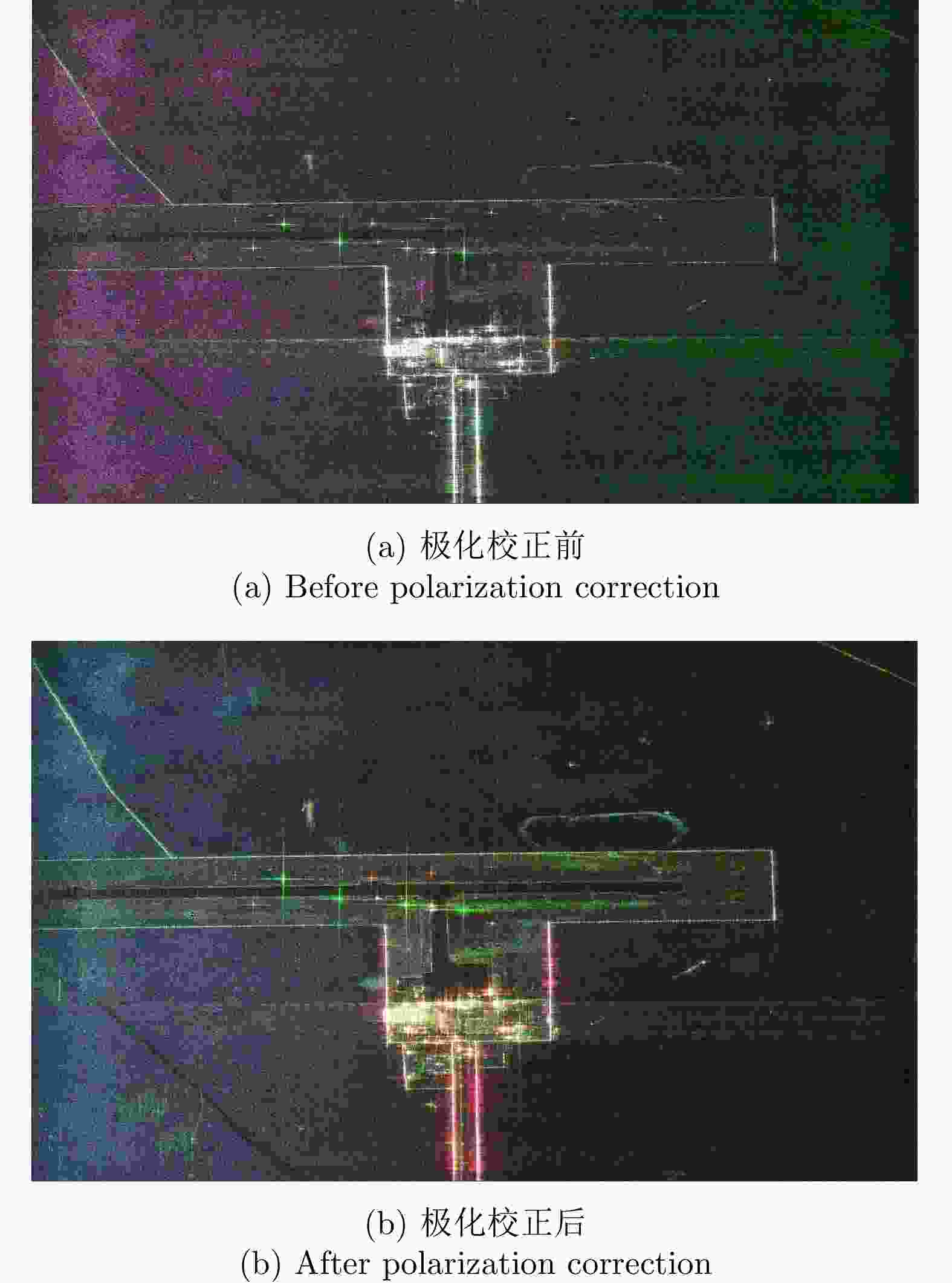
Table 6. Polarization quality evaluation of master data before and after polarization calibration based on trihedral corners
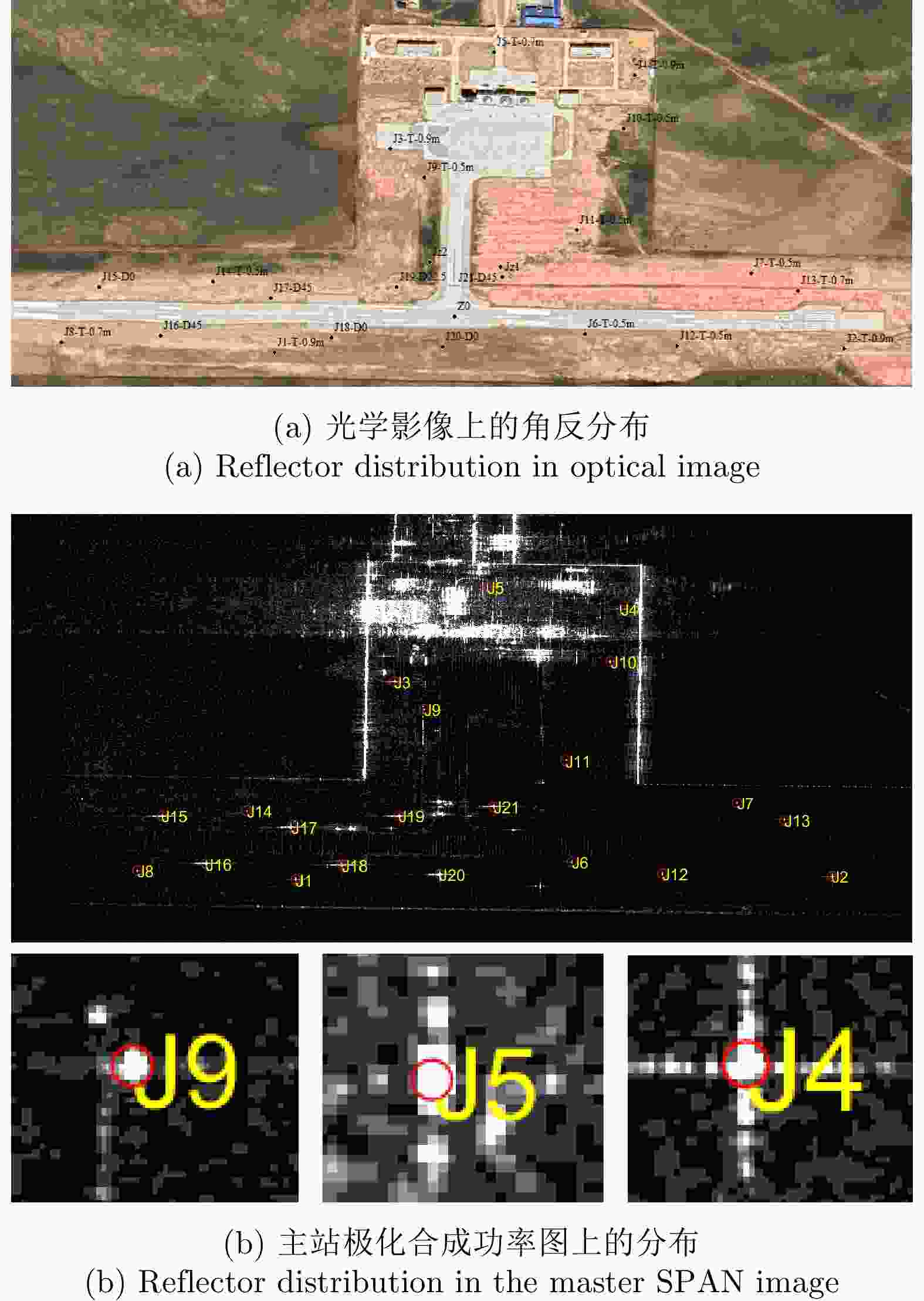
状态 三面角编号 隔离度(dB) 幅度不平衡(dB) 相位不平衡(°) 极化校正前 J2* 29.3217 0.21983 99.8529 J3 36.6858 0.44359 97.3340 J4 28.0391 –0.05674 98.3664 极化校正后 J2* 322.3542 5.786E–15 –7.2788E–15 J3 32.2467 0.15738 –3.2333 J4 37.7835 –0.32067 –1.2498 注:表中带*的J2为定标中使用的三面角,其余定标中未用 表 7 从站数据极化定标前后的三面角极化质量评价
Table 7. Polarization quality evaluation of slave data before and after polarization calibration based on trihedral corners
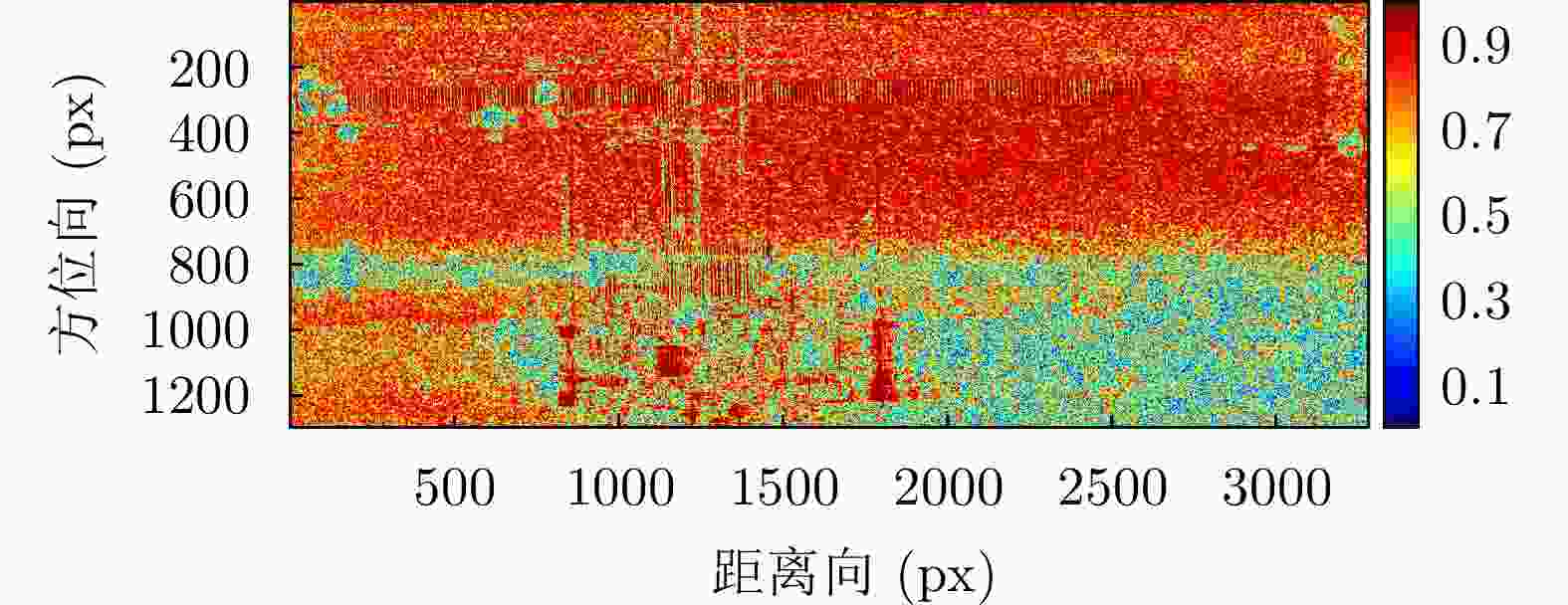
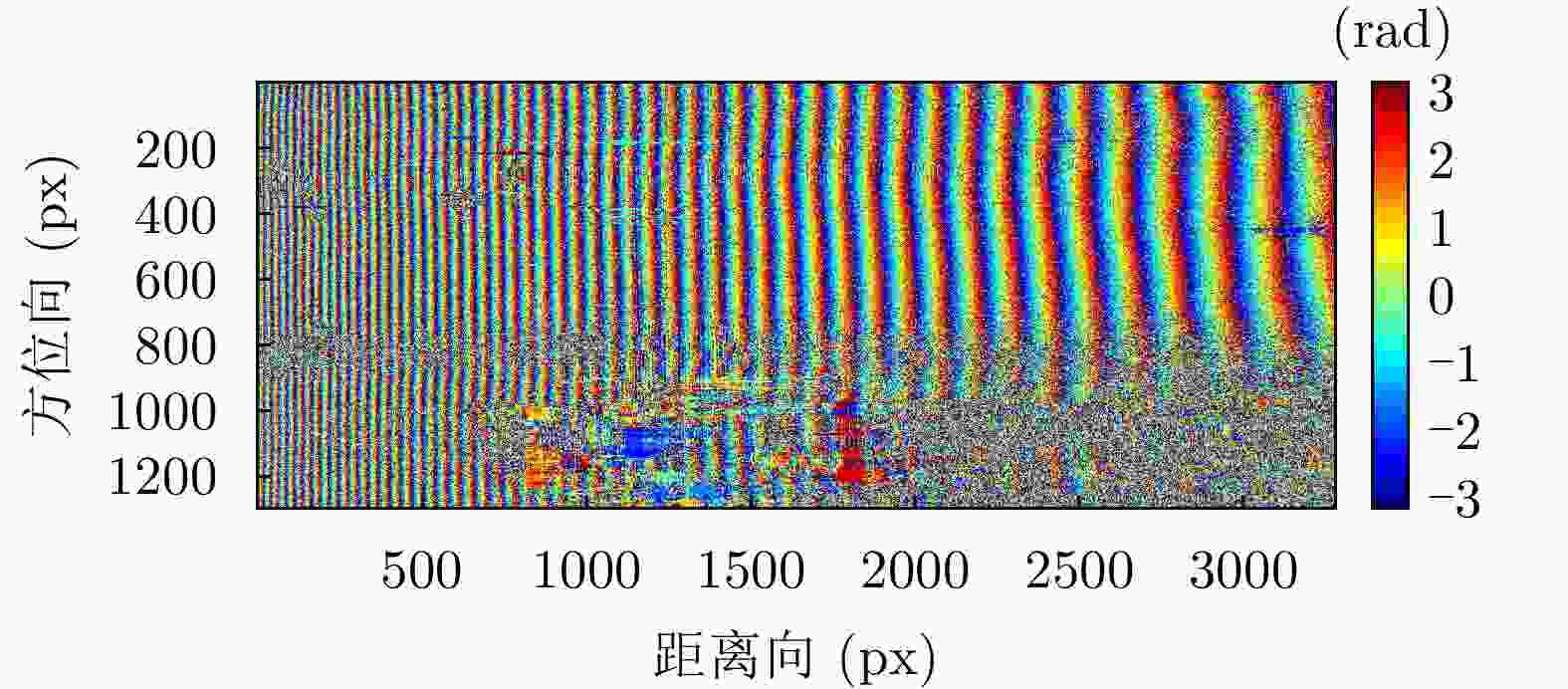
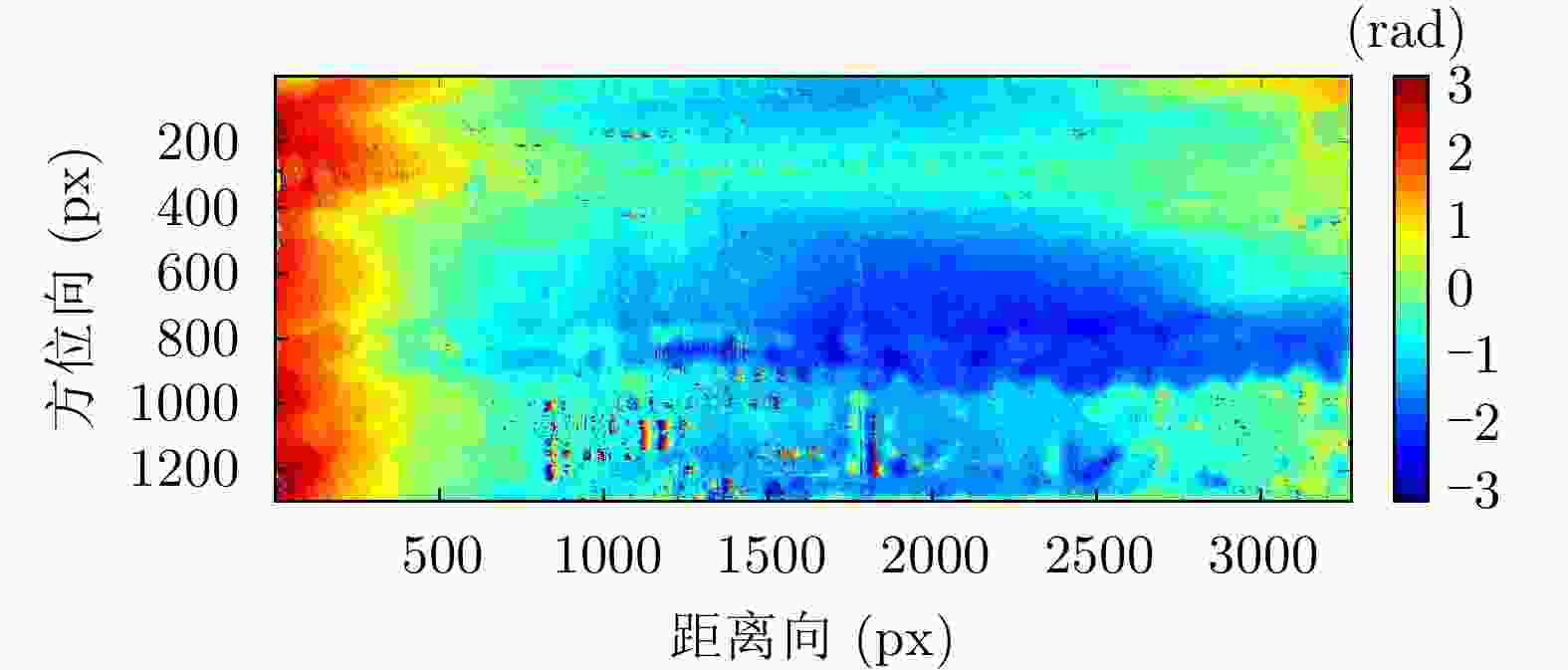
状态 三面角编号 隔离度(dB) 幅度不平衡(dB) 相位不平衡(°) 极化校正前 J2* 28.4590 –0.23950 –90.2117 J3 26.8158 –0.08019 –87.2605 J4 27.9540 –0.71433 –86.5173 极化校正后 J2* 311.252 –2.893E–15 3.317E–14 J3 31.8702 0.065833 2.3704 J4 33.8167 –0.493960 3.3900 注:表中带*的J2为定标中使用的三面角,其余定标中未用 表 8 双站SAR干涉反演高度误差表
Table 8. Table of elevation inversion error of bistatic interferometric SAR
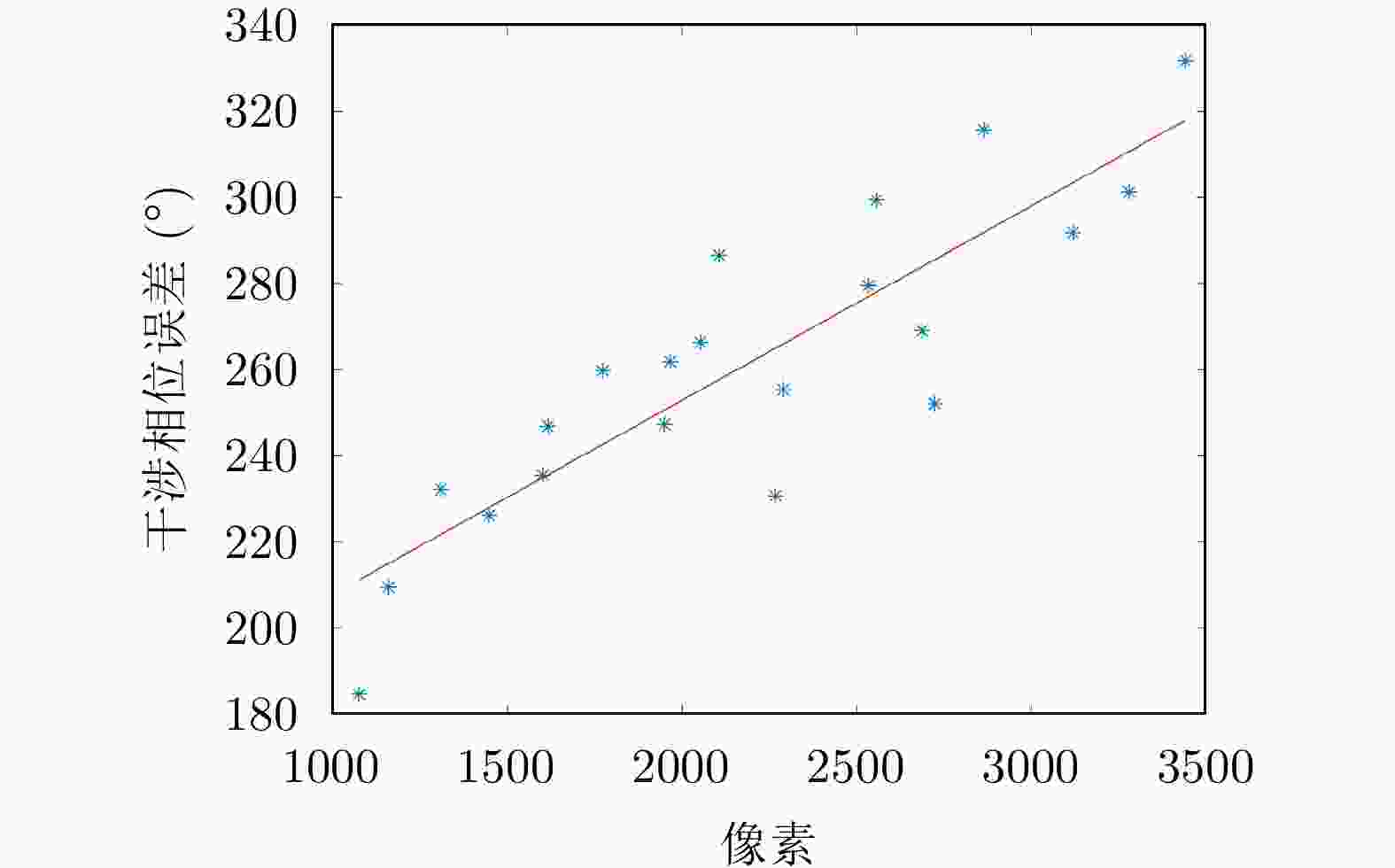
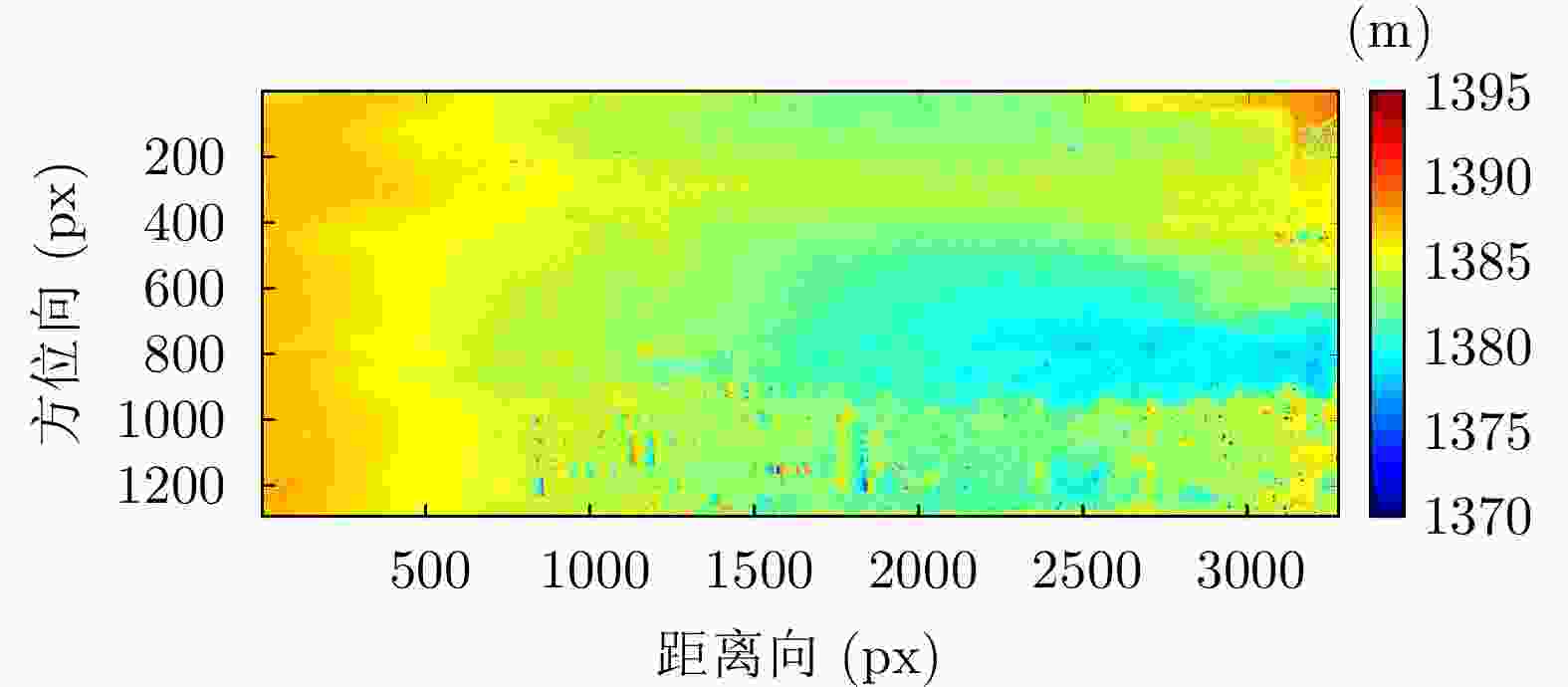
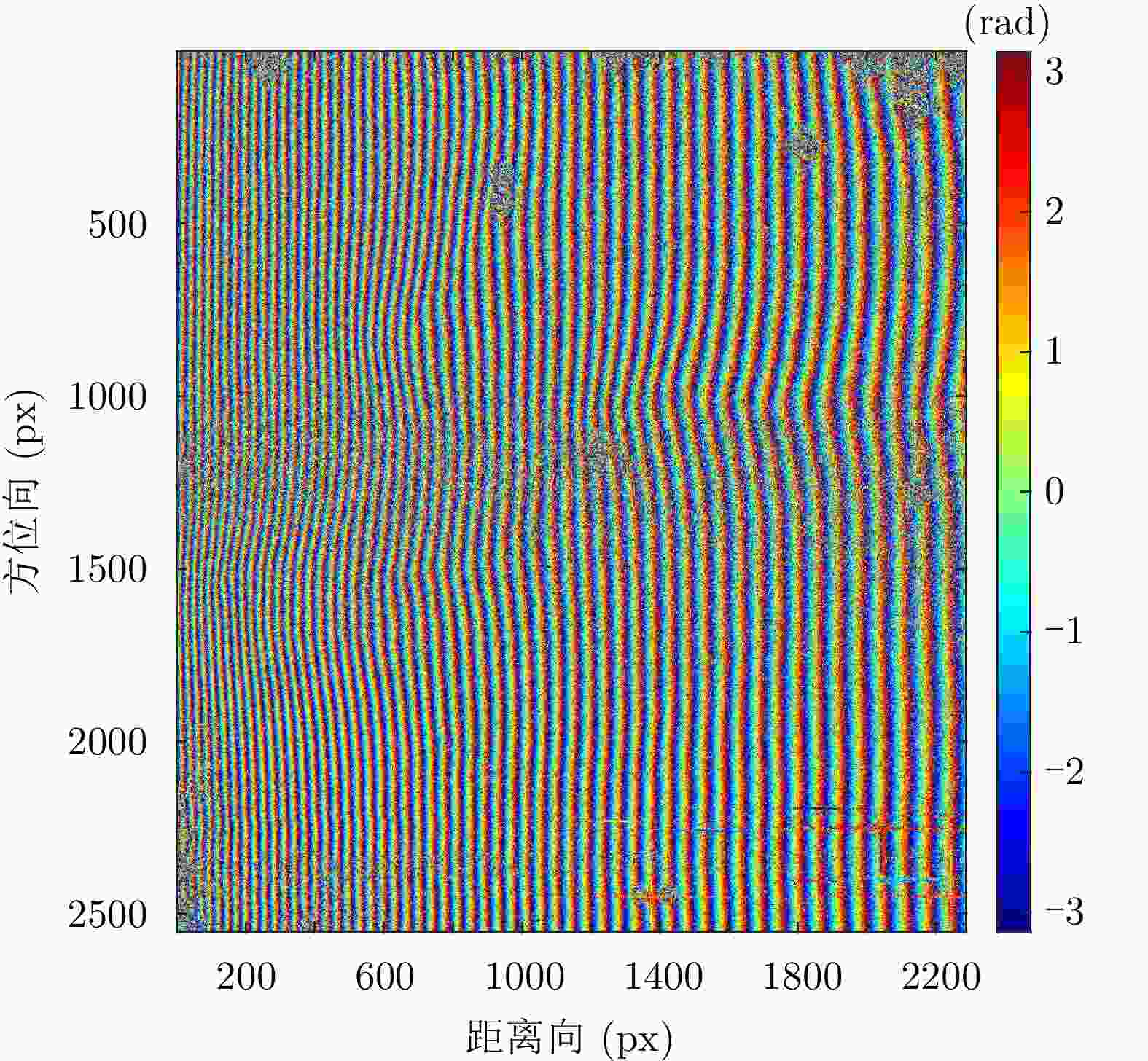
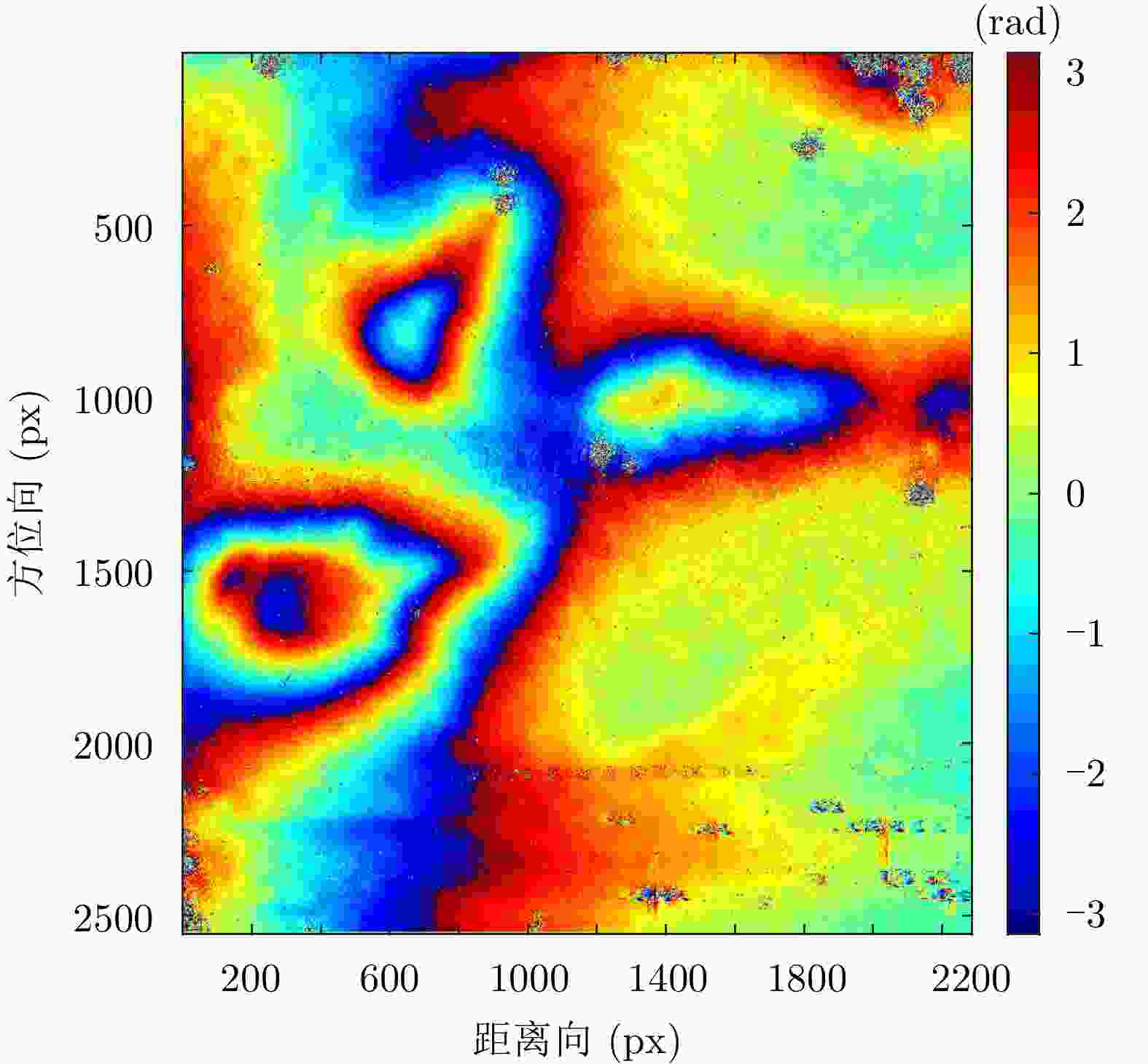
定标点 相干系数 反演高度(m) 实测高度(m) 误差(m) J1 0.97 1385.89 1385.71 0.18 J2 0.89 1383.39 1383.23 0.17 J3 0.93 1385.14 1384.86 0.28 J4 0.97 1382.56 1383.68 –1.12 J5 0.86 1383.23 1384.45 –1.21 J6 0.98 1383.81 1384.38 –0.56 J7 0.99 1382.40 1382.11 0.29 J8 0.96 1387.60 1387.05 0.55 J9 0.92 1383.41 1384.28 –0.87 J10 0.87 1380.68 1383.05 –2.37 J11 0.98 1382.76 1383.38 –0.61 J12 0.96 1383.26 1383.61 –0.35 J13 0.98 1383.29 1382.98 0.31 J14 0.96 1385.93 1386.03 –0.09 J15 0.66 1386.80 1387.79 –1.00 J16 0.89 1388.00 1387.68 0.32 J17 0.48 1385.26 1387.25 –1.99 J18 0.88 1386.49 1386.65 –0.17 J19 0.97 1385.82 1386.09 –0.27 J20 0.93 1385.39 1385.57 –0.18 J21 0.98 1385.53 1385.23 0.30 -
[1] ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, JOUGHIN I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. doi: 10.1109/5.838084 [2] 仇晓兰, 丁赤飚, 胡东辉. 双站SAR成像处理技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 8–11.QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, and HU Dong-hui. Bistatic SAR Imaging Algorithms[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 8–11. [3] 孙亚飞, 江利明, 柳林, 等. TanDEM-X双站SAR干涉测量及研究进展[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2015, 27(1): 16–22. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2015.01.03SUN Yafei, JIANG Liming, LIU Lin, et al. TanDEM-X bistatic SAR interferometry and its research progress[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2015, 27(1): 16–22. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2015.01.03 [4] 章皖秋, 岳彩荣, 颜培东. TanDEM-X极化干涉SAR森林冠层高度反演[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(1): 47–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.011ZHANG Wanqiu, YUE Cairong, and YAN Peidong. Forest canopy height retrieval by PolInSAR with TanDEM-X data[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2017, 45(1): 47–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.011 [5] LIANG Da, LIU Kaiyu, ZHANG Heng, et al. The processing framework and experimental verification for the noninterrupted synchronization scheme of LuTan-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(7): 5740–5750. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3024561 [6] LIN Haoyu, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Heng, et al. On the processing of dual-channel receiving signals of the LuTan-1 SAR System[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(3): 515. doi: 10.3390/rs14030515 [7] HENDRIKS I, META A, TRAMPUZ C, et al. MetaSensing’s novel L-band airborne SAR sensors for the BelSAR project: First Bistatic results[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Izzy-Hendriks/publication/326317566_MetaSensing%27s_Novel_L-Band_Airborne_SAR_Sensors_for_the_BelSAR_Project_First_Bistatic_Results/links/5b45af4b0f7e9b1c72236322/MetaSensings-Novel-L-Band-Airborne-SAR-Sensors-for-the-BelSAR-Project-First-Bistatic-Results.pdf, 2017. [8] META A, TRAMPUZ C, COCCIA A, et al. First results of the BelSAR L band airborne bistatic fully polarimetric Synthetic aperture radar campaign[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 1040–1042. [9] YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, YANG Haiguang, et al. A first experiment of airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR - Preliminary results[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 4202–4204. [10] LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, YI Qingying, et al. Bistatic forward-looking SAR ground moving target detection and imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1000–1016. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130539 [11] LI Zhongyu, YE Hongda, LIU Zhutian, et al. Bistatic SAR clutter-ridge matched STAP method for nonstationary clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5216914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3125043 [12] 傅志豪. 无人机载干涉SAR系统性能分析及应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 应急管理部国家自然灾害防治研究院, 2021.FU Zhihao. Performance analysis and application of UAV SAR system[D]. [Master dissertation], National Institute of Natural Hazards, 2021. [13] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027 [14] LV Zexin, QIU Xiaolan, CHENG Yao, et al. Multi-rotor UAV-borne PolInSAR data processing and preliminary analysis of height inversion in urban area[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2161. doi: 10.3390/rs14092161 [15] 林春辉. 单基/双基SAR成像若干关键问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.LIN Chunhui. Study on some imaging issues of monostatic and bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [16] 刘松林. 双基SAR时频同步系统研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2016.LIU Songlin. Research on time and frequency synchronization system of bistatic SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016. [17] 汤晓涛, 楼良盛, 刘志铭. 编队卫星InSAR系统的相位同步分析[J]. 地球信息科学, 2008, 10(6): 798–801. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1560-8999.2008.06.020TANG Xiaotao, LOU Liangsheng, and LIU Zhiming. Analyses of phase synchronization on InSAR system based on formation- flying satellites[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2008, 10(6): 798–801. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1560-8999.2008.06.020 [18] 丁赤飚, 李芳芳, 胡东辉, 等. 机载干涉合成孔径雷达数据处理技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 17–36.DING Chibiao, LI Fangfang, HU Donghui, et al. Data Processing Technology of Airborne Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 17–36. [19] 李芳芳, 仇晓兰, 孟大地, 等. 机载双天线InSAR运动补偿误差的影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(3): 559–567. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00850LI Fangfang, QIU Xiaolan, MENG Dadi, et al. Effects of motion compensation errors on performance of airborne dual-antenna InSAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 559–567. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00850 [20] 刘琦, 岳彩荣, 章皖秋, 等. 极化干涉SAR森林冠层高反演的地形坡度改正[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(1): 55–60, 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.012LIU Qi, YUE Cairong, ZHANG Wanqiu, et al. Terrain slope correction on PolInSAR forest canopy height inversion[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2017, 45(1): 55–60, 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.012 [21] 朱刚. 超宽带(UWB)原理与干扰[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009: 2–5.ZHU Gang. Ultra Wideband (UWB) Principle and Interference[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009: 2–5. [22] LUECKEN H, STEINER C, and WITTNEBEN A. Location-aware UWB communication with generalized energy detection receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(9): 3068–3078. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.070912.110101 [23] 潘莉娟. 星间高精度时间同步和测距系统的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2008.PAN Lijuan. Research on high-precision time synchronization and ranging systems between satellites[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2008. [24] 张方辉, 梁兴东, 周良将. 双站SAR时间同步误差建模及分析[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2010, 29(8): 36–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2010.08.013ZHANG Fanghui, LIANG Xingdong, and ZHOU Liangjiang. Modeling and analyzing of time synchronization errors in bistatic SAR[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2010, 29(8): 36–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2010.08.013 [25] YOUNIS M, METZIG R, and KRIEGER G. Performance prediction of a phase synchronization link for Bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(3): 429–433. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.874163 [26] 雷科. 机载双基地合成孔径雷达系统同步问题研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008.LEI Ke. Research on synchronization of airborne bistatic synthetic-aperture radar system[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008. [27] WEIB M. Synchronisation of bistatic radar systems[C]. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 1750–1753. [28] 向建冰, 吕孝雷, 付希凯, 等. 天绘二号双星InSAR成像与DSM生成技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(12): 2493–2500. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20210373XIANG Jianbing, LÜ Xiaolei, FU Xikai, et al. Bistatic InSAR interferometry imaging and DSM generation for TH-2[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(12): 2493–2500. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20210373 [29] 孟大地. 机载合成孔径雷达运动补偿算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2006.MENG Dadi. Research on motion compensation algorithm for airborne SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. [30] QIU Xiaolan, HAN Bin, MENG Dadi, et al. An azimuth resample method for bistatic SAR motion compensation[C]. 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 1–4. [31] DALL J, GRINDER-PEDERSEN J, and MADSEN S N. Calibration of a high resolution airborne 3D SAR[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Remote Sensing - A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development, Singapore, 1997: 1018–1021. [32] 张薇. 机载双天线干涉SAR定标方法研究[D]. [博士学位论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2009.ZHANG Wei. Airborne dual-antenna InSAR’s interferometric calibration method research[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electrics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009. [33] 吴迪, 李焱磊, 周良将, 等. 一种基于Whitt算法的SAR极化定标改进方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2018, 16(2): 125–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.02.002WU Di, LI Yanlei, ZHOU Liangjiang, et al. An improved method for SAR polarimetric calibration based on Whitt algorithm[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2018, 16(2): 125–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.02.002 [34] LI Fangfang, DING Chibiao, ZHANG Yueting, et al. Airborne InSAR interferometric phase analysis, unwrapping method, and fast implementation in low coherence areas[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 5241–5250. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3020148 [35] 黄海风, 张永胜, 董臻. 星载合成孔径雷达干涉新技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 52–55.HUANG Haifeng, ZHANG Yongsheng, and DONG Zhen. New Interferometric Technology of Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 52–55. [36] GOLDSTEIN R M and WERNER C L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(21): 4035–4038. doi: 10.1029/1998GL900033 [37] BARAN I, STEWART M P, KAMPES B M, et al. A modification to the Goldstein radar interferogram filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(9): 2114–2118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817212 [38] 张俊娜, 邓喀中, 范洪冬, 等. InSAR相位解缠方法应用比较[J]. 现代测绘, 2011, 34(4): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2011.04.004ZHANG Junna, DENG Kazhong, FAN Hongdong, et al. Comparison on application of InSAR phase unwrapping methords[J]. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 2011, 34(4): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2011.04.004 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
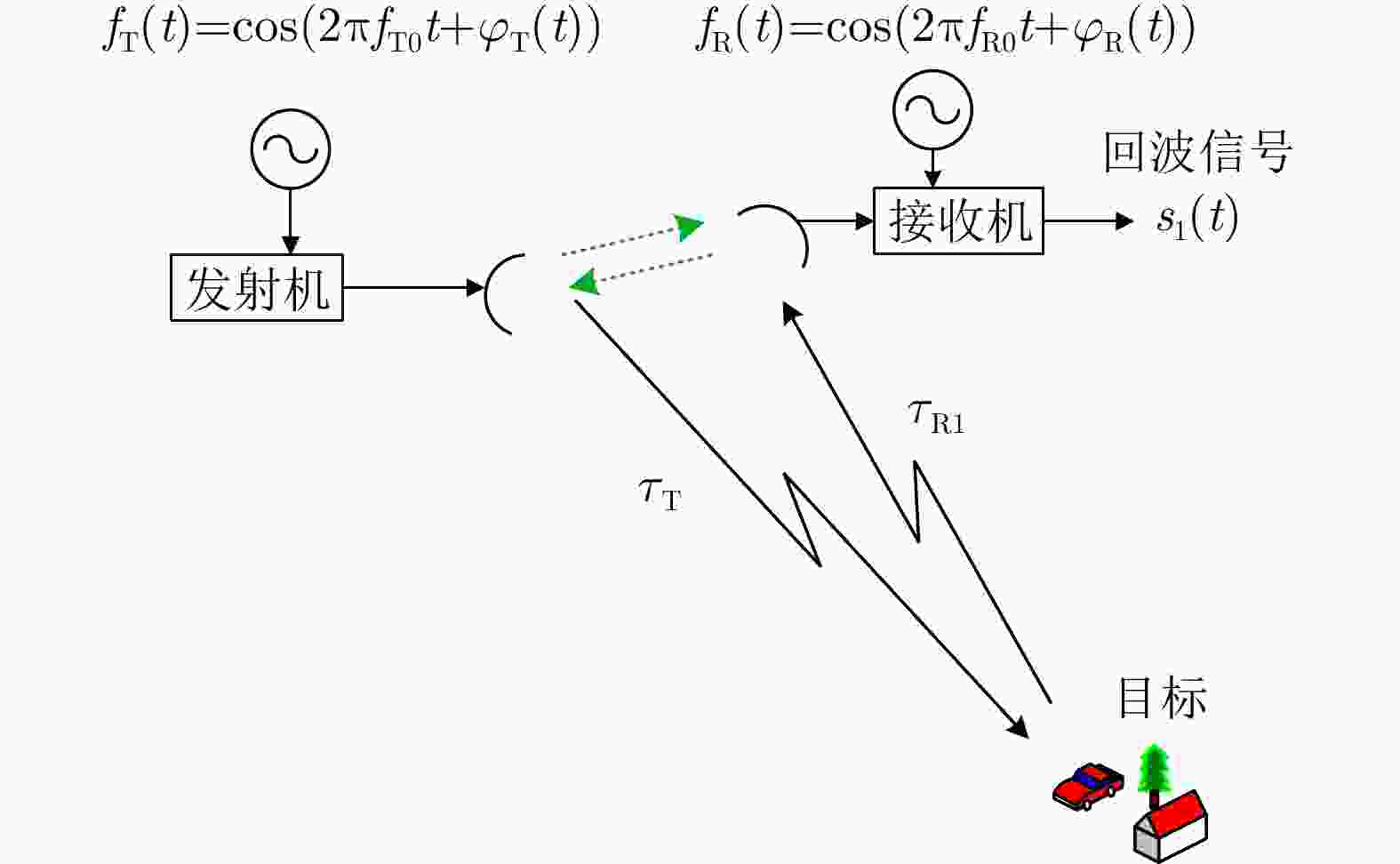
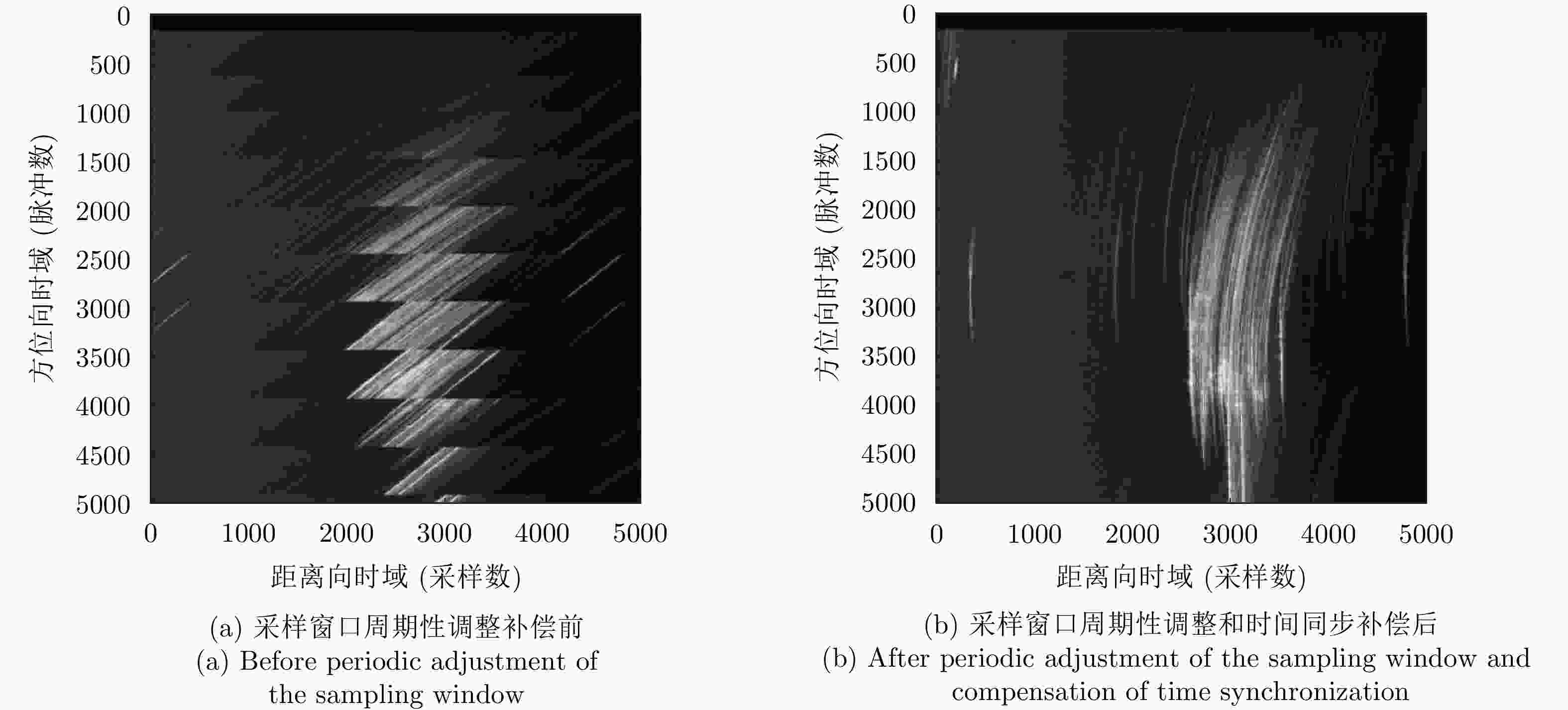
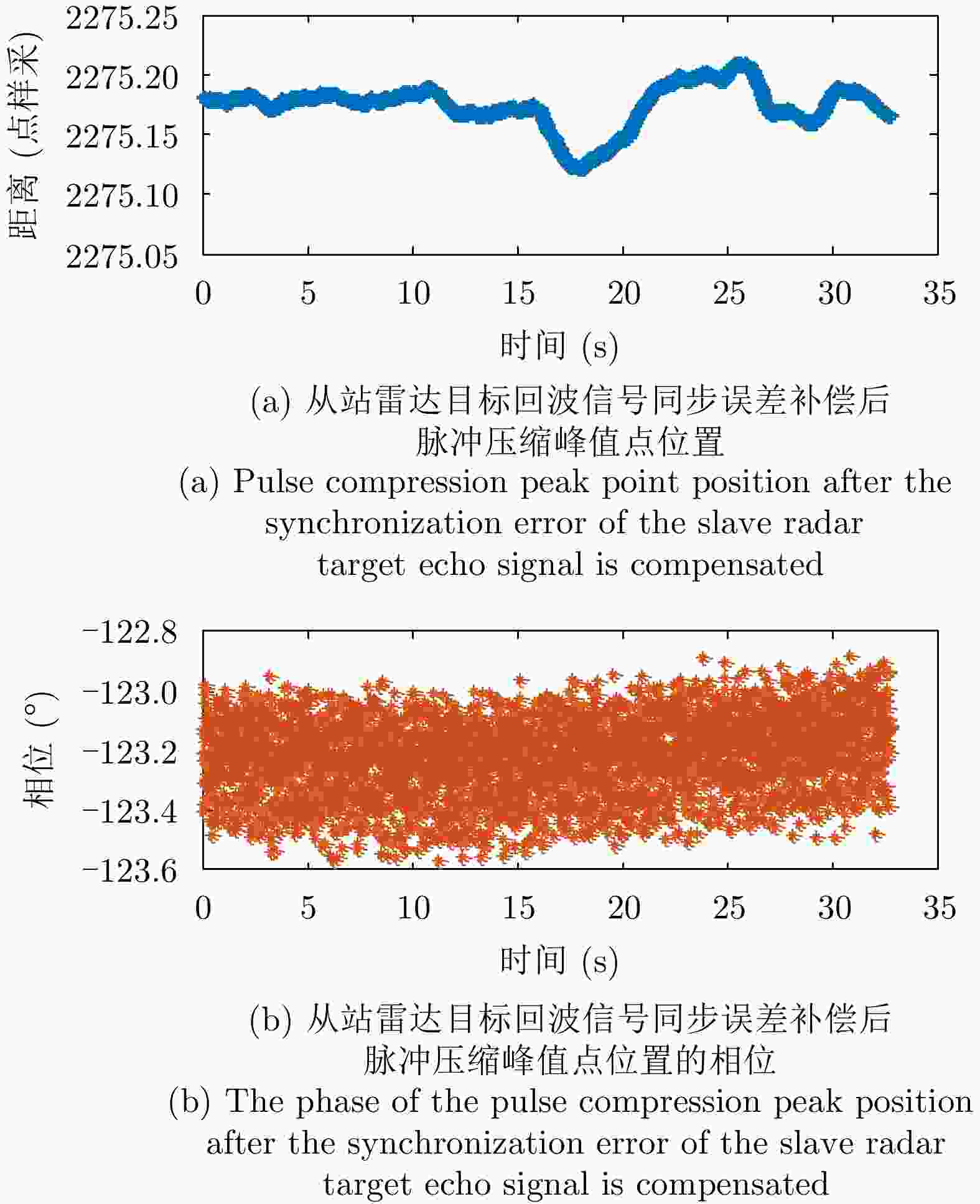
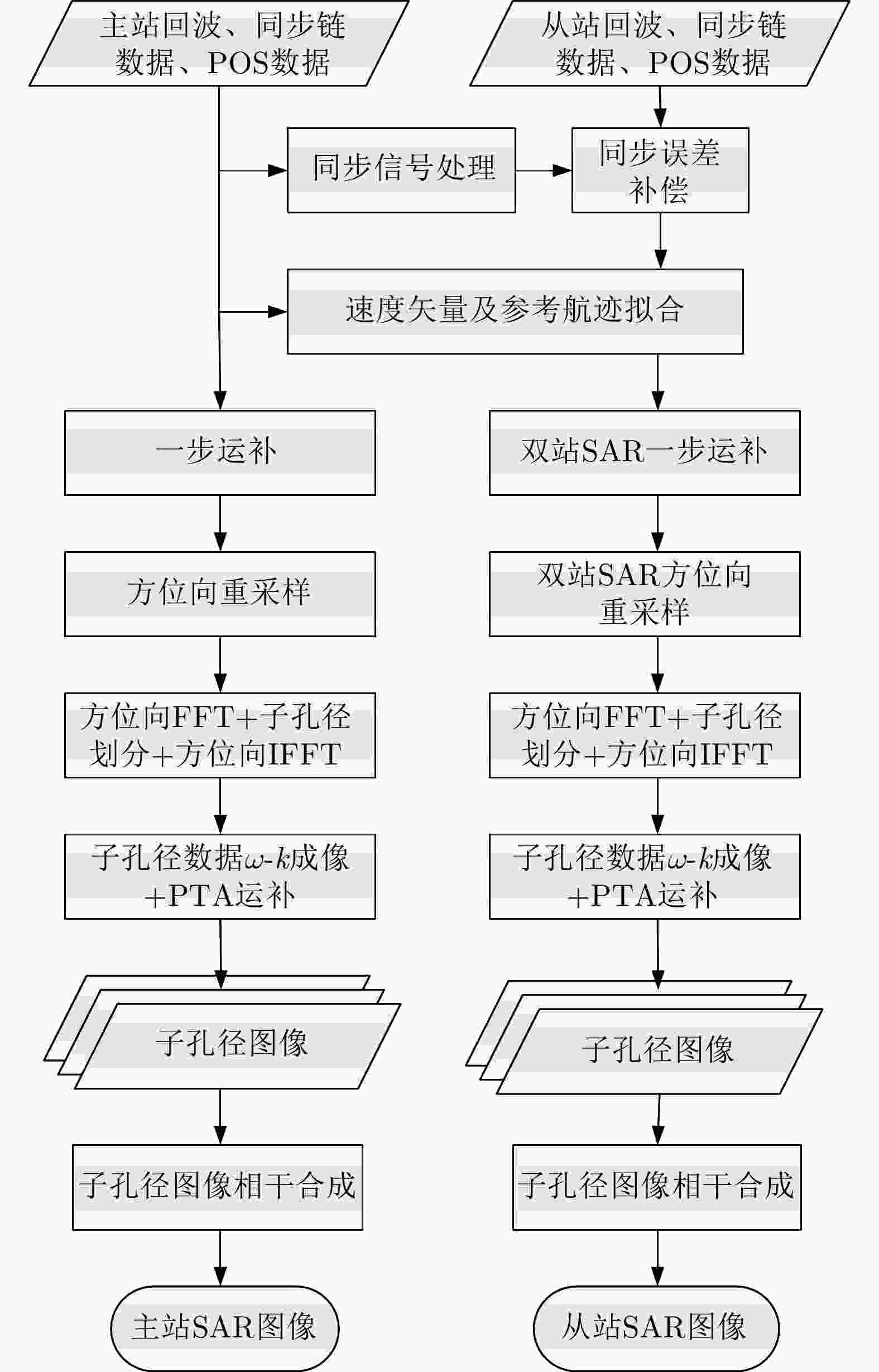
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: