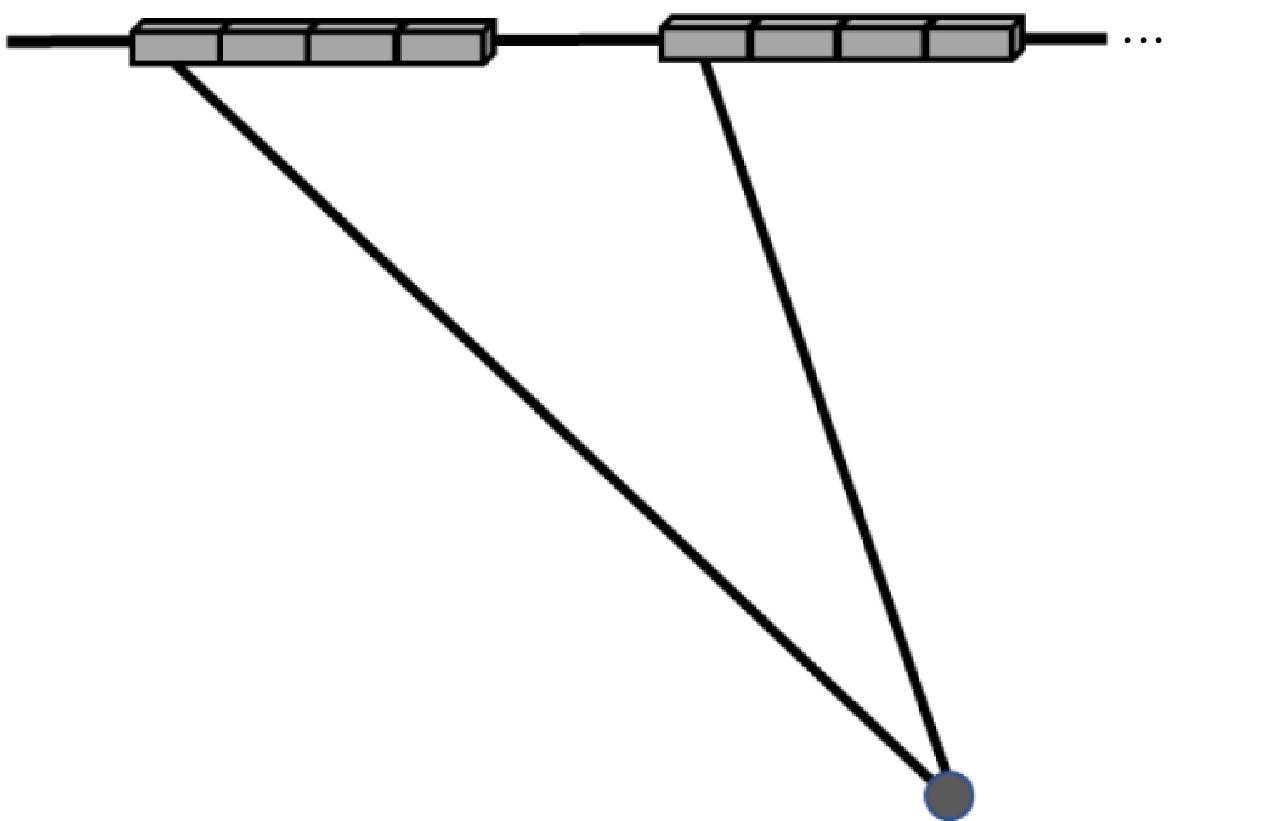
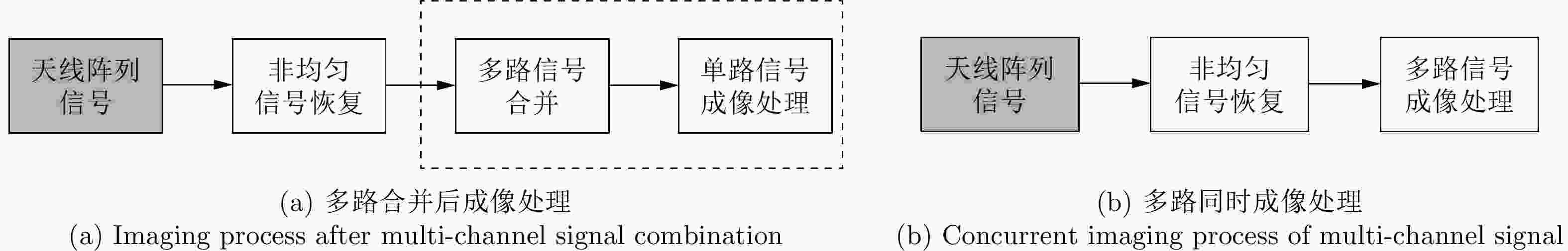
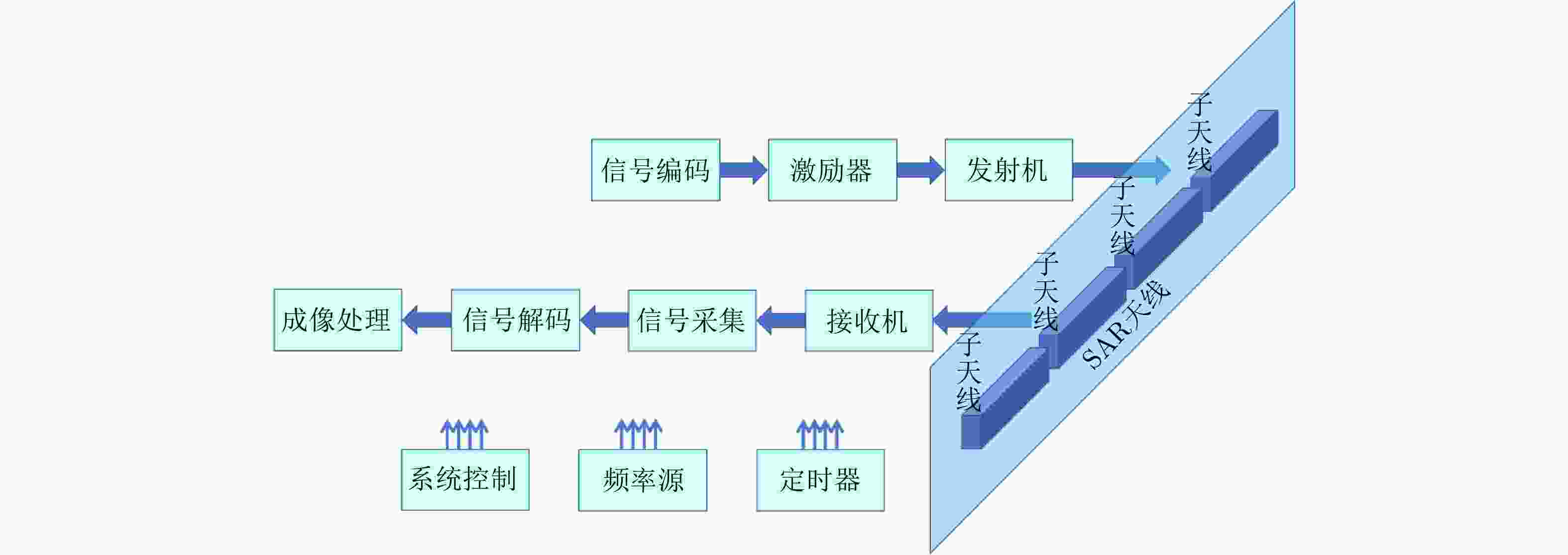
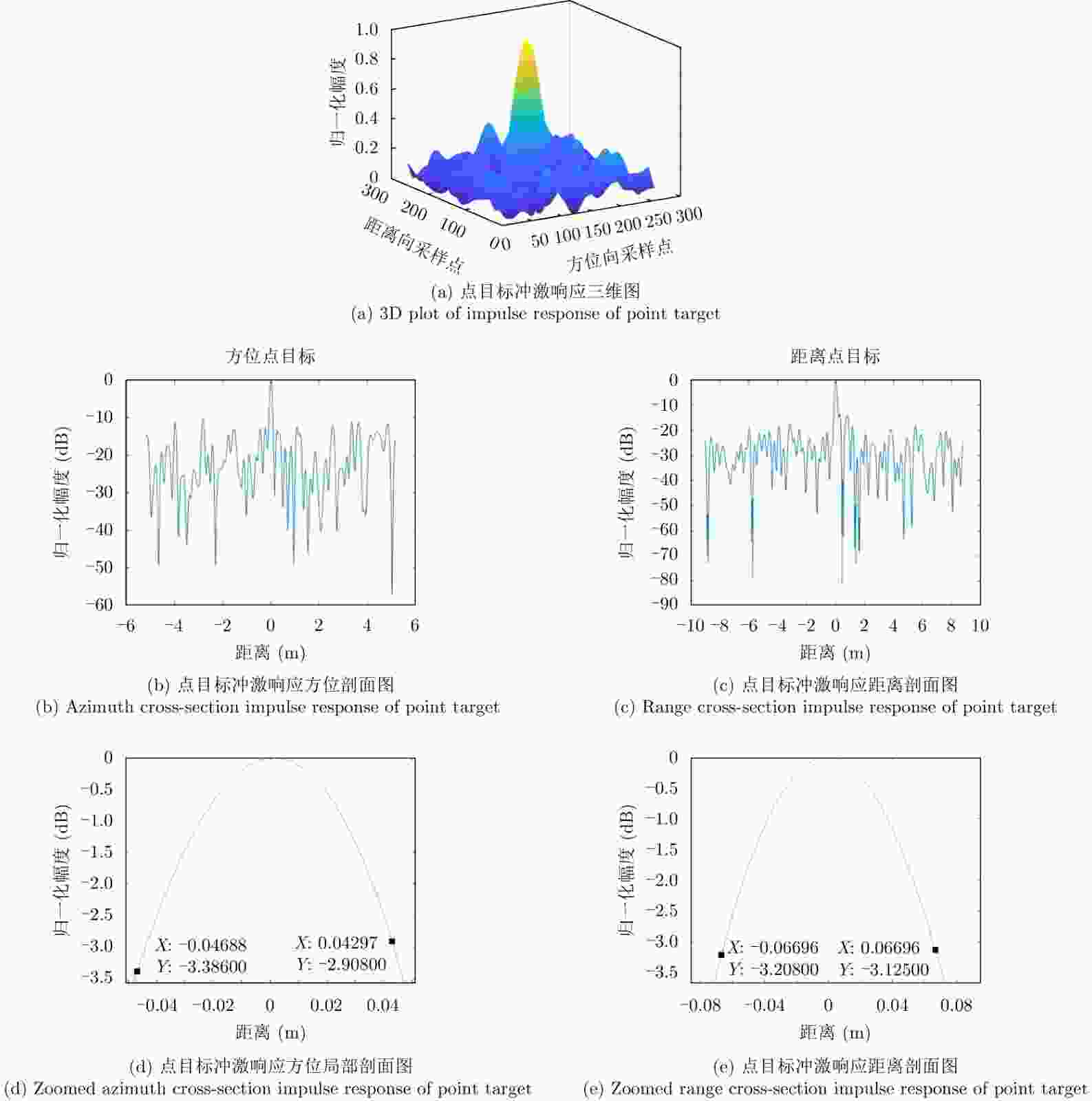
-
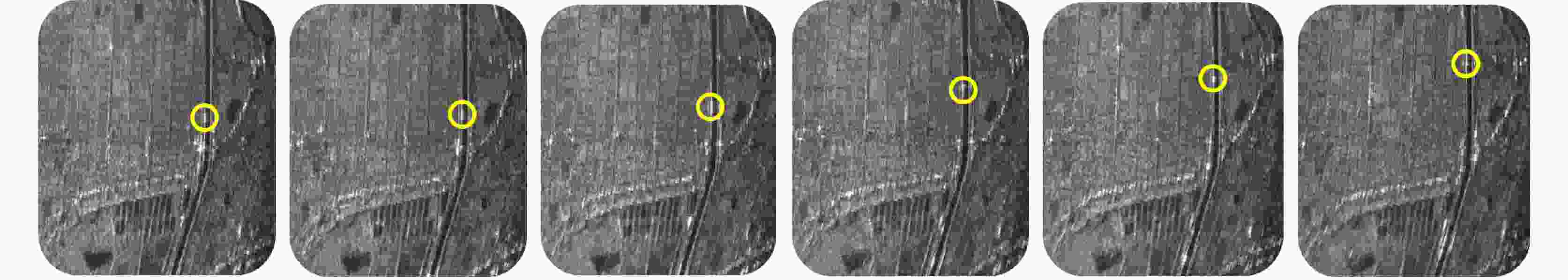
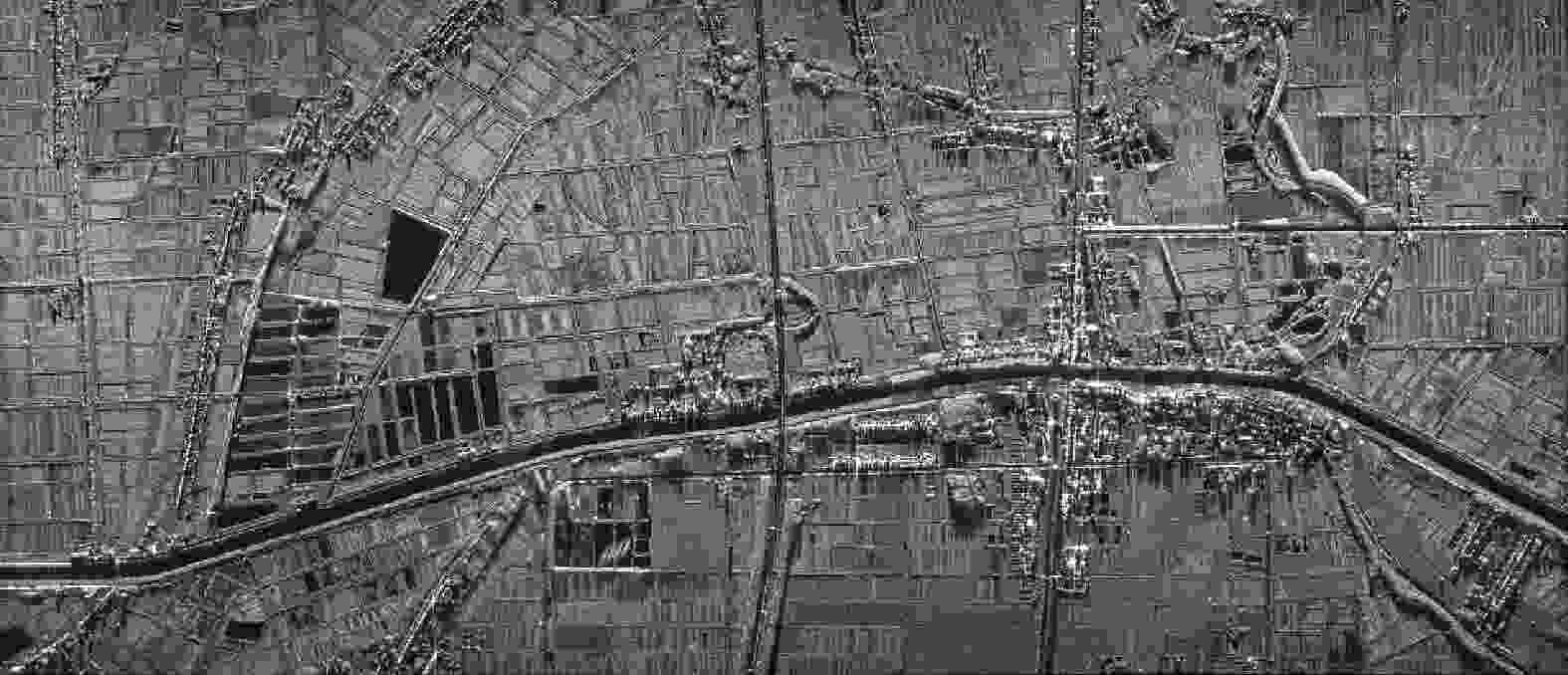
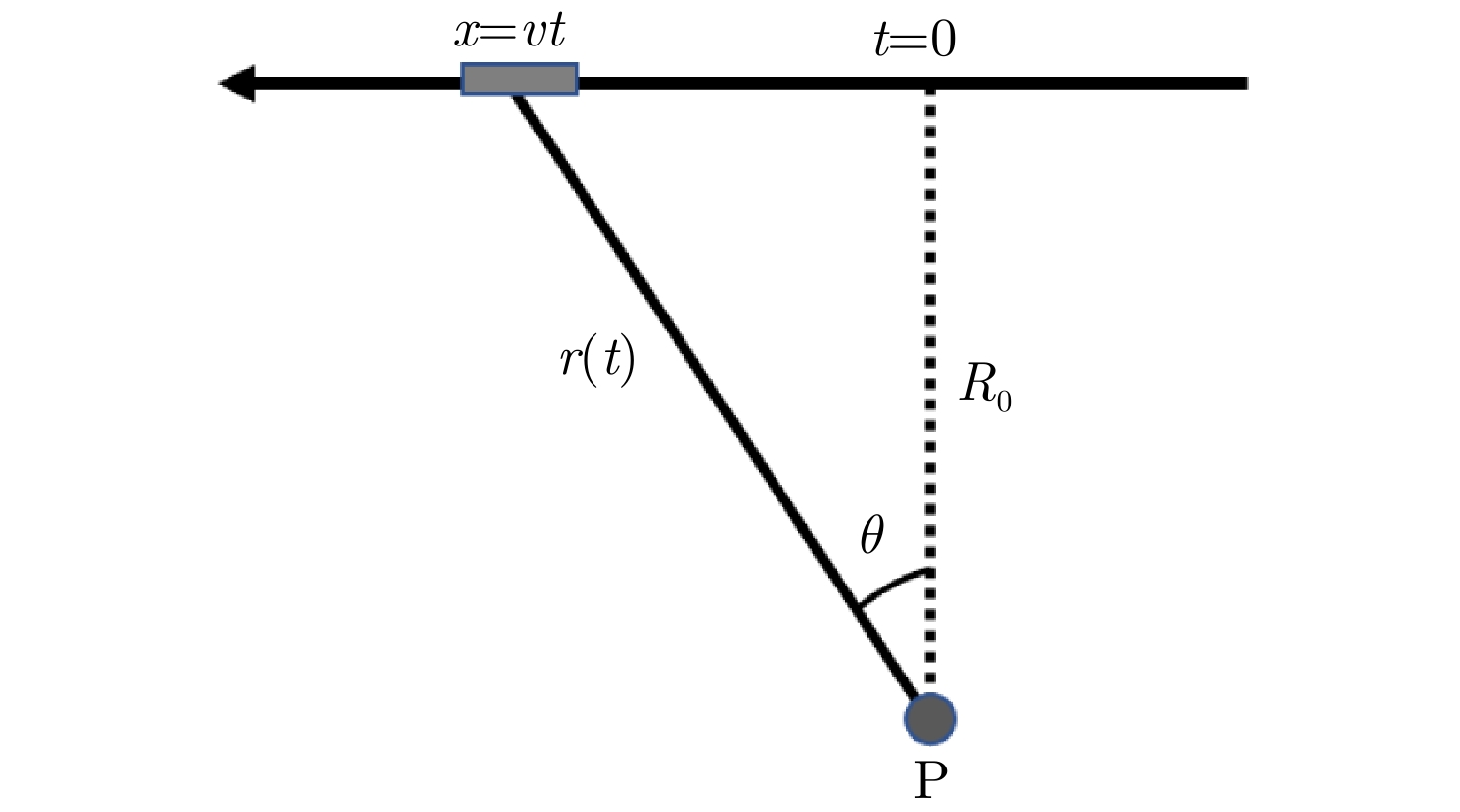
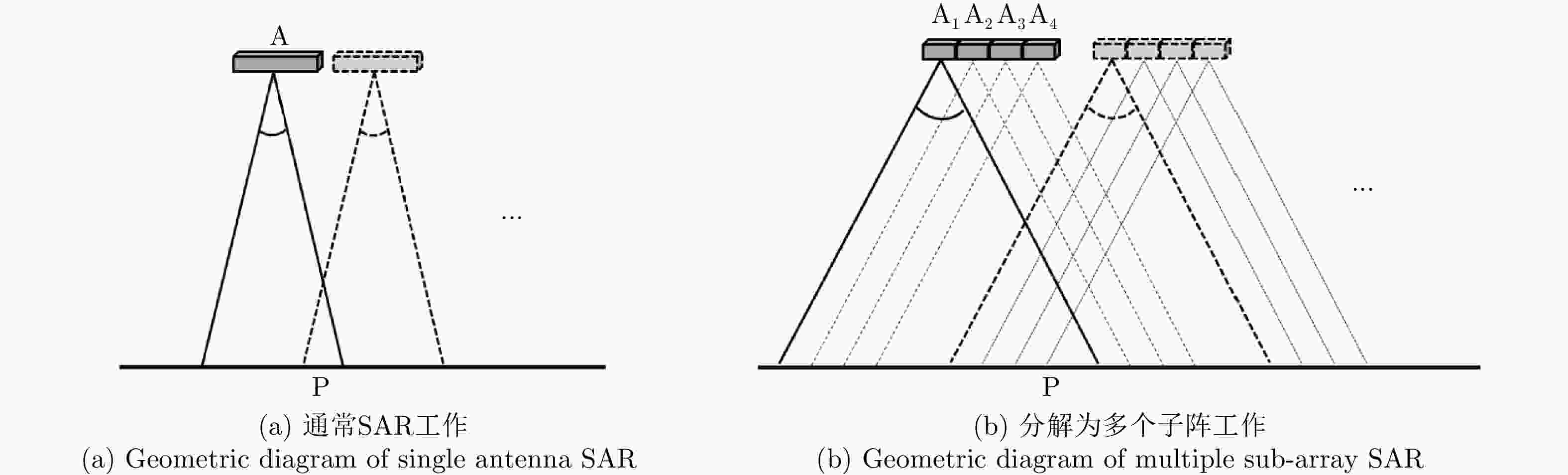
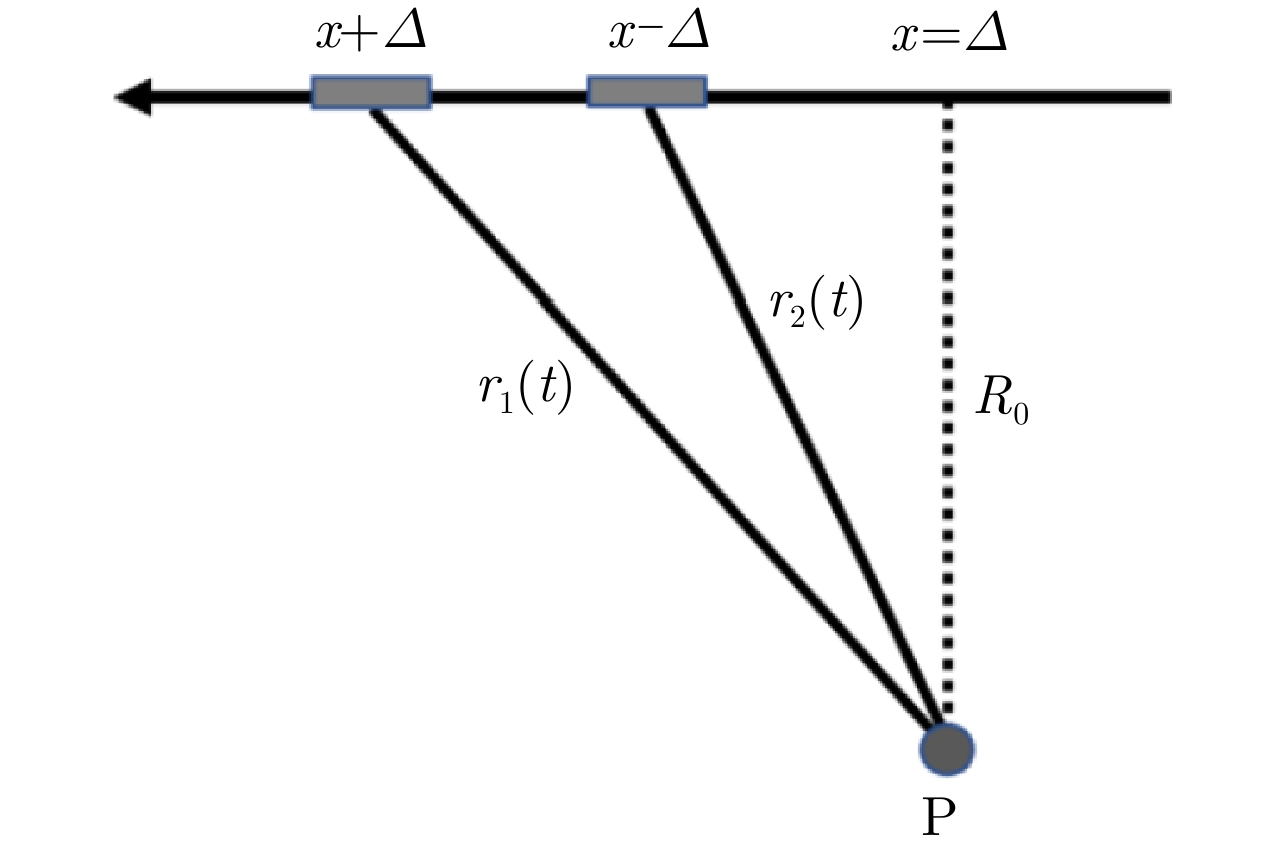
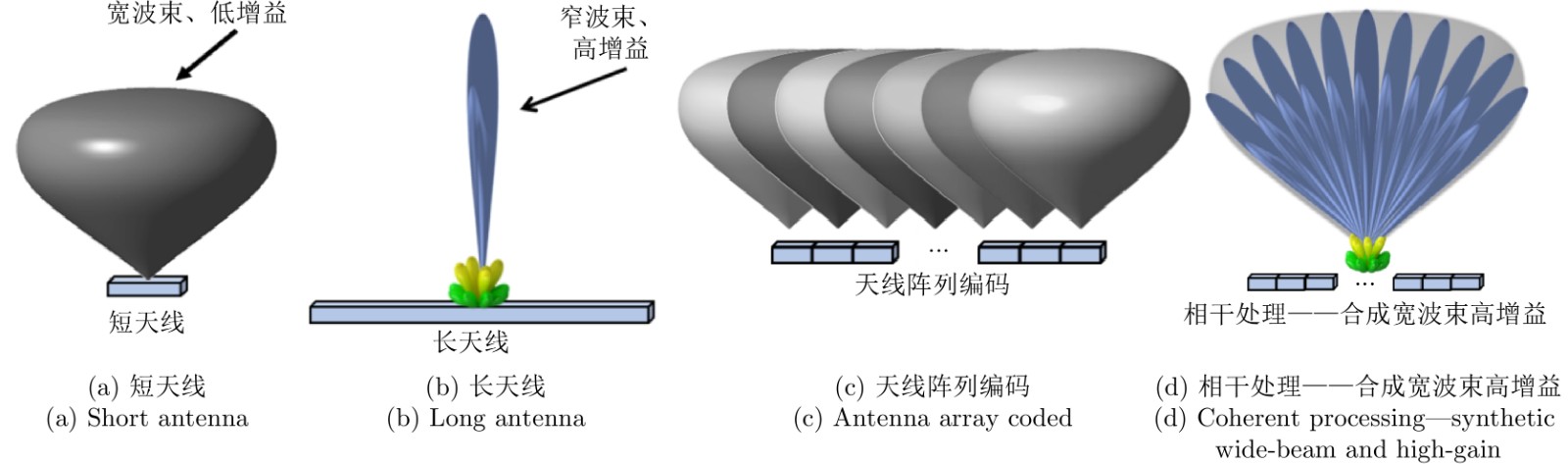
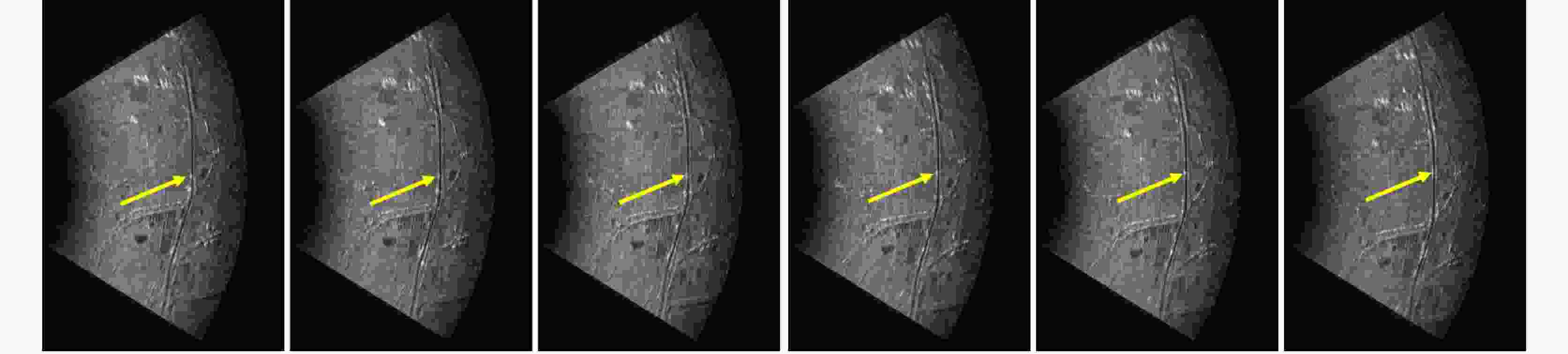
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)方位理论分辨率为天线长度的二分之一,使得SAR高分辨率、远距离成像对天线的要求相互矛盾。该文提出了对天线阵列编码的合成孔径成像方法,通过将长天线分解为子阵、发射不同的信号进行阵列编码、协同工作,提高空间能量利用率,实现子阵小天线的高分辨率以及全阵列长天线的高增益,从而解决了高分辨率与远距离成像难以同时兼顾的问题。在介绍阵列编码基本概念的基础上,给出了阵列编码雷达成像模型及处理流程,对系统的分辨率、信噪比、脉冲重复频率(PRF)及距离方位模糊等性能进行了理论分析与探讨。在飞行测试实验中,用4个子阵获取了方位分辨率优于0.1 m、幅宽超过8 km的连续条带图像,打破了传统SAR采用聚束模式实现高分辨率时只能小范围成像的制约,新方法为解决传统SAR的原理限制问题提供了有效的途径。同时,通过阵列编码扩展了信号维度,为雷达系统能力的增强提供了技术基础。理论分析及实验结果验证了该文天线阵列编码方法的显著优势及工程实现的可行性。Abstract: The theoretical azimuth resolution of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is half the antenna length, presenting conflicting requirements on the antenna for SAR high-resolution and long-distance imaging. In this paper, a method for antenna array coding synthetic aperture imaging is proposed. By dividing long antennas into subarrays to work together, the space energy utilization rate can be improved, a high resolution of the small antennas of the subarrays and a high gain of the long antennas of the whole array are achieved, and the problem that it is difficult to balance high-resolution and far-distance imaging is solved. On the basis of introducing the basic concept of array coding, the imaging model and processing flow of array coding radar are given, and the system performance metrics, such as resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF), and range-azimuth ambiguity, are theoretically analyzed and discussed. In a flight test experiment, a 0.5 m antenna is divided into four sub-arrays, and a strip-map image with a resolution of 0.1 m and a swath width of 8 km is obtained, which breaks the restriction of small-area imaging when traditional SAR adopts the spotlight mode to achieve high resolution. This new method effectively solves the limitations of traditional SAR and extends the signal dimension, providing a technical basis for enhancing radar system capability. Theoretical analysis and experimental results verify the considerable advantages and engineering implementation feasibility of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Antenna array /
- Array coding /
- Nonuniform sampling
-
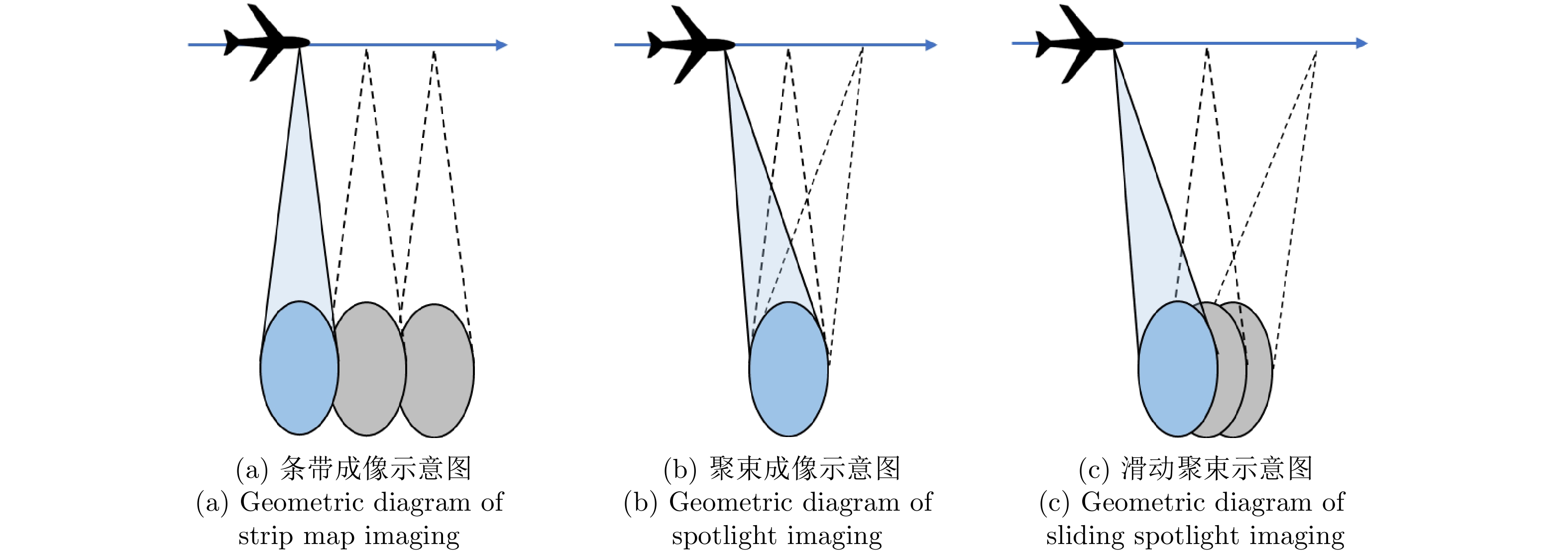
表 1 编码阵雷达系统工作参数
Table 1. Parameters of antenna array coded radar
参数 数值 波段 Ku 方位向天线长度 0.5 m 子阵数 4 系统带宽 1.2 GHz 子阵发射信号带宽 300 MHz 各子阵发射峰值功率 200 W 发射信号脉冲宽度 30 μs 飞行平台速度 80 m/s 作用距离 25 km -
[1] 张澄波. 综合孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.ZHANG Chengbo. Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. [2] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [3] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991. [4] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995. [5] JAKOWATZ C V JR, WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, et al. Spotlight-Mode Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Signal Processing Approach[M]. New York: Springer, 1996. [6] MITTERMAYER J, LORD R, and BORNER E. Sliding spotlight SAR processing for TerraSAR-X using a new formulation of the extended chirp scaling algorithm[C]. The 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1462–1464. [7] PRATS P, SCHEIBER R, MITTERMAYER J, et al. Processing of sliding spotlight and TOPS SAR data using baseband azimuth scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 770–780. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2027701 [8] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. Sliding spotlight and TOPS SAR data processing without subaperture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(6): 1036–1040. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2151174 [9] 唐禹, 王岩飞, 张冰尘. 滑动聚束SAR成像模式研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(1): 26–29. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.00585TANG Yu, WANG Yanfei, and ZHANG Bingchen. A study of sliding spotlight SAR imaging mode[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(1): 26–29. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.00585 [10] ENDER J H G. MIMO-SAR[C]. International Radar Symposium, Cologne, Germany, 2007: 580–588. [11] CRISTALLINI D, PASTINA D, and LOMBARDO P. Exploiting MIMO SAR potentialities with efficient cross-track constellation configurations for improved range resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 38–52. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053715 [12] WANG Wenqin. Space-time coding MIMO-OFDM SAR for high-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(8): 3094–3104. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2116030 [13] KRIEGER G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2628–2645. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2263934 [14] 周伟, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. MIMO-SAR技术发展概况及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074ZHOU Wei, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Brief analysis on the development and application of multi-input multi-output synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074 [15] SABRY R and GELING G W. A new approach for radar/SAR target detection and imagery based on MIMO system concept and adaptive space-time coding[R]. DRDC Ottawa TM 2007-087, 2007. [16] 武其松, 井伟, 邢孟道, 等. MIMO-SAR大测绘带成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(4): 772–775. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01959WU Qisong, JING Wei, XING Mengdao, et al. Wide swath imaging with MIMO-SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(4): 772–775. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01959 [17] FAROOQ J, TEMPLE M A, and SAVILLE M A. Application of frequency diverse arrays to synthetic aperture radar imaging[C]. 2007 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Turin, Italy, 2007: 447–449. [18] FAROOQ J, TEMPLE M A, and SAVILLE M A. Exploiting frequency diverse array processing to improve SAR image resolution[C]. 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–5. [19] CHEN Zhen, ZHANG Zhimin, ZHOU Yashi, et al. Elevated frequency diversity array: A novel approach to high resolution and wide swath imaging for synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4001505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3021043 [20] ZHOU Yashi, WANG Wei, CHEN Zhen, et al. High-resolution and wide-swath SAR imaging mode using frequency diverse planar array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(2): 321–325. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2020.2974041 [21] LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Transceive beamforming with accurate nulling in FDA-MIMO radar for imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 4145–4159. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2961324 [22] 朱圣棋, 余昆, 许京伟, 等. 波形分集阵列新体制雷达研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188ZHU Shengqi, YU Kun, XU Jingwei, et al. Research progress and prospect for the noval waveform diverse array radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188 [23] 王岩飞, 李和平, 韩松. 雷达脉冲编码理论方法及应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 1–16. doi: 10.12000/JR19023WANG Yanfei, LI Heping, and HAN Song. The theory and method of pulse coding for radar and its applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 1–16. doi: 10.12000/JR19023 [24] 张庆君, 韩晓磊, 刘杰. 星载合成孔径雷达遥感技术进展及发展趋势[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(6): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.06.001ZHANG Qingjun, HAN Xiaolei, and LIU Jie. Technology progress and development trend of spaceborne synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(6): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.06.001 [25] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1990. [26] COOK C E and BERNFELD M. Radar Signals: An Introduction to Theory and Application[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1967. [27] COSTAS J P. A study of a class of detection waveforms having nearly ideal range—Doppler ambiguity properties[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1984, 72(8): 996–1009. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1984.12967 [28] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 31–46. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.905974 [29] SKOLNIK M I, 左群声, 徐国良, 马林, 等译. 雷达系统导论[M]. 3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014.SKOLNIK M I, ZUO Qunsheng, XU Guoliang, MA Lin, et al. translation. Introduction to Radar Systems[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014. [30] 赵永波, 刘宏伟. MIMO雷达技术综述[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2018, 33(3): 389–399. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2018.03.001ZHAO Yongbo and LIU Hongwei. Overview on MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2018, 33(3): 389–399. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2018.03.001 [31] 袁赛柏, 金胜, 朱天林. MIMO雷达技术发展综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(8): 5–8, 66. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.002YUAN Saibai, JIN Sheng, and ZHU Tianlin. The development review of MIMO radar technology[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(8): 5–8, 66. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.002 [32] PAPOULIS A. Signal Analysis[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1977. [33] 王岩飞, 刘畅, 詹学丽, 等. 无人机载合成孔径雷达系统技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089WANG Yanfei, LIU Chang, ZHAN Xueli, et al. Technology and applications of UAV synthetic aperture radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: