-
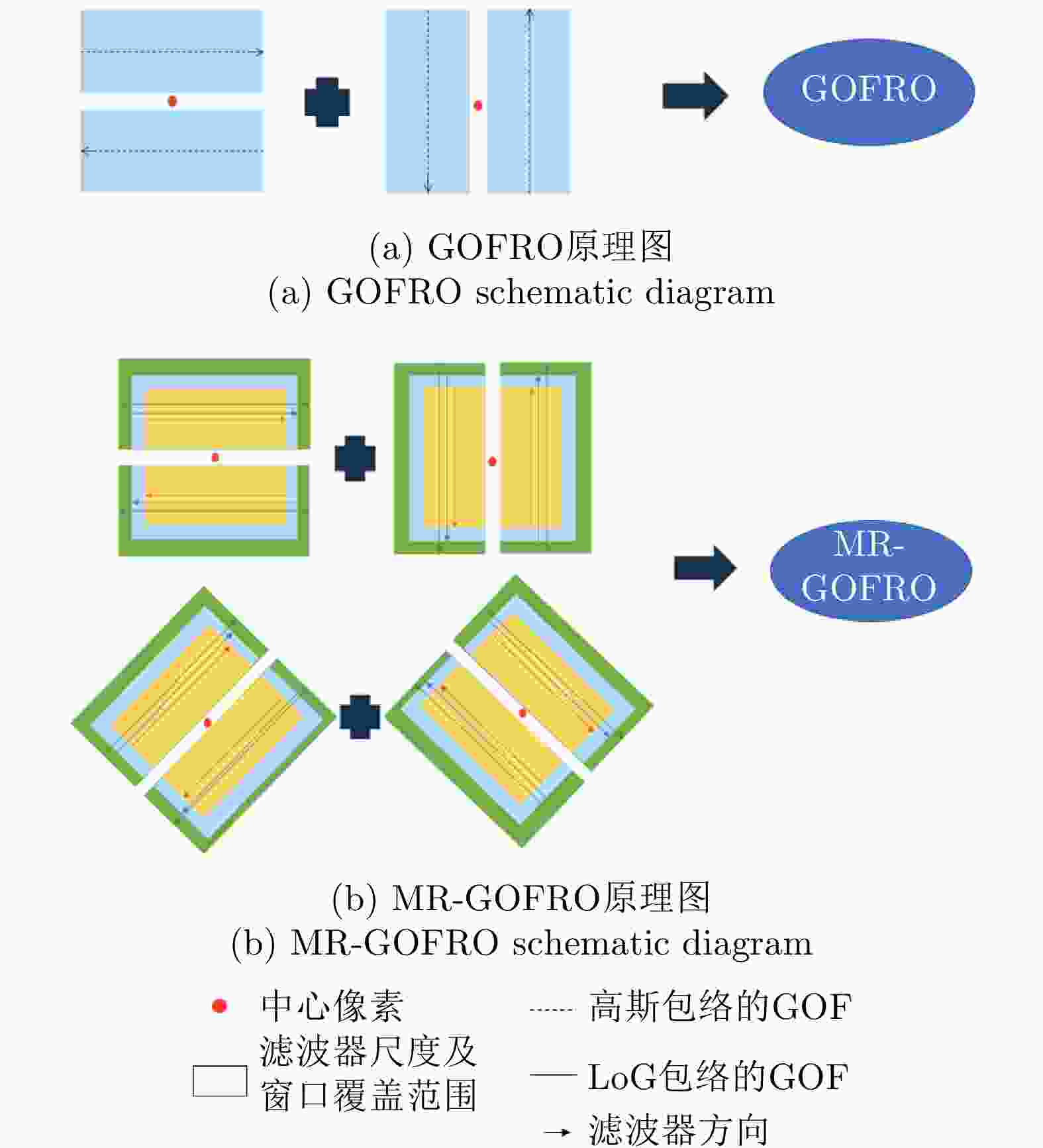
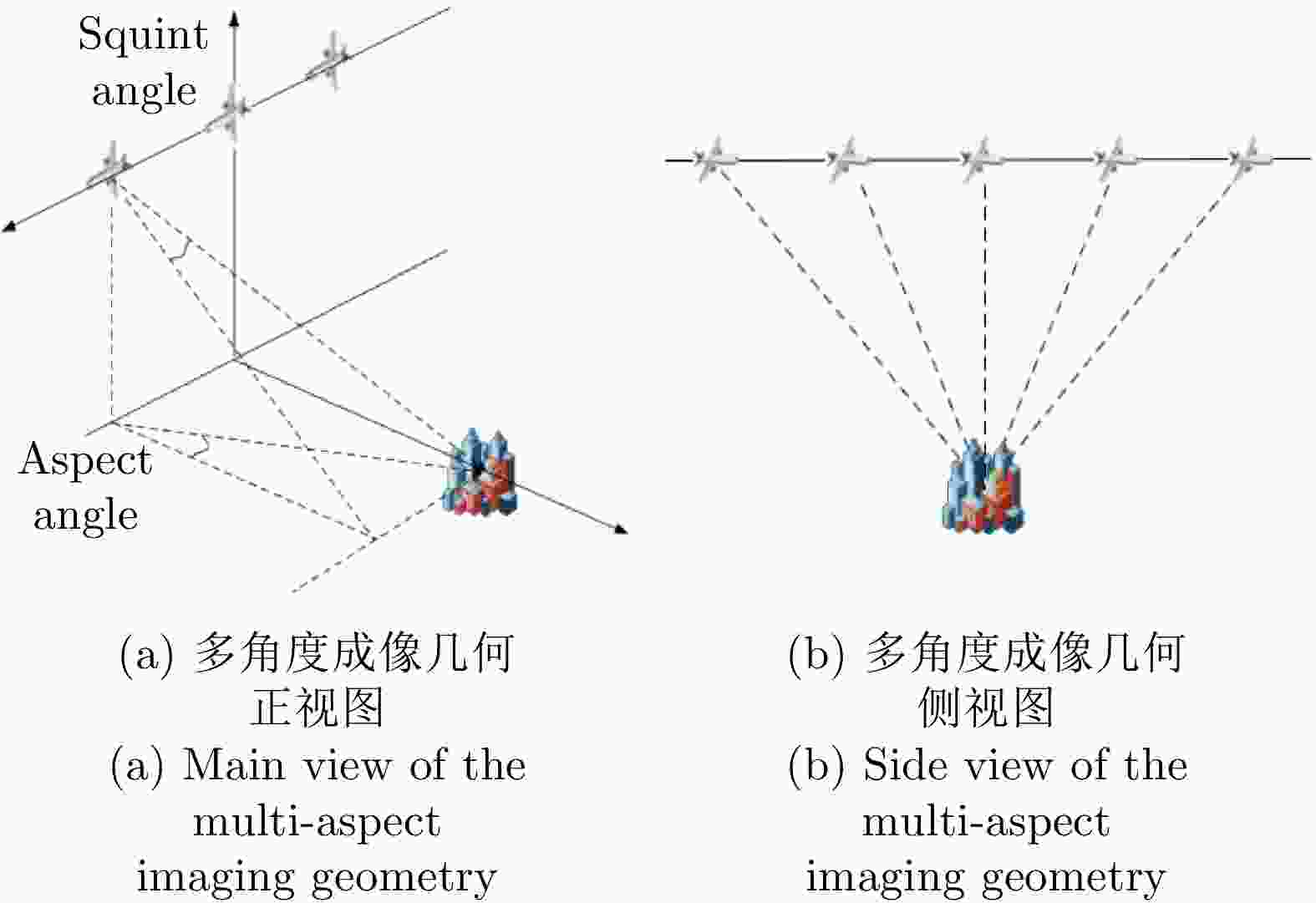
摘要: 针对城市场景中车辆目标分布状态随机,在检测过程中容易受到环境因素干扰等问题,提出一种将多角度合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像用于静止车辆目标提取的检测算法。在特征提取阶段,设计了一种适用于多角度图像上车辆目标的多尺度旋转不变的Gabor滤波器奇分量比例算子(MR-GOFRO)特征提取方法,对原有的GOFRO特征进行了滤波形式、特征尺度、特征方向、特征层次等4个方面的扩展,使其能够适应车辆目标在方向、尺度、形态等方面可能发生的变化。在图像融合阶段,设计了加权的非负矩阵分解(W-NMF)方法,根据特征质量调整来源于不同图像的特征权重,减少由于不同角度间相互干扰造成融合特征质量下降的现象。将该文所提出方法在不同的机载多角度图像数据集上进行验证,实验结果表明,该文提出的特征提取方法与同类方法相比,检测精度平均提升了3.69%;该文提出的特征融合方法与同类方法相比,检测精度提升了4.67%。Abstract: Vehicle targets in urban scenes have the characteristics of random distribution and can be easily disturbed by environmental factors during the detection process. Given the above issues, this paper proposes a detection method that utilizes multi-aspect Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images for stationary vehicle target extraction. In the feature extraction stage, a novel feature extraction method called Multiscale Rotational Gabor Odd Filter-based Ratio Operator (MR-GOFRO) is designed for vehicle targets in multi-aspect SAR images, where the original GOFRO features are improved from four aspects—filter form, feature scale, feature direction and feature level. The improvement allows MR-GOFRO to adapt to possible variations in the target direction, scale, morphology, etc. In the image fusion stage, a Weighted-Non-negative Matrix Factorization (W-NMF) method is developed to adjust the feature weights from various images according to the feature quality. This method can reduce the quality degradation of the fusion features due to mutual interference between different aspects. The proposed method is verified on various airborne multi-aspect image datasets. The experimental results revealed that the feature extraction and feature fusion methods proposed in this paper enhance the detection accuracy by an average of 3.69% and 4.67%, respectively, compared with similar methods.
-
Key words:
- Multi-aspect SAR /
- Vehicle target detection /
- Feature extraction /
- Feature selection /
- Image fusion
-
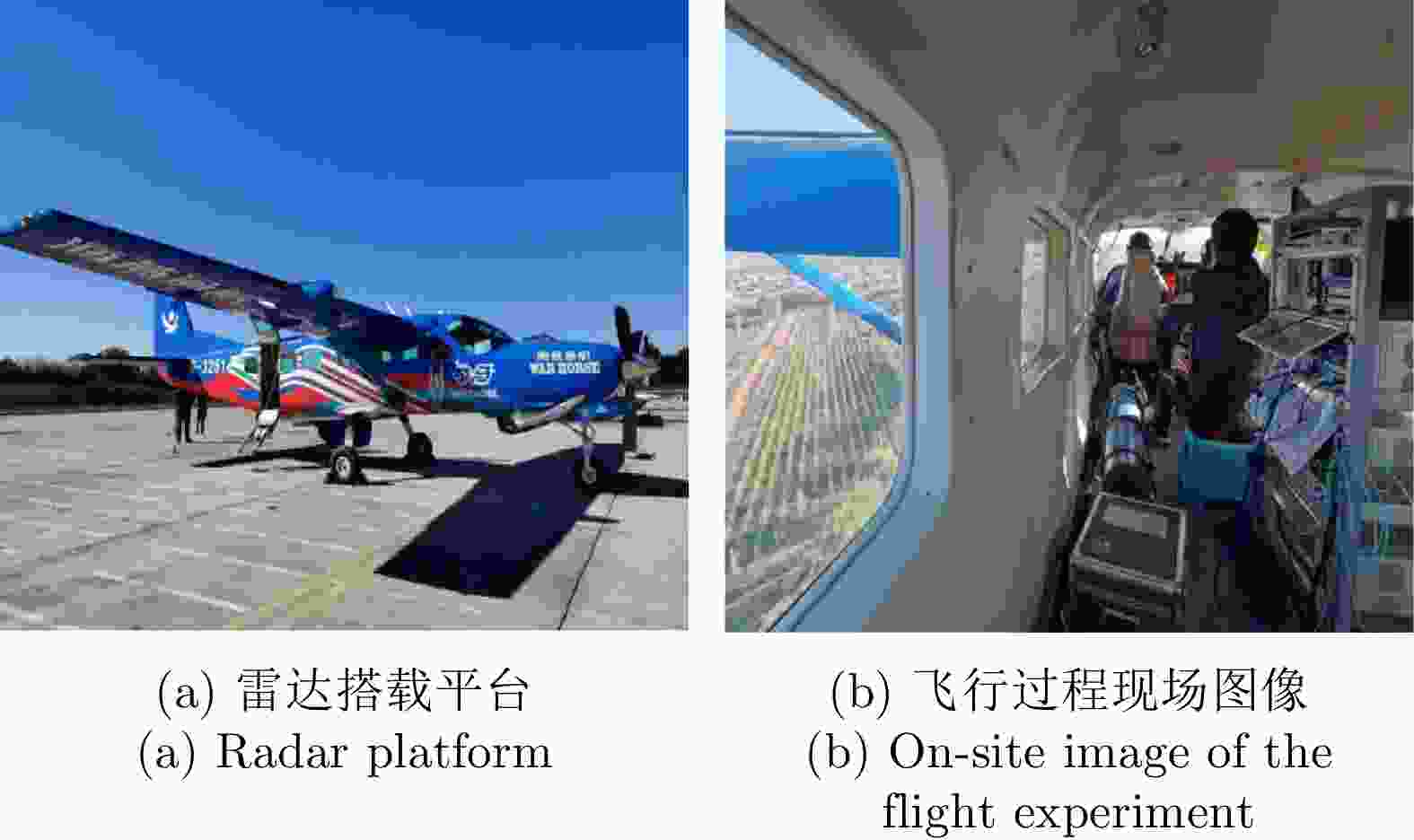
表 1 阳江飞行实验参数
Table 1. Yangjiang flight experiment parameters
实验参数 参数值 中心频率 9.6 GHz 带宽 3600 MHz 脉宽 15 μs 采样频率 4400 MHz 脉冲重复频率 3000 Hz 中心角度 65.5° 平台速度 83.04 m/s 平台高度 3605.44 m 场景中心纬度 21.88° 场景中心经度 111.97° 图像分辨率 1 m 表 2 阳江飞行实验多角度图像方位角度参数
Table 2. Aspect parameters in Yangjiang flight experiment
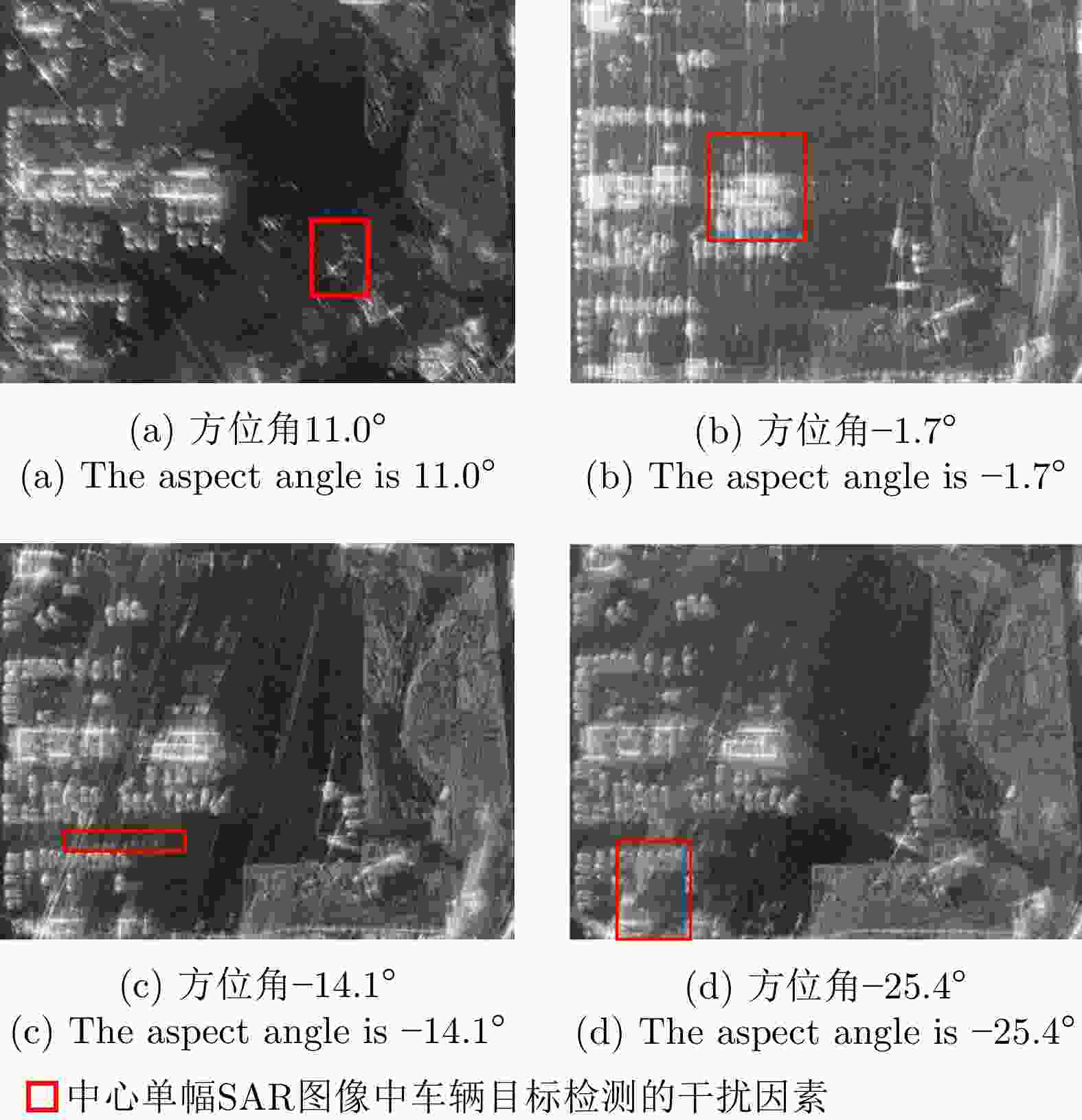
序列号 方位角度
(°)角度间隔
(°)角度范围
(°)角度1 40.8 0 0 角度2 32.6 8.2 8.2 角度3 22.6 10.0 18.2 角度4 11.0 11.6 29.8 角度5 0 11.0 40.8 角度6 –1.7 1.7 42.5 角度7 –14.1 12.4 54.9 角度8 –25.4 11.3 66.2 角度9 –34.9 9.5 75.7 角度10 –42.3 7.4 83.1 表 3 舟山飞行实验参数
Table 3. Zhoushan flight experiment parameters
实验参数 参数值 中心频率 9.6 GHz 带宽 1200 MHz 脉宽 20 μs 采样频率 1400 MHz 脉冲重复频率 3000 Hz 中心角度 55.0° 平台高度 7000 m 平台速度 137.34 m/s 场景中心经度 29.97° 场景中心纬度 122.29° 图像分辨率 0.7 m 表 4 舟山飞行实验多角度图像方位角度参数
Table 4. Aspect parameters of the multi-aspect images in Zhoushan flight experiment
序列号 方位角度(°) 角度间隔(°) 角度范围(°) 角度1 40.4 0 0 角度2 30.2 10.2 10.2 角度3 20.5 9.7 19.9 角度4 10.8 9.7 29.6 角度5 0.4 10.4 40.0 角度6 –10.0 10.4 50.4 角度7 –19.8 9.8 60.2 角度8 –28.9 9.1 69.3 角度9 –39.2 10.3 79.6 表 5 实验中检测算法所选取的参数
Table 5. Detection experiment parameters
实验参数 参数值 MR-GOFRO尺度 12/15/19/24/30 MR-GOFRO方向 $ \left[0,\pi /2\right] $ $ \left[\pi /\mathrm{6,2}\pi /3\right] $ $ [\pi /\mathrm{4,3}\pi /4] $ $ [\pi /\mathrm{3,5}\pi /6] $ NMF输出特征维数 12 车辆目标平均尺寸 13×26 检测窗口半径 12 车辆目标与检测窗口面积比 0.6 检测窗口步长 12 检测窗口采样点距离 6 检测窗口采样点数量 5 表 6 阳江飞行实验数据集中不同场景车辆目标检测结果的衡量指标
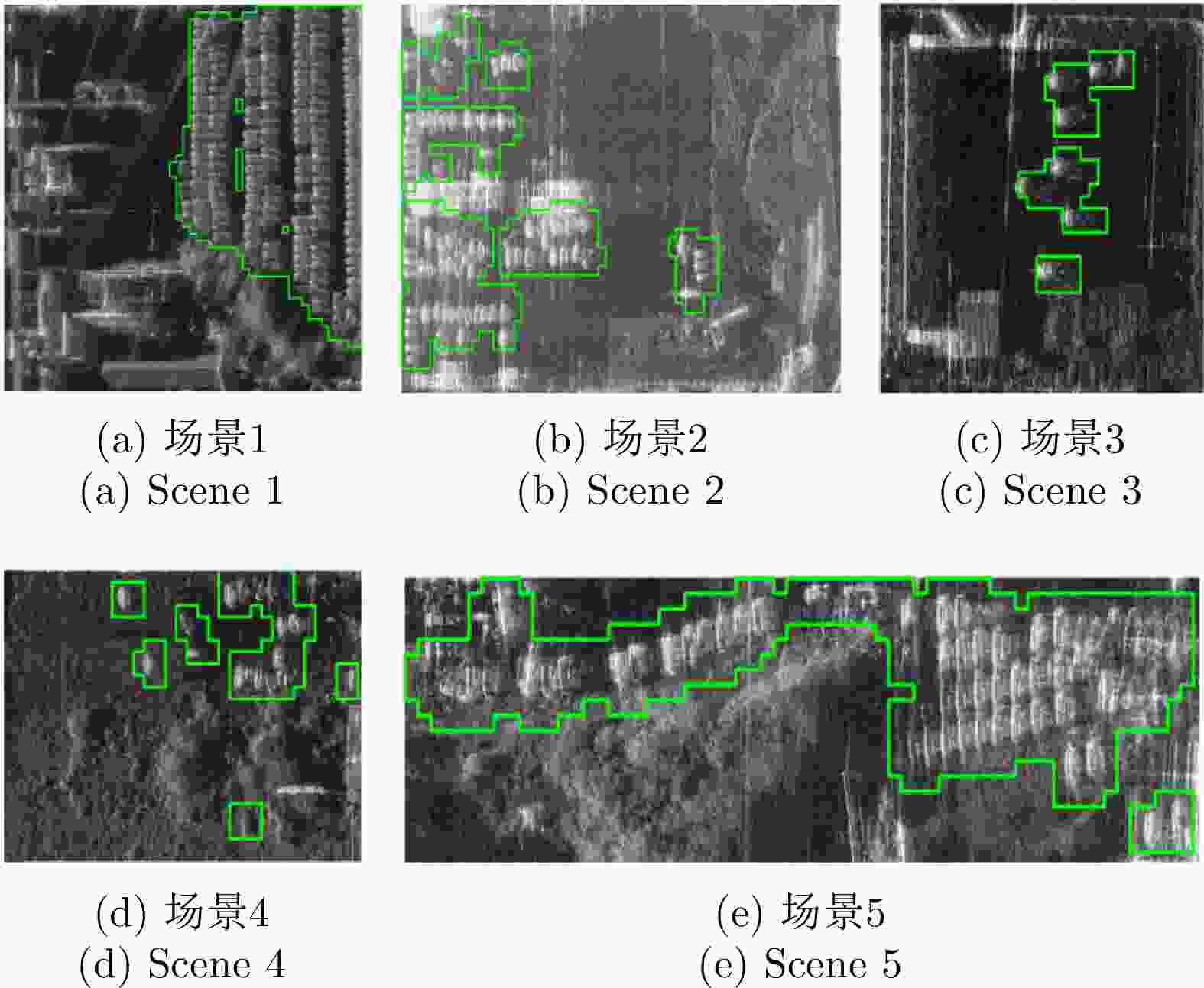
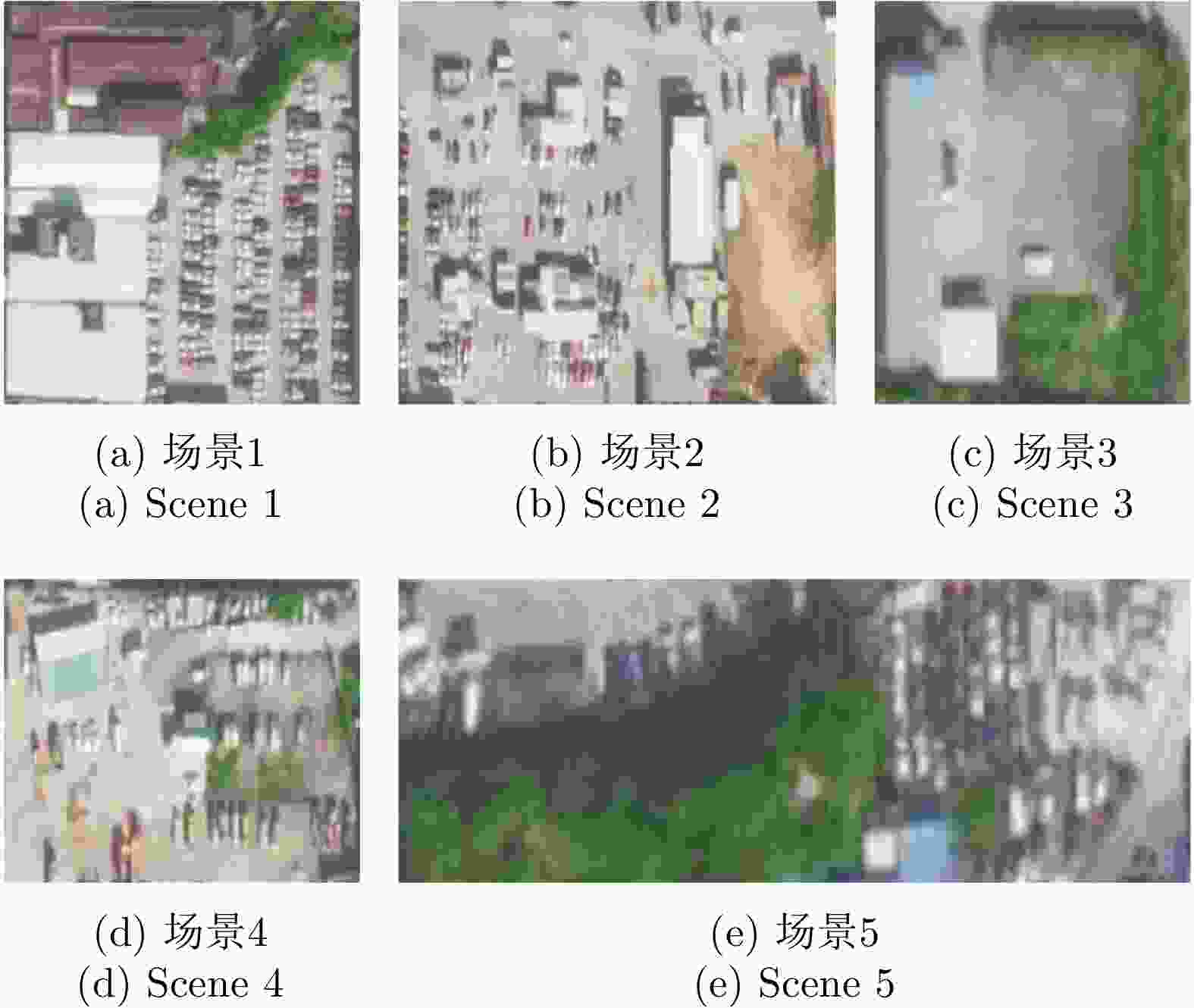
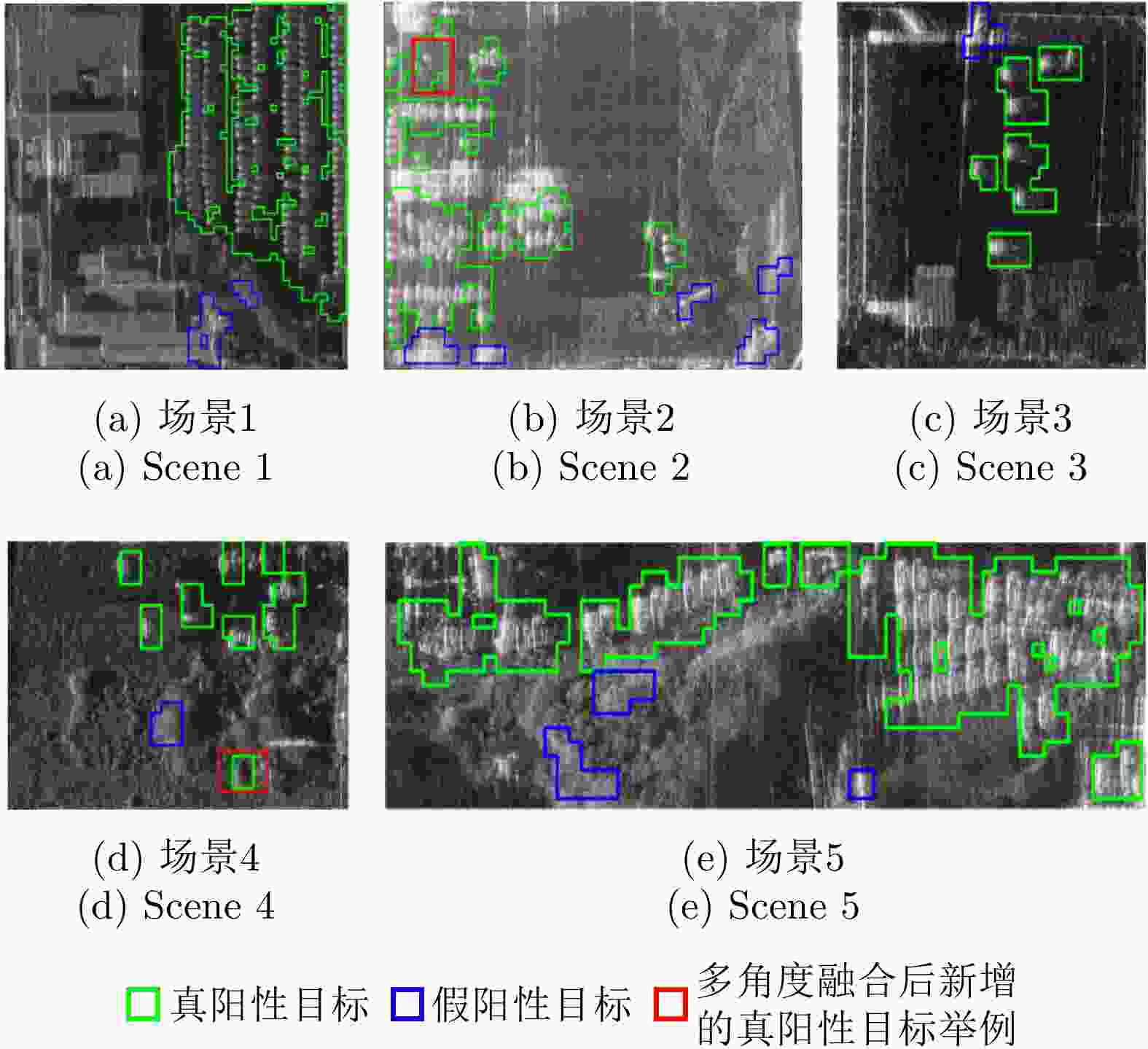
Table 6. Indexes of vehicle detection results in different scenes in Yangjiang flight experiment dataset
序列号 精确率(%) 准确率(%) 漏警率(%) 虚警率(%) 场景1 85.40 93.49 6.97 6.32 场景2 72.49 94.11 11.39 5.07 场景3 71.36 97.57 8.00 2.11 场景4 72.50 96.48 5.07 1.76 场景5 82.79 89.63 10.13 7.88 平均值 76.90 94.25 8.31 4.63 表 7 舟山飞行实验数据集中不同场景车辆目标检测结果的衡量指标
Table 7. Indexes of vehicle detection results in different scenes in Zhoushan flight experiment dataset
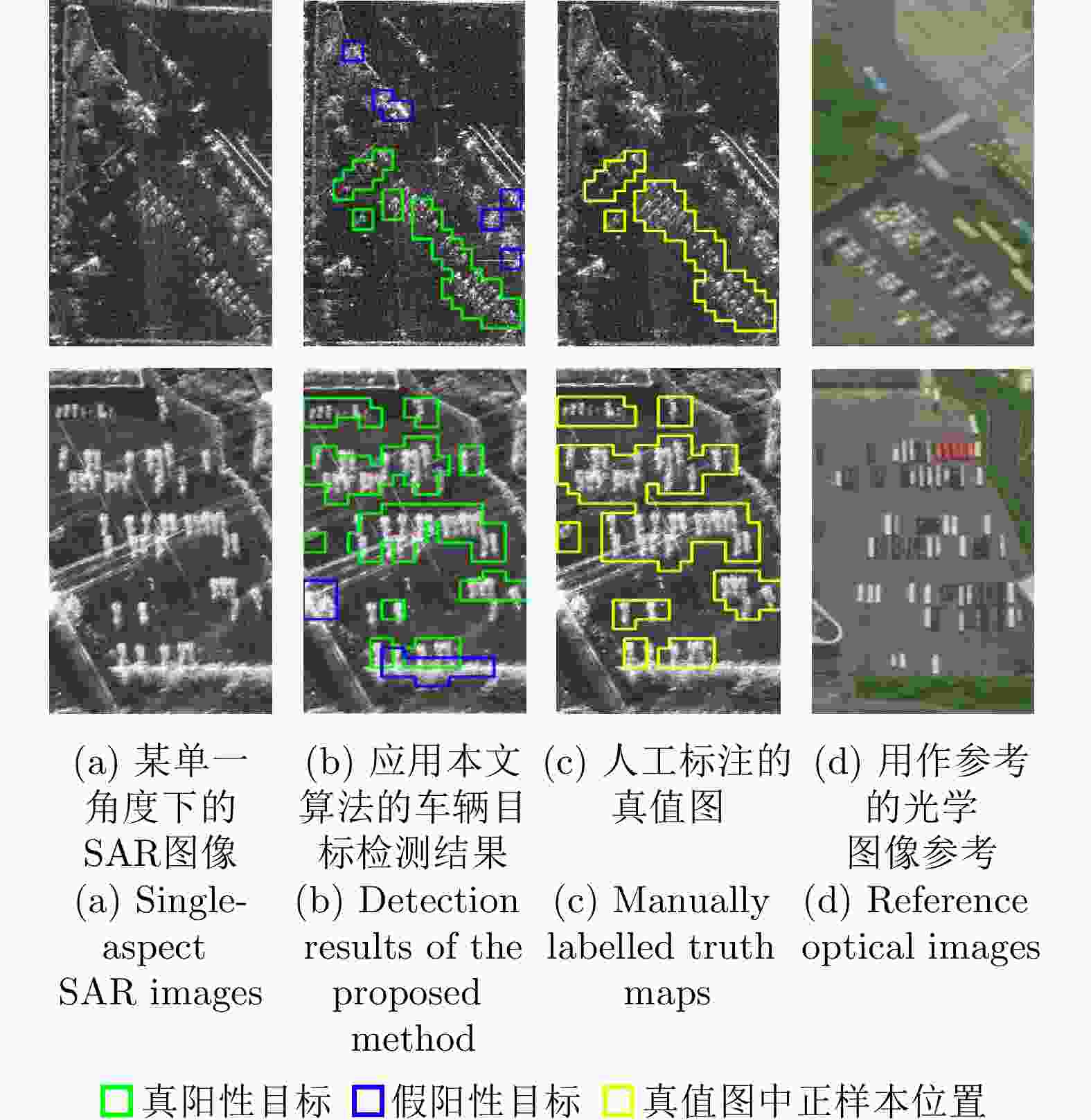
序列号 精确率(%) 准确率(%) 漏警率(%) 虚警率(%) 场景6 88.28 95.64 19.83 3.43 场景7 86.62 94.99 14.85 4.35 平均值 87.45 95.32 17.34 3.89 表 8 MR-GOFRO改进前后的检测结果衡量指标
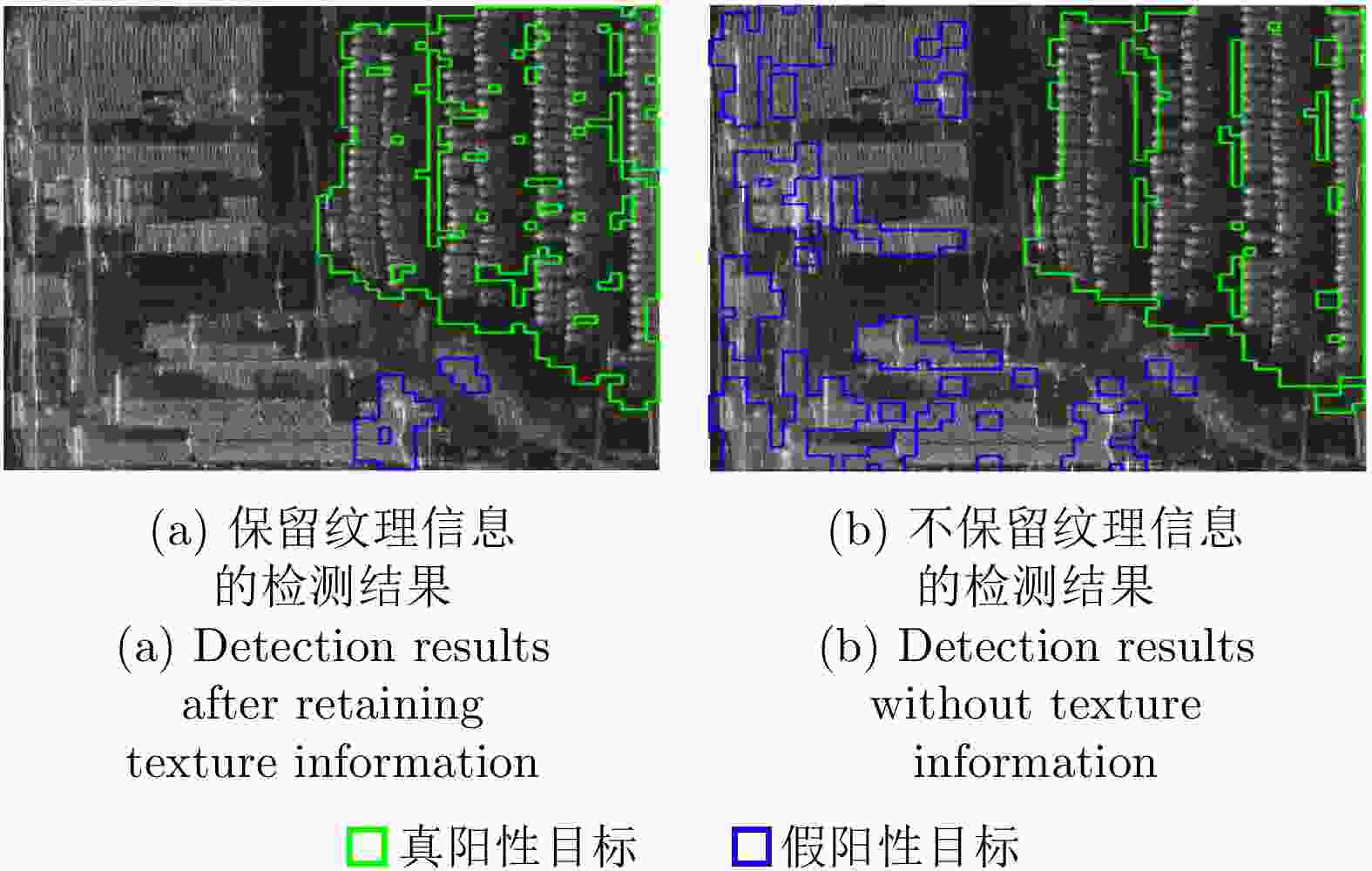
Table 8. Indexes of detection results before and after the MR-GOFRO improvements
检测
方法精确率
(%)准确率
(%)漏警率
(%)虚警率
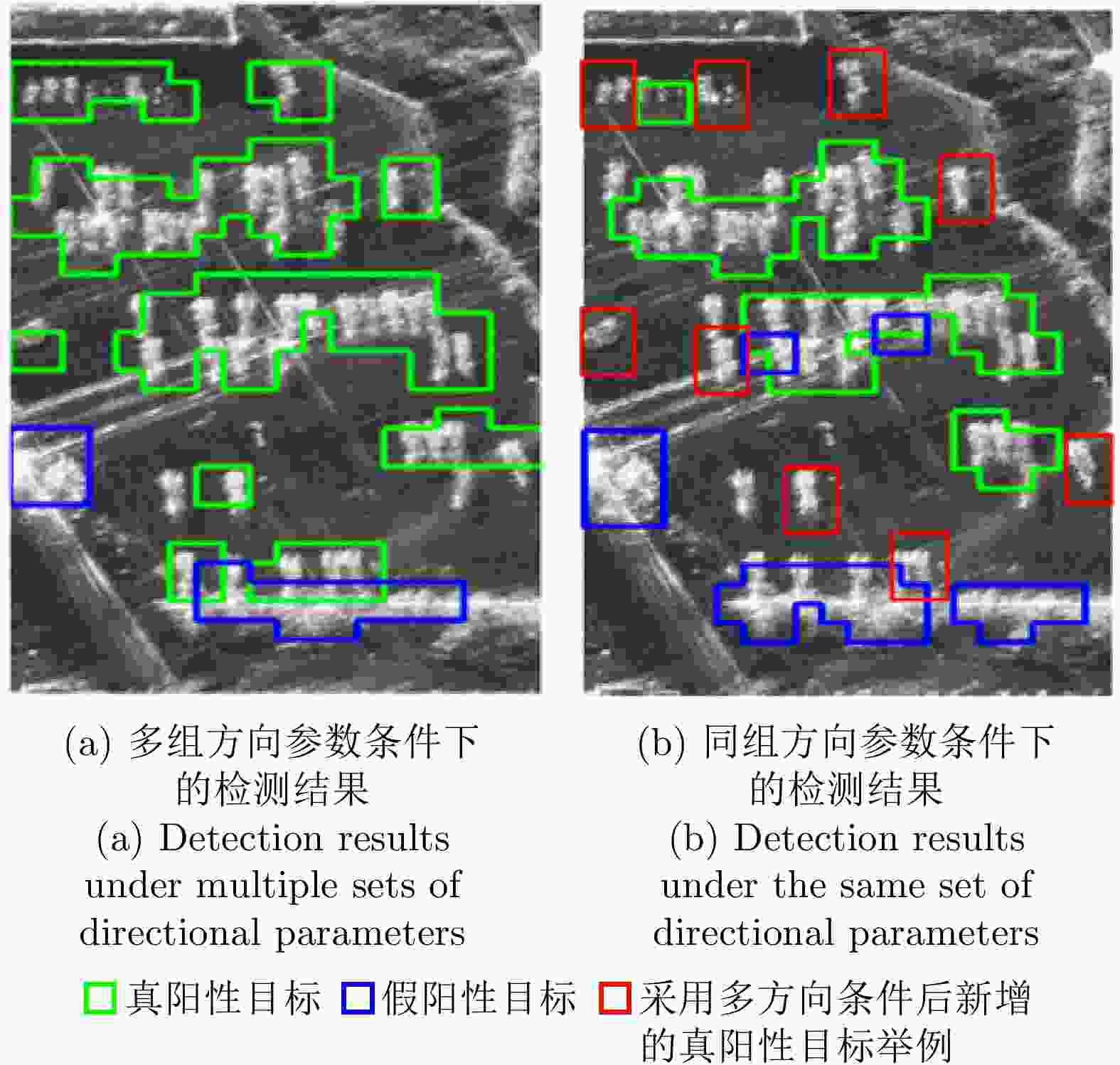
(%)GOFRO(场景1) 85.40 93.49 6.97 6.32 GOFRO(场景7) 86.62 94.99 14.85 4.53 尺度缩放 59.21 83.76 20.68 5.31 方向调节 61.08 84.13 30.42 4.29 纹理信息 66.19 83.91 5.86 20.44 表 9 不同方法检测结果的衡量指标
Table 9. Indexes of the detection results obtained by different methods
检测
方法精确率
(%)准确率
(%)漏警率
(%)虚警率
(%)方法1 66.96 89.00 28.50 8.31 方法2 71.37 93.06 18.52 5.13 方法3 60.89 89.89 21.18 8.29 方法4 72.92 84.59 13.95 5.64 方法5 68.28 90.01 9.15 10.11 本文方法 79.91 94.56 10.89 4.42 表 10 不同图像数量条件下的检测结果衡量指标
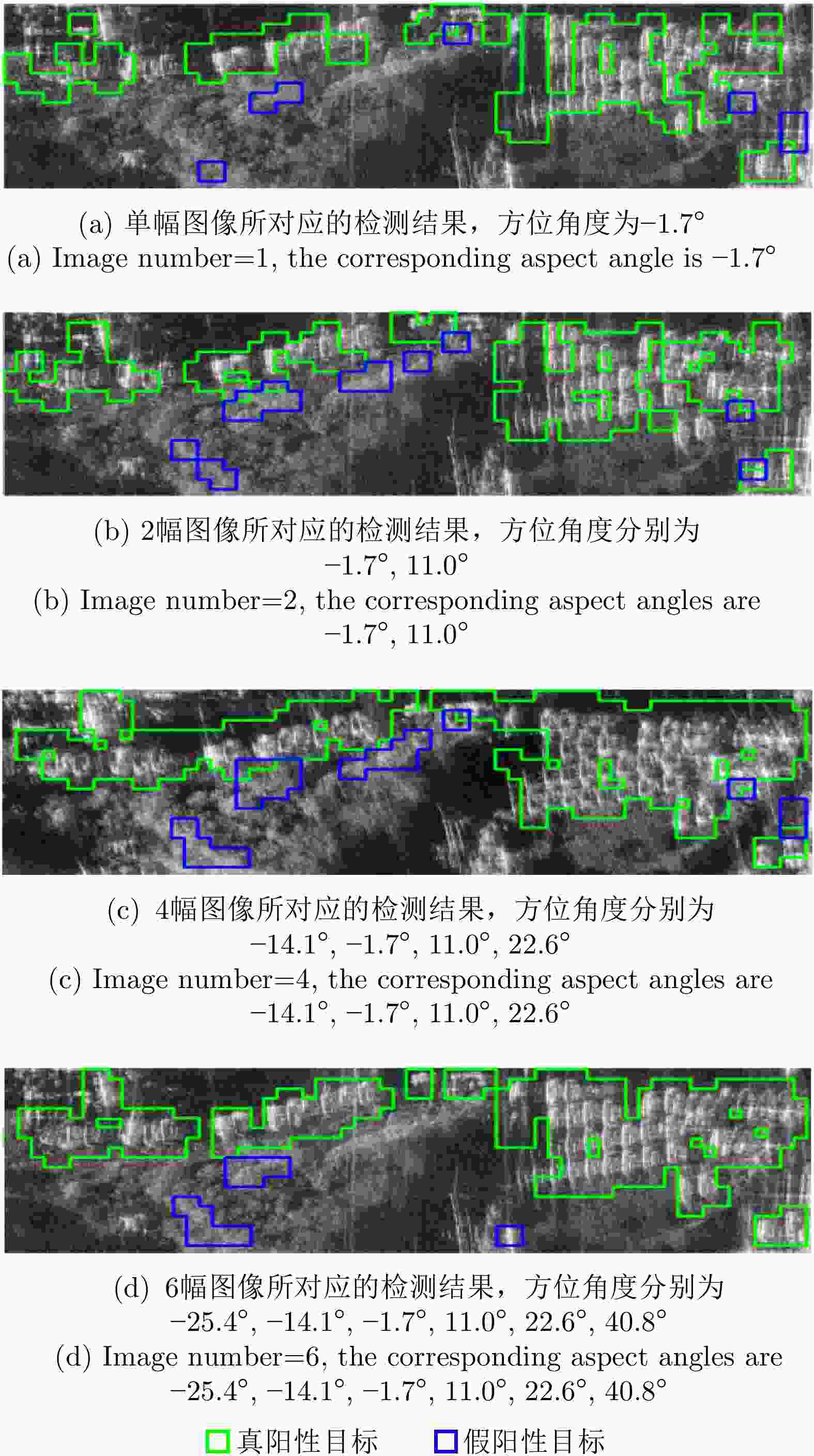
Table 10. Indexes of detection results under different image quantity conditions
图像
数量精确率
(%)准确率
(%)漏警率
(%)虚警率
(%)处理
时间(s)1 80.90 82.56 43.17 5.98 9.08 2 75.83 84.02 30.56 9.63 62.28 4 80.20 89.72 11.67 10.56 100.81 6 82.79 89.63 10.13 7.88 146.98 -
[1] LEITLOFF J, HINZ S, and STILLA U. Vehicle detection in very high resolution satellite images of city areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2795–2806. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2043109 [2] PALUBINSKAS G and RUNGE H. Change detection for traffic monitoring in TerraSAR-X imagery[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: I-169–I-172, [3] MITTERMAYER J, WOLLSTADT S, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. The TerraSAR-X staring spotlight mode concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3695–3706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2274821 [4] ZOU Bin, QIN Jiang, and ZHANG Lamei. Vehicle detection based on semantic-context enhancement for high-resolution SAR images in complex background[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4503905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3139605 [5] MAKSYMIUK O, SCHMITT M, BRENNER A R, et al. First investigations on detection of stationary vehicles in airborne decimeter resolution SAR data by supervised learning[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 3584–3587. [6] BAUMGARTNER S V and KRIEGER G. Real-time road traffic monitoring using a fast a priori knowledge based SAR-GMTI algorithm[C]. 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, USA, 2010: 1843–1846. [7] NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G J, and BROWER W S. Performance of 10- and 20-target MSE classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(4): 1279–1289. doi: 10.1109/7.892675 [8] EL-DARYMLI K, GILL E W, MCGUIRE P, et al. Automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art review[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 6014–6058. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2611492 [9] CHENG Gong and HAN Junwei. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 117: 11–28. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.03.014 [10] WANG Zhixu, XIN Zhihui, HUANG Xiaoqiao, et al. Overview of SAR Image Feature Extraction and Target Recognition[M]. JAIN L C, KOUNTCHEV R, and SHI Junsheng. 3D Imaging Technologies—Multi-dimensional Signal Processing and Deep Learning. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 69–75. [11] LI Lu, DU Yuang, and DU Lan. Vehicle target detection network in SAR images based on rectangle-invariant rotatable convolution[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(13): 3086. doi: 10.3390/rs14133086 [12] YANG Xinpeng, ZHANG Qiang, ZHAO Shixiang, et al. Focal-pyramid-based vehicle segmentation in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4028705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3224904 [13] BRENNER A R, ESSEN H, and STILLA U. Representation of stationary vehicles in ultra-high resolution SAR and turntable ISAR images[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 147–150. [14] WANG Guoli, WANG Xinchao, FAN Bin, et al. Feature extraction by rotation-invariant matrix representation for object detection in aerial image[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(6): 851–855. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2683495 [15] SUN Yi, WANG Wenna, ZHANG Qianyu, et al. Improved YOLOv5 with transformer for large scene military vehicle detection on SAR image[C]. The 2022 7th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing, Xi’an, China, 2022: 87–93. [16] 龙泓琳, 皮亦鸣, 曹宗杰. 基于非负矩阵分解的SAR图像目标识别[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(6): 1425–1429.LONG Honglin, PI Yiming, and CAO Zongjie. Non-negative matrix factorization for target recognition[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(6): 1425–1429. [17] ZHANG Haichao, NASRABADI N M, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Multi-view automatic target recognition using joint sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 2481–2497. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237604 [18] MA Wenping, WEN Zelian, WU Yue, et al. Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 [19] XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, WAN Ling, et al. An advanced multiscale edge detector based on Gabor filters for SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1522–1526. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2720684 [20] PAUL S and PATI U C. A Gabor odd filter-based ratio operator for SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 397–401. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2872979 [21] 张之光, 雷宏. 基于SAR图像样本的本征维数检测人造目标[J]. 电子测量技术, 2016, 39(9): 34–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2016.09.009ZHANG Zhiguang and LEI Hong. Man-made targets detection based on intrinsic dimension of SAR image samples[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2016, 39(9): 34–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2016.09.009 [22] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with HOG feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759 [23] OLUKANMI P O and TWALA B. K-means-sharp: Modified centroid update for outlier-robust k-means clustering[C]. 2017 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017: 14–19, [24] WU Xin, HONG Danfeng, TIAN Jiaojiao, et al. ORSIm detector: A novel object detection framework in optical remote sensing imagery using spatial-frequency channel features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 57(7): 5146–5158. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2897139 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: