Super-resolution DOA Estimation Method for a Moving Target Equipped with a Millimeter-wave Radar Based on RD-ANM
-
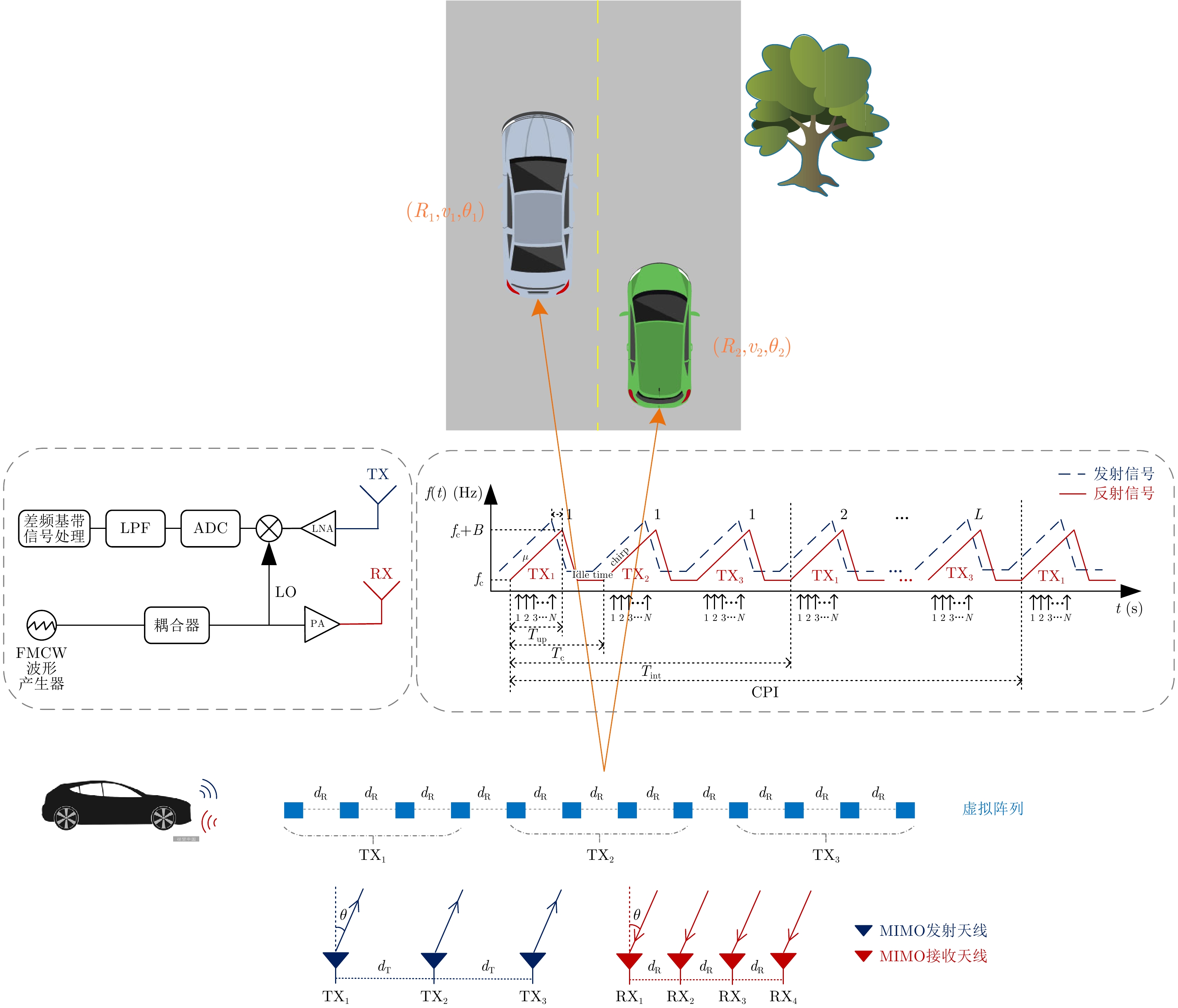
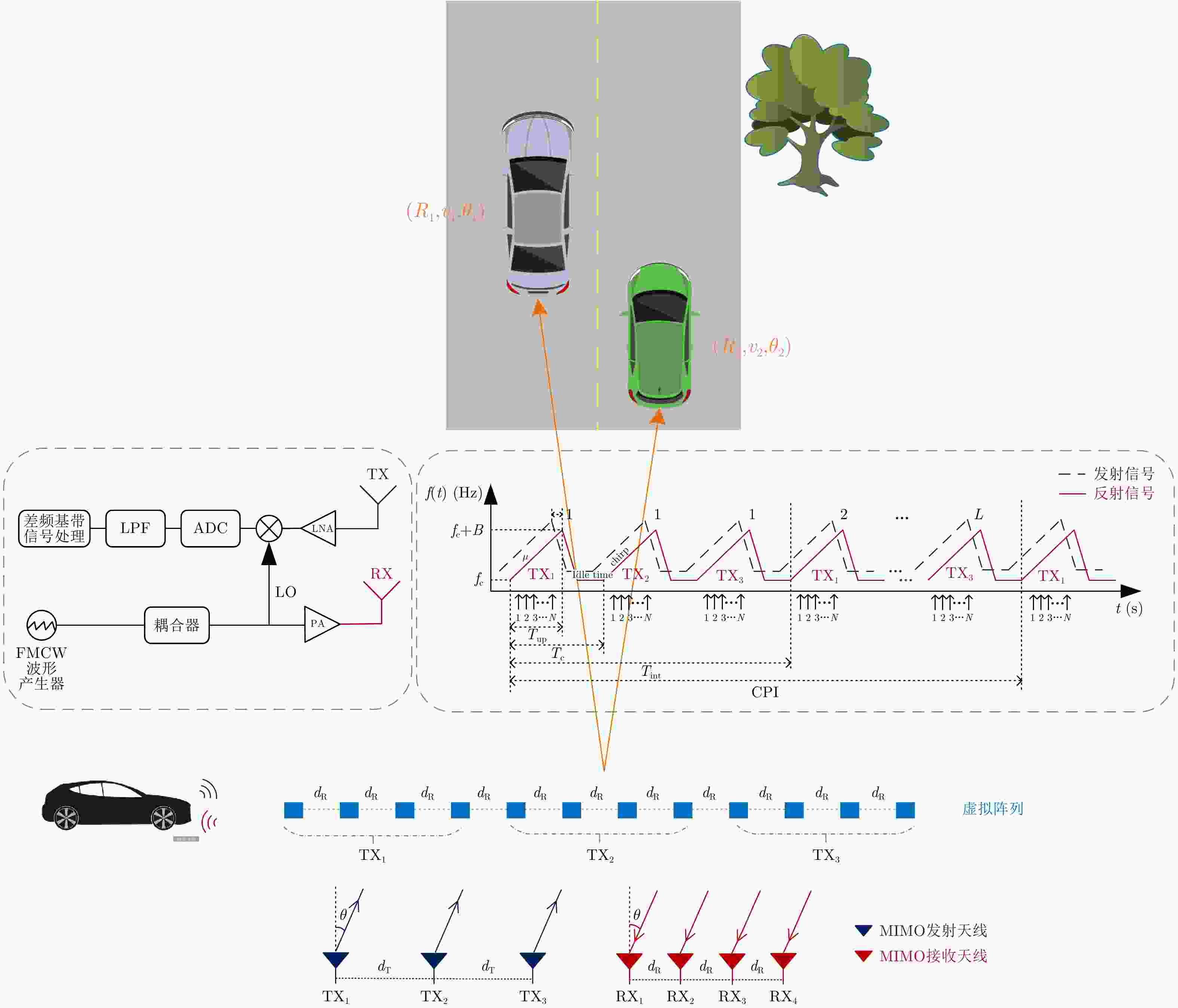
摘要: 超分辨波达方位角估计是车载毫米波雷达实现目标精准定位及跟踪需要解决的关键问题。针对车载场景中常见的阵列孔径受限、少快拍、低信噪比以及信源相干的情况,该文提出了一种基于距离多普勒域原子范数最小化(RD-ANM)的车载毫米波雷达动目标超分辨DOA估计方法:首先,构建了基于动目标雷达回波的距离多普勒域阵列接收信号;其次,设计了动目标多普勒耦合相位补偿矢量,用以削弱目标运动对DOA估计的影响;最后,提出了基于原子范数框架的多目标超分辨DOA估计方法。相较于车载毫米波雷达现使用的DOA估计算法,该文算法能够在基于低信噪比条件和单快拍处理前提下获得较高的测角分辨率和估计精度,以及拥有不牺牲阵列孔径对相干信号进行处理的稳健性能。理论分析、数值仿真以及实测实验验证了该文算法的有效性。Abstract: Super-resolution Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation is a critical problem related to vehicle-borne Millimeter-wave radars that needs to be solved to realize accurate target positioning and tracking. Based on the common conditions of limited array aperture, low snapshot, low signal-to-noise ratio, and coherent sources with respect to vehicle-borne scenarios, a super-resolution DOA estimation method for a moving target with an MMW radar based on Range-Doppler Atom Norm Minimize (RD-ANM) is proposed herein. First, an array for receiving signals in the range-Doppler domain is constructed based on the radar echo of the moving target. Then, the compensation vector for the Doppler coupling phase of the moving target is designed to reduce the influence of target motion on DOA estimation. Finally, a multitarget super-resolution DOA estimation method based on the atomic norm framework is proposed herein. Compared to the existing DOA estimation algorithm, the proposed algorithm can achieve higher angular resolution and estimation accuracy owing to low signal-to-noise ratio and single snapshot processing conditions, as well as robust performance in processing coherent sources without sacrificing array aperture. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is proven via theoretical analyses, numerical simulations, and experiments.
-
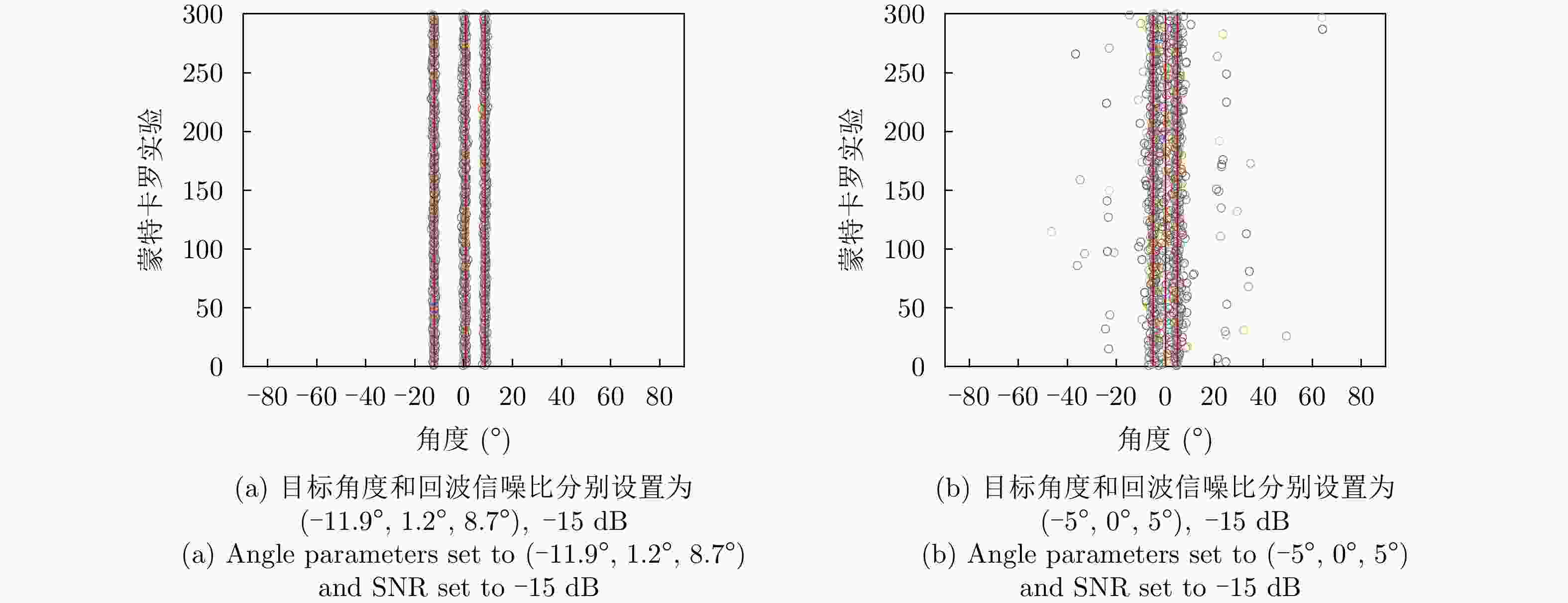
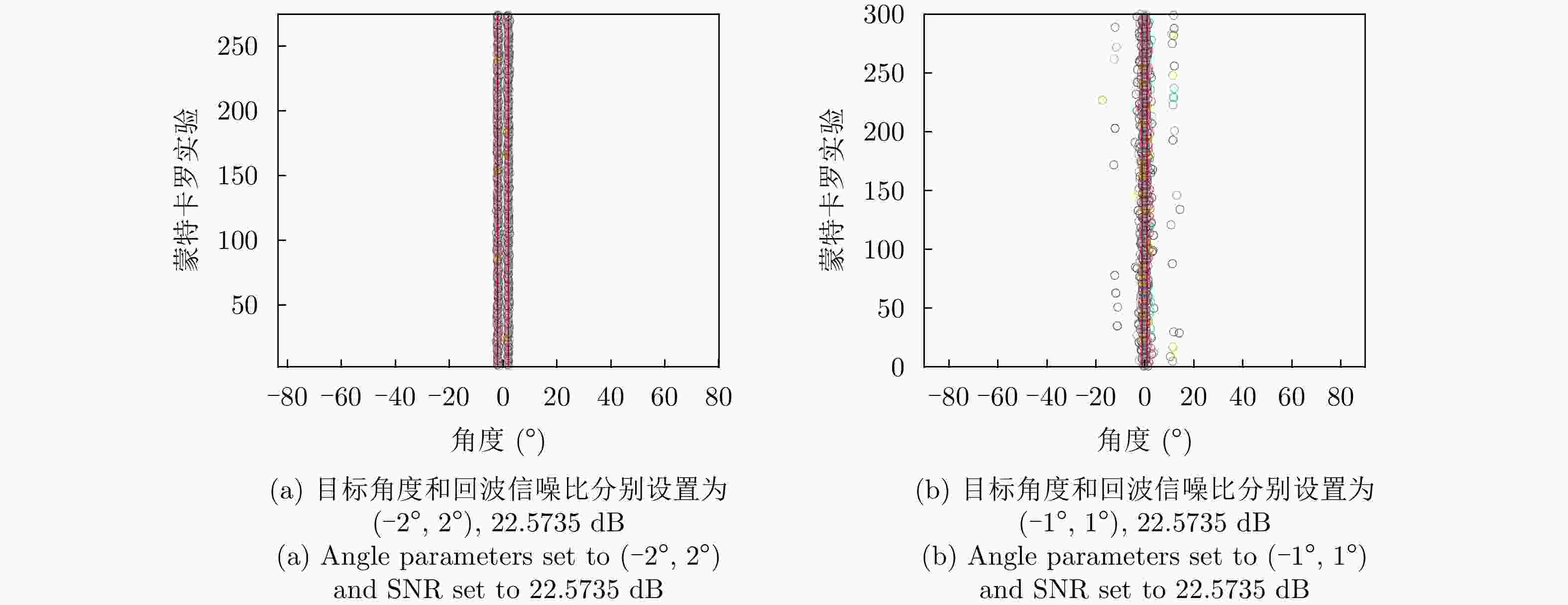
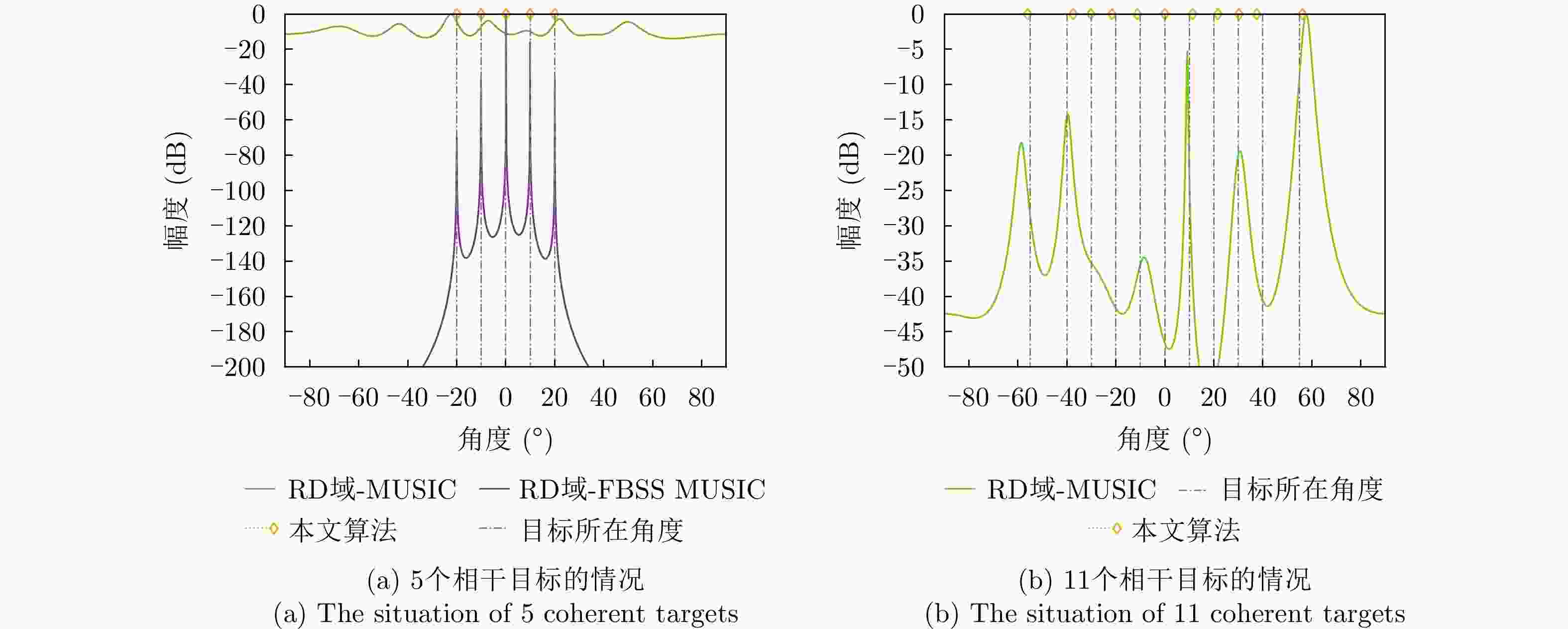
表 1 实验仿真参数
Table 1. The simulation parameters
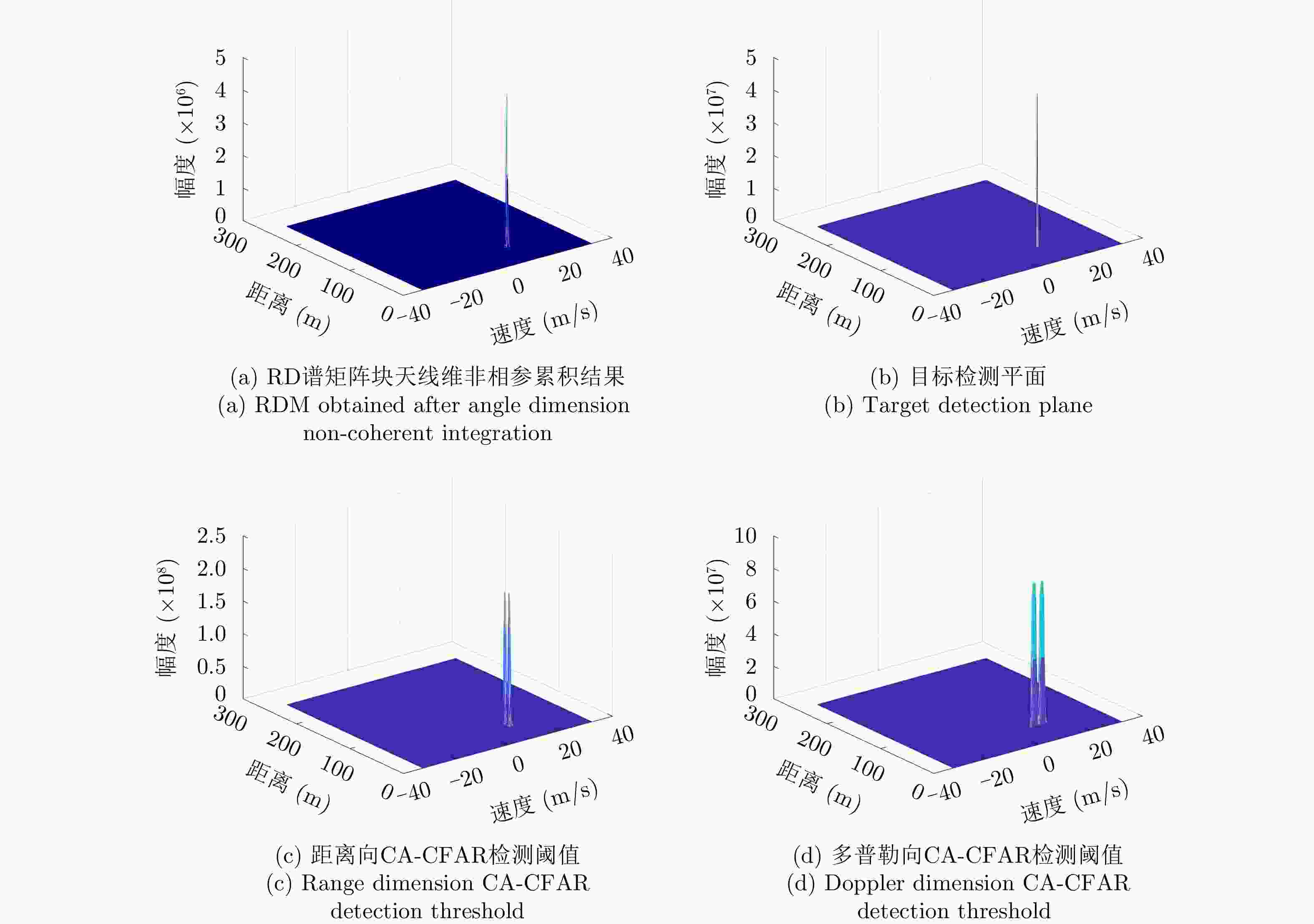
参数 数值 参数 数值 MIMO $3{T}_{{\rm{x}}}4{R}_{{\rm{x}}}$ 发射功率 9.48 dBm CPI数 1 发射天线增益 23 dBi 载频 77 GHz 接收天线增益 34 dBi 有效带宽 150 MHz 最小可检测信噪比 10 dB Chirp重复周期 10 μs 系统损耗 3 dB Chirp数 256 接收机噪声系数 10 dB ADC采样率 25.6 MSPS 接收机带宽 4 GHz ADC采样点数 256 后向散射系数 10 dBsm 表 2 目标参数
Table 2. Target parameter
参数 数值 (相对初始距离,相对运动速度) (50 m, 10 m/s) (距离解算值,速度解算值) (50 m, 9.8925 m/s) 表 3 实测DOA估计结果
Table 3. DOA estimation results based on practical data
组别 设置参数 实测结果 轴向/径向距离(m) 速度(m/s) 角度(推演值)(°) 距离(m) 速度(m/s) 角度(实测值)(°) 1 (4.296, –0.3/0.05) 0 (–3.9946, 0.6668) 4.1016 0 (–4.1, 0.3) 2 (4.296, 0.35/0.5) 0 (0, 6.6386) 4.2969 0 (0.7, 6) -
[1] ENGELS F, HEIDENREICH P, ZOUBIR A M, et al. Advances in automotive radar: A framework on computationally efficient high-resolution frequency estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(2): 36–46. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2637700 [2] GAMBA J. Fundamentals of Radar Systems[M]. GAMBA J. Radar Signal Processing for Autonomous Driving. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 1–14. [3] LI Xinrong, WANG Xiaodong, YANG Qing, et al. Signal processing for TDM MIMO FMCW millimeter-wave radar sensors[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 167959–167971. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137387 [4] 王永良, 丁前军, 李荣锋. 自适应阵列处理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009.WANG Yongliang, DING Qianjun, and LI Rongfeng. Adaptive Array Processing[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009. [5] YARDIBI T, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Source localization and sensing: A nonparametric iterative adaptive approach based on weighted least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(1): 425–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417172 [6] 王永良, 陈辉, 彭应宁, 等. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.WANG Yongliang, CHEN Hui, PENG Yingning, et al. Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithm[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. [7] YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(19): 4959–4973. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2339792 [8] WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A toeplitz covariance matrix reconstruction approach for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 8223–8237. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2695226 [9] ZHANG Zhe, WANG Yue, and TIAN Zhi. Efficient two-dimensional line spectrum estimation based on decoupled atomic norm minimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 163: 95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.04.024 [10] 吕明久, 马建朝, 韦旭, 等. 基于矩阵化原子范数的高频雷达距离-多普勒二维估计方法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(5): 1150–1158. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210479LÜ Mingjiu, MA Jianchao, WEI Xu, et al. Two-dimensional Range-Doppler estimation method for high frequency radar based on matrix atomic norm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1150–1158. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210479 [11] CHANDRASEKARAN V, RECHT B, PARRILO P A, et al. The convex geometry of linear inverse problems[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2012, 12(6): 805–849. doi: 10.1007/s10208-012-9135-7 [12] 陈栩杉, 张雄伟, 杨吉斌, 等. 如何解决基不匹配问题: 从原子范数到无网格压缩感知[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(3): 335–346. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150539CHEN Xushan, ZHANG Xiongwei, YANG Jibin, et al. How to overcome basis mismatch: From atomic norm to gridless compressive sensing[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(3): 335–346. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150539 [13] TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR N B, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451 [14] BHASKAR B N, TANG Gongguo, and RECHT B. Atomic norm denoising with applications to line spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(23): 5987–5999. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273443 [15] YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3139–3153. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2420541 [16] YANG Zai, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Sparse Methods for Direction-of-arrival Estimation[M]. CHELLAPPA R and THEODORIDIS S. Academic Press Library in Signal Processing, Volume 7: Array, Radar and Communications Engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 509–581. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-811887-0.00011-0. [17] HUANG Yan, ZHANG Hui, GUO Kunpeng, et al. Density-based vehicle detection approach for automotive millimeter-wave radar[C]. The IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Shenzhen, China, 2020: 534–537. [18] BARAL A B and TORLAK M. Joint Doppler frequency and direction of arrival estimation for TDM MIMO automotive radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 980–995. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3073572 [19] HALPERN D, WILSON H B, and TURCOTTE L H. Chapter 6: Fourier Series and the Fast Fourier Transform[M]. WILSON H B, TURCOTTE L H, and HALPERN D. Advanced Mathematics and Mechanics Applications Using MATLAB. 3rd ed. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2002. [20] XU Zhihuo, BAKER C J, and POONI S. Range and Doppler cell migration in wideband automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5527–5536. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2912852 [21] 赵春雷, 王亚梁, 毛兴鹏, 等. 基于压缩感知的高频地波雷达二维DOA估计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(4): 733–741. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.04.07ZHAO Chunlei, WANG Yaliang, MAO Xingpeng, et al. Compressive sensing based two-dimensional DOA estimation for high frequency surface wave radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(4): 733–741. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.04.07 [22] YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and STOICA P. Vandermonde decomposition of multilevel toeplitz matrices with application to multidimensional super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(6): 3685–3701. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2553041 [23] RODRÍGUEZ A F, DE SANTIAGO RODRIGO L, GUILLÉN E L, et al. Coding Prony’s method in MATLAB and applying it to biomedical signal filtering[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2018, 19(1): 451. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2473-y [24] 吕明久, 陈文峰, 徐芳, 等. 基于原子范数最小化的步进频率ISAR一维高分辨距离成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2267–2275. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200501LÜ Mingjiu, CHEN Wenfeng, XU Fang, et al. One dimensional high resolution range imaging method of stepped frequency ISAR based on atomic norm minimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2267–2275. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200501 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: